on August 15, 2010
We normally use Services.msc to start or stop or disable or enable any service. We can do the same from windows command line also using net and sc utilities. Below are commands for controlling the operation of a service.
Command to stop a service:
net stop servicename
To start a service:
net start servicename
You need to have administrator privileges to run net start/stop commands. If you are just a normal user on the computer, you would get an error like below.
C:\>net start webclient System error 5 has occurred. Access is denied. C:\>
To disable a service:
sc config servicename start= disabled
To enable a service:
sc config servicename start= demand
To make a service start automatically with system boot:
sc config servicename start= auto
Note: Space is mandatory after ‘=’ in the above sc commands.
This SC command works on a Windows 7 machine and also on the down-level editions of Windows i.e Windows XP/2003 and Windows Vista. Again, if you do not have administrator previliges you would get the below error.
C:\>sc config webclient start= auto [SC] OpenService FAILED 5: Access is denied.
Note that the service name is not the display name of a service. Each service is given a unique identification name which can be used with net or sc commands. For example, Remote procedure call (RPC) is the display name of the service. But the service name we need to use in the above commands is RpcSs.
So to start Remote procedure call service the command is:
net start RpcSsTo stop Remote procedure call service
net stop RpcSs
These service names are listed below for each service. The first column shows the display name of a service and the second column shows the service name that should be used in net start or net stop or sc config commands.
| Display Name of the service | ServiceName which should be used with ‘net’ and ‘sc config’ commands. |
| Alerter | Alerter |
| Application Layer Gateway Service | ALG |
| Application Management | AppMgmt |
| ASP.NET State Service | aspnet_state |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service | BITS |
| Computer Browser | Browser |
| Bluetooth Support Service | BthServ |
| Bluetooth Service | btwdins |
| SMS Agent Host | CcmExec |
| Indexing Service | CiSvc |
| ClipBook | ClipSrv |
| .NET Runtime Optimization Service v2.0.50727_X86 | clr_optimization_v2.0.50727_32 |
| COM+ System Application | COMSysApp |
| Cryptographic Services | CryptSvc |
| Cisco Systems, Inc. VPN Service | CVPND |
| DCOM Server Process Launcher | DcomLaunch |
| DHCP Client | Dhcp |
| Logical Disk Manager Administrative Service | dmadmin |
| Logical Disk Manager | dmserver |
| DNS Client | Dnscache |
| Lenovo Doze Mode Service | DozeSvc |
| Error Reporting Service | ERSvc |
| Event Log | Eventlog |
| COM+ Event System | EventSystem |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Event Log | EvtEng |
| Fast User Switching Compatibility | FastUserSwitchingCompatibility |
| Windows Presentation Foundation Font Cache 3.0.0.0 | FontCache3.0.0.0 |
| Group Policy Monitor | GPMON_SRV |
| Help and Support | helpsvc |
| HID Input Service | HidServ |
| HTTP SSL | HTTPFilter |
| ThinkPad PM Service | IBMPMSVC |
| Windows CardSpace | idsvc |
| IMAPI CD-Burning COM Service | ImapiService |
| iPassConnectEngine | iPassConnectEngine |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateApp | iPassPeriodicUpdateApp |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateService | iPassPeriodicUpdateService |
| IviRegMgr | IviRegMgr |
| Server | lanmanserver |
| Workstation | lanmanworkstation |
| Lenovo Camera Mute | LENOVO.CAMMUTE |
| Lenovo Microphone Mute | Lenovo.micmute |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts |
| Intel(R) Management and Security Application Local Management Service | LMS |
| McAfee Framework Service | McAfeeFramework |
| McAfee McShield | McShield |
| McAfee Task Manager | McTaskManager |
| Machine Debug Manager | MDM |
| Messenger | Messenger |
| NetMeeting Remote Desktop Sharing | mnmsrvc |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator | MSDTC |
| Windows Installer | MSIServer |
| Net Driver HPZ12 | Net Driver HPZ12 |
| Network DDE | NetDDE |
| Network DDE DSDM | NetDDEdsdm |
| Net Logon | Netlogon |
| Network Connections | Netman |
| Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service | NetTcpPortSharing |
| Network Location Awareness (NLA) | Nla |
| NT LM Security Support Provider | NtLmSsp |
| Removable Storage | NtmsSvc |
| Microsoft Office Diagnostics Service | odserv |
| Office Source Engine | ose |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay |
| Pml Driver HPZ12 | Pml Driver HPZ12 |
| IPSEC Services | PolicyAgent |
| Power Manager DBC Service | Power Manager DBC Service |
| Protected Storage | ProtectedStorage |
| Remote Access Auto Connection Manager | RasAuto |
| Remote Access Connection Manager | RasMan |
| Remote Desktop Help Session Manager | RDSessMgr |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Registry Service | RegSrvc |
| Routing and Remote Access | RemoteAccess |
| Remote Registry | RemoteRegistry |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator | RpcLocator |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs |
| QoS RSVP | RSVP |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi Service | S24EventMonitor |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs |
| Smart Card | SCardSvr |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule |
| Secondary Logon | seclogon |
| System Event Notification | SENS |
| Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess |
| Shell Hardware Detection | ShellHWDetection |
| Print Spooler | Spooler |
| System Restore Service | srservice |
| SSDP Discovery Service | SSDPSRV |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | stisvc |
| System Update | SUService |
| MS Software Shadow Copy Provider | SwPrv |
| Performance Logs and Alerts | SysmonLog |
| Telephony | TapiSrv |
| Terminal Services | TermService |
| Themes | Themes |
| ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service | ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service |
| Telnet | TlntSvr |
| On Screen Display | TPHKSVC |
| Distributed Link Tracking Client | TrkWks |
| TVT Scheduler | TVT Scheduler |
| Windows User Mode Driver Framework | UMWdf |
| Intel(R) Management & Security Application User Notification Service | UNS |
| Universal Plug and Play Device Host | upnphost |
| Uninterruptible Power Supply | UPS |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS |
| Windows Time | W32Time |
| WebClient | WebClient |
| Windows Management Instrumentation | winmgmt |
| Portable Media Serial Number Service | WmdmPmSN |
| Windows Management Instrumentation Driver Extensions | Wmi |
| WMI Performance Adapter | WmiApSrv |
| Security Center | wscsvc |
| Automatic Updates | wuauserv |
| SMS Remote Control Agent | Wuser32 |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSVC |
| Network Provisioning Service | xmlprov |
Службы Windows (Windows Service) — приложения (программы), работающие в фоновом режиме, без пользовательского интерфейса. Грубо говоря, некий аналог демонов в Unix системах.
Управление работой служб с помощью консоли управления.
Для управления службами в Windows существует графическая утилита — службы (services.msc), для ее запуска необходимо перейти:
Панель управления (Control Panel) —> Администрирование (Administrative Tools) —> Службы (Services) или в строке поиска меню Пуск (Start) ввести services.msc.
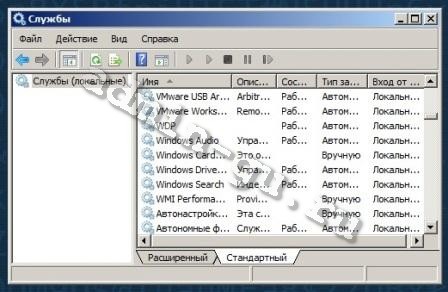
Вид окна службы services.msc.
Из этой консоли можно просматривать, запускать, останавливать, изменять параметры и тип запуска служб.
Различные варианты запуска служб.
1) Автоматически (отложенный запуск) — служба будет запущена спустя некоторое время после старта операционной системы, используется для служб, ненужных при загрузке операционной системы, позволяет оптимизировать процесс загрузки.
2) Автоматически — служба будет запущена при старте операционной системы.
3) Вручную — служба запускается пользователем, приложениями или другими службами.
4) Отключена – службу нельзя запустить.
Примечание: Существует еще один вариант (обязательная служба) — автоматически запускается и пользователь не может остановить эту службу).
Управление службами из командной строки.
Службами window можно управлять не только используя графическую утилиту, но и из командной строки windows cmd. Для запуска переходим в пункт меню: Пуск —> Выполнить —> В строку вводим команду cmd.exe. Ниже приведу команды для управления службами.
Остановка службы.
sc stop [имя_службы]
Запуск службы.
sc start [имя_службы]
Удаление службы.
sc delete [имя_службы]
Установка режима запуска службы:
sc config [имя_службы] start= [параметр_запуска] параметр_запуска: auto - автоматически. demand - вручную. disabled - отключена. Примечание: После start= должен идти обязательно пробел.
Запрос данных конфигурации для службы.
sc qc [имя_службы]
Просмотр всех служб:
sc query
Для удобства чтения выводимой информации используем утилиту more.
sc query | more
Для копирования вывода в буфер используем утилиту clip.
sc query | clip
Вывод справки по команде sc.
sc ?
Примечание: Если имя службы содержит пробелы, то необходимо его заключить в кавычки.
sc delete “Events Utility”
Особенностью служб является то, что они запускаются от имени пользователя LocalSystem — обладающего полными правами в системе.
Список всех служб расположен в ветке реестра:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services
На этом заканчиваем знакомство со службами windows. Надеюсь статья была полезная.
The services in Windows can be started using the Service Manager tool.
To start the Service Manager GUI, press ⊞ Win keybutton to open the start menu, type in services to search for the Service Manager and press Enter to launch it.
The services can also be started using the command-line prompt (CMD) or the PowerShell.
In this note i am showing how to start, stop or check the status of a service in Windows using the command-line prompt (CMD) or the PowerShell.
Cool Tip: List services in Windows from the CMD & PowerShell! Read more →
Start Service Using Command Line (CMD)
To avoid “Access is denied” errors, start CMD as an administrator: press ⊞ Win keybutton to open the start menu, type in cmd to search for the command prompt and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch it as administrator.
Use the following commands to start, stop or check the status of a service in Windows on the command-line prompt (CMD).
Start a service:
C:\> net start serviceName
Get a service status:
C:\> sc query serviceName
Stop a service:
C:\> net stop serviceName
Cool Tip: Kill a hanging process in Windows from the CMD! Read more →
To avoid “Access is denied” errors, start PowerShell as an administrator: press ⊞ Win keybutton to open the start menu, type in powershell to search for the PowerShell and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch it as administrator.
Use the following commands to start, stop or check the status of a service in Windows using the PowerShell.
Start a service:
PS C:\> Start-Service serviceName
Get a service status:
PS C:\> Get-Service serviceName
Stop a service:
PS C:\> Stop-Service serviceName
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
The Task Manager lets you quit apps and stop and start a Windows service. It’s an easy, graphical way to stop a service if you ever need to but you can also stop and start a Windows service from the command prompt. The process is easy enough though it goes without saying that you need administrative rights to stop or start a service on Windows.
SPOILER ALERT: Scroll down and watch the video tutorial at the end of this article.
Open command prompt by entering Command Prompt in Windows Search. Right-click it and select ‘Run as administrator’ from the context menu. Alternatively, you can open Command Prompt with admin rights from the Run box by typing cmd, and hitting Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
Scan For Running Services
If you’re looking to stop and start a Windows service from the Command Prompt, chances are you may not know what a service is called. The task manager lists them so it’s easier but you can also scan for and list all running Windows services. Enter the following command to list all services that are currently running.
net start
You can stop any one of the services with the following commands. If the service name has spaces, you should enclose it in double quotes.
Syntax
NET STOP service name
Example
NET STOP "Apple Mobile Device Service"
Start Service
You can start a service with the following command. If the service name has spaces, make sure you enclose it in double quotes.
Syntax
NET START service name
Example
NET START "Apple Mobile Device Service"
If you want to stop and start a Windows service from the Command Line in one go, you can combine the above two commands as follows;
Syntax
net stop service name && net start service name
Example
net stop "Apple Mobile Device Service" && net start "Apple Mobile Device Service"
Service Status
The Command Prompt has a built-in tool that can perform other operations on a Windows service. For example, if you need to know whether a service is running or not, you can use this tool to query the status. It’s called sc, and again you need admin rights to use all its commands. You can view a complete list of the commands it supports on the official documentation page maintained by Microsoft. To simply check the status of a service, you can use the following command.
Syntax
sc command service name
Example
sc query “Apple Mobile Device Service”
Be careful which services you choose to stop or start. If you accidentally stop a critical service, your system might crash. Some services may be prone to starting up again automatically once they’re stopped.

Fatima Wahab
Fatima has been writing for AddictiveTips for six years. She began as a junior writer and has been working as the Editor in Chief since 2014.
Fatima gets an adrenaline rush from figuring out how technology works, and how to manipulate it. A well-designed app, something that solves a common everyday problem and looks
To start a service using command prompt (cmd), use the `net start` command followed by the name of the service you want to start.
net start "ServiceName"
Understanding Windows Services
What are Windows Services?
Windows services are specialized applications that run in the background and do not require user intervention. They are designed to perform specific functions such as managing network connections, running background tasks, or handling system events. Unlike regular applications, services can start before a user logs in and can run continuously without a user interface. This makes them essential for various system-level operations.
Why Use CMD to Start a Windows Service?
Using the Command Prompt (CMD) to start a Windows service offers several advantages:
- Efficiency: Commands can be executed faster than navigating through graphical interfaces.
- Automation: CMD commands can be easily scripted for batch operations or scheduled tasks.
- Remote Management: CMD may be used to control services on remote machines, especially in server environments, helping system administrators manage resources without GUI access.

Restart Services Cmd: A Quick Guide for Beginners
Starting a Windows Service from CMD
Prerequisites
Before starting a service using CMD, ensure that you have admin privileges. Running the Command Prompt with administrative rights is crucial for executing service-related commands. To open Command Prompt as an administrator, follow these steps:
- Right-click on the Start Menu.
- Select Command Prompt (Admin) or Windows Terminal (Admin) from the menu.
Identifying the Service to Start
To start a service, you first need to know its name. You can list all the services running on your system by using the command:
sc query state= all
This command will display all services, including those that are running, stopped, or disabled. Understanding the output is essential; look for the SERVICE_NAME of the service you want to start, which appears in the format `SERVICE_NAME : YourServiceName`.

Uninstall Service Cmd: A Quick Guide to Mastery
Using the START COMMAND
Syntax of the Start Command
Once you have identified the service’s name, you can use the `sc start` command to start the service. The basic syntax is:
sc start [ServiceName]
Step-by-Step Example
Let’s consider an example: Starting the Print Spooler Service. This service is responsible for managing print jobs sent to the printer.
To start the service, you would execute:
sc start spooler
Upon execution, you should see a message indicating that the command has completed successfully. If the service was already running, you might receive a message stating that the service is already running.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
When starting a service via CMD, you may encounter a few common errors.
- If you see «The specified service does not exist», this usually means the service name is incorrect. Double-check your service name by listing all services again.
- «Access Denied» indicates that you do not have the necessary permissions. Ensure you’re running CMD as an administrator.

Restart Server Cmd: A Quick Guide to Reboot with Ease
Comparison with Other Commands
Using NET START
In addition to `sc start`, you can also use the `net start` command to achieve similar results. The distinction lies in their functionality:
- `sc start` provides more detailed options and is better for service management.
- `net start` is simpler and can be easier for quick operations.
For example, to start the Print Spooler service using `net start`, you would type:
net start spooler
Both commands achieve the same goal, but knowing the differences allows you to choose the best tool for your needs.

List Services Cmd: Mastering Service Commands Effortlessly
Stopping a Windows Service from CMD
While knowing how to start a service is essential, it’s equally important to know how to stop one when necessary.
The `sc stop` command allows you to stop a service quickly. For instance:
sc stop spooler
This command will terminate the Print Spooler service, freeing system resources when it’s no longer needed.
Mastering Windows Services Cmd: A Quick Guide
Additional CMD Commands for Service Management
Querying Service Status
To check the status of a service, you can use the `sc query` command, which provides information about the service’s current state. For example:
sc query spooler
This command will return detailed information, including whether the service is running, stopped, and other related details.
Configuring a Service
The `sc config` command allows you to configure various parameters of a service, such as changing its start type. For example, if you want to disable the Print Spooler service from starting automatically, you could execute:
sc config spooler start= disabled
This command is particularly useful for system administrators who need to manage service configurations proactively.

Restart IIS Cmd: A Quick Guide for Instant Reset
Conclusion
Mastering the ability to start a service cmd is an invaluable skill for Windows users and administrators alike. From enhancing efficiency to providing flexibility in service management, CMD commands enable you to interact with Windows services in a robust and straightforward manner. As you continue to explore CMD, don’t hesitate to practice these commands to become more confident in managing your services directly from the command line.

Mastering The Startup Cmd: A Quick Guide
Resources for Further Learning
Dive deeper into CMD and Windows services through online resources, documentation, and tutorials. Consider exploring books and courses that specialize in CMD and Windows administration to enhance your skills further.
