Как правильно сказал Олег Матрозов Олег Матрозов, ограничение 4ТБ , но возможно у вас 2х процессорный сервак на камнях АМД , и там каждому сокеру соответствует память , то есть в мать можно всунуть 2 проца и к каждому по 32Г оперативки , и если стоит в данный момент только один камень , то сколько не пихни а увидит он только 32 .
Хоятя обычно у нормальных матерей идет 64 и более ГБ на процессорный сокет .
Может есть смысл проверить куда именно воткнута память ?
Написано
Today we were finally able to get our hands on the “preliminary” information about the maximum use of random access memory (RAM) with the new versions of Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 for our operating system data base.
- Source: Microsoft
Generally it remains the case that the 32Bit (x86) versions of Windows 8 are able to address 4 GB memory maximum only. With older hardware, just around 3,2 GB RAM can be used by the operating system.
The Windows 8 PRO and ENTERPRISE editions now have been upgraded to a maximum of 512 GB usable memory.
The Standard Edition supports up to 192 GB.
| Operating system/edition |
Version (32 or 64-bit) |
Maximum memory |
| Windows RT |
32-bit |
4GB |
| Windows 8 |
32-bit |
4GB |
| Windows 8 Pro |
32-bit |
4GB |
| Windows 8 Enterprise |
32-bit |
4GB |
| Windows 8 |
64-bit |
192GB |
| Windows 8 Pro |
64-bit |
512GB |
| Windows 8 Enterprise |
64-bit |
512GB |
- Source:Microsoft
The Windows Server 2012 editions are exclusively available as a 64-bit software and support up to 4 TB RAM now.
| Operating system |
Version (32 or 64-bit) |
Maximum memory |
| Windows Server 2012 Foundation |
64-bit |
32GB |
| Windows Server 2012 Essentials |
64-bit |
64GB |
| Windows Server 2012 Standard |
64-bit |
4TB |
| Windows Server 2012 Datacenter |
64-bit |
4TB |
Was this information useful?
We are looking forward to your feedback.
Tags: Limits, Operating Systems
В данной статье рассмотрим какой максимальный объем оперативной памяти доступен на программном уровне в различных версиях Windows (10, 8.1, 7, Vista и XP), а так же рассмотрим максимальный объем оперативной памяти (ОЗУ) в серверных системах — Windows Server.
Windows 10
В среднем в Windows 10 максимальный объем оперативной памяти — 2 Тб, в x32 битных системах по стандарту — 4 Гб.
| Версии Windows 10 | x64 | x32 (x86) |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 Pro | 2 Тб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 10 Home (Домашняя) | 128 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 10 Enterprise (Корпоративная) LTSC/LTSB | 2 Тб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 10 Education (Для образовательных учреждений) | 2 Тб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 10 Pro for WorkStations | 6 Тб | — |
Windows 8.1
В Windows 8.1 максимальный объем сделан стандартно для всех версий — 512 Гб.
| Версии Windows 8.1 | x64 | x32 (x86) |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 8.1 Pro | 512 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 8.1 Enterprise | 512 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 8.1 (без редакции, аналог Home версии) | 512 Гб | 4 Гб |
Windows 7
В Профессиональной и более расширенных редакциях Windows 7 максимальный объем — 192 Гб. Windows 7 Starter — доступна только в редакции x32.
| Версии Windows 7 | x64 | x32 (x86) |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 Ultimate (Максимальная) | 192 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 7 Enterprise (Корпоративная) | 192 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 7 Professional | 192 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 7 Home Premium (Домашняя расширенная) | 16 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 7 Home Premium (Домашняя базовая) | 8 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows 7 Starter (Начальная) | — | 2 Гб |
Windows Vista
В Профессиональной и более расширенных редакциях Windows Vista максимальный объем — 128 Гб. Windows Vista Starter доступна только в редакции x32.
| Версии Windows Vista | x64 | x32 (x86) |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Vista Ultimate | 128 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows Vista Enterprise | 128 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows Vista Business | 128 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows Vista Home Premium | 16 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows Vista Home Basic | 8 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows Vista Starter | — | 1 Гб |
Windows XP
Максимальный объем ОЗУ в Windows XP доступен в x64 битной версии на 128 Гб.
| Версии Windows XP | x64 | x32 (x86) |
|---|---|---|
| Windows XP | 128 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Windows XP Starter Edition | 512 Мб |
Windows Server
Максимальный объем оперативной памяти в Windows Server отличается в зависимости от редакции.
| Версии Windows Server | x64 |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2019 Standard / Datacenter | 24 Тб |
| Windows Server 2016 Standard / Datacenter | 24 Тб |
| Windows Server 2012 и 2012r2 Standard / Datacenter | 4 Тб |
| Windows Server 2008 Standard / Enterprise / Datacenter | 32 Гб / 1 Тб / 1 Тб |
| Windows Server 2008r2 Standard / Enterprise / Datacenter | 32 Гб / 2 Тб / 2 Тб |
In this article, we will take a look at the minimum, recommended, and suggested requirements for installing and maintaining Windows Server 2012. Like previous versions, Microsoft publishes the bare minimum to get the operating system installed.
However, you need to take into account additional factors that will affect the hardware requirements. According to Microsoft, here are the basic minimum requirements for installing Server 2012.
System Requirements
The following sections cover the system requirements for Windows Server 2012. If your computer does not meet the minimum requirements, you will not be able to install this product correctly.
You should note that while the information below may list minimum or suggested requirements, the actual requirements will vary based on your system configuration, installed applications, roles, and features you install on the system.
Processor
The number of processor cores, processor cache, and clock frequency of the CPU(s) will affect the actual requirements of the processor. From a realistic implementation of Windows Server 2012, it is not recommended to configure your server with the minimum requirements.
You should start with the recommended requirement and take note of the applications, roles, features, and other services that will be running on the server. You may need to add multiple cores and/or increase the clock cycles. Microsoft recommends the following specifications for Server 2012:
| Requirement | Processor |
|---|---|
| Minimum | 1.4 GHz 64-bit or faster single-core |
| Minimum | 1.3 GHz 64-bit or faster multi-core |
| Recommended | 3.1 GHz 64-bit or faster multi-core |
Memory (RAM)
The server heavily depends on its RAM. RAM (Random-access memory) is very important for a server to process data. The processors use memory to temporarily store information while the processors are busy processing instructions. The server’s RAM is also used to store data fetched from secondary storage (hard drives).
While 32-bit systems were limited on the amount of memory that can be accessed by the server, 64-bit systems can take advantage of much more memory space. However, this does not mean that the more memory a server has, the better it will perform. How much memory your server requires depends on the applications, services, roles, and features that are running on the server. Here is a list of minimum and recommended memory requirements.
| Requirement | Memory |
|---|---|
| Minimum | 512 MB of RAM to boot for installation |
| Minimum | 2 GB of RAM for installed system |
| Recommended | 8 GB of RAM or more |
While Microsoft claims that 512 MB of RAM is needed to start the installation process of Windows, it is highly recommended that you start with a few GB of RAM.
Storage
The amount of storage your server will need will depend on the data that you plan on storing locally on the server. Microsoft has published that the installation of the server operating system will require a minimum of 32 GB of RAM. However, keep in mind that the amount of memory will increase the storage requirements because of the pagefile.
Even the minimum requirement of 60 GB seems too little when considering that your server may have 16 GB of RAM. This will require approximately 24 GB of pagefile storage. Realistically, you need over 100 GB for the system partition to have enough space to grow, especially when you start to apply updates and service packs. Storage is relatively inexpensive so do not corner yourself by not configuring enough space on the system partition.
| Requirement | Storage |
|---|---|
| Minimum | 32 GB for Installation |
| Minimum | 60 GB for installed system |
| Recommended | 160 GB or more |
Other Requirements
Of course, your server will also need to have other components such as a DVD drive, Network Adapter, Super VGA (800 x 600) or higher-resolution monitor, keyboard, mouse, and network connectivity.
FREE Hyper-V & VMware Virtualization Backup: FREE for Firewall.cx readers for a Limited Time! Download Now!
Windows Server 2012 Editions
On the 1st of August, 2012 Microsoft released Windows Server 2012– the sixth release of the Windows Server product family. On May 21st 2013, Windows Server 2012 R2 was introduced and is now the latest version of Windows Server in the market. Microsoft has released four different editions of Windows Server 2012 varying in cost, licensing and features. These four editions of Windows Server 2012 R2 are: Windows 2012 Foundation edition, Windows 2012 Essentials edition, Windows 2012 Standard edition and Windows 2012 Datacenter edition.
Let’s take a closer look at each Windows Server 2012 edition and what they have to offer.
Users can also download the free Windows Server 2012 R2 Licensing Datasheet in our Windows Server Datasheets & Useful Resources download section, which provides a detailed overview of the Licensing for Windows Server 2012 and contains extremly useful information on the various Windows Server 2012 edition, examples on how to calculate your licensing needs, Virtualization instances supported by every edition, server roles, common questions & answers, plus much more.
More technical articles covering Windows 2012 Server and Hyper-V Virtualization are available in our Windows 2012 Server section.
Windows Server 2012 Foundation Edition
This edition of Windows Server 2012 is targeted towards small businesses of up to 15 users. The Windows Server 2012 R2 Foundation edition comes pre-installed on hardware server with single physical processor and up to 32GB of DRAM memory. Foundation edition can be implemented in environments where features such as file sharing, printer sharing, security and remote access are required. Advanced server features such as Hyper V, RODC (Read Only Domain Controller), data deduplication, dynamic memory, IPAM (IP Address Management), server core, certificate service role, hot add memory, windows update services and failover clustering are not available in the Foundation edition.
Windows Server 2012 Essentials Edition
The Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials edition is the next step up, also geared towards small businesses of up to 25 users. Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials edition is available in retail stores around the world making it easy for businesses to install the new operating system without necessarily purchasing new hardware. Similar to the Foundation edition, the Essentials edition does not support many advanced server features, however it does provide support of features like Hyper V, dynamic memory and hot add/remove RAM.
Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials edition can run a single instance of virtual machine on Hyper V, a feature that was not available in Windows Server 2012 Essentials (non-R2) edition. This single virtual machine instance can be Windows Server 2012 R2 Essential edition only, seriously limiting the virtualization options but allowing companies to begin exploring the benefits of the virtualization platform.
Windows Server 2012 Standard Edition
The Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard edition of windows server is used for medium to large businesses that require additional features not present in the Foundation & Essential edition. The Standard edition is able to support an unlimited amount of users, as long as the required user licenses have been purchased.
Advanced features such as certificate services role, Hyper V, RODC (Read Only Domain Controller), IPAM (IP Address Management), Data deduplication, server core, failover clustering and more, are available to Windows Server 2012 Standard edition. We should note that the Standard edition supports up to 2 Virtual Machines.
Windows Server 2012 Datacenter Edition
The Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter edition is the flagship product created to meet the needs of medium to large enterprises. The major difference between the Standard and Datacenter edition is that the Datacenter edition allows the creation of unlimited Virtual Machines and is therefore suitable for environments with extensive use of virtualization technology.
Before purchasing the Windows Server 2012 operating system, it is very important to understand the difference between various editions, the table below shows the difference between the four editions of Windows Server 2012:
FREE Hyper-V & VMware Virtualization Backup: FREE for Firewall.cx readers for a Limited Time! Download Now!
|
Editions |
Foundation |
Essentials |
Standard |
Datacenter |
|
Distribution |
OEM Only |
Retail, volume licensing, OEM |
Retail, volume licensing, OEM |
Volume licensing and OEM |
|
Licensing Model |
Per Server |
Per Server |
Per CPU pair + CAL/DAL |
Per CPU pair + CAL/DAL |
|
Processor Chip Limit |
1 |
2 |
64 |
64 |
|
Memory Limit |
32GB |
64GB |
4TB |
4TB |
|
User Limit |
15 |
25 |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
File Services limits |
1 standalone DFS root |
1 standalone DFS root |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
Network Policy & Access Services limits |
50 RRAS connections and 10 IAS connections |
250 RRAS connections, 50 IAS connections, and 2 IAS Server Groups |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
Remote Desktop Services limits |
50 Remote Desktop Services connections |
Gateway only |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
Virtualization rights |
n/a |
Either in 1 VM or 1 physical server, but not both at once |
2 VMs |
Unlimited |
|
DHCP, DNS, Fax server, Printing, IIS Services |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows Server Update Services |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Active Directory Services |
Yes, Must be root of forest and domain |
Yes, Must be root of forest and domain |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Active Directory Certificate Services |
Certificate Authorities only |
Certificate Authorities only |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows Powershell |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Server Core mode |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Hyper-V |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Windows Server 2012 Licensing — Understanding Client Access License (CAL) & Device Access License (DAL) Licensing Models
The standard and datacenter editions of Server 2012 support Client Access License (CAL) or Device Access License (DAL) licensing model. A CAL license is assigned to a user whereas a DAL license is assigned to device (computer). For example, a CAL assigned to a user, allows only that user to access the server via any device. Likewise, if a DAL is assigned to particular device, then any authenticated user using that device is allowed to access the server.
We can use a simple example to help highlight the practical differences between CAL and DAL licensing models and understand the most cost-effective approach:
Assume an environment with Windows Server 2012 R2 standard edition and a total of 50 users and 25 devices (workstations). In this case, we can purchase either 50 CAL licenses to cover the 50 users we have or alternatively 25 DAL licenses to cover the total amount of workstations that need to access the server. In this scenario, purchasing DALs is a more cost effective solution.
If however we had 10 users with a total of 20 devices , e.g 2 devices per user (workstation & laptop), then it more be more cost effective to purchase 10 CAL licenses.
Windows Server 2012 Foundation Edition Licensing Model
Windows Server 2012 Foundation is available to OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) only and therefore can only be purchased at the time of purchasing a n new hardware server. Windows 2012 Foundation edition supports up to 15 users. CALs or DALs are not required for the Foundation edition servers. In addition, Foundation edition owners cannot upgrade to other editions. The maximum number of SMB (Server Message Block or file sharing) connections to the server is 30. Similarly, maximum number of RRAS (Routing and Remote Access Service) and RDS (Remote Desktop Service) connections is 50.
Windows Server 2012 Essentials Edition Licensing Model
The Essential edition of server 2012 is available to OEMs (with the purchase of new hardware) and also at retail stores. The user limit of this server edition is 25 and device limit is 50. This means that a maximum of 25 users amongst 50 computers can access the Windows Server 2012 Essentials edition. For example, you have 20 users rotating randomly amongst 25 computers accessing the Server 2012 Essentials edition, without any problem. CALs or DALs are not required for Windows Server 2012 Essentials edition because no more than 25 users can access the server.
A common question at this point is what if the organization expands and increases its users and computers?
In these cases Microsoft provides an upgrade path allowing organizations to upgrade to the Windows Server 2012 Standard or Datacenter edition license and perform an in-place license transition. Once the transition is complete, the user limitation, and other features are unlocked without requiring migration or reinstallation of the server.
Companies upgrading to a higher edition of Windows 2012 Server should keep in mind that it will be necessary to purchase the required amount of CALs or DALs according to their users or devices.
Administrators will be happy to know that it is also possible to downgrade the Standard edition of Server 2012 to the Essentials edition. For example, it is possible to run Essential edition of Server 2012 as virtual machine utilizing one of two available virtual instances in Standard edition as shown in the figure below. This eliminates the needs to purchase Essential edition of Server 2012.
FREE Hyper-V & VMware Virtualization Backup: FREE for Firewall.cx readers for a Limited Time! Download Now!
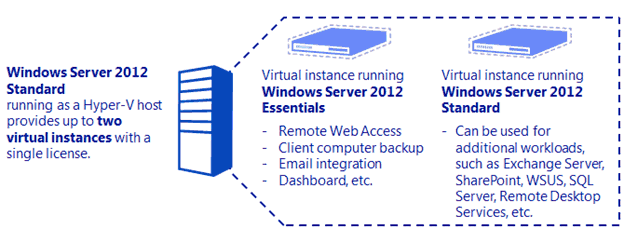
With the release of Windows Server 2012 Essentials R2, Microsoft has updated its licensing model. Unlike Windows Server 2012 Essentials (non-R2), you can now run a single instance of a virtual machine.
The Hyper-V role and Hyper-V Manager console are now included with Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials. The server licensing rights have been expanded, allowing you to install an instance of Essentials on your physical server to run the Hyper-V role (with none of the other roles and features of the Essentials Experience installed), and a second instance of Essentials as a virtual machine (VM) on that same server with all the Essentials Experience roles and features.
Windows Server 2012 Standard Edition & Datacenter Edition Licensing Model
The license of Standard and Datacenter edition is based on sockets (CPUs) and CAL or DAL. Definition of a socket is a CPU or physical processor. Logical cores are not counted as sockets. A single license of Standard and Datacenter edition covers up to two physical processors per physical server. CAL or DAL licenses are then required so that clients/devices can access the Windows server. Standard edition allows up to 2 virtual instances while the Datacenter edition allows unlimited number of virtual instances.
For example, a Windows 2012 Server R2 Standard edition installed on a physical server with one socket (CPU) can support up to two instances of virtual machines. These virtual machines can be Server 2012 R2 Standard or Essentials edition. Similarly, if you install a Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter edition, then you can install an unlimited number of virtual machines.
Let’s look at some examples on deploying Standard and Datacenter edition servers and calculating the licenses required:
Scenario 1: Install Server 2012 Standard/Datacenter Edition on a server box with four physical processors and 80 users.
In this scenario, we will be required to purchase two Standard/Datacenter Edition licenses because a single license covers up to two physical processors, plus 80 CAL licenses so our users can access the server resources.
Scenario 2: Install Server 2012 Standard Edition on a physical server with 1 physical processor, running 8 instances of virtual machines. A total of 50 users will be accessing the server.
Here, four Server 2012 Standard edition licenses are required and 50 CALs or DALs. Remember that a single Standard edition license covers up to two physical processors and up to two instances of virtual machines. Since the requirement is to run 8 instances of virtual machines, we need four Standard edition licenses.
If we decided to use the Datacenter edition in this scenario, a single license with 50 CAL would be enough to cover our needs, because the Datacenter edition license supports an unlimited number of virtual instances and up to two physical processors.
Summary
Microsoft’s Windows Server 2012 is an attractive server-based product designed to meet the demands of small to large enterprises and has a very flexible licensing model. It is very important to fully understand the licensing options and supported features on each of the 4 available editions, before proceeding with your purchase – a tactic that will help ensure costs are kept well within the allocated budget while the company’s needs are fully met.
