System Restore is a Windows feature that creates automatic restore points for your computer in the event of system failure. A restore point is a snapshot of the state of your computer at a given date and time. You can use the System Restore tool to return your system files and settings to an earlier point in time when you experience problems with your PC. However, the System Restore utility helps fix issues like corrupt registry keys or driver issues.
With so many useful features of a system command, it is stupid not to use the feature to your advantage. Read this article to learn how to use the system restore command on Windows 10/11.
To start the system restore, go to the command prompt in Windows 10 and 11.
What Is System Restore Command?
System Restore is a command that allows you to restore the operating system settings and files to a time before you made changes. The command line for system restore is rstrui.
You can use the following commands as part of the System Restore process:
- Restore all files and folders from a backup: rstrui /restore
- Restore individual files and folders from a backup: rstrui /restore /f:\
- Restore individual files and folders from a backup on another drive: rstrui /restore /f:\ /r:

When using System Restore, it’s important to understand how long it takes to complete each command, what it does, whether any files may be affected by the operation, and how long the restoration should take.
Command Lines To Use For System Restore
The following command lines can be used to carry out system restore:
This command will help you perform a system restore.
Command: «rstrui»
This command will create a restore point.
Command: «rstrui /restorehealth»
This command will show you the restore points that have already been created on your system.
Command: «rstrui /restorehealth» /v:1
This command will show you the restore points that have already been created on your system, and allow you to select one of them to use as a backup if needed.
Command: «rstrui /restorehealth» /?
This command shows additional information about the options available for creating a restore point.
- /s: System Restore
- /r: Restore
- /l: Logical Restore (requires /r)
When using the /s option, you can specify an hour and date to restore a specific point in time. When restoring from the Control Panel, choose System and Security > System Protection > Review Disk Space > Restore Files and Settings > System Protection tab > Create A Restore Point.
How to Perform a System Restore from Command Prompt in Windows 10?
The best time to perform a system restore from the command prompt is when you can’t access your Windows session normally because of an error (driver installation, Windows update) or a virus. It allows you to return your system settings to a previous date.
Please note that restoring your computer’s operating system using system restore in safe mode cannot be undone. If you want to reverse this action, use the installation disc that came with your computer. If you don’t have such a disc, creating a Windows 10 recovery drive or installing a disc on another computer with the same hardware is a good idea.
Now, you will learn how to start System Restore from Safe Mode using the Command Prompt and run a system restore in Windows 10.
- Hold the Shift key while selecting Power > Restart from the Start menu.
- You should select Restart when your computer restarts and displays the Choose an option screen.
- Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt by pressing number 6 or function key F6.
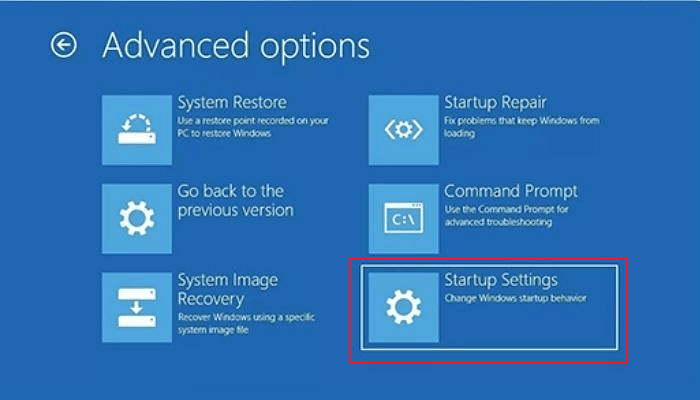
- If necessary, sign in with an administrator account. Once the command prompt appears, enter the command rstrui.exe and press Enter.
Note: The rstrui.exe file is usually found in the C: WindowsSystem32 folder. If your computer has multiple versions of this file or the file names are different, proceed with caution. If the computer is infected with a virus, one of these files may be it.
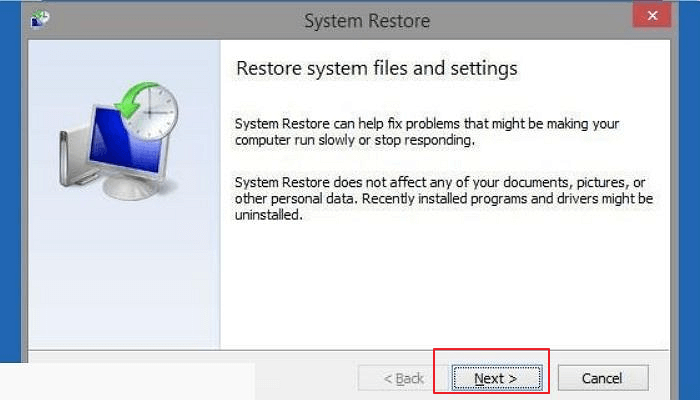
- The System Restore wizard will appear here. You can use the recommended restore point or select a restore point. Then press the Next button. To complete the system restore, follow the instructions displayed on the screen.
Windows 7: How to perform a System Restore?
System Restore in Windows 7 is performed by following the steps below.
- When your computer starts up, press F8 to enter Safe Mode. Next, repeatedly press the F8 key while Windows starts up. This should bring up the Windows Advanced Options menu. Press ENTER to begin Safe mode with Command Prompt.
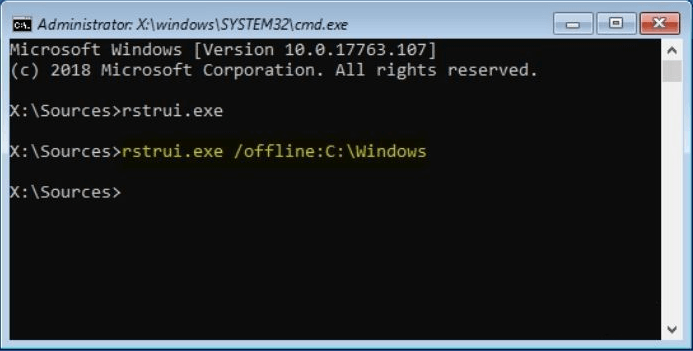
- Enter the following line when Command Prompt Mode loads: cd restore and click Enter
- Next, enter rstrui.exe and press ENTER.
- Click ‘Next’ in the newly opened window.
- Choose one of the available restore points and press the ‘Next’ button.
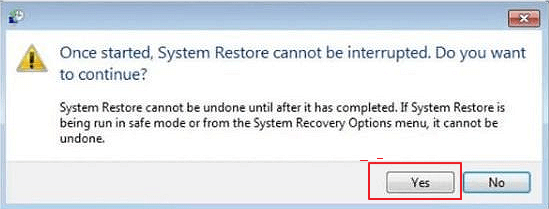
- Click ‘Yes’ in the newly opened window.
- If you have a ransomware infection, restore your computer to a previous date, and then download and scan it with recommended malware removal software.
If you’re looking for a compatible partner to back up your data, EaseUS Todo Backup is the perfect way to go. The Backup tool helps you recover lost data caused by an unexpected system crash or virus attack.
However, both Command Prompt and EaseUS Todo Backup are useful tools for managing your computer. With Command Prompt, you can easily run various commands to perform tasks like restarting or shutting down the computer, creating shortcuts, or renaming files and folders.
With EaseUS Todo Backup, you can back up important files on your PC and create system images to restore the entire computer if it fails to boot.
Final Verdict
System Restore is a powerful command that can quickly restore Windows to any previous state it has been in. The restore point will be created automatically with each change you make to your computer. Another thing to note is that System Restore can reduce downtime due to hardware/software failure and allows you to recover from viruses and other security threats.
FAQs about System Restore with Command Line
1. Is system restoration a good idea?
Yes, it is a good idea to run System Restore if you have problems with your computer. If you can’t fix the problem, try restoring your computer to an earlier time when it was working correctly.
2. Will I lose everything if I do a system restore?
You will lose everything important if something has happened since the last restore point that got corrupted or deleted something on your hard drive.
3. What should I do after the system restore?
After doing a system restore and restarting the computer (if necessary), you should make sure that all files are intact and that everything works properly.
Enter rstrui.exe into Command Prompt to start the System Restore utility from the command line
What to Know
- Open Command Prompt.
- Type rstrui.exe in the window, and then press Enter.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the system restore.
This article explains how to start System Restore from the Command Prompt. The System Restore command is the same in all modern versions of Windows. The article also includes information on the dangers of fake rstrui.exe files.
How to Start System Restore From the Command Prompt
As long as you can start your computer in Safe Mode to access Command Prompt, you can still use System Restore by executing a simple command. Even if you’re only looking for a quick way to start this utility from the Run dialog box, this knowledge might come in handy.
It’ll take you less than a minute to execute the right command, and probably less than 30 minutes for the whole process to complete.
-
Open Command Prompt, if it’s not already open.
You’re more than welcome to use another command line tool, like the Run box. You can open the Run box in any Windows version through WIN + R.
-
Type the following command:
rstrui.exe…and then press Enter or choose the OK button, depending on where you executed the command from.
At least in some versions of Windows, you don’t need to add the .EXE suffix to the end of the command.
-
The System Restore wizard will open immediately. Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the restore process.
Be Cautious of Fake rstrui.exe Files
As we already mentioned, this tool is called rstrui.exe. It’s included with a Windows installation and is located in the System32 folder:
C:\Windows\System32\
If you find another file on your computer that’s called rstrui.exe, it’s more than likely a malicious program that’s trying to trick you into thinking it’s the utility provided by Windows (unless it’s in a subfolder within C:\Windows\WinSxS\). Such a scenario may take place if the computer has a virus.
Do not use any program that’s pretending to be System Restore. Even if it looks like the real thing, it’s probably going to demand that you pay to restore your files or prompt you with an offer to purchase something else to even open the program.
If you’re digging around folders on your computer to find the System Restore program (which you shouldn’t have to do), and end up seeing more than one rstrui.exe file, always use the one in the System32 location mentioned above.
Also take note of the filename. Fake System Restore programs might use slight misspellings to make you think they’re the real thing. One example would be replacing the letter i with a lowercase L, like rstrul.exe, or adding/removing a letter (e.g., restrui.exe or rstri.exe).
Since there shouldn’t be random files named rstrui.exe masquerading as the System Restore utility, it’d also be wise to make sure your antivirus software is updated. Also, see these free on-demand virus scanners if you’re looking for a quick way to run a scan.
Again, you shouldn’t really be peaking around in folders looking for the System Restore utility because you can just open it normally and quickly through the rstrui.exe command, Control Panel, or Start menu, depending on your version of Windows.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
How to Start System Restore From the Command Prompt
In the world of computing, few things are as critical as maintaining the health and performance of your operating system. Sometimes, however, issues can arise that necessitate reverting your system to an earlier state. This is where the System Restore feature comes in. While most users may access System Restore through the graphical user interface, starting it from the Command Prompt can be particularly useful in scenarios where the Windows interface is malfunctioning or inaccessible. This comprehensive guide will cover everything you need to know about starting System Restore from the Command Prompt, including detailed instructions, troubleshooting tips, and key insights into system recovery.
Understanding System Restore
System Restore is a built-in feature in Windows operating systems that allows users to revert their system files, installed applications, Windows Registry, and system settings to a previous state, known as a restore point. This can be particularly helpful in resolving software issues, system instability, or after a problematic update.
When you create a restore point, Windows takes a snapshot of your system, capturing essential system files and settings. If you encounter issues later, you can use System Restore to return to a point before the problems began, effectively undoing recent changes without affecting your personal files like documents and photos.
How System Restore Works
-
Restore Points: Restore points are automatic or manual snapshots of your system. Windows creates them regularly or before significant changes, such as software installations or updates. You can also create them manually.
-
Reverting Changes: During the restoration process, the system restores the specified files and settings. It does not affect personal data. Your installed applications or updates after the selected restore point will be uninstalled.
-
System Files: System Restore is particularly effective for system files and settings, which makes it easier to recover from software conflicts, corrupted files, or after installing problematic drivers.
-
Limitations: System Restore has its limitations. For instance, it may not resolve hardware issues or eliminate malware. Moreover, if the restore points are disabled or purged due to disk space constraints, you may find that no restore points are available.
The Importance of Command Prompt
While the graphical interface of Windows is user-friendly, command-line utilities can sometimes be more powerful and efficient. Accessing System Restore via the Command Prompt can be particularly useful when:
- Windows doesn’t boot correctly, preventing you from accessing the GUI.
- The Windows Explorer is not functioning properly, making it difficult to navigate.
- You prefer using keyboard commands for faster execution.
By using the Command Prompt, you can execute various system-level tasks that might be otherwise inaccessible through the traditional interface.
Preparing to Use System Restore
Before jumping into how to start System Restore from the Command Prompt, it’s important to ensure a few prerequisites are met.
-
Administrative Privileges: You must run the Command Prompt as an administrator to execute System Restore commands. This grants you the necessary permissions to make system-level changes.
-
Enabled System Restore: The System Restore feature must be enabled on your system. If it has been disabled, you won’t have any restore points available.
-
Recent Restore Points: Check that restore points have been created. You will only be able to restore to a point that exists.
-
Back Up Data: Even though System Restore does not affect personal data, it’s wise to back up important files before proceeding. This ensures that you have a fallback in case something goes awry during the restoration process.
Checking Restore Points
Before proceeding, you may want to check if any restore points are available. You can do this through the Command Prompt as well:
-
Open the Command Prompt:
- Press
Windows + Rto open the Run dialog. - Type
cmdand pressEnter. If desired, right-click on Command Prompt and select «Run as administrator.»
- Press
-
Enter the Command:
vssadmin list shadowsThis command will list your available restore points. If no restore points are listed, you’ll need to create one before proceeding with a system restore.
Starting System Restore from Command Prompt
Now that you’re prepared and have confirmed that restore points exist, here’s how to initiate System Restore from the Command Prompt:
Method 1: Using the Command Line Directly
-
Open Command Prompt:
- Ensure you have the Command Prompt window open with administrative privileges.
-
Type the Command:
rstrui.exeThis command launches the System Restore interface. When you press
Enter, it will open a System Restore wizard, allowing you to choose a restore point and proceed with the restoration process. -
Follow the Wizard:
Once the wizard launches, follow these steps:- Click Next to access the list of available restore points.
- Select a Restore Point: Choose a restore point to revert your system to.
- Confirm Your Selection: Review the details and confirm your choice.
- Proceed with the Restoration: The system will begin the restoration process.
Method 2: Using Recovery Environment (if Windows won’t boot)
If your system is unresponsive and won’t boot normally, you can access System Restore from the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE):
-
Access WinRE:
- Turn on your computer and immediately start pressing the
F8,Shift + F8, orF11key during startup. This may vary depending on your PC manufacturer. If Windows fails to boot three times, it usually triggers WinRE.
- Turn on your computer and immediately start pressing the
-
Choose an Option:
Once in WinRE, navigate to:- Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Command Prompt.
-
Open Command Prompt:
Windows will boot you into a command-line environment. -
Start System Restore:
Type the following command:rstrui.exeLike the previous method, this will launch the System Restore wizard from WinRE.
-
Follow the Wizard Steps:
Continue with the restoration process as outlined previously.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
No Restore Points Found
If you find that there are no restore points available, consider the following:
- Enable System Restore: Ensure that System Restore is turned on. You can check this in the System Properties under the System Protection tab.
- Disk Space: If the disk space allocated for restore points is low, Windows may delete older points. Increase the space available for restore points.
- Create a Restore Point: It’s a good habit to create restore points manually after significant system changes.
Restoration Failed
If the restoration process fails:
- Inconsistent Files: This can occur if the files that need to be restored are corrupted. Consider running the System File Checker before attempting to restore again:
sfc /scannow - Antivirus Interference: Your antivirus program may block the restoration process. Temporarily disabling it during the process may help.
System Restore Loop
Sometimes, users encounter a situation where the system will not boot after a restoration attempt. If this occurs, you may need to access advanced recovery options or perform a system reset, being aware that this may lead to data loss.
Additional Command-Line Utilities for System Recovery
While System Restore is a powerful tool, other command-line utilities can help you diagnose and fix issues.
-
System File Checker (SFC):
This utility scans and repairs corrupted system files:sfc /scannow -
Deployment Imaging Service and Management Tool (DISM):
This tool repairs Windows images, including the system image:DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth -
CHKDSK:
Use the Check Disk utility to scan for and repair file system errors:chkdsk /f C: -
Advanced Boot Options:
From the Command Prompt in recovery mode, commands such asbootrec /fixmbrorbootrec /fixbootcan help resolve boot issues.
Conclusion
Starting System Restore from the Command Prompt is a valuable skill that can save your system from impending doom when the graphical interface fails or becomes unusable. With the steps outlined in this guide, you can efficiently navigate through the process, ensuring a smoother recovery experience.
Always remember to back up your critical data regularly, keep your restore points updated, and promptly resolve issues as they arise. Being proactive about system maintenance can tremendously mitigate future complications and keep your Windows environment running smoothly. Whether you enlist the help of System Restore or other recovery tools, your ability to manage system health is crucial for long-term performance and reliability.
Every Windows user should familiarize themselves with these procedures, as they can make a significant difference in managing system stability and recovery options. With these tools at your fingertips, you can be empowered to navigate the complexities of your operating system with confidence.
To initiate a system restore in Windows 10 using the command prompt, you can use the following command, which will open the System Restore wizard:
rstrui.exe
What is System Restore?
System Restore is a built-in feature in Windows 10 that allows users to roll back their system settings and files to a previous state without affecting personal files. It effectively creates snapshots of your system’s state (known as restore points) at various times, enabling you to recover from system malfunctions, software issues, or changes that may have negatively affected performance.
Restoring your system can help resolve issues caused by:
- Corrupted software installations
- Incompatible drivers
- System updates that lead to problems
By using Windows 10 cmd system restore, you can initiate and manage restoration tasks without relying solely on the graphical interface. This can streamline the process and potentially resolve issues more efficiently.

Windows 10 Cmd Recovery: Quick Guide for Every User
The Role of CMD in System Restore
Command Prompt (CMD) is a powerful tool that allows users to execute specific commands to control various aspects of the Windows operating system. Using CMD for system restore has its unique advantages:
- Speed: The command interface can be faster for tech-savvy users.
- Automation: The process can be scripted for repeated tasks or automation.
- Access: It may be useful in situations where the graphical interface is unavailable or unresponsive.

Mastering Windows Cmd Switches: A Concise Guide
Preparing for System Restore via CMD
Check System Protection Settings
Before initiating a restore, it’s essential to verify that System Restore is enabled on your machine. Run the following command to list available restore points:
vssadmin list shadows
This command will display all currently available shadow copies. If there are no shadows listed, you will need to enable System Restore.
Creating a Restore Point
Creating a restore point allows you to go back to a specific state before making any significant changes. To create a restore point via CMD, run the following command:
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "Checkpoint-Computer -Description 'PreRestore' -RestorePointType 'MODIFY_SETTINGS'"
This command utilizes PowerShell to create a restore point named «PreRestore,» which can be particularly useful before installing new software or updates.
Backup Important Data
Before proceeding with a system restore, it is wise to back up any crucial files. You can use the following CMD command to copy files from one directory to another:
xcopy C:\important_folder D:\backup_folder /E /I
This command ensures that all files within the specified directory are copied, preserving the original structure and including subfolders.
Mastering Windows Cmd Version: Essential Tips and Tricks
Steps to Perform System Restore using CMD
Accessing CMD as Administrator
To run commands that require elevated privileges, you must open CMD as an administrator. Here’s how you can do that:
- Type “Command Prompt” in the Windows search bar.
- Right-click on the Command Prompt option.
- Choose Run as administrator.
You will need administrative rights to perform a system restore.
Initiating System Restore
To begin the system restore process via CMD, you will need to execute the following command:
rstrui.exe
Executing this command opens the System Restore wizard. You will see a prompt guiding you through the graphical interface to select the restore point you created or any other available options.
Selecting a Restore Point
In the System Restore wizard, you’ll be presented with a list of restore points. It’s crucial to select a restore point that closely corresponds to a time before you experienced issues. Here are some tips for identifying the right restore point:
- Look for dates: Review the dates and times of available restore points.
- Description: Some restore points will have descriptions. Use these to identify significant changes made, such as software installations or updates.
Mastering Windows 10 Cmd Prompt: A Quick Guide
Completing the System Restore Process
Once you have selected the appropriate restore point, follow the prompts to confirm your choice. The system will then begin the restoration process, which may take several minutes. During this time, your computer will restart, and you may see a progress screen.
It is important not to interrupt this process; doing so could potentially lead to a corrupted system.

Mastering Windows Cmd Copy Directory in No Time
Troubleshooting CMD System Restore Issues
Common Errors and Their Solutions
While restoring using CMD is generally smooth, you may encounter some common issues. Here are a few errors you might face along with suggested solutions:
-
No restore points found: Ensure that System Restore is enabled (as mentioned above) and that restore points have been created.
-
The operation could not be completed: This may indicate that the Volume Shadow Copy Service is not running. You can start the service with the command:
net start vss
Alternatives If CMD Fails
If you are unable to initiate a system restore through CMD due to persistent errors, consider alternative methods:
- Use the Windows Recovery Environment: You can access recovery options by restarting your system and pressing the F8 key or through the settings menus.
- Graphical User Interface (GUI): You can also perform system restore through the Control Panel by navigating to System and clicking on System Protection.

Navigate Your Windows Cmd Home Directory Effortlessly
Conclusion
Incorporating Windows 10 cmd system restore into your troubleshooting toolkit is invaluable for efficient system management. By following a few simple steps, you can leverage CMD to restore your machine to a functioning state promptly. Always remember to create restore points and back up essential data before making any significant changes to your system.
Mastering Windows Cmd Remote Desktop: Quick Command Guide
Additional Resources
For those eager to learn more about Windows CMD commands, consider exploring the official Microsoft documentation. It offers comprehensive guides and references that delve deeper into CMD functionalities.

Mastering Windows Cmd Route: A Concise Guide
Call to Action
If you found this guide helpful, subscribe for more insightful articles on CMD tips, tricks, and other essential tools to empower your technical skills. Don’t forget to comment below with any questions or experiences you have regarding using CMD for system restoration!
Windows 10 gives chances to run System Restore using Command Prompt (popular as CMD) that greatly helps during troubles. It supports to recover a PC from malfunctioning, malware infections, crashing or other problems. System Restore is an attribute of Windows and permits a user to get back to the last point of their computer’s state. This rolls back all the settings including system files, installed applications, Registry keys. Use of Command prompt, takes directly to the System Restore windows so the whole task becomes easier and quicker.
When you can’t perform System restore normally then this way is very handy. Especially, if your machine doesn’t load or display the blue screen, this method pays roles in sending it to earlier date and time using command prompt. System restore takes your PC to the earlier dates and times but it doesn’t affect the application installed in this period. It brings back uninstalled and removed items moreover reinstates the fresh files. Application of the command prompt will fasten its accessing so it’s relevant to bring this into practice. In case, this is interesting then scroll down to know the process.
Way to Run System Restore Using Command Prompt (CMD) in Windows 10
Step 1 – Put in “cmd” in the search bar then look for Command prompt (Desktop app) under best match. Make a right click on this result and opt for “Run as administrator” from the list.
Step 2 – In the Command Prompt console type in the ahead “command”. Do not forget to press Enter to start its execution.
rstrui.exe
Important – Some versions of Windows don’t require the addition of .exe suffix in the command.
Step 3 – The action will instantly prompt “System Restore” window on the screen. Select Next.
Step 4 – In the subsequent window, you will find few restore points (with dates and time) in different rows, select one that suits you then click “Next”.
Step 5 – Finally, you need to Confirm your restore point, so choose Finish here.
The whole process consumes about half an hour as per volume of files in your computer so, wait until your files are reinstated completely.
System Restore shortcut command
The same command rstrui.exe works equally as a shortcut command. For this, you need to hold down the shortcut combination “Win+R”, type “rstrui.exe” and then Enter.
About System Restore CMD Command
Where is System restore in Windows 10, many users want to know? System Store application resides at “C:\WINDOWS\System32\rstrui.exe”. So you can manually open it from the System32 folder.
Carefulness while using the command
When using System restore you need to be extra careful as sometimes Ransomware also evokes the Window. Even though it pretends to be an original one and demands a certain amount of sum payment for the restoration of the files. Or in some other cases, it tries prompting you to buy some other product so that you have the access to at least open the program.
The best and secure way to run System Restore Using Command Prompt (CMD) in Windows 10 is using safe mode. It is a short-term process where does not take even a minute to execute the System Restore command. And the total period of the entire procedure takes probably less than 30 minutes to complete.
Concluding Words
Thus we conclude that to Run System Restore Using Command Prompt (CMD) in Windows 10 is very easy and straightforward. Furthermore, the process becomes the manumitter when malware attacks on your computer. Don’t forget to write us through the comment if you know more methods.
