If Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) is not started on a Windows computer, it cannot detect any available wireless networks. It is an important Microsoft service which normally starts at boot time and this utility manage WiFi connections. If WZC is disabled on a device, it cannot find and join WiFi networks. So if you are facing any WiFi connectivity issues on your computer, the first step is to check whether WZC is enabled. This article tells how to enable WZC on a Windows computer and fix issues related to WiFi connectivity. Here we can see two different methods to activate this service. You can activate it either by executing a Command Prompt command or by following GUI instructions. These two methods are explained in this article.
Steps to Enable Wireless Zero Configuration
- Click on start
- Click on Run
- On Run window type services.msc press OK
Now the services windows will be opened. The Wireless Zero Configuration is the third service from last.
- Open the service and click on start button to enable this service.
Start WZC From Command Prompt
Here we use a DOS command to start Wireless Zero Configuration. The procedure is given below.
- Start Command Prompt
- Type the command net start wzcsvc and press enter
Now onwards it is started on your computer and it will work as long as you manually set its status stop. If you are using third-party utilities like Dell DW WLAN Card Utility or Linksys WiFi Network Monitor etc, they may set the status of WZC as stopped. As long as they work properly it is not necessary to enable it back but if these third-party tools show issues, it is better to disable them and start Microsoft Utility. I recommend this because, in my personal experience, this built-in Microsoft Utility works better than third-party utilities. However, you should not use two different network monitoring utilities at the same time.
Where to Find Wireless Zero Configuration on Windows 7 & 8
I am getting comments regarding wireless zero configuration on Windows 8 and 7 computers. They want to know where to find WZC in Windows 7 and 8 as they couldn’t find it on the services page. Actually, there is no WZC on Windows 8, Vista and Windows 7. It is an important service on Windows XP and Server 2003 but discontinued on later versions. Instead of using it, they use WLAN Autoconfig to manage the wireless network. To know more about this service to find and manage WiFi, visit the link below.
How to Start WLAN AutoConfig Service
Popular Articles
- How to Check LAN Connectivity Issues
- How to Connect to an Ad-hoc Network
- My Laptop Doesn’t Detect WiFi Networks
Home
Author: Alex George
Alex George is the Chief Editor and founder of CoreNetworkZ Tech Solutions. He is a senior software developer with 20 years of experience.
You can contact him at alex.george@corenetworkz.com.
Перейти к содержанию
Запуск службы автоматической настройки беспроводного подключения в Windows XP
Просмотров 83.2к. Опубликовано
На ноутбуке с операционной системой Windows XP после установки драйвера на беспроводной адаптер, в свойствах этого самого адаптера не появилась вкладка “Беспроводные сети”:
При этом ноутбук не находит ни одной беспроводной сети, а система выдает окно с таким сообщением: “Если вы хотите настроить беспроводное подключение с помощью Windows, запустите службу автоматической настройки беспроводного подключения (WZC)”:
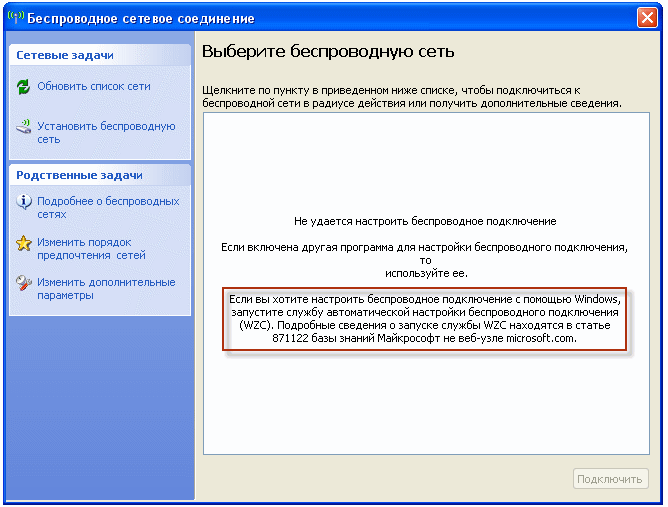
Решается проблема довольно просто: скорее всего на компьютере просто не запущена служба “Беспроводная настройка” (Wireless Zero Configuration).
Чтобы запустить эту службу, идем в “Пуск” – “Панель управления” – “Администрирование” – “Службы”. Находим службу “Беспроводная настройка” – щелкаем по ней дважды мышкой:

В открывшемся окне выставляем Тип запуска – Авто, и обязательно запускаем ее, нажав здесь кнопку “Пуск”. Затем нажимаем “ОК”:
После этого в свойствах Wi-Fi адаптера появится вкладка “Беспроводные сети”, и можно будет настраивать беспроводное подключение средствами операционной системы Windows.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC), also known as Wireless Auto Configuration, or WLAN AutoConfig, is a wireless connection management utility included with Microsoft Windows XP and later operating systems as a service that dynamically selects a wireless network to connect to based on a user’s preferences and various default settings.[1][2] This can be used instead of, or in the absence of, a wireless network utility from the manufacturer of a computer’s wireless networking device. The drivers for the wireless adapter query the NDIS Object IDs and pass the available network names (SSIDs) to the service. The service then lists them in the user interface on the Wireless Networks tab in the connection’s Properties or in the Wireless Network Connection dialog box accessible from the notification area. A checked (debug)[3] build version of the WZC service can be used by developers to obtain additional diagnostic and tracing information logged by the service.
Wireless Zero Configuration was first introduced with Windows XP. In Windows Vista and Windows 7, the service that provides equivalent functionality is called «WLAN AutoConfig». It is based on the Native Wi-Fi architecture introduced in Windows Vista.
Initially, there was no Wireless LAN API in Windows XP for developers to create wireless client programs and manage profiles and connections. After the release of Windows Vista, Microsoft released KB918997,[4] which includes a Wireless LAN API for Windows XP SP2. It was later integrated into Windows XP Service Pack 3.
- List of Microsoft Windows components
- Wireless connection management utility
- Wireless LAN client comparison
- ^ «Windows XP Wireless Auto Configuration: The Cable Guy, dx». TechNet. Microsoft. November 2002.
- ^ Weiss, Aaron (January 12, 2006). «Windows Wireless Zero Configuration: Five Steps to Sanity». Archived from the original on August 30, 2011. Retrieved June 3, 2007. Article on problems with WZC connecting to unwanted APs, etc., and workarounds
- ^ «Checked Build of Windows». MSDN. Microsoft. Retrieved 29 July 2013.
- ^ «Developers cannot create wireless client programs that manage wireless profiles and connections over the Wireless Zero Configuration service in Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2)». Support. Microsoft. December 5, 2006. Archived from the original on December 13, 2006.
- Wireless Zero Configuration application programming interface
- Active Directory Schema Extensions for Windows Vista Wireless and Wired Group Policy Enhancements
- The Cable Guy: Wireless Group Policy Settings for Windows Vista
Windows wants to help you get on a Wi-Fi network, but many times, it just gets in the way. Here’s how to work around, if not bypass, XP’s WLAN connection software.
With the release of Windows XP, Microsoft tried to make configuring and connecting to wireless networks easy for everyone. They partially succeeded. The Wireless Zero Configuration service is the “brains” behind managing wireless connections with Windows. Unfortunately, WZC does not always make sane decisions, which can cause sensations of frustration and annoyance, not to mention itching and burning.
Access Point Whack-a-Mole
In some spaces where wireless access is available, multiple access points are used to blanket a large area. Frequently these access points all broadcast the same network name, or SSID. Wireless Zero Configuration is programmed to assume this is the case – so, when it sees more than one AP with the same SSID, it automatically connects to the one with the strongest signal.
Not a bad strategy on paper. But what if two APs are broadcasting the same SSID and are not on the same network? WZC will connect to the stronger one, whether you want it to or not. Which might hook you up to the wrong network, possibly interrupting an existing session with your desired network.
Of course, if you manage your own wireless network, you can simply change its SSID to a unique name. But maybe you’re in a public space, or a zone managed by your workplace or a provider broadcasting an SSID of their choosing.
WZC will not distinguish access points with the same SSID. They appear only as one in Windows’ “Available Wireless Networks” menu. So you can’t force Windows to connect to a particular AP.
In this troubling scenario, the only solution that might work is to ditch WZC in favor of a third-party wireless client manager. Most wireless network adapters, whether external or internal, include a connection manager provided by the vendor – Linksys/Cisco, Orinoco/Proxim, Netgear, etc. Typically you can’t use both your vendor’s connection manger and WZC at the same time. Skip ahead to “Ditching WZC” for instructions on disabling the Windows connection manager.
Unfortunately, not all vendor-provided client managers solve this particular scenario, either. Unlike WZC, they may display multiple AP’s which are broadcasting the same SSID. But like WZC, they may not allow for forcing an association with one. In that case, if there is a workable solution out there, we’d like to know!
Hidden SSID Syndrome
By default, most access points broadcast their SSID. This allows your connection manager to see their presence and tell you, “Hey, buddy: this access point is in range.” Some people prefer to hide their SSID by configuring their access point not to broadcast. In this case, you manually set the SSID in your connection manager to link the connection.
The problem with Wireless Zero Configuration occurs if a second AP is also within range. If that AP is broadcasting its SSID, WZC will attempt to connect to it – even if you’ve told it that your AP with the hidden SSID is your preferred network. Whether or not WZC can establish a connection with the more promiscuous AP, its attempts can cause instability in your link.
Disabling SSID broadcasting is sometimes suggested as a security precaution. The theory is that your AP won’t advertise its presence to nearby snoops. In fact, this doesn’t provide much security at all. Whether or not it broadcasts its SSID, the AP includes the SSID in transmission packets which are easily sniffed out. In reality, disabling your SSID is no more secure than taping a broom handle across your steering wheel, hoping that thieves will mistake it for The Club. Secure your access point with WPA, or a MAC address filter. Enable SSID broadcasting, and WZC will treat you better.
Of course, the AP with the hidden SSID may not be yours to configure. If you can’t manage the access point yourself, a kludgier solution is to knock WZC senseless. Skip ahead to “The WZC Two-Step” below for details on how to disable WZC after it has established the connection.
Whoosawhatsit? 802.1x Authentication
Many home and small organizations secure their wireless networks using WEP or, preferably, WPA. But some institutions use the enterprise-oriented IEEE 802.1X authentication framework, which Windows XP supports natively.
Unfortunately, if you don’t use 802.1X on your wireless network, Wireless Zero Configuration may interrupt your connection when it periodically attempts to perform 802.1X authentication against your associated access point.
To prevent interruptions in connectivity, disable 802.1X authentication for your wireless network adapter. In Windows, open the Network Connections control panel. Locate your wireless adapter, double-click it, and choose Properties and then Wireless Networks. You should see a tab labeled Authentication, in which you can disable “Enable IEEE 802.1X Authentication for this network”.
Ditching WZC
Fortunately, some vendors provide their own wireless connection management utilities which can replace Microsoft’s Wireless Zero Configuration. Unfortunately, an increasing number of wireless adapters rely on WZC.
Netgear includes their own connection manager, and the ORiNOCO/Proxim connection manager will work with a variety of wireless adapters. Linksys includes their WLAN Monitor with their install CD, but it will actually refuse to install on a system with WZC active.
Some users have had success using the third-party Boingo connection manager, available from free download sites. The Boingo manager is designed to promote connecting to the Boingo wireless network, but it can also manage local wireless connections for some adapters. JiWire provides connection software with its SpotLock security (in fact, you can use the connection part without using the SpotLock hosted VPN at all).
Before using any third-party connection manager, you should first disable WZC. Open the Administrative Tools control panel and choose Services. Scroll down the list of services, and double-click Wireless Zero Configuration. Click Stop to end the service now. Select Manual (or Disabled) for the Startup Type.
Your wireless adapter is now freed from Windows, but you will need to install another connection manager, preferably from your adapter vendor, to connect to a network.
For Linksys owners, several procedures are described on Web message boards (such as this one and this one) for forcing Linksys’ superior WLAN Monitor to install on XP systems. Some involve only partial installs of the Linksys software.
The WZC Two-Step
You may find yourself forced to stick with WZC. Perhaps no vendor connection managers are available for your wireless adapter. Like the 802.1X authentication problem, WZC is known to “do stuff” which can interrupt a perfectly functioning connection. Every few minutes, WZC likes to see if anything better is out there, and it is not always clear what rationale, if any, it uses to make its decisions.
The most common sign that WZC went looking for a better deal is when Windows pops up its friendly taskbar balloon announcing “One or more wireless networks is available” – even though you’re already connected to a network and surfing happily, thank you very much. Or, you may see an equally helpful balloon touting that Windows has successfully connected to such-and-such a network – even though you’re already connected to that network and…
Unfortunately, you may experience instability in your connection when WZC goes roaming. A common (but certainly kludgy) solution is to disable WZC after it has successfully established a connection to your network.
You can do this using the Administrative Tools/Services control panel as described in “Ditching WZC” above, but that procedure can quickly grow tiresome.
As an alternative, follow the “Ditching WZC” procedure, but set its Startup Type to automatic. Now WZC will connect when your system boots.
Create a batch file (a plain text file) containing just the command:
C:WINDOWSsystem32net.exe stop
Save the batch file, or a shortcut to it, on your desktop. Give it a descriptive name like “Kill WZC Now”. Once your wireless connection is established on boot, double-click the shortcut. WZC will go away and bother you no more during this session. Of course, if you move to a new wireless network, you’ll need to relaunch WZC. You can reboot, or create a companion shortcut:
C:WINDOWSsystem32net.exe start
I said it was kludgy. But it works. Got a better solution? Let us know in the forums.
Source: Lifewire.com
Are you looking to start Wireless Zero Configuration on your device but not sure how to get started? Well, you’ve come to the right place! Wireless Zero Configuration, also known as WZC, is a feature found in Windows operating systems that allows you to connect to Wi-Fi networks automatically. This can be incredibly convenient, especially if you frequently switch between different networks or travel with your device.
In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to start Wireless Zero Configuration on your device. Whether you’re using a Windows laptop, desktop, or even a tablet, we will walk you through the necessary steps to enable this feature. So, let’s dive in and get your device connected with Wireless Zero Configuration!
Inside This Article
- What is Wireless Zero Configuration?
- Benefits of Wireless Zero Configuration
- Steps to Start Wireless Zero Configuration
- Troubleshooting Wireless Zero Configuration
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Wireless Zero Configuration, also known as WZC or WLAN AutoConfig, is a feature in Windows operating systems that allows for automatic configuration and connection to wireless networks. It is designed to simplify the process of connecting to and managing wireless networks, eliminating the need for manual configuration.
With Wireless Zero Configuration, users can easily detect and connect to available wireless networks without the hassle of manually entering network information such as SSID and security settings. This feature automatically scans the area for wireless networks and configures the system to connect to the preferred network.
Wireless Zero Configuration supports the most common wireless network protocols, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, making it compatible with a wide range of wireless devices. It provides a seamless experience for users, allowing them to effortlessly connect to and switch between different wireless networks.
This feature is especially useful for laptop users and those who frequently switch between different network environments, such as office, home, or public Wi-Fi hotspots. With Wireless Zero Configuration, users can save time and effort by letting the system take care of the network configuration process.
It is important to note that Wireless Zero Configuration is a native Windows feature and may not be available in other operating systems. However, many non-Windows platforms have their own equivalent or similar mechanisms for configuring and managing wireless networks.
Benefits of Wireless Zero Configuration
Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC), also known as WLAN AutoConfig, is a feature in Windows operating systems that makes it easier for users to connect to wireless networks. This handy feature brings several benefits to users, making their wireless networking experience more seamless and hassle-free.
1. Easy Network Setup: One of the main advantages of Wireless Zero Configuration is its simplicity in setting up wireless networks. Users no longer need to manually configure network settings or deal with complicated network setup procedures. WZC takes care of automatically detecting and connecting to available wireless networks, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
2. Automatic Network Switching: With Wireless Zero Configuration, users can effortlessly switch between different wireless networks without any hassle. Whether it’s moving between home, office, or public Wi-Fi networks, WZC takes care of automatically connecting to the available network, ensuring a seamless transition without the need for manual configuration.
3. Improved Security: Wireless Zero Configuration also enhances security measures when connecting to wireless networks. It supports the automatic configuration of security protocols, such as WEP, WPA, and WPA2, ensuring that users have a secure connection to their network without compromising their data privacy.
4. Increased Compatibility: Another benefit of using Wireless Zero Configuration is its compatibility with a wide range of wireless networking hardware. As it is a standard feature of Windows operating systems, it works seamlessly with most wireless adapters and routers, eliminating compatibility issues that may arise with other third-party network configuration software.
5. Reduced Technical Knowledge Requirements: Wireless Zero Configuration simplifies the wireless network setup process, making it accessible to users with limited technical knowledge. It eliminates the need for in-depth understanding of network configurations and allows users to easily connect to networks with just a few clicks.
6. Enhanced User Experience: By automating the connection process and handling network configuration in the background, Wireless Zero Configuration significantly improves the overall user experience. Users can focus on their tasks without having to troubleshoot network connectivity issues or spend time manually configuring network settings.
Overall, Wireless Zero Configuration brings a myriad of benefits to users, making it easier and more convenient to connect to wireless networks. With its simplified setup process, automatic network switching, enhanced security, and wide compatibility, WZC ensures a seamless and hassle-free wireless networking experience for Windows users.
Steps to Start Wireless Zero Configuration
Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) is a Windows service that enables automatic wireless network connectivity. It allows your device to quickly and easily connect to available Wi-Fi networks without the need for manual configuration. Here are the steps to start Wireless Zero Configuration:
- Access the Services Console: Press the Windows key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box. Type “services.msc” and hit Enter. This will launch the Services console.
- Locate the Wireless Zero Configuration service: Scroll down the list of services until you find “Wireless Zero Configuration”.
- Start the service: Right-click on “Wireless Zero Configuration” and select “Start” from the context menu. If the service is already running, the option will be greyed out.
- Enable the service: Right-click on “Wireless Zero Configuration” again and select “Properties”. In the Properties window, under the General tab, set the Startup type to “Automatic”. This ensures that the service starts automatically every time you boot up your device.
- Apply the changes: Click on the “Apply” button and then click “OK” to save the changes you made to the service properties.
- Restart your device: It’s recommended to restart your device to apply the changes and ensure that Wireless Zero Configuration is fully active.
Once you have completed these steps, Wireless Zero Configuration will be up and running on your Windows device. It will automatically scan for available Wi-Fi networks and connect to them as necessary, providing a seamless wireless networking experience.
Troubleshooting Wireless Zero Configuration
Wireless Zero Configuration can be a convenient feature when it works, but sometimes users may encounter issues that prevent it from functioning properly. If you’re experiencing problems with Wireless Zero Configuration, here are some troubleshooting tips to help you get back on track.
1. Restart the Wireless Zero Configuration service:
The first step in troubleshooting Wireless Zero Configuration is to restart the service responsible for managing wireless connections. To do this, go to the “Services” section in the Control Panel, find “Wireless Zero Configuration,” and choose the option to restart the service. This can often resolve any temporary glitches or conflicts.
2. Check your wireless adapter:
If restarting the service doesn’t solve the issue, the problem may lie with your wireless adapter. Ensure that the adapter is properly installed and functioning correctly. You can do this by checking the Device Manager in the Control Panel. Look for any exclamation marks or warning signs next to your wireless adapter. If you see any, try updating the driver or reinstalling the adapter to resolve any driver-related issues.
3. Verify the wireless settings:
Make sure that your wireless settings are configured correctly. Double-check that you’re connecting to the correct network and that the security settings, such as the Wi-Fi password, are entered correctly. Sometimes, incorrect settings can cause connectivity issues with Wireless Zero Configuration.
4. Disable conflicting software:
There may be other software on your computer that is conflicting with the Wireless Zero Configuration service. This software could be a third-party wireless management tool or a security program that is interfering with the service. Try disabling or uninstalling any such software and then restart the Wireless Zero Configuration service.
5. Reboot your router:
If all else fails, it’s worth rebooting your wireless router. Sometimes routers can encounter problems that affect their compatibility with Wireless Zero Configuration. Unplug the power cable from your router, wait for a few seconds, and then plug it back in. This can help reset the router and resolve any connectivity issues.
By following these troubleshooting tips, you should be able to resolve common issues with Wireless Zero Configuration. Remember to restart the service, check your wireless adapter and settings, disable conflicting software, and reboot your router if needed. If the problem persists, you may want to seek further assistance from technical support or consult online forums for more in-depth troubleshooting steps specific to your situation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, starting Wireless Zero Configuration is a relatively simple process that can greatly enhance your cell phone experience. By enabling this feature, you can seamlessly connect to Wi-Fi networks and enjoy uninterrupted internet access on your device. Whether you’re at home, at work, or on the go, Wireless Zero Configuration empowers you to stay connected and make the most of your cell phone’s capabilities.
With its automated network discovery, configuration, and connection abilities, Wireless Zero Configuration takes the hassle out of manually managing Wi-Fi networks. It ensures that your cell phone is always connected to the best available network, giving you faster speeds and more reliable connections.
So, if you’re ready to optimize your cell phone’s Wi-Fi connectivity, don’t hesitate to enable Wireless Zero Configuration. With just a few simple steps, you can unlock a whole new level of convenience and efficiency in your cell phone usage.
FAQs
FAQ 1: What is Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC)?
Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) is a service provided by Microsoft Windows operating systems that allows you to connect to and manage wireless networks. It provides automatic wireless network configuration and eliminates the need for third-party wireless network management software.
FAQ 2: How do I start Wireless Zero Configuration?
To start Wireless Zero Configuration, you need to follow these steps:
- Open the Control Panel on your Windows computer.
- Click on “Administrative Tools”.
- Double-click on “Services”.
- Scroll down and find “Wireless Zero Configuration”.
- Right-click on “Wireless Zero Configuration” and select “Start”.
FAQ 3: Can I disable Wireless Zero Configuration?
Yes, you can disable Wireless Zero Configuration if you prefer to use third-party wireless network management software. However, it is recommended to keep it enabled unless you have a specific reason to disable it.
FAQ 4: Does Wireless Zero Configuration work with all wireless adapters?
Wireless Zero Configuration is designed to work with most wireless adapters that are compatible with Microsoft Windows operating systems. However, there may be some rare cases where certain wireless adapters may not be fully supported.
FAQ 5: How can I troubleshoot Wireless Zero Configuration connection issues?
If you are experiencing connection issues with Wireless Zero Configuration, you can try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Make sure your wireless adapter is properly installed and recognized by your computer.
- Check if the Wireless Zero Configuration service is running.
- Ensure that your wireless adapter’s drivers are up to date.
- Restart your computer and try connecting to the wireless network again.
- If the issue persists, you may need to consult your wireless adapter’s documentation or contact the manufacturer for further assistance.


