Содержание
Просмотр системного журнала
Если в работе Windows 2016 появляется какая-то нестабильность, или появляются ошибки запуска\установки приложений, то это может быть связано с появлениями ошибок в самой операционной системе.
Все системные ошибки и предупреждения можно найти в «Журнале системы«.
В нем сохраняется информация о событиях, записываемых системными компонентами Windows.
Для просмотра и сохранения системного журнала нужно выполнить шаги:
Открыть «Пуск«:
Открыть «Средства администрирования» -> «Просмотр событий«

В открывшемся окне выбрать «Просмотр событий» -> «Журналы Windows» -> «Система«

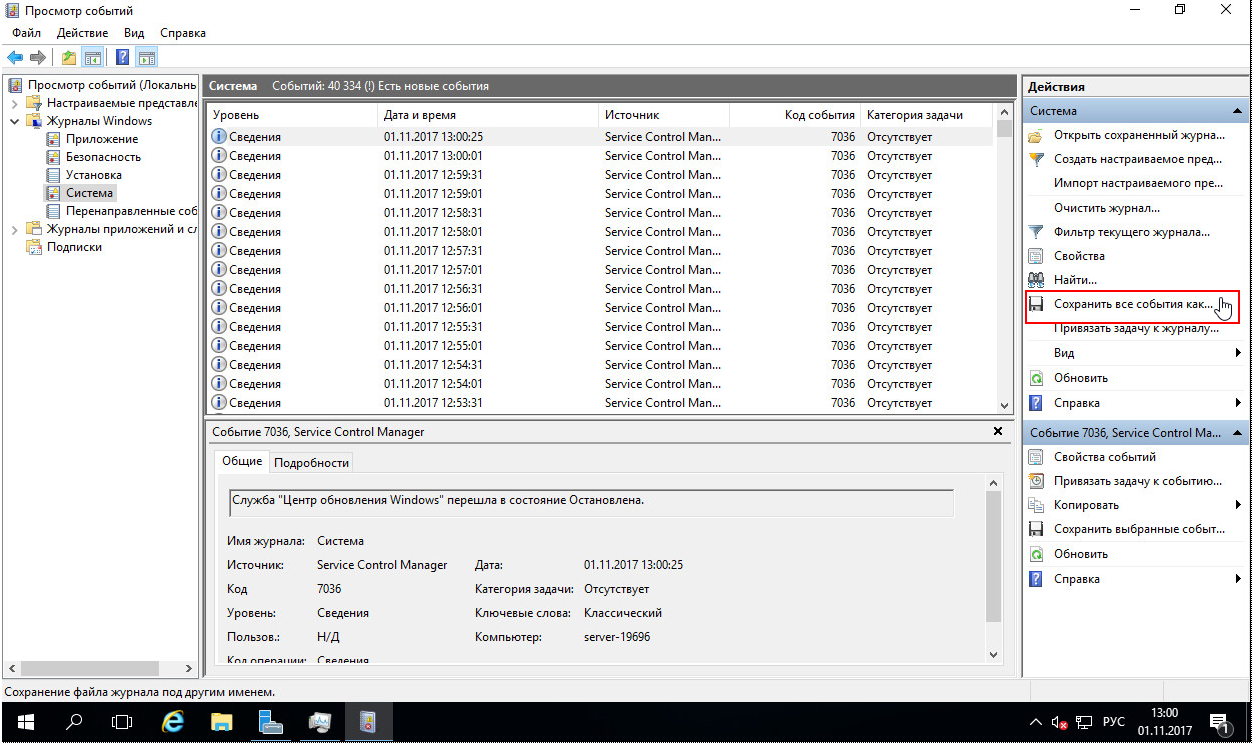
Экспорт журнала
Системный журнал в полном объеме можно выгрузить путем нажатия на ссылку «Сохранить все события как…«
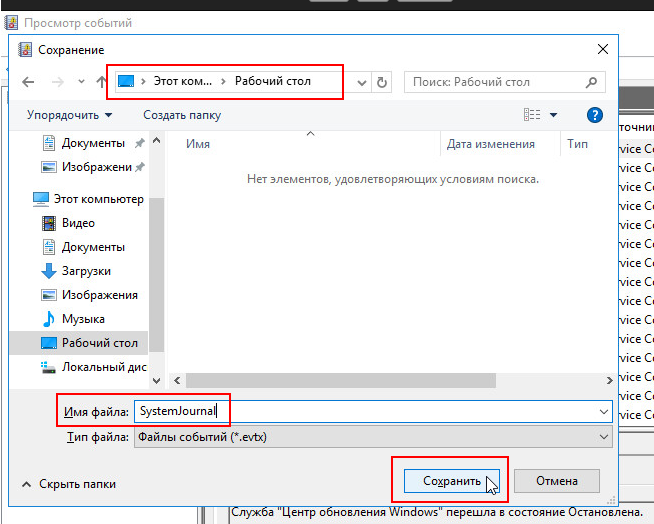
После нажатия ссылки «Сохранить все события как…» нужно выбрать путь и имя файла для сохраняемого журнала.
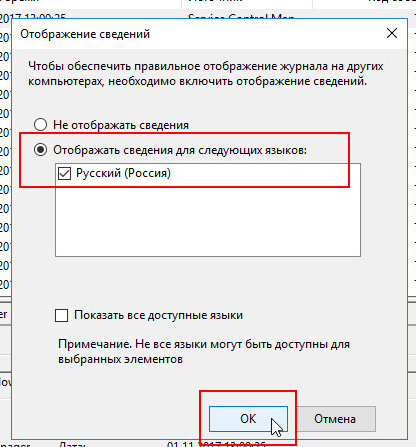
При сохранении файла возможно появление окна «Отображение сведений«.
В данном окне нужно выбрать пункт «Отображать сведения для следующих языков: Русский«
Готово
Для того что бы открыть Журнал Windows сервера нужно последовательно выполнить:
Пуск-Панель управления-Администрирование-Просмотр событий-Журналы WindowsЖурнал Windows сервера состоит из 5 разделов. В каждый раздел идет запись событий в зависимости от категории.
Например если нам нужно посмотреть удачные авторизации в системе по RDP и ip адрес с которого была авторизация, нужно выбрать раздел: Безопасность, далее включить фильтр и установить параметры фильтрации как указано на скрине:
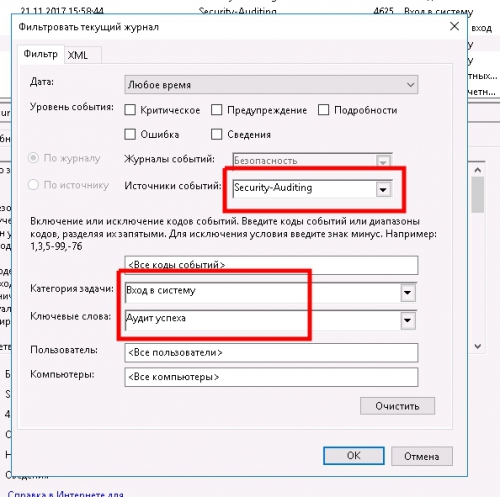
После установки фильтра вы сможете посмотреть ip авторизации и логин пользователя Windows как показано на скрине:
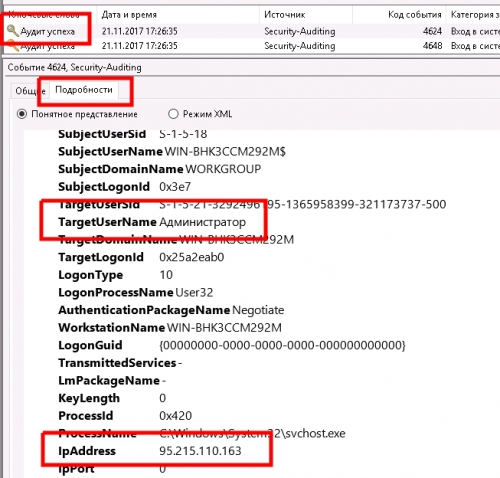
Как узнать кто подключался на тот или иной сервер по RDP.
С помощью логов которые пишет ОС Windows, можно получить информацию о том с каких IP и какие пользователи подключались к виртуальному серверу, и когда они это делали.
Приведенная ниже инструкция может быть использована также на десктопных версиях Windows.
Рассмотрим некоторые наиболее распространенные коды связанные со временем запуска и завершения работы сервера.
1149: Присутствие данного кода говорить об успешной аутентификации пользователя на сервере. (Remote Desktop Services: User authentication succeeded)
21: данный код говорить об успешном входе в систему, то-есть пользователь увидел окно рабочего стола. (Remote Desktop Services: Session logon succeeded)
24: это событие говорить об успешном отключении от RDP (Remote Desktop Services: Session has been disconnected)
25: говорит об переподключении к RDP сессии. (Remote Desktop Services: Session reconnection succeeded)
23: пользователь нажал Logoff и вышел из системы (Remote Desktop Services: Session logoff succeeded )
39: пользователь лично отключился от RDP сессии (не просто закрыл RDP окно). Или его отключил другой пользователь или администратор.
Как просмотреть данные события?
Нажмите Win+R и введите eventvwr
В левой части панели откройте «Журналы Windows => Система»
В колонке Event ID мы увидим список событий, произошедших во время работы Windows. Журнал событий можно сортировать по идентификатору события.
Для того что бы отсортировать нужные нам события, с правой стороны, выберем «Фильтр текущего журнала»
Теперь введите нужные нам события, через запятую, 1149,39,25,24,23,21 и нажмите Ок.
Теперь мы можем наблюдать журнал событий с завершением работы нашего сервера VPS.
Данные ивенты, можно посмотреть в разных разделах. Например:
EventId 1149,4624,4625 — фильтруем в Windows Logs => Security
EventId 25,24,21,39 — фильтруем в Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager -> Operational
EventId 23 — Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TerminalServices-LocalSessionManager -> Operationa
Теперь вы можете самостоятельно проверить по кто и когда заходил по RDP на Ваш сервер.
Posted by
on September 27, 2016
This post will show you where the .evtx log files can be found in Windows Server 2016, as well as how they can be viewed with Event Viewer.
Viewing Log Files
The easiest way to view the log files in Windows Server 2016 is through the Event Viewer, here we can see logs for different areas of the system.
Event viewer can be opened through the MMC, or through the Start menu by selecting All apps, Windows Administrative Tools, followed by Event Viewer.
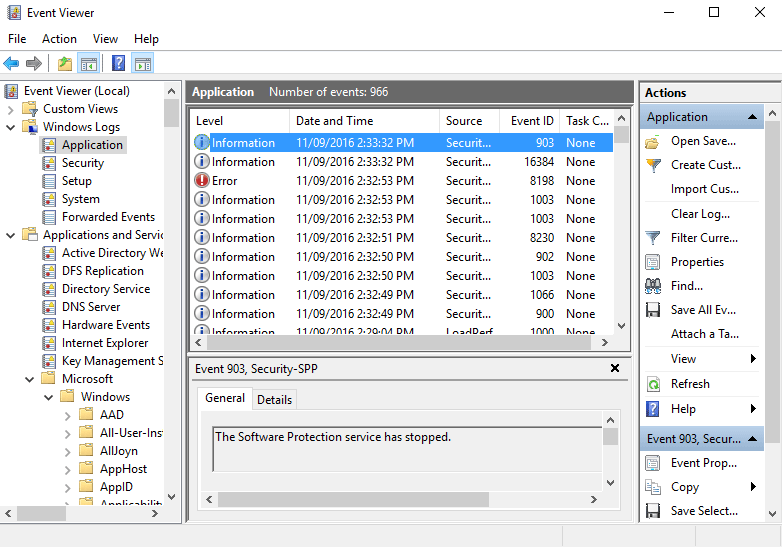
Through Event Viewer we have the ability to search the logs for a particular string, export the logs to a file, and even schedule a task to take place each time a specific event occurs.
Log File Location
While this allows us to read the logs, you may be after the full path to where the actual .evtx files are stored. These log files can be found in the C:\Windows\System32\winevt\logs folder, as shown below.
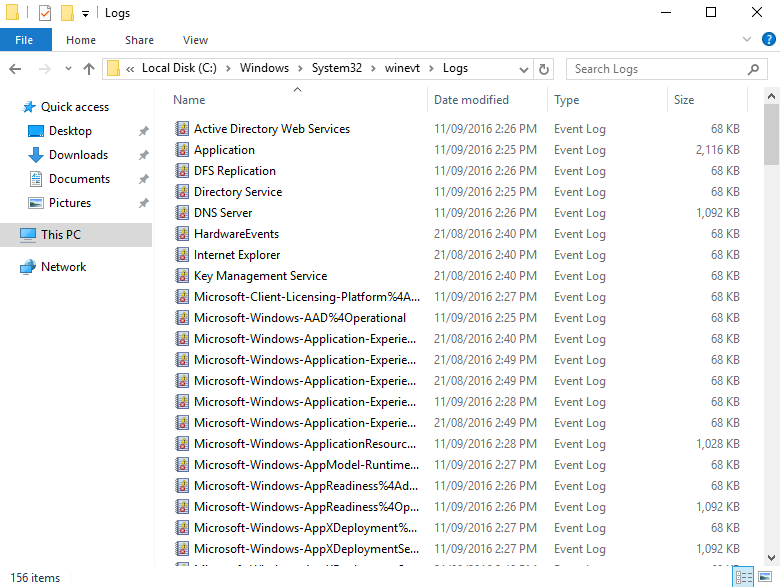
These files can be double clicked and they will automatically open with Event Viewer, and these are the files that are read when browsing through Event Viewer
Note that specific applications may have their own custom log locations, in which case you will need to check the vendors documentation regarding log file location.
Summary
We have seen that important application, security and system events that have been logged are stored in the C:\Windows\System32\winevt\logs directory as .evtx files, which can be viewed through Event Viewer.
- How do I view Windows user logs?
- How do I monitor administrator activity?
- How do I view Active Directory logs?
- How do you audit a domain account?
- How do you audit event logs?
- What is last logon in Active Directory?
- How can I get the last login date from Active Directory for all users?
How do I view Windows user logs?
To access the Windows Event Viewer, press Win + R and type eventvwr. msc in the “Run” dialog box. When you press Enter, the Event Viewer will open. In the left pane, expand “Windows Logs” and select “Security.”
How do I monitor administrator activity?
Go to “Start” ➔ “Administrative Tools” ➔ “Event Viewer”. Expand “Windows Logs” and select “Security”. Event Viewer shows you all the events logged in security logs.
How do I view Active Directory logs?
Active Directory event logging tool
You can open the Event Viewer by clicking on : Start → System security → Administrative tools → Event viewer.
How do you audit a domain account?
Right-click Domain Controllers, and then select Properties. Select the Group Policy tab, select Default Domain Controller Policy, and then select Edit. Select Computer Configuration, double-click Windows Settings, double-click Security Settings, double-click Local Policies, and then double-click Audit Policy.
How do you audit event logs?
Auditing logon events help the administrator or investigator to review users’ activity and detect potential attacks. To log logon events run Local Security Policy. Open Local Policies branch and select Audit Policy. Double click on “Audit logon events” and enable Success and Failure options.
What is last logon in Active Directory?
The Last-Logon attribute contains a Windows FileTime representation of the last time a domain controller successfully authenticated the user. It is the granddaddy of user logon metadata, and has been around since the first version Active Directory.
How can I get the last login date from Active Directory for all users?
You need to use PowerShell Get-ADUser cmdlet to get active directory last logon date. Last Logon date time is stored in lastlogon attribute.
