If you have servers running the Server Core version of Windows Server, you may need to look at what devices and drivers are installed. While you can accomplish this task with various command line tools, the command line tools are difficult to use. Instead, with a bit of configuration work, you can use the familiar Device Manager GUI remotely.
To do this, you’ll need to configure a Group Policy setting for the affected servers:
Computer Configuration \ Policies \ Administrative Templates \ System \ Device Installation \ «Allow remote access to the Plug and Play interface”
Set the value to enabled:

If you don’t do this, you’ll get an error similar to the following:
—————————
Device Manager
—————————
Unable to access the computer SERVER01
Make sure that this computer is on the network, has remote administration enabled, and is running the «Plug and Play» and «Remote registry» services.The error was: Access is denied.
—————————
OK
—————————
Once you’ve got things in place and the policy is effective, you can use Computer Management to target a remote machine and use the Device Manager snap-in:
—————————
Device Manager
—————————
Device Manager is running in read-only mode because you are running it on a remote computer. To uninstall devices or to change device properties or drivers, you must run Device Manager on the computer where you wish to make changes.
—————————
OK
—————————
You won’t be able to make changes, but, you’ll certainly be able to view all of the relevant details.
To enable remote management on a new server 2016 core install I run the following PowerShell commands: Enable-PSRemoting Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName «Windows Management Instrumentation (DCOM-In)»
Full
Answer
How do I enable server manager on a remote server?
To enable your local server to be managed by Server Manager running on a remote server, run the Windows PowerShell cmdlet Configure-SMRemoting.exe –Enable. You can use many snap-ins for Microsoft Management Console (MMC) remotely to manage your Server Core server.
How do I use remote desktop to manage a Server Core?
You can use Remote Desktop to manage a Server Core server from remote computers. Before you can access Server Core, you’ll need to run the following command: This enables the Remote Desktop for Administration mode to accept connections.
How to administer the server core installation from a remote MMC?
Here are some netsh commands that will help you administer your Server Core installation remotely through MMC snap-ins. To administer the Server Core installation from a remote MMC you must configure the Windows Firewall. If you do not configure the firewall to allow remote administration via MMC you will get an error. For example:
How can I use PowerShell remoting to connect to core server?
We can now use PowerShell remoting to connect to our Core server, which is lucky since we need to do a couple of other bits. We need to configure the firewall for file and print sharing, allow remote access for local accounts, and enable remote firewall management. We can now browse the folders on our Core server.
How do I access Device Manager remotely?
To open Device Manager on a remote computer:Open Computer Management (compmgmt. msc).On the Action menu, click Connect to another computer.In the Select Computer dialog box, do one of the following: In the Another computer text box, type the name of the computer to access, and then click OK.
How do I access Device Manager in Windows Server 2016?
Select Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then select Computer Management. Under System Tools in the console tree, select Device Manager. The devices that are installed on your computer are listed in the right pane.
How do I access Server Core remotely?
Start an MMC snap-in, such as Computer Management. Right-click the snap-in, and then click Connect to another computer. Type the computer name of the Server Core server, and then click OK. You can now use the MMC snap-in to manage the Server Core server as you would any other PC or server.
How do I get to the Device Manager in Windows core?
Go to Local Computer Policy / Computer Configuration / Administrative Templates / System / Device Installation and enable «Allow remote access to the PnP interface». Reboot the Server Core box. You should then be able to connect with Device Manager.
How do I open Device Manager on server?
Start device managerOpen the “Run” dialog box by pressing and holding the Windows key, then press the R key (“Run”).Type devmgmt.msc.Click OK .
How do I log into Device Manager as administrator?
Old thread, but thought I’d give me two-pennies worth.Right-click an empty space on the desktop.New > Shortcut.In the Create Shortcut Wizard, type «devmgmt.msc» > click «Next»Name it «Device Manager» > click «Finish»A shortcut will appear on your desktop.Right-click the shortcut and select «Run as Administrator»
What utility can you use to enable remote management on a Server Core installation of Windows Server?
Managing Server Core with Server Manager With Server Manager, you can manage many aspects of the Windows Server Core installation, including installation and removal of Roles & Features. To get to the Server Manager utility, you can type servermanager.exe from a run or cmd window.
How do I open MMC on a remote computer?
StepsTo open the MMC on your Windows server, in Windows Explorer, right-click the icon for the local computer and select Manage.On the left panel, select Computer Management.Select Action > Connect to another computer. … Type the name of the storage system or click Browse to locate the storage system.Click OK.
How do I open Failover Cluster Manager in Windows Core 2016?
From the OS of any of the nodes:Click Start > Windows Administrative tools > Failover Cluster Manager to launch the Failover Cluster Manager.Click Create Cluster. … Click Next. … Enter the server names that you want to add to the cluster. … Click Add.Click Next. … Select Yes to allow verification of the cluster services.More items…
How do you get to Device Manager on Dell?
Run Box MethodTo open Device Manager. Press the Windows logo key and the R key simultaneously. This should open a Run Box (Figure 1). Figure 1.Type: devmgmt.msc.Click OK or press the Enter key.Device Manager will then open (Figure 2). Figure 2.
Why my Device Manager is not opening?
Press the Windows Start button and select PC Settings. Click Update & Security and then select Troubleshoot on the left-hand side. Next, click the View additional troubleshooters option on the right-hand side. Select the Hardware and Devices troubleshooter and then press Run the troubleshooter.
How do I access another computer on my network using CMD?
Type «mstsc /console /v:computername» into Command Prompt, with the specific computer name you wrote down earlier in place of «computername.» This entry takes you straight to the login screen for your remote computer. After you log on, you can use the remote machine as if it is the one you’re sitting infront of.
How do I open Device Manager from Command Prompt?
You can also open Device Manager through a command prompt or the “Run” window. First, press Windows+R to open a “Run” window. In the “Open:” text box, type devmgmt. msc and then click “OK.” Device Manager will appear.
Why my Device Manager is not opening?
Press the Windows Start button and select PC Settings. Click Update & Security and then select Troubleshoot on the left-hand side. Next, click the View additional troubleshooters option on the right-hand side. Select the Hardware and Devices troubleshooter and then press Run the troubleshooter.
What folder is Device Manager in?
System32 subfoldermsc. This means that you can use it directly by double-clicking (or double-tapping) on it to launch Device Manager. But where is it found? The answer: in the System32 subfolder of the Windows folder on your computer.
How do I open administrative Device Manager in CMD?
You can also run Device Manager as an admin by using Run commands. To open the Run window, simultaneously press the Windows and R keys on the keyboard. Once the Run window opens, type “devmgmt. msc” in the field labeled “Open.” Then, press enter to open the Device Manager.
What is the option 3 in Sconfig?
Interesting Enough, under sconfig, then 4) configure remote management. There’s an option 3 to enable server response to Ping.
Does Server Manager work on 2016+?
Otherwise «Server Manager» Seems to work for most things. Same common things apply like Device Manager not being able to be access, needs a GPO setting which AFAIK isn’t even configurable anymore on 2016+ servers.
Does disk management require VDS?
And yes Disk Managment requires VDS service to be started (its not started by deafult and needs to be enabled «net start vds» and «sc config vds start=auto» to set it to start from boot.
Can you run PowerShell commands on Remote Desktop?
Other than that you can enable Remote Desktop, and do an RDP session and run commands or PowerShell Cmdlet natively.
Can you change the settings on a firewall?
You cannot make any changes to the settings. Before you can make any changes to the firewall settings remotely you must first enable remote administration of the firewall by typing the following command at a command prompt:
Do you need permissions to run advfirewall?
In order to run the Netsh advfirewall commands you must have the correct permissions.
Do MMC snap ins need firewall?
Some snap-ins will require more configuration before you can connect to them through a firewall. Also, some MMC snap-ins do not have an associated rule group that allows connections through firewalls. If you look at the chart above you will see Disk Management and its corresponding rule group.
Can you configure a firewall to allow remote management?
Once the firewall has been configured for remote administration you can began to allow remote management through MMC snap-ins. You can configure the firewall to allow remote management via all MMC snap-ins or you can specify particular MMC snap-ins.
What command line version of device manager is used in PowerShell?
They suggest using PowerShell Device Management Cmdlets. Personally I use devcon.exe which is a command line version of device manager. So far everything I needed to do was possible with it, and it is nice, because you can use it in your setup-script.
What is a group policy setting that allows remote access to a machine?
Then there is actually a group policy setting that handles whether or not you are able to remotely access a machine‘s plug and play service (which is what device manager actually connects to) its under Computer ConfigurationPoliciesAdministrative TemplatesSystemDevice Installation and it’s called «Allow remote access to the Plug and Play interface».
What is server role?
Server Roles – When a server role is installed on the server, the appropriate ports are automatically opened to allow the role to function, as well as to allow remote management. No additional configuration is required. Using the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) feature on a full server installation, you can install just the MMC snap-ins for a role and use them to remotely manage the role on Server Core.
Where do you start the Virtual Disk Service?
You must first start the Virtual Disk Service (VDS) on the Server Core installation
Can MMCs remotely manage the box?
But, as the blog describes, it is possible to be more granular and only allow certain MMC snap-ins to remotely manage the box. There may be situations where you would only want to allow certain MMCs to connect for remote administration.
Does every MMC snap-in have a firewall?
Not every MMC snap-in has a firewall group, here are those that do:
Does Server 2008 include GUI?
As you already know by now, in Windows Server 2008, Server Core installation does not include the traditional full graphical user interface (GUI). Read more about Server Core on my “ Understanding Windows Server 2008 Server Core ” article.
Can you remotely enable Windows firewall?
You can also remotely enable these using the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security MMC snap-in. Read my “ Remotely Managing Windows 2008 Server Core Firewall ” article. When looking at the server’s firewall settings you’ll notice that the rules can be sorted by the Group column, making it easier for you to see which group was enabled and which one wasn’t:
What port does RDP listen to?
By default, the RDP server component listens for incoming connections on TCP port 3389 by default, although this can be changed by the administrator for security reasons.
What is the RDP client?
Windows Client and Windows Server both include the Microsoft RDP client, called Remote Desktop Connection. My favorite way to invoke this tool is to:
What is RDP in Windows?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a Microsoft-proprietary remote access protocol that is used by Windows systems administrators to manage Windows Server systems remotely. What sets RDP apart from, say, Windows PowerShell or Secure Shell (SSH) remoting is the presence of the full graphical desktop, as shown in Figure 1.
What is remote desktop hyperlink?
The Remote Desktop hyperlink is simply a shortcut to the System Properties sheet from the System Control Panel item. Select Allow remote connections to this computer, and optionally enable Allow connections only from computers running Remote Destkop with Network Level Authentication (recommended).
Can you use RDP on Windows Server 2016?
Regardless, many admins are accustomed to RDP-based remote administration, and seek to do so even in the newly released Windows Server 2016 operating system. Let’s learn how to enable RDP in Server 2016 (tl;dr: the process is identical to Windows Server 2012 R2).
Does Windows Server 2016 have RDP?
If you’ve configured RDP on previous Windows Server versions, then you’ll find that Windows Server 2016 behaves the exact same way. Keep in mind, however, that Microsoft’s ever-widening embrace of «assume breach» security posture and the hybrid cloud scenario and its accompanying » manage herds, not pets » philosophy means the emphasis is on command-line automation rather than on-off RDP GUI sessions.
Can you customize the membership in the servers’ built-in Remote Desktop Users group?
You can customize the membership in the servers’ built-in Remote Desktop Users group; members of this group can establish RDP sessions to the server. Note that the local Administrators group (and, by extension, the Domain Admins global group) is automatically granted this privilege in Active Directory.
Popular Posts:
What is Device Manager
Device Manager in Windows Server Operating Systems is a system tool which is used to manage the device drivers. Click the following link to learn what is device driver software. Device manager tool can be used to add new hardware, view installed devices, remove a device, uninstall a driver, manage driver settings and manage device resource settings.
Device Manager system tool is shown in below screenshot.
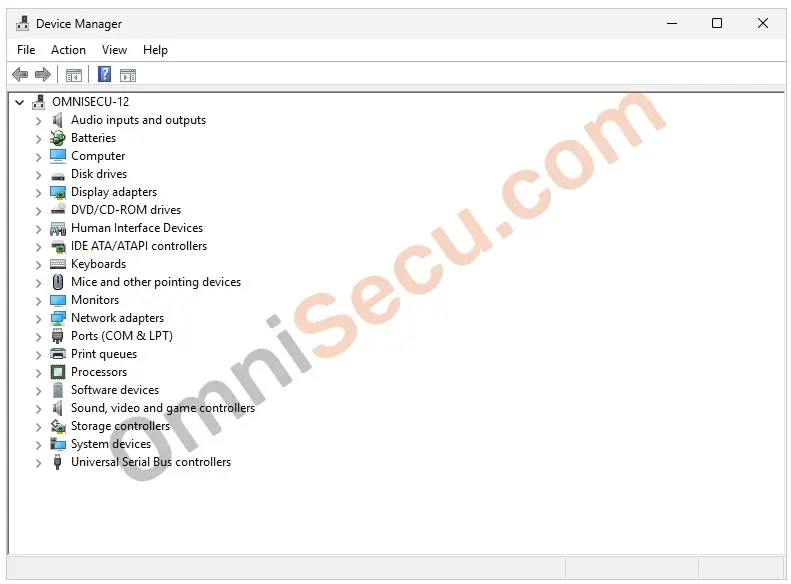
How to open Device Manager
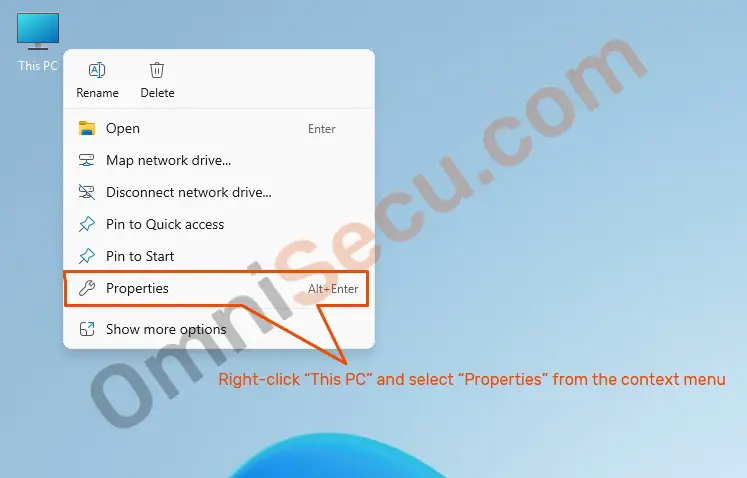
1 — Open Device Manager from System Properties
Step 01 – Right–click «This PC» and select «Properties» from the context menu.
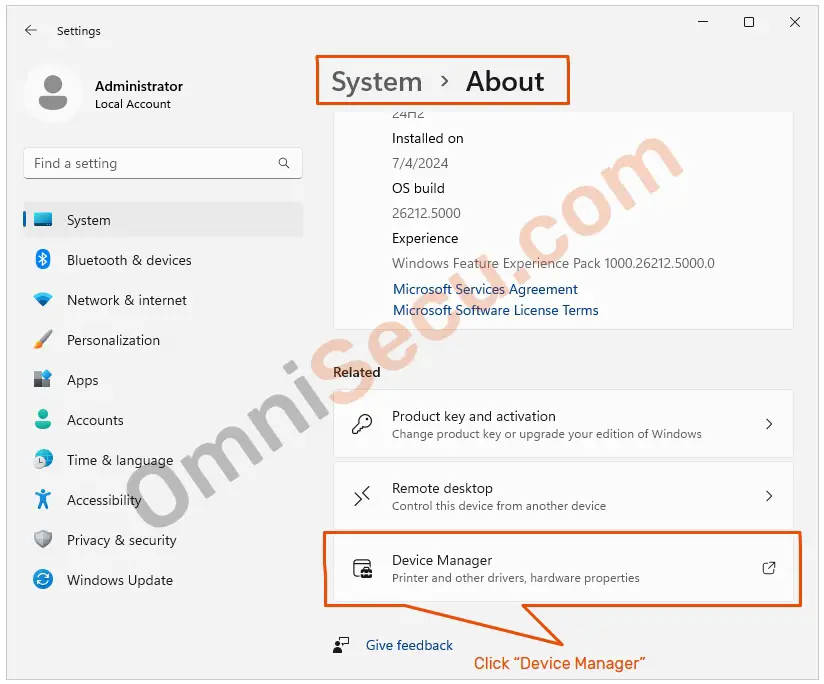
Step 02 – Click «Device Manager» from Systen > About tab, as shown in below image.
Device Manager system tool will be opened as shown in below screenshot.
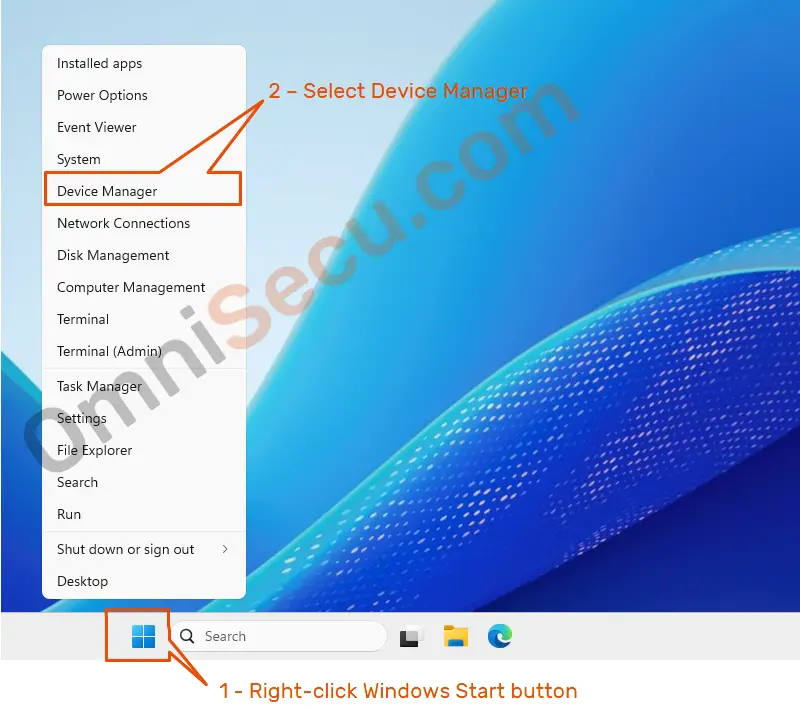
2 — Open Device Manager from Windows Start Button
Right–click Windows Start button and select «Device Manager» from the context menu, as shown in below image.
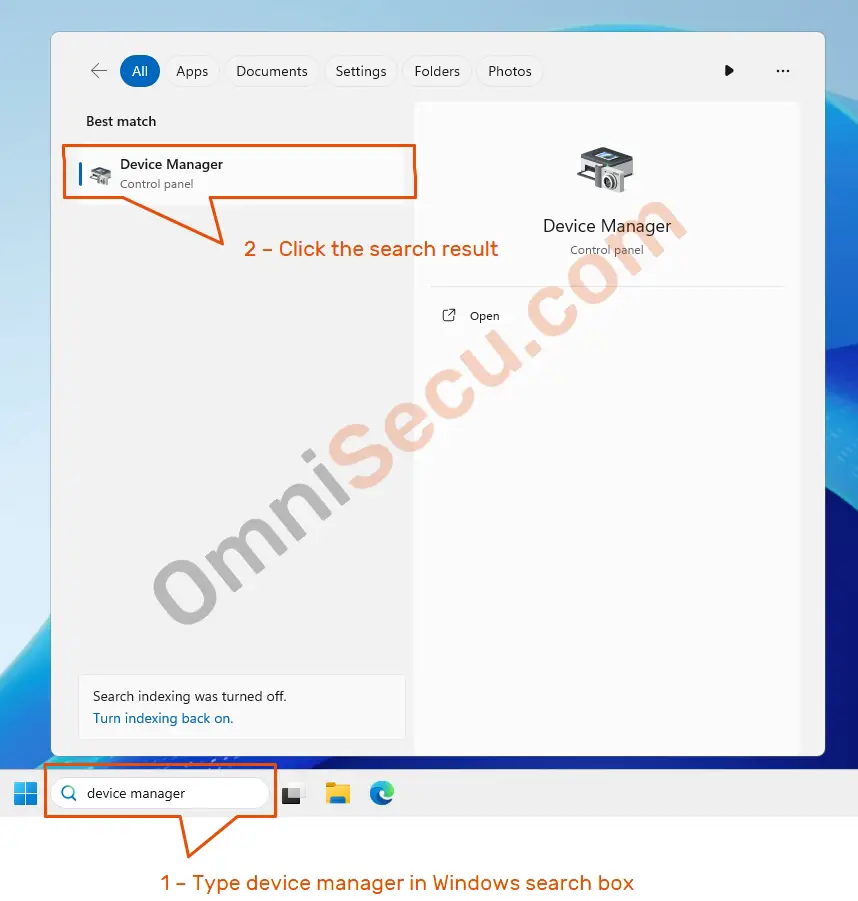
3 — Open Device Manager from Windows Search box
Type «device manager» inside Windows Search box and then click «Device Manager» from the Windows search results, as shown in below image.
Written by Jajish Thomas.
Last updated on 12th July, 2024.
В предыдущей статье я рассказал про установку Windows Server Core, теперь о том, как управлять серверами развернутыми в core. Сервера, с которых будет выполнятся администрирование будем называть source, а сервера которые будем администрировать – target.
Target и source могут входить как в домен, так и в рабочую группу. Source может быть рабочим ПК администратора и работать под управлением Windows 7/8/8.1/10 с установленным пакетом RSAT соответствующей версии.
Рабочий ПК администратора не должен быть единственным местом откуда инфраструктурой можно управлять, его можно дополнить высокодоступным сервером размещенным в Microsoft Azure или Amazon, но их точкой отказа будет Интернет-канал.
Кроме RSAT, управлять серверами можно с помощью PowerShellWebAccess, но это скорее дополнительная возможность на случай недоступность RSAT. О настройке PSWA Вы можете почитать в моей статье “Настройка PowerShell Web Access“.
Перейдем непостредственно к настройке удаленного управления.
Чтобы посмотреть текущее значение удаленного управления на target можно выполнить:
Configure-SMRemoting.exe -get
Для удаленного управления, на целевом сервере должен быть настроен WinRM, его текущую конфигурацию можно запросить так:
winrm get winrm/config
Обратите внимание, Device Manager недоступен для удаленного управления в любых сценариях:

А все дело в том, что Microsoft “выпилила” удаленный доступ к PnP из соображений безопасности – http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2781106/en-us
Вместо этого, предлагается использовать PowerShell – http://blogs.technet.com/b/wincat/archive/2012/09/06/device-management-powershell-cmdlets-sample-an-introduction.aspx
Если Вам все-таки нужнен полноценный Device manager, вам придется установить хотя бы minimal GUI (о том, как это сделать написано выше).
Создадим и распространим на source и на target групповую политику, которой включим правила Firewall Remote Event Log Management, Remote Service Management, Windows Firewall Remote Management, Remote Volume Management:

В кажом правиле можно указать с каких сетей (лучше выделить админов в отдельную сеть, чем указывать список IP админских машин) разрешен этот трафик, на каких профилях и т.д. Хорошим вариантом будет использование IPSec.
Этот вопрос важен и требует индивидуального планирования чтобы, с одной стороны, минимизировать возможности атак, а с другой стороны, обеспечить возможность администрирования из нескольких мест, вт.ч. на случай аварии.
Если вас интересует управление Windows Firewall с помощью PowerShell рекомендую эту статью.
Теперь рассмотрим сценарий когда source находится в домене, а target в рабочей группе. В начале нужно убедится что source и target корректно разрешают fqdn и netbios имена друг друга, если нет – нужно поправить это в DNS. Как и в большинстве случаев, предпочтительно использование fqdn имен.
После этого, на source нужно добавить имя target в TrustedHosts:
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Value %target_fqdn% -Concatenate -Force
После этого, можно будет использовать PowerShell remote sessions.
Вы можете посмотреть содержимое TrustedHosts:
Get-Item -Path WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts | fl Name, Value
.. и очистить его содержимое при необходимости:
Clear-Item -Path WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts
Теперь доступ к target есть по PowerShell, bus воспользуемся им чтобы включить на target таке правила firewall:
Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Windows Remote Management" -Enabled True -RemoteAddress "192.168.1.0/24" Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Remote Event Log Management" -Enabled True -RemoteAddress "192.168.1.0/24" Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Remote Service Management" -Enabled True -RemoteAddress "192.168.1.0/24" Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Windows Firewall Remote Management" -Enabled True -RemoteAddress "192.168.1.0/24" Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Remote Volume Management" -Enabled True -RemoteAddress "192.168.1.0/24" Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "File and Printer Sharing" -Enabled True -RemoteAddress "192.168.1.0/24"
Чтобы снять ограничения которые накладывает UAC на target нужно выполнить:
New-ItemProperty -Name LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy -path HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System -propertyType DWord -value 1
Теперь можно добавить target в ServerManager на source и, а затем нужно выбрать опцию “Manage As..” и ввести учетные данные администратора target

Последний сценарий – когда source находится в рабочей группе, а target в домене – аналогичен предыдущему, и не требует дополнительных комментариев.
Если вам нужно управлять старыми версиями Windows Server, это сделать можно, 2012R2 и 2012 добавляются без проблем, а вот на 2008R2 и 2008 нужно будет поставить WMF 3.0 + Hotfix + выполнить:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned Enable-PSremoting -Force
После этого (само собой нужно включить правила firewall, о которых выше) серверами 2008 и 2008R2 можно будет ограниченно управлять, но нельзя, например, устанавливать роли и фичи.
Вообще, запускать скрипты без цифровой подписи в рабочей инфраструктуре не очень хорошо, поэтому есть смысл поставить политику AllSigned:
Set-ExecutionPolicy AllSigned
Если серверов больше чем несколько, есть смысл сделать это через групповую политику (Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows PowerShell):

Вот еще наглядный пример, почему большинство задач желательно выполнять через Remote Access:


Для подписи скриптов я буду использовать Comodo Code Signing certificate:

Для подписывания используется командлет Set-AuthenticodeSignature :

Подписанный скрипт будет выглядеть следующим образом:

При запуске необходимо будет принять решение по издателю, я обычно использую Run once – работая с большим количеством скриптов от коллег это становится необходимостью.

Если вы используете для подписывания самозаверенный сертификат его нужно будет добавить на все сервера где планируется запуск подписанных им скриптов.
Так что самозаверенные сертификаты, как всегда, лучше не использовать.
Добавление Windows Sever 2003 я не описываю т.к. во-первых в нем потолок PS 2.0, во-вторых его поддержка заканчивается в обозримом будущем, а в-третьих за годы его эксплуатации процессы управления наверняка налажены и менять их нецелесообразно.

Новый Server Manager сделал большой шаг перед на пути к выполнению массовых операций, но на практике PowerShell более функционален.
Команду на удаленном компьютере можно выполнить указав в Invoke-Command -ComputerName (по-умолчанию Invoke-Command добавляется ко всем командлетам выполняемым локально):

Если команду нужно выполнить на нескольких сервера, откроем на них сессии и выполним операции на каждом параллельно:

Можете посмотреть разницу в скорости выполнения командлетов:

Подробнее про управление:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831456.aspx
… старыми версиями –
http://blogs.technet.com/b/servermanager/archive/2012/09/10/managing-downlevel-windows-based-servers-from-server-manager-in-windows-server-2012.aspx
Надеюсь озвученная информация будет полезной, а если нужна будет помощь — используйте форму на главной странице моего сайта.
