Skip to content
Understanding ReFS Deduplication in Windows Server 2019
Quick Bites:
- Deduplication saves space: Eliminates duplicate data in Hyper-V environments, potentially saving 10x the storage space
- ReFS + Deduplication now available: Windows Server 2019 unlocks ReFS deduplication, removing a major limitation
- Performance benefits: ReFS offers fast virtual disk provisioning and efficient checkpoint merging
- Considerations exist: ReFS CSVs with Hyper-V clusters still work best with NTFS, while ReFS shines with Storage Spaces Direct
One of the evolutions of technologies with Windows Server in general and Windows Server Hyper-V, in particular, is in the realm of storage.
Protect Your Data with BDRSuite
New storage technologies have created interesting capabilities that allow organizations to solve very complex and demanding business challenges and problems they face. Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V have some pretty incredible new storage abilities that no doubt administrators will want to note and take advantage of.
Table of Contents
- What is Data Deduplication?
- Microsoft’s ReFS File System – No Longer Handicapped
- How to Enable ReFS in Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V ReFS Benefits and Considerations
- Wrapping Up
One of the existing areas of improvements made with Windows Server 2019 is in the area of data deduplication.
In this post, we will take a look at Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V ReFS Deduplication to see how new features with Microsoft’s latest file system ReFS have created great new capabilities that can be utilized in the realm of Hyper-V virtualization.

Let’s begin by taking a step back and looking at data deduplication and ReFS in general.
What is Data Deduplication?
Most likely if you have been around storage or virtualization technologies for any length of time, you have no doubt heard about data deduplication or deduplication for short. This can certainly be used as a buzzword among storage vendors. However, it is an important technology feature of today’s modern storage solutions.
What exactly is deduplication?
Most of today’s complex storage systems store data in various chunks of data using different technologies. When storing very similar servers, files, and other stored items, it is very probable you will have multiple bits of data that could be identical between a number of servers stored on a volume such as is found in storage backing a Hyper-V virtualized environment.
“Deduplication is the ability to recognize and find these identical pieces of information that exist between the bits on disk and get rid of the extra copies of them.”
Example: If you had the same identical set of files that were found in 20 different servers, you could effectively eliminate 19 copies and only keep 1 copy that could be used for all 20.
This enables a much more efficient storage system from a space perspective and prevents unnecessarily keeping extra copies of identical data on expensive storage subsystems when there is no need for that. Especially in the realm of virtualized systems when there tends to be a tremendous amount of duplication between the server operating systems contained therein, there can potentially be HUGE space savings with deduplication.
Microsoft’s ReFS File System – No Longer Handicapped
Microsoft introduced a brand new and exciting file system technology with Windows Server 2016 called ReFS or Resilient File System.
This came as a surprise since NTFS has been the default file system on Windows Server operating systems since the very beginning. However, ReFS touted some pretty incredible resiliency as well as performance advantages of ReFS when compared to NTFS.
Is ReFS better than NTFS?
ReFS is not mean to be a replacement of NTFS however. Why not? At least for now, ReFS is not bootable. This is a huge show stopper for ReFS totally replacing NTFS and other file systems. Its design is not so much for running the operating system itself but rather for the secondary utility storage that is often presented to workloads.
Learn more in detail here: Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V ReFS vs NTFS
One of the primary purposes of ReFS is to be used with Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) as the file system for formatting the S2D volumes to be used for Hyper-V virtual machine storage.
There are several advantages to ReFS as introduced with Windows Server 2016. These include:
- Has a maximum volume size of 1 Yottabyte or 1 trillion terabytes
- Uses file metadata to protect file system health and provides other features:
- This is used when extending a disk or zeroing out new blocks on a disk
- Leads to extreme performance enhancements of ReFS
- Operations are performed on the metadata and not the actual data on disk such as merging checkpoints, etc
- NTFS would take minutes to do the same operation as it is actually zeroing out blocks instead of metadata
- This is referred to as the Sparse VDL technology
- Windows Server 2016 contains the new block cloning technology found in ReFS
One of the huge drawbacks with ReFS with Windows Server 2016 was the fact that you couldn’t use deduplication. However, with Windows Server 2019, deduplication is now a fully supported feature of the ReFS file system! This offers tremendously huge space savings benefits to Hyper-V storage.
Hyper-V environments have arguably some of the most “duplicated” files and resources of any type of environment. According to Microsoft, customers can look to see as much as 10 times the space savings in Hyper-V environments using ReFS deduplication.
How to Enable ReFS in Windows Server 2019
Since ReFS is a file system format for a volume, you can use standard tools such as the Disk Management utility or the diskpart command line utility to enable it.
Below is the New Simple Volume Wizard that appears when creating a new volume.
On the Format Partition screen, you can select ReFS under the Format this volume with the following settings.
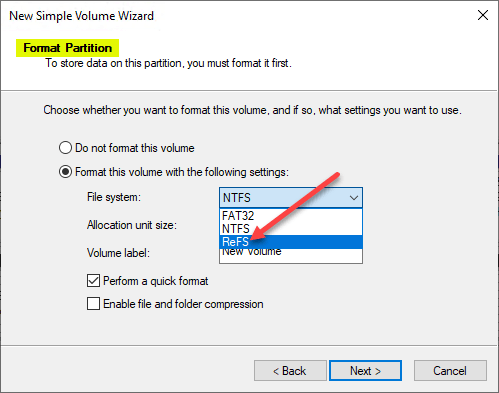
Using Disk Management to format a volume with the ReFS file system
Additionally, as mentioned, you can use the diskpart command line utility to format a new volume with ReFS as well.
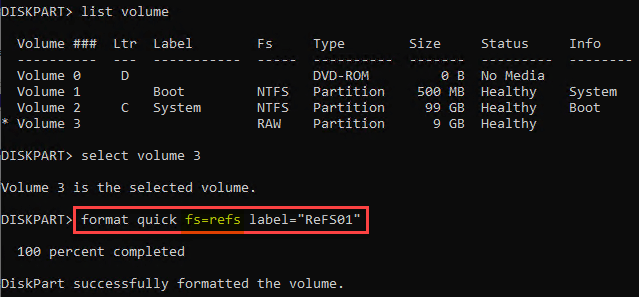
Using Disk Management to format a volume with the ReFS file system
Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V ReFS Benefits and Considerations
Benefits
We have spoken to many of the benefits in the earlier sections, however, ReFS offers tremendous advantages when related to Hyper-V, in terms of performance, reliability, and capabilities. When virtualization admins think of the tremendous advantages to using ReFS for virtualization tasks it certainly is worth consideration.
- The Sparse VDL technology that allows quickly provisioning virtual disks is exciting. This means you can provision Fixed Disk “thick provisioned” disks in seconds and no longer minutes
- Block cloning technology provides tremendous benefits in terms of Checkpoint merge operations that with ReFS are only working with the metadata on disk instead of actual blocks of data. This allows for “lightning fast” checkpoint merge operations as well as much more efficient use of disk I/O. Other file operations are more efficient with ReFS
- With Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V ReFS volumes, deduplication can now be enabled and result in those tremendous space savings we have already mentioned a few times
Microsoft is certainly removing the roadblocks to using ReFS, especially with Hyper-V, now that it can be configured with deduplication. Additionally, few organizations want to be “early adopters” with brand new technologies. Brand new certainly describes ReFS running on Windows Server 2016. Now with Windows Server 2019, it has a few miles of road behind it and has developed a bit of maturity.
Considerations
There are still a few points to keep in mind with ReFS when thinking about best practices and performance.
One might assume for Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V Cluster Shared Volumes or CSV, it would be advisable to use ReFS. However, this is not the case. ReFS CSVs always runs in file system redirection mode which sends all I/O over the cluster network to the coordinator node for the volume.
In deployments utilizing NAS or SAN, this can dramatically impact CSV performance. When CSVs are used you want to always make use of NTFS as the preferred file system in production environments in this configuration. Microsoft has not really clarified or changed this direction at the time of this writing, so it appears, for now, this is still the guidance with Windows Server 2019.
ReFS is definitely the recommended file system to use for Windows Server 2016 or 2019 Hyper-V running Storage Spaces Direct or S2D since the required use of RDMA network cards does not utilize the file redirection mode found in ReFS CSVs.
Wrapping Up
Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V ReFS Deduplication has come a long way since its introduction in Windows Server 2016. It has matured as a technology and Microsoft has removed major roadblocks to using the technology such as the lack of deduplication. ReFS in Windows Server 2019 now supports deduplication and provides an extremely effective use case for Hyper-V environments running VDI or other highly duplicated virtual environments.
There is no question that Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V ReFS deduplication will pave the way for a larger number of adopters running ReFS technology backing business-critical production workloads.
Related Posts
Windows Hyper-V NTFS vs ReFS: A Comparison
Follow our Twitter and Facebook feeds for new releases, updates, insightful posts and more.
Try BDRSuite for Free!
Schedule a live demo with one of our product experts
Start your full-featured 30-day free trial
Explore detailed pricing, editions & features
Windows Server 2019 offers many exciting benefits across the board. However, when thinking about storage features with this release and, more importantly, how they affect backups, one feature we want to take a closer look at is Windows Server 2019 ReFS file system version 3.4. It offers huge improvements over previous file systems in certain use cases as well as predecessor versions of ReFS found in Windows Server 2012 and 2016.
What Is the ReFS File System?
The ReFS file system, which stands for Resilient File System, is the newest file system developed by Microsoft, with the first version released with Windows Server 2012. It gets its name from the resiliency features in this file system. In addition to resiliency, the Microsoft file system is designed with the goals of maximizing availability, scalability, and integrity. You can create volumes with this file system in Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 Pro for Workstations.
Administrators no longer have to worry about running the chkdsk utility, which detects errors in the file system. This is due in part to ReFS having the ability to perform online checks of the file system health in real-time.
ReFS uses checksums that allow it to detect any data corruption and recover from that corruption quickly. In fact, if you look at a ReFS formatted volume and run Tools > Check on the volume, you receive the message: You don’t need to check this drive. The ReFS file system does not need to be checked.
Windows Server 2019 ReFS Benefits
Two of the use cases where ReFS really shines are in the areas of virtualization and use by modern backup solutions. Some of the high-level benefits of the Windows Server 2019 ReFS file system are:
- ReFS takes advantage of B+ trees in the file structure. B+ tree is very efficient in storing data as there is a very high fanout of children nodes in the structure. By using pointers, the B+ tree can reduce the amount of I/O operations to retrieve an element in the tree.
- The maximum volume size for ReFS is 1 yottabyte or 1 trillion terabytes!
- File metadata is periodically scrubbed by reading and performing checksum operations on the data. This new scrubber is another mechanism to ensure file resiliency.
- File integrity streams provide additional file data checksums.
Note: With the added resiliency benefits, ReFS is the recommended file system for Exchange Server 2019 database/log locations.
- Windows Server 2019 ReFS includes the block cloning technology. This allows for pointer references to blocks that would otherwise have to be moved around.
- Copy on write is a mechanism used by ReFS to ensure integrity when writing data and to avoid data corruption in case of power loss. A resilient file system creates a copy of metadata to new blocks when editing the metadata (instead of overwriting the existing metadata) and links the latest copy of metadata to a corresponding file after writing data to the disk. We look at this in more detail below. However, when it comes to backups, block cloning in ReFS greatly increases the performance of backup solutions that take advantage of block cloning technology. Synthetic full backups would no longer need to move data around but instead can utilize pointers to existing blocks for the synthetic operation.
- Sparse VDL. Sparse VDL or valid data length allows ReFS to zero out files very rapidly. When creating a fixed-size VHD disk in Hyper-V, the operation could take minutes to complete to allocate the disk size. However, with sparse VDL ReFS can zero out the Hyper-V disk files rapidly. It now takes seconds to create a large fixed-size disk on a ReFS volume.
Creating the default size 127-GB fixed-size disk in a Hyper-V cluster with a ReFS clustered shared volume, shown below, took seconds. This operation would have taken minutes on a traditional NTFS formatted volume. The time to create fixed-size disks is reduced in this case.

Backup Technology Use Cases
Utilizing ReFS block cloning in modern backup solutions can yield great results. Many backup solutions that back up virtual environments use a process called synthetic full backups. Before we define a synthetic full backup, let’s consider a traditional full backup.
With a traditional active full backup of a virtual machine, all needed data is retrieved for the full backup from the production VMware or Hyper-V virtual machine itself. In doing that, essentially both the production network and storage are used to create that full backup.
With synthetic backups, the data for the full backup is synthesized from backup data that you already have in the backup repository. New full backups are synthesized, and the backup chain is moved forward. Block cloning technology with Windows Server 2019 ReFS can greatly speed up the process in which legacy backup solutions can synthesize backups due to the movement of pointers rather than the blocks themselves.
With modern backup solutions such as NAKIVO Backup & Replication, this is not required, though. VM backups are stored in the full synthetic mode. Each recovery point is aware of the blocks that are needed to fully recover a virtual machine. This means there is no need to run the transformation of backup files or recreate full backups using the synthetic process.
Windows Server 2019 ReFS Best Practices
While ReFS is certainly a remarkable file system bringing forth many improvements, are there use cases where we do not use ReFS? Yes, there are some ReFS disadvantages. Below are a few areas to note:
- ReFS cannot be used for the system drive/boot drive of the Windows operating system. In fact, you do not see an option to format your boot drive with ReFS during Windows installation, as NTFS is still the way to go for the operating system.
- ReFS supports Windows Data Deduplication starting from Windows Server 2019 1809 LTSC. If you use an older version and if you want to utilize deduplication for a Windows volume by using the native Windows deduplication capability, you need to stick with NTFS.
- ReFS does not support file-level encryption. You can use BitLocker encryption with ReFS. However, this is a volume-level encryption technology. If you want to encrypt at the file/folder level, you will need to use NTFS.
- Disk Quotas are not supported with Microsoft ReFS.
- ReFS doesn’t support short 8.3 (DOS-compatible) file names like progra~1.txt that are supported in NTFS for compatibility.
- ReFS consumes more system resources for operation. A larger ReFS array consumes more RAM, CPU resources, and disk input/output operations per second (IOPS).
- It is not recommended that you install applications on ReFS volumes. ReFS doesn’t support hard links (until ReFS v.3.5).
To take advantage of Microsoft ReFS, it is recommended that you use this server file system in the following scenarios:
- Building a file server with support of extra-large volume size and file size.
- Creating volumes to store Hyper-V virtual machines.
- Opt for ReFS on Windows servers rather than on Windows workstations.
- ReFS is preferred if you use Storage Spaces and Storage Space Direct on your server.
Note: Storage Spaces is a feature that allows you to create a virtual volume by using multiple physical disks on one computer. Storage Spaces support mirroring like RAID 1.
Thoughts
The features included in Windows Server 2019 ReFS greatly benefit environments with resiliency, scalability, and performance improvements. Now you know the advantages of ReFS, the limitations, and when you should not use this file system. The 3.4 version of ReFS has advantages in some aspects but is not a direct replacement for NTFS. You can store Hyper-V VMs on ReFS volumes to get better results but don’t forget about Hyper-V backups.
Download the Free Edition of NAKIVO Backup & Replication to protect your Hyper-V environment. The NAKIVO solution supports synthetic backup with encryption and compression. Using the ReFS file system by following the best practices and the NAKIVO solution allows you to achieve the best results.
Hello World,
Windows 2019 server has reached General Availability (GA) in October 2018. This release ships with a bunch of new features and improvements in Hyper-v, containers, Failover cluster, ReFs, deduplication, storage Direct spaces, SOFS improvements…So, it’s time to have a look at some of these features….
Windows 2019 Server has introduced an improved version of the Resilient File system (ReFS). ReFs is not widely used (as far as I know) because NTFS is the default and well known file system in Windows systems and because ReFS was missing major features when first introduced in Windows 2012 Server. This might change in the future because of the improvements and because Microsoft start to recommend its usage in specific scenario.
This post will not explain benefits or key factors of ReFS in deep details. If you need to have more technical information, please have a look at this post (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/refs/refs-overview). The aim of this post is to present situation where ReFS can be used and when it’s not recommended to use.
Let’s go !
Overview
Resilient File System (ReFS) is not a new feature of Windows 2019 server. ReFS technology has been made available with the release of Windows Server 2012. However, because of some limitations of the new file system, not a lot of people have been deploying or using this technology. This changed a little bit with the release of Windows 2016 server as significant improvements have been made.
The most common scenario where ReFs partition would have been recommended in Windows 2016 is for Virtual infrastructure. ReFs includes “Accelerated VM operations” feature that basically allows you to quickly copy VM disk or create new VM disks in seconds instead of minutes when using NTFS partitions. Technology like block cloning and sparse VDL improve speeds of disk operations for Hyper-V infrastructure. If you have a hyper-v server running on top of windows 2016 Server, you could try to create a brand new VM disk on NTFS partition and do the same on ReFS partitions and you will see the difference. On ReFS, creation time is really done in seconds…
NTFS partition needs to reboot if a check disk operation is needed. This is not the case anymore for ReFS partitions. The ReFS file was designed with resiliency in mind and checksum are done while system is running (so no need to reboot with CHKDSK).
ReFS support different storage Tier configuration. You can create Capacity Tier or Performance Tier. ReFS technology allows you to mix these kind of storage tier and will allow to configure systems using hot disks (used for performance) and cold disks (used for large data not changing a lot).
As you can see, ReFS seems to be production ready and can be used in a number of scenarios. Now, ReFS supports the following features
Source Table : https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/refs/refs-overview
As you can see, there is a lot of stuff that needs to be covered when speaking about ReFs in order to become an expert and get the best of this new technology. Again, this is not the purpose of this post…What we wanna know is basically when to use this technology…or not.
Bootable Volumes
ReFs has seen a lot of improvements. However, there are still some limitations that make ReFS not useable in certain conditions. The most common situation where ReFS cannot be used would be when you install a new Operating System and you have to configure bootable volumes.
ReFS cannot be used on boot drives. You will have to use NTFS. When installing your system, you will see that there is basically no option to format the boot disk with ReFS.
Another limitation often mentioned is related to Disk Quotas. If you plan to provide file services and you need to control disk consumption, you would need to format the disk using NTFS technology
Other features are still not supported on ReFS file system. Some of them are:
- File encryption not supported (i.e.EFS)
- File compression not supported
- short names not supported
- Hard links not supported
- ….
Complete list of limitation can be found here
When to use ReFS
Virtualization Infrastructure
Accelerated VHDX operations
Based on the initial information provided here above, one of the obvious (and most common) scenario when to use ReFS file system is for Virtualization situation. Hyper-V CheckPoint and quick disk creation will benefit tremendously and speed up operations when working with your hyper visor.
Deduplication Support
ReFs would be beneficial to use in Virtual environment since Deduplication is now supported in Windows 2019. However, so far, Microsoft guidance is to use ReFs with deduplication when deploying VDI infrastructure. Because VDI will use the same disk template, deduplication can be indeed beneficial to use in conjunction with ReFs volumes.
Note :
Some people have been using ReFs and deduplication when using Hyper-v server to save some disk space in their Lab environment. This scenario is not recommended by Microsoft but seem to work. More testing and validation might be needed to make it production ready (and if it will be production ready for such scenario…)
Backup & Archive Infrastructure
ReFs come up with some block cloning technology as well (see https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/refs/block-cloning) which can improve backup time and storage space consumed. Block technology API can be used by backup software vendors which result in copying pointers instead of full data.
ReFs file system can be also beneficial in Enteprise where archival data is needed. Combining all storage technology made available within Windows 2019 (Storage Spaces and ReFS), ReFS by design will provide high resilient file system and will ensure that archived data corruption can be find and fixed quickly ensure high data integrity
Exchange 2016/2019
This something I discovered recently while digging into ReFS technology. Exchange 2013 support ReFS for Database files, logs files and index files (again not operating system and no exchange system files can be hosted on ReFS)
A dedicated post would be needed in order to see how ReFS can be used with Exchange technology. This might be one of the coming post…
Cluster Shared Volume (CSV)
This one is still unclear to me. Should I use NTFS or ReFS filesystem when using CSV ? Guidance in Windows 2016 was to use NTFS for CSV volumes because File system redirection mode technology used. In windows 2016, ReFs usage is supported and can be used only when using Storage Space direct technology. So, we could assume that the same recommendation is valid for Windows 2019 even if some improvements have been made in the way CSV handle redirect traffic….
Final Notes
As you can see, Windows 2019 is bringing some new stuff and new recommendations about ReFs usage. Reading and digging through internet, it’s seems obvious that ReFS can be really beneficial (speed and performance) in virtualization and backup scenarios.
Initially, this post was to provide a quick overview of what ReFS can do and when to use. A quite straight forward task, isn’t it. However, more we are reading about Windows 2019 and ReFs, more we see how Microsoft has introduced really new cool storage possibilities that needs to be understood in order to implement them properly.
This is probably one of the last post in year 2018. However, we can already how much work and study would be needed in 2019 in order to learn and master all these new features, technologies and recommendations shipping with Windows 2019 server…
It’s seem that year 2019 will be a busy one….:-)
Till next time
За последние несколько лет, объем устройств хранения увеличился в несколько раз, и параллельно с ним увеличивается объем используемых данных. Появляются мощные инструменты, позволяющие наиболее эффективно использовать выделенное пространство. Одна из технологий, доступных в Windows Server — это дедупликация. Microsoft продолжает добавлять новые возможности к функции дедупликации с каждым новым выпуском Windows.
Рассмотрим само понятие дедупликации, инсталляцию компонентов и работу в Windows Server. Включение дедупликации на томе, использование Планировщика заданий, а также использование PowerShell для проверки статуса работы и управления.
Что такое дедупликация данных в Windows Server?
Файловый сервер предприятия – хороший пример, с помощью которого можно визуализировать, на сколько могут быть огромны объемы пользовательских данных. На файловом ресурсе можно найти множество копий одних и тех же файлов или близко схожих по внутренней структуре, т.е. в нескольких файлах будут дублироваться блоки данных. Одни и те же отчеты, письма, служебные документы пересылаются и сохраняются пользователями разных подразделений на одном и том же файловом сервере. А это, в свою очередь, приводит к появлению избыточных копий, которые влияют на эффективность хранения данных и последующего резервирования.
В традиционных средах хранения так и происходит. Дедупликация предоставляет средства для однократного сохранения данных и создания ссылок на фактическое расположение данных. Таким образом, среда хранения перестает хранить дублирующуюся информацию. Компания Microsoft также продолжает совершенствовать функции дедупликации. В Windows Server 2019 появилась возможность выполнять дедупликацию томов NTFS и ReFS. До Windows Server 2019 дедупликация ReFS была невозможна.
Как работает дедупликация данных Windows Server?
Для реализации дедупликации данных в Windows Server использует два принципа
- Процесс дедупликации с данными выполняется не моментально. Это означает, что процесс дедупликации не будет влиять на производительность в процессе записи файла. Когда данные записываются в хранилище, они не оптимизируются. После этого запускается процесс оптимизации дедупликации, чтобы гарантировать дедупликацию данных.
- Конечные пользователи не знают о процессе дедупликации — дедупликация в Windows Server полностью прозрачна. Пользователи не подозревают, что они могут работать с дедуплицированными данными.
Для успешной дедупликации данных в соответствии с принципами, перечисленными выше, Windows Server использует следующие шаги:
- Файловая система сканирует хранилище, чтобы найти файлы, соответствующие политике оптимизации дедупликации.
- Файлы дробятся на фрагменты.
- Идентифицируются уникальные фрагменты данных
- Фрагменты помещаются в хранилище фрагментов.
- Создаются ссылки на хранилище фрагментов, чтобы было перенаправление при чтении этих файлов на соответствующие фрагменты.
Использование дедупликации
Ниже описана примерная экономия места при использовании дедупликации.
- 80–95% для сред виртуализации VDI, ISO файлы.
- 70–80% для файлов программного обеспечения, файлов CAB и других файлов.
- 50–60% для общих файловых ресурсов, которые могут содержать огромное количество дублированных данных.
- 30–50% для стандартных пользовательских файлов, которые могут включать фотографии, музыку и видео.
Установка компонентов дедупликации в Windows Server
Процесс установки Data Deduplication прост. Дедупликация данных является частью роли файловых служб и служб хранения. Можно установить используя графический интерфейс Server Manager, используя Windows Admin Center или командлет PowerShell.
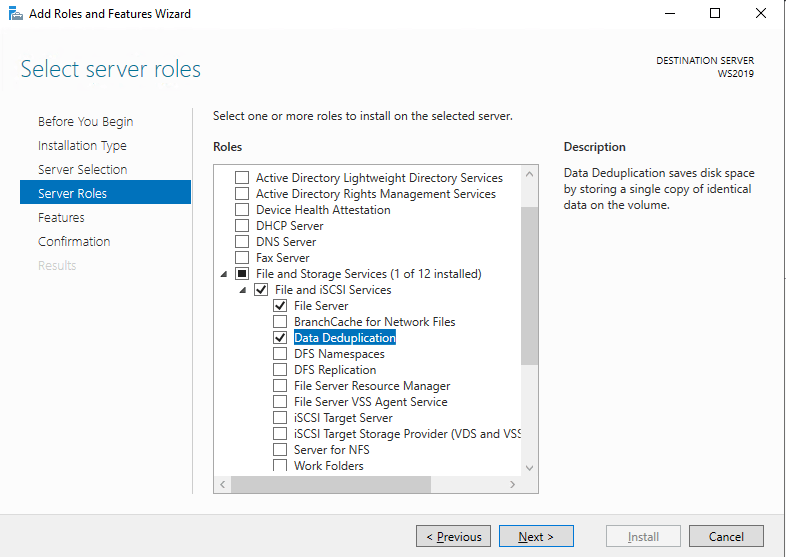
Включить Дедупликацию из PowerShell можно следующим командлетом:
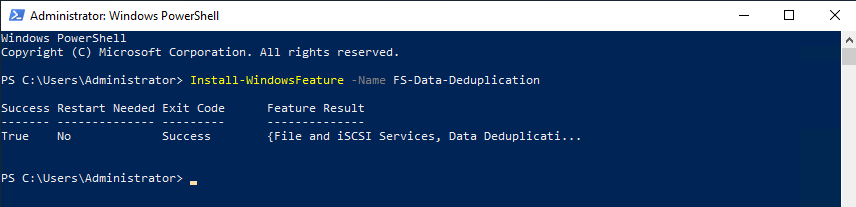
Install-WindowsFeature -Name FS-Data-Deduplication
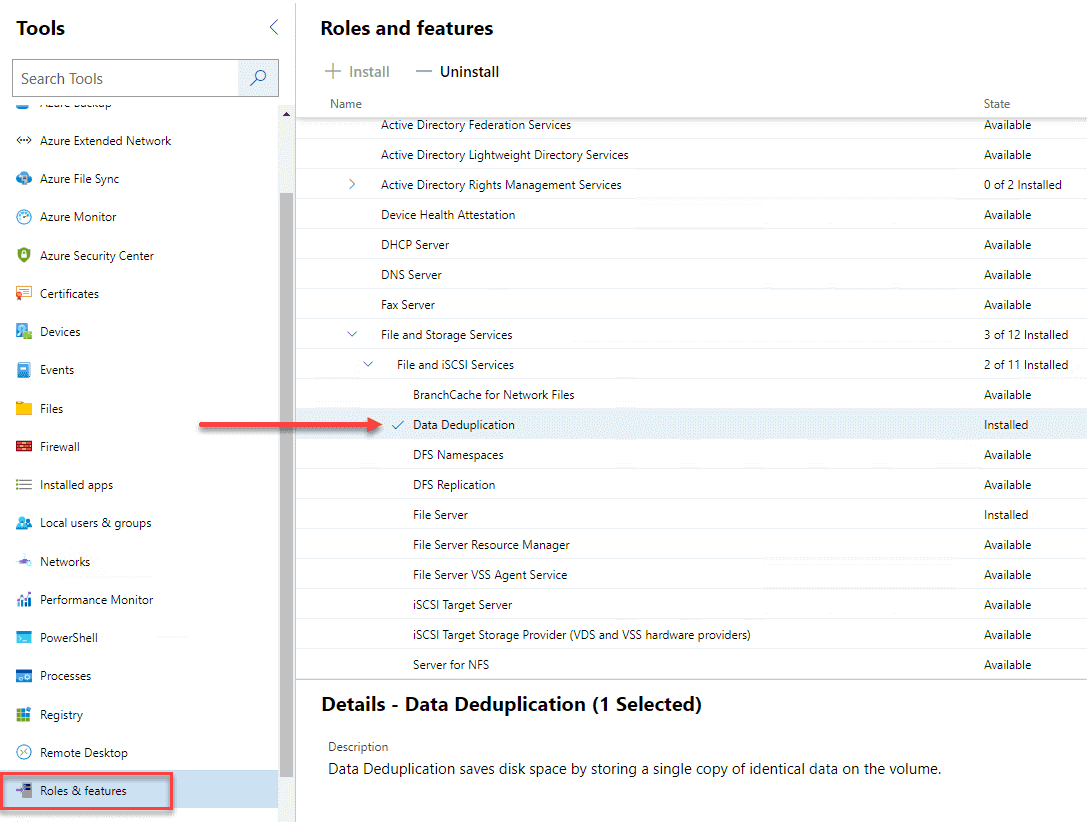
Третий способ установить Дедупликацию данных – через Windows Admin Center перейдя в меню Roles & Features и установить галку напротив Data Deduplication. Затем нажать Install. Windows Admin Center предварительно должен быть установлен!
Включение дедупликации данных на томе
После того, как была установлена Дедупликация данных, процесс включения на томе будет простым. Используя Server Manager (Диспетчер серверов) перейдите к File and Storage Services (Файловым службам и службам хранения) -> Volumes (Тома) -> Disks (Диски). Выберите нужный диск. Затем выберите том, который находится на диске, на котором нужно запустить процесс дедупликации.
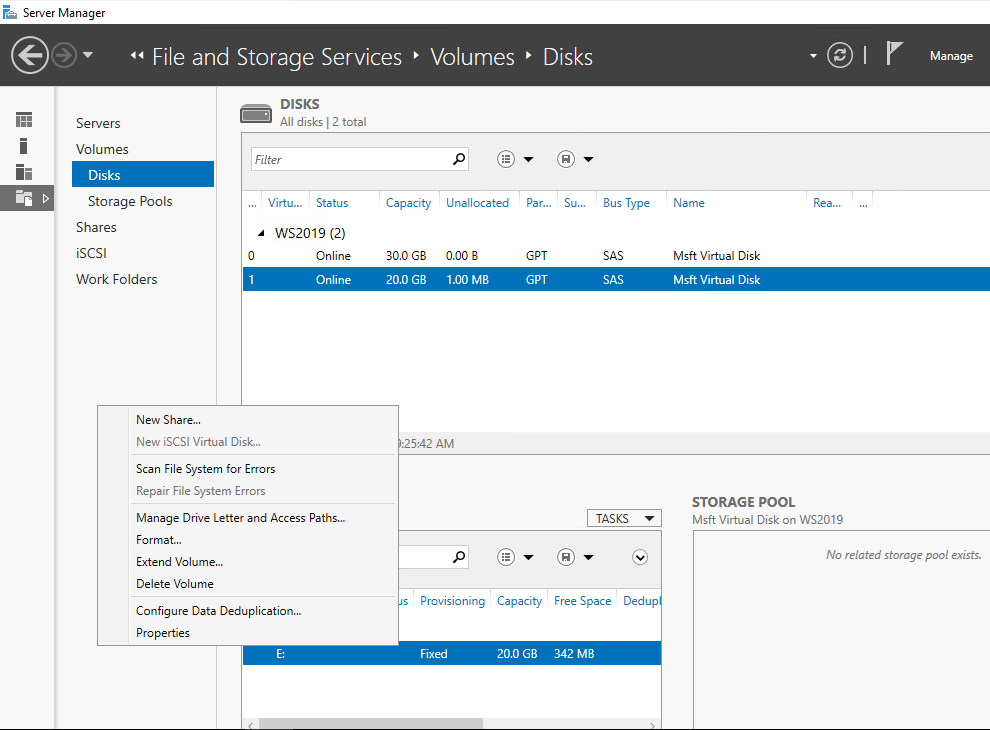
Выберем Configure Data Deduplication
На этом этапе можно выбрать тип данных для дедупликации: файловый сервер, VDI или Backup Server, в Параметрах установить возраст файлов для дедупликации, возможность добавить файлы или папки для исключения.
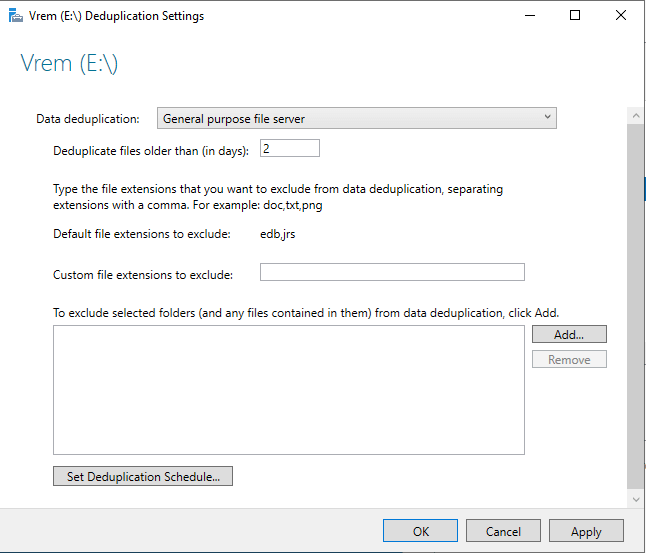
Здесь же настраивается расписание
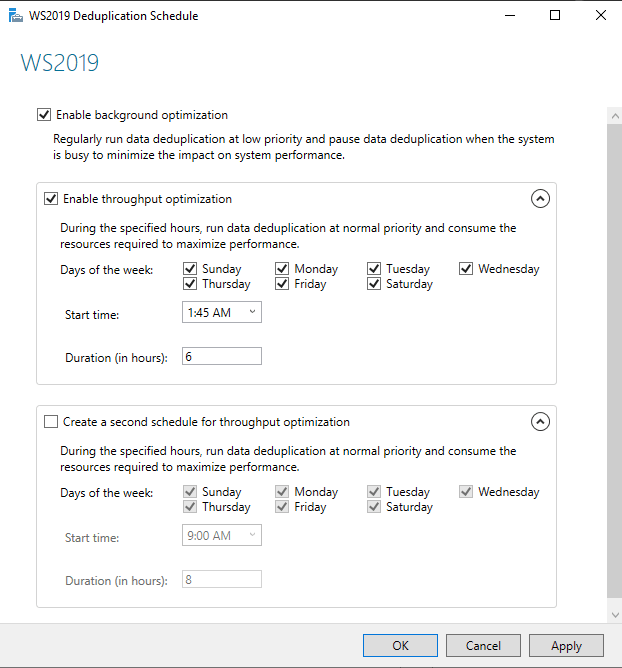
В конфигурации расписания можно добавить дополнительное задание на то время, когда сервер используется минимально, чтобы максимально использовать возможности дедупликации.
Выполнение запланированных задач дедупликации данных
После создания расписания, в Task Scheduler (Планировщик заданий) создается новая задача, работающая в фоновом режиме. По умолчанию процесс дедупликации стартует каждый час. Запустив Task Scheduler и перейдя по пути MicrosoftWindowsDeduplication можно запустить задачу BackgroundOptimization вручную.
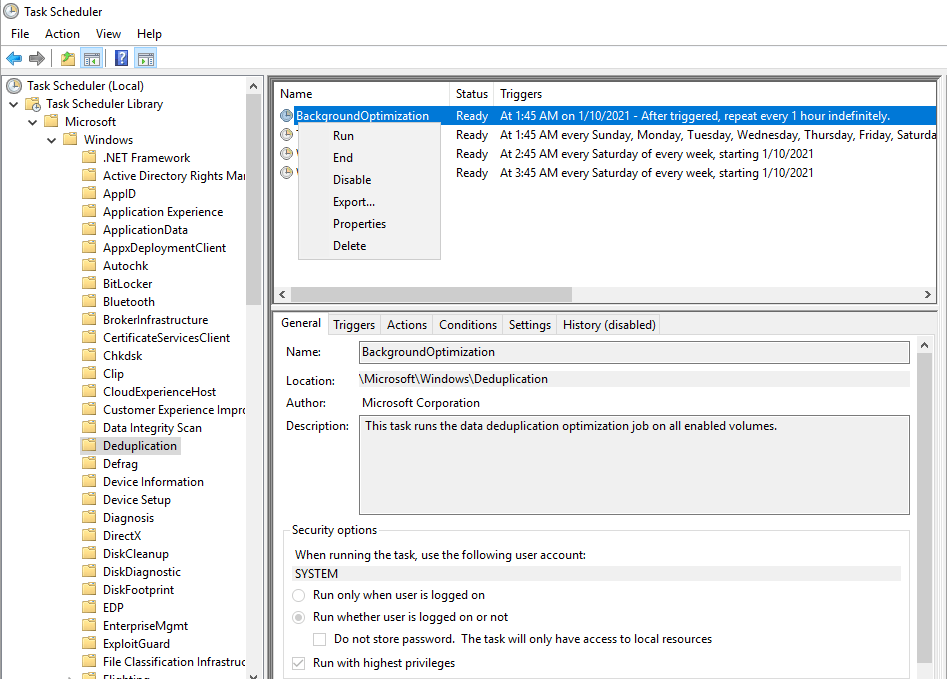
Использование PowerShell для проверки работы и управления дедупликацией
В PowerShell имеются командлеты для мониторинга и управления дедупликацией
Get-DedupSchedule – покажет расписание заданий
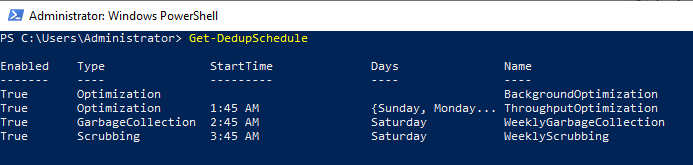
Можно создать отдельное дополнительное задание по оптимизации дедупликации на томе E: с максимальным использованием ОЗУ 20%
Start-DedupJob -Volume "E:" -Type Optimization -Memory 20
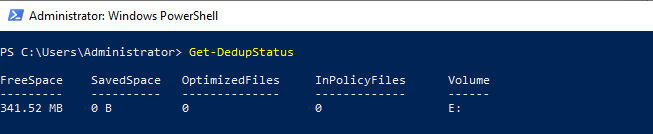
Get-DedupStatus – отобразит состояние операций дедупликации и процент дедупликации
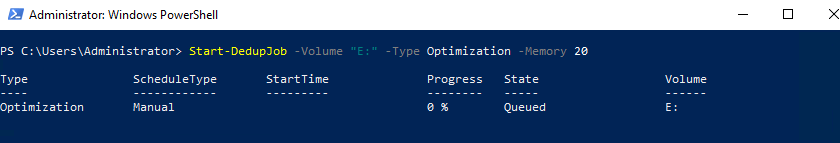
На данном этапе нет экономии места после включения дедупликации данных. В настройках расписания указано дедуплицировать файлы старше 2-х дней.
После запуска процесса мы начинаем видеть экономию места на томе.
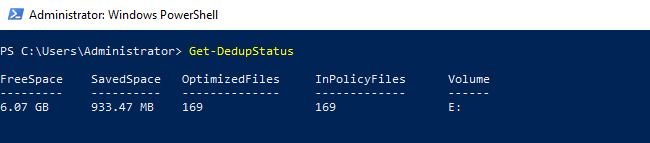
Get-DedupMetadata — просмотр метаданных по дедупликации
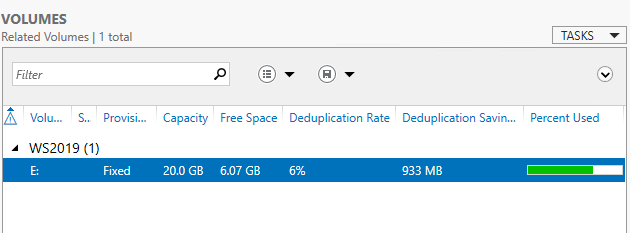
Server Manager также отобразит измененную информацию.
Если нужно отключить использование дедупликации, нужно использовать два командлета:
Disable-DedupVolume -Volume <буква тома>
Start-DedupJob -type Unoptimization -Volume <буква тома>
Необходимо учесть, что обратный процесс уменьшит свободное пространство на томе и у вас должно быть достаточно для этого места.
Вывод
Дедупликация данных в Windows Server — отличный способ эффективно использовать место на устройствах хранения данных. С каждым выпуском Windows Server возможности дедупликации продолжают улучшаться. Дедупликация обеспечивает огромную экономию места, особенно для файловых серверов и сред виртуализации VDI. Для последних экономия места может достигать 80 и более %.
Использование дополнительных опций, таких как расписание, управление типами файлов и возможность использовать исключения позволяет гибко настраивать дедупликацию. PowerShell предоставляет несколько командлетов, которые позволяют взаимодействовать, управлять и контролировать дедупликацию данных в Windows Server.
ReFS is a file system introduced by Microsoft several years ago. It’s important to know about it if you work on the Windows server platform or even with client versions like 10 and 11, as this could improve your experience performing various tasks!
The file format is available in specific versions of Windows 10/11 client operating systems. As you are aware that NTFS (New Technology File System) was introduced almost 26 years ago, and we can clearly say that it is no more a newer file system in the market. Meanwhile, the ReFS (Resilient File System) has advantages and disadvantages in the production environment. In this guide, let us see how to use and format a disk partition in ReFS format (64 kilobytes) in Windows 10/11 and Windows 2019 server versions.
Advantage or Disadvantage?
We will not be looking more at the advantages, disadvantages and tech specifications of this file format. If you want to learn more, you can check this guide.
What I found out is that the ReFS is the best file format if you’re going to store the larger files which rarely get accessed. Especially if you save larger backup files on a disk, it is better to format in ReFS. This file system is most resilient against data corruption compared to NTFS.
Even though it is missing a few features of NTFS such as file-level encryption and compression but if you store larger files (like backup, media, data files), they don’t require encryption. We need better protection against data corruption. Microsoft and other major backup solutions such as Veeam recommend using ReFS file format.
Remember a few key elements of ReFS before you format a disk:
- You can’t install Operating System on the partition.
- Windows App store can’t install apps on this partition.
- Even the installed programs on the partition may not work/open perfectly.
- No file-level compression and encryption (Full disk encryption and BitLocker still work)
As ReFS consumes more computer resources to work, it may impact the lower-level servers and desktop computers. It may not be a significant issue in the data center which usually have high end (right configuration) servers.
Windows Pro and Home Edition do not support the ReFS file format. You will not get an option to format in this file system. Also, a few registry hacks suggested by other websites will not work if you have the wrong version of Windows 10, or 8.1.
You should have Windows 10 or Windows 11 Enterprise to get the ReFS file format. Microsoft has slowly removed ReFS support from Windows 10 Pro with the latest Windows updates.
Right-click on the partition you need to format and select format. Here choose the ReFS file format and unit size. You can leave the unit size to default if you do not have any specific size requirement. Few programs such as backup applications may require the disk in ReFS format with a certain unit size like 64kb, in that case, select the option and format.
You can confirm the file system by checking the properties.
If you want to format in command prompt or change the block
size to a different one (in this case, 4K to 64K), follow the below steps.
Type the below command (Open the command prompt as administrator)
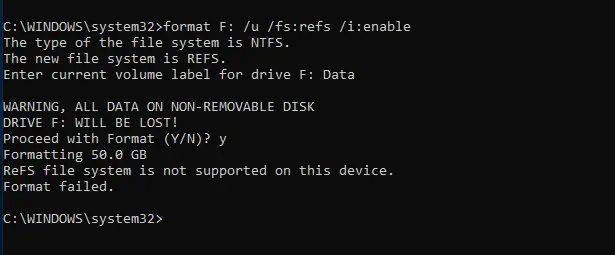
format K: /u /fs:refs /A:64k /i:enable
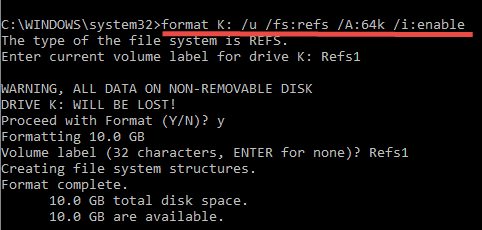
Here is the partition with a 64K block size. Obviously, this conversion will format the entire disk which leads to data loss.
fsutil fsinfo refsinfo <drive letter:> is a useful command to get the details such as the block size of a ReFS partition. It will be handy when you have the Core version of the Windows server or check through PowerShell.
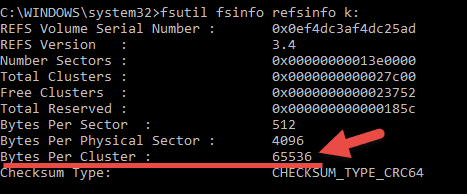
By the way, if you want to know about partition details from a command prompt, here is another useful command you must know as a server administrator.
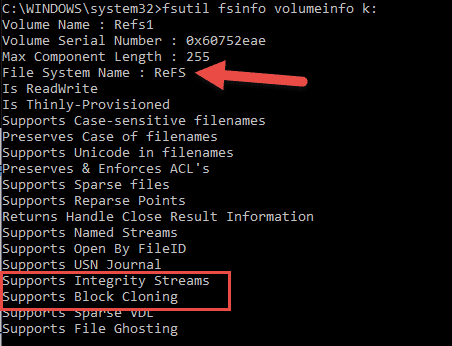
fsutil fsinfo volumeinfo <drive letter:>
Format ReFS from Storage Pool
You can get ReFS formatted disk pool from Storage Space in Windows 10. We are not covering it here since you need to have a minimum of two hard disks to create a storage pool which may not be applicable for personal Windows 11/10 computers.
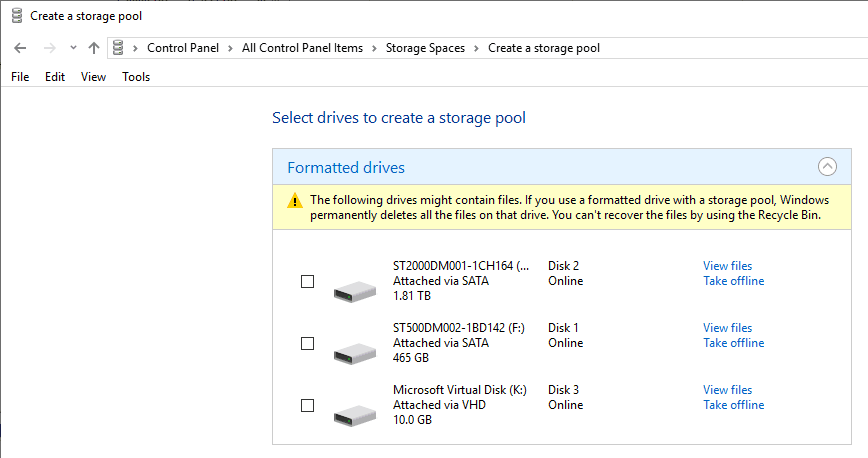
It is easy to create a Storage Pool on the latest Windows system as long as you have more than 2 physical disks. Do not add/modify OS disk. It should be done with the additional 2 more hard disks to create a storage pool. If you want to test it without extra physical hard disks, you can create VHD (Virtual hard disk files) on your existing partition and see how it works (like I created the last 10GB disk in the above example)
Create Partitions in ReFS file format on Windows 2019/2022 Servers
The steps mentioned earlier for Windows 10 workstations are suitable for server versions (like 2012R2 and 2016) s also.
You can format a disk in ReFS format on most of the Windows servers easily without any registry hacks.
The CMD and PowerShell commands work well on the server OS in case you need to use them on Server Core or without desktop experience versions.
Generally, Servers have more disks such as Physical disks, virtual disk files and NAS storage (iSCSI and Fiber disks). Therefore creating a storage pool (space) and formatting it with ReFS gives extra advantages of expanding the disk space whenever wanted in the pool.
Hope this guide gives an overview of the ReFS file system in Windows 10/11 and server versions 2012R2, 2016/2019 and the latest 2022. Also, how to format the disks in ReFS by GUI and command prompt shown with examples in this guide.
