Если вы подозреваете, что встроенный Windows Defender Firewall блокирует некоторые сетевые подключений (от определенной программы или сервиса), плохим решением будет его полное отключение. Вместо этого вы можете включить логирование сетевого трафика, проходящего через брандмауэр, определить заблокированные используемые порты и/или IP адреса источника/назначения и создать корректное разрешающее правило.
В этой статье мы покажем, как включить логирование сетевых подключений в Windows Firewall и выполнить поиск по логам.
Настройка логирования Windows Firewall в текстовый файл
Содержание:
- Запись логов Windows Firewall в журнал событий Windows
Windows Defender Firewall позволяет записывать в лог файл как успешные так и заблокированные сетевые подключения. Логирование можно включить отдельно для каждого сетевого профиля (частная, общедоступная или доменная сеть). По умолчанию логирование трафика в брандмауэре отключено. Чтобы включить ведение логов в Windows Firewall:
- Откройте MMC оснастку Windows Firewall with Advanced Security (
wf.msc
). - Щелкните правой кнопкой по корню консоли и выберите Properties;
- Затем выберите вкладку сетевого профиля Windows, для которого вы хотите включить логирование (Domain, Private или Public Profile).
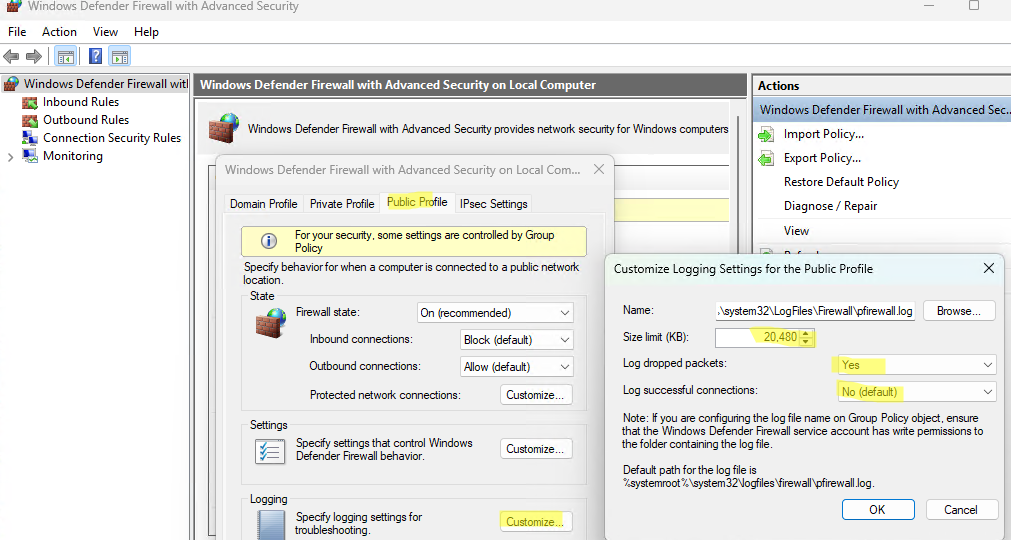
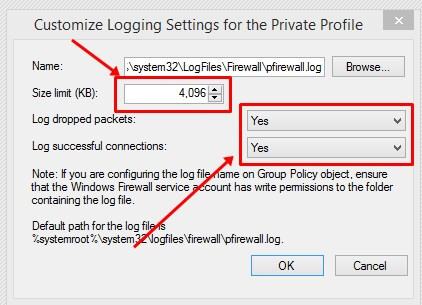
- На вкладке профиля в секции Logging нажмите кнопку Customize.
- Здесь можно изменить следующие настройки:
Файл лога: по умолчанию
%systemroot%\system32\LogFiles\Firewall\pfirewall.logМаксимальный размер лога: увеличьте с 4 Мб до 20 Мб (
20480
Кб)Log dropped packets: нужно ли записывать в лог отфильтрованные сетевые пакеты
Log successful connections: нужно ли логировать успешные сетевые подключения (может получиться очень большой лог)
Чтобы понять, какой сетевой профиль заблокировал или пропустил определенное сетевое подключение, можно писать лог файервола в отдельный файл для каждого профиля. Например:
-
%windir%\system32\logfiles\firewall\pfirewall_domain.log -
%windir%\system32\logfiles\firewall\pfirewall_private.log -
%windir%\system32\logfiles\firewall\pfirewall_public.log
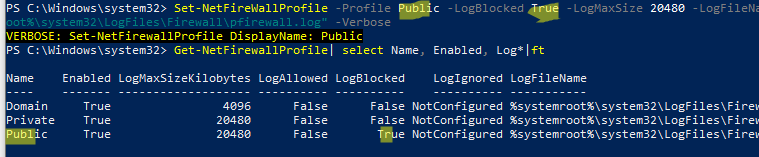
Также можно включить эти же параметры логирования Windows Firewall с помощью PowerShell:
Set-NetFireWallProfile -Profile Public -LogBlocked True -LogMaxSize 20480 -LogFileName "%systemroot%\system32\LogFiles\Firewall\pfirewall.log" -Verbose
Вывести текущие настройки логирования брандмауэра для всех профилей:
Get-NetFirewallProfile| select Name, Enabled, Log*|ft
Теперь Windows Firewall будет записывать в лог файлы все сетевые подключения. Вы можете открыть файл лога вручную или выполнить поиск по нему с помощью PowerShell. Командлет Select-String совмещает в себе аналог grep и tail для Windows.
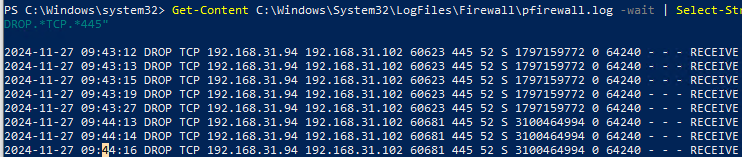
Например, следующая команда будет выводить в реальном времени на экран все отфильтрованные (DROP) сетевые подключения на порт TCP порт 445 (SMB):
Get-Content C:\Windows\System32\LogFiles\Firewall\pfirewall.log -wait | Select-String -pattern "DROP.*TCP.*445"
Используется такой формат лог файла:
date time action protocol src-ip dst-ip src-port dst-port size tcpflags tcpsyn tcpack tcpwin icmptype icmpcode info path pid
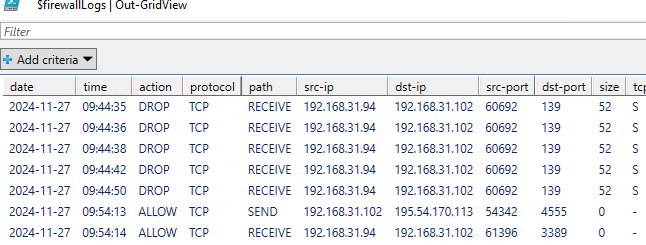
Для анализа лог файлов файервола можно воспользоваться такой PowerShell функцией, которая представит лог в виде удобной графической таблицы Out-GridView:
function Get-WindowsFirewallLog {
param(
[parameter(Position=0,Mandatory=$false)]
[ValidateScript({Test-Path $_})]
[string]$LogFilePath = "$env:SystemRoot\System32\LogFiles\Firewall\pfirewall.log"
)
$headerFields = @("date","time", "action","protocol","src-ip","dst-ip","src-port","dst-port","size", "tcpflags","tcpsyn", "tcpack","tcpwin","icmptype","icmpcode", "info","path")
$firewallLogs = Get-Content $LogFilePath | ConvertFrom-Csv -Header $headerFields -Delimiter ' '
$firewallLogs | Out-GridView
}
Get-WindowsFirewallLog
Запись логов Windows Firewall в журнал событий Windows
По сравнению с текстовыми файлам иногда более удобно записывать логи сетевых подключений Windows Firewall в журнал событий (Event Viewer). Для этого нужно включить политики аудита в локальной GPO:
- Откройте редактор локальной GPO (
gpedit.msc
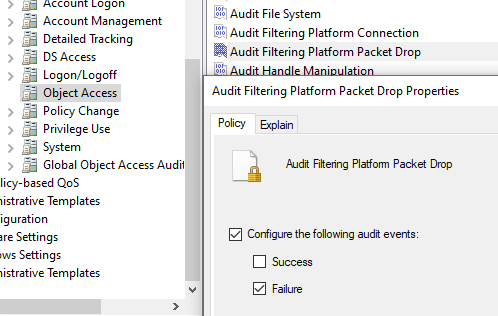
) - Перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Advanced Audit Policy Configuration -> System Audit Policies — Local Group Policy Object -> Object Access
- Параметр Audit Filtering Platform Packet drop позволяет включить аудит заблокированных подключений Windows Firewall. Откройте настройки политики и активируйте опцию Failure.
- Audit Filtering Platform Connection позволяет логировать успешные подключения. Используется эта политика аудита довольно редко, т.к. в лог будет писаться очень много событий (потребуется увеличение размеров журнала Event Viewer)
- Обновите настройки локальной GPO командой
gpupdate /force
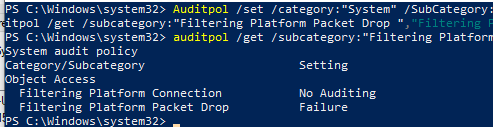
Такую политику аудита можно включить командой:
Auditpol /set /category:"System" /SubCategory:"Filtering Platform Packet Drop" /failure:enable
Вывести текущие настройки политика аудита Windows Firewall:
auditpol /get /subcategory:"Filtering Platform Packet Drop","Filtering Platform Connection"
Чтобы посмотреть события Windows Firewall, откройте Event Viewer (
eventvwr.msc
). Разверните Windows Logs -> Security. Включите фильтр событий по категории Filtering Platform Packet Drop.
В списке событий появится все сетевые подключения, заблокированные Windows Firewall. Такие события будут иметь Event ID 5152 (
The Windows Filtering Platform has blocked a packet
). В описании события можно получить сетевую информацию: номер протокола (TCP-6, UDP-17, ICMP-1), IP адрес и порт источника/приемника, направление (Inbound, Outbound), процесс (для исходящих подключений).
Для поиска и фильтрации событий Windows Firewall в Event Viewer можно использовать PowerShell командлет Get-WinEvent. Следующий PowerShell скрипт выполнит поиск всех заблокированных брандмауэром событий (попыток) подключений на порт 3388 и выведет таблицу с временем подключения и источником:
$destinationPort = "3388"
$filterXml = @"
<QueryList>
<Query Id="0" Path="Security">
<Select Path="Security">
*[System[(EventID=5152)]]
and
*[EventData[Data[@Name='DestPort'] and (Data='$destinationPort')]]
</Select>
</Query>
</QueryList>
"@
$FirewallLogs = @()
$events=Get-WinEvent -FilterXml $filterXml
foreach ($event in $events) {
$eventXml = [xml]$event.ToXml()
$SourceAddress = $eventXml.Event.EventData.Data | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq 'SourceAddress' } | Select-Object -ExpandProperty '#text'
$DestPort = $eventXml.Event.EventData.Data | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq 'DestPort' } | Select-Object -ExpandProperty '#text'
$FirewallLog = New-Object PSObject -Property @{
SourceAddress= $SourceAddress
Time=$event.TimeCreated
DestPort=$DestPort
}
$FirewallLogs += $FirewallLog
}
$FirewallLogs
Таким образом, включив логи брандмауэра вы можете детально инспектировать все отброшенные и разрешенные взодящие/исходящие сетевые соединения, найти ошибки в своих правилах Windows Firewall и создать корректные.
The Windows operating system has a built-in firewall. If logging is enabled for the firewall, files named “pfirewall.log” will be generated in a specific directory. This MiniTool post is for you if you want to learn the location of Windows Firewall logs and how to manage them to ensure better security.
Windows Firewall has developed over the years to improve security and safeguard against new threats and unauthorized entries. It also produces logs and offers visibility into its operations, allowing you to supervise and address security issues. To manage Windows Firewall logs, you may want to know the location of Windows Firewall logs.
By default, the firewall doesn’t log network traffic, but it can be set up to do so, allowing for retrieving logs that detail both allowed and denied traffic. If the logging feature is enabled, these logs can offer valuable information such as source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols, helping users analyze and respond to security incidents. The Windows Firewall log file can also monitor TCP and UDP connections and blocked packets.
The location of Windows Firewall logs varies depending on the Windows version. Did you know where are Windows Firewall logs stored? If not, you are in the right place. Keep reading to get more details.
What Is the Location of Windows Firewall Logs on Windows 10/11
When it comes to the location of Windows Firewall logs, the location is specific to a computer. If you want to know where are Windows Firewall logs located, there are 3 ways to get them.
Note:
You must ensure the logging feature is enabled on your PC and have logged in with an administrator account.
#1. Using the Event Viewer Tool
The default location where Windows Firewall logs are stored varies depending on your Windows version. On most Windows operating systems, such as Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 and Windows Server editions, you can find the logs in a directory called “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security” within the Windows Event Viewer. To access the logs, please follow the steps below:
Through the Windows Log Folder
Step 1: Press Win + R together to open the Run command line, type eventvwr.msc in the box, and press Enter.
Step 2: In the pop-up Event Viewer window, expand the Windows Logs folder.
Step 3: Select the Security option to view the firewall logs.
Through the Applications and Services Logs Folders
Step 1: Press Win + R together to open the Run command line, type eventvwr.msc in the box, and press Enter.
Step 2: Navigate to Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
Step 3: Here, you will find various log categories, including Firewall, Connection Security, and IPsec Operational. Double-click the Firewall option to check its logs.
#2. Using the Windows File Explorer
As a file, the Windows Firewall log can be checked in the File Explorer. Just follow the steps to find the location of Windows Firewall logs:
Step 1: Press Win + E simultaneously to open the File Explorer.
Step 2: Go to the system drive; in most cases, it is the C drive.
Step 3: Navigate to Windows > System32 > LogFiles > Firewall.
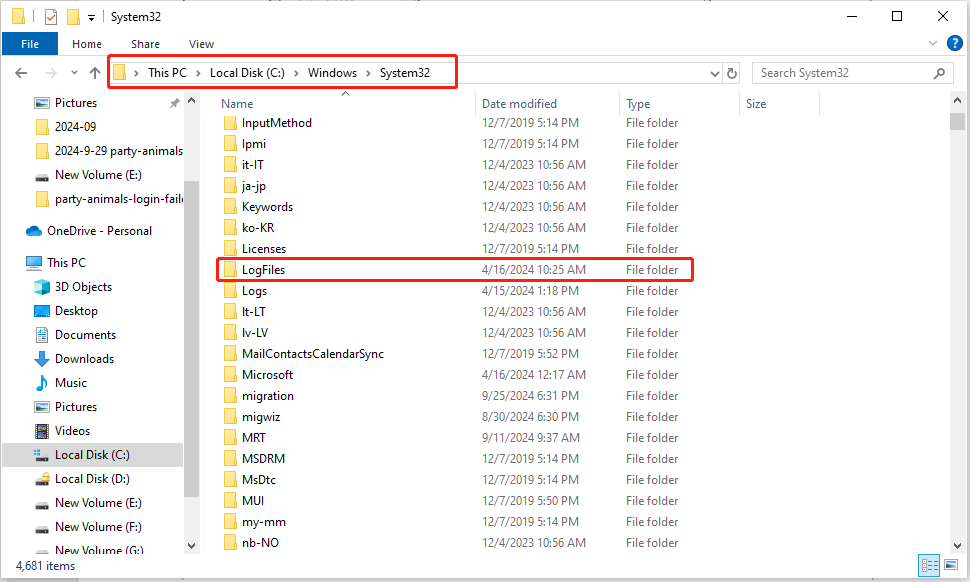
Step 4: Find and click pfirewall.log.
#3. Using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
In addition, the Windows Firewall log file is stored in a folder called “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security”. Therefore, you can follow the steps to find this folder to check your firewall logs:
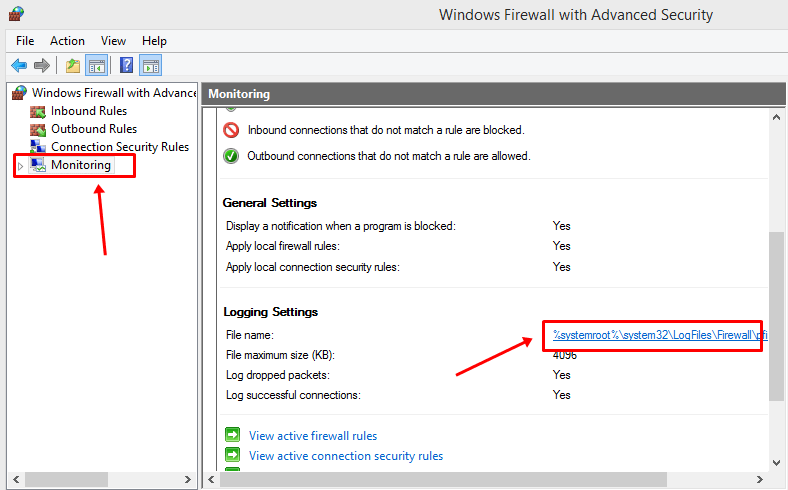
Step 1: Press the Win + R key combination to launch the Run dialog box, type wf.msc, and press Enter to open the Windows Defender Firewall with the Advanced Security window.
Step 2: Click Monitoring on the right pane, and locate the Logging Settings section on the left panel.
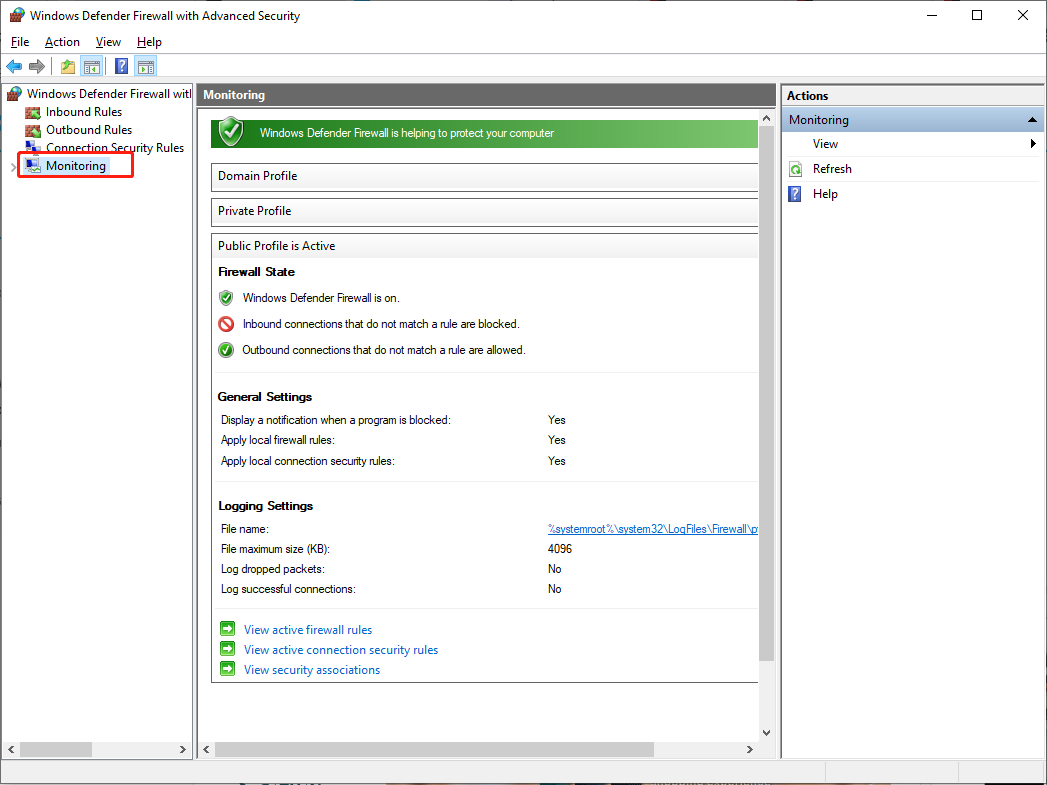
Step 3: You will see a path with a hyperlink after the File name; click the hyperlink to open the log file location.
Modifying the Storage Location of Windows Firewall Logs
Sometimes, there may be a need to alter the default storage location of Windows Firewall logs. The graphical user interface (GUI) in Windows Firewall settings does not provide a built-in feature to facilitate this modification. However, it is possible to adjust the storage location by making changes to the Windows Registry.
Note:
It is imperative to exercise caution when modifying the Windows Registry, as any incorrect alterations can lead to data loss. Before making any changes, it is strongly advised to create a backup of the registry and proceed with careful consideration. MiniTool ShadowMaker is the ideal option for you to back up your data carefully.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
This process necessitates administrative privileges and careful attention. The following are the sequential steps to modify the storage location of Windows Firewall logs:
Step 1: Press the Win + R key combination to launch the Run dialog box, type regedit, and press Enter to open the Windows Registry Editor.
Step 2: In the pop-up UAC prompt, click Yes.
Step 3: Navigate to the following registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsFirewall
Step 4: Find the LogFilePath value under the WindowsFirewall key.
Step 5: Double-click on LogFilePath and enter the desired path for the new storage location of the logs
Step 6: Click OK to save the changes
In Summary
After reading, you must know the location of Windows Firewall logs and how to modify the location of the firewall logs. Hope you can have a good experience!
A firewall monitors traffic entering and exiting the protected environment. It is possible to see the source and type of traffic that is coming into this environment with some firewalls as well. Rules are used to set up a firewall’s security settings. For a firewall’s ruleset to be effective, it must include an effective logging feature.
The firewall’s logging feature keeps track of how it handles different types of traffic. If an attack is detected, the logs can be used by a SIEM to help identify the source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and ports.
All firewalls have a logging feature that documents how the firewall handled various types of traffic while filtering Internet traffic. In addition to the IP addresses, ports, and protocols, these logs can provide valuable information. Using the Windows Firewall log file, you can also monitor TCP and UDP connections and packets that the firewall blocks.
What is Firewall Logging?
When it comes to a firewall, the most basic function is to prevent connections from being made to suspicious networks. Is it safe to trust a network by inspecting the source address of all connections, as well as the destination address and port?
Our source and destination addresses and ports are aggregated for convenience’s sake. An attempt to connect can be identified by this information, which is tracked by the firewall.
When it comes to making connections, this quality is similar to a set of rules that determine which connections are allowed and those that must be blocked.
By using an address that matches that of an already established connection, this source address can connect to its target via the allowed port. As a result, the network is open to traffic.
A successful logging feature should be added to a firewall ruleset in order to maximize its effectiveness.
The firewall’s logging feature reveals how it handles various types of traffic. Information like source and destination IP addresses, protocol versions, and port numbers can be gleaned from these logs.
Why Firewall Logging Is Important?
Here’s why firewall logging is important:
- To see whether newly added firewall rules are working properly to debug them or not.
- In order to determine if the Windows Firewall is causing application errors, firewall logging allows you to check for port openings that are either disabled or dynamic and to analyze packets that are either pushed or urgently dropped on the send path.
- With the Firewall logging feature, you can determine whether or not your network is experiencing any malicious activity. However, you must keep in mind that it does not provide enough information to identify or track down the source.
- If you notice that a particular IP address (or group of IP addresses) is repeatedly failing to enter your firewall and/or other high-profile systems, you may want to write a rule to drop all connections from that IP space.
- Outgoing connections from internal systems, such as Web servers, may indicate that your system is being used to attack computers on other networks.
Here’s how you can easily track firewall activity with the Windows Firewall log:
The log file is disabled by default, so no data is recorded in the log file at all. Follow these simple steps to create a log file:
- First, open the Run dialog box by pressing Win + R together.
- In the Run dialogue box opens, type wf.msc and press Enter.
- Now, the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security screen will open.
- In that window, from the right side, click on Properties.
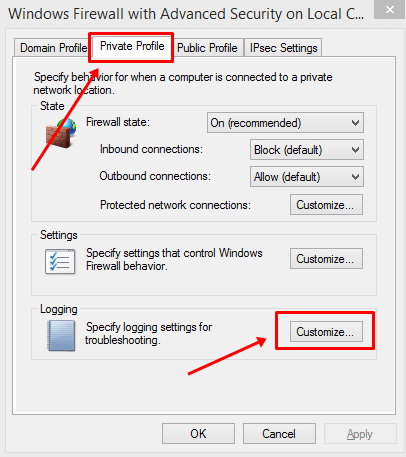
- Next, in the new dialog box, switch to the Private Profile tab. Click on Customize under the Logging section.
- In the new window that pops up, you can select the maximum log size and location, as well as whether or not you want to log only dropped packets or successful connections.
When a packet is rejected by Windows Firewall, it is known as a dropped packet. It is possible for an intruder to make a successful connection to your computer, but this does not necessarily mean that the intruder is successful to connect to your computer.
Windows Firewall, by default, logs all of its activity here:
%SystemRoot%\System32\LogFiles\Firewall\Pfirewall.log
However, it only saves the most recent 4 MB of data. In most production environments, this log will write to your hard disk on a regular basis, and changing the log file’s size limit (to log activity over a longer period of time) may have a performance impact.
Consequently, you should only enable logging when actively troubleshooting a problem, and then turn it off as soon as you’re done.
- Next, on the Public Profile tab, follow the same steps as you did for the Private Profile“. For both private and public network connections, you have now enabled the log.
- After that, on the left panel, click on the Monitoring tab.
- Now click the file path next to File Name in the Details pane under Logging Settings.
- Notepad will now open the log file.
The log file will be saved in the W3C extended log format (.log), which you can examine in any text editor or import into a spreadsheet.
Since a single log file can contain thousands of text entries, you should disable word wrapping in Notepad to preserve column formatting. Further, if you open the log file in a spreadsheet, all of the fields will be organized into columns for easier analysis.
Windows Firewall logs contain information about allowed and blocked attempts to communicate with your computer through the firewall. If you’re troubleshooting a connection problem or trying to find out whether someone’s trying to break into your computer, examining these logs can be helpful.
Where are Windows Firewall Logs?
Windows Firewall logs are stored in the %WINDIR%\system32\Logfiles\Firewall directory.
If you’re not sure where that is, you can open up File Explorer and type “%WINDIR%\system32\Logfiles\Firewall” into the address bar. That will take you right to the folder.
How to View Windows Firewall Logs?

Via Control Panel
Windows Firewall logs can be viewed using the Event Viewer tool.
- To access the Event Viewer, open the Control Panel and navigate to System and Security > Administrative Tools > Event Viewer.
- Once in the Event Viewer, expand the Windows Logs folder and select the Security log.
- The Security log will contain all of the events that have been logged by the Windows Firewall.
Via Run Program
1. Open Event Viewer
To open Event Viewer, press the Windows key + R, type eventvwr, and press Enter.
2. Expand the Windows Logs Folder
Once the Event Viewer is open, expand the Windows Logs folder. This folder contains all of the logs for events that have occurred on your computer, including the firewall logs.
3. Select Security Log
Within the Windows Logs folder, select the Security log. This log contains all of the events related to security, including those related to the firewall.
4. Filter Events
You can use the Filter Current Log option to filter the events that are displayed in the security log.
- For example, you can filter by Event ID, which will only display events with a specific ID number.
- Alternatively, you can filter by Source, which will only display events from a specific source. In this case, you would want to filter by Source=” Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing” to only display firewall-related events.
5. View Events
Once you have filtered the security log to only display firewall-related events, you can then view the details of each event by double-clicking it. The details of each event will include information such as when it occurred, what action was taken (e.g., allow or block), and which program or process was affected.