Как завершить процесс службы Windows, которая зависла в статусе stopping (остановка) или starting (запуск)? Большинство администраторов Windows встречалось с ситуациями, когда при попытке остановить (перезапустить) службу из графического интерфейса консоли управления службами (
Services.msc
), служба зависает намертво и висит в статусе Stopping (или Starting). При этом все кнопки управления службой в консоли (Start, Stop, Restart) становятся недоступными (серыми). Самый простой способ – перезагрузить сервер, но это не всегда допустимо. Рассмотрим альтернативные способы, позволяющие принудительно завершить зависшую службу или процесс без необходимости перезагрузки Windows.
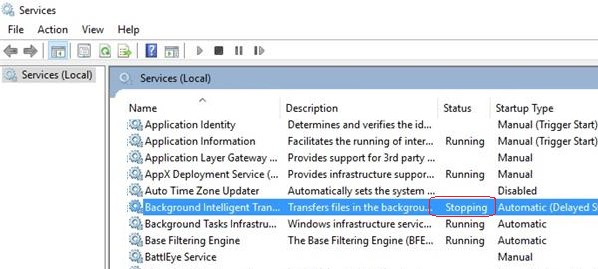
Если в течении 30 секунд после попытки остановки службы, она не останавливается, Windows выводит сообщение:
Не удалось остановить службу xxxxxxx Windows на локальном компьютере. Ошибка 1053. Служба не ответила на запрос своевременно.
Windows Could not stop the xxxxxx service on Local Computer Error 1053: The service did not respond in a timely fashion.
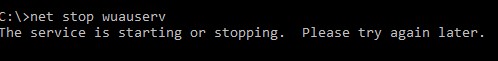
При попытке остановить такую службу командой:
net stop wuauserv
, появляется сообщение:
The service is starting or stopping. Please try again later.
Или:
[SC] ControlService: ошибка: 1061: Служба в настоящее время не может принимать команды.
Windows could not stop the Service on Local Computer. Error 1061: The service cannot accept control messages at this time.
Содержание:
- Как остановить зависшую службу Windows из командной строки?
- Принудительное завершение зависшей службы в PowerShell
- Анализ цепочки ожидания зависшего приложения с помощью ResMon
- Process Explorer: Завершение зависшего процесса из-под SYSTEM
Как остановить зависшую службу Windows из командной строки?
Самый простой способ завершить зависшую служу – воспользоваться утилитой taskkill. В первую очередь нужно определить PID (идентификатор процесса) нашей службы. В качестве примера возьмем службу Windows Update. Ее системное имя wuauserv (имя можно посмотреть в свойствах службы в консоли
services.msc
).
Важно. Будьте внимательными. Принудительная отставка процесса критичной службы Windows может привести к BSOD или перезагрузке операционной системы.
Отройте командную строку с правами правами администратора (иначе будет ошибка access denied) и выполите команду:
sc queryex wuauserv
В данном случае PID процесса —
9186
.
Чтобы принудительно завершить зависший процесс с PID 9186 воспользуйтесь утилитой taskkill:
taskkill /PID 9168 /F
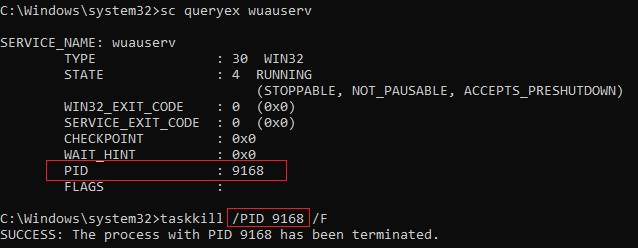
SUCCESS: The process with PID 9168 has been terminated.
Данная команда принудительно завершит процесс службы. Теперь вы можете запустите службу командой sc start servicename или через консоль управления службами (или совсем удалить эту службу, если она не нужна).
«Выстрел в голову» зависшей службы можно выполнить и более элегантно, не выполняя ручное определение PID процесса. У утилиты taskkill есть параметр /FI, позволяющий использовать фильтр для выбора необходимых служб или процессов. Вы можете остановить конкретную службу командой:
TASKKILL /F /FI “SERVICES eq wuauserv”
Или можно вообще не указывать имя, службы, завершив все сервисы в зависшем состоянии с помощью команды:
taskkill /F /FI “status eq not responding”
После этого служба, зависшая в статусе Stopping должна остановиться.
Также вы можете использовать утилиту taskkill для принудительной остановки зависших служб на удаленном компьютере:
TASKKILL /S CORPFS01 /F /FI “SERVICES eq wuauserv”
Принудительное завершение зависшей службы в PowerShell
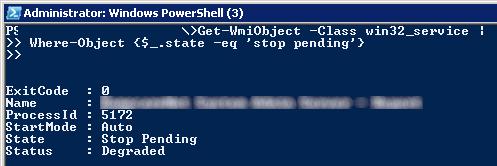
Также вы можете использовать PowerShell для принудительной остановки службы. С помощью следующей команды можно получить список служб, находящихся в состоянии Stopping:
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service | Where-Object {$_.state -eq 'stop pending'}
Завершить процесс для всех найденных служб поможет командлет Stop-Process. Следующий PowerShell скрипт завершит все процессы зависших служб в Windows:
$Services = Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service -Filter "state = 'stop pending'"
if ($Services) {
foreach ($service in $Services) {
try {
Stop-Process -Id $service.processid -Force -PassThru -ErrorAction Stop
}
catch {
Write-Warning -Message " Error. Error details: $_.Exception.Message"
}
}
}
else {
Write-Output "No services with 'Stopping'.status"
}
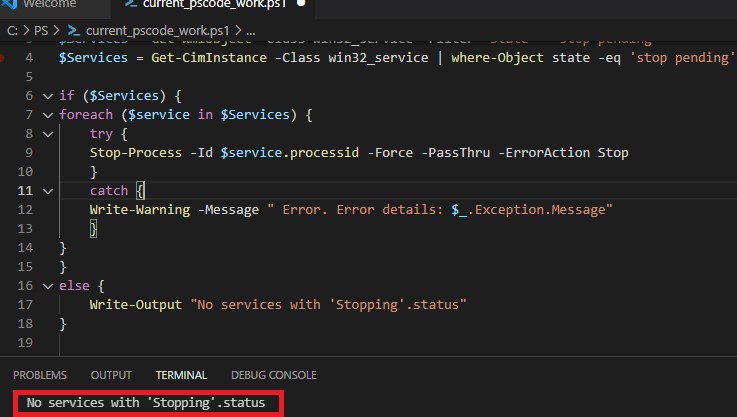
В новом PowerShell Core 6.x/7.x вместо командлета Get-WmiObject нужно использовать Get-CimInstance. Замените первую команду скрипта на:
$Services = Get-CimInstance -Class win32_service | where-Object state -eq 'stop pending'
Анализ цепочки ожидания зависшего приложения с помощью ResMon
Вы можете определить процесс, из-за которого зависла служба с помощью монитора ресурсов (
resmon.exe
).
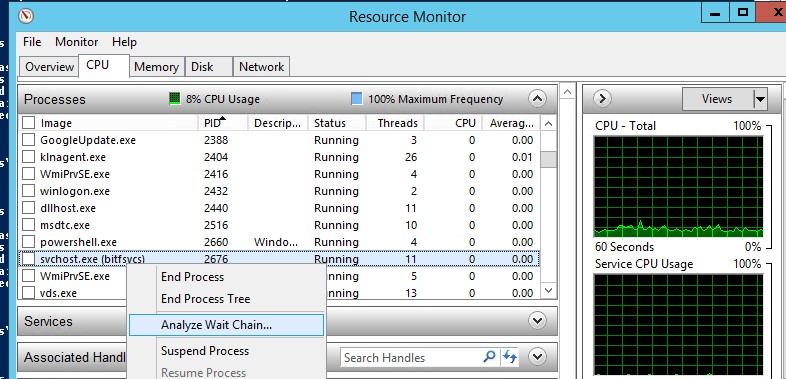
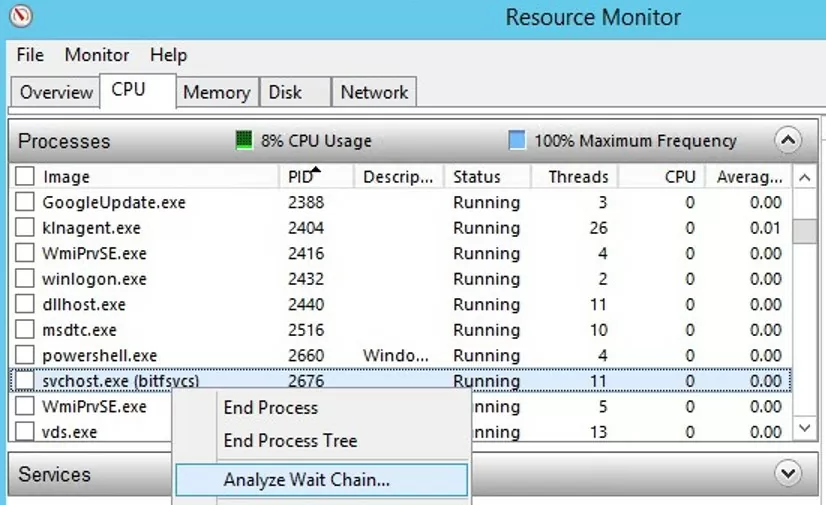
- В окне Монитора ресурсов перейдите на вкладку ЦП (CPU) и найдите процесс зависшей службы;
- Выберите пункт Анализ цепочки ожидания (Analyze Wait Chain);
- В новом окне скорее всего вы увидите, что вам процесс ожидает другой процесс. Завершите его. Если выполняется ожидание системного процесса svchost.exe, завершать его не нужно. Попробуйте проанализировать цепочку ожидания для этого процесса. Найдите PID процесса, которого ожидает ваш svchost.exe и завершите его
Process Explorer: Завершение зависшего процесса из-под SYSTEM
Некоторые процессы, запущенные из-под SYSTEM, не может завершить даже локальный администратора сервера. Дело в том, что у него просто может не быть прав на некоторые процессы или службы. Чтобы завершить такие процесс (службы), вам необходимо предоставить локальной группе Administrators права на службу (процесс), а потом завершить их. Для этого нам понадобятся две утилиты: psexec.exe и ProcessExplorer (доступны на сайте Microsoft).
- Чтобы запустить утилиту ProcessExplorer с правами системы (SYSTEM), выполните команду:
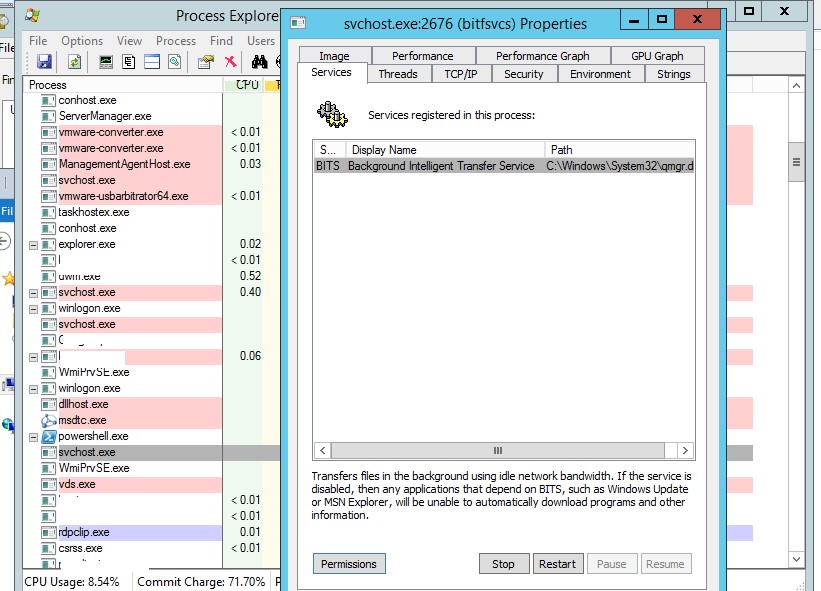
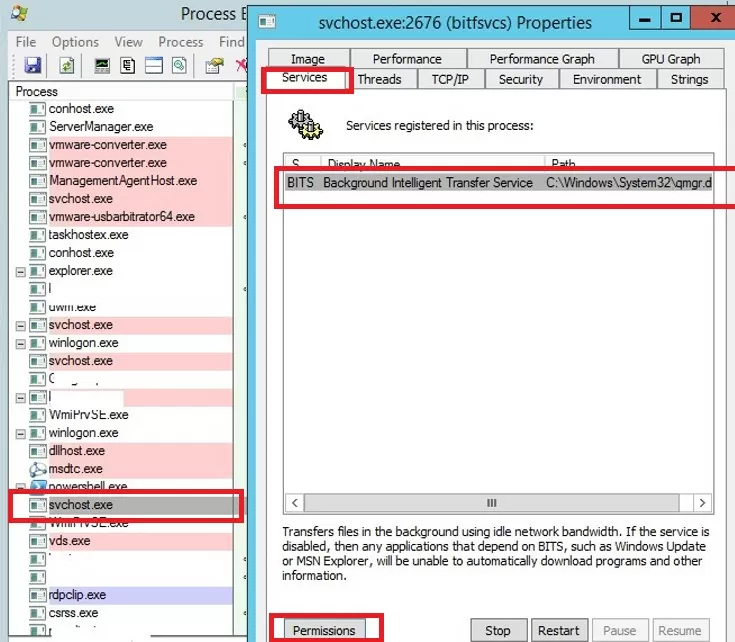
PSExec -s -i ProcExp.exe - В списке процессов Process Explorer найдите процесс зависшей службы и откройте ее свойства;
- Перейдите на вкладку Services, найдите свою службу и нажмите кнопку Permissions;
- В разрешения службы предоставьте права Full Control для группы администраторов (Administrators). Сохраните изменения;
- Теперь попробуйте завершить процесс службы.
Обратите внимание, что права на службу и ее процесс выдались временно, до ее перезапуска. Для предоставления постоянных прав на службы познакомьтесь со статьей Права на службы в Windows.
Таймаут, в течении которого Service Control Manager ждет ожидания запуска или остановки службы можно изменить через параметр реестра ServicesPipeTimeout. Если служба не запускается в течении указанного таймаута, Windows записывает ошибку в Event Log (Event ID: 7000, 7009, 7011, A timeout was reached 30000 milliseconds). Вы можете увеличить этот таймаут, например до 60 секунд:
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control /v ServicesPipeTimeout /t REG_SZ /d 600000 /f
Это бывает полезным при запуске/остановки тяжелых служб, которые не успевают завершить все процессы быстро (например, MS SQL Server).
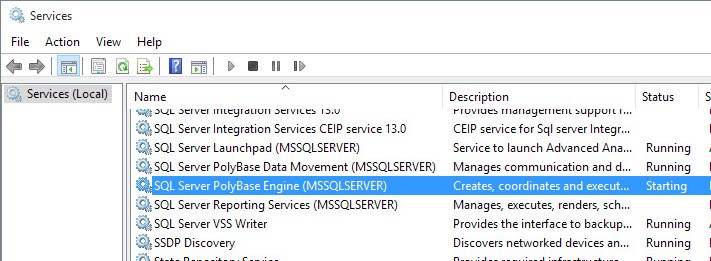

Sometimes when trying to restart a service in Windows, the service happens to have a status of Stopping. As a result, it ends up getting stuck and without the possibility of giving the stop and start command. Here in this case, we can see the Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager service crashed:

So we need to terminate the process of this service through the command prompt. For that, you need to use the following command:
sc queryex <service>Now we can obtain the PID (process identifier) of the process related to the crashed service:

With the PID number in hands, just run the command below:
taskkill /pid <PID> /fThis way the process is closed and you can start it again normally:

Very cool @wolff.mateus learn something new today. Will keep this reference for future use. Thanks for sharing
Yep @wolff.mateus to check list of services you also can use
tasklist | findstr Services
or
tasklist | findstr Nameofservice
this command list all (or specific) services with PID number and mem usage and you can kill it.
The biggest problem is its troubleshooting that need to spent a lot of time.
Yep @wolff.mateus to check list of services you also can use
tasklist | findstr Services
or
tasklist | findstr Nameofservice
this command list all (or specific) services with PID number and mem usage and you can kill it.
The biggest problem is its troubleshooting that need to spent a lot of time.
Nice to know @Andanet! Thanks for that.
For the PowerShell folks:
$id = (get-wmiobject win32_service | where { $_.name -eq ‘ServiceName’}).processIDStop-Process $id -Force
For the PowerShell folks:
$id = (get-wmiobject win32_service | where { $_.name -eq ‘ServiceName’}).processIDStop-Process $id -Force
Ah yes good old PowerShell. Love this for sure.
I tend to use “taskkill /IM executablename.exe /F” to kill off the processes, but that requires you know the image name.
These are handy commands! A a lot of users will find this content useful..
For the PowerShell folks:
$id = (get-wmiobject win32_service | where { $_.name -eq ‘ServiceName’}).processIDStop-Process $id -Force
Awesome! Sometimes, the Get-WMIObject cmdlets still works and other times they don’t. By the way, this cmdlets have been superseded with the CimInstance cmdlet.
Comment
Stopping a Windows service might not always work as expected. In this case, you might want to force the service to stop.
A service stuck at stopping won’t normally react to a net stop command:
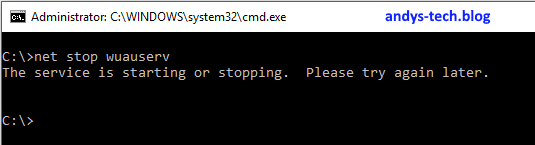
Some services may take a while to stop. But if you are sure that the service is stuck, you have to kill it.
Open the services add-in (Start > run > services.msc) and search the service to stop. Double click on the service to open the properties. Remember the name “Service name”.
The next steps requires a command prompt (Start > cmd.exe). Depending on your system settings, you have to open it as administrator (right-click the start menu entry and select “Run as administrator”).
Enter sc queryex <servicename> and press enter.
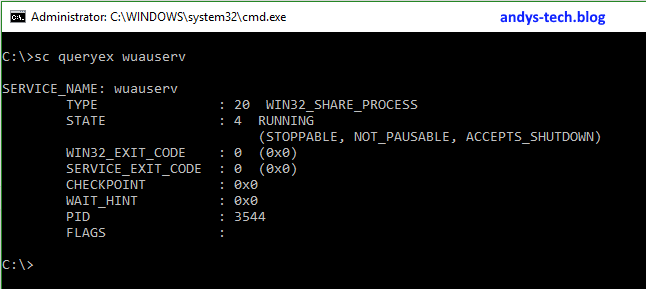
This example show the Windows Update service (wuauserv). In this example the service is running (state) and the important information is the PID (3544 in this image).
Now enter taskkill /PID <your pid> /f
This will kill the process for the service:
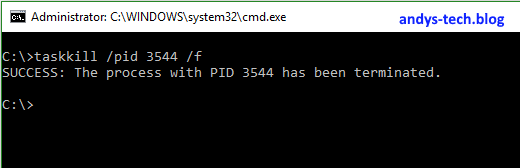
Now the service has been stopped and can restart or reconfigure it.
You can use this tutorial to remotely kill a stuck service: Use PSEXEC to execute the commands above. You can replace the services.msc step with the command sc query to get a list of all services on the target system.
Sometimes as an IT Support administrator you may need to kill a service which is stuck at stopping in order to avoid having to reboot a server in the middle of the day.
Here’s what you need to do:
Step 1. Find out the Service Name
To do this, go in to services and double click on the service which has stuck. Make a note of the “Service Name”.
Step 2. Find out the PID of the service
Open an elevated command prompt and type in:
sc queryex servicename
(where servicename is the name of the service you obtained from Step 1.)
Make note of the PID
Step 3. Kill the PID
From the same command prompt type in:
taskkill /f /pid [PID]
Where [PID] is the service number.
If it is successful you should receive the following message:
SUCCESS: The process with PID XXXX has been terminated.
Be careful of what you are killing though. If you kill a critical windows service you may end up forcing the machine to reboot on it own.
Note: By forcing a service to stop you can also use these instructions to Kill a Windows Service which is stuck at starting as well. This will allow you to restart the service.
Click to rate this post!
[Total: 503 Average: 4.9]
How to manually kill a Windows service process that is stacked at “Stopping” or “Starting” state? Most Windows administrators have faced a problem when they try to start/stop/restart a service, but it gets stuck with the Stopping (or Starting) status. You won’t be able to stop this service from the Service management console (services.msc), since all control buttons for this service become inactive (grayed out). The easiest way is to restart Windows, but it is not always acceptable. Let’s take a look at alternative ways, that allow to forcefully kill a stuck Windows service or process without a system reboot.
If within 30 seconds after trying to stop the service, it doesn’t stop, Windows displays this message:
Windows Could not stop the xxxxxx service on Local Computer Error 1053: The service did not respond in a timely fashion.
The timeout that the Service Control Manager waits for a service to start or stop can be changed by using the ServicesPipeTimeout registry parameter. If the service doesn’t start within the specified timeout, Windows sends an error to the Event Viewer (Event ID: 7000, 7009, 7011, a timeout was reached 30000 milliseconds). You can increase this timeout to 60 seconds, for example:
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control /v ServicesPipeTimeout /t REG_SZ /d 600000 /f
This is useful when starting/stopping heavy services that do not have enough time to properly terminate all processes and close the files (for example, MS SQL Server).
If you try to stop such a service from the command prompt: net stop wuauserv, a message appears:
The service is starting or stopping. Please try again later.
or:
Windows could not stop the Service on Local Computer. [SC] ControlService Error 1061: The service cannot accept control messages at this time.
Contents:
- How to Force Kill a Stuck Windows Service Using TaskKill?
- Force Stop a Stuck Windows Service with PowerShell
- Analyzing the Wait Chains on Hung Services Using ResMon
- Killing a Hung Service Using Process Explorer
How to Force Kill a Stuck Windows Service Using TaskKill?
The easiest way to stop a stuck service is to use the built-in taskkill command-line tool. First of all, you need to find the PID (process identifier) of the service. As an example, let’s take the Windows Update service. Its system name is wuauserv (you can check the name in the service properties in the services.msc console).
Important. Be attentive. Forced termination of critical Windows services can result in BSOD or an unexpected system restart.
Run this command in the elevated command prompt (it is important, or an access denied error will appear):
sc queryex wuauserv
In our case, the PID of the wuauserv service is 9186.
To force kill a stuck process with the PID 9186, run the command:
taskkill /PID 9168 /F
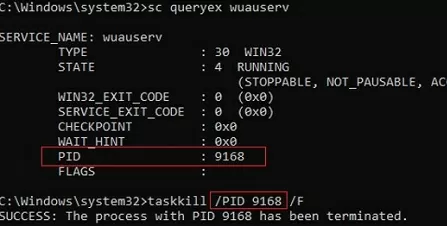
SUCCESS: The process with PID 9168 has been terminated.
This command will forcibly terminate the service process. Now you can start the service with the sc start servicename command or through the service management console
You can stop a hung service more elegantly without manually checking the PID of the service process. The taskkill tool has the /FI option, which allows you to use a filter to select the necessary services or processes. You can kill a specific service with the command:
taskkill /F /FI "SERVICES eq wuauserv"
Or you can skip the service name and kill all services in a hung state with the command:
taskkill /F /FI "status eq not responding"
After that, the service that is stacked in the Stopping status should stop.
You can also use the taskkill utility to force stop the hang services on a remote computer:
taskkill /S mun-fs01 /F /FI "SERVICES eq wuauserv"
Force Stop a Stuck Windows Service with PowerShell
You can also use PowerShell to force the service to stop. Using the following command, you can get a list of services in the Stopping state:
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service | Where-Object {$_.state -eq 'stop pending'}
Or in the Starting state:
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service | Where-Object {$_.state -eq 'start pending'}
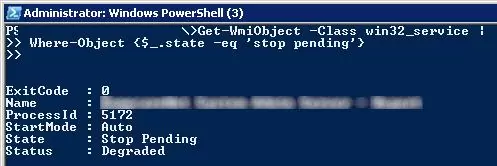
The Stop-Process cmdlet allows terminating the processes of all found services. The following PowerShell script will terminate all stuck service processes on Windows:
$Services = Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service -Filter "state = 'stop pending'"
if ($Services) {
foreach ($service in $Services) {
try {
Stop-Process -Id $service.processid -Force -PassThru -ErrorAction Stop
}
catch {
Write-Warning -Message "Error. Error details: $_.Exception.Message"
}
}
}
else {
Write-Output "No services with 'Stopping'.status"
}
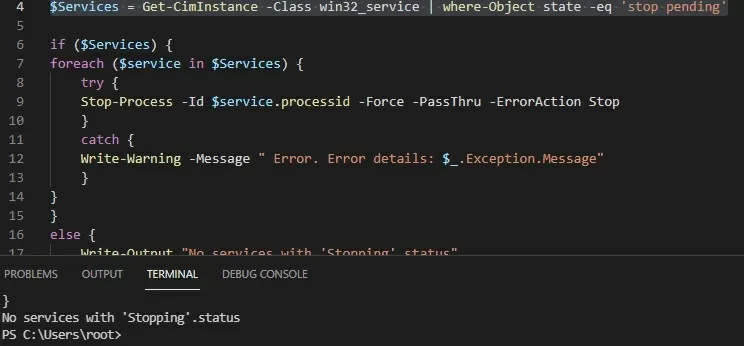
You must use the Get-CimInstance instead of the Get-WmiObject cmdlet in the new PowerShell Core 6.x/7.x. Replace the first command of the script with:
$Services = Get-CimInstance -Class win32_service | where-Object state -eq 'stop pending'
Analyzing the Wait Chains on Hung Services Using ResMon
You can detect the process that caused the service to hang using the resmon.exe (Resource Monitor).
- In the Resource Monitor window, go to the CPU tab and find the hung service process;
- Select the item Analyze Wait Chain from the context menu;
- In the new window, you will most likely see that your process is waiting for another process. End the process. If you are waiting for the svchost.exe or another system process, you don’t need to terminate it. Try to analyze the wait chain for this process. Find the PID of the process that your svchost.exe is waiting for and kill it.
Killing a Hung Service Using Process Explorer
Even the local administrator cannot terminate some processes that run under the SYSTEM account. The fact is that the admin account simply hasn’t permissions on some processes or services. To stop such a process (service), you need to grant permissions to the service (process) to the local Administrators group and then kill them. To do this, we will need two small tools: psexec.exe and ProcessExplorer (available on the Microsoft website).
- To start the ProcessExplorer with the system privileges (runas SYSTEM), use the command:
PSExec -s -i ProcExp.exe - In the Process Explorer process list, find the stuck service process and open its properties;
- Go to the Services tab, find your service, and click the Permissions button;
- Grant the Full Control right in the service permissions for the Administrators group. Save the changes;
- Now try to stop the service process.
Please note, that the permission on the service is granted temporarily until it is restarted. To grant permanent permissions on service follow the article Set permissions on a Windows service.