-
Home
-
Partition Magic
- How to Run PowerShell Script on Windows 10? [Full Guide]
By Ariel | Follow |
Last Updated
The PowerShell script is a collection of commands that can be used to change system settings and do other tasks. However, many users don’t know how to run PowerShell script on Windows 10. Don’t worry! MiniTool will walk you through a full guide to do that.
Windows PowerShell is a command-line shell that enables you to run commands in the scripting environment. If you want to run a PowerShell script, you need to create a script file first. PowerShell script is saved in a text file by using the .ps1 extension.
However, you may receive the error message “cannot be loaded because running script is disabled on this system” when double-clicking the .ps1 file. To run PowerShell script successfully, you can keep reading the following context.
How to Create PowerShell Script on Windows 10
First of all, you need to create PowerShell scripts files. It can be created by using the Notepad. Alternatively, you can use ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment) that is a built-in tool in the preinstalled environment. Here’s how:
Method 1. Create a PowerShell Script File with Notepad
Step 1. Type notepad in the search box and click the Notepad on the top result.
Step 2. Now you can write a new script on the context file. For example, copy and paste Write-Host “Congratulations! Your first script executed successfully” into the context file.
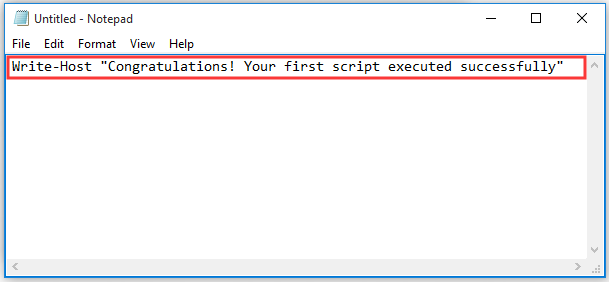
Step 3. Then click on the File menu on the upper left corner and click the Save as button.
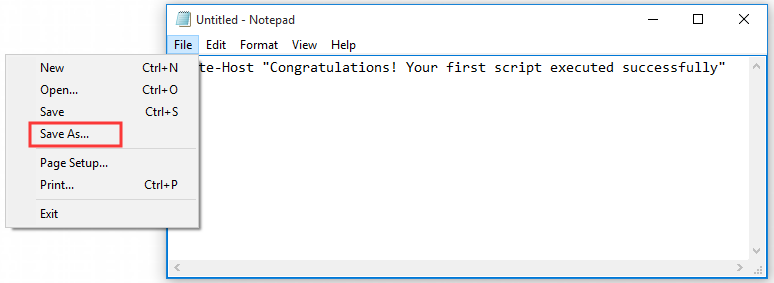
Step 4. Select a location where t you want to save the file and type a new name for the script file followed by the end of .ps1 such as first_script.ps1. After that, click on the Save button.
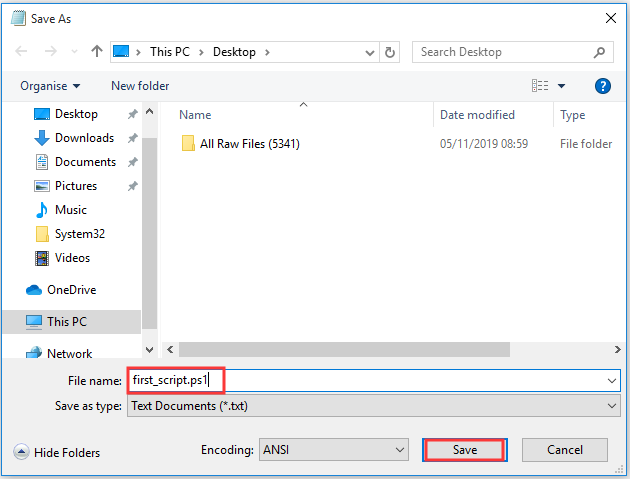
Method 2. Create a PowerShell Script File with Integrated Scripting Environment
In addition, you can use the Windows built-in tool ISE to create a script file. This method is relatively complex, please read the following part carefully.
Step 1. Type Windows PowerShell ISE in the search box, and then right-click the top result and select Run as administrator option.
Step 2. Press Ctrl + N keys on the keyboard to create a new empty .ps1 file.
Step 3. In the new empty file, type or paste a new script file that you want to run. For example, we write Write-Host “Congratulations! Your first script executed successfully”.
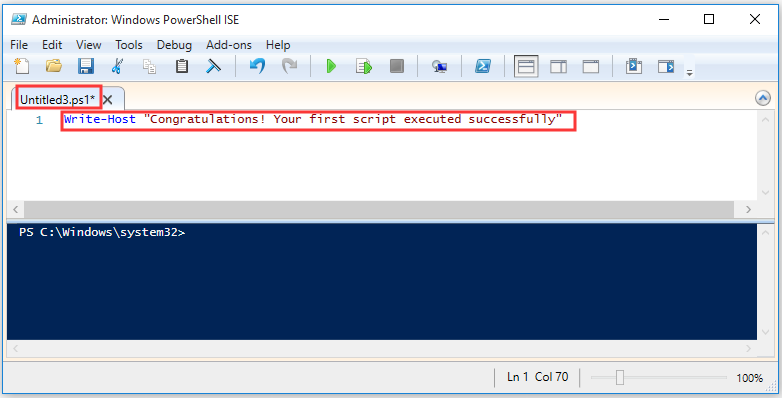
Step 4. Press Ctrl + S keys on the keyboard to save the script file.
Step 5. In the file explorer, select a location that you want to save in and rename it followed by the end of .ps1. After that, click on the Save button.
After you create the script file using Notepad or PowerShell ISE, it should be ready to run. However, it will fail to work by default, because the default PowerShell settings will always prevent any script from executing.
How to Run PowerShell Script on Windows 10
Now, you may wonder how to run a PowerShell script on Windows 10. To run PowerShell scripts on Windows 10, you need to change the execution policy. Here’s how to do that:
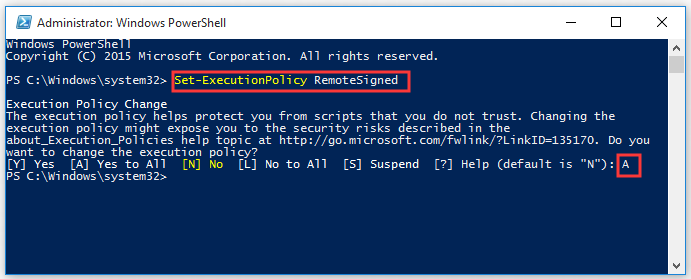
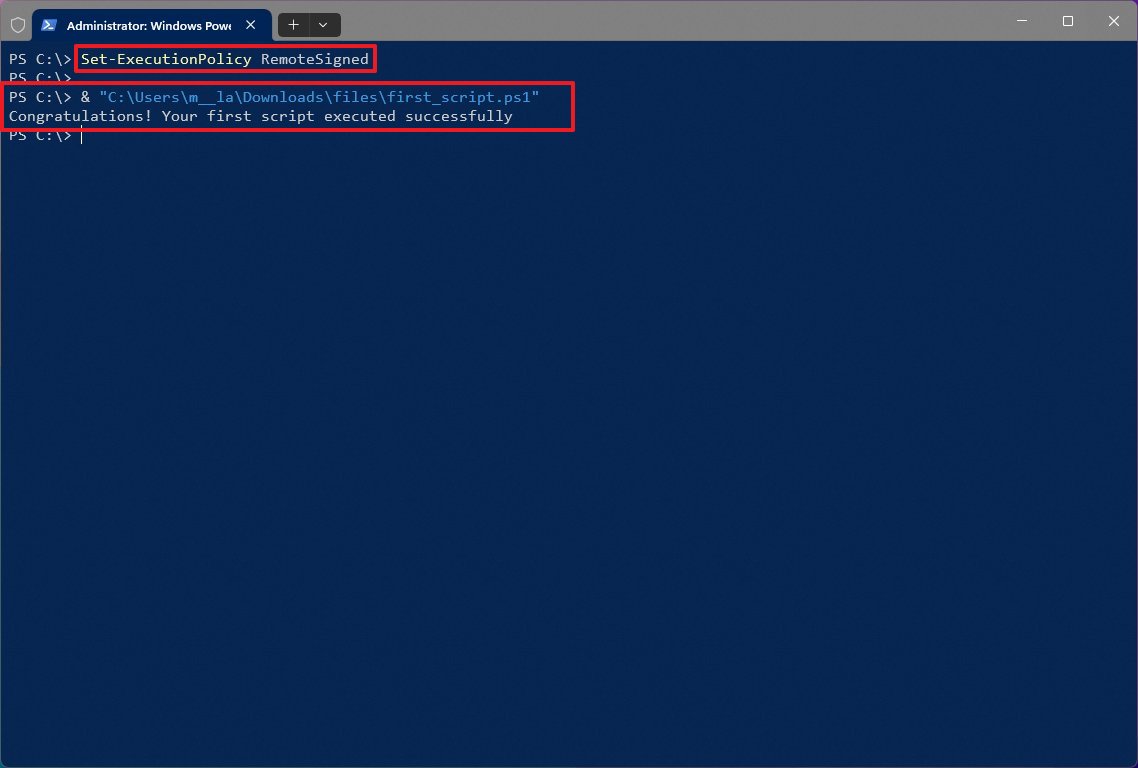
Step 1. Type PowerShell in the search box, and then right-click the top result and select Run as administrator option.
Step 2. Type the Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned command in the window and press Enter.
Step 3. Type A and hit Enter.
Tip: RemoteSigned is an execution policy that enables the script to run on the computer. However, if you create the script on another computer, it won’t run unless the script contains a signature of a trusted publisher.
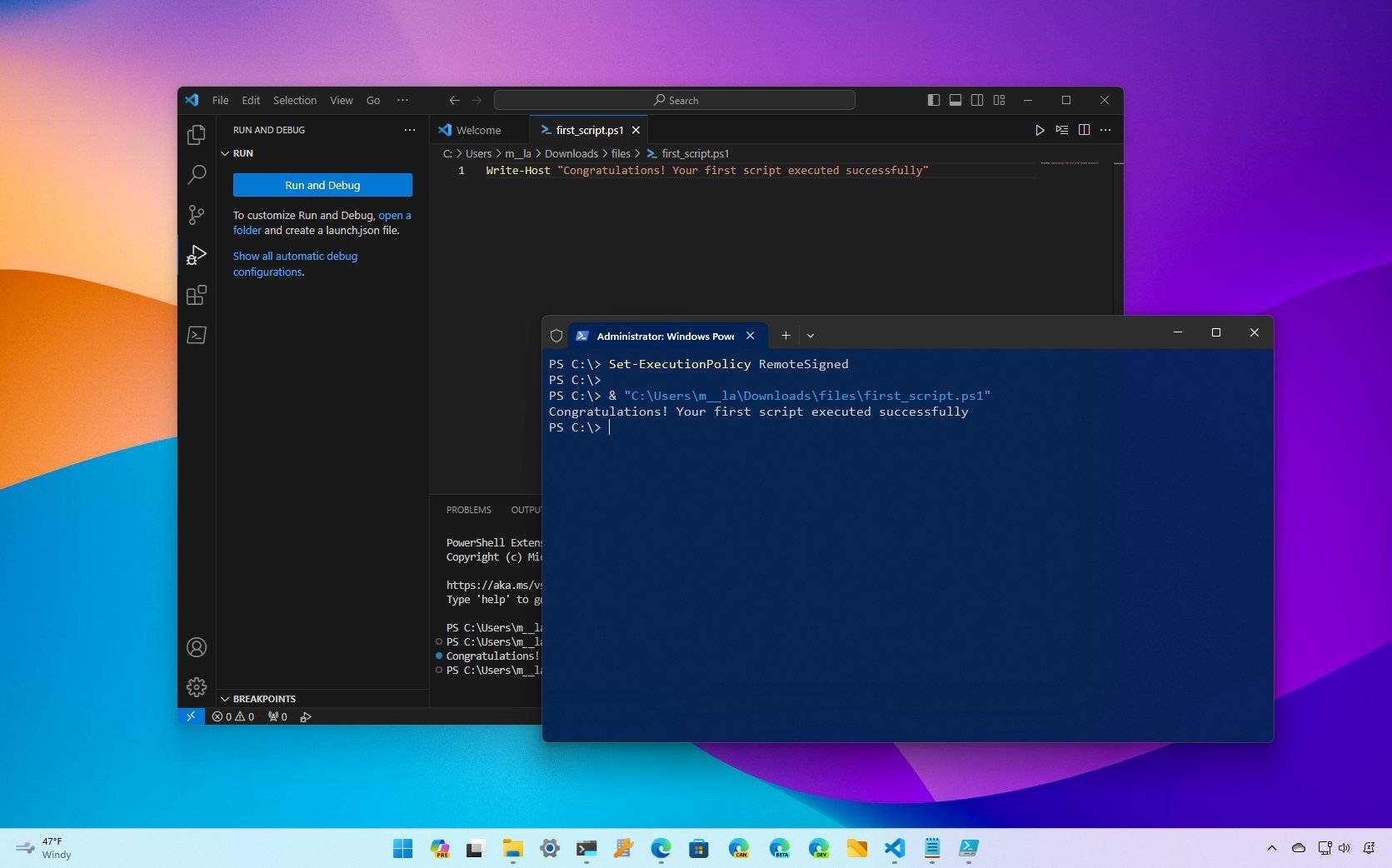
Step 4. Then type & “C:PATHTOSCRIPTfirst_script.ps1 command and hit Enter to run the PowerShell scripts.
Note: In the command, replace the PATHTOSCRIPT with the actual location where you saved the script.
After you complete all the above steps, you should run PowerShell scripts smoothly and see the outputs.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Ariel has been working as a highly professional computer-relevant technology editor at MiniTool for many years. She has a strong passion for researching all knowledge related to the computer’s disk, partition, and Windows OS. Up till now, she has finished thousands of articles covering a broad range of topics and helped lots of users fix various problems. She focuses on the fields of disk management, OS backup, and PDF editing and provides her readers with insightful and informative content.
(Image credit: Mauro Huculak)
On Windows 11 (or 10), PowerShell is a command-line interface (CLI) to run commands and scripts to automate tasks and change settings on your device, similar to Command Prompt. However, PowerShell is a more powerful CLI, offering more tools and flexibility. In addition, unlike Command Prompt, PowerShell is available across platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
A script is a collection of instructions written to a text file (using the «.ps1» extension) that PowerShell understands and executes in sequence to run different actions.
The only caveat is that the default security protocol prevents scripts from running on your computer. This means that when double-clicking a «.ps1» file, the system won’t do anything, and if you try to run the script within PowerShell, you will see the «cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system» error message. However, running scripts on your device is possible. You only need to enable the correct execution policy.
In this how-to guide, I will walk you through the steps to create and run your first script file on PowerShell using Visual Studio Code, Notepad, and the PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE) console, whether you use Windows 10 or 11.
How to create PowerShell script file on Windows 11 and 10
It’s possible to create PowerShell script files using any text editor or the legacy ISE application. However, the Visual Studio Code editor is the preferred option for writing scripts moving forward.
Create a script with VS Code
Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is a free, extensible, cross-platform code editor that works to write virtually any programming language. And when adding the PowerShell extension, you get an interactive scripting editing experience, which even comes with IntelliSense (code-completion) support.
You can still use PowerShell ISE, but Visual Studio Code with the PowerShell extension is meant to be the new default experience. Also, consider that the legacy experience won’t get any new features and doesn’t support PowerShell 7 or future releases.
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
Install VS Code
To install Visual Studio Code on Windows 11 (or 10), use these steps:
- Open the Visual Studio Download page.
- Click the Windows button to download the installation file.
- Double-click the installer to begin the process.
- Select the «I accept the agreement» option.
- Click the Next button.
- Confirm additional tasks as necessary.
- Click the Next button again.
- Click the Install button.
- Click the Finish button.
Once you complete the steps, you can continue installing the PowerShell extension for VS Code.
Install PowerShell extension
To install the PowerShell extension on VS Code, use these steps:
- Open VS Code.
- Click the Extensions tab («Ctrl + Shift + X» keyboard shortcut) from the left pane.
- Search for PowerShell and select the top result.
- Click the Install button.
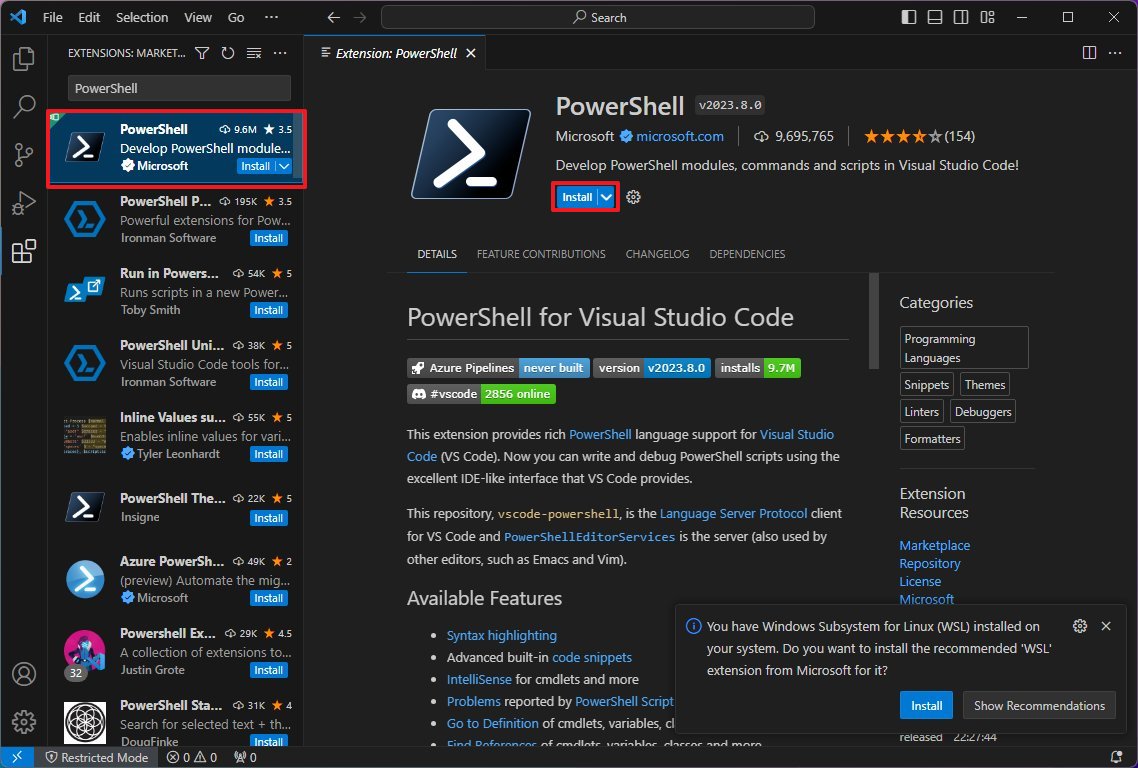
- Click the «Trust Workspace & Install» button.
After you complete the steps, you can start writing PowerShell scripts from Visual Studio Code.
Create PowerShell script with Visual Studio Code
To create a script with Visual Basic Code on Windows 11 (or 10), use these steps:
- Open VS Code.
- Click the File menu and select the «New Text File» option.
- Click the File menu and select the Save As option.
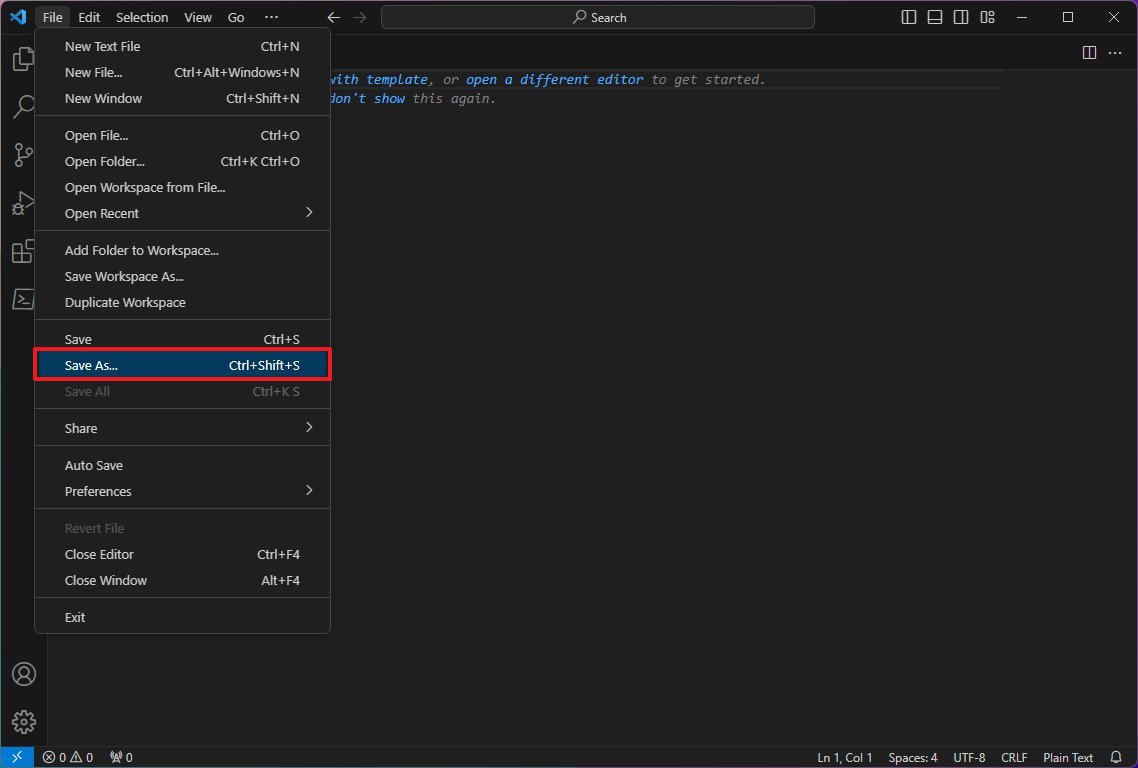
- In the «File name» field, specify a name for the file with the «.ps1» extension — for example, first_script.ps1.
- Click the Save button.
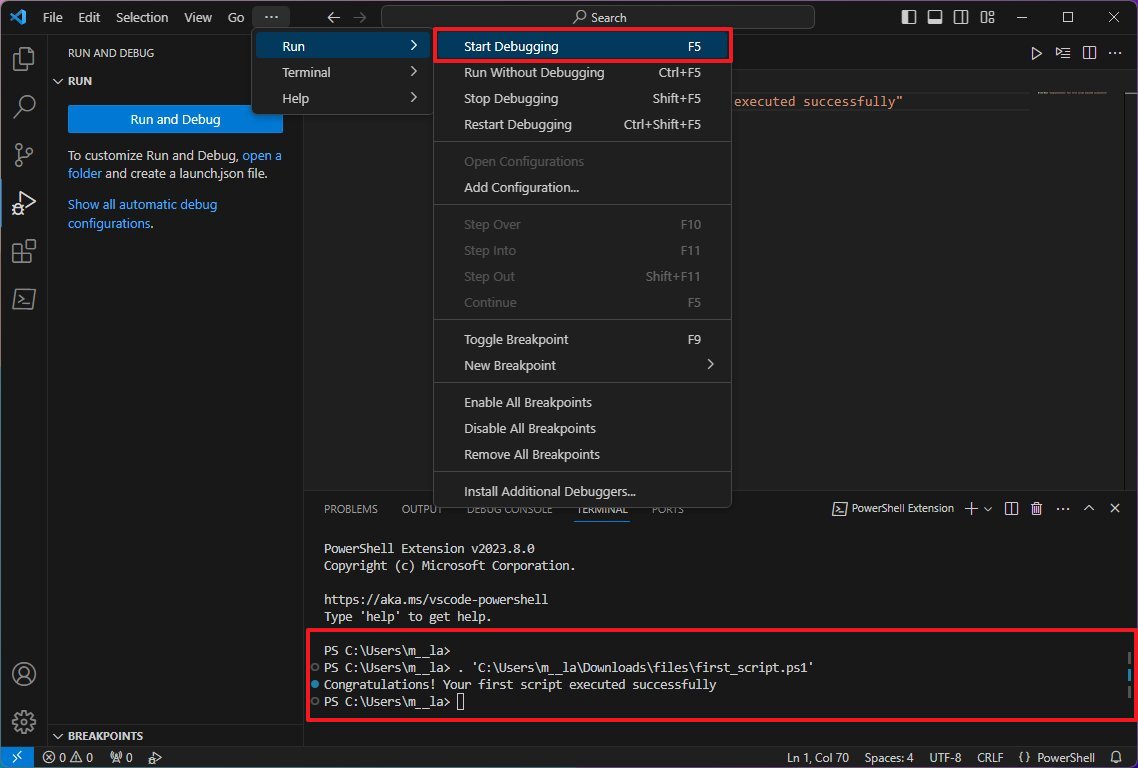
- Write a new or paste the script you want to run — for example, Write-Host «Congratulations! Your first script executed successfully»
- Quick note: The above script will output on the screen that says: «Congratulations! Your first script executed successfully.»
- (Optional) Open the Run menu, select the Start Debugging option from the command bar, or press the F5 key) to run the script.
- Click the File menu.
- Click the Save option.
Create PowerShell script with Notepad
To create a PowerShell script with the Notepad app, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Notepad, and click the top result to open the app.
- Write a new or paste your script in the text file — for example, Write-Host «Congratulations! Your first script executed successfully»
- Quick note: Although the Notepad app looks a little different on Windows 11, the instructions will also apply.
- Click the File menu.
- Select the Save As option.
- Confirm a descriptive name for the script — for example, first_script.ps1.
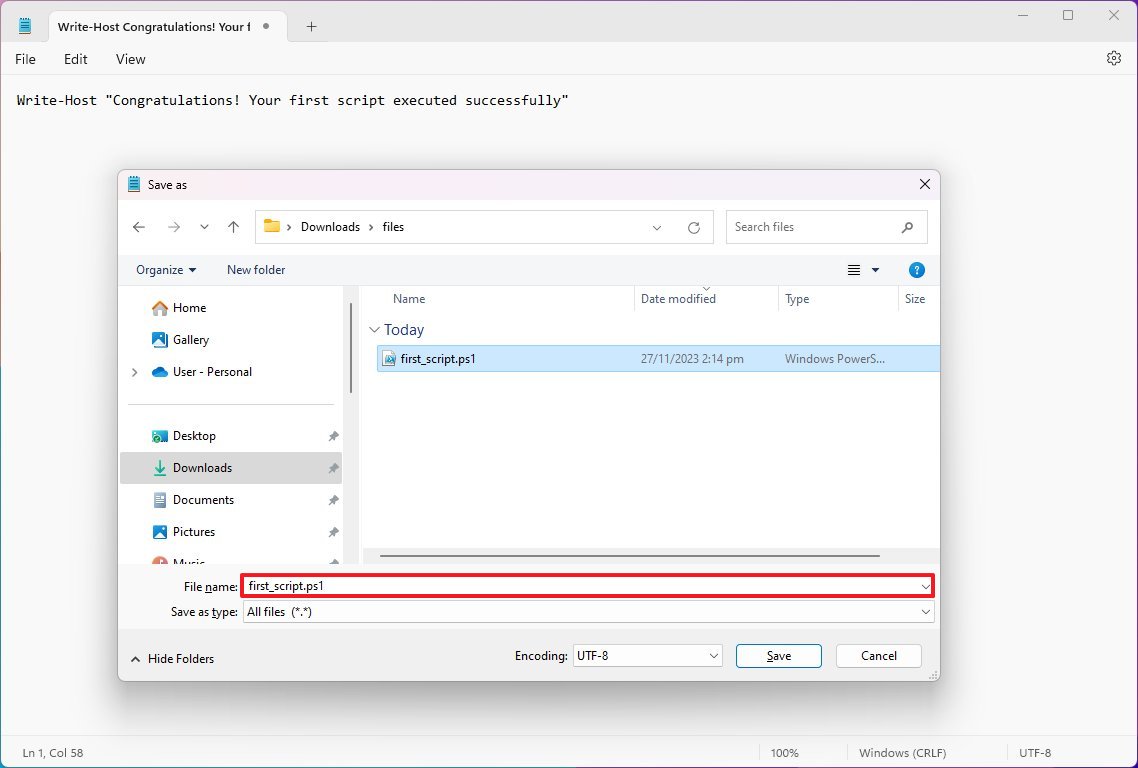
- Click the Save button.
Create PowerShell script with Integrated Scripting Environment
You can also use the built-in PowerShell ISE app to code your scripts on Windows.
The Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE) is a complex tool, but you can get started using these easy steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows PowerShell ISE, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Click the File menu.
- Select the New option to create a new empty «.ps1» file.
- Write a new script or paste the script you want to run — for example, Write-Host «Congratulations! Your first script executed successfully»
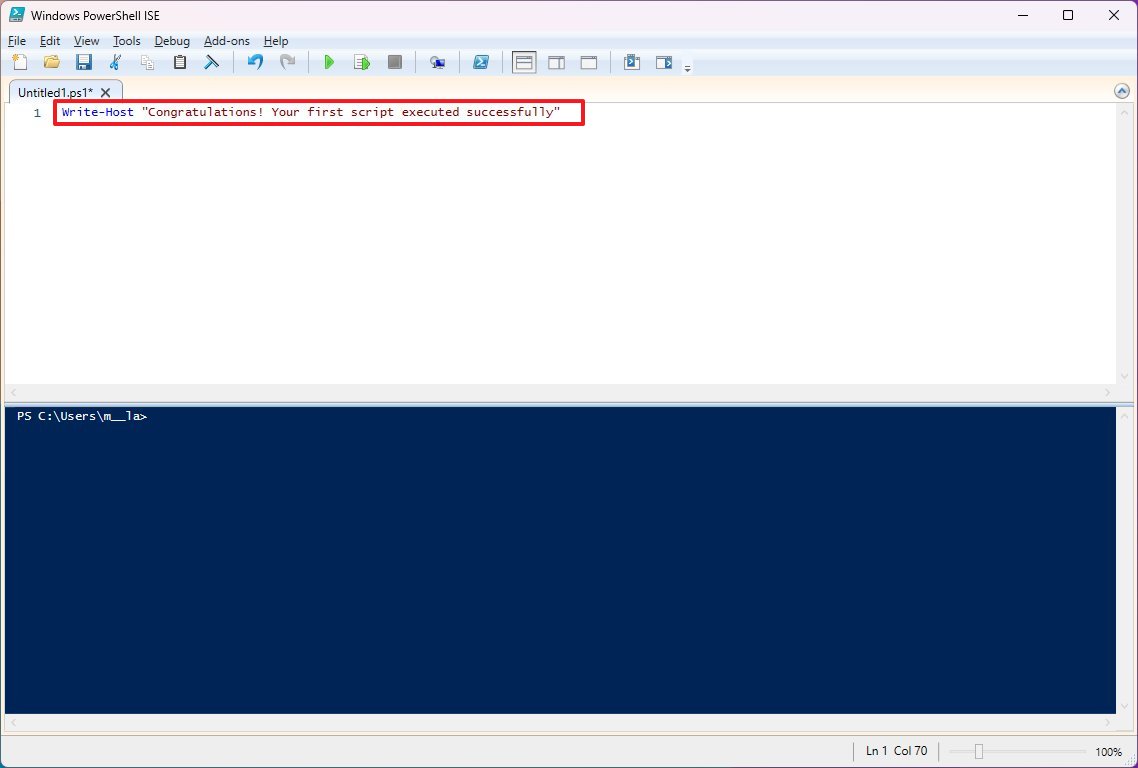
- Click the File menu.
- Click the Save option.
- Type a name for the script — for example, first_script.ps1.
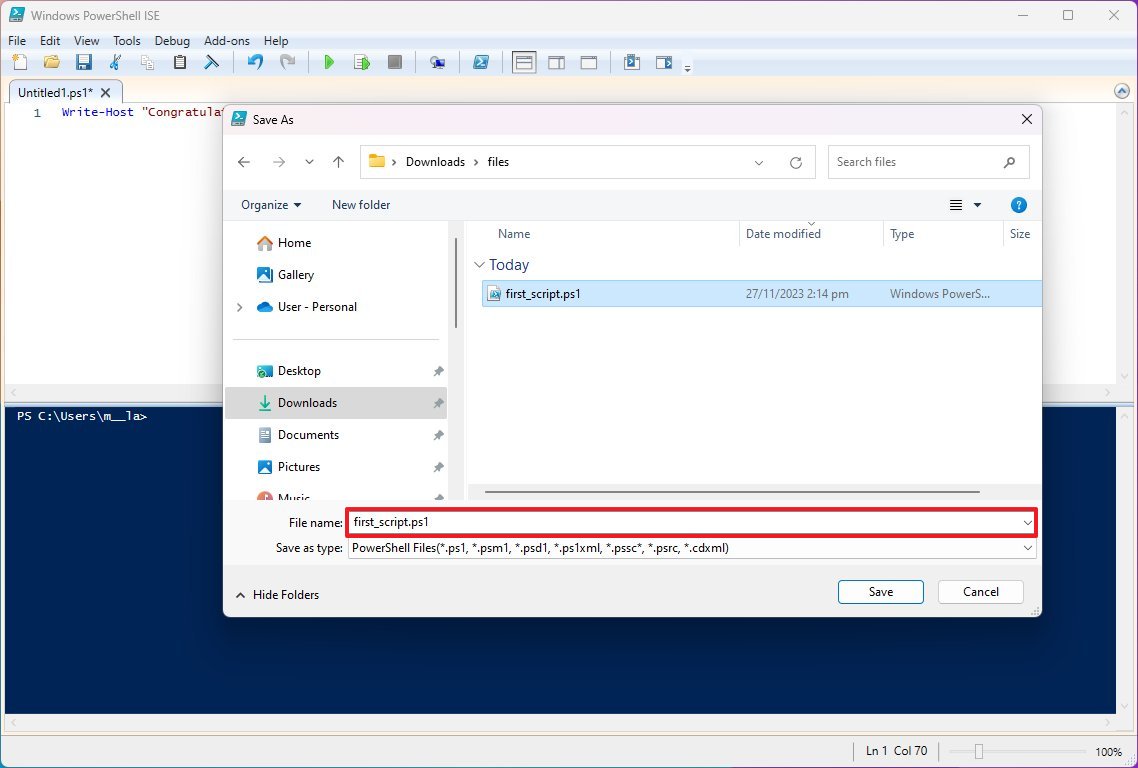
- Select the folder to save the script file.
- Click the Save button.
- (Optional) Click the Run button on the top-right side (or press the F5 key) to run the script.
Once you complete the steps using Notepad, Visual Studio Code, or PowerShell ISE, the script will be ready to run, but it will fail due to the default system settings. The reason is that the default PowerShell settings are configured to block the execution of any script. (The only exception is if you run the script’s contents within Visual Studio Code or PowerShell ISE.)
How to run PowerShell script file on Windows 11 and 10
Whether you use Windows 11 or 10 on your computer, you must change the execution policy to run a script with PowerShell.
To change the execution policy to run PowerShell scripts on Windows 11 (or 10), use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to allow scripts to run and press Enter: Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
- Type «A» and press Enter (if applicable).
- Type the following command to run the script and press Enter: & «C:\PATH\TO\SCRIPT\first_script.ps1»
In the above command, change «PATH\TO\SCRIPT» to the location of your script. For example, this command runs a script stored in the «Downloads» folder: & «C:\Users\username\Downloads\first_script.ps1»
After you complete the steps, the script will run, and if it was written correctly, you should see its output on the screen without issues.
PowerShell includes four execution policies that apply to the operating system:
- Restricted — Prevents any script from running.
- RemoteSigned — Allows scripts created on the computer, but scripts created on another device won’t run unless they include a trusted publisher’s signature.
- AllSigned — All the scripts will run, but only if a trusted publisher has signed them.
- Unrestricted — Runs any script without any restrictions.
It’s recommended to allow local scripts to run a script only from a trusted source. If you don’t plan to run scripts regularly, it’s best to restore the default settings to block untrusted scripts using the same instructions outlined above, but in step 4, use the «Set-ExecutionPolicy Restricted» command.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
Download Windows Speedup Tool to fix errors and make PC run faster
A script is just a collection of commands saved into a text file (using the special .ps1 extension) that PowerShell understands and executes in sequence to perform different actions. In this post, we will outline the process involved in how to create and run a PowerShell script file on Windows 11/10.
PowerShell is a command-line tool designed by Microsoft to run commands and scripts to change settings and automate tasks. In a way, it’s similar to Command Prompt. However, PowerShell is a more capable command-line interface (CLI) that offers an extensive set of tools and more flexibility and control. Also, unlike Command Prompt, PowerShell is available on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
To see how to create and run the PowerShell script file on Windows 11/10, follow the instructions for each of the tasks as shown in the respective sections.
On Windows 11/10, you can create PowerShell script files using virtually any text editor or the ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment) console. However, the preferred option to build scripts moving forward is to use the Visual Studio Code editor with the PowerShell extension.
Visual Studio Code — also known as VS Code — is a free and extensible cross-platform code editor that provides an environment to edit virtually any kind of programming language. And when adding the PowerShell extension, you get a fully interactive scripting editing experience, even with IntelliSense (code-completion) support.
Here’s how to create PowerShell script file on Windows 11/10 using VS Code:
- Head to Visual Studio Download page.
- Click the Windows button to download the installer.
- Double-click the downloaded file to start the installation process of VS Code.
- Confirm the agreement terms.
- Click the Next button.
- Click the Next button again.
- Click the Next button one more time.
- Confirm additional tasks as necessary.
- Click the Next button.
- Click the Install button.
- Click the Finish button.
Once you complete the steps, you can proceed to install the PowerShell extension. Here’s how:
- Open VS Code.
- Click the Extensions tab from the left pane or press the CTRL + SHIFT + X key combo.
- Search for PowerShell and select the top result.
- Click the Install button.
After you complete the installation steps, you can start writing PowerShell scripts using Visual Studio Code. Here’s how:
- Open VS Code.
- Click the File menu and select the New File option.
- Click the File menu and select the Save as an option.
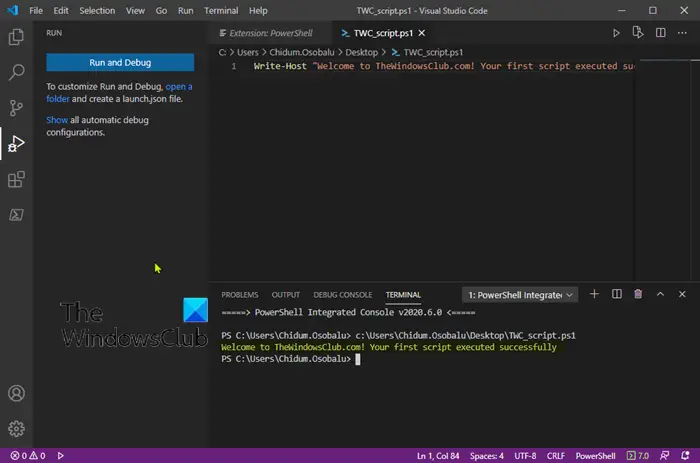
- In the File name field specify a name for the file with the .ps1 extension — for example, TWC_script.ps1.
- Click the Save button.
Write a new, or paste the script you want to run — for example:
Write-Host "Welcome to TheWindowsClub.com! Your first script executed successfully"
The above script will output the phrase below on the screen.
Welcome to TheWindowsClub.com! Your first script executed successfully
You can click the Run button from the top-right side (or press the F5 key) to run the script.
- Click the File menu.
- Click the Save option.
Once you complete the steps using Visual Studio Code, the script will be ready to run, but it will fail by default. This is because the default PowerShell settings are always set to block the execution of any script. (The only exception is if you run the contents of the script within Visual Studio Code or PowerShell ISE.)
How to run PowerShell script file on Windows 11/10
To run a script file with PowerShell, you have to change the execution policy on Windows 11/10.
On Windows 11/10, PowerShell includes four execution policies, including:
- Restricted — Stops any script from running.
- RemoteSigned — Allows scripts created on the device, but scripts created on another computer won’t run unless they include a trusted publisher’s signature.
- AllSigned — All the scripts will run, but only if a trusted publisher has signed them.
- Unrestricted — Runs any script without any restrictions.
Here’s how to run PowerShell script file on Windows 11/10:
- Press Windows key + X to open Power User Menu.
- Press A on the keyboard to launch PowerShell in admin/elevated mode.
- In the PowerShell console, type in the command below and hit Enter.
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
- Type A and hit Enter (if applicable).
Next, type the command below and hit Enter to run the script. Make sure to change “PATH\TO\SCRIPT” placeholder to the location of your script.
& "C:\PATH\TO\SCRIPT\TWC_script.ps1"
After you complete the steps, the script will run, and if it was written correctly, you should see its output without issues.
That’s it on how to create and run the PowerShell script file on Windows 11/10!
Related: How to run local PowerShell Scripts without Signing.
Obinna has completed B.Tech in Information & Communication Technology. He has worked as a System Support Engineer, primarily on User Endpoint Administration, as well as a Technical Analyst, primarily on Server/System Administration. He also has experience as a Network and Communications Officer. He has been a Windows Insider MVP (2020) and currently owns and runs a Computer Clinic.
Навигация по странице
- Как сделать и запустить скрипт PowerShell?
- Как запустить скрипт в PowerShell?
- Как разрешить выполнение неподписанного скрипта PowerShell?
- Как запустить скрипт PowerShell в фоновом режиме?
- Как запустить скрипт через PowerShell с параметрами?
- Как запустить скрипт PowerShell с помощью ярлыка?
- Полезные сценарии для Windows
- Что такое командные скрипты Windows?
- Что такое Bat-скрипты Windows?
- Что такое исполняемые скрипты Windows?
- Какое расширение имеют файлы скриптов PowerShell?
- Какие скрипты PowerShell используются администраторами?
Выполнение скриптов в PowerShell
PowerShell представляет собой новую командную оболочку для операционной системы Windows, созданную Microsoft с целью полного замещения и улучшения cmd. Эта оболочка уже включена в состав операционных систем Windows 7 и выше. Если у вас старая версия операционной системы или вы хотите загрузить более новую версию PowerShell. Windows — операционная система, пользующаяся огромной популярностью среди миллионов пользователей по всему миру. В ее арсенале множество функций и возможностей, однако некоторые из них остаются недостаточно известными обычным пользователям. В данной статье мы расскажем о нескольких полезных сценариях, способных сделать вашу работу с Windows более эффективной и удобной.
Политика исполнения PowerShell-скриптов представляет собой механизм безопасности, управляющий условиями загрузки конфигурационных файлов и запуска сценариев в данной среде. Её основное предназначение — предотвращение выполнения потенциально вредоносных сценариев.

Как сделать и запустить скрипт PowerShell
Создать скрипт PowerShell довольно просто. Вот шаги, которые вы можете выполнить, чтобы создать свой первый скрипт:
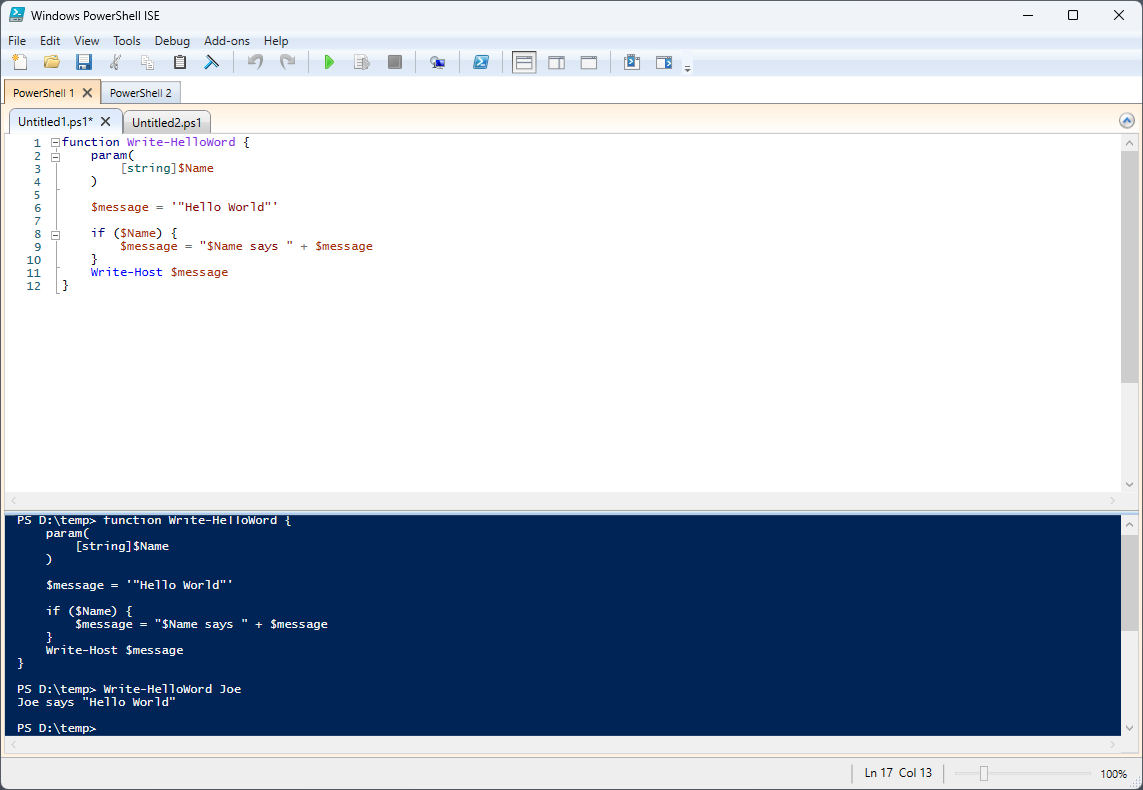
1. Откройте редактор PowerShell ISE:
PowerShell ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment) предоставляет удобную среду для написания и отладки скриптов. Вы можете его найти в меню «Пуск» (Start) под разделом «Стандартные» (Standard) или выполнить команду `PowerShell_ise` в командной строке.
2. Напишите свой скрипт:
В окне редактора PowerShell ISE напишите свой скрипт. Ниже приведен пример простого скрипта, который выводит «Hello, World!» в консоль:
Write-Host «Hello, World!»
3. Сохраните скрипт:
- Нажмите `Ctrl + S` или выберите «Файл» (File) -> «Сохранить» (Save).
- Укажите имя файла и добавьте расширение `.ps1` (например, `MyScript.ps1`).
4. Запустите скрипт:
- Выберите весь текст скрипта.
- Нажмите `F5` или выберите «Запустить сценарий» (Run Script) в PowerShell ISE.
Примеры более сложных скриптов:
#Скрипт, создающий новую папку:
$folderPath = «C:\Path\To\NewFolder»
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path $folderPath
#Скрипт, удаляющий все файлы старше 7 дней в папке:
$folderPath = «C:\Path\To\Folder»
$limitDate = (Get-Date).AddDays(-7)
Get-ChildItem $folderPath | Where-Object { $_.LastWriteTime -lt $limitDate } | Remove-Item
#Скрипт, проверяющий статус службы:
$serviceName = «wuauserv»
$serviceStatus = Get-Service -Name $serviceName | Select-Object Status
Write-Host «The status of service $serviceName is: $($serviceStatus.Status)»
Ваши скрипты могут включать более сложные команды, использовать условия, циклы и вызывать функции. Как только вы освоите основы, вы сможете создавать более мощные и гибкие скрипты PowerShell.

Скрипты для Windows — не просто строки кода, а волшебные ключи, открывающие дверь в мир автоматизации. В руках умелого пользователя они становятся инструментом, способным не только сэкономить время, но и превратить рутинные задачи в захватывающее путешествие по потокам байтов и командам.
Как запустить скрипт в PowerShell?
Существует несколько способов запуска скрипта, вот основные из них:
- Запустить оболочку PowerShell и выполнить в ней скрипт, указав путь к файлу и его имя (например, C:\Scripts\test.ps1) или перейдя в каталог скрипта командой cd C:\Scripts и выполнить его с помощью команды .\test.ps1.
- Оболочку можно найти и запустить разными способами. Один из них — через меню «Пуск». Для Windows 7 пройдите по следующему пути: «Все программы» — «Стандартные» — «Windows PowerShell» и запустите оболочку «Windows PowerShell». Для Windows 10 найдите группу по букве «W» и в ней выберите «Windows PowerShell».
- Запустить «Интегрированную среду сценариев Windows PowerShell ISE», которая представляет собой среду разработки, позволяющую редактировать и отлаживать скрипты PowerShell. Откройте программу, выберите «Открыть» или в меню Файл выберите «Открыть» и укажите нужный скрипт, затем нажмите F5 или кнопку «Выполнить скрипт». Поиск Windows PowerShell ISE можно осуществить так же, как и оболочки PowerShell, через меню «Пуск».
- Запустить стандартный командный интерфейс и ввести следующую команду:
PowerShell -file <имя_скрипта> (например: PowerShell -file myscript.ps1)
Если вы ранее не запускали скрипты PowerShell, возможно, вы получите сообщение о том, что файл <имя_скрипта> не может быть загружен, так как выполнение скриптов запрещено для данной системы. В этом случае введите «get-help about_signing» для получения дополнительной информации. Это связано с безопасностью и предотвращением случайного выполнения вредоносного кода, поэтому все скрипты должны быть подписаны цифровой подписью.
Как разрешить выполнение неподписанного скрипта PowerShell?
- В оболочке PowerShell перед запуском скрипта выполните следующую команду для разрешения выполнения неподписанных скриптов в текущем сеансе оболочки:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process
- При запуске из стандартного командного интерфейса используйте параметр -executionpolicy, например:
PowerShell -executionpolicy RemoteSigned -file <имя_скрипта>
Оба способа устанавливают политику только для текущего сеанса, при этом политика безопасности выполнения скриптов PowerShell, установленная в реестре, остается неизменной. Если вы хотите изменить политику безопасности выполнения скриптов «навсегда», используйте следующий способ:
- Разрешить выполнение навсегда: запустите оболочку PowerShell от имени «Администратора» и выполните команду:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Однако рекомендуется избегать этого способа, чтобы не подвергать ваш компьютер возможным угрозам, поскольку это разрешает выполнение всех скриптов всегда.
Примечание: Если скрипт был загружен из интернета, чтобы избежать запроса на подтверждение выполнения, используйте параметр Bypass вместо RemoteSigned — это полное отключение любых запросов и предупреждений.

Как запустить скрипт PowerShell в фоновом режиме?
Для этого используйте параметр -WindowStyle, который может принимать значения: Normal, Minimized, Maximized и Hidden. Чтобы запустить неподписанный скрипт в фоновом режиме, выполните команду:
PowerShell -executionpolicy RemoteSigned -WindowStyle Hidden -file <имя_скрипта>
Также при желании вы можете добавить -NonInteractive, чтобы скрипт не задавал никаких вопросов. Таким образом, скрипт выполнится незаметно для пользователя. Однако будьте внимательны, используя этот способ.

Как запустить скрипт через PowerShell с параметрами?
Запуск осуществляется аналогично запуску обычной программы или bat-файла с параметрами. Например, чтобы запустить скрипт с параметрами из командной строки, используйте следующую команду:
PowerShell -executionpolicy RemoteSigned -file <имя_скрипта> param1 param2 «еще один текстовый параметр«
В самом скрипте параметры могут быть получены так:
param ($var1, $var2, $var3)
echo $var1, $var2, $var3
В интегрированной среде PowerShell ISE скрипт с параметрами можно запустить аналогично, используя область команд.

Как запустить скрипт PowerShell с помощью ярлыка?
Это можно сделать двумя способами:
- Создать файл bat/cmd, в котором прописать команду для запуска скрипта (с параметрами, как описано выше).
- Создать ярлык на PowerShell, который находится в папке c:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v<версия>\. В свойствах ярлыка в поле «Объект» добавьте необходимые параметры.
Таким образом, например, чтобы запустить скрипт PowerShell при входе пользователя, просто создайте ярлык, как описано во втором пункте, и поместите его в автозагрузку. Также создание ярлыка с использованием одного из вышеописанных методов позволяет легко запускать скрипт от имени администратора или от имени любого другого пользователя, как обычную программу.
Скриптовый язык PowerShell — мощный инструмент для решения различных задач. Однако следует использовать его с осторожностью, поскольку он может быть использован не только для полезных, но и для вредоносных целей. Будьте внимательны при работе с ним.
Полезные сценарии для Windows
1. Скрипт выключения Windows (или перезагрузки):
Простейшая операция выключения компьютера. Откройте блокнот и введите:
shutdown -s -t 0
Сохраните файл с расширением *.cmd* (например, *shutdown.cmd*). При запуске этого файла компьютер выключится. Замените «-s» на «-r» для перезагрузки. Параметр «-t» устанавливает таймер; в данном случае, он равен 0 секунд, но можно установить, например, на 60 для выключения через 60 секунд.
2. Удаление ненужных приложений:
С помощью следующего скрипта можно удалить предустановленные приложения:
get-appxpackage -name *APPNAME* | remove-appxpackage
Замените *APPNAME* на название ненужного приложения. Хотя удаление можно выполнить стандартным способом или через программы, этот скрипт делает процесс более удобным.
3. Управление процессами:
Воспользуйтесь PowerShell для борьбы с медленными процессами. Выведите все службы:
Get-Service
Или получите информацию о конкретной службе с кодовым именем *NAME*:
Get-Service *NAME*
Создайте файл, который закрывает процессы с повышенным потреблением ресурсов:
Stop-Service -Name *ANTIVIRUS*
Stop-Service -Name *BROWSER*
Замените *ANTIVIRUS* и *BROWSER* на соответствующие названия.
4. Переименование группы файлов:
Решите проблему однотипных файлов с помощью скрипта группового переименования:
$path = «$comp\desktop\journey\russia»
$filter = ‘*.jpg’
get-childitem -path $path -filter $filter | rename-item -newname {$_.name -replace ‘HGNMD’,’RUSSIA’}
Укажите путь, расширение и выполните замены в строке.
5. Поиск файлов:
Используйте PowerShell для поиска файлов в директории:
Get-Childitem C:\Windows\*.log
Для более сложного поиска в подпапках:
Get-ChildItem C:\Windows\* -Include *.log -Recurse -Force
6. Справка:
Пользуйтесь командой *Get-Help* для получения информации:
Get-Help Services
Для более подробной справки по конкретной команде:
Get-Help —Name *CMDLET*
7. Получение информации о системе:
Используйте PowerShell для получения данных о системе, например, уровне заряда аккумулятора:
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms
[Windows.Forms.PowerStatus].GetConstructor(‘NonPublic, Instance’, $null, [Type[]]@(), $null ).Invoke($null)
Информация об архитектуре процессора удаленного компьютера:
[PSObject].Assembly.GetType(‘System.Management.Automation.PsUtils’).GetMethod(‘GetProcessorArchitecture’, [Reflection.BindingFlags]40).Invoke($null, @())
Проверка прав администратора текущего пользователя:
[PSObject].Assembly.GetType(‘System.Management.Automation.Utils’).GetMethod(‘IsAdministrator’, [Reflection.BindingFlags]40).Invoke($null, @())
Эти простые и полезные сценарии помогут вам эффективнее управлять вашей системой Windows.
Командные скрипты Windows
Это общий термин, который включает в себя различные типы скриптов и командных файлов, используемых в операционной системе Windows для автоматизации задач. Включают в себя как скрипты на языке командной строки (например, скрипты CMD), так и на более современных языках, таких как PowerShell. Например, Bat-скрипты (*.bat), PowerShell-скрипты (*.ps1), а также другие сценарии, созданные для автоматизации определенных задач.
Bat-скрипты Windows
Bat-скрипты, или файлы пакетных команд (Batch-файлы), представляют собой текстовые файлы, содержащие команды и инструкции для выполнения в командной строке Windows. Основаны на языке пакетных команд (Batch scripting language). Расширение файла: *.bat* (например, *myscript.bat*).
Пример простого bat-скрипта:
«`batch
@echo off
echo Hello, World!
pause
Выполняемые скрипты Windows
Это скрипты, которые могут быть выполнены в среде операционной системы Windows и обычно предназначены для автоматизации различных задач. Включают в себя bat-скрипты (командные файлы), PowerShell-скрипты, а также другие типы скриптов, которые можно выполнять в Windows. Общее отличие между bat-скриптами и PowerShell-скриптами заключается в языке программирования, используемом для написания команд и инструкций. Bat-скрипты используют язык пакетных команд, который является устаревшим и имеет ограниченные возможности по сравнению с PowerShell, который представляет более современный и мощный язык с разнообразными функциональными возможностями для автоматизации задач в Windows.
Какое расширение имеют файлы скриптов PowerShell
PowerShell-скрипты имеют расширение *.ps1*, и для их выполнения часто требуется предварительная настройка политики выполнения скриптов (Execution Policy), чтобы разрешить запуск скрипта через PowerShell в системе.
Скрипты PowerShell для администратора
PowerShell — мощный инструмент для сисадминов Windows, предоставляя широкий набор команд и сценариев для автоматизации и управления системой. Ниже приведены несколько примеров PowerShell-скриптов, которые могут быть полезны администраторам:
1. Создание резервной копии файлов:
$sourcePath = «C:\Path\To\Source»
$destinationPath = «D:\Backup»
$timestamp = Get-Date -Format «yyyyMMddHHmmss»
$backupFolder = «$destinationPath\Backup_$timestamp»
Copy-Item -Path $sourcePath -Destination $backupFolder -Recurse
2. Мониторинг дискового пространства:
$threshold = 80
$disks = Get-WmiObject Win32_LogicalDisk | Where-Object { $_.DriveType -eq 3 }
foreach ($disk in $disks) {
$freeSpacePercentage = [math]::Round(($disk.FreeSpace / $disk.Size) * 100, 2)
$diskLetter = $disk.DeviceID
if ($freeSpacePercentage -lt $threshold) {
Write-Host «Warning: Disk $diskLetter is running low on free space ($freeSpacePercentage%)»
# Можно добавить уведомление администратора
}
}
3. Создание нового пользователя:
$username = «NewUser»
$password = ConvertTo-SecureString «SecurePassword123» -AsPlainText -Force
$fullname = «New User»
$description = «Description of the new user»
$ou = «OU=Users,DC=Domain,DC=com»
New-ADUser -SamAccountName $username -UserPrincipalName «$username@domain.com» -Name $fullname -GivenName $fullname -Surname $username -Description $description -AccountPassword $password -Enabled $true -PassThru -Path $ou
4. Мониторинг событий в журнале событий:
$logName = «System»
$events = Get-WinEvent -LogName $logName -MaxEvents 10
foreach ($event in $events) {
Write-Host «Event ID $($event.Id): $($event.Message)»
}
5. Обновление всех установленных модулей PowerShell:
Get-Module -ListAvailable | ForEach-Object {
Update-Module -Name $_.Name -Force
}
6. Удаление временных файлов в системной директории:
$tempPath = [System.IO.Path]::GetTempPath()
Remove-Item «$tempPath\*» -Force
7. Создание отчета о состоянии служб:
$services = Get-Service | Select-Object DisplayName, Status, StartType
$services | Export-Csv -Path «C:\Path\To\ServiceReport.csv» -NoTypeInformation
8. Настройка правил брандмауэра:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName «Allow-SSH» -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 22 -Action Allow
9. Удаление неиспользуемых профилей пользователей:
$inactiveDays = 90
$userProfiles = Get-WmiObject Win32_UserProfile | Where-Object { $_.Special -eq $false }
foreach ($profile in $userProfiles) {
$lastUseDate = $profile.LastUseTime
$difference = (Get-Date) — $lastUseDate
if ($difference.Days -ge $inactiveDays) {
Remove-WmiObject -InputObject $profile -Confirm:$false
Write-Host «User profile $($profile.LocalPath) deleted.»
}
}
Эти примеры предоставляют общее представление о том, как PowerShell может использоваться администраторами для автоматизации различных задач в Windows-среде. Помните, что некоторые команды могут потребовать выполнения от имени администратора.
Для вызова скриптов PowerShell, вы можете использовать команду `Invoke-Expression` или просто указать путь к файлу скрипта. Предположим, у вас есть следующие скрипты: `ClearDisk.ps1`, `InstallPrograms.ps1`, `BackupScript.ps1`, и `UpdateSystem.ps1`.
1. Скрипт очистки диска (ClearDisk.ps1):
# ClearDisk.ps1
# Ваш код для очистки диска
# Пример: удаление временных файлов
Remove-Item -Path «$env:TEMP\*» -Recurse -Force
Как вызвать:
# Используйте Invoke-Expression
Invoke-Expression -Command «.\ClearDisk.ps1»
# Или просто указывайте путь к файлу скрипта
.\ClearDisk.ps1
2. Скрипт автоматической установки программ (InstallPrograms.ps1):
# InstallPrograms.ps1
# Ваш код для автоматической установки программ
# Пример: установка программы Chocolatey и установка пакетов
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString(‘https://chocolatey.org/install.ps1’))
choco install packageName -y
Как вызвать:
# Используйте Invoke-Expression
Invoke-Expression -Command «.\InstallPrograms.ps1»
# Или просто указывайте путь к файлу скрипта
.\InstallPrograms.ps1
3. Скрипт резервного копирования (BackupScript.ps1):
# BackupScript.ps1
# Ваш код для создания резервной копии
# Пример: копирование файлов в другую директорию
$sourcePath = «C:\Path\To\Source»
$destinationPath = «D:\Backup»
Copy-Item -Path $sourcePath -Destination $destinationPath -Recurse
Как вызвать:
# Используйте Invoke-Expression
Invoke-Expression -Command «.\BackupScript.ps1»
# Или просто указывайте путь к файлу скрипта
.\BackupScript.ps1
4. Скрипт автоматического обновления системы (UpdateSystem.ps1):
# UpdateSystem.ps1
# Ваш код для автоматического обновления системы
# Пример: обновление всех установленных модулей PowerShell
Get-Module -ListAvailable | ForEach-Object {
Update-Module -Name $_.Name -Force
}
Как вызвать:
# Используйте Invoke-Expression
Invoke-Expression -Command «.\UpdateSystem.ps1»
# Или просто указывайте путь к файлу скрипта
.\UpdateSystem.ps1
Убедитесь, что вы находитесь в той же директории, что и ваши скрипты, или укажите полный путь к файлу скрипта.
В этой статье мы коснулись всех аспектов создания, запуска и использования скриптов в Windows. Надеемся, что эти советы и примеры помогут вам освоить этот увлекательный мир автоматизации и сделают вашу работу более эффективной и приятной.
Editor’s note: Adam Bertram originally wrote this article, and Reda Chouffani has expanded it.
Even though administrators can accomplish many tasks with ad hoc PowerShell commands, learning how to script brings your productivity to the next level.
Most administrators get introduced to PowerShell by working with its cmdlets from the command line. Once you’re familiar with executing commands and learn how to work with objects and the PowerShell pipeline, then it’s time to stitch these commands together into a script.
Going from entering commands to scripting isn’t difficult if you think about a script as a long-form command. Scripts execute one or more PowerShell commands together to accomplish a single task.
What are the basics of PowerShell scripting?
The purpose of PowerShell is to provide a command-line shell and scripting capabilities to automate and configure Microsoft’s platforms. This helps IT professionals with many of their administrative tasks.
The platform provides several capabilities that some of the administrative portals don’t offer. Scripting is also available to administrators to automate some of their administrative activities.
PowerShell scripting starts with opening some of the PowerShell terminals on the administrator’s machine. This can be done from a Windows machine or a Linux machine as well. Once the administrator launches the PowerShell tool, they can enter any of the desired commands they need.
The syntax used is specific to PowerShell and provides a way for administrators to interact and confirm or extract information from different systems based on the modules used. PowerShell also offers admins the ability to script their tasks to automate any repeatable processes or tasks they perform on the different systems.
This PowerShell scripting tutorial for beginners helps you make the transition from basic use to advanced functions to help with tasks like server deployments or assigning licenses to users.
How to write and create a PowerShell script
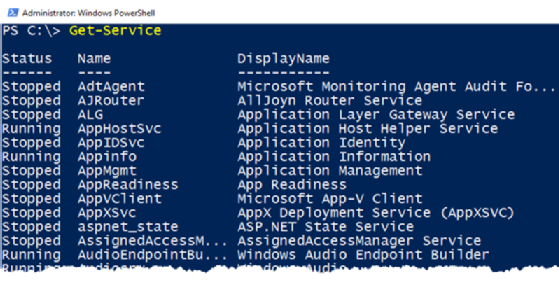
Let’s start with an example of querying Windows services from Windows Server. The Get-Service cmdlet queries all the services running on a local Windows computer from the PowerShell console.
If you want to find all of the stopped services, try to start them and add some logging capabilities, you need to create a PowerShell script.
In the example below, the PowerShell script contains more than one line, a construct known as a loop, as well as containing references to multiple commands:
$services = Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq 'Stopped'}
foreach ($service in $services) {
Add-Content -Path 'C:\ScriptLog.log' -value "Attempting to start
$($_.DisplayName)…"
$service | Start-Service
}
You can build the script in the PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE) editor that comes with Windows. Open the PowerShell ISE editor, copy the code and save it as Start-StoppedServices.ps1. All PowerShell scripts have a PS1 extension for Windows that prompts the PowerShell engine to execute the script.
As another example, in Windows 10 and Windows 11 machines, you can use PowerShell to retrieve some of the Windows Update logs to determine if a recent workstation issue is the result of a recent Windows update. To perform this task, run the following command in PowerShell:
Get-WindowsUpdateLogOnce the command completes its execution, a file is generated to provide all the details of all updates performed on the specific machine.
How to save a PowerShell script
Microsoft provides several ways to create PowerShell scripts, including the following:
- PowerShell ISE.
- Notepad.
- Notepad++.
- Visual Studio (Standard, Pro, Enterprise, Code).
Once the script is created, you can save it locally or to server storage using the PS1 extension. You can also use code repository platforms to ensure the versioning of your scripts.
How to execute a PowerShell Script
With your script saved in a single file, instead of typing out all that code, you can execute it as a single command by passing the entire script to PowerShell.
If you go back to the PowerShell console, you can run C:-StoppedServices.ps1 to execute all the code in that script. Creating scripts is similar to creating commands; it lets you piece together code and run it as a single unit.
You can also run PowerShell scripts from the cmd.exe command interpreter or from a batch file. You can launch a script from anywhere by invoking the PowerShell engine and passing a script to it.
In the following example, you use the File parameter to pass the script to PowerShell without opening the PowerShell console.
powershell -File C:\Start-StoppedServices.ps1
Best practices when designing PowerShell scripts
Once you build up a proficiency with PowerShell cmdlets and its scripting language, there are endless ways to solve problems with code. This scripting tutorial wouldn’t be complete without a few best practices that can help you construct proper scripts.
Simplify things, and think of your script as something that performs a single task or that solves a single problem. In our example, the script starts all the services that have stopped. Administrators can benefit from writing basic scripts that complete repetitive tasks, providing them with more time to work on more demanding tasks.
In addition, design scripts that require little maintenance. If your script only performs one task, you can eventually combine it with other scripts to create building blocks. Make scripts modular so you don’t have to change the code constantly. Parameters can help you further customize your scripts by defining variables to pass different values during script execution.
This should start you on your way from clicking through multiple menu options to complete a task to producing code that handles complex jobs in a flash.
