The wuauclt.exe is a background process for Windows Update AutoUpdate and its job is to check for available updates. With Automatic Updates enabled, the process will run in the background. It is also used to force Windows to check for Updates right away, using the command line.
However, according to users, wuauclt.exe /updatenow, /reportnow, /detectnow, etc. commands are not working on their Windows computers. In this post, we will talk about this and see what you can do if wuauclt.exe is not working or recognized on Windows.

If wuauclt.exe /updatenow, /reportnow, /detectnow, etc. commands are not working on Windows 11/10, follow the solutions mentioned below to resolve the issue.
- Use a different network or disable Metered Connection
- Run Windows Update Troubleshooter
- Run wuauclt.exe in Clean Boot State
- Repair Windows Update System Files.
Let us talk about them in detail.
1] Use a different network or disable Metered Connection
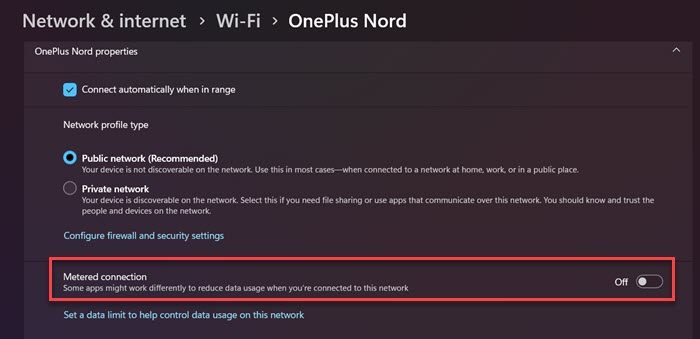
If you use a mobile hotspot and run the wuaclt command, it is very likely that Windows will not update your device. That’s because Windows consider the mobile network to be relatively slow and limited. Although sometimes, it also misidentifies a WiFi connection as that of a Mobile Hotspot. In that case, we recommend you switch to some other network. If you can’t do that, you should disable Metered Connection. Follow the steps given below to do the same.
- Open Settings by Win + I.
- Go to Network & Internet> WiFi.
- Now, navigate to the connected network and make sure that the Metered Connection toggle is disabled.
Once done, restart your computer and run the command again. Hopefully, this time, the update will be installed.
2] Run Windows Update Troubleshooter
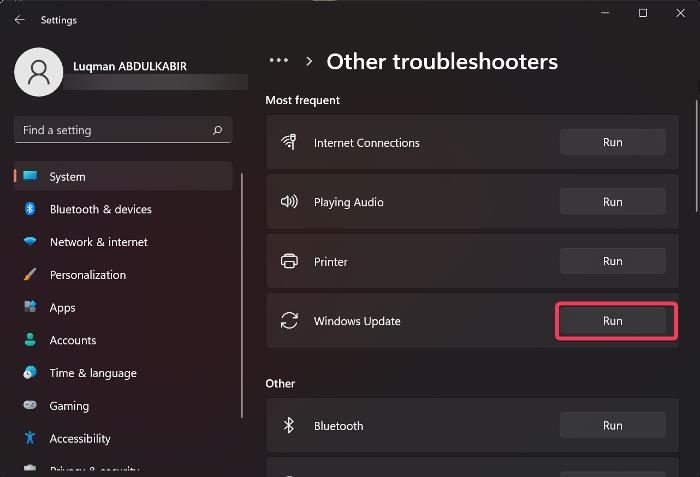
Windows Update Troubleshoot is a built-in Windows utility that can scan what’s scan with your update components and if something is wrong, it will apply the required fixes. In most cases, if the issue is a result of some kind of corruption running this tool does the trick. Follow the steps given below to do the same.
Windows 11:
- Open Windows Settings.
- Now, go to System > Troubleshoot.
- Then click on the Other troubleshooters button.
- Click on the Run button associated with Windows Updates.
- Finally, follow the on-screen instructions to complete the task.
Windows 10:
- Launch Windows Settings.
- Go to Update & Security > Troubleshoot.
- Click on the Additional troubleshooter option.
- Select Windows Updates and click on Run the troubleshooter.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to do the task.
Hopefully, this will resolve the issue for you.
3] Run wuauclt.exe in Clean Boot State
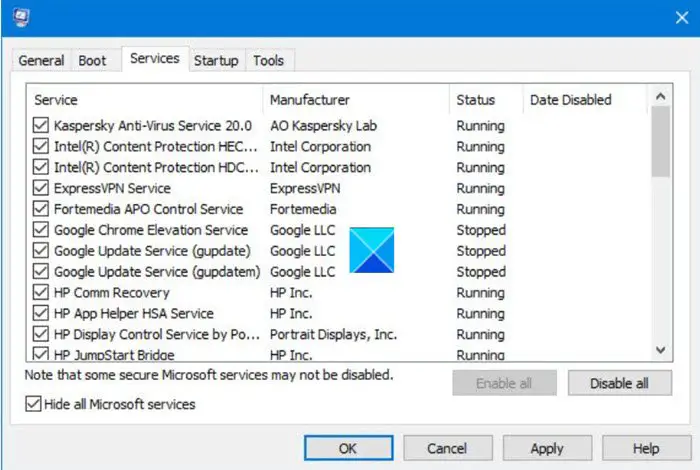
If the Windows Update components are not corrupted but you are unable to run wuauclt, boot your computer in Clean Boot state and then try. As the name suggests, Clean Boot State opens with only essential services and programs, so, one has the option to stop every single non-Microsoft app and then run the command. We do this to check if there is a third-party application that has stopped the command. Follow the steps given below to do the same.
- Open Run, type “msconfig” and click Ok.
- Now, go to the Services tab, tick the box next to Hide all Microsoft services, and click Disable all.
- Finally, click on Apply > Ok.
So, once you reboot your computer, it will open with no services that can interfere with the command. You can then run the Windows Update AutoUpdate command and check if the issue is resolved.
Read: What is MoUSOCoreWorker.exe?
4] Repair Windows Update System Files
If nothing works, we can assume that corrupted system files are causing this issue.
You have two options then:
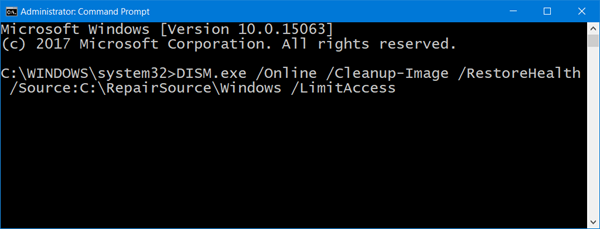
- Fix corrupted Windows Update system files using DISM Tool or
- Repair your computer using Installation Media
Having done that, check if the issue is resolved.
Read: Windows Upgrade errors 8007002C, 80246007, 80070004, 80240020
Where is Wuauclt located in Windows?
Wuaclt is a core Windows component and is located inside the C:\Windows\System32 folder. You can easily access it using the File Explorer. Just open Explorer, go to the aforementioned location and search for wuauclt.exe. If you see wuauclt running in the background and want to know if the process is fake or real, right-click on it and go to Properties. You can then check and match the location.
Read: Make Windows repair corrupt components when pointed to WSUS
How to run Windows Update through cmd?
To run Windows Update through Command Prompt, open Run, type “cmd” and hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter. You will get a UAC prompt. Click Yes to confirm your action. Finally, run wuauclt.exe /updatenow. This command will do the job for you.
Also Read: How to force Windows to Update or Upgrade.
UPDATED: Feb 20, 2024
We use WSUS for Windows Update with the vast majority of our corporate clients large and small and while it is usually seamless come up when it goes wrong there’s a few commands we’re always struggling to find so we decided to list them out here so we can find them easily. You like them too.
1 – How To Determine Where Windows Updates Are Coming From
$(New-Object -ComObject "Microsoft.Update.ServiceManager").Services | Select-Object Name, IsDefaultAUService

2 – How To Force Windows Update Clients To Check in With WSUS
Officially to get your Windows 10, Windows 11 and Windows Server clients to check in with WSUS you simply have to run wuauclt /reportnow, but any tech that has done this for a few years knows how frustrating it can be to not have this command work.
For the last few years we have used two commands to really force the Windows client computers to check in with WSUS:
$updateSession = new-object -com "Microsoft.Update.Session"; $updates=$updateSession.CreateupdateSearcher().Search($criteria).UpdatesRunning this command will “prime” the Windows Update engine to submit its most recent status on the next poll. To trigger that next poll, use:
wuauclt /reportnowhttps://pleasework.robbievance.net/howto-force-really-wsus-clients-to-check-in-on-demand/
3 – How To Force Windows To Check For Updates
There are two Command Line Interface (CLI) programs to manage Windows Update so, which one you need is dependent on the version of Windows you are using.
Don’t forget to run these in an elevated command prompt.
3a – Windows Update CLI For Windows 10, 11 & 12, Windows Server 2016 2019 2022 2025
Usoclient is the ‘new’ command line app for Window Update and it comes with many useful switches:
usoclient StartScan: Start scanning for new patches- we use this one frequently when a server has already checked for updates and only offers the INSTALL NOW button
- If you want your computer to check for updates again, before you click INSTALL NOW, this is the command for you
- you can see the GUI start checking immediately in Windows Server 2016, but the Windows 11 Windows Update window shows nothing
- we use this one frequently when a server has already checked for updates and only offers the INSTALL NOW button
usoclient StartDownload: Start download of patchesusoclient StartInstall: Install downloaded patchesusoclient RefreshSettings: Refresh settings (i.e. check for changes)usoclient StartInteractiveScan: Ask for user input and/or open dialogues to show progress or report errors if requiredusoclient RestartDevice: Restart device to finish update installationusoclient ScanInstallWait: Combined scan, download, & installusoclient ResumeUpdate: Resume update installation after rebooting
3b – Windows Update CLI For Windows 7 & 8, Windows Server 2008 2012 R2
WUAUCLT.exe is the old command line app for Window Update and it comes with a few useful switches:
wuauclt /detectnow– forces Windows to Check for Updateswuauclt /reportnow– forces Windows to check in with its update manager (i.e. WSUS)- We know this often does not work, so see #2 above for a helper command
wuauclt /updatenow– forces Windows to install updates
These three switches can be combined. For instance wuauclt.exe /detectnow /updatenow should have Windows scan for new updates and then install them.
4 – Command To Create a Searchable Windows Update Log in Text Format
Get-WindowsUpdateLog
This command merges and converts Windows Update trace files (.etl files) into a single human readable WindowsUpdate.log file on your desktop named WindowsUpdate.log.
You can then open the log with Notepad and search for the word ERROR and we also like to confirm where our Windows Updates are actually coming from:
- Scroll to the very bottom
- Press CNTL+F (ie. find)
- Enter ProtocolTalker
- Click Direction = UP (radio button)
- Click the FIND NEXT button

5 – How To Confirm Connection Can Be Established to Your WSUS Server
Test-NetConnection (wsus-server-name) -PORT 8530

6 – Easy Way To Check Connectivity with WSUS
http://(name-of-wsus-server):8530/selfupdate/iuident.cab

Change the (name-of-wsus-server) to whatever yours is and it should download the iuident.cab file in second or two.
If this does not happen, ty using the IP address instead of the host name of your WSUS SERVER:
- If it works with the IP address but not the name, you have a DNS (name resolution problem). You should fix that, but you can get around the issue by using the IP address in the GPO that specifies the intranet location of your WSUS server
- If it doesn’t work either way, you have a firewall (i.e. blocking the traffic) or permissions problem (i.e. perhaps you are working across different domains).
7 – How To Reset Your Windows Update Client Connection To WSUS
We used to run these steps separately but ajek has a nice little all in one script.
Step 1 – In WSUS, right click on the problematic machine and click DELETE
Step 2 – On the problematic machine, open a PowerShell as an Administrator and paste this script in all at once:

Stop-Service -Name BITS, wuauserv -Force
Remove-ItemProperty -Name AccountDomainSid, PingID, SusClientId, SusClientIDValidation -Path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\WindowsUpdate\ -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Remove-Item "$env:SystemRoot\SoftwareDistribution\" -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Start-Service -Name BITS, wuauserv
wuauclt /resetauthorization /detectnow
(New-Object -ComObject Microsoft.Update.AutoUpdate).DetectNow()Usually the results show up in a hour or two but it could take a full day. If you don’t see any change, “this was not the fix you are looking for”.
by | Last updated 2022.10.29 | Published on 2020.10.06 | Guides, WSUS

What is wuauclt.exe?
It stands for Windows Update Automatic Update CLienT
There are many switches through the years that have been found, and with the help of Strings (Sysinternals), on a current version of Windows 10, you can see that the only ones listed are:
/UpdateDeploymentProvider
/IdleShutdownNow
/ResetEulas
/ResetAuthorization
/RunHandlerComServer
/ReportNow
On older systems (Windows 8.1 and earlier, Server 2012R2 and earlier) you can see that you have a lot more.
/DemoUI
/BeginInteractiveOSUpgrade
/InstallOSUpgrade
/IdleShutdownNow
/ShowOptions
/ShowCheckForUpdates
/ShowWUAutoScan
/UpdateNow
/SelfUpdateUnmanaged
/SelfUpdateManaged
/CloseWindowsUpdate
/ShowWindowsUpdate
/ShowWU
/ResetEulas
/ResetAuthorization
/ShowSettingsDialog
/RunHandlerComServer
/ReportNow
/DetectNow
As you can see, the bolded ones are common between old versions and new versions of Windows.
If you notice, /DetectNow is no longer in the list for Windows 10. This is because Microsoft has deprecated and removed it. Windows 10 has replaced it with: PowerShell.exe (New-Object -ComObject Microsoft.Update.AutoUpdate).DetectNow() or UsoClient.exe StartScan (Still undocumented by Microsoft as of October 2020, but used in forums with success).
As you can see, /ReportNow is still listed, but it has a has a special use case. Microsoft’s official documentation on this switch says “Sends all queued reporting events to the server asynchronously.” but what does that really mean? It means that if there are events to report back to WSUS which have been queued up by the detection sequence (/DetectNow OR the PowerShell or UsoClient equivalent), then when this command is run, it will force the immediate reporting back to WSUS – but only if you have events that were queued up.
One thing to remember is that the detection sequence WILL ALWAYS REPORT BACK if there are queued events, but it has a 20 minute cool-down delay.
The purpose of the /reportnow parameter is to immediately expire that 20 minute delay.
So, when executing these two commands together or immediately one after the other, the wuauclt /reportnow command actually does nothing at all.
The proper way to use these two commands, is to first launch the wuauclt /detectnow task (and now the PowerShell equivalent for Windows 10+/Server 2016+), and then WAIT for the completion of the detection event. Typically this could take a couple of minutes, but on a healthy, fully patched system, it may complete in a matter of seconds.
Once the WUAgent is idle, then executing wuauclt /reportnow will cause the call to the ReportingWebService to occur immediately, rather than waiting for the built-in 20 minute delay.
Wuauclt.exe – Ключи (Параметры командной строки) и секреты использования
Часто, бывает необходимо, подтолкнуть агента WSUS для проверки имеющихся обновлений и немедленной установки. Я для того использую простую команду wuauclt /detecnow
Но помимо этого, эта утилита имеет множество других применений и соответствующих параметров командной строки. Рассмотрим их:
/DetectNow — Запустить немедленный опрос сервера WSUS на наличие обновлений
/resetAuthorization — Сбросить авторизацию на сервере и клиенте. Фактически это новая регистрация на сервере WSUS. Полезна когда клиент подглюкивает, удаляем его на сервере и командой wuauclt /detectnow /resetAuthorization заново регистрируем на сервере с одновременным запросом списка обновлений
/reportnow Сбросить статистику на сервер
Остальные параметры не столь очевидны и самое главное их применение непонято и обычно не вызывает никаких изменений
/RunHandlerComServer — неизвестно
/RunStoreAsComServer — неизвестно
/ShowSettingsDialog — Показывает диалог настройки расписания установки обновлений
/ResetEulas — сбросить соглашение EULA для обновлений
/ShowWU — переход на сайт обновлений MS
/ShowWindowsUpdate — переход на сайт обновлений MS
/SelfUpdateManaged — неизвестно
/SelfUpdateUnmanaged — неизвестно
/UpdateNow — Немедленно запускает процесс обновления, аналогичен клику кнопки в окне уведомлений о наличии обновлений
/ShowWUAutoScan — неизвестно
/ShowFeaturedUpdates — неизвестно
/ShowOptions — неизвестно
/ShowFeaturedOptInDialog — неизвестно
/DemoUI — Показывает значок в трее — диалог настройки расписания установки обновлений или установки в зависимости от статуса
Опубликовано
20.10.2011 11:08
и размещено в рубрике Windows, О работе.
Подпишитесь на RSS 2.0 ленту комментариев этого сообщения.
Комментирование закрыто.
The windows Update CLI commands are useful for troubleshooting Windows Update errors. And they are helpful when you need to automate the windows update tasks. In newer versions of windows, the WUAUCLT command has been deprecated and replaced with the usoclient. In this article we have included the options and syntax for using wuault, usoclient, and powershell to detect and install windows updates
The windows update command utility in windows is: WUAUCLT. This stands for Windows Update Automatic Update Client. This client has been deprecated in windows 10 and server 2016. Howeve,r it is still available through windows 7 and server 2012R2.
Below is a list of arguments you can pass to the WUAUCLT commands and a short explanation of what each argument does.
Search:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| /DetectNow | Detect and download updates that are available (will vary by system settings) |
| /ReportNow | Tell the client to report its status back to the WSUS server |
| /RunHandlerComServer | |
| /RunStoreAsComServer | |
| /ShowSettingsDialog | Show Windows Update settings dialog |
| /ShowWindowsUpdate | Shows the windows update dialog box or web page (depending on windows version) |
| /ResetAuthorization | when an update check occurs a cookie is stored that prevents a new update or check for 1 hour. So, you should use this to delete this cookie |
| /ResetEulas | Resets the accepted EULA’s |
| /ShowWU | Shows the windows update dialog on windows vista and above. Opens Windows update on XP |
| /SelfUpdateManaged | Scan for windows updates using WSUS |
| /SelfUpdateUnmanaged | Triggers a windows update scan using the windows update website |
| /ShowOptions | Open the windows update settings window |
| /ShowFeaturedOptInDialog | Show Opt-In dialog for featured updates |
| /DemoUI | Show the icons for windows update |
| /ShowFeaturedUpdates | Open windows update dialog and shows the featured updates |
| /ShowWUAutoScan | |
| /UpdateNow | Install updates now |
Showing 1 to 17 of 17 entries
Examples
See below for some examples of running the wuauclt. All examples should be run from an elevated/administrative command prompt
If all you want to do is detect and install updates right now, you would run:
Wuauclt /dectectnow /updatenow
If it is refusing to install, you can run:
Wuauclt /resetauthorization
If you want to have the client report its status back to the WSUS server, you would run:
Wuauclt /reportnow
Powershell
Powershell will give you the most flexibility in installing windows updates. The other methods are fine for simply downloading and installing all updates. However, with the powershell cmdlets you can do things like get a list of updates, search for updates with a specific word in them, then only install those updates.
The first step is to download the powershell module here:
https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/2d191bcd-3308-4edd-9de2-88dff796b0bc
If you have Powershell verison 5, you can install the module from the gallery by running:
Install-module PSWindowsUpdate
Before you can run any commands, you need to import the windows update module:
Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate
You might need to install the Microsoft Update service. That can be done with this command:
Add-WUServiceManager -ServiceID 7971f918-a847-4430-9279-4a52d1efe18d
You can get a list of available cmdlets in the PSWindowsUpdate module with the following command:
Get-command -module PSWindowsUpdate
I have also included a list of commands below:
- Add-WUOfflineSync
- Add-WUServiceManager
- Get-WUHistory
- Get-WUInstall
- Get-WUInstallerStatus
- Get-WUList
- Hide-WUUpdate
- Invoke-WUInstall
- Get-WURebootStatus
- Get-WUServiceManager
- Get-WUUninstall
- Remove-WUOfflineSync
- Remove-WUServiceManager
- Update-WUModule
Examples
The most important cmdlet is Get-WUInstall . This will be apparent in the examples below
Download and install updates from Microsoft Update, then reboot:
Get-WUInstall –MicrosoftUpdate –AcceptAll –AutoReboot
**Note, I usually only reboot if required. For that reason, I don’t like to use the AutoReboot flag.
Check if a reboot is required
Get-wurebootstatus
List available updates on Microsoft Update
Get-WUInstall –MicrosoftUpdate –ListOnly
USOClient
The USO client is new to windows 10 and Server 2016. This replaces the wuauclt command in these Operating systems. I would recommend using powershell instead of this client when you are doing automation, since it will work on newer and older clients. However, this client is very simple to use. and is useful for one-off purposes. See the table below for all of the command arguments:
Show 102550100 entriesSearch:
| startscan | scan for updates |
|---|---|
| startdownload | download updates |
| startinstall | install updates |
| Refreshsettings | Refresh settings if any changes were made |
| StartInteractiveScan | Open a dialog and start scanning for updates |
| RestartDevice | Restart computer to finish installing updates |
| ScanInstallWait | Scan, Download, and install updates |
| ResumeUpdate | Resume installing updates on next boot |
Showing 1 to 7 of 7 entries
PreviousNext
Examples
See below for some examples of how to use the USO client. All of these examples should be run in an administrative command prompt
Scan for updates
usoclient startscan
Download updates
Usoclient startdownload
Install updates
usoclient startinstall
Here are other related links
In case you would like to see some additional information, I hae included some links to good resources on these topics:
WSUS Server Cmdlets http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh826166.aspx
http://blogs.technet.com/b/heyscriptingguy/archive/2012/01/16/introduction-to-wsus-and-powershell.aspx
Powershell Execution Policy:http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee176961.aspx
Troubleshoot computers not in WSUS:
http://msmvps.com/blogs/athif/archive/2005/09/04/65174.aspx
Client Side Powershell Module:
http://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/2d191bcd-3308-4edd-9de2-88dff796b0bc
