Applies ToWindows 10, version 1809, all editions Windows Server version 1809 Windows Server 2019, all editions
Version:
Windows 10, version 1809, Windows Server, version 1809, and Windows Server 2019
March 8, 2019 11:15 PM PST
Windows Update customers were recently affected by a network infrastructure event on January 29, 2019 (21:00 UTC), caused by an external DNS service provider’s global outage. A software update to the external provider’s DNS servers resulted in the distribution of corrupted DNS records that affected connectivity to the Windows Update service. The DNS records were restored by January 30, 2019 (00:10 UTC), and the majority of local Internet Service Providers (ISP) have refreshed their DNS servers and customer services have been restored.
While this was not an issue with Microsoft’s services, we take any service disruption for our customers seriously. We will work with partners to better understand this so we can provide higher quality service in the future even across diverse global network providers.
If you are still unable to connect to Windows Update services due to this problem, please contact your local ISP or network administrator. You can also refer to our new KB4493784 for more information to determine if your network is affected, and to provide your local ISP or network administrator with additional information to assist you.
Windows 10, version 1809, Windows Server, version 1809, and Windows Server 2019 re-released
On November 13, 2018, we re-released the Windows 10 October Update (version 1809), Windows Server 2019, and Windows Server, version 1809. We encourage you to wait until the feature update is offered to your device automatically. A summary of the current status of the October Update can be found below.
Note for Commercial Customers: November 13 marks the revised start of the servicing timeline for the Semi-Annual Channel (“Targeted”) releasefor Windows 10, version 1809, Windows Server 2019, and Windows Server, version 1809. Beginning with this release, all future feature updates of Windows 10 Enterprise and Education editions that release around September will have a 30-month servicing timeline.
For more information about the update and how to get it, see:
-
Resuming the rollout of the Windows 10 October 2018 Update
-
Windows 10 Quality approach for a complex ecosystem
-
Windows 10, version 1809 rollout resumes; now available on VLSC
-
How to get the Windows 10 October 2018 Update
-
Windows 10 Release Information
-
Windows lifecycle fact sheet
Updates for Windows 10, version 1809
On the left side of this page, you’ll find a list of all the updates released for this version of Windows. You can also find more information about releases and any known issues. Installing the most recent update ensures that you also get any previous updates you might have missed, including any important security fixes.
Current status of Windows 10, version 1809, Windows Server, version 1809, and Windows Server 2019
Windows 10, version 1809 rollout status as of March 28, 2019
-
Available for any user who manually selects “Check for updates” via Windows Update.
-
Designated for broad deployment and Semi-Annual Channel for servicing status (recommended option).
For the most up-to-date information about Known Issues for Windows and Windows Server, please go to the Windows release health dashboard.
Notes and messages
General
IMPORTANT Starting in July 2020, we will resume non-security releases for Windows 10 and Windows Server, version 1809 and later. There is no change to the cumulative monthly security updates (also referred to as the «B» release or Update Tuesday release). For more information, see the blog post Resuming optional Windows 10 and Windows Server non-security monthly updates.
IMPORTANT Starting in July 2020, all Windows Updates will disable the RemoteFX vGPU feature because of a security vulnerability. For more information about the vulnerability, seeCVE-2020-1036 and KB4570006. After you install this update, attempts to start virtual machines (VM) that have RemoteFX vGPU enabled will fail, and messages such as the following will appear:
If you re-enable RemoteFX vGPU, a message similar to the following will appear:
-
“The virtual machine cannot be started because all the RemoteFX-capable GPUs are disabled in Hyper-V Manager.”
-
“The virtual machine cannot be started because the server has insufficient GPU resources.”
-
«We no longer support the RemoteFX 3D video adapter. If you are still using this adapter, you may become vulnerable to security risk. Learn more (https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2131976)”
End of servicing
IMPORTANT Windows 10, version 1809 reached end of service on November 10, 2020 for devices running Windows 10 Home, Pro, Pro for Workstation, and IoT Core editions. These devices will no longer receive monthly security and quality updates that contain protection from the latest security threats. To continue receiving security and quality updates, Microsoft recommends updating to the latest version of Windows 10.
IMPORTANT We have been evaluating the public health situation and understand the impact this is having on many of our customers. To help ease some of the burdens customers are facing, we are going to delay the scheduled end of service date for the Home, Pro, Pro Education, Pro for Workstations, and IoT Core editions of Windows 10, version 1809 to November 10, 2020. This means devices will receive monthly security updates only from May to November. The final security update for these editions of Windows 10, version 1809 will be released on November 10, 2020 instead of May 12, 2020.
Known issues
|
Symptom |
Workaround |
|
After installing KB5001342 or later, the Cluster Service might fail to start because a Cluster Network Driver is not found. |
This issue occurs because of an update to the PnP class drivers used by this service. After about 20 minutes, you should be able to restart your device and not encounter this issue. |
Troubleshooting
If you have questions or need help activating or troubleshooting Windows, see our help topics below:
-
For information about how to update, see Update Windows 10.
-
If you have questions about manually installing or removing an update, see Windows Update: FAQ.
-
Getting an error message when updating? See Troubleshoot problems updating Windows 10.
-
If you need to activate Windows, see Activation in Windows 10. If you’re having trouble with activation, see Get help with Windows activation errors.
Related info
Thank you for visiting the Windows 10, version 1809 update history page today. If you would like to learn more about how to use these pages and make the most of them, see our blog post.
To improve the information presented in the history pages and related KBs and make them more useful to our customers, we have created an anonymous survey for you to share your comments and feedback.
-
Windows as a service — Overview
-
Windows Server 2016 servicing guidelines
-
Windows 10 release information
-
Windows Update: FAQ
-
Microsoft Surface update history
-
For more information about .NET Framework cumulative updates for Windows 10 version 1809, see History of Cumulative Updates for .NET Framework for Windows 10 version 1809
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Software, firmware and hardware updates
The product life cycle of Microsoft Windows Server 2019 is presented in chronological order in the following summary.. This overview includes important technical updates such as bug fixes, new features, as well as news about product launches, recalls, and end-of-life announcements, sourced from Microsoft, selected partners, or the devicebase editorial team. By joining the devicebase community, you can stay up-to-date with Windows Server 2019 and its developments..
Update
KB5059091: Out-of-band Fix Update
Update
Update
KB5058922: addresses a known issue where Audit Logon/Logoff events in the local policy
Update
Update
KB5055519: This update addresses security issues for your Windows operating system
Update
Update
KB5053596: Enables system processes to store temporary files in a secure directory
Update
Update
KB5052000: adds to the list of drivers that are at risk for Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) attacks
Update
Update
KB5050008: list of drivers that are at risk for Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) attacks
Update
Update
KB5048661: [Motherboard replacement] Fixed
Update
Update
KB5046615: Windows Kernel Vulnerable Driver Blocklist file (DriverSiPolicy.p7b) Fixed
Update
Update
KB5044277 : Fix for Remote Desktop (known issue)
Update
Was the content helpful to you?
Remarks

Windows Server 2019
You can check the applied Windows Update updates (security patches) on a Windows Server 2019 by displaying and outputting a list using the GUI and commands (PowerShell / command prompt). This article describes the procedure for checking 5 types of installed updates.
table of contents
- Windows Server 2019:View update history display screen
- Windows Server 2019:Display screen for installed updates
- Windows Server 2019:Event Viewer: Windows Log (System)
- Windows Server 2019:Windows PowerShell: Get-Hotfix command
- Windows Server 2019:Command prompt: wmic qfe command
Windows Server 2019:View update history display screen
Step 1:
Right-click on the Windows mark at the bottom left of your desktop –> select Settings.
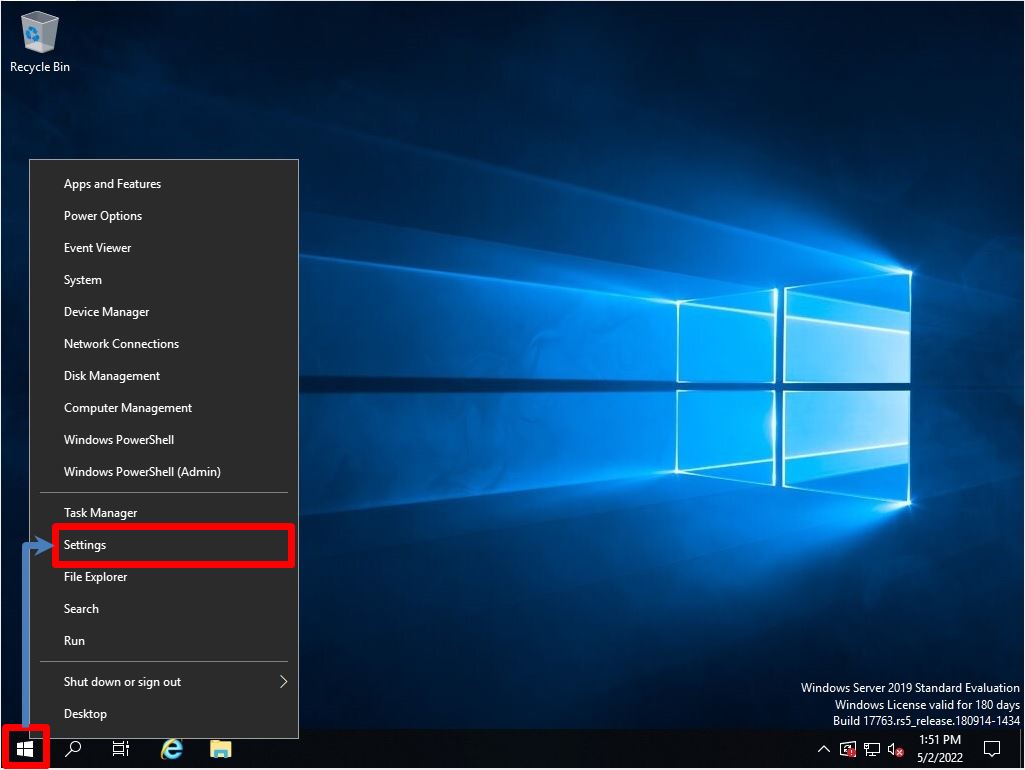
Step 2:
Select Update & Security.
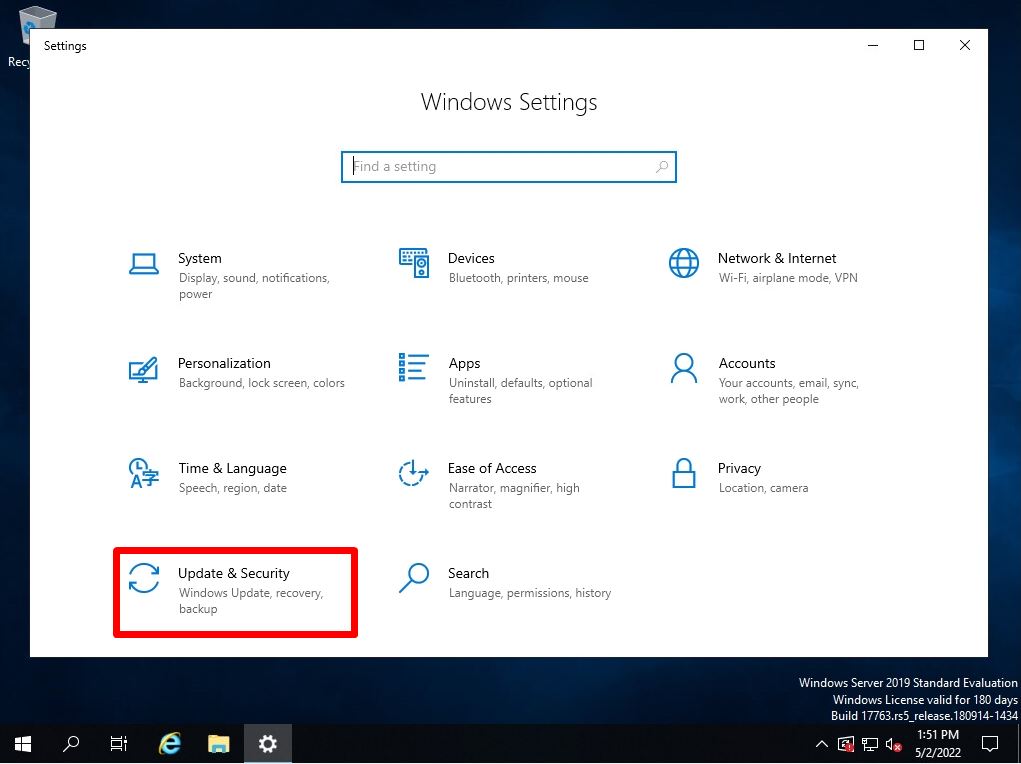
Step 3:
Select “View update history”.
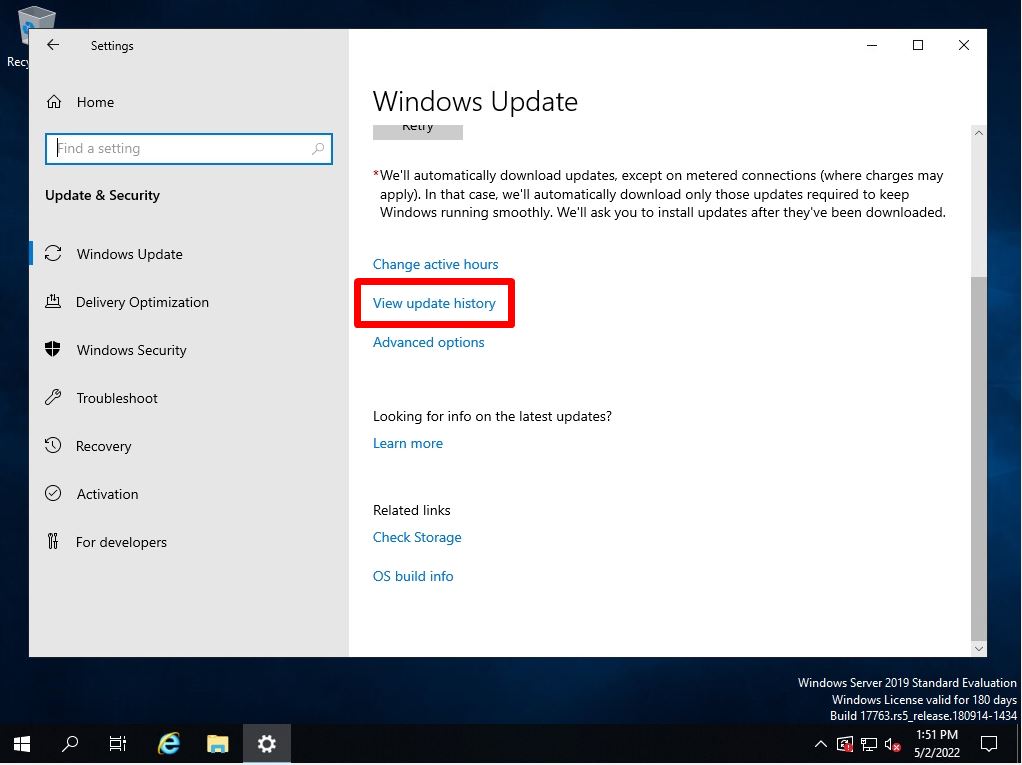
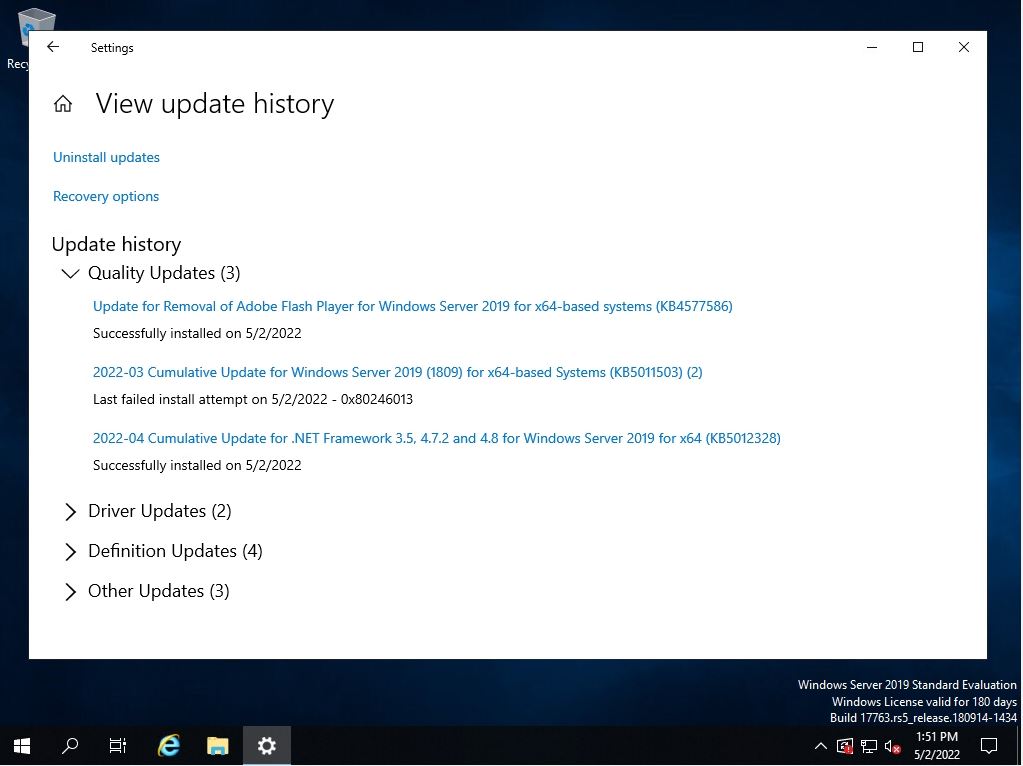
Step 4:
You can check the security patch with the installed KB number in “View update history” and the patch display list of the installation date and time.
Windows Server 2019:Display screen for installed updates
Step 1:
Click the Windows mark at the bottom left of your desktop –> Windows System –> Control Panel.
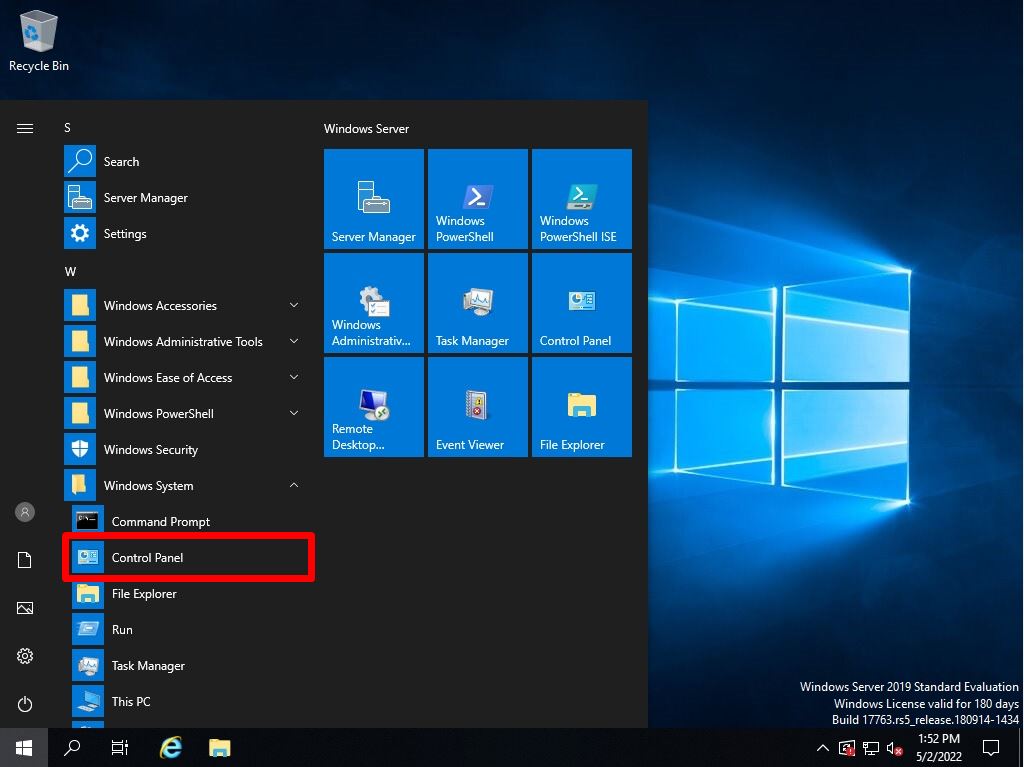
Step 2:
View by: Category -> Select Uninstall a program.
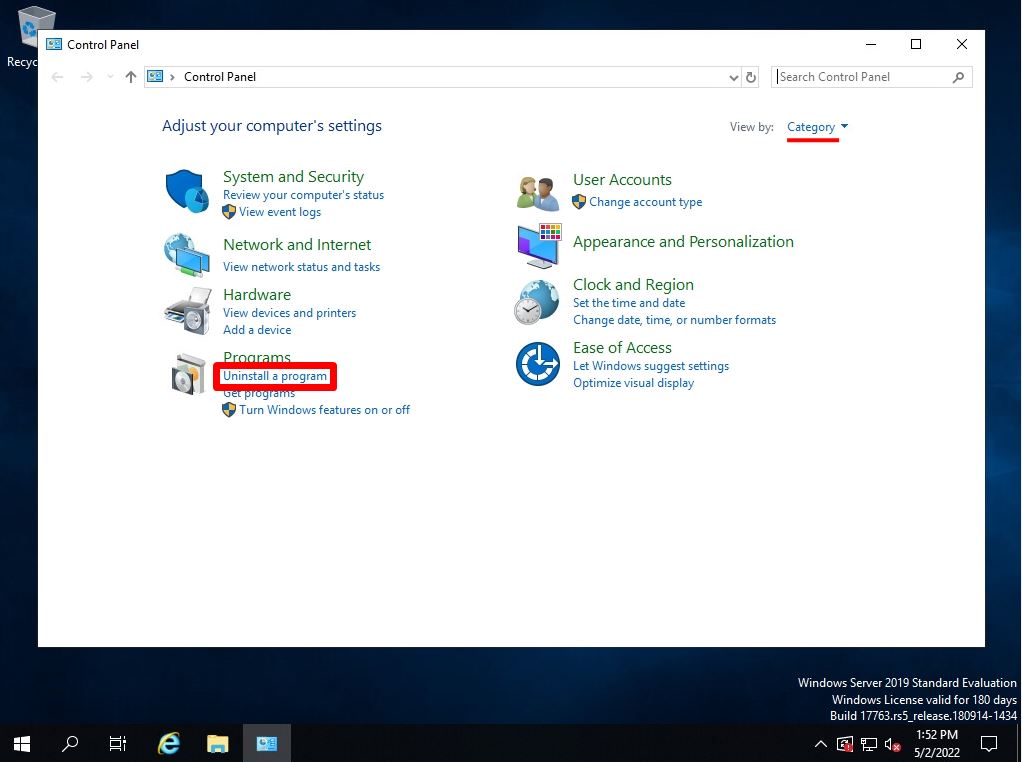
Step 3:
Select View installed updates.
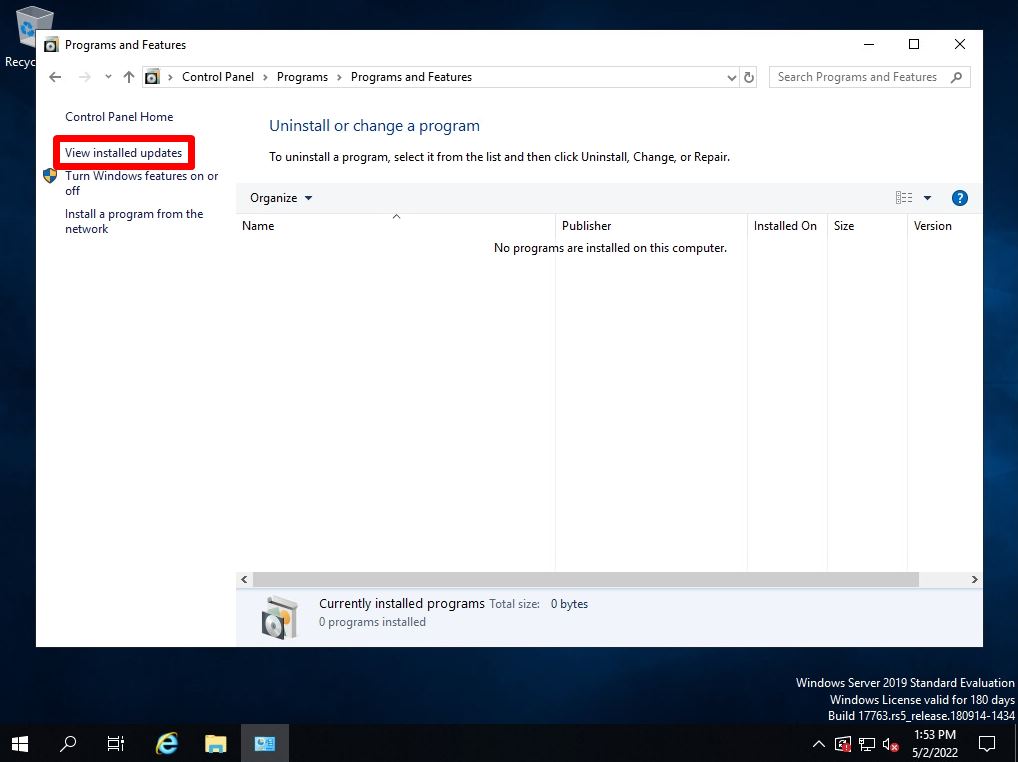
Step 4:
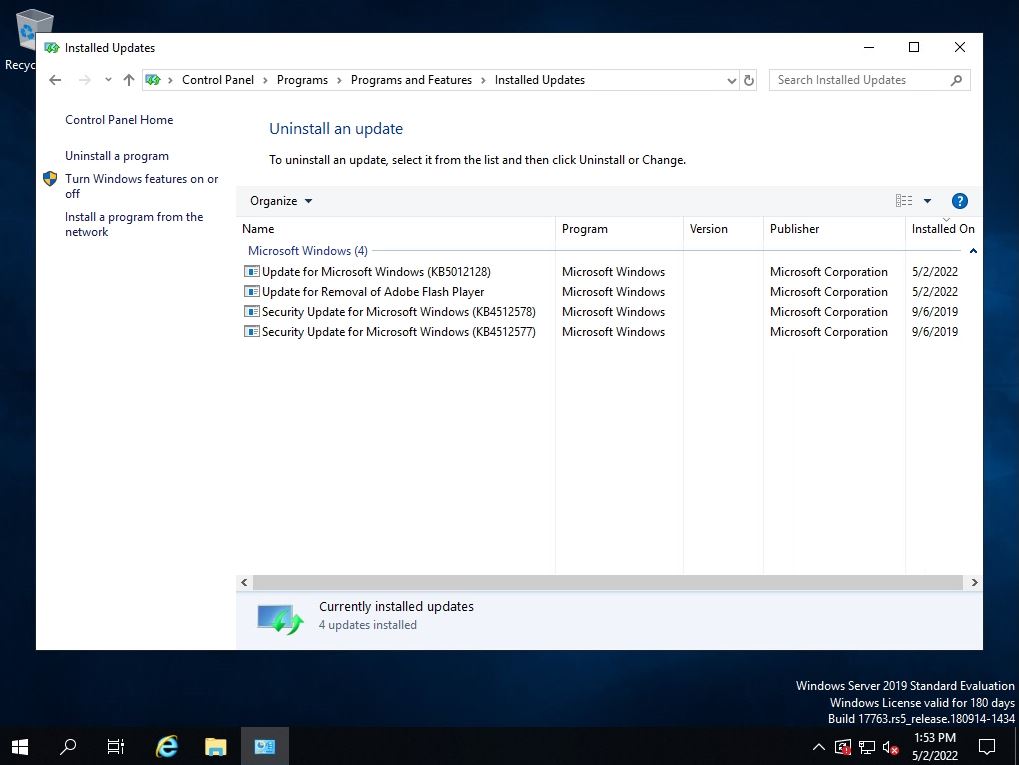
You can check the security patch with the installed KB number in “Installed Updates” and the patch display list of the installation date and time.
Windows Server 2019:Event Viewer: Windows Log (System)
Step 1:
Right-click on the Windows mark at the bottom left of your desktop –> select Event Viewer.
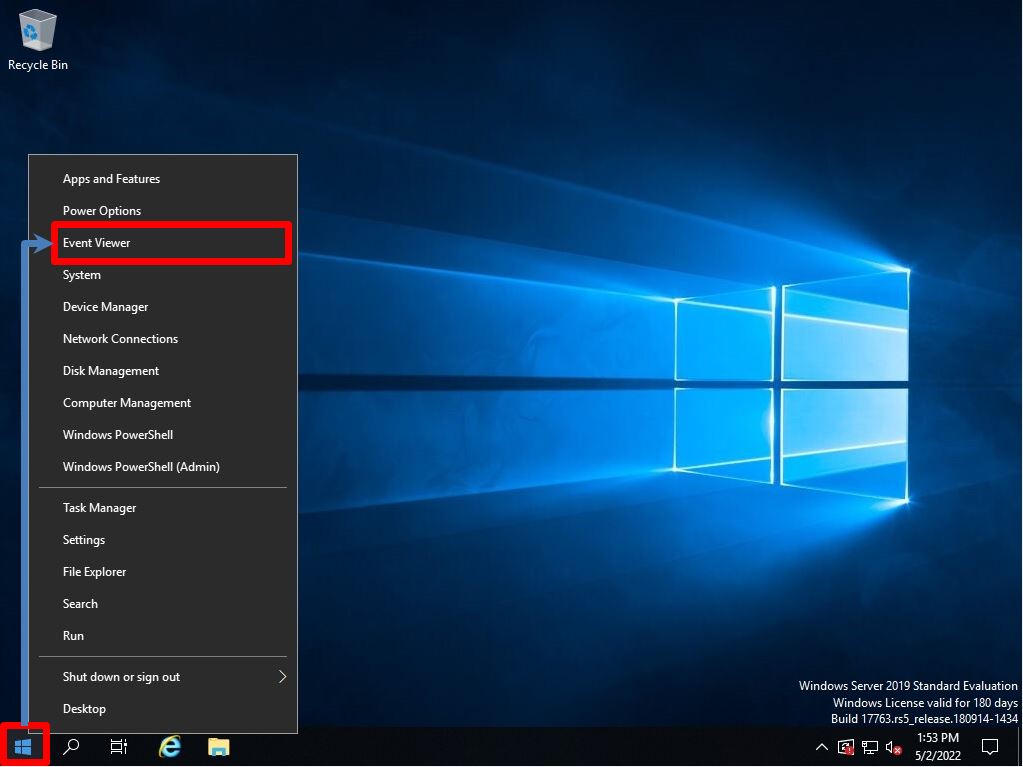
Step 2:
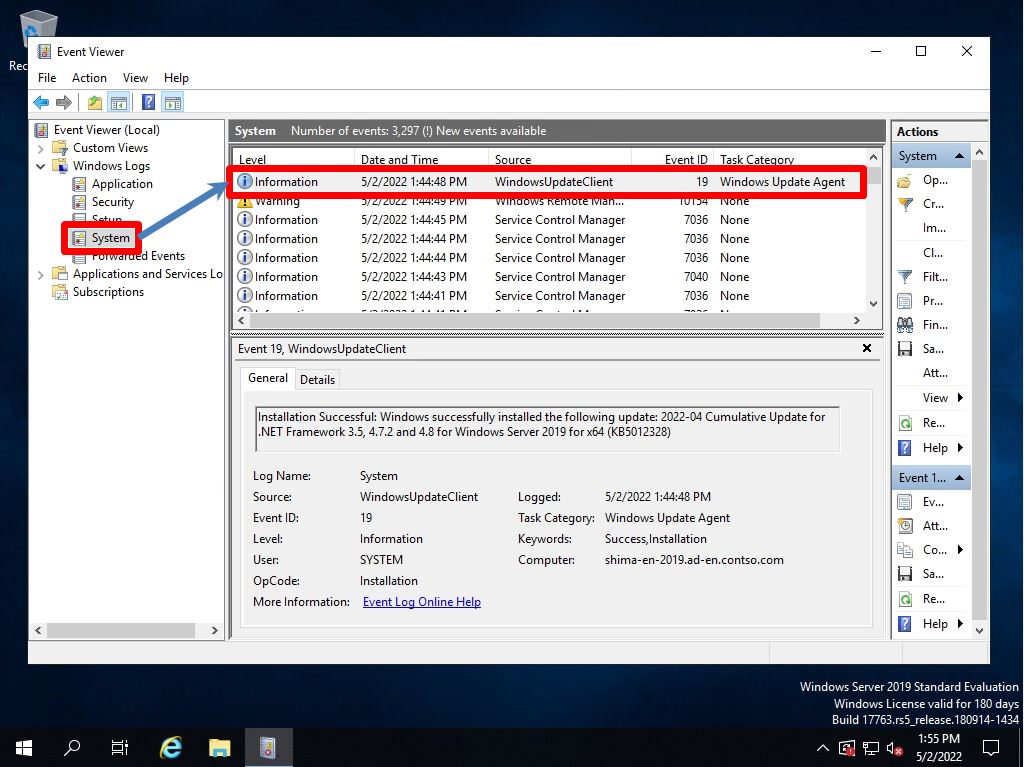
Select Event Viewer –> Windows Logs –> System.
Event ID: 19, Source: Windows Update Client will output a log of the installation status of Windows Update updates (security patches).
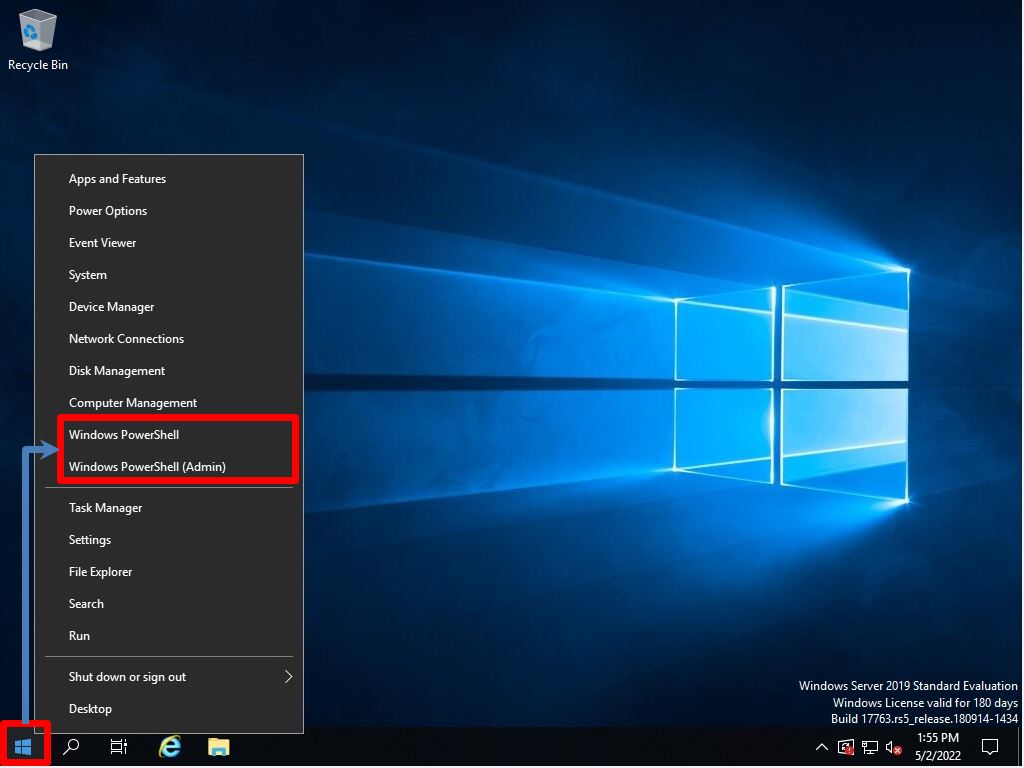
Windows Server 2019:Windows PowerShell: Get-Hotfix command
Step 1:
Right-click on the Windows mark –> select Windows PowerShell.
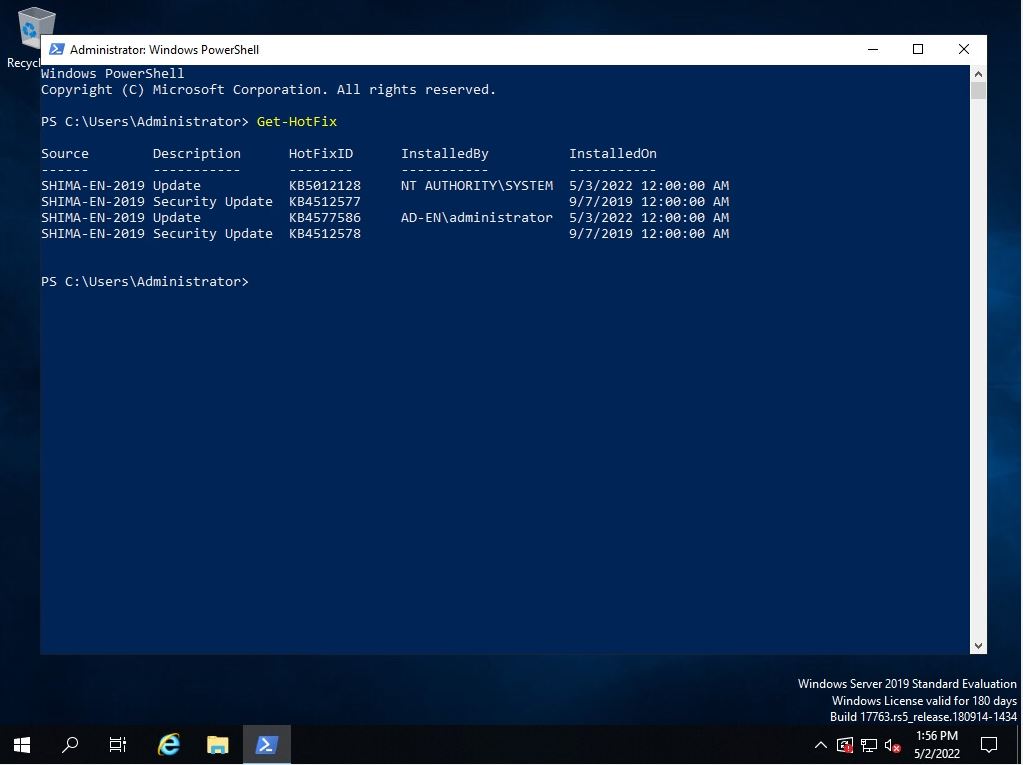
Step 2:
You can check the commands to be displayed and output by PowerShell with “Get-HotFix”. You can check the security patch with the installed KB number in “HotFix ID / Installed On” and the patch display list of the installation date and time.
Windows Server 2019:Command prompt: wmic qfe command
Step 1:
Right-click on the Windows mark –> select “Run”.
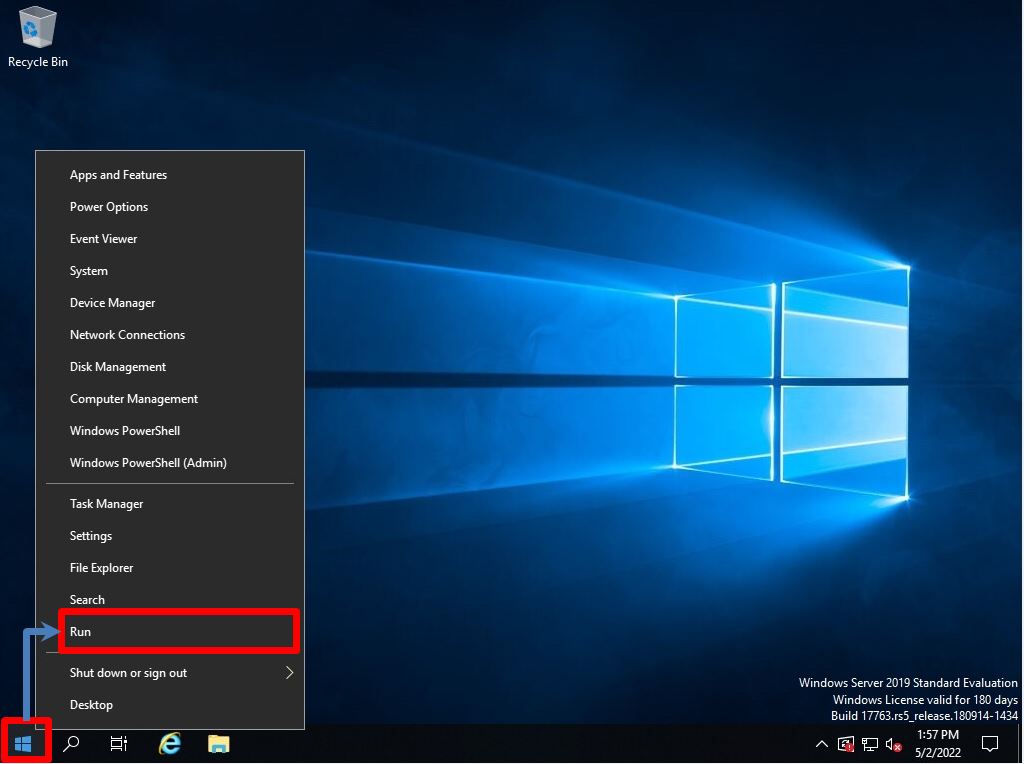
Step 2:
Enter cmd to start the command prompt.
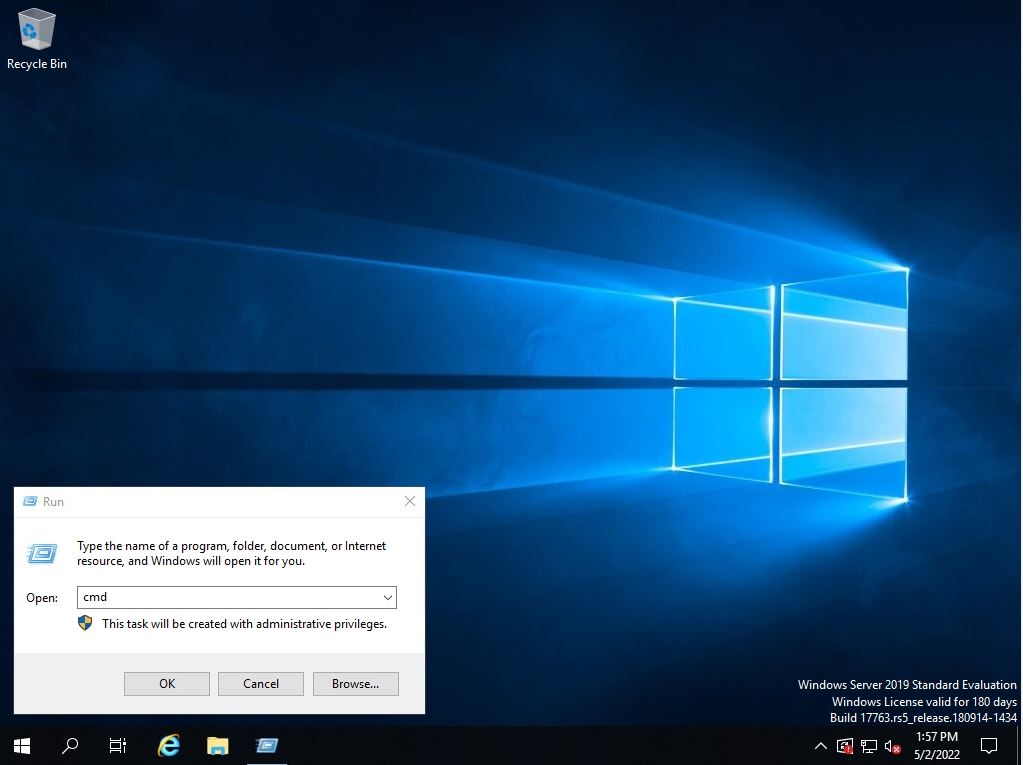
Step 3:
You can check the commands to be displayed and output at the command prompt with “wmic qfe”. You can check the security patch with the installed KB number in “HotFix ID / Installed On” and the patch display list of the installation date and time.
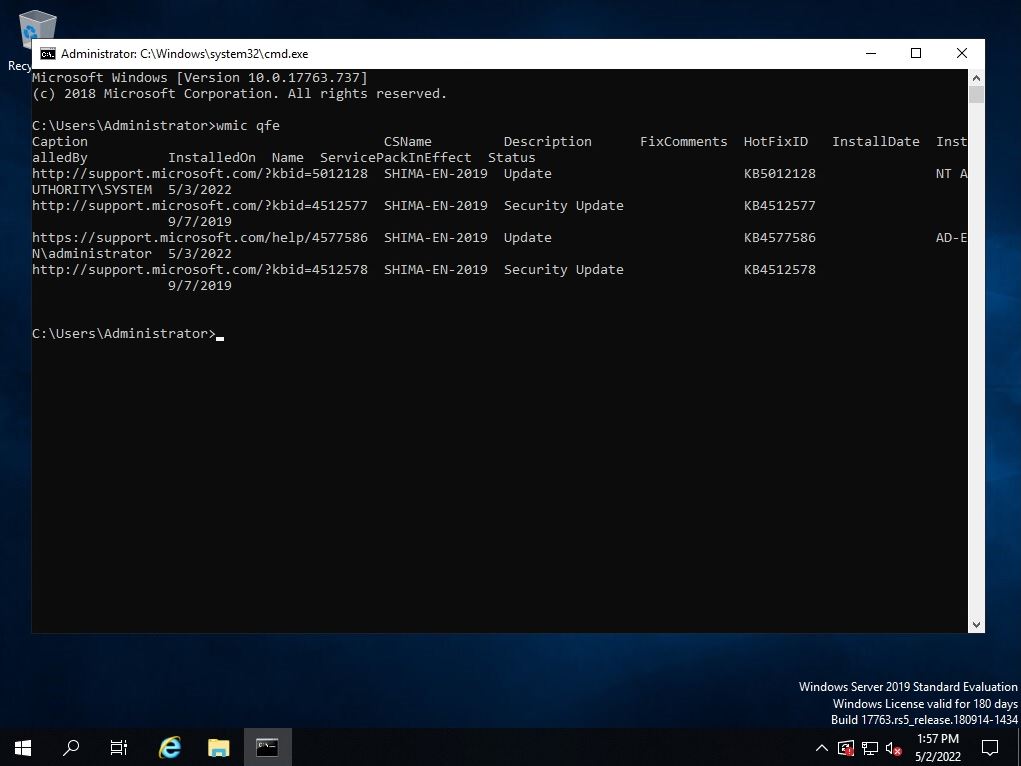
Checking for installed patches on your Windows Server 2019 system is an important task to ensure that your server is up to date with the latest security fixes and updates. In this tutorial, we will walk you through the steps to check the installed patches on your Windows Server 2019.
Step 1: Open the Windows Server 2019 Start menu by clicking on the Windows icon located on the bottom-left corner of the screen.
Step 2: From the Start menu, click on the «Settings» icon, which looks like a gear cog.
Step 3: In the Settings window, click on the «Update & Security» option.
Step 4: In the Update & Security window, select the «Windows Update» tab located on the left panel.
Step 5: On the Windows Update page, click on the «View update history» link.
Step 6: After clicking on the «View update history» link, a new window will open, displaying the list of installed updates on your Windows Server 2019. You can view the details of each update, including the KB number, installation date, and status.
Step 7: If you want to check for new updates, you can click on the «Check for updates» button on the Windows Update page to see if there are any available updates for your server.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. Helps ensure that your server is up to date with the latest security fixes and updates. | 1. May require a large amount of disk space and system resources to install some updates. |
| 2. Allows you to review the details of installed updates, including the KB number and installation date. | 2. Some updates may cause compatibility issues with certain software or hardware configurations. |
| 3. Provides an option to check for new updates, ensuring that your server is always updated. | 3. Installing updates may require a server restart, causing a temporary disruption in services. |
By following these steps, you can easily check the installed patches on your Windows Server 2019 and stay up to date with the latest security updates and fixes. It is important to regularly check for updates and install them to ensure the security and stability of your server.
Video Tutorial:How do I find patches installed on Windows Server?
How to check installed updates using cmd?
As a tech blogger, understanding how to check installed updates using the command prompt (CMD) is a valuable skill. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do it:
1. Press the Windows key on your keyboard to open the Start menu.
2. Type «cmd» in the search bar, and you’ll see the «Command Prompt» app listed. Click on it to open the command prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type the following command and press Enter:
wmic qfe list brief
This command will retrieve a list of all installed Windows updates on your system.
4. As the command executes, you’ll see a list of installed updates. Each entry will display information such as the HotFixID, Description, InstalledBy, InstalledOn, and other relevant details.
By following these steps, you can easily check the installed updates on your Windows system using the command prompt. Remember, it’s important to have administrative privileges for this task, as regular user accounts may not have the necessary permissions to access this information.
It’s worth mentioning that this method is specific to Windows operating systems, and the command mentioned works on most supported versions, including the latest ones.
To check installed patches in Windows Server PowerShell, follow these steps:
1. Open PowerShell: Press the Windows key, type «PowerShell,» and select the Windows PowerShell app.
2. Run PowerShell as an administrator: Right-click on the Windows PowerShell app and choose «Run as administrator.» This step is necessary to ensure you have sufficient privileges to access patch information.
3. Use the Get-Hotfix cmdlet: In the PowerShell window, type the following command and press Enter:
«`powershell
Get-Hotfix
«`
This cmdlet retrieves information about the hotfixes and updates installed on the Windows Server.
4. Analyze the output: The command will display a list of installed hotfixes in the PowerShell window. The output typically includes columns like «Source,» «Description,» «HotfixID,» and «InstalledOn.» You can review this information to check the patch details and installation dates.
By following these steps, you can quickly access the information about the installed patches on your Windows Server using PowerShell.
How do I check my server patches?
Checking server patches is a critical task for ensuring the security and stability of your server infrastructure. Here are the steps to check your server patches:
1. Access the Server: Log in to your server using Secure Shell (SSH) or Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) depending on the operating system.
2. Update Repository: Run the command `sudo apt update` for Ubuntu or `sudo yum update` for CentOS to update the software repository.
3. Check Available Updates: Use the command `sudo apt list –upgradable` or `sudo yum check-update` to display the available updates and patches.
4. Install Updates: Install the updates using the appropriate command. For Ubuntu, use `sudo apt upgrade` or `sudo apt full-upgrade` to install the available updates. In CentOS, run `sudo yum upgrade` to install the latest updates.
5. Verify Patch Installation: Once the updates are installed, you can verify their installation by checking the version numbers of the patched software packages. You can do this by running specific commands for each software component or using centralized server management tools capable of tracking patch levels.
6. Schedule Regular Patching: It is crucial to schedule regular patching to keep your server up to date. Set up automated patch management processes or create a calendar reminder to periodically check for and install updates.
7. Monitor Patch Status: Utilize server monitoring software or tools to monitor the patch status of your server constantly. These tools can provide alerts and notifications when critical patches are available, ensuring that you don’t miss important updates.
By following these steps, you can effectively check and install server patches, thus maintaining a secure and reliable server environment. Remember, regularly updating your server with the latest patches helps protect against security vulnerabilities and ensures optimal performance.
How to check last patching on Windows Server?
Checking the last patching on a Windows Server is crucial for maintaining the security and stability of your system. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how you can do it:
1. Open the Windows Server Administrative Tools: Go to the Start menu, search for «Administrative Tools,» and click on the corresponding result to open it.
2. Launch the Windows Update application: In the Administrative Tools window, locate and click on the «Windows Update» option. This will open the Windows Update configuration panel.
3. Check for installed updates: Within the Windows Update panel, you’ll see an option labeled «View update history» on the left-hand side. Click on it to view the update history for the server.
4. Review the update history: A new window will appear displaying the server’s update history. This history will show the most recent updates installed, along with their installation dates and status.
5. Check the last patching date: Scroll through the update history to find the most recent update installation date. This will indicate the last time your Windows Server was patched.
6. Verify Windows Server’s update status: To ensure the server is up to date, you can manually check for new updates by clicking on the «Check for updates» option in the Windows Update panel. This will initiate a search for available updates.
7. Install additional updates if necessary: If any updates are found during the manual check, proceed to install them by clicking on the «Install updates» button. This will ensure your server remains secure and up to date.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to check the last patching on your Windows Server and take necessary actions to keep it updated with the latest security patches and bug fixes.
What is the Wmic command?
The WMIC (Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line) command is a powerful tool in the Windows operating system that provides a command-line interface to access various management and monitoring features. It allows users to interact with the WMI infrastructure, which provides access to system information, configuration settings, and even control various aspects of the Windows environment.
Here are some essential points about the WMIC command and its functionality:
1. Accessing system information: The WMIC command provides an extensive range of options to retrieve valuable system information. For example, you can use the command `wmic bios get serialnumber` to obtain the serial number of the computer’s BIOS. Similarly, `wmic cpu get name` will display the name of the computer’s CPU.
2. Process management: With the WMIC command, you can manage running processes on your system. For instance, you can use `wmic process list brief` to display a list of running processes along with their essential details such as process ID, priority, and executable path.
3. Software management: WMIC allows you to manage software installations on your system. For instance, you can use the command `wmic product get name` to list all installed software applications on your computer.
4. System configuration: Using the WMIC command, you can access and modify various system configuration settings. For example, `wmic computersystem get name` retrieves the computer name, and `wmic computersystem where name=«%computername%» get username` gives you the username of the currently logged-in user.
5. Remote system management: WMIC enables you to manage remote systems as well. By specifying the `/node` parameter followed by the remote system’s name or IP address, you can execute WMIC commands on remote machines. For example, `wmic /node:192.168.1.100 process list brief` will display the list of running processes on the specified remote system.
Remember, the WMIC command offers a wide range of functionalities, and it’s crucial to have a good understanding of the specific commands and their syntax to make the most of this powerful tool. Refer to Microsoft’s documentation or other reliable sources for more details and specific use cases.
Windows Server 2019 remains a popular server operating system for many organizations due to its reliability and support for modern technologies. On this page, you will find a selection of key updates for Windows Server 2019 that enhance system security, performance, and compatibility. You can download them via links to the official Microsoft website or directly from our server. Each update is accompanied by a description of its features and purpose.
You can purchase licensed product keys for Windows Server 2019 activation in our catalog with instant delivery to your email in automatic mode. Orders are processed 24/7.
You can also download official Windows Server 2019 installers from our catalog.
List of Updates
– Download KB5052000
– Download KB5050008
– Download KB5048661
– Download KB5046615
– Download KB5044277
– Download KB5043050
– Download KB5041578
Updates for Windows Server 2019
Download KB5052000
Update KB5052000, released in February 2025, is a cumulative update for Windows Server 2019, bringing the OS build to version 17763.6893. This update includes the latest security fixes, performance improvements, and new features relevant as of early 2025.
Key Features and Changes:
1. Addresses vulnerabilities in the system kernel and network components discovered in early 2025, including potential attacks via the Kerberos protocol.
2. Optimizes Hyper-V performance for improved virtual machine stability, reducing switch times between host and guest OS.
3. Fixes Active Directory request handling errors, enhancing authentication, especially with complex group policies.
4. Updates drivers to support new server hardware, such as next-generation NVMe drives.
5. Recommended for all servers in production environments.
6. Resolves issues with Windows Search service malfunctioning during indexing of large file systems.
7. Improves cluster performance for large data processing, reducing latency in failover scenarios.
8. Updates root certificates to meet 2025 encryption standards.
– Download from Microsoft
– Download from our server
Download KB5050008
Update KB5050008, released in January 2025, is a cumulative update for Windows Server 2019, updating the build to 17763.6775. It includes fixes released as part of January’s Patch Tuesday.
Key Features and Changes:
1. Mitigates vulnerabilities in Remote Desktop Services (RDP), preventing unauthorized access via exploits like BlueKeep-style attacks.
2. Enhances file service performance under high loads, eliminating delays in accessing SMB shared folders.
3. Resolves crashes in Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), fixing update synchronization issues.
4. Updates security certificates for 2025 standards, including support for new SHA-3 algorithms.
5. Improves stability of cluster configurations.
6. Fixes resource leaks in the DNS service during recursive query processing.
7. Corrects Windows Defender errors related to false positives on system files.
8. Adds support for new Intel X710 series network adapters for improved bandwidth.
– Download from Microsoft
– Download from our server
Download KB5048661
Update KB5048661, released in December 2024, updates Windows Server 2019 to build 17763.6659. This December cumulative update wraps up the fixes for 2024.
Key Features and Changes:
1. Mitigates vulnerabilities in the SMBv3 protocol, enhancing file access security and preventing man-in-the-middle attacks.
2. Fixes backup errors with Windows Server Backup, resolving shadow copy skips.
3. Optimizes DNS server performance for high query volumes, reducing response time by 15%.
4. Addresses memory leaks in the Windows Event Log service during high event logging rates.
5. Essential for preparing for 2025 updates.
6. Resolves issues with Hyper-V Integration Services when using older guest OS.
7. Enhances compatibility with newer VMware ESXi versions for hybrid environments.
8. Updates drivers to support the latest Broadcom RAID controllers.
– Download from Microsoft
– Download from our server
Download KB5046615
Update KB5046615, released in November 2024, upgrades Windows Server 2019 to build 17763.6532. This cumulative update includes critical security and performance fixes.
Key Features and Changes:
1. Closes kernel vulnerabilities related to privilege escalation (e.g., CVE-2024-XXXX), preventing malicious code execution.
2. Fixes crashes in high-availability clusters (Failover Clustering), resolving node-switching issues.
3. Improves compatibility with new network adapter drivers, supporting 100 Gbps interfaces.
4. Resolves TLS session handling errors in IIS, preventing connection drops on high-traffic sites.
5. Enhances Windows Time service reliability for synchronization, reducing drift to 0.1 seconds.
6. Corrects Storage Replica errors during large volume replication.
7. Mitigates excessive CPU usage by the BITS service during background file downloads.
8. Updates .NET Framework components for new library support in server applications.
– Download from Microsoft
– Download from our server
Download KB5044277
Update KB5044277, released in October 2024, updates Windows Server 2019 to build 17763.6414. This October cumulative update focuses on security and stability.
Key Features and Changes:
1. Addresses Print Spooler vulnerabilities related to remote code execution, including CVE-2024-XXXX.
2. Fixes Hyper-V crashes during virtual machine migration, resolving Live Migration hangs.
3. Improves disk operation performance in Storage Spaces, reducing SSD latency by 20%.
4. Resolves DHCP service hangs under high load from mass IP requests.
5. Updates components for new encryption standards, including TLS 1.3.
6. Fixes Windows Search service crashes when indexing network drives.
7. Corrects performance metric display errors in PerfMon.
8. Adds support for new Dell PERC H755 controllers for PowerEdge servers.
– Download from Microsoft
– Download from our server
Download KB5043050
Update KB5043050, released in September 2024, upgrades Windows Server 2019 to build 17763.6293. This September cumulative update enhances server security and functionality.
Key Features and Changes:
1. Closes network stack vulnerabilities related to IPv6 packet handling, preventing DoS attacks.
2. Fixes Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) errors, resolving token expiration issues.
3. Improves Windows Server container performance, reducing startup time by 30%.
4. Resolves Event Viewer log display errors when filtering by categories.
5. Updates libraries for new API support in applications, including .NET 6.0.
6. Fixes Windows Update service crashes when installing patches on memory-constrained servers.
7. Enhances compatibility with newer Kubernetes versions for containerization.
8. Corrects BitLocker errors during large disk encryption.
– Download from Microsoft
– Download from our server
Download KB5041578
Update KB5041578, released in August 2024, updates Windows Server 2019 to build 17763.6189. This August cumulative update ensures stability and security.
Key Features and Changes:
1. Mitigates Windows kernel vulnerabilities related to driver handling, including CVE-2024-XXXX, preventing privilege escalation.
2. Fixes Windows Defender crashes during large data scans, reducing CPU load.
3. Enhances compatibility with newer SQL Server versions, fixing database replication errors.
4. Resolves domain network policy issues causing user login delays.
5. Improves SSD performance in RAID configurations, optimizing TRIM operations.
6. Corrects DFS Replication errors during large file synchronization.
7. Fixes CAL license tracking issues in RDS environments.
8. Updates drivers to support new QLogic Fibre Channel HBA adapters.
– Download from Microsoft
– Download from our server

