В декабре Microsoft выпустила документ, описывающий основные изменения в версиях, политике лицензирования и ценовой политике на редакции своего нового флагмана в нише серверных ОС Windows Server 2016, который готовится к выходу во второй половине грядущего года .
Примечание. Информация об особенностях лицензирования Windows Server 2016 в данной статье основана на документации, которая была опубликована компанией Майкрософт в декабре 2015 года. Скорее всего, до выхода RTM версий Windows Server 2016 политика лицензирования и цены не изменятся. В любом случае, перед покупкой лицензии рекомендуем получить от Microsoft или партнеров актуальную информацию о ценах и правилах лицензирования.
Содержание:
- Лицензирование серверных ядер
- Редакции Windows Server 2016
- Client Access License (CAL) лицензии
- Цены на редакции Windows Server 2016
- FAQ по лицензированию Windows Server 2016

Лицензирование серверных ядер
Главное нововведение в политике лицензирования Windows Server 2016 — переход от лицензирования физических процессоров (подробнее о лицензировании Windows Server 2012 R2) к лицензированию процессорных ядер. Теперь стоимость лицензий будет рассчитываться не по числу процессоров, а по числу ядер системы (аналогично лицензированию Microsoft SQL Server).
Одна лицензия Windows Server 2016 будет стоить в восемь раз дешевле, чем лицензия Windows Server 2012 на два процессора, но одна новая лицензия будет покрывать только два физических ядра.
Этот шаг Microsoft в общем-то ожидаем, т.к. разработчики процессоров за последние несколько лет существенно увеличили количество ядер (и собственно производительность). В частности Intel уже предлагает заказчикам 60 ядерный процессор Intel® Xeon Phi стоимостью 2500$. В Майкрософт представили сколько они потеряют денег при лицензировании по старой модели в случае массового внедрение таких систем и быстренько разработали новую политику лицензирования.
Порядок лицензирования физических ядер сервера таков:
- Должны быть лицензированы все физические ядра сервера (ядра с Hyper-threading считаются одним ядром)
- Минимальное количество приобретаемых лицензий на ядра одного процессора: 8 шт
- Минимальное количество лицензий на ядра одного сервера : 16 шт
- Если процессор отключен на уровне системы, его ядра лицензировать не нужно.
Таким образом, для лицензирования одного физического сервера с двумя четырехядерными процессорами нужно приобрести 8 комплектов двухъядерных лицензий (что будет равно по стоимости одной двухпроцессорной лицензии Windows Server 2012). Для лицензирования однопроцессорного 16-ядерного сервера также понадобится комплект из восьми 2-ядерных лицензий.
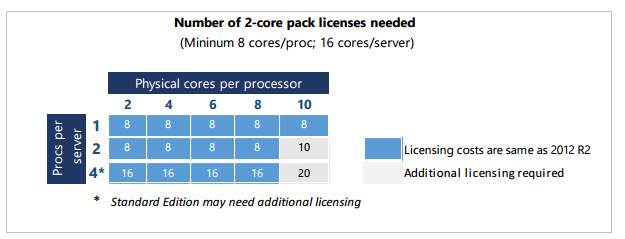
Примечание. Таким образом, по сравнению с Windows Server 2012, стоимость лицензий на маломощные сервера не изменится, но для высокопроизводительных систем с несколькими 10-ядерными процессорами, расходы на лицензирование вырастут на 25%.
Редакции Windows Server 2016
На сегодняшний день известно о двух редакциях Windows Server 2016 (как это было с Windows Server 2012/ 2012 R2):
- Windows Server 2016 Datacenter
- Windows Server 2016 Standard
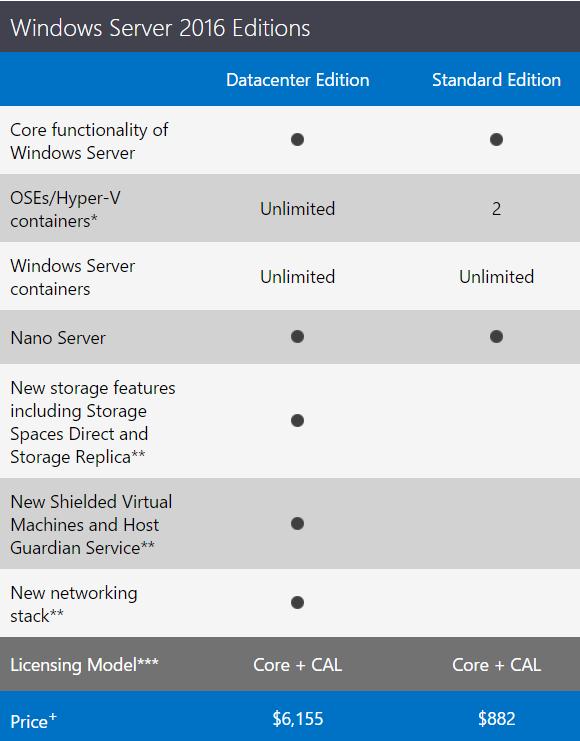
В отличии от Windows Server 2012 R2, в котором разница в редакциях Standard Edition и Datacenter Edition заключалась в количестве поддерживаемых виртуальных машин (2 и неограниченное количество соответственно) и в наличии возможности автоматической активации виртуальных машин в редакции Datacenter. В Windows Server 2016 помимо разницы в возможностях виртуализации, появились и другие функциональные отличия.
В частности Windows Server 2016 Datacenter поддерживает следующие технологии:
- Storage Spaces Direct — расширение технологии Storage Spaces для создания HA хранилищ для кластеров
- Storage Replica – технология блочной синхронной мультисайтовой репликации между кластерами
- Shielded Virtual Machines — технологию создания защищенных виртуальных машин, чей контент защищен от администратора хост-системы Hyper-V
- Host Guardian Service – роль сервера для поддержки защищенных виртуальные машины (Shielded Virtual Machines) и данные на них от несанкционированного доступа
- Network Fabric
- Microsoft Azure Stack — SDN стек на основе Azure
Примечание. Информация о других редакциях Windows Server 2016 и Windows Storage Server 2016 появится в первом квартале 2016 года.
Client Access License (CAL) лицензии
Windows Server Standard и Datacenter по прежнему требуют приобретения лицензий Windows Server CAL для всех устройств или пользователей, использующих сервер.
Клиентские CAL лицензии для Remote Desktop Services и AD Rights Management Services также требуется приобретать отдельно.
Цены на редакции Windows Server 2016
Майкрософт также опубликовала официальные цены на Windows Server 2016. Комплект лицензий на 16 ядер (8 пакетов лицензий по 2 ядра) будет стоить:
- Windows Server 2016 Standard — 882 $
- Windows Server 2016 Datacenter — 6155 $
FAQ по лицензированию Windows Server 2016
В этом разделе буду собирать и отвечать на частые вопросы по лицензированию Windows Server 2016
- Как лицензируется Nano Server?Nano Server это опция установки Windows Server 2016 и не требует дополнительного лицензирования
- Как лицензировать процессоры с Hyper-Threading?В Windows Server и System Center 2016 лицензируются только физические ядра. С этой точки зрения ядро с поддержкой технологии Hyper-Threading являются одним ядром.
- Если процессор/ ядро отключено и не используется Windows, нужно ли покупать на него лицензии?Отключенные процессоры и ядра лицензировать не требуется.
- Как лицензируются виртуальные контейнеры (Hyper-V Containers)Hyper-V Containers контейнеры лицензируются также, как обычные виртуальные машины Hyper-V. На редакции Standard можно запустить 2 виртуальные машины, на Datacenter – неограниченное количество
Корпорация Microsoft выпустила серверную операционную систему Windows Server 2016, дополнив ее поддержкой контейнеров и новым изданием Nano Server. Windows Server 2016 разрабатывалась несколько лет и параллельно с совершенствованием ОС выходили ее предварительные версии. С 1 октября 2016 года доступна линейка продуктов Windows Server 2016, состоящая из шести изданий: WS 2016 Datacenter, Standard, Essentials, MultiPoint Premium Server, CAL, Windows Remote Desktop Services CAL 2016.
Одним из основных направлений при разработке Microsoft Server 2016 стала поддержка публичных и частных облаков. Многие инновации Windows Server 2016 заимствованы из Azure и доведены до уровня мейнстрима. В Windows Server 2016 также значительно усовершенствован гипервизор Hyper-V, появилась поддержка контейнеров и Nano Server – новая «урезанная» версия Windows Server. Цель все та же – нативная поддержка облачных приложений.

10 причин полюбить Windows Server 2016: безопасность (управление привилегиями/идентификационными данными, средства защиты), платформа для приложений (Nano Server, контейнеры), платформа для программно-определяемых дата-центров (вычисления, хранение данных, сетевые функции, RDS), управление (средства управления сервером, новая версия PowerShell).
По сути эта ОС напоминает Windows 10 в серверном исполнении. В Server 2016 используется то же ядро, что и в Windows 10 Anniversary, и, введя ver в командной строке, вы получите тот же ответ: Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.14393]. В Windows Server 2016 — то же меню «Пуск», что и в Windows 10 Anniversary (при инсталляции с Desktop Experience).

Windows Server 2016, теперь с «рабочим столом» Windows 10.
Что интересного можно отметить? В списке Microsoft – более 40 новых средств, включая вложенную виртуализацию для контейнеров Hyper-V и развертывания хостов Hyper-V в Azure или других публичных облаках. Многие новые средства Hyper-V относятся к созданию и обслуживанию гостевых ВМ.
Можно «на лету» менять емкость виртуальных дисков, памяти, добавлять и удалять виртуальные сетевые карты. Виртуальным машинам можно предоставлять дискретный доступ к устройствам на шине PCIe, таким как контроллеры дисков. А кластер Windows Server 2012 R2 с Hyper-V можно обновить до Server 2016 без прерывания сервисов.
Конечно, некоторые решения не дешевы, а потому к категории массовых не относятся. Например, защищенная от аварий конфигурация с двумя разнесенными на разные площадки системами Azure Stack. Конечно, можно запустить Azure Stack и на одном сервере, но, скорее, с целью тестирования. Тем не менее, большинство изменений касаются самого широкого круга пользователей.
Обновленный гипервизор
Многочисленным доработкам подвергся гипервизор Hyper-V. Можно выделить следующие изменения:
- Клиент Hyper-V поддерживает Windows 10.
- Совместимость с Connected Standby.
- Назначение дискретного устройства.
- Мониторинг активности виртуальных машин для оптимизации использования системных ресурсов (RCT).
- Использование альтернативных аккаунтов при подключении к другой системе Windows Server 2016.
- Обновленный протокол управления и другие улучшения.

Новые функциональные возможности Hyper-V – самые востребованные и ожидаемые новшества Windows Server 2016 (по данным опроса SpiceWorks). Их отмечают более 30% респондентов.
В нем появилась и поддержка вложенной виртуализации (Nested virtualization), позволяющая запускать виртуальные машины на гипервизоре, который сам установлен в виртуальном окружении.

Вложенная виртуализация означает, что можно запустить Hyper-V в ВМ, являющейся гостевой на сервере Hyper-V, гостевом на сервере Hyper-V и т.д.
Такая возможность может быть актуальной для разработчиков и моделирования виртуальных инфраструктур, а также для более эффективного использования контейнерных приложений. Устранены и многие прежние ограничения.

Hyper-V в Server 2016 стал более масштабируемым.
Теперь Microsoft Hyper-V позволяет выделять виртуальной машине до 12 Тбайт ОЗУ (вместо одного) и до 240 виртуальных процессоров (вместо 64). Хост Hyper-V поддерживает ОЗУ до 24 Тбайт. Для снижения непроизводительных потерь и усиления безопасности на хосте Hyper-V можно запустить Nano Server. Для администрирования в этом случае можно использовать PowerShell и удаленный доступ.
Безопасность
В Windows Server 2016 дальнейшее развитие получили механизмы обеспечения безопасности. В частности, в отдельный контейнер Hyper-V под названием Virtual Security Module (VSM) помещены самые ценные системные данные, криптографические модули Windows Server 2016, компоненты, отвечающие за целостность ядра ОС, пароли и пр. Доступ к этим данным невозможен даже при компрометации системы.
Еще одно важное средство — виртуальный TPM (Trusted Platform Module), позволяющий задействовать в виртуальных машинах средства шифрования с использованием Bitlocker, и Credential Guard для безопасного хранения идентификационных данных. Применение Virtual TPM особенно актуально, например, при размещении ВМ в облаке.

Host Guardian Service – важный компонент обеспечения безопасности. Он работает в сочетании с другими компонентами Windows Server 2016 и обеспечивает высокий уровень защиты Shielded VM.
В плане безопасности интересным решением стали защищенные виртуальные машины — Shielded VM, но для их создания требуется Windows Server Datacenter и отдельный сервер со службой Host Guardian Service для хранения ключей и проверки прав ВМ на запуск на конкретной платформе.

Host Guardian Service используется для верификации запуска Shielded VM. А с помощью инструментария Guarded Fabric можно гибко сконфигурировать сетевую инфраструктуру и разбить ее на отдельные изолированные сетевые сегменты.
Технология Shielded VM позволяет создавать в облачной инфраструктуре защищенные виртуальные машины, доступ к которым может получить только их владелец. Администратору разрешено только включать и выключать такие виртуальные машины. Вмешиваться в их работу, читать данные, перехватывать трафик, менять их конфигурацию он не имеет права. Механизм Shielded VM может быть востребован хостинг-провайдерами, предоставляющими услуги аренды виртуальных серверов.
Возможность подключения виртуального дисплея к ВМ средствами администрирования Hyper-V в Shielded VM также заблокирована. Как же исправить ВМ, если что-то пошло не так, и она не запускается? На этот случая Microsoft предлагает хитрое решение – запуск такой ВМ внутри другой Shielded VM. При создании Shielded VM нужно также учитывать, что требования к системным ресурсам у них повышенные.
Улучшенный PowerShell обеспечивает более легкий и всесторонний контроль над средами, что значительно повышает уровень безопасности системы. Также одной из ключевых функций безопасности является разграничение прав доступа при администрировании.
В Windows Server 2016 также появилось средство под названием Just Enough Administration (JEA). Это означает, что администраторы могут логиниться под временными аккаунтами, ограниченными определенными ролями. То есть администратор, войдя в систему с зараженного вирусом ПК, большого вреда не причинит. Windows Credential Guard также ограничивает возможный ущерб от вредоносных программ при таком сценарии. А временные права администрирования (Just in Time Administration) можно предоставить с помощью Microsoft Identity Manager Privileged Access Manager.
Хранение данных и сети – Software Defined
Как известно, в Window Server 2012 помощью Storage Spaces можно создавать отказоустойчивые пулы памяти на дисках SAS, подключенных к серверу без помощи традиционной SAN (Storage Area Network). Storage Spaces Direct дает возможность напрямую подключать к кластеру Server 2016 накопители SAS, SATA или SSD. Это можно использовать для создания программно-конфигурируемых систем хранения (Software-Defined Storage, SDS).

Storage Spaces Direct можно использовать для прямого подключения накопителей.
Появилась возможность динамического управления пропускной способностью виртуальных дисков Storage Quality of Service (QoS). Применять политики Storage QoS можно как к дисковой подсистеме отдельной виртуальной машины, так и к группе ВМ.

Storage Replica реализует блочную синхронную репликацию между сконфигурированными серверами с использованием протокола SMB 3.1.1.
С помощью инструментария Storage Replica администраторы могут реплицировать данные между удаленными серверами, кластерными системами и центрами обработки данных, повышая тем самым их катастрофоустойчивость и предотвращая потери на уровне файловой системы.
Для поддержки SDN (Software Defined Networking) в Server 2016 добавлена роль Network Controller. Сетевой контроллер предназначен для управления в Hyper-V виртуальными коммутаторами, балансировщиками нагрузки, правилами межсетевых экранов и виртуальными шлюзами. Поддерживаются также VXLAN (Virtual Extensible Local Area Network).
Nano Server
Nano Server – это еще более компактный вариант Server Core. Его удобно использовать как хост-систему для развертывания виртуальных машин, использовать в качестве сервера DNS или IIS, для запуска приложений в контейнерах.

Улучшения в уровне обслуживания: меньше уязвимостей, меньше перезагрузок.
По данным Microsoft, у Nano Server на 93% меньше размер VHD, он требует на 80% меньше перезагрузок. Такую систему можно применять для различных специальных функций и задач. Причем Nano Server работает как на физическом сервере, так и в ВМ. GUI у него нет – только инструменты Sysinternals.
Nano Server удобно также использовать в инфраструктуре Microsoft Cloud Platform для поддержки облачных служб и обслуживания приложений, функционирующих в виртуальном окружении, контейнерах или на физических серверах. Его можно применять для развертывания вычислительных кластеров и построения горизонтально-масштабируемых файловых хранилищ.

Благодаря своей компактности и эффективному использованию ресурсов Nano Server обеспечивает более высокую плотность ВМ, то есть на одном физическом хосте можно разместить больше экземпляров ОС, что сокращает расходы на ИТ-инфраструктуру.
Контейнеры
Важное отличие Windows Server 2016 от предыдущих версий серверных операционных систем Microsoft — поддержка технологий контейнеров. Контейнеры Windows Server — часть открытого проекта Docker. Они позволяют запускать приложения в изолированных средах на разных платформах, оперативно развертывать и перемещать их между серверами.
В Windows поддерживаются контейнеры двух видов — контейнеры Windows Server и контейнеры Hyper-V. Облегченные серверные контейнеры не требуют лицензии Windows. Контейнеры Windows Server функционируют подобно контейнерам Docker для платформы Linux. Они используют общее ядро операционной системы, что делает их более компактными и гибкими, чем обычные виртуальные машины.

У каждого контейнера Hyper-V своя копия ядра Windows Server, и изоляцию осуществляет не операционная система, а гипервизор.
Контейнеры Windows Server делят ресурсы ОС, но ведут себя как независимые экземпляры операционной системы. Однако в среде ОС Windows Server нельзя запустить контейнер Linux и наоборот. Для запуска контейнера его образ берется из репозитория (публичного или частного) и при необходимости модифицируется.

Контейнер Docker, работающий в Windows Server 2016.
Контейнеры Hyper-V изолированы средствами виртуализации, имеют свою копию ядра Windows, а в версии Standard лицензия для них не нужна. У таких контейнеров более высокий уровень изоляции, сравнимый с виртуальными машинами. Данный подход более требователен к ресурсам сервера, но повышает стабильность работы серверной ОС и надежность функционирования контейнеров.
Управляются оба вида контейнеров одинаково. Управление контейнерами Windows Server и Hyper-V может осуществляться как средствами PowerShell и WMI, так и при помощи инструментов Docker. Последние предоставляют единую среду администрирования и позволяют управлять контейнерными приложениями в среде Windows Server или Linux.

Конфигурирование контейнеров в Windows Server 2016. Контейнеры Hyper-V могут использоваться для запуска приложений с повышенными требованиями к информационной безопасности.
Хороший вариант для развертывания контейнеров — Nano Server. Однако нужно помнить, что Nano Server – это урезанная Windows. Если IIS, например, в нем работает, то .NET Framework – уже нет (только кросс-платформенная .NET Core). Не все приложения в настоящее время совместимы с Nano Server.

Образы Docker в Nano Server могут быть очень компактными.
Контейнеры Docker в Windows — пока что на начальном этапе. Потребуется время, чтобы администраторы их освоили, а разработчики – довели до ума. Microsoft понадобится также пополнить соответствующими опциями имеющийся инструментарий вроде Visual Studio.
Другие возможности
В Windows Server 2016 реализовано и множество других новшеств. Система получила новый механизм скачивания и раздачи обновлений, функционирующий по принципу P2P-протокола BitTorrent, поддержку протокола SSH. Windows Server 2016 поставляется с Windows Management Framework 5.1 и новой версией PowerShell, использующей .NET Framework 4.6.
Обновленный Windows PowerShell позволяет оперировать еще большим количеством командлетов (cmdlets), которые выполняют различные задачи управления. В частности, PowerShell 5 предлагает командлеты для управления локальными пользователями и группами и командлет Get-ComputerInfo для получения подробной информации о системе.
Нововведения коснулись и служб Active Directory. Теперь можно использовать смарт-карты для аттестационных ключей. Доменные службы Active Directory обеспечивают еще более высокий уровень безопасности при идентификации корпоративных и персональных устройств.
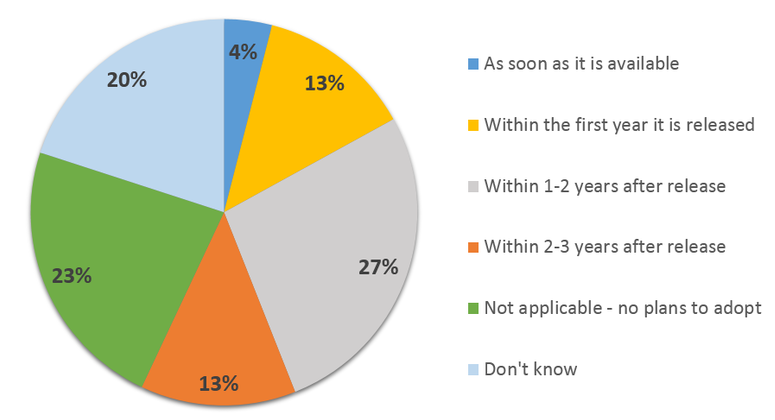
Планы перехода организаций на Windows Server 2016 (по данным опроса SpiceWorks, проведенного в ноябре 2015 года).
Появился новый формат файлов конфигурации виртуальных машин (.VMCX и .VMRS) с более высокой степенью защиты от сбоев на уровне хранилища, была добавлена возможность безопасной загрузки гостевых операционных систем Linux и поддержка OpenGL и OpenCL службой удаленных рабочих столов Remote Desktop Service (RDS).
Механизм обновления ОС хостов кластера без его остановки (Cluster Operating System Rolling Upgrade) дает возможность с нулевым временем простоя обновить кластер последовательным апдейтом отдельных его узлов.
В состав Windows Server 2016 включен также инструментарий IP Address Management (IPAM), позволяющий упростить управление IP-адресами. Конечно, обо всех новшествах новой ОС в одной статье рассказать невозможно. Это лишь весьма поверхностный «первый взгляд».
Издания Windows Server 2016
Сколько всего изданий у Windows Server 2016? Хороший вопрос. Выше говорилось о шести. Есть издания Standard и Datacenter, различающиеся схемами лицензирования. Standard включает лицензии только для двух ВМ или контейнеров Hyper-V под Windows Server, в то время как в Datacenter количество ВМ не ограничивается. Версия Datacenter потребуется для работы с некоторыми новыми средствами, включая Storage Spaces Direct, Storage Replica, Shielded Virtual Machine и ряд сетевых функций. Стоит версия Standard от 882 долл. для 16 ядер. Datacenter обойдется минимум в 6155 долл.

Функциональные отличия изданий Datacenter и Standard в Windows Server 2016.
Ниже представлены функции, которые есть только в редакции Windows Server 2016 Datacenter:
- Storage Spaces Direct — расширение технологии Storage Spaces для создания высокодоступных кластерных хранилищ;
- Storage Replica — технология блочной репликации данных между хранилищами;
- Shielded Virtual Machines — технология защиты содержимого виртуальных машин Hyper-V;
- Host Guardian Service — серверная роль, предназначенная для поддержки защищенных виртуальных машин (Shielded VM) и предотвращения несанкционированного доступа к ним;
- Network Fabric — централизованный мониторинг и управление сетевой инфраструктурой;
- Microsoft Azure Stack — поддержка SDN-стека для построения гибридных решений.
Nano Server лицензируется как средство Windows Server, но требует лицензии Software Assurance вместо базовой и отдельно не продается. Есть еще бесплатная Windows Hyper-V Server, используемая только как хост Hyper-V, а также версия Windows Server Essentials для малого бизнеса — до 25 пользователей и 50 устройств, для которой не нужны лицензии CAL (Client Access Licenses). Essentials стоит 501 долл., но существуют более дешевые OEM-версии. OEM-версии Windows Server Foundation больше не поставляются.

Назначение изданий Windows Server 2016 и модели лицензирования.
Есть еще пара специальных изданий: Windows Storage Server для систем хранения и Multipoint Premium Server, в основном для удаленных десктопов в сфере образования. Версии Standard и Datacenter по умолчанию инсталлируются без GUI (опция Server Core).
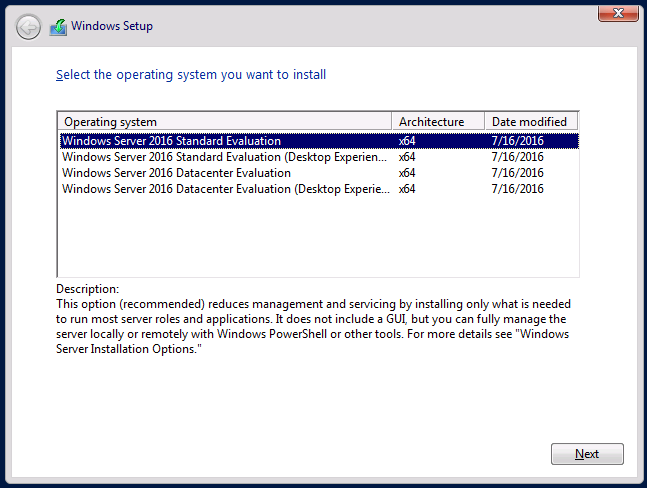
По умолчанию процедура установки Windows Server 2016 выполняется без GUI.
Резюмируя, можно отметить, что Windows Server 2016 предоставляет много возможностей для полноценного развертывания и функционирования ИТ-инфраструктуры в облаке. Новая ОС облегчает возможность доступа и идентификации служб и приложений организации в том случае, если они размещены и в облаке, и на физических серверах. Серверная платформа Microsoft активно развивается в соответствии с тенденциями развития индустрии и предпочтениями бизнеса. Работа проделана немалая, система развивается в правильном направлении. Проверить работу Windows Server 2016 можно, взяв виртуальный VPS сервер на бесплатный тестовый период в 3 дня.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Windows Server 2016
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
|
Screenshot of Windows Server 2016 with Desktop Experience |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Written in |
|
| OS family | Windows Server |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
September 26, 2016; 8 years ago[1] |
| General availability |
October 12, 2016; 8 years ago[2] |
| Latest release | 1607 (10.0.14393.7973) (April 11, 2025; 32 days ago[3]) [±] |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (Graphical) Windows PowerShell (Command line) |
| License | Trialware, Volume licensing, Microsoft Software Assurance, MSDN subscription, Microsoft Imagine |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2012 R2 (2013) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2019 (2018) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2016 (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
|
Windows Server 2016 is the eleventh major version of the Windows NT operating system produced by Microsoft to be released under the Windows Server brand name. It was developed alongside Windows 10 and is the successor to the Windows 8.1-based Windows Server 2012 R2. The first early preview version (Technical Preview) became available on October 1, 2014 together with the first technical preview of System Center.[5] Windows Server 2016 was released on September 26, 2016 at Microsoft’s Ignite conference[1] and reached general availability on October 12, 2016.[2]
It was succeeded by Windows Server 2019 and the Windows Server Semi-Annual Channel, which was released in 2017. Mainstream support for Windows Server 2016 ended on January 11, 2022, and extended support will end on January 12, 2027.
Windows Server 2016 has a variety of new features, including
- Active Directory Federation Services: It is possible to configure AD FS to authenticate users stored in non-AD directories, such as X.500 compliant Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directories and SQL databases.[6]
- Windows Defender: Windows Server Antimalware is installed and enabled by default without the GUI, which is an installable Windows feature.[7]
- Remote Desktop Services: Support for OpenGL 4.4 and OpenCL 1.1, performance and stability improvements; MultiPoint Services role (see Windows MultiPoint Server)[8]
- Storage Services: Central Storage QoS Policies; Storage Replicas (storage-agnostic, block-level, volume-based, synchronous and asynchronous replication using SMB3 between servers for disaster recovery).[9] Storage Replica replicates blocks instead of files; files can be in use. It’s not multi-master, not one-to-many and not transitive. It periodically replicates snapshots, and the replication direction can be changed.
- Failover Clustering: Cluster operating system rolling upgrade, Storage Replicas[10]
- Web Application Proxy: Preauthentication for HTTP Basic application publishing, wildcard domain publishing of applications, HTTP to HTTPS redirection, Propagation of client IP address to backend applications[11]
- IIS 10: Support for HTTP/2
- Windows PowerShell 5.1[12]
- Windows Server Containers [13]
Networking features
[edit]
- DHCP: As Network Access Protection was deprecated in Windows Server 2012 R2, in Windows Server 2016 the DHCP role no longer supports NAP[14]
- DNS:
- DNS client: Service binding – enhanced support for computers with more than one network interface[15]
- DNS Server: DNS policies, new DDS record types (TLSA, SPF, and unknown records), new PowerShell cmdlets and parameters[16]
- Windows Server Gateway now supports Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnels[17]
- IP address management (IPAM): Support for /31, /32, and /128 subnets; discovery of file-based, domain-joined DNS servers; new DNS functions; better integration of DNS, DHCP, and IP Address (DDI) Management[18]
- Network Controller: A new server role to configure, manage, monitor, and troubleshoot virtual and physical network devices and services in the datacentre[19]
- Hyper-V Network virtualization: Programmable Hyper-V switch (a new building block of Microsoft’s software-defined networking solution); VXLAN encapsulation support; Microsoft Software Load Balancer interoperability; better IEEE Ethernet standard compliance.[20]
- Rolling Hyper-V cluster update: Unlike upgrading clusters from Windows 2008 R2 to 2012 level, Windows Server 2016 cluster nodes can be added to a Hyper-V Cluster with nodes running Windows Server 2012 R2. The cluster continues to function at a Windows Server 2012 R2 feature level until all of the nodes in the cluster have been upgraded and the cluster functional level has been upgraded.[21]
- Storage quality of service (QoS) to centrally monitor end-to-end storage performance and create policies using Hyper-V and Scale-Out File Servers
- New, more efficient binary virtual machine configuration format (.VMCX extension for virtual machine configuration data and the .VMRS extension for runtime state data)
- Production checkpoints
- Hyper-V Manager: Alternate credentials support, down-level management, WS-Management protocol
- Integration services for Windows guests distributed through Windows Update
- Hot add and remove for network adapters (for generation 2 virtual machines) and memory (for generation 1 and generation 2 virtual machines)
- Linux secure boot
- Connected Standby compatibility
- Storage Resiliency feature of Hyper-V is formed for detecting transitory loss of connectivity to VM storage. VMs will be paused until connectivity is re-established.[22]
- RDMA compatible Virtual Switch[23]
Microsoft announced a new installation option, Nano Server, which offers a minimal-footprint headless version of Windows Server. It excludes the graphical user interface, WoW64 (support for 32-bit software) and Windows Installer. It does not support console login, either locally or via Remote Desktop Connection. All management is performed remotely via Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), Windows PowerShell and Remote Server Management Tools (a collection of web-based GUI and command line tools).[24] However, in Technical Preview 5, Microsoft has re-added the ability to administer Nano Server locally through PowerShell.
According to Microsoft engineer Jeffrey Snover, Nano Server has 93% lower VHD size, 92% fewer critical security advisories, and 80% fewer reboots than Windows Server.[25][26]
Nano Server is only available to Microsoft Software Assurance customers[2] and on cloud computing platforms such as Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services.
Starting with the new feature release of Windows Server version 1709, Nano Server can only be installed inside a container host.[27]
Microsoft has been reorganized by Satya Nadella, putting the Server and System Center teams together. Previously, the Server team was more closely aligned with the Windows client team. The Azure team is also working closely with the Server team.[28]
In March 2017, Microsoft demonstrated an internal version of Server 2016 running on the ARMv8-A architecture. It was reported that Microsoft was working with Qualcomm Centriq and Cavium ThunderX2 chips. According to James Vincent of The Verge, this decision endangers Intel’s dominance of the server CPU market.[29][30][31] However, later inquiry from Microsoft revealed that this version of Windows Server is only for internal use and only impacts subscribers of Microsoft Azure service.[32]
A public beta version of Windows Server 2016 (then still called vNext) branded as «Windows Server Technical Preview» was released on October 1, 2014; the technical preview builds are aimed toward enterprise users. The first Technical Preview was first set to expire on April 15, 2015 but[33] Microsoft later released a tool to extend the expiry date, to last until the second tech preview of the OS in May 2015.[34] The second beta version, «Technical Preview 2», was released on May 4, 2015. Third preview version, «Technical Preview 3» was released on August 19, 2015. «Technical Preview 4» was released on November 19, 2015. «Technical Preview 5» was released on April 27, 2016.
Windows Server 2016 Insider Preview Build 16237 was released to Windows Insiders on July 13, 2017.[35][36]
Windows Server 2016 was officially released at Microsoft’s Ignite Conference on September 26, 2016. Unlike its predecessor, Windows Server 2016 is licensed by the number of CPU cores rather than number of CPU sockets—a change that has similarly been adopted by BizTalk Server 2013 and SQL Server 2014.[37] The new licensing structure that has been adopted by Windows Server 2016 has also moved away from the Windows Server 2012/2012R2 CPU socket licensing model in that now the amount of cores covered under one license is limited. Windows Server 2016 Standard and Datacenter core licensing now covers a minimum of 8 core licenses for each physical processor and a minimum of 16 core licenses for each server. Core licenses are sold in packs of two with Standard Edition providing the familiar rights to run 2 virtualized OS environments. If the server goes over 16 core licenses for a 2 processor server additional licenses will now be required with Windows Server 2016.[38]
Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview, released on October 1, 2014, was the first beta version of the operating system made publicly available. Its version number was 6.4.9841.[5]
Technical Preview 2
[edit]
Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 2 was made available on May 4, 2015. Its version number was 10.0.10074. (A similar jump in the most significant part of the version number from 6 to 10 is seen in Windows 10.) Highlights of this version include:[39]
- Nano Server installation option[40][41]
- Hyper-V: hot add and remove memory and NIC; resilient virtual machines to keep running even when their cluster fabric fails[42]
- Rolling upgrades for Hyper-V and Storage clusters[40][42]
- Networking: Converged NIC across tenant and RDMA traffic; PacketDirect on 40G[42]
- Storage: Virtual Machine Storage Path resiliency; Storage Spaces Direct to aggregate Storage Spaces across multiple servers; Storage Replica[42]
- Security: Host Guardian Service, helping to keep trust and isolation boundary between the cloud infrastructure and guest OS layers; Just Enough Administration, restricting users to perform only specific tasks[42]
- Management: PowerShell Desired State Configuration; PowerShell Package Manager; Windows Management Framework 5.0 April Preview and DSC Resource Kit[42]
- Other: Conditional access control in AD FS; application authentication support for OpenID Connect and OAuth; full OpenGL support with RDS for VDI; Server-side support for HTTP/2, including header compression, connection multiplexing and server push[42]
- Installation options: Minimal Server Interface was made default and renamed the Server installation option to “Server with local admin tools”.[43]
Technical Preview 3
[edit]
The third technical preview of Windows Server 2016 was made available on August 19, 2015. Its version number was 10.0.10514. Highlights of this version include:
- Windows Server Containers[44]
- Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS): authentication of users stored in Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directories[44]
- Installation options: The Server installation option had been renamed to “Server with Desktop Experience” having the shell and Desktop Experience installed by default. Due to the structural changes required to deliver the Desktop Experience on Server, it is no longer possible to convert from Server with Desktop Experience to Server Core or to convert Server Core up to Server with Desktop Experience.[43]
Technical Preview 4
[edit]
The fourth technical preview of the operating system was made available on November 19, 2015, one year and one month after the initial technical preview. Its version number was 10.0.10586, based on Windows 10 version 1511. Its highlights include:
- Nano Server supports the DNS Server and IIS server roles, as well as MPIO, VMM, SCOM, DSC push mode, DCB, Windows Server Installer, and the WMI provider for Windows Update. Its Recovery Console supports editing and repairing the network configuration. A Windows PowerShell module is now available to simplify building Nano Server images.[45]
- Hyper-V Containers encapsulates each container in a light weight virtual machine.[45]
Technical Preview 5
[edit]
The last technical preview of Windows Server 2016 was made available on April 27, 2016. Its version number was 10.0.14300. Its highlights include:[46]
- Mostly general refinements. Greater time accuracy in both physical and virtual machines
- Container support adds performance improvements, simplified network management, and support for Windows containers on Windows 10
- Nano Server: an updated module for building Nano Server images, including more separation of physical host and guest virtual machine functionality as well as support for different Windows Server editions. Improvements to the Recovery Console, including separation of inbound and outbound firewall rules as well as the ability to repair configuration of WinRM
- Networking: traffic to new or existing virtual appliances can now be both mirrored and routed. With a distributed firewall and Network security groups, this enables dynamically segmented and secure workloads in a manner similar to Azure. One can deploy and manage the entire Software-defined networking (SDN) stack using System Center Virtual Machine Manager. Docker can be used to manage Windows Server container networking, and associate SDN policies not only with virtual machines but containers as well
- Remote Desktop Services: a highly available RDS deployment can leverage Azure SQL Database for the RD Connection Brokers in high availability mode
- Management: ability to run PowerShell.exe locally on Nano Server (no longer remote only), new Local Users & Groups cmdlets to replace the GUI, added PowerShell debugging support, and added support in Nano Server for security logging & transcription and JEA (Just Enough Administration)
- Shielded Virtual Machines:
- New «Encryption Supported» mode that offers more protections than for an ordinary virtual machine, but less than «Shielded» mode, while still supporting vTPM, disk encryption, Live Migration traffic encryption, and other features, including direct fabric administration conveniences such as virtual machine console connections and Powershell Direct
- Full support for converting existing non-shielded Generation 2 virtual machines to shielded virtual machines, including automated disk encryption
- Shielded virtual machines are compatible with Hyper-V Replica
Release to manufacturing
[edit]
Windows Server 2016 was released to manufacturing on September 26, 2016, bearing the version number of 10.0.14393 (same as Windows 10 Anniversary Update). Microsoft added the following final touches:
- Available for a 180-day evaluation
- Fixed Start menu corruptions
- Improved user experience and performance
- Windows Store apps have been removed
- Login screen now has a background
- The Windows Hello feature has been added
- Dark theme has been added
Semi-Annual Channel releases
[edit]
Windows Server, version 1709 (version shared with Windows 10 Fall Creators Update) was released on October 17, 2017. The release has dropped the Windows Server 2016 name and is just called Windows Server by Microsoft.[47] It is offered to the Microsoft Software Assurance customers who have an active Windows Server 2016 license and has the same system requirements. This is the first Windows Server product to fall under the «Semi-Annual Channel» (SAC) release cadence.[48] This product only features the Server Core and the Nano Server modes. Of the two, only the Server Core mode of the OS can be installed on a bare system. The Nano Server mode is only available as an operating system container.[49]
Windows Server, version 1803 (version shared with Windows 10 April 2018 Update) is the second Semi-Annual Channel release of Windows Server.[50] It is also the final version to be branched off the Server 2016 codebase, as the next release shares the version number 1809 with Windows Server 2019.[51]
- Microsoft Servers
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- History of Microsoft Windows
- Comparison of operating systems
- List of operating systems
- ^ a b Chapple, Erin (September 26, 2016). «Announcing the launch of Windows Server 2016». Hybrid Cloud. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 21, 2017. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ^ a b c Foley, Mary Jo (October 12, 2016). «Microsoft’s Windows Server 2016 hits general availability». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on October 15, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «April 11, 2025—KB5058921 (OS Build 14393.7973) Out-of-band». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Server 2016 — Microsoft Lifecycle». Microsoft Learn. Microsoft. Retrieved February 17, 2025.
- ^ a b «Announcing availability of Windows Server Technical Preview and System Center Technical Preview». Hybrid Cloud. Microsoft. March 17, 2015. Archived from the original on August 2, 2017. Retrieved April 1, 2015.
- ^ Mathers, Bill; Poggemeyer, Liza; Tobin, John (September 8, 2017). «What’s new in Active Directory Federation Services for Windows Server 2016». Microsoft Docs. Windows Server, Identity and access. Archived from the original on February 28, 2018. Retrieved January 22, 2018.
- ^ «TechNet: Windows Server Antimalware Overview for Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 19 February 2015)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Remote Desktop Services in the Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Storage Services in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Failover Clustering in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Web Application Proxy in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ O’Shea, Mark (September 4, 2016). «What’s New In Windows Server 2016 Standard Edition Part 9 – Management And Automation». Microsoft Australia OEM Team blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 17, 2016. Retrieved September 9, 2016.
- ^ «About Windows Containers». Archived from the original on November 4, 2016. Retrieved November 1, 2016.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in DHCP in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in DNS Client in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in DNS Server in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: GRE Tunneling in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 1 October 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in IPAM in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 6 February 2015)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: Network Controller (Updated: 18 December 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Hyper-V Network Virtualization in Windows Server Technical Preview (Updated: 11 March 2015)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Hyper-V in Technical Preview (Updated: 12 November 2014)». Archived from the original on April 9, 2015. Retrieved April 4, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet Wiki: Hyper-V Features in Windows Server 2016». Archived from the original on March 12, 2016. Retrieved March 12, 2016.
- ^ «Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and Switch Embedded Teaming (SET)». Microsoft. May 17, 2016. Archived from the original on August 10, 2016. Retrieved July 6, 2016.
- ^ Jindal, Kriti (February 9, 2016). «Introducing Server management tools». Nano Server Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ Neil, Mike (April 8, 2015). «Microsoft Announces New Container Technologies for the Next Generation Cloud». Server & Cloud Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 27, 2016. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- ^ Snover, Jeffrey; Mason, Andrew; Back, Alan (April 8, 2015). «Microsoft Announces Nano Server for Modern Apps and Cloud». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 19, 2016. Retrieved July 24, 2016.
- ^ «Changes to Nano Server in the next release of Windows Server». Archived from the original on January 27, 2018. Retrieved June 18, 2017.
- ^ Patrizio, Andy (February 10, 2015). «Microsoft to release next generation of Windows Server in 2016». Network World. IDG. Archived from the original on April 26, 2024. Retrieved April 10, 2015.
- ^ Vincent, James (March 9, 2017). «Microsoft unveils new ARM server designs, threatening Intel’s dominance». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on December 23, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (March 8, 2017). «Windows Server on ARM: It’s happening». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on March 10, 2017. Retrieved March 10, 2017.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 8, 2017). «Microsoft’s latest open source servers shown off with Intel, AMD, and even ARM chips». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on March 10, 2017. Retrieved March 10, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (March 10, 2017). «Microsoft’s Windows Server on ARM move: More questions and answers». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on March 11, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ «Windows IT Pro: Windows Server Technical Preview expires 15 April 2015». Archived from the original on April 10, 2015. Retrieved April 5, 2015.
- ^ «Neowin: Second tech preview of Windows Server 2016 coming next month». Archived from the original on April 5, 2015. Retrieved April 5, 2015.
- ^ «RedmondMag: Windows Server ‘Insider’ Testing Program Coming This Summer». Archived from the original on August 5, 2017. Retrieved May 14, 2017.
- ^ «Announcing Windows Server Insider Preview Build 16237». Windows Blog. Microsoft. July 13, 2017. Archived from the original on December 3, 2017. Retrieved July 24, 2017.
- ^ Bright, Peter (December 4, 2015). «Windows Server 2016 moving to per core, not per socket, licensing». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Archived from the original on December 4, 2015. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft (2017). «Windows Server 2016 Licensing Datasheet — Microsoft» (PDF). Microsoft. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 26, 2017. Retrieved October 8, 2017.
- ^ Berkouwer, Sander (May 5, 2015). «Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 2 now available». The things that are better left unspoken. Archived from the original on April 6, 2016. Retrieved March 26, 2016.
- ^ a b «The Register: Try to contain your joy: Microsoft emits Windows Server 2016 with nano-services». The Register. Archived from the original on September 11, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
- ^ «WinBeta: Microsoft shows off what’s new in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 2». May 4, 2015. Archived from the original on May 5, 2015. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g «Windows Server Blog: What’s new in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 2». Archived from the original on May 7, 2015. Retrieved May 5, 2015.
- ^ a b «Windows Server Blog: Windows Server 2016 Installation Option Changes». August 27, 2015. Archived from the original on November 11, 2016. Retrieved November 11, 2016.
- ^ a b «TechNet: What’s New in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 3». Archived from the original on September 6, 2015. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- ^ a b Anderson, Kareem (November 19, 2015). «Microsoft has released Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 4». WinBeta. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved November 20, 2015.
- ^ «TechNet: What’s New in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 5». Archived from the original on June 3, 2016. Retrieved April 27, 2016.
- ^ «Windows Server, version 1709 available for download». October 17, 2017. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved November 1, 2017.
- ^ Jawad, Usama (September 25, 2017). «Microsoft launches Windows Server version 1709». Neowin. Archived from the original on March 13, 2018. Retrieved March 12, 2018.
- ^ «Introducing Windows Server, version 1709». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Windows Server. Archived from the original on January 21, 2018. Retrieved January 21, 2018.
- ^ «Windows Server servicing channels». Archived from the original on November 15, 2018. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019 update history». Archived from the original on December 18, 2019. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
Обновлено:
Опубликовано:
Общее описание
Дата выхода: 29.09.2016 Платформа: NT Поддержка до: 2026 г.
Как попробовать/скачать
Пробная версия Windows Server 2016 доступна для скачивания с официального сайта. Тестовый период длится 180 дней, в течение которого доступны все функциональные возможности. После окончания данного периода необходимо купить и перевести систему на платную основу или отказаться от ее использования.
Скачанный ISO-образ позволяет развернуть Windows в 3-х вариантах:
- Полная версия — с графическим интерфейсом.
- Windows Core — с управлением из командной строки Powershell или удаленной консоли.
- Nano Server — урезанная Server Core с управлением только с удаленной консоли.
Редакции и их сравнение
Основные редакции
Standard Edition и Datacenter Edition. По сравнению с Windows Server 2012 имеют различия не только в части лицензирования виртуальных машин, но и некоторых функциональных возможностей.
| Функции | Standard | Datacenter |
|---|---|---|
| Лицензирование виртуальных машин | 2 бесплатно | Не требуется |
| Высокодоступное хранилище Storage Spaces Direct | — | + |
| Блочная репликация Storage Replica | — | + |
| Защита виртуальных машин Shielded Virtual Machines и Host Guardian Service | — | + |
| Управление сетью Network Fabric | — | + |
| SDN Microsoft Azure Stack | — | + |
| Примерная стоимость в долларах США (на 16 ядер) | $ 900 | $ 6 200 |
Дополнительные редакции
- Windows Server 2016 Essentials — разрешено использование не более чем для 25 пользователей и 50 устройств.
- MultiPoint Premium Server — для одновременной работы нескольких пользователей на одном компьютере (через KVM). Для образовательных учреждений.
- Windows Storage Server 2016 — решения для хранения данных. Доступно только для ОЕМ поставщиков.
- Hyper-V Server 2016 — бесплатная платформа для виртуализации.
Лицензирование
Лицензирование Windows Server 2016 для основных редакций претерпело некоторые изменения — теперь учет ведется по физическим ядрам процессора.
Ключевые особенности лицензирования по ядрам
- Лицензирование по физическим ядрам, а не процессорам, как в предыдущих версиях.
- Покупка дополнительных лицензий осуществляется комплектами по 2 ядра.
- Минимальное количество ядер — 16. Если используется процессор с 4 ядрами, купить нужно одну лицензию. Если используем 24 ядра — одну лицензию + 4 комплекта по 2 ядра.
- Минимальное количество ядер на процессор — 8. Если у нас 4 процессора по 4 ядра, купить нужно две лицензии по 16 ядер.
Сводная таблица лицензирования для выпусков
| Выпуск | Как лицензируется | Необходимость CAL |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | На ядра | Да |
| Datacenter | На ядра | Да |
| Essentials | На процессоры | Нет |
| MultiPoint Premium Server | На процессоры | Да + Remote Desktop Services CAL |
| Storage Server | На процессоры | Нет |
Лицензирование виртуальных машин
- Если в качестве хоста виртуализации используется Datacenter, лицензирование виртуальных машин не требуется.
- При использовании Standard Edition — не лицензируются только 2 машины. Для остальных покупаются лицензии по вышеописанной схеме.
- Для Windows Server Hyper-V и платформ других разработчиков необходимо лицензирование по ядрам (как описано выше).
Что нового
Так как Windows Server 2016 позиционируется как облачная операционная система, большая часть изменений коснулась вопросов безопасности, виртуализации и кластеризации.
Новое для виртуализации
- Появление контейнерной виртуализации.
- Более удобное управление сетью в Hyper-V — появился виртуальный сетевой контроллер.
- Повышенная защита от сбоев виртуальных машин с новым форматом виртуальных дисков — .VMCX и .VMRS
- Создание снапшотов из гостевых систем.
- Добавление оперативной памяти и Ethernet адаптеров на лету (без выключения виртуальной машины).
Новинки для кластеров
- Возможность обновления кластера без остановки.
- Блочная репликация файлов.
Другие обновления
- Дополнительный вариант установки — Nano.
- OpenGL и OpenCL для RDP.
- Встроенная поддержка HTTP/2.
Системные требования
Standard и Datacenter
| Минимум | Рекомендовано | Максимум | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц | — |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) | 4 Гб | 24 Тб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб | — |
Essential
| Минимум | Рекомендовано | Максимум | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц | 2 процессора |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | 64 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб | — |
Был ли полезен этот ответ?
Да Нет
When looking to install Microsoft Hyper-V, you need to install the Hyper-V role on Window Server. One option is to use the GUI to run and manage your server and VMs. However, in certain situations, you can save resources by running Windows Server in command line (without GUI).
To install the Hyper-V role, you need to install the Windows Server 2016 Datacenter Server Core as your operating system (OS) platform. For the purposes of this walkthrough, we are using the Datacenter edition of Windows Server, as it unlocks the most powerful enterprise features for Hyper-V. Most enterprises use Windows Server Datacenter or Windows Server Standard because of the Windows licensing advantages. Note that the steps for other editions will differ.
Hyper-V Server is basically Windows Server Core with the Hyper-V role already installed. Thus, simply installing Hyper-V Server can get you up and running with the hypervisor for free. However, it may be better to install Hyper-V on Windows Server for advanced functionality if you have a license. In this case, you should install the OS first and then enable the Hyper-V role. Let’s cover how to install Windows Server 2016 Core and configuration.
Windows Server 2016 ISO Download
To start, you need to download the ISO file. You need MSDN or any other login with Microsoft to download the Windows Server 2016 ISO. However, if you don’t have that, you can download an evaluation copy of Windows Server 2016 from the TechNet Evaluation Center on the Windows Server 2016 download page. The TechNet evaluation copy is a time-limited 180-day version of Windows Server 2016 intended for trial purposes. You are asked to create an account with Microsoft before getting the Windows Server 2016 ISO download link.
Windows Server 2016 Datacenter Server Core Installation
You need to write the ISO image to a DVD disc or USB flash drive. Insert this medium into your computer and boot from this medium to start Windows Server installation.
When installing the Windows Server 2016 OS, you can choose to install the operating system alone, which is a Server Core installation. Server Core is a minimal installation without a graphical interface or management tools. This is the preferred installation method for use in a production environment over the Desktop Experience, which is the regular GUI Windows Server OS.
To demonstrate the installation process for a single standalone Hyper-V host, we use the Server Core installation of Windows Server 2016 Datacenter.
Note: For Windows Server 2016 Datacenter with the graphical user interface (GUI), you can read our blog post on running Hyper-V virtual machines (VMs).
Start by choosing Windows Server 2016 Datacenter in the list with Windows Server editions to install Server Core after you boot from the installation medium. See the screenshot of the Windows Server 2016 installer below with the OS list.

The Windows Server 2016 Core installation is similar to any other Windows Server installation. Go through the steps in the setup wizard:
- Accept the license agreement.
- Choose Custom Install.
- Select the target hard drive on which you want to install Windows.
- Proceed with the installation.
- Once the Windows Server 2016 Datacenter Server Core installation process is complete, you are asked to change the Administrator password. Press Enter.

- Once you set the password, press Enter (OK) to continue.

You have finished the Windows Server installation. Now you need to configure the operating system.
Windows Server 2016 OS Configuration
You now reach a CMD command prompt and no visible menu. It is recommended that you configure network settings for your Windows Server 2016 setup.
Configuring network settings
Network settings and most other settings in Windows Server 2016 Core are configured in the console interface:
- Type sconfig in the command prompt to launch the Server Core configuration utility.
- You are then presented with the Server Configuration menu.

- Type 8 and press Enter to open Network Settings and launch the network configuration menu. It is recommended that you assign a static IP address for Windows Server 2016 setup.
- Choose the network adapter you want to configure. Type the appropriate number and press Enter. You need to always press Enter after entering a value in this configuration menu.
- Now you should see the menu with four entries:
- Set Network Adapter Address
- Set DNS Servers
- Clear DNS Server Settings
- Return to Main Menu
- Type 1 to set the IP address, subnet, and gateway.

- Type S to use the static IP address configuration.
- Enter the appropriate values to meet your network configuration. Once done, you are returned to the previous Network Adapter Settings menu with four entries.

- Type 2 to set DNS servers for the network configuration.
- Enter a new preferred DNS server and alternate DNS server.
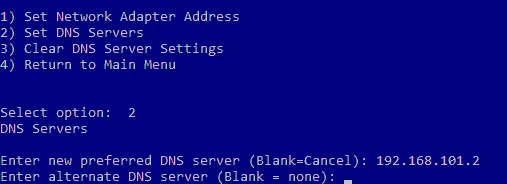
Once done, you are returned back to the previous Network Adapter Settings menu.
After configuring the network settings, you should test network connectivity. You can use option 15, Exit to Command Line. This takes you to the cmd prompt, where you can ping your gateway, DNS server, etc.
Changing the computer name
Now let’s run the sconfig command in cmd to open the Server Configuration menu again. You should join a Windows domain and change the computer name. Using an Active Directory domain with a domain controller allows you to manage all Windows machines centrally.
Do the following steps to change the computer name:
- Choose 2 in the Server Configuration menu.
- Enter a new computer name.
- Restart the computer to apply the changes.

Changing Domain/Workgroup options
Open the Server Configuration menu after computer restart (sconfig).
Do the following steps to change the Domain/Workgroup settings:
- Choose the 1) Domain/Workgroup option in the Server Configuration menu.
- Type D to join a domain.
- Enter the domain name.
- You are asked to provide the credentials of a user who has permissions for the needed domain.
- Once you have set up the domain configuration, reboot your Windows Server machine.

After the reboot, you have a functioning Windows Server 2016 Datacenter Server Core and are ready to install the Hyper-V server role.
You can also read about the difference between the GUI and Core Windows Server 2016 installation and configuration to run Hyper-V.
Conclusion
Windows Server installation is not a difficult process. Installing the core version of Windows Server 2016 Datacenter allows you to reduce the footprint and related overhead, as well as install the Hyper-V role on the Windows Server to run VMs. As for the core version, Windows Server 2016 setup is performed mostly in the command line interface.
If you use Hyper-V, don’t forget to back up virtual machines. Download NAKIVO Backup & Replication to protect your physical and virtual environments. The NAKIVO solution supports physical Windows Server backup, Active Directory backup, Hyper-V VM backup and more.
