В этой статье мы рассмотрим два способа организации условного разрешения имен в DNS сервере на Windows Server 2016: DNS conditional forwarding и DNS policy. Эти технологии позволяют настроить условное разрешение DNS имен в зависимости от запрошенного имени, IP адреса и местоположения клиента, времени суток и т.д.
Содержание:
- Настройка DNS Conditional Forwarder в Windows Server
- Настройка DNS Conditional Forwarding с помощью PowerShell
- Фильтрация запросов DNS, политики разрешения имен в Windows Server 2016
Условная пересылка DNS (Conditional Forwarding) позволяет перенаправить DNS запросы об определенном домене на определенные DNS-сервера. Обычно Conditional Forwarders используется, когда нужно настроить быстрое разрешение имен между несколькими внутренними приватными доменами, или вы не хотите, чтобы DNS запросы с вашего сервера пересылались через публичную сеть Интернет. В этом случае вы можете создать на DNS сервере правило DNS пересылки DNS запросов для определенной доменной зоны (только !!!) на определенный DNS сервер.
Настройка DNS Conditional Forwarder в Windows Server
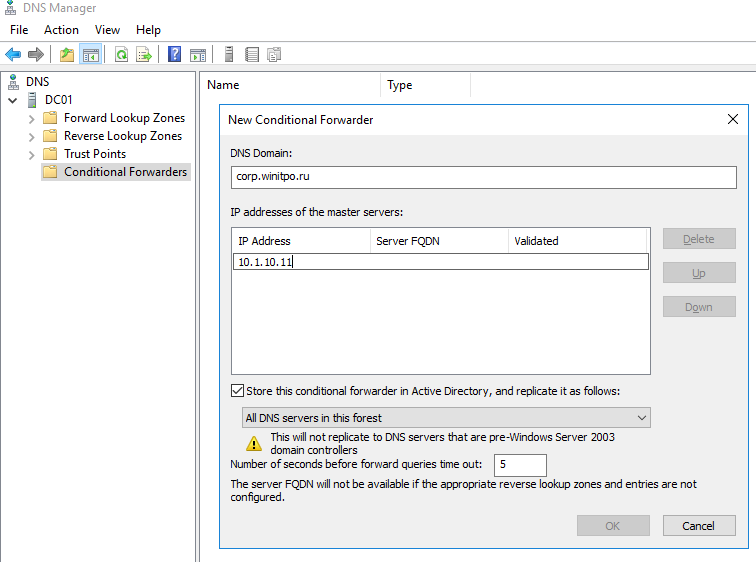
Попробуем настроить условное перенаправление DNS запросов для определенной доменной зоны на Windows Server 2016. Например, я хочу, чтобы все DNS запросы к зоне corp.winitpro.ru пересылались на DNS сервер 10.1.10.11.
- Запустите консоль управления DNS (
dnsmgmt.msc
); - Разверните ваш DNS сервер, щелкните правой кнопкой по разделу Conditional Forwarders и выберите New Conditional Forwarder;
- В поле DNS domain укажите FQDN имя домена, для которого нужно включить условную пересылку;
- В поле IP addresses of the master servers укажите IP адрес DNS сервера, на который нужно пересылать все запросы для указанного пространства имен;
- Если вы хотите хранить правило условной переадресации не только на этом DNS сервере, вы можете интегрировать его в AD. Выберите опцию “Store this conditional forwarder in Active Directory”;
- Выберите правило репликации записи conditional forwarding (All DNS servers in this forest, All DNS servers in this domain или All domain controllers in this domain).
Настройка DNS Conditional Forwarding с помощью PowerShell
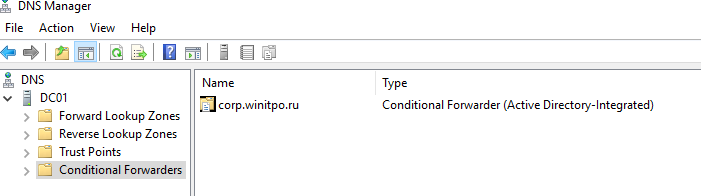
Вы можете создать правило Conditional Forward для определенной DNS зоны с помощью PowerShell. Воспользуйтесь командлетом Add-DnsServerConditionalForwarderZone:
Add-DnsServerConditionalForwarderZone -Name dmz.winitpro.ru -MasterServers 192.168.1.11,192.168.101.11 -ReplicationScope Forest
Чтобы вывести список DNS Conditional Forwarders на определенном сервере, выполните следующий PowerShell скрипт:
$DNSServer = "DC01"
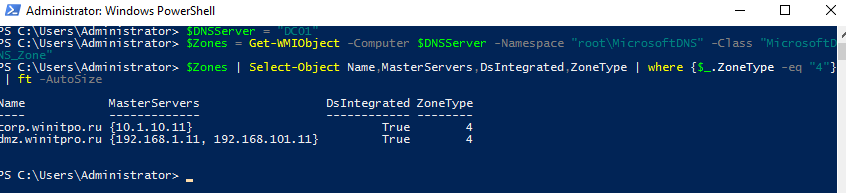
$Zones = Get-WMIObject -Computer $DNSServer -Namespace "root\MicrosoftDNS" -Class "MicrosoftDNS_Zone"
$Zones | Select-Object Name,MasterServers,DsIntegrated,ZoneType | where {$_.ZoneType -eq "4"} | ft -AutoSize
Фильтрация запросов DNS, политики разрешения имен в Windows Server 2016
В Windows Server 2016 появилась новая фича в службе DNS сервера – DNS политики. DNS политики позволяют настроить DNS сервер так, чтобы он возвращал различные ответы на DNS запросы в зависимости от местоположения клиента (с какого IP адреса или подсети пришел запрос), интерфейса DNS сервера, времени суток, типа запрошенной записи (A, CNAME, PTR, MX) и т.д. DNS политики в Windows Server 2016 позволяют реализовать сценарии балансировки нагрузки, фильтрации DNS трафика, возврата DNS записей в зависимости от геолокации (IP адреса клиента) и многие другие сложные сценарии.
Вы можете создать политику как на уровне DNS сервера, так и на уровне всей зоны. Настройка DNS политик в Windows Server 2016 возможна только из командной строки PowerShell.
Попробуем создать простую политику, которая позволяет вернуть разный ответ на DNS запрос в зависимости от геолокации клиента. Допустим, вы хотите, чтобы клиенты в каждом офисе использовали собственный прокси на площадке. Вы создали политику назначения прокси в домене (на всех клиентах будет указано proxy.winitpro.ru). Но клиент из каждого офиса должен резолвить этот адрес по-разному, чтобы использовать для доступа свой локальный прокси-сервер.
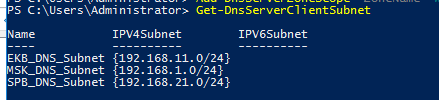
Я создал 3 подсети для разных офисов компании:
Add-DnsServerClientSubnet -Name "MSK_DNS_Subnet" -IPv4Subnet "192.168.1.0/24"
Add-DnsServerClientSubnet -Name "EKB_DNS_Subnet" -IPv4Subnet "192.168.11.0/24"
Add-DnsServerClientSubnet -Name "SPB_DNS_Subnet" -IPv4Subnet "192.168.21.0/24"
Эти команды придется выполнить на всех DNS серверах, на которых должна работать условная политика DNS. Эти записи не реплицируются в DNS и хранятся локально в реестре DNS сервера. Вы можете указать имя сервера с помощью параметра
-ComputerName dc01
.
Чтобы вывести список всех IP подсетей клиентов, выполните:
Get-DnsServerClientSubnet
Теперь нужно для каждого офиса создать отдельную DNS область:
Add-DnsServerZoneScope -ZoneName “winitpro.ru” -Name “MSKZoneScope”
Add-DnsServerZoneScope -ZoneName “winitpro.ru” -Name “EKBZoneScope”
Add-DnsServerZoneScope -ZoneName “winitpro.ru” -Name “SPBZoneScope”
Следующие команды добавят 3 DNS записи с одним именем, но указывающие на разные IP адреса в разных областях DNS:
Add-DnsServerResourceRecord -ZoneName “winitpro.ru” -A -Name “proxy” -IPv4Address “192.168.1.10” -ZoneScope “MSKZoneScope”
Add-DnsServerResourceRecord -ZoneName “winitpro.ru” -A -Name “proxy” -IPv4Address “192.168.11.10” -ZoneScope “EKBZoneScope”
Add-DnsServerResourceRecord -ZoneName “winitpro.ru” -A -Name “proxy” -IPv4Address “192.168.21.10” -ZoneScope “SPBZoneScope”
Вы можете вывести все ресурсные DNS записи для области с помощью команды:
Get-DnsServerResourceRecord -ZoneName “winitpro.ru” -ZoneScope SPBZoneScope
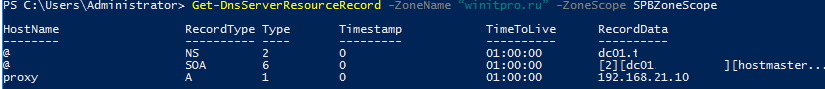
Теперь нужно создать DNS политики, которые свяжут IP подсети, DNS области и A записи.
Add-DnsServerQueryResolutionPolicy -Name “MSKResolutionPolicy” -Action ALLOW -ClientSubnet “eq,MSK_DNS_Subnet” -ZoneScope “MSKZoneScope,1” -ZoneName “winitpro.ru” –PassThru
Add-DnsServerQueryResolutionPolicy -Name “EKBResolutionPolicy” -Action ALLOW -ClientSubnet “eq,EKB_DNS_Subnet” -ZoneScope “EKBZoneScope,1” -ZoneName “winitpro.ru” -PassThru
Add-DnsServerQueryResolutionPolicy -Name “SPBResolutionPolicy” -Action ALLOW -ClientSubnet “eq,SPB_DNS_Subnet” -ZoneScope “SPBZoneScope,1” -ZoneName “winitpro.ru” –PassThru
В DNS политиках доступны следующие действия:
-
-Action ALLOW -
-Action DENY -
-Action IGNORE
Можно использовать следующие параметры в фильтре DNS:
-InternetProtocol "EQ,IPv4,NE,IPv6"
-TransportProtocol "EQ,UDP,TCP"
-ServerInterfaceIP "EQ,192.168.1.21"
-QType "EQ,A,AAAA,NE,PTR"
-TimeOfDay "EQ,9:00-18:00"
Вывести список всех DNS политик для DNS зоны на сервере можно так:
Get-DnsServerQueryResolutionPolicy -ZoneName winitpro.ru
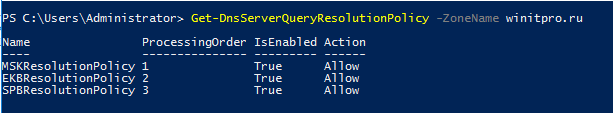
Теперь с устройств из различных офисов проверьте, что DNS сервер на один и тот же запрос возвращает различные IP адреса прокси:
nslookup proxy.winitpro.ru
Можно запретить DNS серверу возвращать DNS адреса для определенного пространства имен (домена):
Add-DnsServerQueryResolutionPolicy -Name 'BlockFidhingPolicy' -Action IGNORE -FQDN "EQ,*.cberbank.ru"
To put it simple, you can understand DNS forwarding as a method for DNS server to resolve a query by “asking for a help” from another DNS server. It is supported by on Windows DNS server, including Windows Server 2012 R2. The default behaviour is that Windows DNS Server will forward query that it cannot resolve to a list of public DNS servers on the internet which is called the root hints. But if you Configure DNS Forwarding in Windows Server 2012 R2, then it will forward the query to the designated DNS server which is called the forwarder.
If you install DNS server on Windows Server 2012 R2, you can configure DNS forwarding by using DNS Manager or PowerShell.
Using DNS Manager
On the server where DNS Server role installed, open Server Manager then navigate to Tools > DNS to open up the DNS Manager.

In the DNS Manager, right click the DNS server hostname on the left-pane and select Properties.
Click on Forwarders tab, then click on Edit button.

Enter the IP address of the other DNS server (forwarder) then press Enter. If the IP address is a valid DNS server then it will show green checklist icon as in the picture below. Repeat this for each forwarder servers that you want.

You can click OK to confirm the settings.
Using PowerShell
You can also configure DNS forwarding in Windows Server 2012 R2 by using PowerShell. Below is the command you need to enter in an elevated PowerShell window:
Add-DnsServerForwarder —IPAddress FORWARDER_IP
Alternatively, you can also use the command below:
Set-DnsServerForwarder —IPAddress FORWARDER_IP
You only need to adjust the FORWARDER_IP value to match your configuration plan. You can specify more than one forwarder in a single command by separating each IP address with a comma. Note that there is difference between the two commands above. The “Add” command will append the specified forwarder IP to the existing list of forwarders that you have. Meanwhile, the “Set” command will overwrite the existing forwarders list with the specified IP address.
Here’s example of adjustment in the query that will resulting the same as the previous example:

Verification
To verify that DNS forwarding works, you can attempt to resolve any names that is not in the DNS server data. In this example, our DNS server only has data for names in domain mustbegeek.com. Therefore, now we will test to resolve for domain corp.mbg.com.
Before we have DNS forwarding configured to the authoritative server for domain corp.mbg.com, our DNS clients unable to get the name resolution for corp.mbg.com.

After DNS forwarding configured, our clients able to get the name resolution for corp.mbg.com.

Working with DNS Forwarding in Windows DNS Server
Before you configure DNS forwarding, you should make sure that recursion is not disabled on the server. DNS forwarding requires recursion to request for information from the forwarders on behalf of the client.
By default recursion is enabled on Windows DNS Server but in some case it may be disabled. To check if recursion enabled, you can go to the DNS server properties in the Advanced tab. Then, under Server Options, confirm that no tick mark on the check box for Disable recursion setting.

And that’s all you need to know to configure DNS forwarding in Windows Server 2012 R2.
The following two tabs change content below.
- Bio
- Latest Posts
I am IT practitioner in real life with specialization in network and server infrastructure. I have years of experience in design, analysis, operation, and optimization of infrastructure solutions for enterprise-scaled network. You can send me a message on LinkedIn or email to arranda.saputra@outlook.com for further inquiry regarding stuffs that I wrote or opportunity to collaborate in a project.
This guide is for system administrators running their internal DNS using Windows Server 2016/2019.
When running your own DNS, we recommend configuring CleanBrowsing as a forwarder on your network. This ensure you retain full control of your network, while taking advantage of the filtering our service offers.
What is a DNS Forwarder?
DNS forwarding allows you to designate a third-party to resolve all, or a specific set, of DNS queries from your network while offering the administrator full control of what is happening on the network. Having this type of configuration also allow you to differentiate from internal and external queries, and configure the traffic accordingly.
DNS Forwarder on Windows Server 2016/2019
Configuring a forwarder on the Windows Server 2019 DNS server is a matter of a few clicks.
1 – Open the DNS Manager ( Server Manager > Tools > DNS or dnsmgmt.msc)
2 – Right-click Hostname and select Properties
3 – Click the Forwarders tab and click the Edit button
4 – Enter the IPv4 DNS values provided in your dashboard:
That’s it, click OK and you should see a new Forwarders file appear in the DNS Manager.
As essential parts of a DNS Server, the DNS Forwarders and the DNS Conditional Forwarders are the two topics that we will configure after installing the DNS role and configuring the DNS zones. A DNS Forwarder is responsible for serving external DNS requests. We manually configure the DNS Forwarder on our DNS Server and specify the DNS server(s) it should refer to for any external DNS requests. A DNS Conditional Forwarder resolves the external DNS requests only for a specific domain that we specify. Mainly, we configure it between partners and trusted organisations. With this brief introduction in mind, we will cover how to configure a DNS Forwarder and a DNS Conditional Forwarder in Windows Server 2022. We will cover each one in a separate section following a straightforward step-by-step approach.
Also, read Install DNS In Server 2022 Using Server Manager And Powershell.
Configure a DNS Forwarder in Server 2022
We discussed a brief overview of the DNS Forwarder. In this section, we will go step-by-step to see how we can configure it in a Windows Server 2022.
1. Pull up the DNS Manager console. To do so, press down the Windows Key + R keys on your keyboard. Then, typednsmgmt.mscin the Run dialogue box and hit enter. An alternative way is to navigate through Server Manager >>Tools >> DNS.

2. On the DNS Manager console, select the server name on the left pane and double-click on Forwarders at the right pane.
3. Select the Forwarders tab on the DNS server’s properties, and click on the Edit button, afterwards.

4. Now, add the IP address of the DNS server(s) to which you want to forward the DNS external requests. You can add many DNS servers. As of our example, we have added two Google public DNS servers (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4). Click on a DNS server you have added, and you can set the order or delete it using the buttons on the right pane. Once everything is set, click on the OK button.
5. As you can see in the below picture, our two DNS servers are added to DNS Forwarders. Now our DNS server forwards any external DNS requests to one of these two DNS servers. Finally, Click on OK to close the window.

All right. In five simple steps with picture illustration, we have explained how to configure a DNS forwarder in Windows Server 2022.
Configure a DNS Conditional Forwarder in Server 2022
A Conditional Forwarder, as we discussed earlier, resolves the external DNS requests only for a specific domain. We define that external domain in our DNS server. Our DNS server then resolves the external DNS request only for that domain. It forwards any external DNS requests other than for that domain to the DNS server(s) defined in forwarders or to the DNS servers in the root hint. Having said this stuff, let’s move on and see the steps to configure a DNS Conditional Forwarder in Windows Server 2022.
1. Open up the DNS Manager console (step 1 of the previous section)
2. Expand the DNS server and right-click on Conditional Forwarders. Select the New Conditional Forwarder option from the list.
3. On the New Conditional Forwarder window, first, enter the domain’s name that your DNS server should resolve the request for it. Then, enter the IP address of that domain. Next, if you want to store this conditional forwarder in the active directory, check out the relevant checkbox (labelled 3 in the below picture) and choose the appropriate replication option. Otherwise, leave this option unchecked. Finally, click on the OK button.

These are all the steps required to configure a conditional forwarder on a DNS server with Windows Server 2022. Pretty easy!
Conclusion
Throughout this article, first, we discussed a brief overview of the DNS Forwarder and DNS Conditional Forwarder. Then, in two separate sections, we covered a step-by-step guide on how to configure a DNS Forwarder and DNS Conditional Forwarder in Windows Server 2022.
I hope you find this article helpful in any way. Make sure to share your thoughts and queries in the comment section below.
Read More:
- DHCP PowerShell Commands.
- How To See Wi-Fi Password On Windows 11?
- How To Bypass Windows 11 Requirements?
This article is a step-by-step tutorial on how to configure DNS forwarding in Windows Server 2012 R2 version. In the continuation of this tutorial, we will teach you how to create a DNS forwarder using DNS Manager and PowerShell.
Simply put, DNS forwarding is asking for help finding an address. The default method is that DNS server sends queries that cannot be answered to a list of DNS servers on the Internet called root hints.
But if DNS forwarding is configured, it sends queries to the destination we call the forwarder.
Table of Contents
DNS server installation on Windows Server is done with the help of DNS manager or PowerShell.
How to create a DNS forwarder using DNS Manager
In the server where the DNS server roll is installed, open Sever Manager and then go to Tool> DNS to enter DNS Manager.
Right-click on the DNS Server name and click Properties.
Enter the Forwarder tab and click Edit.
Enter the IP address of the other DNS server (forwarder) and then press Enter. If the IP address is valid, a green tick will be displayed. Do this for each other forwarder server.
Click OK to save the settings.
How to create a DNS forwarder using PowerShell
As we said, you can do this with PowerShell as well. To do this, enter the following command:
Add-DnsServerForwarder –IPAddress < IP Address >The following command is used for the same purpose:
Set-DnsServerForwarder –IPAddress < IP Address >Just enter the relevant IP address to execute the command correctly. You can add multiple forwarders in one command by separating their IP addresses using commas (,). Note that there is a difference between the above two commands. The Add command adds the specified forwarder to the list of forwarders, but the Set command replaces the existing forwarders with the specified IP address.
You can see an example of putting the IP address in the forwarder command in the image below.
How to work with DNS Forwarding on Windows DNS server
Before configuring DNS forwarding, you need to make sure that recursion is not disabled. DNS forwarding requires recursion to request information from forwarders for clients.
By default, recursion is enabled, but in some cases, it may be disabled. To check this, you need to enter the DNS server settings and go to the Advanced tab. Then in the Server Option section, make sure that the disable recursion option is not checked.
Conclusion
This article teaches you how to configure DNS Forwarding in Windows Server 2012 R2 version using DNS manager and PowerShell. Then the steps for creating a DNS forwarder were explained with pictures. If you are interested in MikroTik, you can refer to the DNS configuration tutorial in MikroTik.