This page gives specific instructions on setting up Node-RED in a Microsoft Windows environment. The instructions are specific to Windows 10. They may also work for Windows 7 and Windows Server from 2008R2, but it is advisable not to use them due to lack of current support.
Note : Some of the following instructions mention the «command prompt». Where this is used, it refers to either the Windows cmd or PowerShell terminal shells. It is recommended to use PowerShell on all newer versions of Windows as this gives you access to commands and folder names that are closer to those of Linux/Mac.
Quick Start
1. Install Node.js
Download the latest LTS version of Node.js from the official Node.js home page. It will offer you the best version for your system.
Run the downloaded MSI file. Installing Node.js requires local administrator rights; if you are not a local
administrator, you will be prompted for an administrator password on install. Accept the defaults when installing. After installation completes, close any open command prompts and re-open to ensure new environment variables
are picked up.
Once installed, open a command prompt and run the following command to ensure Node.js and npm are installed correctly.
Using Powershell: node --version; npm --version
Using cmd: node --version && npm --version
You should receive back output that looks similar to:
2. Install Node-RED
Installing Node-RED as a global module adds the command node-red to your system path. Execute the following at the command prompt:
npm install -g --unsafe-perm node-red
3. Run Node-RED
Once installed, you are ready to run Node-RED.
Alternative Installations on Windows
In this section, we provide you with information on alternative ways to install Node.js, npm and the Windows Build Tools needed to install some Nodes for Node-RED on Windows.
Note : You should not use an administrative (a.k.a. «elevated») command prompt unless specifically instructed to. You will very likely need to be quite familiar with command prompts as you learn about Node-RED and Node.js and it will be worth while reading some of the Microsoft articles on PowerShell. the PowerShell Tutorial and PowerShell One-Liners sites may also be helpful.
Standard installations of Node.js on Windows require local administrator rights. Download the appropriate version from the official Node.js home page. It will offer you the best version. While you can use either 32 bit or 64 bit versions on 64 bit Windows, it is recommended to use the 64bit version of Node. If for some reason, you need a different installation, you can use the Downloads Page.
There are two potentially useful alternatives to installing Node.js with the MSI installer.
-
Using the Chocolatey package manager
Chocolatey is a package manager for Windows similar to APT or yum on Linux and brew on the Macintosh platforms. If you are already using Chocolatey, you may want to use this tool to install Node.js (e.g. using the
nodejs-ltspackage). Note however, that many packages have uncertain management and that these packages may use different folder locations than those mentioned above. -
Using a Node version manager
Using a Node.js version manager such as nvm-windows can be very helpful if you are doing Node.js development and need to test against different versions. Keep in mind that you will need to reinstall global packages and may need to re-install local packages when when you switch the version of Node you are using.
Note : Microsoft maintain a parallel version of Node that uses the Microsoft Chakra Core JavaScript engine instead of V8. This is not recommended for Node-RED as it has not been tested.
npm on Windows
When you install Node.js, you are also installing the npm package manager. You may see some instructions on the web that recommend installing later releases of npm than the one that comes with the Node.js release. This is not recommended as it is too easy to later end up with an incompatible version. Node.js releases are very regular and that is sufficient to keep npm updated.
Sharing Node-RED between Users
Node.js is installed into the Program Files folder as you would expect. However, if you install a global package like Node-RED using npm -g, it is installed into the $env:APPDATA\npm folder (%APPDATA%\npm using cmd) for the current user. This is less than helpful if you are installing on a PC with multiple user logins or on a server and installing using an admin login rather than the login of the user that will run Node applications like Node-RED.
Note : To see what a folder name like %APPDATA% translates to, you can simply type it into the address bar of the Windows File Explorer. Alternatively, in PowerShell, type the command cd $Env:APPDATA(cd %APPDATA% using cmd).
To fix this, either give permissions to the folder to other users and make sure that the folder is included in their path user environment variable.
Alternatively, change the global file location to somewhere accessible by other users. Make sure that you use the user that will be running Node-RED to make these changes. For example, to change the location to $env:ALLUSERSPROFILE\npmglobal using PowerShell:
mkdir $env:ALLUSERSPROFILE\npmglobal
npm config set prefix $env:ALLUSERSPROFILE\npmglobal
You will then want to change the npm cache folder as well:
mkdir $env:ALLUSERSPROFILE\npmglobal-cache
npm config set cache $env:ALLUSERSPROFILE\npmglobal-cache --global
If using the above changes, you can add the new prefix folder to the PATH System variable and remove the old folder from the user’s Path variable. To change the PATH Environment variable, type environment into the start menu or Cortana and choose Edit Environment Variables.
For each of the users running Node-RED, check that the above settings for the other users are correct.
Installing Node.js Windows Build Tools
Many Node.js modules used by Node-RED or installed nodes have binary components that will need compiling before they will work on Windows. To enable npm to compile binaries on the Windows platform, install the windows-build-tools module using the command prompt as an Administrator:
npm install --global --production windows-build-tools
If you wish to have the built-in Python v2.7 install exposed for use, use the command:
npm install --global --production --add-python-to-path windows-build-tools
Notes:
- Not all Node.js modules will work under Windows, check the install output carefully for any errors.
- During the install some errors may be reported by the
node-gyp
command. These are typically non-fatal errors and are related to optional dependencies
that require a compiler in order to build them. Node-RED will work without these
optional dependencies. If you get fatal errors, first check that you installed thewindows-build-toolsmodule and that you have closed and opened your command prompt window.
Running on Windows
Once installed, the simple way to run Node-RED is to use the node-red command in a command prompt:
If you have installed Node-RED as a global npm package, you can use the node-red command:
This will output the Node-RED log to the terminal. You must keep the terminal open in order to keep Node-RED running.
Note that running Node-RED will create a new folder in your %HOMEPATH% folder called .node-red. This is your userDir folder, think of it as the home folder for Node-RED configuration for the current user. You will often see this referred to as ~/.node-red in documentation. ~ is shorthand for the user home folder on Unix-like systems. You can use the same reference if using PowerShell as your command line as recommended. If you are using the older cmd shell, that won’t work.
You can now create your first flow.
Using PM2
If you are using Windows to develop Node-RED flows or nodes, you may find it helpful to use PM2 to run Node-RED. This can be configured to automatically restart when files change, always keep Node-RED running and manage log output.
Run Node-RED on Startup
If you want to use Windows as a production platform for Node-RED, you will want to have a Windows Task Scheduler job set up. To do so:
- Go to the start menu and type “task scheduler” and click on the result.
- Click on “Create Task…” in the right-hand menu. Follow the steps to create a new task.
Make sure that you use the user login that you’ve used to set up and do the initial run of Node-RED. You can use an “At startup” trigger to always run Node-RED at system startup. Use the Action “Start a program” with details set to C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Roaming\npm\node-red.cmd (replacing <user> with your actual user name).
You may wish to make sure that it only starts if the network is available. You may also wish to restart if the job fails. Perhaps restarting every minute but only 3 times — if it won’t start by then, the error is fatal and will need some other intervention. You can check for failures by looking in the event log. If you want to access to the logs when running this way, you should amend the node-red.cmd file to redirect std and error outputs to a file (creating an alternative startup file would be better so that it isn’t overwritten on updates).
Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Software & Equipment Requirements
- 3. Installing Node-RED
- 3.1 Node.js
- 3.2 Install Node-RED
- 4. Additional packages you will need
- 4.1 Node-RED-dashboard
- 4.2 node-red-contrib-modbus
- 5 Running Node-RED
- 6. An Overview of Node-RED
- 6.1. Palette
- 6.2. Workspace
- 6.3. Sidebar
- 6.4. Header

1. Introduction
Node-RED is a visual programming tool aimed at connecting hardware devices, APIs and online services in alternative ways, without the need for traditional programming experience. The software provides a browser-based editor that makes it easy to wire together flows using the wide range of nodes in the palette that can be deployed to its run-time in a single-click.
Although the concept of flows, nodes & palettes may sound unfamiliar, Node-RED makes programming simple by using a visual representation of code in blocks with lines between them.
Some examples of the many functions available are:
- REST clients to query data on other servers
- Modbus TCP client to talk to Brainboxes Remote IO devices
- JavaScript functions can be created within the rich text editor
- A built-in library allows you to save useful functions, templates or flows for re-use
- The flows created in Node-RED are stored using JSON which can be easily imported and exported for sharing with others
- An online flow library allows you to share your best flows with the world.
2. Software & Equipment Requirements
You will need:
- A Brainboxes Remote Ethernet I/O device
- Any Windows PC/laptop
- Network connection
3. Installing Node-RED
The following are instructions on how to install Node-RED on a Windows based operating system. All required download links can be found on the official Node-RED and NodeJS websites.
3.1 Node.js
Node-RED uses a runtime engine called Node.js. Node.js is a JavaScript based programming language and must be installed before Node-RED. Node.js can be downloaded from the official Node.js website. When installing Node.js for use with Node-RED it is recommended that you install the 10.XX.X. LTS variant:
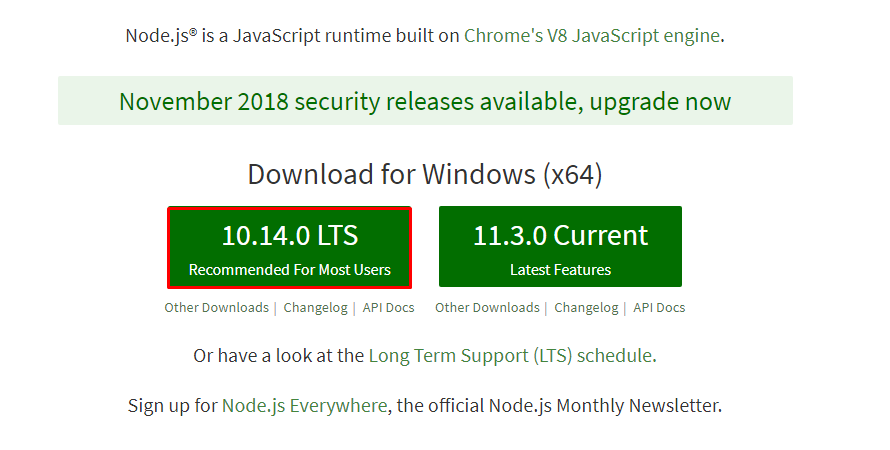
Once the installation is complete, open up a Windows command prompt, you can open a command prompt by using the keyboard shortcut (Windows key + r) type cmd and then once the command prompt has opened, input the following:
node --version && npm --version
This command checks if both Node.js and NPM are correctly installed, and if so it will return a version number.
The output should look something like this:
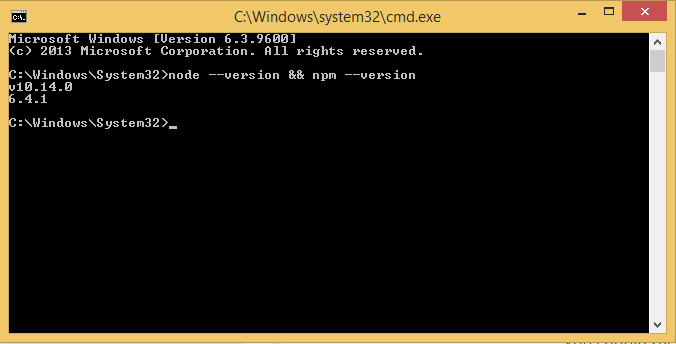
NPM is a package manager for the JavaScript programming language, this is needed for installing additional Node-RED packages which we will need later. NPM should be installed by default when installing Node.js.
3.2 Install Node-RED
Now we can begin to install Node-RED, navigate to CMD and input the command:
npm install -g --unsafe-perm node-red
Please note if the module does not install and throws up error messages regarding permissions, you will need to run CMD in Administrator mode. If you are having trouble with this please contact your System Administrator. Once this command is ran Node-RED will begin to install. Please note this can take some time to complete:
Once complete, the output should look like this:
4. Additional packages you will need
There are some additional packages you will need to install when following this guide.
4.1 Node-RED-dashboard
The first package you will need to install is the Node-RED dashboard, this module adds nodes which allow us to easily create a live data dashboard.
To install this module simply open up a command prompt and input:
npm install -g node-red-dashboardPlease allow a few minutes for this to package install:
Please note if the module does not install and throws up error messages regarding permissions, you will need to run CMD in Administrator mode. If you are having trouble with this please contact your System Administrator.
When the module is successfully installed the response should look something like this:
4.2 node-red-contrib-modbus
The next package you will need to install is contrib-modbus, this module adds nodes that allow us to communicate in ModbusTCP
To install this module simply open up a command prompt and input:
npm install -g node-red-contrib-modbus
Again, please allow a few minutes for this to install:
Please remember you may need to run this command on an elevated command prompt.
When the module is successfully installed the response should look something like this:
5 Running Node-RED
Once everything has been successfully installed you can now begin to run your Node-RED webserver.
You can do this by navigating to a command prompt and typing in the following command:
Node-RED
As we installed Node-RED as a global NPM module it adds the command node-red to your system path which you can then input into a command prompt to start Node-RED:
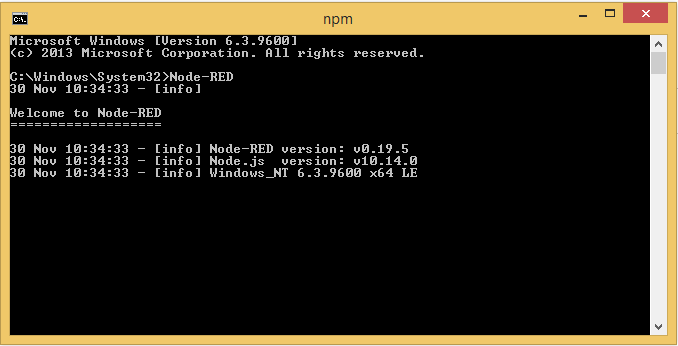
Once the server has booted up successfully the command prompt will let us know that the server is now running, and what IP address it is on:
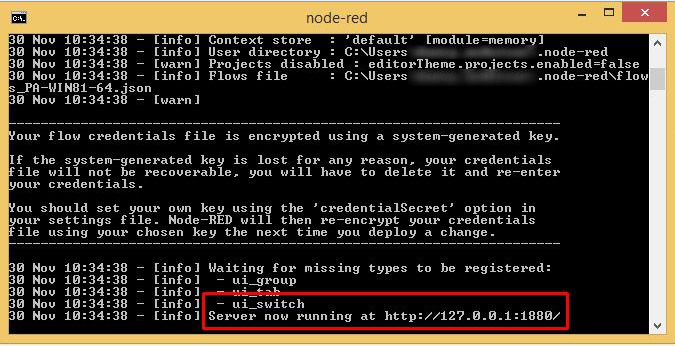
Take note of the Node-RED webserver’s IP address and input it into your web browser:
You have now successfully installed, booted up, and accessed your Node-RED webserver.
You can now begin to create your own flows.
6. An Overview of Node-RED
So how do we get started? Below is an overview of the Node-RED interface, with a brief description of each section:
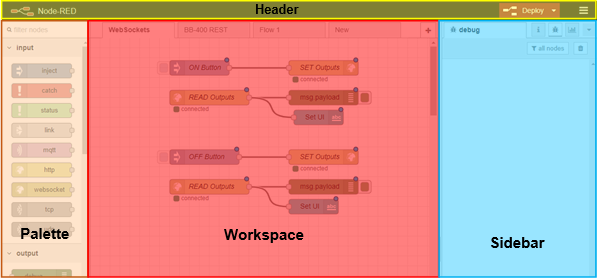
6.1. Palette
The palette on the left contains all the different nodes available for use. From injecting different types of information (strings, Booleans, numbers, etc.), executing Linux command lines and the ability to make different types of connections, to recording simple debug traces, sending emails notifications and displaying information on a text box:
6.2. Workspace
The workspace in the middle is where your flows will be created. As you follow through this simple guide, you will learn how the flows connect and work together in an easy to use, programmable way.
The sidebar on the right provides additional settings and debug information. Using the debug node available from the palette will show the user what information is being sent, or the information which is being received from the node it is attached to.
The header at the top, contains the deploy button, which is used for deploying your current workspace. Deploying it will make it available for execution, or it will immediately start running, depending on how you have it set up. You will also find the main menu which allows you to import/export workspaces, or change several configurations regarding your Node-RED project.
May 12, 2021
In our previous tutorials, we covered installing Node-RED on Raspberry Pi. Now, let’s explore how to set it up on Windows with step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting tips, and best practices. Whether you’re building IoT projects or automation workflows, this guide ensures a smooth installation.
Why Install Node-RED on Windows?
Node-RED is a visual programming tool for wiring devices and APIs. Installing it on Windows lets you:
- Use the same features as Raspberry Pi (dashboard, HTTP nodes, etc.).
- Create automation flows without coding expertise.
- Simulate IoT projects before deploying them to hardware.
Installing Node-Red on Windows
Step-1: Install Node.js
Node-RED uses a runtime engine called Node.js. Node.js is a JavaScript based programming language and must be installed before Node-RED. Node.js can be downloaded from the Official Node.js website.
This installation also will take care of installing necessary tools required for Node-Red.
Step-2: Verify Node.js installation
Once the installation is complete, open up a Windows command prompt and ensure the Node.js installed correctly with below command
node --version && npm --version
This command will check and print the which node.js version got installed in your windows. This package also install the NPM manager which needs to get install other Node-Red packages later.
Step-3 : Install Node-RED
Use npm to install Node-RED globally:
3.1 Run as Administrator
- Right-click Command Prompt > Run as Administrator (prevents permission errors).
3.2 Install Node-RED
npm install -g --unsafe-perm node-red
It is recommended that always run the command windows in administrative mode to get Node-Red installation smoothly. Once this command is ran Node-RED will begin to install. Please note this can take some time to complete.
- Flags Explained:
-g: Installs globally (accessible system-wide).--unsafe-perm: Bypasses permission issues on Windows.
Wait 2–5 minutes for installation. A successful install ends with:
+ [email protected]
added 245 packages in 45s
- Once complete, the output should look like this:
Step-4 : Install Node-RED-dashboard
After completing the Node-Red installation we need to install Node-RED-dashboard with below command :
npm install -g node-red-dashboard
This installation will take few more minutes to get install successfully on you Windows os. When the module is successfully installed the response should look something like this
Step-5 : Running Node-RED
5.1 Launch Node-RED
Once everything has been successfully installed you can now begin to run your Node-RED webserver. You can do this by navigating to a command prompt and typing in the following command:
Node-RED
- As we installed Node-RED as a global NPM module it adds the command node-red to your system path which you can then input into a command prompt to start Node-RED.
5.2 Verify Server Status
- Once the server has booted up successfully the command prompt will let us know that the server is now running, and what IP address it is on.
- The result command window for Node-Red command will be looks like below:
Note : Do not close this command windows when you wants to run the Node-Red on your webserver.
Note down the webserver address from command prompt windows for your Node-Red and type it in your webserver url. The address for Node-Red will be in the below format :
127.0.0.1 :1880 >>> localhost: port number
Step 6: Access Node-RED in Your Browser
- Open Chrome/Firefox and navigate to
http://localhost:1880. - You’ll see the Node-RED editor:
Result windows for Node-Red on your web will be likes below:
Step 7: Auto-Start Node-RED (Optional)
To run Node-RED automatically on system boot:
7.1 Install PM2 (Process Manager)
npm install -g pm2 pm2 startup pm2 start node-red -- --verbose pm2 save
- PM2 Commands:
pm2 list: Check running processes.pm2 stop node-red: Stop Node-RED.
Updating Node-RED
Keep your installation current:
Update Node-RED
npm update -g node-red
Update Node.js
- Reinstall from the Node.js website.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Port Conflicts
- If
localhost:1880isn’t loading:- Check if another app is using port 1880:
netstat -ano | findstr :1880 - Terminate the conflicting process or restart your PC.
- Check if another app is using port 1880:
Permission Errors
- Always run Command Prompt as Administrator.
- If
npm installfails, try:npm cache clean --force
Firewall Access
- Allow Node-RED through Windows Defender Firewall:
- Go to Windows Security > Firewall > Allow an app.
- Add
Node.jsto the allowed list.
Conclusion
You have now installed Node-RED on Windows! To build your first flow:
- Drag an Inject node to the workspace.
- Connect it to a Debug node.
- Click Deploy and trigger the Inject node to see output in the Debug tab.
Check These Out!
Discover more from Electronics — Microcontrollers
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Running Node-RED on Windows 10
Node-RED is an open-source flow-based programming platform by IBM working on software and hardware. This article will explain how to install Node-RED on the Windows platform. The following instructions are based on Windows 10. However, anyone can install Node-Red in any version of the Windows environment.

Quick Install Node-RED in Windows 10
Step 1 (Install Node.js):
Search for «Node.js download» and install Node.js latest LTS version from the official node.js website.
Or go to node js official website and download/download/button node js latest LTS version. Select 32 or 64-bit based on your operating system. After downloading, run the MIS file with administrative privilege and follow the installation instructions.
After successful installation, open the command prompt. Press win+r, type cmd, and hit enter to run the command prompt in Windows. Then run the following command to check the node js and npm versions.
node —version && npm —version
The command prompt should return the output node js and npm installed successfully.

Step 2 (Install Node-RED):
To install Node-RED as a global module, adds the command node-red to your system path and execute the following at the command prompt:
npm install -g —unsafe-perm node-red
Step 3 (Run Node-RED):
Once installed, we are ready to use Node-Red. Just run the command «node-red» in the command prompt. And you are good to go.

Once started, you can access Node-RED from any web browser. The node-red will be available in the following URL:
http://localhost:1880
Video demonstration on How to install Node-RED in Windows:
For more detailed instructions, please watch the next video.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to install Node-RED on Windows and how to use Node-RED dashboard locally with Windows. This guide includes the installation of Node.js and Node-Red on Windows, an overview of the user interface, and an example where we will create a simple graphical UI.
We have a similar guide with Raspberry Pi:
- Install Node-RED on Raspberry Pi (32-bit and 64-bit RPI OS)
Node-Red Installation on Windows
It is a free-to-use tool used in IoT applications that provides visual programming through connecting nodes wired together as flows.
“Node-RED is a flow-based development tool for visual programming developed originally by IBM for wiring together hardware devices, APIs, and online services as part of the Internet of Things. Node-RED provides a web browser-based flow editor, which can be used to create JavaScript functions.”
Install Node.js on Windows
To work with Node-RED locally, we will require a supported version of Node.js in our system. Refer to this link to get to know about the version you are required to install. It is recommended to use the latest 14.x LTS version. Go to the Node.js webpage by clicking here and download it. you will be able to access it from Downloads > Previous Releases :
Click to download the setup file according to your system.
After downloading the Node.js setup, click ‘Next’ to install it on your PC.
Check the agreement box and click ‘Next’ to proceed further.
After specifying the relevant saving location click on ‘Install’ to finish the installation process.
A few moments later, you will receive the following prompt indicating that the installation was performed successfully.
Click the ‘Finish’ button to exit the setup.
Install Node-Red on Windows
Now open your command prompt and type node –version && npm –version to verify that Node.js and npm have successfully been installed in your system or not.
Now to install Node-Red type the following command: npm install -g –unsafe-perm node-red
You should get similar results:
To initiate Node-Red, type node-red in the command prompt. Node-Red will start.
Head over to ‘Server now running at http://…..” and copy the HTTP URL.
Note: Depending on your Windows Defender Firewall security settings you will be asked to Allow access to some of the features of Node.js.
Type this URL in a new web browser and Node-Red editor will open up.
Note: Make sure you do not close your Command Prompt while using Node-Red otherwise the connection will be lost.
Install Node-Red Dashboard on Windows
Now we will install the Node-Red Dashboard so that we can access the set of nodes consisting of it. Go to Menu > Manage palette
The following User Settings appears. Go to the Install tab and then write ‘Dashboard’ in the search bar and press enter. Click Install for the Node-Red Dashboard as shown below:
You will receive a notification that will refer you to the official Node-Red dashboard site for a brief overview. Click ‘Open node information’ to view that. To proceed with the installation just click ‘Install’ as highlighted below:
After a few moments the Node-Red Dashboard will successfully get installed. You will receive a notification that the Dashboard nodes have been added to the Palette.
Now head over to the Nodes section found at the far left and scroll down to view the nodes under Dashboard already added. It includes various functions provided by the dashboard. If for some reason you are not able to view the nodes, restart Node-Red.
Overview of Graphical User Interface
Now let us understand how to use the dashboard nodes to build an interactive graphical user interface. Notice that each of the dashboard nodes act as widgets inside the UI.
Layout
The graphical user interface is arranged by:
- Tabs: These are separate pages on the UI
- Groups: These are found inside each tab. They are used to divide the tabs in various sections in order to place the widgets in a systematic order. Each widget is associated with a group therefore specifying the exact placement of the widget on the UI.
Create Tabs
Now let us see how to create tabs and groups for our UI. Open Node-Red with the dashboard already installed. Head over to the extreme right side and find dashboard.
After you click it, the Dashboard tab appears:
Here we are inside the Layout. To add a tab click +tab as shown below:
This will create a new tab where you will have the option to add groups, edit it and also change its layout.
To edit this newly created tab, click the edit button and you will get an option to change the name and icon of the tab, then click the update button for the changes to take place.
Note: You can use any name according to your preference but for the icon you have to use one available at these three links found below:
- Angular Material Icons
- Font Awesome Icons
- Weather Icons Lite
Create Groups
Now to create a group for the tab, click the +group button.
This is where we will place our widget. You can add several groups under a tab to organize your UI.
To edit this newly created group, click the edit button and you will get an option to set the name, select the corresponding tab and change the width .Then click the update button for the changes to take place.
Set Dashboard Theme
Now after learning how to add the Tabs and Groups forming the layout of the UI, let us move ahead and set the theme of the dashboard.
Inside the Dashboard tab, go to Theme tab and the following window appears. Here we have an option to select the style, colour and font for the user interface.
As you may see, by default the style is set as ‘light’ with colour blue with the default font.
Change according to your preference.
Further Dashboard Customization
For further customization, head over to the Site tab and click it.
Here as you may see you have further categories which you can modify according to your needs. Change the Title of the UI, the sizes of the widgets, date format and several other options. Feel free to try different options until you get a satisfactory outcome.
Demonstration: Build a Graphical User Interface
To show everything we have learnt this far regarding the Node-Red dashboard, let us create a simple user interface as a demonstration example. We will show you how to edit and place the widgets.
The user interface we will create will consist of two tabs: one named Garage and another named Lounge. Further both of these tabs will have two groups each where we will place the widgets. For the Garage we will add a gauge and a slider. Likewise, for the Lounge we will add a button and a switch.
So let us start building!
Create Tabs
The first step is to create the tabs. Head over to the Dashboard tab and click +tab to create a new tab. Specify the name and icon and click Update for the changes to take place. Here we are using icons from Angular Material Icons.
We will create two tabs: one named Garage and another named Lounge
Create Groups to add Widgets
The next step is to add the widgets. We will add two groups to both the tabs. Click +group in each of the tab and create the groups. Our dashboard layout looks like this:
As mentioned before we will add a gauge and a slider for the Garage. Likewise, for the Lounge we will add a button and a switch.
Therefore we will be adding these four nodes to the flow. Head over to the Nodes section found at the far left and scroll down to view the nodes under Dashboard. Drag and drop the gauge to the flow as shown below:
Next include all the rest of the nodes to the flow as well.
Now double click the gauge. A new window will appear. Here select group where this widget will be placed. We will choose Group1 of Garage. You have other options to change as well including size, type, label etc.. We are leaving it as default.
Likewise, add the rest of the widgets to the respective groups.
- gauge: Group1(Garage)
- slider: Group2(Garage)
- button: Group1(Lounge)
- switch: Group2(Lounge)
You can also change the theme of the dashboard but we will leave it as default. Now deploy the changes by clicking the Deploy button found at the top.
To view the UI, open a new web browser and type: http://Your_local_IP_address:1880/ui
The user interface will open up once you press enter.
Here you can view the dashboard consisting of two tabs: Garage and Lounge
Head over to each tab to view how the widgets look. Our Garage tab with two groups:
Our Lounge tab with two groups:
