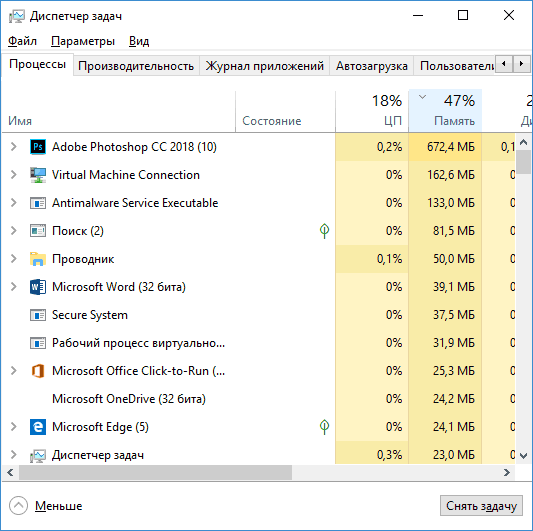
Did you know that the Windows Task Manager is a powerful tool that can help you monitor and manage the processes and performance of your computer? It’s located in the Windows operating system, providing users with valuable insights into the applications and services running on their system.
The Windows Task Manager can be accessed by pressing the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys simultaneously or by right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting «Task Manager» from the menu. This handy feature has been a part of Windows since the early versions and continues to be a go-to resource for troubleshooting and optimizing system performance.
Windows Task Manager can be easily accessed by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc on your keyboard. Alternatively, you can right-click on the taskbar and select «Task Manager» from the menu. You can also open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete and selecting «Task Manager» from the options. It’s a powerful tool that allows you to monitor running processes, check system performance, and manage applications.

Introduction: Understanding the Location of Windows Task Manager
The Windows Task Manager is a powerful tool that allows users to monitor and manage their computer’s processes, performance, and applications. Whether you need to troubleshoot performance issues or terminate an unresponsive program, the Task Manager is an essential resource. However, many users may wonder where exactly they can find the Task Manager on their Windows operating system. In this article, we will explore the different ways you can access the Task Manager and how its location can vary depending on the Windows version and user preferences.
1. Accessing Task Manager Through Keyboard Shortcuts
One of the quickest ways to access the Task Manager is through keyboard shortcuts. These shortcuts work in most versions of Windows and can be especially helpful if your computer is unresponsive or you’re dealing with a frozen application.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc simultaneously: This keyboard combination directly opens the Task Manager without the need for any additional steps. It is one of the fastest ways to access the Task Manager, especially for experienced users.
- Press Ctrl + Alt + Del and select «Task Manager»: This key combination opens the Windows Security screen, where you can choose various options including the Task Manager. This method works in all Windows versions and provides a reliable way to access the Task Manager.
Using these keyboard shortcuts, you can quickly access the Task Manager regardless of your current screen or the active applications.
1.1. Task Manager Location in Windows 10
In Windows 10, accessing the Task Manager through keyboard shortcuts follows the same process as mentioned above. However, you can also access it through right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting «Task Manager». This provides an alternative method where you don’t have to remember the keyboard shortcuts.
Additionally, Windows 10 introduced the use of the «Ctrl + Shift + Esc» shortcut to launch the Task Manager directly, without going through the Windows Security screen. This shortcut is particularly useful when you need to access the Task Manager quickly.
1.2. Task Manager Location in Windows 8 and 8.1
In Windows 8 and 8.1, you can access the Task Manager using the same keyboard shortcuts mentioned earlier. Alternatively, you can right-click on the taskbar and select «Task Manager» from the context menu.
Windows 8 and 8.1 also introduced a more user-friendly way to access the Task Manager. By pressing «Ctrl + Shift + Esc», you can directly open the Task Manager without going through the Windows Security screen.
1.3. Task Manager Location in Windows 7, Vista, and XP
In Windows 7, Vista, and XP, the process of accessing the Task Manager through keyboard shortcuts is the same as mentioned earlier. You either use «Ctrl + Shift + Esc» or «Ctrl + Alt + Del» and select «Task Manager» from the menu that appears.
However, in Windows 7 and previous versions, you can also right-click on the taskbar and choose «Start Task Manager» from the context menu.
2. Accessing Task Manager Through the Start Menu
A common method to access the Task Manager is through the Windows Start menu. This method is particularly useful for those who prefer graphical interfaces over keyboard shortcuts.
To access the Task Manager through the Start menu:
- Click on the «Start» button in the bottom-left corner of the screen.
- Scroll through the list of programs and locate the «Windows System» folder.
- Click on the «Windows System» folder to expand it, and then click on «Task Manager» to open it.
This method is consistent across various Windows versions, making it a reliable way to access the Task Manager.
2.1. Task Manager Location in Windows 10
In Windows 10, accessing the Task Manager through the Start menu follows the exact steps mentioned above. Click on the «Start» button, locate the «Windows System» folder, and open the Task Manager.
2.2. Task Manager Location in Windows 8 and 8.1
Similar to Windows 10, accessing the Task Manager through the Start menu in Windows 8 and 8.1 involves the same steps mentioned earlier. Click on the «Start» button, find the «Windows System» folder, and open the Task Manager from there.
2.3. Task Manager Location in Windows 7, Vista, and XP
Windows 7, Vista, and XP also follow the same process of accessing the Task Manager through the Start menu. Click on the «Start» button, locate the «Windows System» folder, and open the Task Manager.
3. Task Manager Location Through Run Command
An alternative method to access the Task Manager involves using the Run command. This method can be particularly useful for advanced users or those who prefer using command-based interfaces.
To access the Task Manager through the Run command:
- Press Windows key + R simultaneously to open the Run dialog box.
- Type in «taskmgr» or «taskman» and press Enter or click on «OK».
This will directly launch the Task Manager without requiring any additional steps or navigating through menus.
3.1. Task Manager Location in Windows 10
The process of accessing the Task Manager through the Run command is the same in all Windows versions, including Windows 10. Open the Run dialog box, type in «taskmgr» or «taskman», and launch the Task Manager.
3.2. Task Manager Location in Windows 8 and 8.1
Windows 8 and 8.1 also allow you to access the Task Manager through the Run command. Open the Run dialog box, type in «taskmgr» or «taskman», and open the Task Manager.
3.3. Task Manager Location in Windows 7, Vista, and XP
In Windows 7, Vista, and XP, follow the same process of opening the Run dialog box, typing in «taskmgr» or «taskman», and launching the Task Manager.
4. Task Manager Location Through Taskbar Context Menu
Another way to access the Task Manager is through the taskbar context menu. This method allows you to directly open the Task Manager without any additional steps.
To access the Task Manager through the taskbar context menu:
- Right-click on an empty area of the taskbar.
- From the context menu, click on «Task Manager».
By right-clicking on the taskbar, you can quickly access the Task Manager without the need to navigate through menus or use keyboard shortcuts.
4.1. Task Manager Location in Windows 10
In Windows 10, you can access the Task Manager through the taskbar context menu by right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting «Task Manager». This provides a convenient shortcut to open the Task Manager without using any keyboard shortcuts or going through additional menus.
4.2. Task Manager Location in Windows 8 and 8.1
The process of accessing the Task Manager through the taskbar context menu in Windows 8 and 8.1 is the same as in Windows 10. Right-click on the taskbar and choose «Task Manager» from the menu.
4.3. Task Manager Location in Windows 7, Vista, and XP
Windows 7, Vista, and XP also allow you to access the Task Manager through the taskbar context menu. Right-click on the taskbar and select «Start Task Manager».
Exploring Alternate Methods for Locating Windows Task Manager
In addition to the methods mentioned above, there are some other ways you can locate the Windows Task Manager by using the Search bar, the Control Panel, or even the File Explorer.
1. Using the Search Bar
If you prefer a more streamlined approach, you can use the Search bar in the Windows taskbar to locate and open the Task Manager.
To use the Search bar:
- Click on the Search bar located in the taskbar.
- Type in «Task Manager» and click on the result that appears.
This method works across various Windows versions and offers a convenient way to access the Task Manager without the need for additional menus or shortcuts.
2. Using the Control Panel
The Control Panel provides access to various system settings and utilities, including the Task Manager. This method is useful if you prefer navigating through a more traditional interface.
To access the Task Manager through the Control Panel:
- Click on the «Start» button in the bottom-left corner of the screen.
- Type in «Control Panel» and click on the result that appears.
- In the Control Panel window, select «System and Security».
- Under the «System» section, click on «Task Manager».
This method works consistently across different versions of Windows and provides an alternative way to access the Task Manager.
3. Using the File Explorer
The File Explorer, a file management tool in Windows, can also be used to locate the Task Manager executable file and open it.
To use the File Explorer:
- Open the File Explorer by clicking on the folder icon in the taskbar or pressing the Windows key + E simultaneously.
- Navigate to C:\Windows\System32 or C:\Windows\SysWOW64 (for 64-bit systems).
- Scroll through the list of files and locate «taskmgr.exe».
- Double-click on «taskmgr.exe» to open the Task Manager.
Using the File Explorer method, you can directly open the Task Manager by locating and launching its executable file.
In Conclusion
Location of the Windows Task Manager
The Windows Task Manager is an essential tool for monitoring and managing processes, performance, and applications on a Windows operating system. It provides valuable information about the processes running on your computer, CPU and memory usage, and allows you to close unresponsive programs or manage startup applications.
To access the Windows Task Manager, you can use the following methods:
- Press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys simultaneously.
- Right-click on the taskbar and select «Task Manager» from the context menu.
- Press Ctrl + Alt + Del, then select «Task Manager» from the options menu.
The Task Manager window will open, displaying several tabs that allow you to monitor different aspects of your system. These tabs include Processes, Performance, App History, Startup, and more. You can navigate between tabs to view detailed information and manage various tasks.
Key Takeaways: Where Is Windows Task Manager Located
- The Windows Task Manager is located in the Ctrl+Shift+Esc shortcut or by right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting «Task Manager.»
- You can also access the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete and selecting «Task Manager» from the list of options.
- The Task Manager window will open, displaying information about the processes, performance, and applications running on your computer.
- You can use the Task Manager to monitor and manage running processes, close unresponsive applications, and check system performance.
- If you can’t find the Task Manager, you can search for it in the Start menu or in the Windows system folder located in the C:\Windows\System32 folder.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we answer some commonly asked questions about the location of the Windows Task Manager.
1. How can I access the Windows Task Manager?
To access the Windows Task Manager, you can use one of the following methods:
— Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc simultaneously on your keyboard.
— Right-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager from the context menu.
Both methods will launch the Windows Task Manager.
2. What if I can’t access the Task Manager using the above methods?
If you are unable to access the Windows Task Manager using the keyboard shortcut or the context menu, try the following:
— Press Ctrl + Alt + Del on your keyboard and select Task Manager from the menu that appears.
This alternate method should open the Windows Task Manager even if the previous methods didn’t work.
3. Can I find the Task Manager in the Control Panel?
No, the Windows Task Manager is not located in the Control Panel. It is a separate utility that can be accessed directly using the methods mentioned above.
4. Is the Task Manager available in all versions of Windows?
Yes, the Windows Task Manager is available in all versions of the Windows operating system, including Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, and previous versions.
5. Can I use the Task Manager to end unresponsive programs?
Yes, the Task Manager allows you to end unresponsive programs or processes. Simply open the Task Manager, locate the program or process under the «Processes» or «Applications» tab, right-click on it, and select «End Task» or «End Process.» This can help resolve issues and free up system resources.
So, to recap, the Windows Task Manager is an important tool that allows users to monitor and manage processes, applications, and performance on their computer. It can be accessed in several ways, including using the Ctrl+Shift+Esc shortcut, right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting «Task Manager,» or pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete and choosing «Task Manager» from the options menu.
Once open, users can navigate through the different tabs to view and manage running processes, track system performance, manage startup programs, and resolve unresponsive applications. It is a powerful tool that can help diagnose and troubleshoot issues on Windows computers. Remember to use it wisely and only make changes if you are familiar with the potential consequences to your system.
Have you ever wondered where Windows Task Manager is located on your computer? It’s actually just a few clicks away, tucked neatly into the depths of your operating system. So, the next time you encounter a frozen program or curious about your computer’s performance, knowing where to find Task Manager is crucial.
Windows Task Manager has been a built-in tool in the Windows operating system since its introduction in Windows NT 4.0 in 1996. Over the years, it has become an indispensable utility for troubleshooting and managing system processes, monitoring performance, and terminating unresponsive applications. To access Task Manager, simply press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc key combination, right-click on the taskbar and select «Task Manager,» or use the «Ctrl + Alt + Delete» shortcut and choose «Task Manager» from the menu.
Windows Task Manager can be accessed by pressing the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys simultaneously. Alternatively, you can right-click the taskbar and select «Task Manager» from the menu that appears. Another way is by pressing Ctrl + Alt + Del and selecting «Task Manager» from the options listed. Whichever method you choose, Task Manager provides valuable information about system processes, performance, and applications running on your Windows computer.

Exploring the Location of Windows Task Manager
Windows Task Manager is a powerful tool that allows users to monitor and manage their computer’s performance, processes, and applications. However, for users who are new to Windows or unfamiliar with the operating system’s layout, finding the Task Manager can be a bit tricky. In this article, we will explore the various ways to locate the Windows Task Manager on different versions of the operating system, ensuring that users can access this essential tool with ease.
Locating Windows Task Manager on Windows 10
In Windows 10, the Task Manager can be accessed in several ways. The most common method is by right-clicking on the taskbar, the horizontal bar at the bottom of the screen, and selecting «Task Manager» from the contextual menu that appears. Alternatively, you can press the «Ctrl+Shift+Esc» keyboard shortcut to open the Task Manager directly.
Another method to access the Task Manager on Windows 10 is by using the «Start Menu.» Click on the «Start» button in the bottom-left corner of the screen and scroll through the list of installed applications to find the «Windows System» folder. Expand this folder and click on «Task Manager» to launch the tool.
For those who prefer using the keyboard, you can also press the «Ctrl+Alt+Delete» combination and select «Task Manager» from the options screen that appears. This method has been a staple of Windows for many years and can be used on previous versions as well.
Using a Quick Run Command
An additional way to open the Task Manager on Windows 10 is by using the «Run» command. Press the «Windows+R» keyboard shortcut to open the «Run» dialog box. Type in «taskmgr» and hit Enter or click «OK.» This will launch the Task Manager instantly.
Using the «Run» command is a handy method for advanced users who prefer using keyboard shortcuts or are familiar with command-based operations. It offers a quick and efficient way to access the Task Manager without navigating through menus or the taskbar.
Now that we have explored the various methods to locate the Task Manager in Windows 10 let’s move on to understanding how to find it on other versions of Windows.
Finding Task Manager on older versions of Windows
For users running Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, accessing the Task Manager is quite similar to Windows 10. You can right-click on the taskbar or use the «Ctrl+Shift+Esc» keyboard shortcut to open the taskbar. You can also press «Ctrl+Alt+Delete» and select «Task Manager» from the options screen. The «Run» command method is also applicable for these versions.
On Windows 7, right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting «Task Manager» from the context menu works exactly the same as in Windows 10 and 8.1. Additionally, pressing «Ctrl+Shift+Esc» or «Ctrl+Alt+Delete» and choosing «Task Manager» will also open the tool. The «Run» command can be used here as well.
For Windows XP and Vista users, the default method to launch the Task Manager is by pressing «Ctrl+Shift+Esc» or «Ctrl+Alt+Delete» and selecting «Task Manager.» These older versions of Windows do not have the option to right-click on the taskbar to access the Task Manager directly. The «Run» command remains a quick alternative.
Alternate Methods and Tips
Aside from the conventional methods mentioned above, there are a few additional ways to access the Task Manager in Windows. One method is by using the search bar. In Windows 10, click on the search bar or press the «Windows+S» keyboard shortcut to open the search function. Type in «Task Manager» and click on the search result to open the tool.
Another useful way to open the Task Manager is through the «Ctrl+Alt+Del» screen. Press «Ctrl+Alt+Delete» and select «Task Manager» from the options screen. This screen provides quick access to various system functions, including the Task Manager.
It’s important to note that the specific location and accessibility of the Task Manager may vary slightly between different versions of Windows, but the core functionality remains the same. Whether you’re running Windows 10 or using an older version, these methods should help you locate and open the Task Manager without any hassle.
In conclusion, finding the Windows Task Manager is essential for monitoring and managing your computer’s performance. The location of the Task Manager may vary depending on the version of Windows you are using, but there are several methods available to access it. Whether it’s through the taskbar, keyboard shortcuts, the Start menu, the Run command, or other alternative methods, you can easily locate and open the Task Manager in Windows. Regularly utilizing this powerful tool will help you optimize your system’s performance and troubleshoot any issues efficiently.

Locating the Windows Task Manager
As a professional, it is important to know where to find the Windows Task Manager to effectively manage system performance and troubleshoot issues. The Windows Task Manager is a powerful tool that allows users to monitor and control various aspects of the operating system.
To locate the Windows Task Manager, follow these steps:
- Press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys simultaneously on your keyboard. This keyboard shortcut will directly open the Task Manager.
- Alternatively, right-click on the taskbar (the bar at the bottom of your screen) and select «Task Manager» from the context menu.
- You can also press Ctrl + Alt + Delete, and then select «Task Manager» from the options that appear.
Once you have opened the Task Manager, you will find various tabs such as «Processes,» «Performance,» «App history,» and more. These tabs provide detailed information about running processes, system performance metrics, and the impact of apps on your system’s resources.
By accessing the Windows Task Manager, professionals can effectively manage their system’s performance, identify resource-hungry processes, and take necessary actions to optimize their computer’s functionality.
Key Takeaways — Where Is Windows Task Manager Located:
- Windows Task Manager is located in different places depending on the Windows version.
- In Windows 10 and 8, you can open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc or by right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting Task Manager.
- In Windows 7, you can open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Alt + Delete or by right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting Task Manager.
- You can also access Task Manager by searching for it in the Start menu or by using the Run dialog box (press Win + R) and typing «taskmgr».
- Task Manager provides information about running processes, CPU usage, memory usage, and allows you to end unresponsive tasks or processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Windows Task Manager is a powerful tool that allows users to monitor and manage their system’s performance. Whether you need to end a process, check resource usage, or troubleshoot performance issues, the Task Manager provides valuable insights. If you’re wondering where you can find the Task Manager on your Windows computer, we’ve got you covered with the following frequently asked questions.
1. How do I access the Windows Task Manager?
To access the Task Manager in Windows, you can use one of the following methods:
— Press the «Ctrl + Shift + Esc» keys simultaneously on your keyboard.
— Right-click on the taskbar and select «Task Manager» from the context menu.
Both methods will launch the Task Manager and give you access to its various features and tabs.
2. Can I open the Task Manager using the Start menu?
Yes, you can also open the Task Manager using the Start menu. Here’s how:
— Click on the «Start» button in the bottom-left corner of your screen.
— Type «Task Manager» in the search bar.
— Click on the «Task Manager» app that appears in the search results.
3. Is the Task Manager available in all versions of Windows?
Yes, the Task Manager is a built-in tool that is available in all versions of Windows, including Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, and older versions. The interface and features may vary slightly depending on the version, but the basic functionality remains the same.
4. Can I customize the Task Manager?
Yes, you can customize the Task Manager according to your preferences. Here are some ways you can do it:
— Click on the «Options» menu in the Task Manager and select «Always on Top» to keep the Task Manager window visible at all times.
— Click on the «View» menu and choose the columns you want to display in the Processes, Performance, or Details tabs.
— Right-click on any column header and select «Select Columns» to customize the columns further.
5. Is there an alternative to the Task Manager?
Yes, there are alternative task management tools available for Windows. Some popular alternatives include Process Explorer, System Explorer, and Wise System Monitor. These tools offer additional features and more in-depth system monitoring capabilities.
In summary, the Windows Task Manager is a vital tool that helps users monitor and manage processes on their computer. It is located within the Windows operating system and can be accessed in multiple ways.
Users can access the Task Manager by right-clicking on the taskbar and selecting «Task Manager» or by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc on the keyboard. Once open, they can view a wealth of information about running processes, CPU and memory usage, and make adjustments to improve performance.
The Windows Task Manager is an essential tool for any user of the Windows operating system, whether they are casual users, IT professionals, or advanced developers. Task Manager provides an array of features that allow users to monitor and manage the performance of their system, keep an eye on running processes, end problematic applications, and even view network usage. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the various ways to access the Windows Task Manager, the functionality it offers, and how it can be effectively used to ensure your system is running smoothly.
What Is Windows Task Manager?
Before diving into the specifics of how to locate and access the Windows Task Manager, it’s crucial to understand what it is and what it does. Task Manager is a built-in utility in Microsoft Windows that provides information about the computer’s performance, running applications, processes, and services. It also allows users to-ending unresponsive programs, monitor system resource usage, and manage startup processes.
The Task Manager has evolved over the years, improving its interface and functionality with each Windows release. While its core functions remain unchanged, Windows 10 and Windows 11 include several enhancements that make it a more robust tool for diagnostics and system monitoring.
Accessing Windows Task Manager
Now that we understand what Task Manager is, let’s explore where it is located and how to access it. There are multiple methods to open Task Manager, each of which is suited to different types of users and scenarios. Here are some of the most common ways to access Task Manager in Windows 10 and Windows 11:
1. Using Keyboard Shortcuts
One of the fastest ways to open Task Manager is by using keyboard shortcuts. Here are a few key combinations you can use:
- Ctrl + Shift + Esc: This shortcut opens Task Manager directly. It’s the quickest way to launch the application without any additional steps.
- Ctrl + Alt + Delete: This combination takes you to a screen where you can choose from multiple options, including opening Task Manager. Simply select «Task Manager» from the list.
2. Via the Windows Search Bar
Another simple method to locate Task Manager is through the Windows Search functionality:
- Click on the search bar or the Start menu icon located in the taskbar.
- Type «Task Manager» in the search box.
- Click on the Task Manager app from the search results.
This method is particularly useful for users who may not remember specific key combinations.
3. Using the Run Dialog
Advanced users may prefer to access Task Manager via the Run dialog:
- Press Windows key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog.
- Type in
taskmgrand hit Enter or click OK.
This method provides a direct way to launch Task Manager without having to navigate through menus or the Start screen.
4. Through the Start Menu
You can also access Task Manager through the Start menu:
- Right-click on the Start button (or press Windows key + X).
- From the menu that opens, select «Task Manager.»
This is a straightforward method that can be performed using a mouse.
5. From the Command Prompt or PowerShell
For those who are comfortable with the command line, Task Manager can be launched from either Command Prompt or PowerShell:
- Open Command Prompt or PowerShell.
- Type
taskmgrand press Enter.
This method is beneficial for users who are already working in the command-line environment or scripts.
6. Using the Windows Settings
Lastly, Task Manager can also be accessed from the Windows Settings:
- Go to the Start menu and click on «Settings» (gear icon).
- Click on «Privacy & Security» (in Windows 11) or «Privacy» (in Windows 10).
- Scroll down and you’ll find «Task Manager» listed under «Related Settings.»
This is not the most common method, but it’s useful for those exploring system settings.
Exploring Task Manager Interface
Once you have launched Task Manager, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the interface. The layout of Task Manager has evolved over the years to become more user-friendly while still packing in a myriad of features. Here is a breakdown of the components you will encounter upon opening Task Manager:
1. Overview Tab
When you first open Task Manager, you might see the «Processes» tab, which gives you a live view of all currently running applications and background processes. This section provides detailed information, including CPU, Memory, Disk, and Network usage for each process.
2. Performance Tab
The Performance tab displays real-time graphs and statistics about CPU usage, memory, disk activity, and network utilization. This graphical representation is user-friendly and helps users quickly assess system performance, identify bottlenecks, and monitor resource consumption over time.
3. App History Tab
The App History tab records resource usage for Windows Store apps. It shows data for CPU time and network usage, allowing users to determine which applications are hogging resources. This tab is especially useful for users who rely heavily on UWP (Universal Windows Platform) apps.
4. Startup Tab
The Startup tab enables users to manage which applications launch at startup. You can disable or enable applications from this tab, which can help improve boot times and system performance. Managing startup applications is a critical part of system optimization.
5. Users Tab
In a multi-user environment, the Users tab displays all active users and their processes. Here, you can see how much resource each user is consuming. This is useful for administrators managing multiple accounts on a single machine.
6. Details Tab
Under the Details tab, you can get a more granular view of each running process. This tab provides the ability to adjust process priority and access additional options for each running application, allowing for advanced systems management.
7. Services Tab
The Services tab lists all Windows services currently running on your machine, including their status (running, stopped, etc.). Users can start, stop, or restart services directly from this tab, which can be crucial for troubleshooting issues related to system services.
Using Task Manager Effectively
With a comprehensive understanding of how to access and navigate Task Manager, let’s explore some practical applications of this powerful tool that can enhance your productivity and help maintain system stability.
1. Troubleshooting Application Issues
One of the most common uses of Task Manager is troubleshooting unresponsive or slow applications. If an application becomes unresponsive, users can navigate to the Processes tab, right-click on the application, and choose «End Task.» This action forces the application to close, thereby freeing up system resources.
Additionally, the Performance tab can be used to monitor resource usage and identify which applications may be consuming excessive CPU or memory. This is particularly useful for understanding whether a simple restart or software patch may resolve ongoing issues.
2. Monitoring Resource Utilization
For those requiring more in-depth monitoring, the Performance tab is invaluable. Users can keep an eye on CPU and memory usage over time, identifying patterns and potential performance issues before they become severe. If the system is consistently running low on memory, it may indicate the need for a hardware upgrade or the optimization of currently running applications.
3. Managing Startup Applications
Startup applications can slow down the boot process significantly. By navigating to the Startup tab, users can identify applications that are set to launch at startup but are not necessary. Disabling these applications can lead to a more efficient boot time, allowing for faster overall system responsiveness.
4. Understanding Services
The Services tab is particularly useful for system administrators. Understanding which services are running and their impacts on system performance can aid in troubleshooting slowdowns or issues within an application. For example, if a particular service is consistently causing problems, it may be necessary to disable it or find an alternative solution.
5. Performance Improvement
Using the information provided in Task Manager, you can make informed decisions about performance improvements. If multiple applications are consuming high amounts of CPU or memory, consider whether they are all necessary for your tasks. Closing or uninstalling non-essential applications can significantly enhance overall system performance.
Advanced Features of Task Manager
While the core functionalities of Task Manager are incredibly useful, there are also advanced features that users may find beneficial. Delving into these features enhances your ability to manage system resources effectively.
1. Managing Process Priority
In the Details tab, you have the option to set the priority level of running processes. This capability allows you to allocate more or fewer resources to specific applications based on your current needs. For example, if you’re rendering a video or performing heavy calculations, you might want to set those applications to «High» priority. Be cautious, however; setting too many processes to high priority can lead to system instability.
2. Creating a Dump File
If you encounter a process that is not responding or appears to be malfunctioning, you can create a dump file for further analysis. This feature is particularly useful for developers and IT professionals who wish to debug the application later. Right-click the problematic process in the Details tab and select «Create dump file.» The generated file can then be analyzed with debugging tools.
3. Networking Information
The Performance tab includes a network graph that provides detailed information about how much network bandwidth each process is consuming. This is helpful for identifying applications that may be eating up bandwidth, impacting other tasks like video streaming or online gaming.
4. Resource Monitor
Task Manager integrates with Resource Monitor, a more advanced utility that provides deeper insights into system usage. You can access Resource Monitor from the Performance tab by clicking on the “Open Resource Monitor” link. Resource Monitor reveals detailed graphs and information about CPU, memory, disk, and network usage, helping users further diagnose performance issues.
Using Task Manager for System Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity of your computer and optimal performance. Incorporating Task Manager into your routine can streamline this process.
1. Regular Process Review
Make it a habit to check Task Manager regularly for any unfamiliar processes. Research any unknown applications to determine whether they are necessary and understand their impact on system performance. If you find unnecessary processes, consider removing them.
2. Task Scheduling
If you frequently use specific applications that have a high startup impact, consider using Task Scheduler, which works in tandem with Task Manager. Setting up scheduled tasks can help manage background processes that you want to run during off-peak hours rather than at startup.
3. Resource Optimization
If your computer often runs out of memory, consider using Task Manager to identify and disable resource-heavy applications that are running unnecessarily. This small action can significantly enhance performance during critical tasks, especially for gamers, video editors, or software developers.
Conclusion
In sum, the Windows Task Manager is an indispensable tool that serves multiple purposes for users at all levels. Whether you are troubleshooting a problematic application, monitoring your system’s performance, managing startup items, or performing regular maintenance, Task Manager is your go-to resource. With the various methods of access, advanced features, and integration with other utilities, Task Manager offers users comprehensive functionalities to maintain a healthy computing environment.
By regularly utilizing Task Manager, users can ensure their systems run efficiently, respond quickly to user inputs, and handle demanding tasks without unnecessary strain. Understanding where Task Manager is located and how to leverage its full potential can dramatically enhance your computing experience and contribute to a more productive digital workflow.
Рассказываем, как открыть диспетчер задач в Windows и что делать, если привычные методы не работают.
Функции
Как открыть
Альтернативные методы
Не открывается
Доступ запрещен
Функции
Как открыть
Альтернативные методы
Не открывается
Доступ запрещен

Если компьютер начал тормозить, первое, что стоит сделать — запустить менеджер процессов. Он помогает увидеть, какие приложения запущены сейчас, сколько они потребляют ресурсов и что нагружает программное обеспечение. Это ключ к управлению системой.
Инструмент часто нужен в тот момент, когда система зависает и перестает реагировать на команды. Поэтому полезно знать разные способы открыть диспетчер задач в Windows. Делимся подборкой методов и разбираемся, почему средство мониторинга может не открываться. Выясняем, как вернуть к нему доступ.
Функции диспетчера задач
Если утилита перестает открываться, это не просто неудобство, а серьезное ограничение в управлении Windows. Пользователь теряет инструмент контроля, поскольку диспетчер задач — это не только список процессов.
Вот что позволяет делать менеджер.
-
Следить за тем, какие процессы перегружают систему и могут снижать производительность.
-
Завершать работу зависших или конфликтующих между собой приложений.
-
Принудительно завершать зависшие процессы программ, которые не закрылись корректно.
-
Просматривать активные приложения и фоновые процессы.
-
Отслеживать нагрузку на процессор, оперативную память, диск, сеть и видеокарту.
-
Управлять автозагрузкой программ при старте системы.
-
Просматривать список активных пользователей и уровень их нагрузки на систему.
-
Вручную запускать новые задачи.
-
Получать подробную информацию о каждом процессе — от пути к файлу до цифровой подписи.
-
Принудительно закрывать вредоносные программы или нестабильные процессы.
Как быстро открыть диспетчер задач на компьютере
Самые простые и надежные способы, которых в большинстве случаев вполне достаточно.
1. Горячие клавиши
Нажмите одновременно горячие клавиши Ctrl + Shift + Esc. Пока клавиатура работает без сбоев и система хоть немного откликается, этот метод станет вашим главным способом.

2. Экран безопасности
Нажмите комбинацию Ctrl + Alt + Del. В появившемся служебном меню выберите пункт диспетчер задач. Эта легендарная комбинация, вошедшая в поп-культуру, выручает, например, во время игр, которые не дают использовать стандартное Ctrl + Shift + Esc. Комбинация будет работать, поскольку имеет приоритет над большинством процессов. После ее ввода можно заблокировать компьютер, сменить пользователя, выйти из системы, перезагрузить или перевести компьютер в режим ожидания.

3. Меню «Пуск»
Кликните по кнопке «Пуск» и начните вводить в поисковом окне диспетчер задач или Task Manager.

4. Панель задач
Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по пустому месту на панели задач и выберите пункт диспетчер задач в открывшемся меню.

5. Панели управления
Нажмите [Windows] + S и введите диспетчер задач или Task Manager.

6. Win + X меню
Щелкните правой кнопкой по иконке «Пуск» или нажмите [Windows] + X. Удобный вариант, особенно если клавиатура не работает и приходится пользоваться мышью. Меню опытного пользователя содержит множество полезных инструментов — в том числе и диспетчер задач.
Альтернативные методы открытия диспетчера задач
В некоторых ситуациях стандартные варианты бывают недоступны. Например, если приложение блокирует работу горячих клавиш. Тогда на помощь приходят альтернативные методы.
1. Диалоговое окно Win + R
Нажмите [Windows] + R, в диалоговом окне введите taskmgr и нажмите OK.

2. Проводник
Откройте любой каталог в Проводнике, впишите taskmgr в адресную строку и подтвердите.

3. Командная строка
Нажмите [Windows] + R, введите cmd и нажмите Enter. В открывшейся командной строке наберите taskmgr и снова подтвердите ввод кнопкой Enter. Это не самый быстрый путь, но он выручит, если, например, не работает Проводник или вы уже находитесь в терминале.

4. Запуск исполняемого файла вручную
У диспетчера задач есть свой .exe-файл, как у любого другого приложения.
-
Откройте Проводник.
-
Перейдите в папку C:\Windows\System32.
-
Найдите файл с именем Taskmgr и запустите его двойным щелчком.
Если файлов в папке много, проще вбить имя в строку поиска. А если Windows установлена не на диске C, просто замените букву на ту, где находится система.

Другой вариант: введите адрес C:\Windows\System32\ в строке поиска Проводника, чтобы напрямую получить доступ к местоположению утилиты.

Что делать, если диспетчер задач не открывается
Если утилита в Windows не открывается вообще — ни с клавиатуры, ни через поиск, ни каким-либо другим способом — скорее всего, система столкнулась со сбоем. Он может быть вызван поврежденными файлами, действиями вредоносного программного обеспечения или некорректной работой интерфейса.
Первое, что стоит сделать — проверить систему на вирусы. Некоторые вредоносные программы намеренно деактивируют диспетчер задач, чтобы скрыть свою активность.
Если с безопасностью все в порядке, проверьте целостность системных файлов. Прежде чем перейти к следующим шагам и вносить серьезные изменения в систему, создайте точку восстановления системы и сделайте резервную копию важных данных.
Для этого потребуется запустить командную строку от имени администратора и ввести команду sfc /scannow. Система начнет сканирование и автоматически исправит найденные ошибки. Иногда программа не запускается из-за неправильных записей в реестре. Если вы уверены, что причина в этом, отредактируйте соответствующие ключи самостоятельно.
Иногда проблема связана не с системой в целом, а с конкретной учетной записью. В таком случае стоит попробовать создать нового пользователя и проверить, откроется ли интерфейс мониторинга там. Если все работает, значит, дело в настройках или повреждениях профиля, и возможно, имеет смысл перенести данные на созданный аккаунт.
Если ни один из этих способов не помогает, возможно, повреждения системы слишком серьезные. Тогда потребуется восстановление Windows — через встроенные средства или с установочного носителя.
Как восстановить диспетчер задач после отключения администратором
Если утилита отключена администратором, при попытке ее открыть появляется сообщение, что доступ запрещен. Это бывает сделано намеренно — например, в организациях, где пользователям ограничивают возможности управления системой. Но если вы уверены, что блокировка неуместна или появилась после сбоя, ее возможно снять.
Один из способов — через изменение системного реестра.
-
Откройте окно «Выполнить» комбинацией [Windows] + R и введите команду regedit.
-
В редакторе перейдите в HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System.
-
Если в правой части окна есть параметр DisableTaskMgr, его значение, скорее всего, установлено в 1 — это и блокирует программу.
-
Поменяйте значение на 0 или удалите параметр совсем, после чего перезагрузите систему. Если параметра нет — можно ничего не трогать. Просто проверьте, не задан ли он.
Будьте осторожны с корректировками в реестре — лучше не менять ничего лишнего.
Иногда блокировка задается через групповую политику. Если у вас есть права администратора, откройте редактор локальной групповой политики.
-
Нажмите [Windows] + R и напишите gpedit.msc.
-
В открывшемся окне перейдите в «Конфигурация пользователя», затем — «Административные шаблоны», «Система».

-
Выберите раздел «Параметры Ctrl + Alt + Del». Там есть настройка «Удалить диспетчер задач».

-
Убедитесь, что она отключена или не задана — тогда система больше не будет мешать запуску инструмента.

После внесения этих изменений менеджер процессов должен снова открываться без ограничений. Если этого не происходит, стоит перезагрузить компьютер и проверить еще раз.
В этой инструкции для начинающих 8 способов открыть диспетчер задач Windows 10. Сделать это не сложнее, чем в предыдущих версиях системы, более того, появились и новые методы для открытия диспетчера задач.
Базовая функция диспетчера задач — отображение информации о запущенных программах и процессах и используемых ими ресурсах. Однако, в Windows 10 диспетчер задач все время совершенствуется: теперь там можно отслеживать данные по загрузке видеокарты (раньше только процессора и оперативной памяти), управлять программами в автозагрузке и не только это. Подробнее о возможностях в статье Диспетчер задач Windows 10, 8 и Windows 7 для начинающих.
8 способов запустить диспетчер задач Windows 10
Теперь подробно обо всех удобных способах открыть диспетчер задач в Windows 10, выбирайте любой:
- Нажмите Ctrl + Shift + Esc на клавиатуре компьютера — сразу запустится диспетчер задач.
- Нажмите Ctrl + Alt + Delete (Del) на клавиатуре, а в открывшемся меню выберите пункт «Диспетчер задач».
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск» или клавиши Win+X и в открывшемся меню выберите пункт «Диспетчер задач».
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши в любом пустом месте панели задач и выберите «Диспетчер задач» в контекстном меню.
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре, введите taskmgr в окно «Выполнить» и нажмите Enter.
- Начните вводить «Диспетчер задач» в поиск на панели задач и запустите его оттуда, когда он будет найден. Также можно использовать поле поиска в «Параметры».
- Зайдите в папку C:\Windows\System32\ и запустите файл taskmgr.exe из этой папки.
- Создайте ярлык для запуска диспетчера задач на рабочем столе или где-то ещё, в качестве объекта указав файл из 7-го способа запуска диспетчера задач.
Думаю, этих способов будет более чем достаточно, если только вы не столкнетесь с ошибкой «Диспетчер задач отключен администратором».
Как открыть диспетчер задач — видео инструкция
Ниже — видео с описанными способами (разве что 5-й почему-то забыл, а потому получилось 7 способов запуска диспетчера задач).
Думаю, продемонстрированных вариантов будет достаточно для решения задачи.