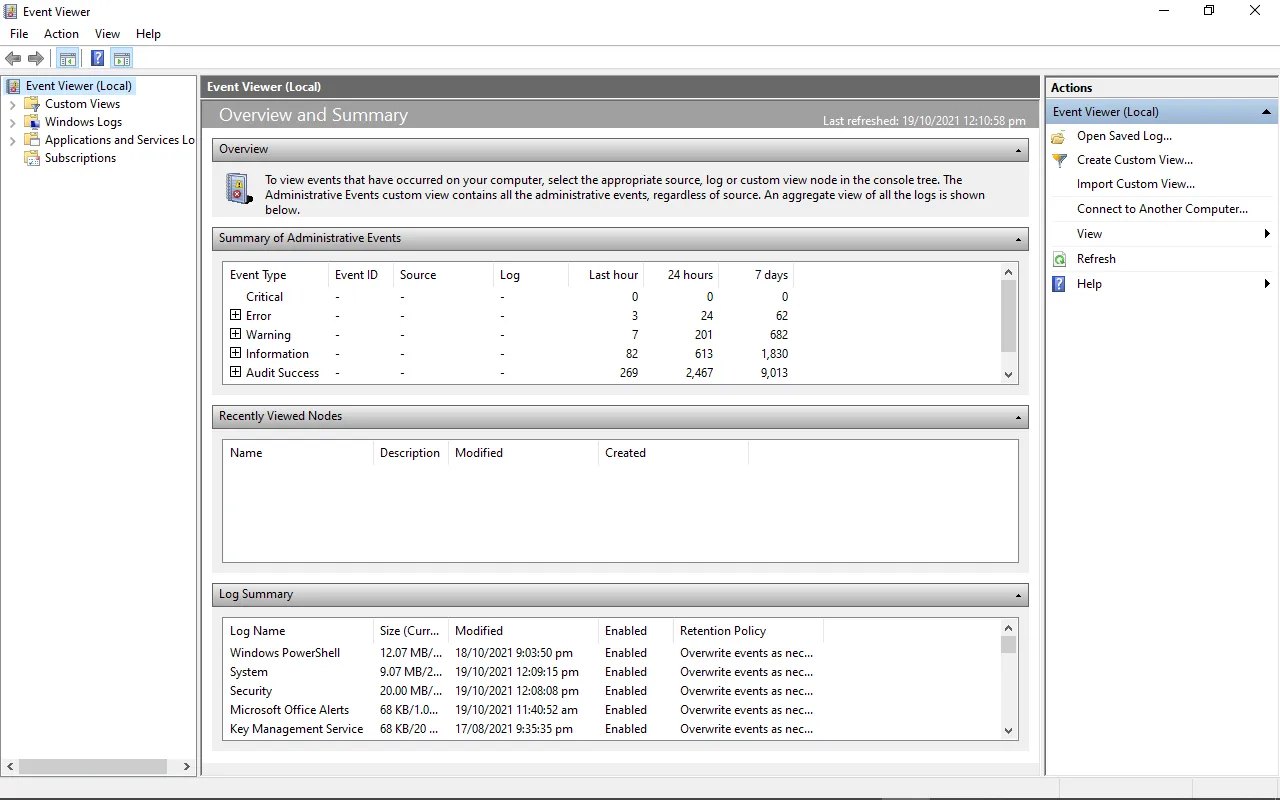
В журналах событий Windows хранится полезная информация, которая нужна при анализе состояния служб и приложений в Windows, отладки ошибок и аварийный ситуаций, аудите различных событий безопасности. По умолчанию для журналов Event Viewer в Windows заданы максимальные размеры, при достижении которых новые события начинают перезаписывать более старые. Если на вход Event Viewer попадает слишком большое количество событий, может случится, что в журнал помещаются события лишь за последние несколько часов, что может быть не достаточно.
Чтобы предотвратить перезапись старых событий и всегда иметь под рукой события за достаточно большой промежуток времени, вы можете увеличить максимальный размер журналов Event Viewer.
Содержание:
- Получить информацию о журналах событий Windows с помощью PowerShell
- Изменить размер журнала событий из консоли Event Viewer
- Увеличить размер журнала событий Windows через GPO
Получить информацию о журналах событий Windows с помощью PowerShell
Файлы журналы событий Windows хранятся в каталог
%SystemRoot%\System32\Winevt\Logs\
в виде файлов с расширением .EVTX. Обратите внимание, что для каждого журнала используется собственный файл. Соответственно, вы можете управлять размерами только того лога Windows, который вам нужен и оставить остальные значения по-умолчанию.
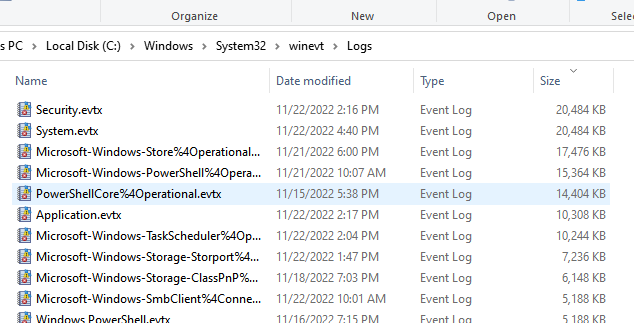
Текущие лимиты на все включенные журналы событий в Windows можно вывести с помощью PowerShell:
Get-Eventlog -List
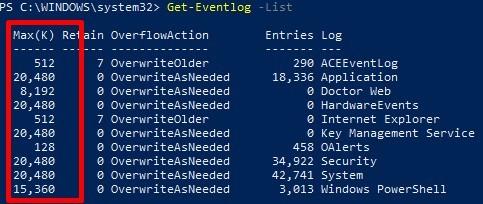
Вы можно вывести размер определенного лога с помощью командлета Get-WinEvent. Например, получим текущий и максимальный размер журнала Security:
Get-WinEvent -ListLog Security| Select MaximumSizeInBytes, FileSize, IsLogFull, OldestRecordNumber, IsEnabled, LogMode
Суммарный размер паки с файлами журналов событий можно получить с помощью PowerShell:
«{0:N2} MB» -f ((gci c:\windows\System32\Winevt\Logs\| measure Length -s).sum / 1Mb)
Чтобы увеличить максимальный размер лога, можно использовать утилиту wevtutul (новый размер задается в Кб):
wevtutil sl "Application" /ms:200000
Или с помощью PowerShell:
Limit-Eventlog -Logname Application -MaximumSize 200MB -OverflowAction OverwriteOlder
Изменить размер журнала событий из консоли Event Viewer
Проще всего увеличить максимальный размер журнала прямо из консоли Event Viewer.
- Откройте
eventvwr.msc
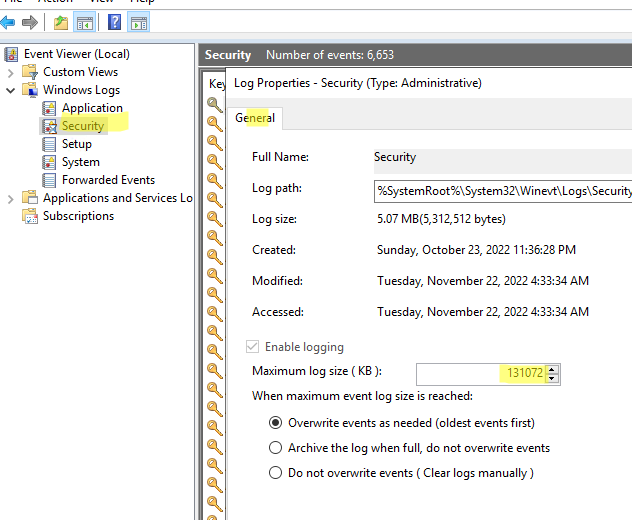
; - Найдите в консоли свойства нужного журнала и откройте его свойства (например, Security);
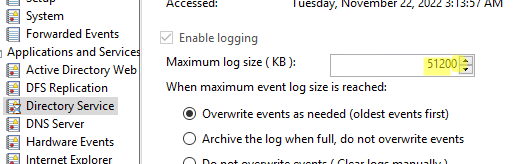
- Задайте ограничение в разделе Maximum log size (KB) и сохраните изменения;
- Здесь же можно изменить поведение при достижение максимального размера:
Owerwrite events as needed (oldest events first) – этот режим исопльзуется по умолчанию. Новые события просто перезаписывают более старые.
Archive the log when full, do not owerwrite events – текущий журнал событий при заполнении архивируется в папке \System32\Winevt\Logs\ и новые события записываются в новый evtx файл. Архивные файлы событий можно открыть через меню Open Saved Log в Event Viewer.
Do not owerwrite events (Clear log manually) – события никогда не перезатираются. Для записи новых событий нужно очистить журнал.
Увеличить размер журнала событий Windows через GPO
Чтобы централизованно управлять размерами журналов событий на компьютерах или серверах в домене Active Directory, можно использовать групповые политики.
- Запустите консоль Group Policy Management (
gpmc.msc
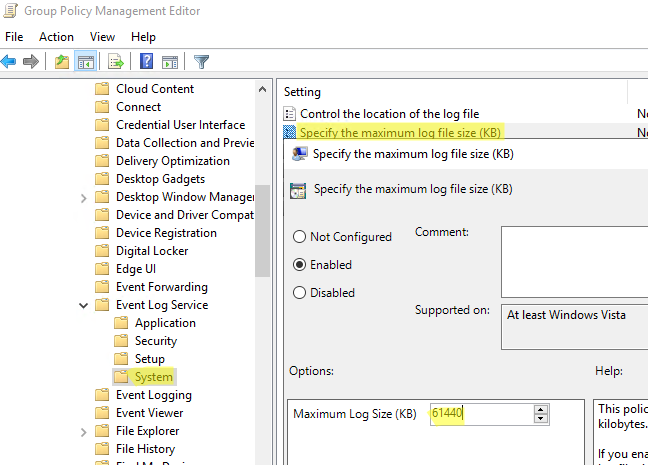
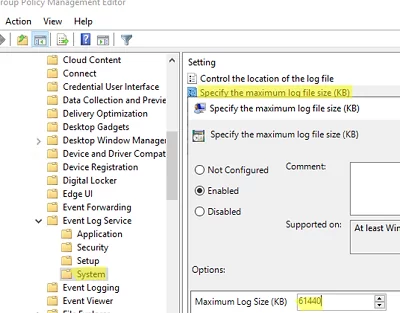
), создайте новую GPO и назначьте на OU с компьютерами или серверами, для которых вы хотите изменить настройки Event Viewer (или назначьте GPO на корень домена); - Перейдите в раздел GPO Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Event Log Service. Как вы видите, в этом ветке есть подразделы для управления базовыми журналами Windows:
Application Security Setup System
- Чтобы увеличить максимальный размер любого из журналов, откройте параметр Specify the maximum log file size (KB), включите его и задайте нужный вам размер;
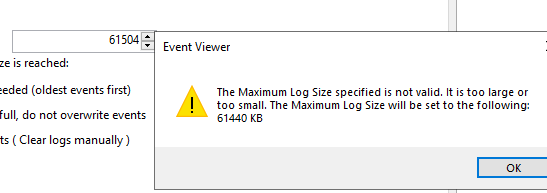
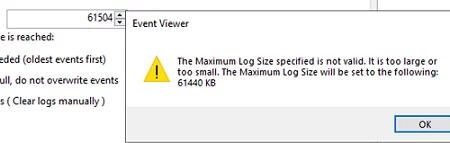
- Обновите настройки политики на клиентах и проверьте, что в свойствах журнала теперь указан новый размер, который вы не можете изменить. При попытке задать другой размер появится ошибка:
Event Viewer
The Maximum Log Size specified is not valid. It is too large or too small. The Maximum Log Size will be set to the following: 61440 KB
Обратите внимание, что в описанном выше разделе GPO отсутствуют настройки для других журналов из раздела Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft.Если вам нужно увеличить размер любого другого журнала событий (кроме стандартного), это можно сделать через реестр. Настройки журналов событий Windows хранятся в разделе реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\EventLog\<log_name>. Размер журнала задается с помощью параметра MaxSize (тип REG_DWORD). Вы можете распространить нужное вам значение параметра реестра MaxSize на компьютеры домена с помощью Group Policy Preferences.
Подробнее о настройке ключей и параметров реестра через GPO здесь.
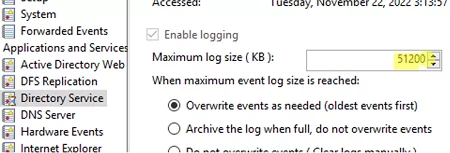
В этом примере мы увеличим размер журнала Directory Service на контроллерах домена. Настройки этого лога хранятся в ветке HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\EventLog\Directory Service.
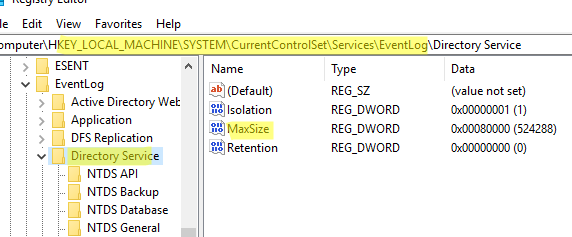
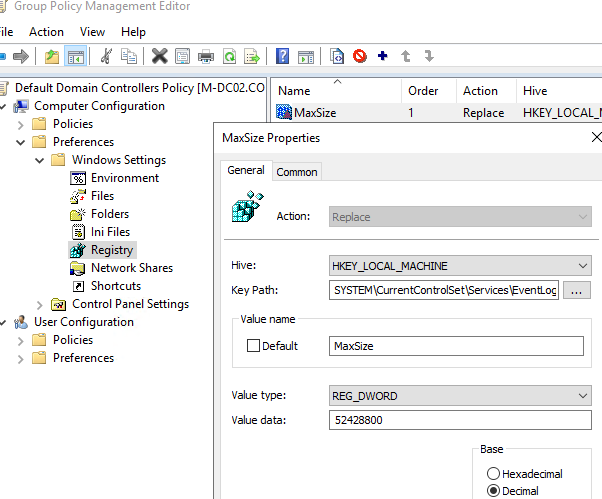
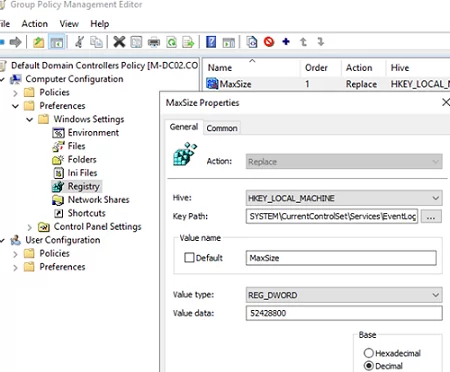
- Откройте GPO и перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Registry;
- Выберите New -> Registry Item;
- Создайте новый параметр со следующими настройками:
Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE Key path: SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\EventLog\Directory Service Value name: MaxSize Value type: REG_DWORD Value data: 52428800 (значение задается в байтах. В нашем примере это 50 Мб)
- Проверьте, что после обновления GPO на DC увеличится максимальный размер журнала.
Например, если вам нужно хранить историю RDP подключений к RDS хосту за продолжительное время, нужно увеличить размер лога Terminal-Services-RemoteConnectionManager.
За счет увеличения размеров журналов событий Windows вы можете получить различную информацию за более длительный промежуток времени. Например, из журналов событий можно получить историю перезагрузок Windows, понять кто удалил файл в сетевой папке или кто изменил NTFS права доступа.
Всем привет!
Очистка следов работы в операционной системе — один из важнейших этапов для скрытия каких либо действий.
Во время расследования криминалисты проверяют следы активности на компьютерах для выявления каких либо действий. Это один из примеров, почему вам стоит научиться работать с логами и понять как это работает.
ВНИМАНИЕ!
Автор статьи никого не призывает к правонарушениям и отказывается нести ответственность за ваши действия. Вся информация предоставлена исключительно в ознакомительных целях. Спасибо!
Для начала разберёмся с некоторыми типами журналов и их расположением для примера.
Журналы DHCP-сервера — это журналы, в которых ведется учет присвоения IP-адресов в сети. В этом журнале хранятся все события при взаимодействии между потенциальным DHCP-клиентом и DHCP-сервером. Наибольший интерес здесь представляют MAC-адреса клиентов, которые будут занесены в соответствующий журнал событий.
Журналы DHCP хранятся в каталоге % SystemRoot% \ System32 \ dhcp
Журналы веб-сервера хранят сообщения обо всех действиях при взаимодействии между веб-сервером и клиентским веб-браузером.
Файлы журнала Internet Information Server (IIS) находятся в
% SystemDrive% \ inetpub \ logs \ LogFiles
Event logs фиксируют все, что происходит в системе, с момента ее включения и до выключения. В Windows 10 конфигурация журналов событий хранится в следующем разделе реестра:
HKLM \ System \ ControlSet00x \ Services \ EventLog
Чтобы просмотреть список имён доступных журналов событий в Windows 10, используйте команду
wevtutil el
Использование команды wevtutil gl <имя журнала> представит информацию о конфигурации для выбранного журнала:
Стоит отметить, что сами системные журналы Windows хранятся по пути C:\Windows\System32\winevt \Logs в локальной системе:
В Windows средство просмотра событий является приложением, которое объединяет журналы приложений, безопасности, установки и системы на единой информационной панели. Это приложение располагается в следующем каталоге:
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools\Просмотрщик событий
Также для открытия средства просмотра событий в Windows достаточно ввести сочетание клавиш Win + R , и в окне «Выполнить» ввести eventvwr.msc и нажать OK:
В окне «Просмотр событий» журналы можно очистить, просто выбрав функцию «Очистить журнал» кнопкой на панели «Действия». Чтобы очистить журналы для определенной категории, например всех журналов, которые находятся в группе «Приложение», просто щелкните правой кнопкой мыши имя группы и выберите «Очистить журнал»:
Также можно очистить журналы с помощью консоли:
for / F «tokens = *»% 1 в (‘wevtutil.exe el’) DO wevtutil.exe cl «% 1»
Либо мы можем воспользоваться Powershell.
Для этого вводим следующую команду:
wevtutil el | Foreach-Object {wevtutil cl “$_”}
После выполнения команды журналы стираются, как показано в средстве просмотра событий:
Meterpreter разработан, чтобы быть скрытым, мощным и динамически расширяемым. После успешного закрепления в системы вы можете использовать команду clearev для очистки журналов приложений, системы и безопасности:
clearev
Meterpreter очищает журналы каждой категории в целевой системе. Также указано количество очищенных записей.
В этой статье мы рассмотрели способы скрытия активности во время тестирования на проникновение, а также обычного использования системы.
На этом мы заканчиваем. Спасибо за внимание.
Следите за мной в соц-сетях:
• Tik-Tok: aferium
• Группа ВК: aferium_vk
• Телеграм: aferium
• Яндекс Дзен: aferium
• VC.RU: aferium
• Teletype: aferium
If you’re using a Windows server and want to know what happened to your machine, Windows logs are an essential resource. Windows logs record various system activities, errors, and other significant events, providing valuable information for troubleshooting, auditing, and ensuring system integrity. Understanding how to access, interpret, and utilise these logs enables efficient, problem solving, enables security measures and ensures the smooth operation of your system.
In this guide, you will learn about Windows event logs, its different categories, how to filter and create Custom Views.
What is a Windows Event Log?
A Windows event log is a file that keeps track of system events and errors, application issues, and security events. Windows Event log can also provide insights into an application’s behavior by tracking its interactions with other processes and services. With the right knowledge of the information stored in these logs, you can easily diagnose and easily resolve issues within your system and applications.
You can access the windows events logs as follows:
Using the Start Menu:
- Click on the Start button or press the Windows key.
- Type
Event Viewerin the search box and select it from the search results.
Using the Run Dialog:
- Press
Windows + Rto open the Run dialog. - Type
eventvwrand press Enter.
Using the Control Panel:
- Open the Command Prompt and run as administrator.
- Type
eventvwrand press Enter.
You can see the detailed steps below. Now let’s discuss and understand windows events logs in detail.
Understanding Windows Event Logs categories & Types
There are different Windows logs, each serving a specific purpose in tracking and recording events related to your system, applications, and security. They include:
- System Events: System events log information is about the core operations of your Windows operating system. System events are essential for maintaining your system’s health and functionality because it records events related to the system’s hardware and software components. Some system events are as follows:
- Hardware Failures: Logs any issues related to hardware components, such as disc failures or memory errors.
- Driver Issues: Records events related to the loading, unloading, or malfunctioning of device drivers. This helps in identifying driver-related problems that could affect system stability.
- System Startups and Shutdowns: Tracks the times when the system starts up or shuts down. This can be useful for understanding system uptime and diagnosing issues related to improper shutdowns or startup failures.
- Application Events: Data related to software applications running on the system includes application errors, warnings, and informational messages. If you are using a Windows server to run your production-level application, you can use the application errors, warnings, and messages provided here to solve the issue. There are different types of Application events some are as follows:
- Application Errors: Application errors are events generated by software applications when they encounter issues that prevent them from functioning correctly.
- Warnings: Logs warnings from applications about potential issues that might not be critical but could lead to problems if not addressed.
- Informational Messages: Provides general information about application activities, such as successful operations or status updates, helping to understand the normal functioning of applications.
- Security Events: Security events are logs that capture all security-related activities on your Windows system. They are essential for monitoring, maintaining, and auditing the security of your system. These events help detect unauthorised access attempts, monitor access to sensitive resources, and track changes to system policies. Some security events are as follows:
- Successful and Failed Login Attempts: Successful and failed login attempts are critical events that are logged by a system to monitor access and ensure security. These logs provide valuable insights into user activity, helping to detect unauthorised access attempts and identify potential security threats.
- Resource Access: These events log attempts to access protected resources such as files, folders, or system settings. Monitoring these logs ensures that sensitive data is accessed appropriately and helps identify unauthorised access attempts.
- System Policy Changes: These logs record any changes to system policies, including modifications to user permissions or security settings. This is important for auditing purposes and ensuring compliance with security policies, helping to maintain the integrity and security of the system.
- Setup Events: Setup events are logs that contain detailed information about the installation and setup processes on your Windows system. These logs are valuable for diagnosing and resolving issues that occur during the installation or configuration of software and system components. Some Setup events are as follows:
- Installation Processes: Installation processes refer to the series of steps and operations carried out to install software, updates, or system components on a Windows system. It contains log details about software installation, updates, or system components. This helps in diagnosing issues related to incomplete or failed installations.
- Setup Configurations: Records information about system configurations during the setup process. This can be useful for understanding your system’s initial setup and configuration.
- Forwarded Events: Forwarded events are logs sent from other computers to a centralised logging server. This is particularly useful in larger environments where centralised log management is needed. They include:
- Logs from Remote Systems: Collects event logs from multiple systems, allowing for centralised monitoring and management.
- Centralised Logging Scenarios: Useful for organisations that need to aggregate logs from various systems to a single location for easier analysis and monitoring.
Accessing the Windows Event Viewer
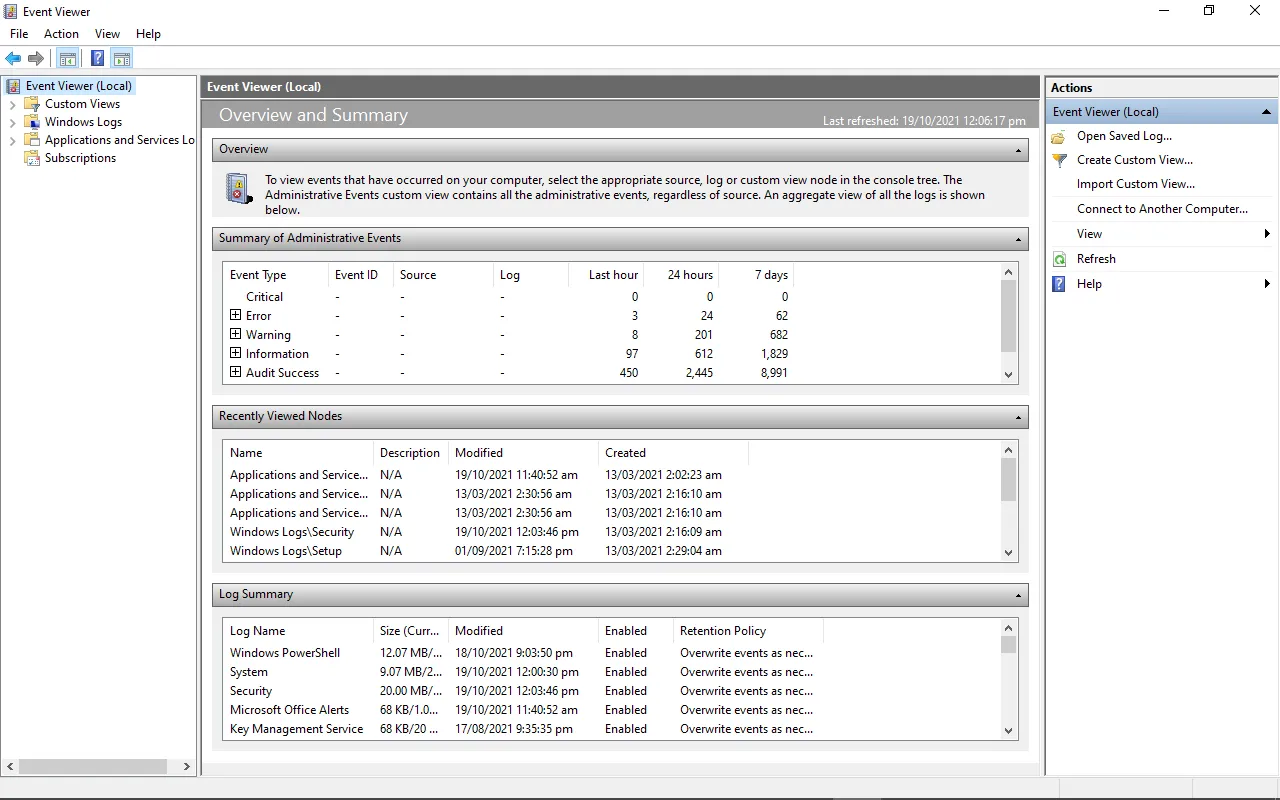
Windows Event Viewer is a Windows application that lets you see your computer’s logs, warnings, and other events. Each application you open generates entries that are recorded in an activity log, which can be viewed from the Event Viewer.
There are several ways to access the Windows Event Viewer. Here are some of them:
-
Using the Start Menu:
- Click on the Start button or press the Windows key.
- Type
Event Viewerin the search box.
Using start menu to open Event viewer — Select Event Viewer from the search results which will popup something like this.
Event Viewer main page 2. Using the Run Dialog: — Press
Windows + Rto open the Run dialog. — Typeeventvwrand press Enter.Windows Run App to open Event Viewer Windows Event viewer landing page 3. Using Control Panel: — Open the Command Prompt and run as administrator
Open CMD as Administrator from start menu — Once open, type
eventvwrand press enter, and you will be redirected to Event Viewer page.CMD terminal
Windows Log Location
Windows event logs are stored in files located in the C:\\Windows\\System32\\winevt\\Logs directory. Each log file corresponds to a specific log category, such as System, Application, or Security. It may differ depending on which version of Windows you are using.
The main event log files are:
- Application.evtx: Logs events from applications and programs.
- Security.evtx: Logs security events like successful or failed logins.
- System.evtx: Logs events related to Windows system components and drivers
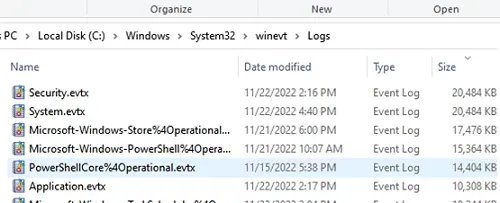
You can find many other log files which could be related to system operations & other processes that are happening inside the Windows System. Windows 11uses the .evtx format rather than using the classic EVT format.
Understanding Event Viewer Entries
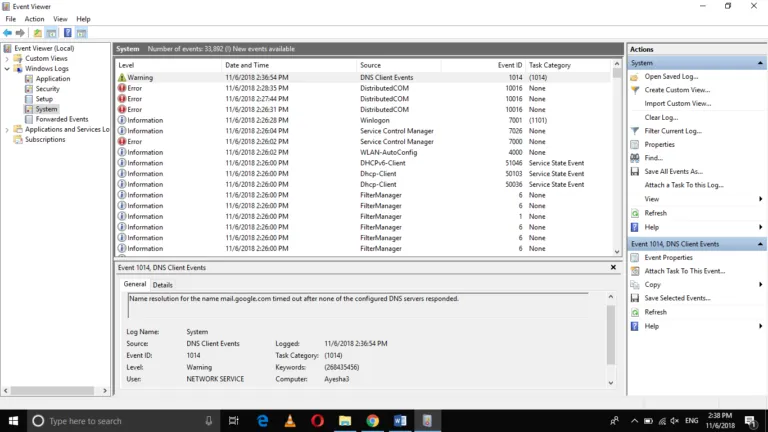
Event Viewer entries provide detailed information about each logged event. It is like a log book for your Windows system. They record important happenings within the system, including applications, systems, security, failed events, etc. Understanding these entries is key to effective log management.
The key components of an Event Viewer entry are:
- Date and Time: When the event occurred.
- Source: The application or system component that generated the event.
- Event ID: A unique identifier for the event type.
- Level: The severity of the event (Information, Warning, Error, Critical).
- User: The user account under which the event occurred.
- Computer: The name of the computer where the event was logged.
- Description: Detailed information about the event.
Each event in the Event Viewer has a severity level, indicating the importance and type of the event:
- Information (Green Light): These events resemble a green traffic light, signifying smooth sailing. They indicate successful operations or occurrences within your system.
- Warning (Yellow Light): Treat these entries with caution, like a yellow traffic light. They signal potential issues that warrant attention but might not cause immediate problems.
- Error (Orange Light): Think of error entries as an orange traffic light; proceed with care. They denote significant problems that could affect system functionality. Imagine an error message indicating a driver failure.
- Critical (Red Light): Critical entries are akin to a red traffic light; stop and address the situation immediately. They represent severe errors that have caused a major failure. A critical event might report a complete system shutdown or a critical service crashing.
Filtering and Custom Views
Event Viewer allows you to filter events using a variety of parameters, including date, event level, source, and more. Consider the following scenario: your system exhibits weird behaviour, but the Event Viewer is overflowing with hundreds, if not thousands, of entries. Filtering steps and generating custom views can significantly reduce the workload. You may also construct custom views to focus on specific kinds of events:
- In the Event Viewer, you’ll see Administrative Events, to create special logs right-click on «Custom Views» and select «Create Custom View.»
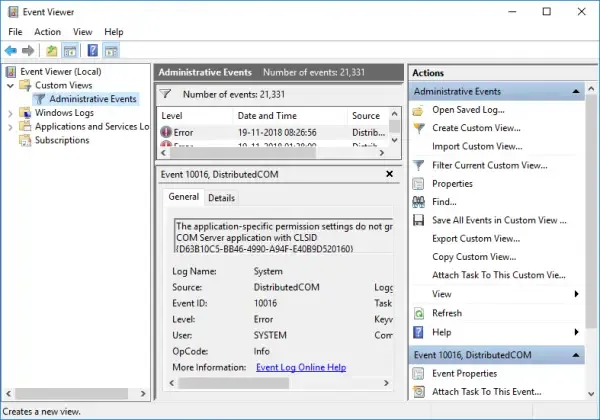
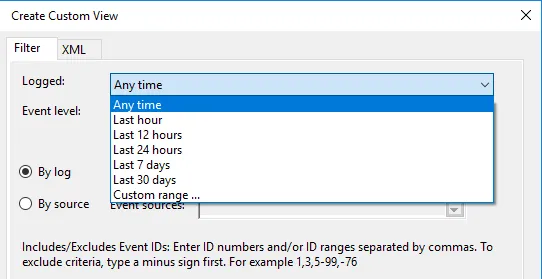
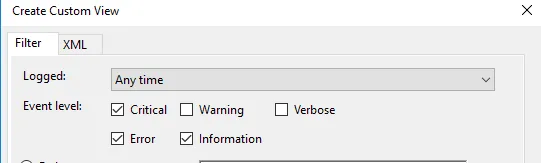
1. In the Custom View page, you can see logged drop down, choose a preferred time or it gives you an option to create a custom time to set. 2. On the Event Level choose an appropriate level for your custom view, You can choose among the 5 levels.
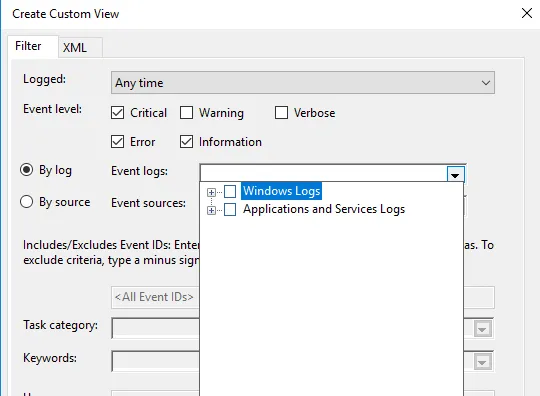
1. Once done, choose how you want the events to be filtered, By log or By source.
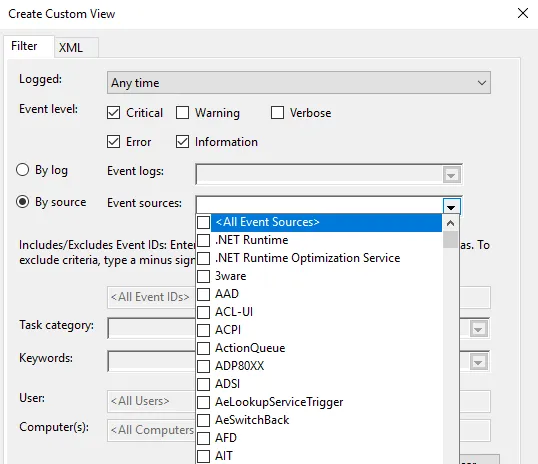
Once everything is set up according to your needs, save all events in Custom View as
from the drop-down menu and choose an appropriate location to save the logs. Click on the Save button. (A log file with the extension .evtx will be saved on your device).
Conclusion
This blog provides an understanding how you can use the Windows Event Viewer which is provided by the Windows in default and using it to monitor Windows logs.
- Main event log files are stored in
C:\\Windows\\System32\\winevt\\Logs. - Windows logs are crucial for understanding the activities, errors, and significant events on your machine. They provide valuable information for troubleshooting, auditing, and ensuring system integrity.
- They record a variety of system activities, errors, and other significant events, providing valuable information for troubleshooting, auditing, and ensuring system integrity.
- We learnt how to setup Filtering and Custom Views to optimise what we see and solve the problems and where it happened.
By grasping the significance of different event types such as System, Application, Security, Setup, and Forwarded Events, and knowing how to filter and export logs, you can effectively manage your Windows system.
FAQ’s
How to view Windows logs?
To view Windows logs, use the built-in Event Viewer:
- Press
Win + R, typeeventvwr, and press Enter. - Navigate through the console tree to find the log you want to view (e.g., Windows Logs > Application).
Where are Microsoft logs?
Microsoft logs, including Windows logs, can be found in the Event Viewer under sections like Application, Security, and System. Log files are also located in the C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs directory.
How do I audit Windows logs?
To audit Windows logs:
- Open Event Viewer.
- Navigate to Security logs under Windows Logs.
- Configure auditing policies via the Local Security Policy or Group Policy Management Console.
How do I check my Windows activity log
Check your Windows activity log by viewing the Security logs in Event Viewer. These logs record user logins, logoffs, and other security-related activities.
Which is Windows log key?
The Windows log key, often referred to as the Windows key, is the key on your keyboard with the Windows logo. It is used in various shortcuts to open system tools, including Event Viewer (Win + X > Event Viewer).
Where is the logs folder?
The logs folder is located at C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs. This folder contains all the event log files in .evtx format.
Why are Windows logs important?
Windows logs are important because they provide detailed information about system operations, security events, and application behavior, which is crucial for troubleshooting, auditing, and ensuring system integrity.
How to view log files?
View log files using Event Viewer:
- Open Event Viewer (
Win + R, typeeventvwr, press Enter). - Expand the Windows Logs section and select the log you want to view.
Where are login logs?
Login logs are located in the Security logs section of Event Viewer. They record all login attempts, both successful and failed.
What are system logs?
System logs contain information about the core operations of the Windows operating system, including hardware events, driver issues, and system startups and shutdowns. They are found under the System section in Event Viewer.
How do I find Windows log files?
Find Windows log files in the Event Viewer or directly in the C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs directory.
How do I view user logs in Windows 10?
View user logs in Windows 10 through the Event Viewer:
- Open Event Viewer.
- Go to Windows Logs > Security to see logs related to user activities, including logins and logoffs.
How do I view Windows setup logs?
To view Windows setup logs:
- Open Event Viewer.
- Navigate to Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > Setup.
How do I view Windows app logs?
To view Windows application logs:
- Open Event Viewer.
- Navigate to Windows Logs > Application to see logs related to software applications running on your system.
Was this page helpful?
Windows Event Viewer Logs store useful information that is needed when analyzing the status of services and applications in Windows, troubleshooting errors, and auditing security events. By default, the sizes of the Event Viewer logs in Windows are limited and when the file sizes are exceeded, new events begin to overwrite older ones. If too many events are sent to the Event Viewer, only the last few hours of events may be logged, which may not be sufficient for efficient monitoring and log analysis.
To prevent old events from being overwritten, and to ensure that you always have events for a long enough period, you can increase the maximum size of Event Viewer logs.
Contents:
- How to Set Windows Event Log Size with PowerShell?
- Adjusting the Event Log File Size from the Event Viewer Console
- Increase the Size of Windows Event Log Files Using GPO
How to Set Windows Event Log Size with PowerShell?
Windows event log files are stored in the %SystemRoot%\System32\Winevt\Logs\ directory as .EVTX files. Note that there is a separate file for each log. So you can manage the maximum size of only the Windows log you need and leave the default settings for others.
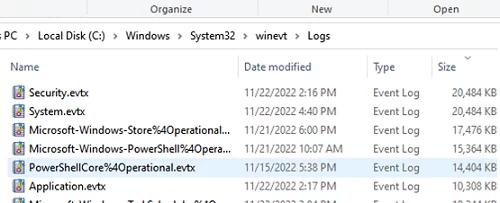
You can use PowerShell to view the current limits for all enabled Event Viewer Logs on Windows:
Get-Eventlog -List
You can use the Get-WinEvent cmdlet to get the size of a specific event log file. For example, here’s how you can get the current and maximum size of the Security log file:
Get-WinEvent -ListLog Security| Select MaximumSizeInBytes, FileSize, IsLogFull, OldestRecordNumber, IsEnabled, LogMode
To increase the maximum size of the log, you can use the wevtutul command line tool (the new size is set in bytes):
wevtutil sl "Application" /ms:200000000
Or you can use PowerShell to set a new maximum Application log file size:
Limit-Eventlog -Logname Application -MaximumSize 200MB -OverflowAction OverwriteOlder
Adjusting the Event Log File Size from the Event Viewer Console
The easiest way to increase the maximum log size is directly from the Event Viewer console.
- Open the Event Viewer MMC snap-in (
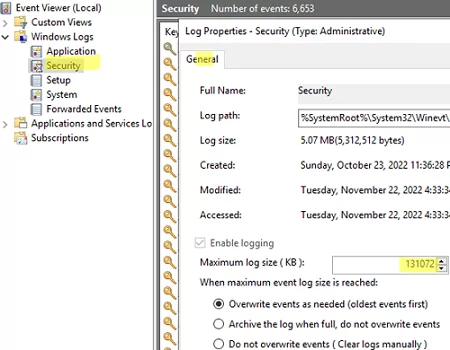
eventvwr.msc); - Select the required log (for example, Security) and open its properties;
- Set a new limit under Maximum log size (KB) and save the changes;
- You can also select the action to be taken when the maximum log file size is reached: Overwrite events as needed (oldest events first). This mode is used by default and implies that new events simply overwrite older events.
Archive the log when full, do not overwrite events – the current event log is archived in the\System32\Winevt\Logs\folder when full, and new events are written to a new EVTX file. You can access the archived event files through the Open Saved Log menu in the Event Viewer.
Do not overwrite events (Clear log manually) – enable this option to protect your old events from being overwritten. Note that the log must be cleared manually to write new events.
Increase the Size of Windows Event Log Files Using GPO
You can use Group Policies to centrally manage the size of event log files on computers or servers in an Active Directory domain.
- Run the Group Policy Management snap-in (
gpmc.msc), create a new GPO, and link it to the Organizational Units with the computers or servers you want to change the Event Viewer settings for (you may also link the GPO to the domain root); - Navigate to the following GPO section Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Event Log Service. This directory contains nodes for managing the basic Windows logs:
Application Security Setup System
- To increase the maximum size of the log, select the Specify the maximum log file size (KB) option, enable it, and set the required size
;
- Update the Group Policy settings on the clients and check that the new maximum log file is now specified in the log properties and that you cannot change it. If you try to set a different size, an error will appear:
Event Viewer The Maximum Log Size specified is not valid. It is too large or too small. The Maximum Log Size will be set to the following: 61440 KB
The GPO section described above doesn’t contain options for other Event Logs from Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft. If you need to increase the size of another event log (other than the standard one), you can do it through the registry. Windows event log settings are stored in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\EventLog\<log_name> registry key. The maximum log file size is determined by the MaxSize parameter (REG_DWORD type). You can configure the registry value of the MaxSize parameter for a custom event log on domain computers by using Group Policy Preferences.
In this example, we are going to increase the size of the Directory Service log on the domain controllers. This log’s settings are stored in the following registry key HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\EventLog\Directory Service.
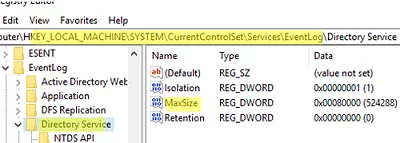
- Open GPO and go to Computer Configuration -> Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Registry;
- Select New -> Registry Item;
- Create a new registry parameter with the following settings:
Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE Key path: SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\EventLog\Directory Service Value name: MaxSize Value type: REG_DWORD Value data: 52428800 (the maximum file size is given in bytes. In our example it is 50 MB.)
- Check that the maximum log size is after updating the GPO on the DCs.
For example, if you want to store logs with a history of Remote Desktop connections to an RDS host for a long period, you need to increase the size of the Terminal-Services-RemoteConnectionManager log.
By increasing the size of Windows event logs, you can get more information over a longer time. For example, you can use event logs to get the Windows reboot history, find out who deleted a file from a shared network folder, or changed NTFS permissions.
Логи — это ценный инструмент для любого системного администратора или разработчика. Они позволяют отслеживать события, диагностировать ошибки и улучшать работу приложений. Правильное чтение логов помогает быстро выявлять и устранять проблемы, повышая надежность и безопасность систем. В этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, где хранятся логи в операционных системах Windows и Linux, как их читать и использовать для оптимизации работы.
Что такое логи и зачем они нужны
Лог — это файл, в который система или приложение записывают информацию о событиях, происходящих во время их работы. Журнал сервера (server log) содержит записи о различных аспектах функционирования сервера: от успешных операций до критических ошибок.
Основные причины использовать логи:
- Диагностика ошибок. Быстрое обнаружение и устранение сбоев.
- Мониторинг безопасности. Отслеживание несанкционированного доступа и подозрительной активности.
- Анализ производительности. Оптимизация ресурсов и улучшение отклика системы.
- Аудит действий. Контроль изменений и действий пользователей.
Где хранятся логи в системах Windows и Linux
Windows
В Windows логи хранятся в «Просмотре событий». Это встроенная утилита, которая собирает и отображает системные и события приложения.
Как открыть «Просмотр событий»:
- Нажмите Win + R и введите eventvwr.msc, нажмите Enter.
- В открывшемся окне вы увидите разделы:
- Журналы Windows: включает в себя системные, приложенческие, установочные и другие логи.
- Журналы приложений и сервисов: специфические логи для отдельных приложений.
Где хранятся файлы логов. Логи Windows сохраняются в файлах с расширением .evtx и находятся по пути:
C:\Windows\System32\winevt\Logs\Linux
В Linux системные логи обычно находятся в каталоге /var/log/. Этот каталог содержит множество файлов логов для различных системных компонентов и приложений.
Основные файлы логов:
- /var/log/syslog или /var/log/messages: общесистемные сообщения.
- /var/log/auth.log: события аутентификации и безопасности.
- /var/log/kern.log: сообщения ядра системы.
- /var/log/dmesg: информация о загрузке системы и аппаратных компонентах.
- /var/log/apache2/: логи веб-сервера Apache.
Где хранятся логи Nginx
Чтение логов и их анализ
Windows
Использование «Просмотра событий»:
- В «Просмотре событий» выберите нужный журнал в левой панели.
- В центральной панели отобразятся события с деталями: дата и время, источник, уровень (информация, предупреждение, ошибка).
- Двойным щелчком по событию откройте подробную информацию.
Поиск и фильтрация:
- Используйте функцию «Фильтр текущего журнала» для отображения только необходимых событий.
- Можно фильтровать по ключевым словам, уровням и источникам событий.
Чтение логов в Linux
Командная строка. Просмотр последних строк лога:
tail -n 100 /var/log/syslogРеальное время обновления:
tail -f /var/log/syslogПоиск по ключевому слову:
grep "ошибка" /var/log/syslogИспользование специальных приложений:
less: удобный просмотр больших файлов.
less /var/log/sysloglogwatch: утилита для анализа и создания отчетов по логам.
logwatch --detail High --mailto admin@example.com --service all --range todayПримеры использования логов для решения проблем
Пример 1. Устранение ошибки приложения в Linux
Ситуация. Веб-приложение на сервере перестало отвечать.
Действия. Проверить лог веб-сервера:
tail -n 50 /var/log/apache2/error.log- Найти строки с ошибками и обратить внимание на время события.
Если ошибка связана с базой данных, проверить лог базы:
tail -n 50 /var/log/mysql/error.log- По полученной информации принять меры: перезапустить сервис, исправить конфигурацию или обратиться к разработчикам.
Пример 2. Обнаружение несанкционированного доступа в Windows
Ситуация. Подозрение на взлом учётной записи.
Действия:
- В «Просмотре событий» открыть «Журналы Windows» → Безопасность.
- Фильтровать события по ID 4625 (неудачная попытка входа).
- Проанализировать время и частоту попыток, IP-адреса.
- При необходимости изменить пароли, настроить политику блокировки и уведомить службу безопасности.
Особенности настройки журналов сервера
Настройка логирования в Linux с помощью syslog
syslog — это системный сервис для обработки и хранения логов.
Конфигурационный файл:
- /etc/rsyslog.conf: основной файл настроек rsyslog.
Настройка уровня логирования:
- Измените уровень логирования для определенных сервисов.
Например, чтобы записывать только ошибки:
*.err /var/log/errors.logУдалённое логирование. Настройте отправку логов на удаленный сервер для централизованного хранения.
*.* @logserver.example.com:514Настройка логирования в приложениях
- Уровни логирования: DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL.
- Формат логов. Настройте формат записи для удобства чтения и анализа.
- Ротация логов. Используйте утилиты вроде logrotate для автоматического архивирования и удаления старых логов.
Инструменты для просмотра и анализа логов
Windows
- Event Log Explorer — расширенная замена стандартному «Просмотру событий», предоставляющая больше возможностей для поиска, фильтрации и анализа журналов Windows.
- Microsoft Log Parser — утилита для анализа логов с помощью SQL-подобных запросов, позволяющая быстро извлекать нужные данные из большого объёма журналов.
Linux
- GoAccess — интерактивный инструмент для анализа веб-логов в реальном времени, который отображает статистику по трафику, запросам и ошибкам прямо в терминале или веб-интерфейсе.
- Graylog и ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) — системы для централизованного сбора, хранения и визуализации логов, позволяющие анализировать события, отслеживать аномалии и повышать безопасность инфраструктуры.
- journald — системный журнал в дистрибутивах с systemd, сохраняющий структурированные логи и поддерживающий удобный поиск по параметрам.
Советы по эффективному использованию логов
- Регулярный мониторинг. Настройте оповещения при появлении критических ошибок.
- Автоматизация. Используйте скрипты и инструменты для автоматического анализа и отчётов.
- Безопасность. Ограничьте доступ к логам, так как они могут содержать конфиденциальную информацию.
- Оптимизация хранения. Следите за размером логов, чтобы избежать заполнения диска.
Заключение
Логи являются неотъемлемой частью системного администрирования и разработки. Понимание того, где хранятся логи и как их читать, позволяет эффективно решать проблемы, улучшать работу приложений и обеспечивать безопасность систем. Используйте предоставленную информацию и инструменты для углубленного анализа и оптимизации вашей инфраструктуры.
Читайте в блоге:
- Где хранятся логи Nginx
- Как установить и настроить веб-сервер Nginx на Ubuntu
- Шесть способов узнать версию Nginx