Creating files and folders with names based on the current date and time is a crucial aspect of organizing data, automating backups, and logging in Windows environments. Windows Batch Script, the scripting language for Windows Command Prompt, offers straightforward methods to incorporate date and time stamps into your filenames and directory names. This article explores how to achieve this, ensuring your scripts can dynamically generate unique and descriptive names.
Understanding Windows Batch Script Date & Time
In Windows Batch Script, the %DATE% and %TIME% environment variables provide the current date and time, respectively. However, their format is influenced by the system’s regional settings, which can vary. Typically, %DATE% returns the date in the format “Fri 03/01/2024“, and %TIME% provides the time in the format “12:30:45.78”.
Formatting Date and Time
To create file or folder names with date and time, you must extract and format these values accordingly. Since direct formatting options like in Linux’s date command are not available, you’ll often need to use substring extraction and replacement techniques.
Extracting Date Components
Here’s how you can extract year, month, and day from the %DATE% variable, assuming the format is MM/DD/YYYY:
set YEAR=%DATE:~10,4%
set MONTH=%DATE:~4,2%
set DAY=%DATE:~7,2%
Extracting Time Components
Similarly, to extract hour, minute, and second from %TIME%, you might use:
set HOUR=%TIME:~0,2%
set MINUTE=%TIME:~3,2%
set SECOND=%TIME:~6,2%
Generating Names Based on Date and Time
With the date and time components extracted, you can now combine them to form unique file or folder names.
Creating a Timestamped File Name
set FILENAME=Log_%YEAR%-%MONTH%-%DAY%_%HOUR%-%MINUTE%-%SECOND%.txt
echo Log entry > %FILENAME%
This script creates a log file named like Log_2024-03-01_12-30-45.txt.
Creating a Directory Based on the Date
For organizing backups or logs by date, you might create a directory like so:
set DIRNAME=Backup_%YEAR%-%MONTH%-%DAY%
mkdir %DIRNAME%
This command creates a directory named Backup_2024-03-01.
Handling Single-Digit Day and Month
One challenge is that single-digit months and days can lead to names with unexpected formats due to leading spaces. To ensure a consistent two-digit format, you can add a zero padding where necessary:
if %MONTH% LSS 10 set MONTH=0%MONTH:~1,1%
if %DAY% LSS 10 set DAY=0%DAY:~1,1%
To utilize the script in a Windows environment for generating timestamped filenames and directory names, follow these steps: Create a new file named script.bat and input the content outlined below. This script is designed to extract the current date and time, format these elements for consistency, and then employ them to construct a unique log file and a backup directory.
@echo off
:: Extract year, month, and day from the system's date
set YEAR=%DATE:~10,4%
set MONTH=%DATE:~4,2%
set DAY=%DATE:~7,2%
:: Ensure month and day are two digits (add leading zero if necessary)
if %MONTH% LSS 10 set MONTH=0%MONTH:~1,1%
if %DAY% LSS 10 set DAY=0%DAY:~1,1%
:: Extract hour, minute, and second from the system's time
set HOUR=%TIME:~0,2%
set MINUTE=%TIME:~3,2%
set SECOND=%TIME:~6,2%
:: Ensure hour, minute, and second are two digits (add leading zero if necessary)
if %HOUR% LSS 10 set HOUR=0%HOUR:~1,1%
if %MINUTE% LSS 10 set MINUTE=0%MINUTE:~1,1%
if %SECOND% LSS 10 set SECOND=0%SECOND:~1,1%
:: Create a log file with the current timestamp in its name
set FILENAME=Log_%YEAR%-%MONTH%-%DAY%_%HOUR%-%MINUTE%-%SECOND%.txt
echo Log entry > %FILENAME%
:: Create a directory with the current timestamp in its name
set DIRNAME=Backup_%YEAR%-%MONTH%-%DAY%
mkdir %DIRNAME%
After saving the script as script.bat, you can run it by double-clicking the file or executing it from the command prompt.
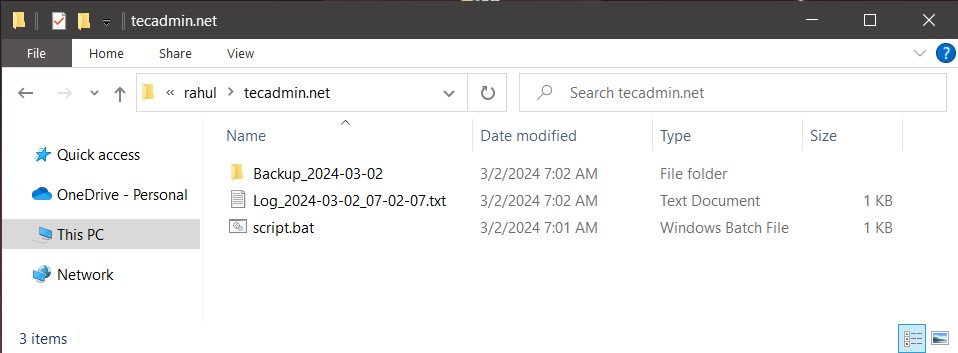
You will find that a directory is created with the name “Backup_2024-03-02”. Also, a file created in the current directory with the name “Log_2024-03-02_07-02-07.txt” (Filename will be according to current date and time and will change during your testing)
Conclusion
Generating file and folder names based on the current date and time in Windows Batch Script requires a bit more manual effort compared to other scripting environments. However, by extracting and formatting date and time components, you can create meaningful, unique names for files and directories. This approach is invaluable for automated data management tasks, ensuring your scripts can handle files in an organized, chronological manner.
When working with Windows scripts, it’s often necessary to date an output file or backup folder created from the script. One common challenge is that the `%DATE%` variable returns a value with slashes in, which cannot be used on its own. In this blog post, we will explore a method for formatting the date to the ISO standard YYYYMMDD format and how to use it in your scripts.
The `%DATE%` variable is a built-in Windows command that returns the current date and time. However, the output is in the format “MM/DD/YYYY HH:MM:SS”, which can be inconvenient when working with dates only. To overcome this limitation, you can use the `STRFTIME` function to format the date to the desired ISO standard YYYYMMDD format.
Here’s an example of how to use the `STRFTIME` function to format the current date to the YYYYMMDD format:
“`
@echo off
for /f “tokens=2 delims=” %%a in (‘strftime “%Y%m%d”‘) do (
echo(%%a)
)
“`
In this example, the `strftime` function is used to format the current date to the YYYYMMDD format. The `for /f` loop iterates over each token in the output of the `strftime` command, and the `echo` command is used to print each token.
To use this method in your scripts, you can simply replace the `%DATE%` variable with the formatted date. For example, if you want to create a dated folder or file, you can use the following code:
“`
@echo off
mkdir “backup_%%Y%%m%%d”
“`
In this example, the `mkdir` command is used to create a new folder with the name “backup_%%Y%%m%%d”. The `%%Y%%m%%d` syntax uses the formatted date returned by the `strftime` function to create a unique folder name for each day.
Another common use case for this method is when you need to backup files to a dated folder. You can use the following code to create a dated folder and copy the files to it:
“`
@echo off
mkdir “backup_%%Y%%m%%d”
xcopy /y “C:\files” “backup_%%Y%%m%%d\*”
“`
In this example, the `mkdir` command is used to create a new folder with the name “backup_%%Y%%m%%d”. The `xcopy` command is then used to copy all files from the “C:\files” directory to the dated folder. The `/y` option tells `xcopy` to preserve the file dates, so the backup will include the correct date for each file.
In conclusion, this method provides a simple and effective way to date an output file or backup folder created from a Windows script. By using the `STRFTIME` function to format the current date to the ISO standard YYYYMMDD format, you can easily create unique dated folders and files for each day. This technique is versatile and can be used in a variety of scenarios, making it an essential tool for any Windows scripting enthusiast.
A VMware Troubleshooting Internet Resource on everything VMware related
Many times it becomes necessary to append date stamp on your export dumps. In Unix systems, shell scripting is very liberal with variables you can define yourself eg:
expdate=`date ‘+%d%m%Y’`
dat=`date ‘+%m%d%y %H:%M:%S’`
And then go onto define in your script as
./expdp system/system directory=export_dir dumpfile=exp_swx_$expdate.dmp logfile=exp_swx_$expdate.log schemas=swx
But on Windows it can be done in a more easier way, using the Date and Time function. Just input the string below as part of the file name any time you want the current system date and/or time included as part of the file name.
Date: %date:~4,2%-%date:~7,2%-%date:~12,2%
Time: %time:~0,2%-%time:~3,2%-%time:~6,2%
Example: copy c:\test.txt c:\test-%date:~4,2%-%date:~7,2%-%date:~12,2%.txt will output c:\test-mm-dd-yy.txt
exp edate/edate file=edate%date:~4,2%-%date:~7,2%-%date:~12,2%.dmp log=edate%date:~4,2%-%date:~7,2%-%date:~12,2%.txt owner=edate statistics=none
-
Understanding Batch Scripting for Filename Generation
-
Generating a Timestamped Filename in Batch Script
-
Using Git Commands with Timestamped Filenames
-
Conclusion
-
FAQ
Creating a system-generated filename with a timestamp in a Batch script can streamline your file management process. Whether you’re logging data, backing up files, or maintaining version control, a timestamped filename can help you easily identify when the file was created.
In this tutorial, we’ll explore how to generate a filename that includes the current date and time using Batch scripting. This method is particularly useful in automation tasks or when working with Git repositories. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to implement this in your own scripts.
Understanding Batch Scripting for Filename Generation
Batch scripting is a powerful tool for automating tasks in Windows environments. When you need to create a file with a unique name, incorporating a timestamp is essential. A timestamp not only makes your filenames unique but also adds context about when the file was created.
To achieve this, we’ll use the built-in Windows commands to format the current date and time correctly. The challenge lies in how Windows formats dates and times, often with characters that are not allowed in filenames. Therefore, we’ll need to manipulate these formats to create a valid filename.
Generating a Timestamped Filename in Batch Script
To generate a timestamped filename in a Batch script, you can follow these steps. Here’s a simple example that demonstrates how to create a filename with the current date and time:
@echo off
setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
rem Get the current date and time
for /f "tokens=1-3 delims=/ " %%a in ('date /t') do (
set year=%%c
set month=%%a
set day=%%b
)
for /f "tokens=1-2 delims=: " %%a in ('time /t') do (
set hour=%%a
set minute=%%b
)
rem Format the filename
set filename=Backup_%year%-%month%-%day%_%hour%-%minute%.txt
rem Create the file
echo This is a backup file created on %date% at %time% > %filename%
endlocal
Output:
This is a backup file created on 10/10/2023 at 10:30 AM
In this script, we first retrieve the current date and time using the date and time commands. The for loops parse the output to extract the year, month, day, hour, and minute. We then format these values into a filename using a specific structure, ensuring that it is both readable and unique. Finally, we create a file with the generated name and add a simple message to it.
Using Git Commands with Timestamped Filenames
If you are working within a Git environment, it’s beneficial to integrate timestamped filenames into your version control practices. This can help you keep track of changes and backups more effectively. Below is an example of how you can generate a timestamped filename while performing Git operations:
@echo off
setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
rem Get the current date and time
for /f "tokens=1-3 delims=/ " %%a in ('date /t') do (
set year=%%c
set month=%%a
set day=%%b
)
for /f "tokens=1-2 delims=: " %%a in ('time /t') do (
set hour=%%a
set minute=%%b
)
rem Format the filename
set filename=GitBackup_%year%-%month%-%day%_%hour%-%minute%.txt
rem Create the file and log the changes
git log > %filename%
endlocal
Output:
Git log saved to GitBackup_2023-10-10_10-30.txt
In this example, we follow a similar procedure to create a timestamped filename. However, instead of just writing a message to the file, we use the git log command to capture the commit history of the current repository. This file can serve as a backup of your project’s history at a specific point in time, making it easier to review changes later.
Conclusion
Creating system-generated filenames with timestamps in Batch scripts is a straightforward process that can greatly enhance your file management. Whether you’re automating backups or integrating with Git, having a timestamp in your filenames provides clarity and organization. With the examples provided, you can easily implement this in your own scripts and improve your workflow. Remember, a well-structured filename can save you time and frustration in the long run.
FAQ
-
What is a Batch script?
A Batch script is a text file containing a series of commands that are executed in sequence by the Windows command line interpreter. -
Why should I use timestamped filenames?
Timestamped filenames help you keep track of when files were created, making it easier to manage versions and backups. -
Can I customize the format of the timestamp in the filename?
Yes, you can modify the formatting of the date and time in the script to suit your preferences. -
Is it possible to automate this process?
Absolutely! You can schedule your Batch script to run at specific intervals using Windows Task Scheduler. -
How does this relate to Git?
Integrating timestamped filenames with Git commands allows you to create backups of your commit history, enhancing your version control practices.
Enjoying our tutorials? Subscribe to DelftStack on YouTube to support us in creating more high-quality video guides. Subscribe
