Как вы знаете Server Core в Windows Server 2008 не включает в себя традиционный полный графический интерфейс пользователя (GUI).
Как и в стандартной (полной) установке Windows Server 2008, брандмауэр Windows включен по умолчанию, и большинство сетевых портов сразу после установки блокируются. Однако, поскольку основной задачей севера является предоставление некой услуги (будь то некая служба, файл, или что-то другое, что должно быть доступно по сети), вам необходимо разрешить определенный сетевой трафик на брандмауэре.
Одной из причин для открытия входящего трафика на брандмауэре – необходимость дистанционного управления сервером. Как уже упоминалось в предыдущих статьях, вы можете управлять Server Core с помощью локальной командной строки, дистанционно с помощью обычной MMC оснастки, через WinRM и WinRS, и даже через удаленный рабочий стол (хотя вы все равно получите обычное окно командной строки …)
В большинстве случаев после начальной конфигурации сервера, у Вас возникнет необходимость управления ролями и функциями, установленными на сервере, и вероятно, вы захотите использовать MMC-оснастку Administration tools. Есть три сценария удаленного управления через MMC:
- Роль сервера — когда роль сервера установлена на Вашем сервере, соответствующие порты открываются автоматически, позволяя вам удаленно управлять им. Никаких дополнительных настроек не требуется. Установив необходимые оснастки из Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) на вашей полноценной рабочей станции(сервере), вы сможете удаленно управлять сервером с Server Core.
- Сервер член домена — после того как сервер включен в домен, брандмауэр использует преднастроенный доменный профиль, который разрешает удаленное управление. Опять же, никаких дополнительных настроек не требуется.
- Сервер в рабочей группе — это сценарий, в котором потребуется внести изменения в конфигурацию брандмауэра. Если вы просто хотите задействовать все функции удаленного управления, можно использовать следующую команду:
Netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group=“remote administration” new enable=yes
Эта команда разрешает использование большинства методик удаленного управления и разрешает доступ к большинству оснасток MMC. Однако есть оснастки, удаленный доступ к которым настраивается дополнительно:
Диспетчер устройств (Device Manager)
Чтобы разрешить подключаться к диспетчеру устройств, нужно включить параметр политики «Allow remote access to the PnP interface».
Управление дисками (Disk Management)
Для этого на Server Core нужно запустить службы виртуальных дисков (Virtual Disk Service -VDS)
IPSec Management
Вы должны сначала установить удаленное управление для IPSec. Это можно сделать с помощью скрипта scregedit.wsf (он лежит в папке system32):
Cscript scregedit.wsf /im 1
Таким образом, доступ к большинству MMC оснасток удаленного администрирования, включается одним правилом на брандмауэре — Remote Administration firewall rules. Однако зачастую бывает необходимость предоставить доступ только ограниченному числу MMC-оснасток.
В брандмауэре существуют правила не для всех оснасток, в таблице перечислены существующие правила:
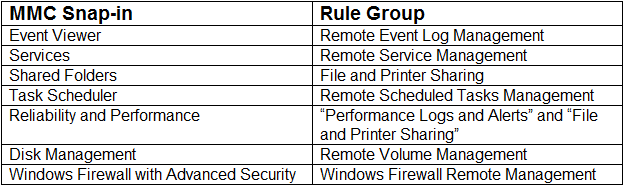
Чтобы включить любую из этих групп, нужно набрать команду:
Netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group=“<rule group>” new enable=yes
Где <rule group> — имя из приведенной таблицы.
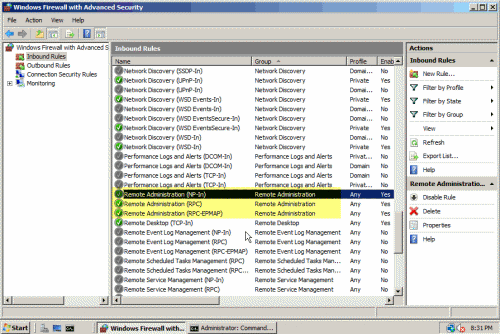
Вы также можете удаленно включить их из брандмауэра Windows, запущенного в режиме Advanced Security. Для просмотра всех правил, просто сделайте сортировку по столбцу “Enable”:
Здравия всем! Для некоторых задач, к примеру сервер AD DS, хватает установки Windows Server без графического ядра. Для первоначальной настройки я предпочитаю отключать встроенный Firewall.
Заходим в наш сервер. Открывается консоль
Введем в консоли команду
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off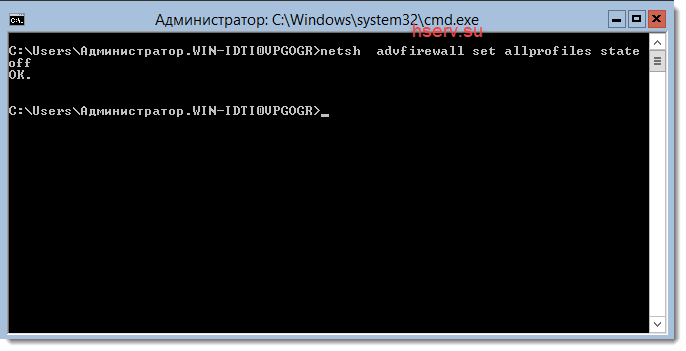
После этого сервер отключит Firewall.
Включение Firewall
Для включение обратная команда
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state on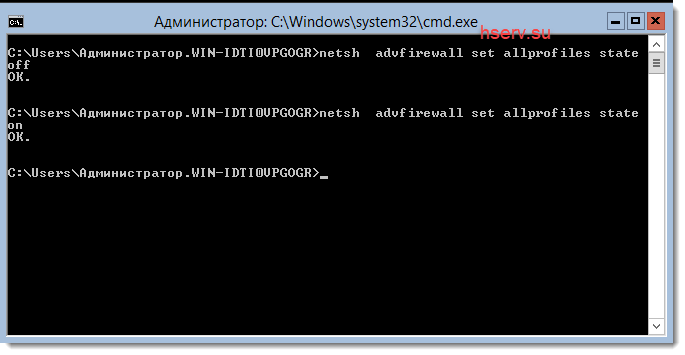
Заключение
Как видим из заметки отключаются все профили Firewall. Я не рекомендую оставлять сервер в таком виде в боевом режиме. Я использую этот режим, только для настройки сервера. После настройки сервера, я настраиваю Firewall и включаю его обратно.
Reading Time: 4 minutes
In Server Core installations of Windows Server 2008 the Windows Firewall is enabled by default. This means it’s locked up by default and offers little weakness towards unfriendly administrators and users. When you want to do something with your Server Core box you might want to open up the Windows Firewall a little bit to allow certain types of traffic.
From the console
First let’s look at managing the Windows Firewall from the Console of your Server Core box.
Disabling the firewall
To completely disable the firewall you can use the following commandline command straight from the console of your Server Core box:
netsh firewall set opmode disable
I should point out you should avoid using this command because it eliminates the firewall as a security measure completely, which is a bad thing. Temporarily disabling the firewall might be useful to troubleshoot network connectivity though. The command to enable the firewall after you successfully troubleshooted the problem is:
netsh firewall set opmode enable
Opening up the firewall
There are three ways to open up the Windows Firewall from the console of your Server Core box, without compromising the security of the system all together. You can:
- Enable specific services
- Open specific ports or specific port ranges
- Allow specific programs
To enable service exceptions
The Windows Firewall in a Server Core installation of Windows Server 2008 comes with a couple of default firewall exceptions. You can enable these exception to allow specific types of traffic through the firewall. For example, to allow File and Printer Sharing you can run the following command:
netsh firewall set service fileandprint
If at any point you need help with the set service command just type netsh firewall set service which will show you some help. Extra command line switches may allow you to specify another firewall profile and/or specify a firewall scope. (all, subnet or custom)
To open specific ports
If your situation demands you open up specific ports to allow incoming traffic through your firewall you can add specific port openings in your firewall. You can specify whether the traffic is UDP or TCP, which port number you’d like to open and which name you’d like to give your portopening, like this:
netsh firewall set portopening protocol=TCP | UDP port=PortnumberHere name=AnyNameHere
If at any point you need help with the set service command just type netsh firewall set portopening which will show you some help. Extra command line switches may allow you to specify another firewall profile and/or specify a firewall scope. (all, subnet or custom)
To allow specific programs
Another way to open up the firewall is to allow specific programs to communicate with the outside world. The Windows Firewall will allow any traffic to the executables you specify. Again you can also specify a name for the rule. Use this command to allow specific programs:
netsh firewall set allowedprogram program=FullPathToExecutable name=AnyNameHere
If at any point you need help with the set service command just type netsh firewall set allowedprogram which will show you some help. Extra command line switches may allow you to specify another firewall profile and/or specify a firewall scope (all, subnet or custom)
Using Advanced Firewall commands
Alternatively you can use the spanking new Advanced Firewall, which enables you to control incoming as well as outgoing traffic, allows you to edit the firewall configuration in offline mode, (so you can change the settings, without committing any changes yet) monitor connections and import/export your firewall configuration.
There’s a nice webpage with more information on the Advanced Firewall functionality here. It shows you how to change settings through the commandline and how to change them using Group Policies.
Through Group Policy
Another way to manage the Windows Firewall on your Server Core box is to use Group Policy Objects. You can edit the local group policy of your Server Core box from a remote Windows box, which is useful if you want to set the settings in a graphical user interface for small amounts of Server Core boxes.
Alternatively you may harness the power of Active Directory, to change the settings on loads of Windows Server 2008 (Server Core) boxes automatically and without loads of administrative effort.
The settings for Windows Firewall are located in the WindowsFirewall.admx Administrative Template are located in the Computer Configuration part of the policy. The template includes the following settings for both the Standard Profile and the Domain Profile:
- Allow Authenticated IPSec Bypass
- Allow ICMP exceptions
- Allow inbound file and printer sharing exception
- Allow inbound remote administration exception
- Allow inbound Remote Desktop exceptions
- Allow inbound UPnP framework exceptions
- Allow local port exceptions
- Allow local program exceptions
- Allow logging
- Define inbound port exceptions
- Define inbound program exceptions
- Do not allow exceptions
- Prohibit notifications
- Prohibit unicast response to multicast or broadcast requests
- Protect all network Connections
Concluding
Completely disabling the Windows Firewall is a tempting way to circumvent the security measures in Windows Server 2008. As an alternative this blogpost shows you how to selectively and gradually open up the Windows firewall from the console of your Server Core box. For the faint of heart I included some hints to edit the local group policy.
Enterprise admins will probably already have a Windows Firewall policy in place, which they only have to adapt to manage Windows Server 2008 Server Core boxes.
Further reading
Group Policy Settings Reference Windows Server 2008 Beta 3
Command line firewall configuration
Netsh Command Line Switches And Examples For Windows 2003 And Windows XP
Wonderful Netsh
Networking and firewall
Managing Windows Firewall with Netsh
Improvements to the Windows firewall in Vista
How to configure the new Windows Server 2008 advanced firewall MMC snap-in
Still Very Much Alive and Kicking – netsh
New Networking Features in Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista
The New Windows Firewall in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008
Using the Netsh Advfirewall Command-Line Tool
Disclaimer Beta Software
The information on this webpage applies to software from Microsoft that was in testing phase but utilizable by experienced users by the time the webpage was written. This software has not been released for sale, distribution or usage for the general public. The information on this webpage and the beta software are provided «as is» without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose.
Windows Server 2019 contains a firewall program called Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security. The firewall filters incoming and outgoing traffic on your Windows Server 2019 instance to safeguard it from common network attacks. By default, the firewall is configured to allow access to all pre-installed system programs.
However, several programs may use multiple different ports for operation, and these will be automatically blocked because they don’t match with the rules in your firewall configuration. In this case, you need to open the specific port on Windows Server.
Prerequisites
- Deploy a Windows Server 2019 Instance on Vultr
- A Remote Desktop Connection App
Establish a connection to your server by logging in through any remote desktop app or click the console on your Vultr dashboard to access your server. After you connect you can start configuring your Windows server 2019 firewall rules.
Turn Windows Firewall ON
By default, Windows Defender Firewall is turned on, but in any case, you should confirm the current status and turn on firewall. To do this, click the tools node under server manager and select Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security from the drop down list.
From the open group policy management window, check the current status of Windows Firewall profiles if it is set to ON; otherwise, click the Windows Defender Firewall properties option and turn the service on per profile.
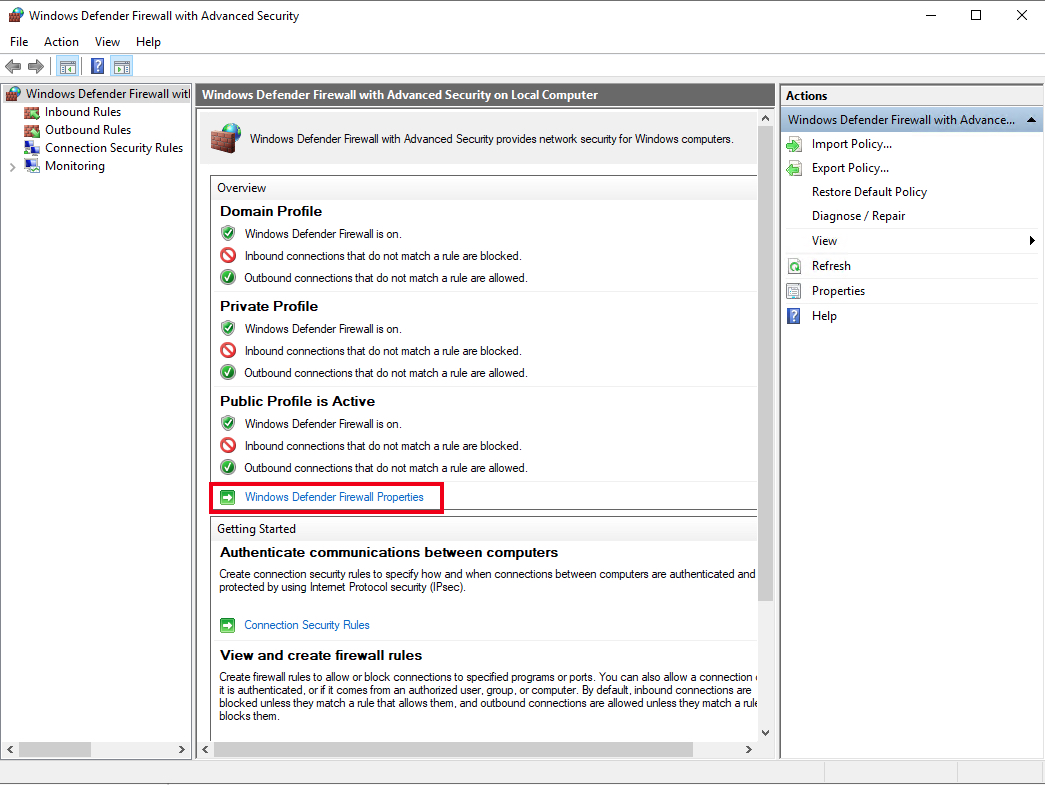
Firewall Rules
Windows Firewall rules allow you to either permit or block specific incoming and outgoing network packets on your server. You can choose multiple parameters for each inbound or outbound rule. A rule can consist of a TCP or UDP port, program name, service, or a protocol to filter for every server profile.
Windows server profiles are grouped into, Domain, Private and Public. Domain represents your server’s connection to a corporate domain network, Private applies to your home or workplace network connection, and Public represents non-secure public network locations.
Open an Inbound Port (Incoming connections)
Launch windows defender firewall from the tools sub-menu under server manager. Then, select Inbound Rules on the left panel of the Firewall console.
A list of current rules will be displayed. Now, on the left Inbound Rules sub-menu under actions, click New Rule.
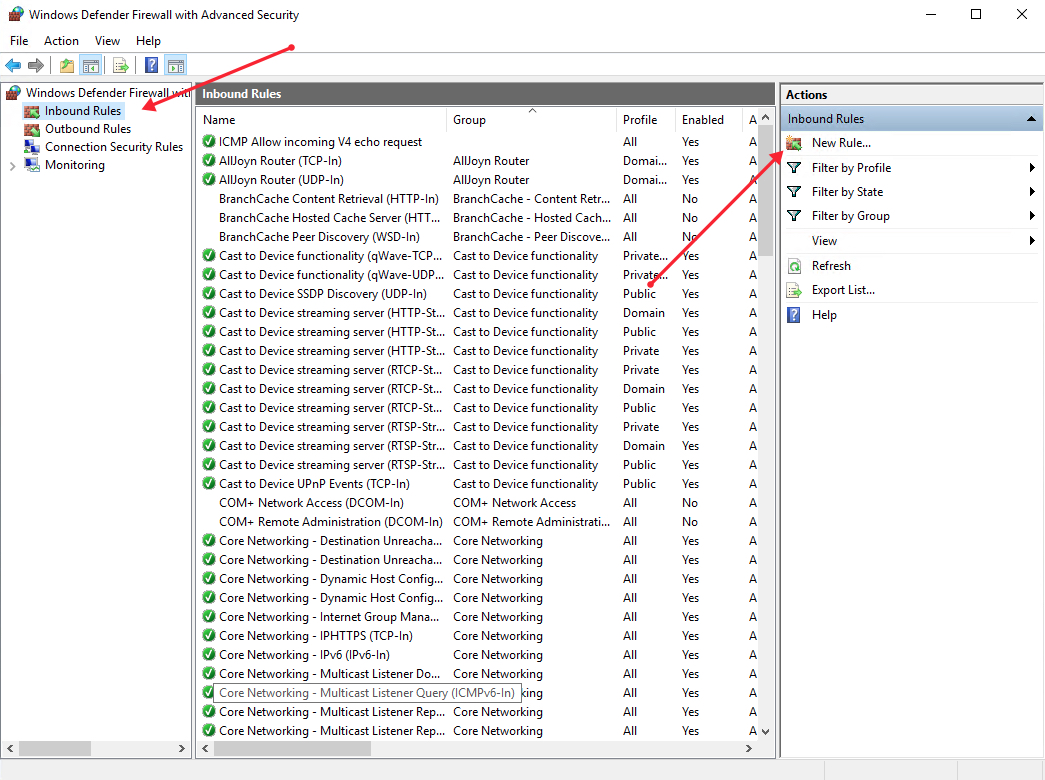
Select Port as the rule type in the rule wizard and click Next.
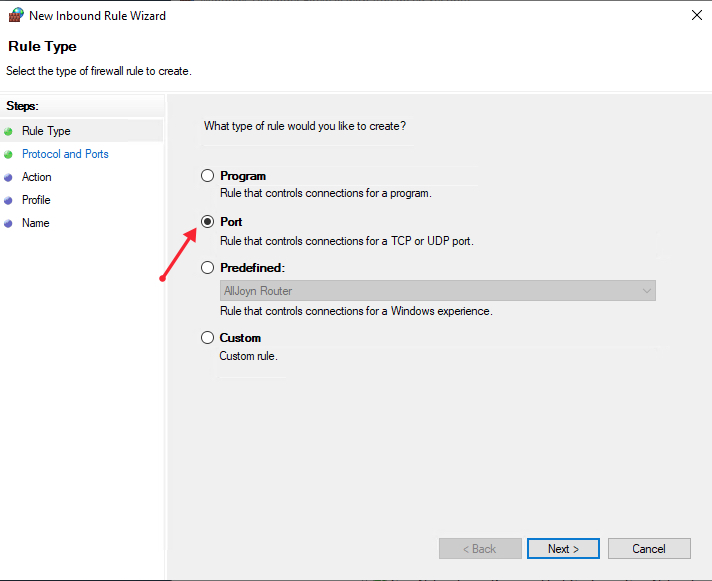
Now, choose whether the new rule applies to a TCP or UDP port on your server. Then, select specific ports and enter your target port number, you can enter a ports range, or multiple ports separated by - and , respectively, then click Next.
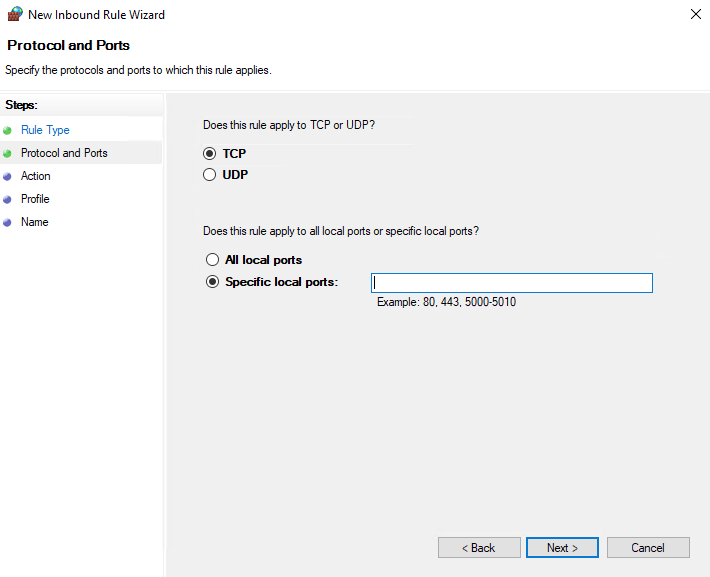
Define your TCP or UDP port rule.
Allow the connectionwill allow incoming connections to the specified server portAllow the connection if it is securewill authenticate with IP security and either deny or allow the connection. For example,httpsconnections will be allowed andhttpblocked.Block the connectionwill block all incoming connections to your server through the specified port
In this case, choose Allow the connection to open the port.
Click Next to assign the new rule to one or more profiles. You can select between Domain, Private, and Public, or choose all to apply the firewall rule on multiple profiles.
Next, give your new firewall rule a custom name and description for easy identification. Then, Click finish to enable the new rule. Your new Inbound (Incoming) port rule will be enabled, and all connections to the server that match the port will be accepted.
Open an Outbound Port (Outgoing connection)
From the Windows Defender Firewall console, click Outbound Rules on the left pane, and a list of available outgoing connection rules will be displayed.
Now, click New Rule on the right pane under the outbound rules node.
In the new outbound rule wizard, select Port as the rule type and click Next.
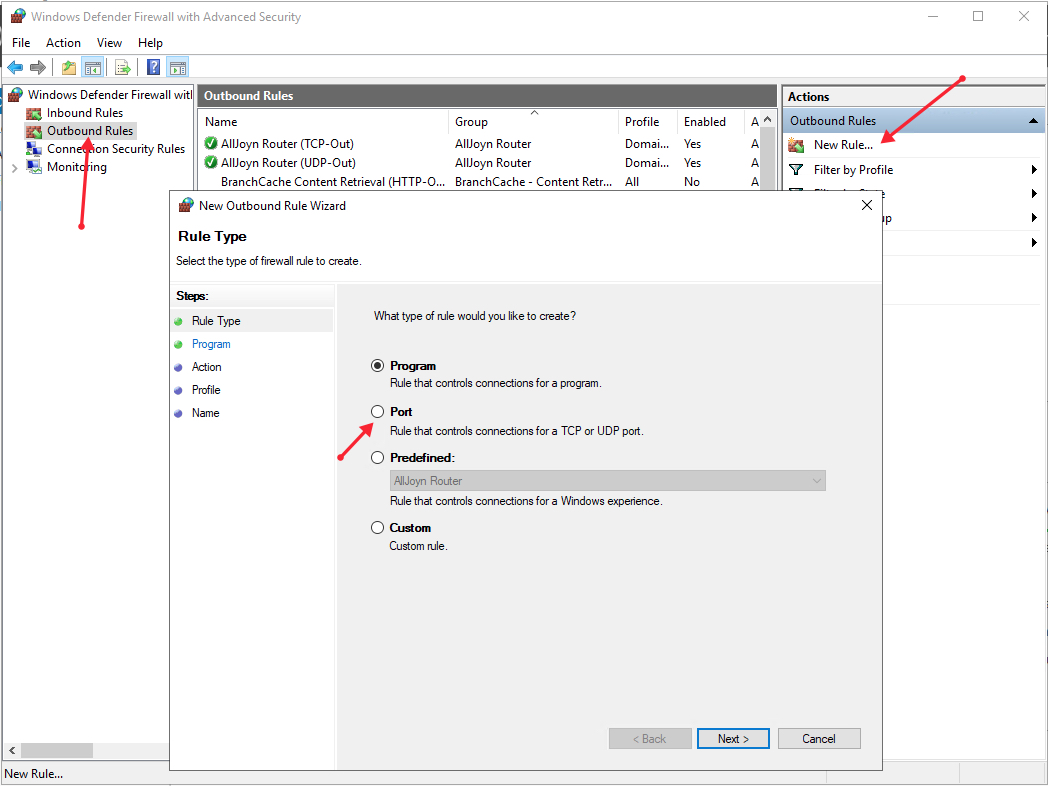
Now, let’s choose whether the new rule applies to a TCP or UDP port. Then, select specific remote ports and enter the target server port number; you can enter a range of ports, a single port, or multiple different ports you intend to open.
Next, on the Action page, select Allow the connection, then click next to select the server profile on which the rule should be enabled.
Give the new outbound rule a name and description that uniquely describes it. Then, click Finish to enable the outbound rule for the target port to be open on all selected server profiles.
Open a Port through Windows PowerShell
From the Windows start menu, open PowerShell. Then, edit the following command and replace it with your settings.
New-NetFirewallRule -Enabled:True -LocalPort 21 -Protocol TCP -Direction Inbound -Profile Domain -Action Allow -DisplayName example opening a port rule" New-NetFirewallRuleCreates a new Firewall rule.EnabledThis enables the new rule, by default, it will be set to True.LocalPortYour target port number.ProtocolSpecifies the protocol associated with your port number.DirectionSets your target direction to either Inbound (Incoming) or Outbound (Outgoing).ProfileAssigns the new rule to a server profile; you can choose domain, private, or public.Actiondefines the state for the new firewall rule, enter allow.DisplayNamesets a custom name for the new firewall rule
Your Output should be similar to the one below.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> New-NetFirewallRule -Enabled:True -LocalPort 21 -Protocol TCP -Direction Inbound -Profile Domain -Action Allow -DisplayName "example opening a port rule"
Name : {427a1b12-ece6-4d54-847d-de482b227c6c}
DisplayName : example opening a port rule
Description :
DisplayGroup :
Group :
Enabled : True
Profile : Domain
Platform : {}
Direction : Inbound
Action : Allow
EdgeTraversalPolicy : Block
LooseSourceMapping : False
LocalOnlyMapping : False
Owner :
PrimaryStatus : OK
Status : The rule was parsed successfully from the store. (65536)
EnforcementStatus : NotApplicable
PolicyStoreSource : PersistentStore
PolicyStoreSourceType : LocalCongratulations, you just opened a network port on your Windows Server 2019. The server will accept incoming and outgoing connections through the selected ports, but the firewall will block connections from a profile that doesn’t match the port rule.
Introduction
Firewalls are a critical component of securing modern networks with internet access. Without firewalls in place, malicious actors could easily access and infect devices on a network. Properly configured firewalls substantially reduce undesirable communications.
This article explains how to create firewall rules using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console and Windows PowerShell on Windows Server 2016 / 2019 / 2022.
What is a Firewall?
A firewall controls the flow of data packets in and out of a network. It acts like a barrier, similar to how a physical firewall prevents the spread of fire between compartments. The firewall allows or blocks connections according to configured firewall rules.
Computers behind a firewall cannot receive data until it passes the filters. This greatly enhances security and reduces unauthorized access risks. Benefits of firewalls:
- Protect devices by blocking undesired traffic
- Notify administrators of connection attempts
- Log activity for monitoring
- Prevent spread of infections
- Reduce hacking risks
How Windows Server 2016 / 2019 / 2022 Firewalls Work
The Windows firewall acts as a barrier between local network devices and external networks. When a connection is attempted to a server, the firewall intercepts the traffic and evaluates it against the defined rules.
Only network packets that match the configured rules are allowed through. For example, a rule could allow TCP traffic on port 80 while blocking other ports. Carefully configured rules optimize security while allowing desired connections.
Windows provides inbound rules to control incoming traffic and outbound rules to filter outgoing traffic. Rules can be tailored for each network profile.
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
Windows Firewall with Advanced Security provides the management interface for configuring Windows firewall settings. It comes built-in to Windows Server without needing additional licensing or hardware.
There are three default firewall profiles:
- Domain – For corporate networks with detected domain controllers
- Private – For home or office networks behind a gateway device
- Public – For untrusted public networks with internet access
Profiles allow custom rules per network type. You can enable, disable, or configure profiles independently.
Accessing the Firewall Console
To open the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security console:
- Open Server Manager > Tools > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
- Search for “firewall” in the Start menu and launch the Windows Firewall shortcut
- Run wf.msc in the Run command (Win + R)
The left menu allows configuring inbound rules, outbound rules, connection security, and monitoring.
Configuring Firewall Rules
Firewall rules control whether to allow or block specific network connections. Rules can filter by:
- Program path
- Port and protocol
- Predefined service
- Source/destination IP
- Network interface
- And more…
Follow these steps to create an inbound firewall rule:
1. Open the Firewall console and select Inbound Rules
2. Click New Rule to launch the rule wizard
3. Select the rule type – Program, Port, Predefined, or Custom
4. Choose All Programs or a Program path
5. Choose Action (allow or block) or allow if connection is secured
6. Choose profiles
7. Name the rule and click Finish
Repeat the wizard for outbound rules. Once created, rules can be edited or disabled from the console.
Rules can also be created from PowerShell. For example:
PS C:\Users\Administrator> New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "Allow SSH" -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 22Monitor active connections under the Monitoring tab.
Conclusion
The Windows Firewall provides a flexible and granular rule-based firewall solution for Windows Server 2016, 2019 and 2022. The advanced interface allows creating detailed rules to filter incoming and outgoing traffic as needed. Monitor activity to verify your rules are working correctly. Careful configuration enhances security while allowing desired connections.
