Popular Posts:
«Lenovo Camera Mute …
What is «Lenovo Camera Mute» in a service on Lenovo laptop computer that supports the camera on/off …
Windows 10 Setup — «…
Why I am getting the «Why did my PC restart?» message? After taking the quick setup information, you…
Removing msmsgs.exe …
How to remove msmsgs.exe from the startup application list to gain performance and reduce security r…
Microsoft Research T…
What is Microsoft Research Extra Toolbar Button and Extra Tools Menu Item for Internet Explorer (IE)…
tfswctrl.exe — Proce…
What is tfswctrl.exe process — Sonic Drive Letter Access Component? Process tfswctrl.exe is the Driv…
Содержание
- Что такое роли Windows
- Windows server роли
- Компоненты IIS
- Компоненты служб печати
- Компоненты NPAS
- Компоненты WDS
- Компоненты Службы сертификации Active Directory
- Компоненты RDS
- Компоненты ADRMS
- Компоненты ADFS
- Компоненты файловых служб
- Компоненты windows server 2012 R2
- Как посмотреть в командной строке windows server роли
Если вы вдруг как и я любите писать скрипты, которые вам упрощают жизнь и ускоряют процесс выполнения задач, то вам это будет полезно. Тут собраны все названия ролей и компонентов которые используются при установке через командную строку в windows server 2008R2/2012R2. Особенно это актуально когда вы устанавливаете роли windows server 2012, через Powershell на большом количестве серверов, либо у вас есть удаленный офис в котором нет it специалистов, а поставить нужные серверные службы необходимо, и передав такой вот скрипт, простому менеджеру можно без особых усилий получить нужный результат, просто попросив его там запустить.
Что такое роли Windows
И так сам по себе Windows Server 2012 R2 или предыдущая версия ни кому не нужны, так как при их установке вы получаете просто обычную систему, но благодаря тому, что это конструктор, вы можете его собирать как вам угодно. Собирается он благодаря так называемым ролям Windows, и у каждой из них своя задача, которая превратит ваш сервер в нужный вам сервис.
Что такое компоненты Windows Server 2012 R2, это по сути мини роли, те которые несут не совсем существенные задачи, например сервер TFTP или Net.Framwork 3.5, согласитесь он на роль не тянет.
В операционной системе посмотреть windows server роли можно в окне Диспетчер сервера. В версии 2012 R2, этот значок выглядит вот так, и уже в пункте Управление вы добавляете либо роль, либо компонент.
В windows Server 2008 R2 это выглядит так же, но тут разница в том, что роли и компоненты разнесены по разным вкладкам.
Для того, чтобы посмотреть роли windows server 2012 r2, нажмите добавить роль и увидите полный список. Самих ролей не так уж и много и вы их наверняка еще знаете с 2008 r2.
Windows server роли
Ниже я собрал полный список содержащий роли windows server 2012 r2 и 2008 r2. Тут синтаксис такой слева просто описание названия службы, а справа то что нужно указывать в скрипте при установке.
1. DHCP-сервер [DHCP] > на сайте я приводил кучу вариантов реализации данный серверной роли, так и на различном сетевом оборудовании.
2. DNS-сервер [DNS] > роль необходимая для Active Directory
3. Hyper-V [Hyper-V] > подробнее про данную роль советую почитать соответствующий раздел. Если в двух словах то это гипервизор, для создания виртуальных машин.
4. Веб-сервер IIS [Web-Server] > роль windows server 2012 r2 для превращения его в хостинг сайтов.
Компоненты IIS
- Веб-сервер [Web-WebServer]
- Основные возможности HTTP [Web-Common-Http]
- Статическое содержимое [Web-Static-Content]
- Стандартный документ [Web-Default-Doc]
- Обзор каталогов [Web-Dir-Browsing]
- Ошибки HTTP [Web-Http-Errors]
- Перенаправление HTTP [Web-Http-Redirect]
- Веб-публикация DAV [Web-DAV-Publishing]
- Разработка приложений [Web-App-Dev]
- ASP.NET [Web-Asp-Net]
- Расширяемость .NET [Web-Net-Ext]
- ASP [Web-ASP]
- CGI [Web-CGI]
- Расширения ISAPI [Web-ISAPI-Ext]
- Фильтры ISAPI [Web-ISAPI-Filter]
- Включения на стороне сервера (SSI) [Web-Includes]
- Работоспособность и диагностика [Web-Health]
- Ведение журнала HTTP [Web-Http-Logging]
- Средства ведения журналов [Web-Log-Libraries]
- Монитор запросов [Web-Request-Monitor]
- Слежение [Web-Http-Tracing]
- Особое ведение журнала [Web-Custom-Logging]
- Ведение журнала ODBC [Web-ODBC-Logging]
- Безопасность [Web-Security]
- Обычная проверка подлинности [Web-Basic-Auth]
- Windows — проверка подлинности [Web-Windows-Auth]
- Дайджест-проверка подлинности [Web-Digest-Auth]
- Проверка подлинности с сопоставлением сертификата клиента [Web-Client-Auth]
- Проверка подлинности с сопоставлением сертификата клиента IIS [Web-Cert-Auth]
- Авторизация URL-адресов [Web-Url-Auth]
- Фильтрация запросов [Web-Filtering]
- Ограничения по IP-адресам и доменам [Web-IP-Security]
- Производительность [Web-Performance]
- Сжатие статического содержимого [Web-Stat-Compression]
- Сжатие динамического содержимого [Web-Dyn-Compression]
- Средства управления [Web-Mgmt-Tools]
- Консоль управления IIS [Web-Mgmt-Console]
- Сценарии и средства управления IIS [Web-Scripting-Tools]
- Служба управления [Web-Mgmt-Service]
- Совместимость управления IIS 6 [Web-Mgmt-Compat]
- Совместимость метабазы IIS 6 [Web-Metabase]
- Совместимость WMI в IIS 6 [Web-WMI]
- Службы сценариев IIS 6 [Web-Lgcy-Scripting]
- Консоль управления IIS 6 [Web-Lgcy-Mgmt-Console]
- FTP-сервер [Web-Ftp-Server]
- Служба FTP [Web-Ftp-Service]
- Расширяемость FTP [Web-Ftp-Ext]
- Ведущий базовый экземпляр IIS [Web-WHC]
- Доменные службы Active Directory [AD-Domain-Services]
- Контроллеры домена Active Directory [ADDS-Domain-Controller]
- Диспетчер удостоверений для UNIX [ADDS-Identity-Mgmt]
- Сервер для служб NIS [ADDS-NIS]
- Синхронизация паролей [ADDS-Password-Sync]
- Средства администрирования [ADDS-IDMU-Tools]
- Сервер приложений [Application-Server]
- Платформа .NET Framework 3.5.1 [AS-NET-Framework]
- Поддержка веб-сервера (IIS) [AS-Web-Support]
- Доступ к сети COM+ [AS-Ent-Services]
- Общий доступ к TCP-портам [AS-TCP-Port-Sharing]
- Поддержка службы активации процессов Windows [AS-WAS-Support]
- Активация по HTTP [AS-HTTP-Activation]
- Активация через очередь сообщений [AS-MSMQ-Activation]
- Активация по TCP [AS-TCP-Activation]
- Активация по именованным каналам [AS-Named-Pipes]
- Распределенные транзакции [AS-Dist-Transaction]
- Входящие удаленные транзакции [AS-Incoming-Trans]
- Исходящие удаленные транзакции [AS-Outgoing-Trans]
- Транзакции WS-AT [AS-WS-Atomic]
- Веб-сервер IIS [Web-Server] > роль windows server 2012 r2 для превращения его в хостинг сайтов.
5. Службы Active Directory облегченного доступа к каталогам [ADLDS]
6. Службы Windows Server Update Services [OOB-WSUS]
7. Службы печати и документов [Print-Services]
Компоненты служб печати
- Сервер печати [Print-Server]
- Служба LPD [Print-LPD-Service]
- Печать через Интернет [Print-Internet]
- Сервер распределенного сканирования [Print-Scan-Server]
8. Службы политики сети и доступа [NPAS] > данные роли windows server 2012 r2, превратят ваш сервер в маршрутизатор или VPN сервер.
Компоненты NPAS
- Сервер политики сети [NPAS-Policy-Server]
- Службы маршрутизации и удаленного доступа [NPAS-RRAS-Services]
- Служба удаленного доступа [NPAS-RRAS]
- Маршрутизация [NPAS-Routing]
- Центр регистрации работоспособности [NPAS-Health]
- Протокол авторизации учетных данных узла [NPAS-Host-Cred]
9. Службы развертывания Windows [WDS] > Автоматизированная установка операционных систем по сети, за счет протокола PXE.
Компоненты WDS
- Сервер развертывания [WDS-Deployment]
- Транспортный сервер [WDS-Transport]
10. Службы сертификации Active Directory [AD-Certificate]
Компоненты Службы сертификации Active Directory
- Центр сертификации [ADCS-Cert-Authority]
- Служба регистрации в центре сертификации через Интернет [ADCS-Web-Enrol
lment] - Сетевой ответчик [ADCS-Online-Cert]
- Служба регистрации на сетевых устройствах [ADCS-Device-Enrollment]
- Веб-служба регистрации сертификатов [ADCS-Enroll-Web-Svc]
- Веб-служба политик регистрации сертификатов [ADCS-Enroll-Web-Pol]
12. Службы удаленных рабочих столов [Remote-Desktop-Services] > очень часто эта роль windows server 2012 r2 используется в компаниях.
Компоненты RDS
- Узел сеансов удаленных рабочих столов [RDS-RD-Server]
- Узел виртуализации удаленных рабочих столов [RDS-Virtualization]
- Службы Core Services [RDS-Virtualization-Core]
- RemoteFX [RDS-RemoteFX]
- Лицензирование удаленных рабочих столов [RDS-Licensing]
- Посредник подключений к удаленному рабочему столу [RDS-Connection-Broke
r] - Шлюз удаленных рабочих столов [RDS-Gateway]
- Веб-доступ к удаленным рабочим столам [RDS-Web-Access]
13. Службы управления правами Active Directory [ADRMS]
Компоненты ADRMS
- Сервер управления правами Active Directory [ADRMS-Server]
- Поддержка удостоверений в службе федерации [ADRMS-Identity]
14. Службы федерации Active Directory [AD-Federation-Services]
Компоненты ADFS
- Служба федерации [ADFS-Federation]
- Прокси-сервер службы федерации [ADFS-Proxy]
- Веб-агенты AD FS [ADFS-Web-Agents]
- Агент, поддерживающий утверждения [ADFS-Claims]
- Агент Windows на основе токенов [ADFS-Windows-Token]
15. Файловые службы [File-Services]
Компоненты файловых служб
- Файловый сервер [FS-FileServer]
- Распределенная файловая система [FS-DFS]
- Пространства имен DFS [FS-DFS-Namespace]
- Репликация DFS [FS-DFS-Replication]
- Диспетчер ресурсов файлового сервера [FS-Resource-Manager]
- Службы для NFS [FS-NFS-Services]
- Служба Windows Search [FS-Search-Service]
- Файловые службы Windows Server 2003 [FS-Win2003-Services]
- Служба индексирования [FS-Indexing-Service]
- Служба BranchCache для сетевых файлов [FS-BranchCache]
- Факс-сервер [Fax]
Так, что вы теперь знаете сколько windows server имеет ролей, правильный ответ 15
Компоненты windows server 2012 R2
Так роли windows server 2008 r2 и 2012 r2 мы рассмотрели, давайте узнаем какие компоненты windows server 2012 R2 имеет под капотом.
- BranchCache [BranchCache]
- Quality Windows Audio Video Experience [qWave]
- RPC через HTTP-прокси [RPC-over-HTTP-Proxy]
- Telnet-сервер [Telnet-Server]
- Windows TIFF IFilter [TIFF-IFilter]
- WINS-сервер [WINS-Server]
- Балансировка сетевой нагрузки [NLB]
- Биометрическая платформа Windows [Biometric-Framework]
- Внутренняя база данных Windows [Windows-Internal-DB]
- Возможности .NET Framework 3.5.1 [NET-Framework]
- .NET Framework 3.5.1 [NET-Framework-Core]
- Активация WCF [NET-Win-CFAC]
- Активация через HTTP [NET-HTTP-Activation]
- Не-HTTP активация [NET-Non-HTTP-Activ]
- Возможности рабочего стола [Desktop-Experience]
- Возможности системы архивации данных Windows Server [Backup-Features]
- Система архивации данных Windows Server [Backup]
- Программы командной строки [Backup-Tools]
- Диспетчер системных ресурсов [WSRM]
- Диспетчер хранилища для сетей SAN [Storage-Mgr-SANS]
- Интегрированная среда сценариев (ISE) Windows PowerShell [PowerShell-ISE]
- Клиент Telnet [Telnet-Client]
- Клиент TFTP [TFTP-Client]
- Клиент интернет-печати [Internet-Print-Client]
- Консоль управления DirectAccess [DAMC]
- Многопутевой ввод-вывод [Multipath-IO]
- Монитор LPR-портов [LPR-Port-Monitor]
- Очередь сообщений [MSMQ]
- Службы очереди сообщений [MSMQ-Services]
- Сервер очереди сообщений [MSMQ-Server]
- Интеграция служб каталогов [MSMQ-Directory]
- Триггеры очереди сообщений [MSMQ-Triggers]
- Поддержка HTTP [MSMQ-HTTP-Support]
- Поддержка многоадресной рассылки [MSMQ-Multicasting]
- Служба маршрутизации [MSMQ-Routing]
- DCOM-прокси очереди сообщений [MSMQ-DCOM]
- Пакет администрирования диспетчера подключений [CMAK]
- Подсистема для UNIX-приложений [Subsystem-UNIX-Apps]
- Простые службы TCP/IP [Simple-TCPIP]
- Протокол PNRP [PNRP]
- Расширение WinRM IIS [WinRM-IIS-Ext]
- Сервер SMTP [SMTP-Server]
- Сервер службы имен хранилищ Интернета [ISNS]
- Служба активации процессов Windows [WAS]
- Модель процесса [WAS-Process-Model]
- Среда .NET [WAS-NET-Environment]
- API-интерфейсы конфигурации [WAS-Config-APIs]
- Служба беспроводной локальной сети [Wireless-Networking]
- Службы SNMP [SNMP-Services]
- Служба SNMP [SNMP-Service]
- WMI-поставщик SNMP [SNMP-WMI-Provider]
- Службы рукописного ввода [Ink-Handwriting]
- Поддержка рукописного ввода [IH-Ink-Support]
- Распознавание рукописного ввода [IH-Handwriting]
- Средства миграции Windows Server [Migration]
- Средства удаленного администрирования сервера [RSAT]
- Средства администрирования ролей [RSAT-Role-Tools]
- Средства служб сертификации Active Directory [RSAT-ADCS]
- Средства центра сертификации [RSAT-ADCS-Mgmt]
- Средства сетевого ответчика [RSAT-Online-Responder]
- Средства AD DS и AD LDS [RSAT-AD-Tools]
- Инструменты AD DS [RSAT-ADDS]
- Оснастки AD DS и средства командной строки [RSAT-ADDS-Tools]
- Административный центр Active Directory [RSAT-AD-AdminCenter]
- Средства сервера для NIS [RSAT-SNIS]
- Оснастки AD LDS и средства командной строки [RSAT-ADLDS]
- Модуль Active Directory для Windows PowerShell [RSAT-AD-PowerShell]
- Средства службы управления правами Active Directory [RSAT-RMS]
- Средства DHCP-сервера [RSAT-DHCP]
- Средства DNS-сервера [RSAT-DNS-Server]
- Средства факс-сервера [RSAT-Fax]
- Средства файловых служб [RSAT-File-Services]
- Средства распределенной файловой системы (DFS) [RSAT-DFS-Mgmt-Con]
- Средства диспетчера ресурсов файлового сервера [RSAT-FSRM-Mgmt]
- Средства служб для NFS [RSAT-NFS-Admin]
- Средства Hyper-V [RSAT-Hyper-V]
- Средства служб политики сети и доступа [RSAT-NPAS]
- Средства служб печати и документов [RSAT-Print-Services]
- Средства служб удаленных рабочих столов [RSAT-RDS]
- Средства узла сеансов удаленных рабочих столов [RSAT-RDS-RemoteApp]
- Средства шлюза удаленных рабочих столов [RSAT-RDS-Gateway]
- Средства лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов [RSAT-RDS-Licensing]
- Средства посредника подключений к удаленному рабочему столу [RSAT-RDS-Conn-Broker]
- Средства веб-сервера (IIS) [RSAT-Web-Server]
- Средства служб развертывания Windows [RSAT-WDS]
- Средства администрирования возможностей [RSAT-Feature-Tools]
- Средства администрирования программы шифрования дисков BitLocker [RSAT-BitLocker]
- Средства шифрования диска BitLocker [RSAT-Bitlocker-DriveEnc]
- Средство просмотра пароля BitLocker [RSAT-Bitlocker-RecPwd]
- Средства серверных расширений BITS [RSAT-Bits-Server]
- Средства отказоустойчивости кластеров [RSAT-Clustering]
- Средства балансировки сетевой нагрузки [RSAT-NLB]
- Средства SMTP-сервера [RSAT-SMTP]
- Средства WINS-сервера [RSAT-WINS]
- Средство отказоустойчивости кластеров [Failover-Clustering]
- Средство просмотра XPS [XPS-Viewer]
- Удаленное разностное сжатие [RDC]
- Удаленный помощник [Remote-Assistance]
- Управление групповой политикой [GPMC]
- Фоновая интеллектуальная служба передачи (BITS) [BITS]
- Облегченный сервер загрузки [BITS-Compact-Server]
- Расширение сервера IIS [BITS-IIS-Ext]
- Шифрование диска BitLocker [BitLocker]
Как посмотреть в командной строке windows server роли
Для того, чтобы посмотреть windows server роли в 2008 R2, есть два метода это утилита командной строки servermanagercmd. Вводим вот такую команду для получения списка ролей и компонентов.
В итоге получите вот такой вывод команды
Второй метод, просмотреть роли windows server 2008 r2 это конечно же powershell, вводим вот такую команду:
В итоге вы получаете список всех доступных ролей и компонентов Windows Server
Для 2012 r2 и 2016 версии Windows server роли ставятся, только через Powershell, если мы имеем ввиду GUI интерфейс. Уверен, что кому то данная статья поможет.
Содержание
- Исследуйте службы Windows Server 2012 и повысьте эффективность вашего бизнеса
- Возможности Windows Server 2012 для бизнеса
- Основные возможности Windows Server 2012 включают:
- Оптимизация работы бизнес-приложений на Windows Server 2012
- Улучшение безопасности с использованием служб Windows Server 2012
- Основные преимущества служб Windows Server 2012 для повышения безопасности:
- Облегчение управления серверами с помощью Windows Server 2012
- Основные возможности Windows Server 2012:
- Расширение возможностей хранения данных на Windows Server 2012
- Увеличение производительности с помощью служб Windows Server 2012
- Интеграция с облачными службами на Windows Server 2012
Исследуйте службы Windows Server 2012 и повысьте эффективность вашего бизнеса
Windows Server 2012 является одной из наиболее популярных операционных систем, которая широко используется в сетевом окружении. Она предоставляет множество функций и служб, которые помогают упростить управление сетью и обеспечить безопасность данных. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как посмотреть службы Windows Server 2012 и узнать, какие службы запущены на вашем сервере.
Когда вы управляете сетью с помощью Windows Server 2012, важно иметь возможность просматривать и контролировать запущенные службы. Это помогает вам определять проблемы в работе сети, отслеживать использование ресурсов и обеспечивать стабильную работу сервера. Для этого в Windows Server 2012 есть несколько способов просмотра служб.
Один из способов просмотра служб — использовать менеджер служб. Это инструмент, который позволяет просматривать и управлять службами на вашем сервере. Чтобы открыть менеджер служб, нажмите клавишу «Пуск», введите «services.msc» в поле поиска и нажмите клавишу Enter. В менеджере служб вы увидите список всех служб, которые запущены на вашем сервере.
Кроме менеджера служб, вы также можете использовать командную строку для просмотра служб. Для этого откройте командную строку, введите команду «sc query» и нажмите клавишу Enter. Это покажет вам список всех служб на сервере, их состояние и идентификаторы.
Еще один способ просмотра служб — использование Windows PowerShell. Windows PowerShell — это мощный инструмент для автоматизации и управления с помощью команд. Чтобы просмотреть список служб в Windows PowerShell, откройте его и введите команду «Get-Service». Это выведет список всех запущенных служб на вашем сервере.
Вот несколько способов просмотра служб в Windows Server 2012. Выберите тот, который наиболее удобен для вас и начните управлять вашей сетью более эффективно.
Возможности Windows Server 2012 для бизнеса
Windows Server 2012 предлагает широкий набор функций и возможностей, которые делают его идеальным выбором для бизнеса. Он предоставляет мощные инструменты управления, безопасности и масштабируемости, которые помогают организациям управлять своими IT-ресурсами эффективно и надежно.
Одной из главных возможностей Windows Server 2012 является его способность управлять виртуализацией. С помощью гипервизора Hyper-V, который входит в состав операционной системы, вы можете создавать и управлять виртуальными машинами. Это позволяет вам максимально эффективно использовать оборудование и упрощает развертывание новых приложений и сервисов.
Windows Server 2012 также предлагает продвинутые функции безопасности, которые помогают защитить вашу корпоративную сеть и данные. Например, встроенная система защиты от вредоносных программ помогает предотвратить атаки и обнаружить подозрительную активность. Кроме того, с помощью функций контроля доступа и аутентификации вы можете обеспечить уровень доступа к данным, который соответствует вашим бизнес-потребностям.
Другой важной возможностью Windows Server 2012 является его возможность масштабирования. Операционная система поддерживает горизонтальное и вертикальное масштабирование, что позволяет организациям увеличивать ресурсы при необходимости. Это особенно полезно для компаний, которые имеют быстро меняющиеся потребности и требуют гибкости в управлении своими IT-инфраструктурами.
Основные возможности Windows Server 2012 включают:
- Виртуализацию с помощью Hyper-V
- Продвинутые функции безопасности
- Масштабирование ресурсов
- Улучшенную систему управления
- Облачные возможности
В целом, Windows Server 2012 предлагает широкий спектр возможностей, которые могут значительно повысить производительность и эффективность вашего бизнеса. Он является надежным и гибким решением для управления IT-инфраструктурой, позволяя организациям адаптироваться к изменяющимся потребностям и требованиям рынка.
Оптимизация работы бизнес-приложений на Windows Server 2012
Одной из важных функций Windows Server 2012 является управление памятью. ОС позволяет эффективно распределять и использовать память в зависимости от нужд бизнес-приложений. Благодаря этому ресурсы сервера используются максимально эффективно, что способствует повышению производительности системы в целом.
Другой важной возможностью Windows Server 2012 является оптимизация работы сети. ОС предоставляет инструменты для настройки и управления сетевыми соединениями, а также обеспечивает балансировку нагрузки и резервирование соединений. Это особенно полезно для бизнес-приложений, которые требуют стабильного и высокоскоростного сетевого соединения.
Кроме того, Windows Server 2012 предлагает множество возможностей для защиты данных и повышения безопасности бизнес-приложений. ОС имеет встроенные механизмы обнаружения и предотвращения атак, а также обеспечивает шифрование данных и управление доступом пользователей. Это позволяет бизнес-приложениям работать безопасно и надежно, минимизируя риски утечки информации или неправомерного доступа.
В целом, Windows Server 2012 предлагает множество инструментов и функций, которые помогают оптимизировать работу бизнес-приложений. ОС обеспечивает эффективное использование ресурсов, повышение производительности, стабильное сетевое соединение и надежную защиту данных. Это делает ее идеальным выбором для предприятий, которые хотят максимально оптимизировать работу своих бизнес-приложений.
Улучшение безопасности с использованием служб Windows Server 2012
С безопасностью данных становится все более важно обеспечивать защиту информации и предотвращать несанкционированный доступ. Операционная система Windows Server 2012 предлагает различные службы и функции, которые помогают улучшить безопасность и защиту вашей информации.
Одна из ключевых функций Windows Server 2012, способствующих повышению безопасности, — это служба аутентификации и авторизации. С помощью Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) вы можете управлять пользователями и группами, устанавливать права доступа и настраивать политики безопасности. AD DS позволяет вам создавать комплексные структуры безопасности и контролировать доступ к ресурсам сети.
Windows Server 2012 также предоставляет службу обнаружения вторжений (Intrusion Detection System, IDS), которая помогает уловить и блокировать попытки несанкционированного доступа или вторжения в сеть. IDS анализирует сетевой трафик и обнаруживает подозрительную активность. В случае обнаружения потенциальной угрозы IDS может принять меры для ее блокирования и защиты сети.
Основные преимущества служб Windows Server 2012 для повышения безопасности:
- Централизованное управление безопасностью: С использованием служб Windows Server 2012 вы можете централизованно управлять безопасностью вашей сети. Это позволяет вам настраивать политики безопасности, управлять доступом к ресурсам и контролировать активность пользователей.
- Межсетевой экран: Windows Server 2012 предоставляет встроенный межсетевой экран (Firewall), который помогает защитить сеть от внешних угроз. Вы можете настраивать правила фильтрации трафика и контролировать доступ к портам и сервисам.
- Обновления безопасности: Службы Windows Server 2012 регулярно обновляются с целью устранения уязвимостей и обеспечения безопасности системы. Предлагается система автоматических обновлений, которая позволяет вам установить последние патчи и исправления безопасности.
В целом, службы Windows Server 2012 предоставляют множество инструментов для повышения безопасности вашей сети. Он предлагает возможности централизованного управления, контроля доступа, обнаружения вторжений и защиты от внешних угроз. Использование этих служб поможет улучшить безопасность вашей инфраструктуры и защитить ваши данные от несанкционированного доступа.
Облегчение управления серверами с помощью Windows Server 2012
Одной из главных особенностей Windows Server 2012 является возможность использования групповых политик для управления серверами. Групповые политики позволяют администраторам определять уровни доступа для пользователей, настройки безопасности, сетевые параметры и многое другое. Это упрощает и стандартизирует процесс управления серверами, особенно если в сети присутствует большое количество серверов.
Windows Server 2012 также предлагает возможность виртуализации серверов с помощью Hyper-V. Этот инструмент позволяет создавать виртуальные серверы, которые могут работать на одном физическом сервере. Виртуализация упрощает управление серверами и повышает их производительность. Благодаря Hyper-V можно легко масштабировать сеть, добавлять или удалять серверы при необходимости, а также легко создавать резервные копии и восстанавливать данные.
Основные возможности Windows Server 2012:
- Централизованное управление серверами с помощью Server Manager
- Использование групповых политик для управления серверами
- Виртуализация серверов с помощью Hyper-V
- Повышение производительности и упрощение управления сетью
- Создание резервных копий и восстановление данных
С помощью Windows Server 2012 администраторы могут значительно облегчить управление серверами и повысить их эффективность. Благодаря разнообразным инструментам и возможностям, предлагаемым этой операционной системой, управление серверами становится проще, быстрее и надежнее. Windows Server 2012 — это незаменимый инструмент для всех администраторов серверов, которые стремятся оптимизировать работу своей сети и гарантировать ее стабильность и безопасность.
Расширение возможностей хранения данных на Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 предлагает мощные инструменты для расширения возможностей хранения данных в корпоративной среде. Благодаря новым функциям и усовершенствованиям, этот серверный операционной системе обеспечивает высокую производительность, гибкость и надежность в обработке и хранении огромных объемов информации.
Одной из ключевых возможностей Windows Server 2012 является встроенный сервер файловых служб (File Server), который обеспечивает централизованное хранение и управление данными. Данный сервер позволяет создавать и управлять сетевыми дисками, а также предоставляет возможность для организации доступа к данным через протоколы SMB (Server Message Block) и NFS (Network File System).
Другой важной функцией Windows Server 2012 является система хранения Storage Spaces. Она позволяет объединять различные физические или виртуальные накопители в единое хранилище данных, обеспечивая высокую отказоустойчивость и возможность масштабирования. Благодаря этой функции, администраторы смогут создавать гибкие и надежные решения для хранения информации, а также эффективно управлять ресурсами хранилища.
Также, на Windows Server 2012 присутствуют инструменты для резервного копирования и восстановления данных, такие как система резервного копирования Windows Server Backup и функция Hyper-V Replica. Они позволяют создавать резервные копии важных данных и обеспечивать их восстановление в случае сбоев или потерь информации. Эти инструменты повышают уровень безопасности и надежности хранения данных на сервере Windows Server 2012.
Увеличение производительности с помощью служб Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 предоставляет множество служб и возможностей, которые помогают увеличить производительность вашей организации. Эти службы и функции специально разработаны для оптимизации работы серверов, повышения эффективности и ускорения процессов.
Одной из таких служб является технология виртуализации Hyper-V, которая позволяет создавать и управлять виртуальными машинами. Виртуализация позволяет использовать больше ресурсов сервера, таких как процессорное время и память. Это позволяет увеличить производительность, разделять нагрузку между несколькими виртуальными машинами и эффективно использовать ресурсы сервера.
Другой важной службой Windows Server 2012 является служба кеширования памяти. Эта служба позволяет снизить задержки при чтении данных с жесткого диска, кэшируя часто запрашиваемые данные в оперативной памяти сервера. Благодаря этому, доступ к данным становится быстрее, что увеличивает производительность загрузки и обработки данных.
Кроме того, Windows Server 2012 предоставляет службы мониторинга и управления, которые помогают оптимизировать работу серверов и обнаружить потенциальные проблемы. Например, служба мониторинга ресурсов позволяет отслеживать загрузку сервера, использование памяти и процессора, а также ресурсов сети. Это дает возможность реагировать на увеличение нагрузки и принимать меры заранее для предотвращения снижения производительности.
Еще одной важной службой в Windows Server 2012 является служба восстановления после сбоя. Она позволяет автоматически восстанавливать сервер после сбоя или сбоя в работе приложений. С помощью этой службы можно уменьшить время простоя сервера и минимизировать влияние сбоев на производительность и доступность сервисов.
Интеграция с облачными службами на Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 предоставляет множество возможностей для интеграции с облачными службами, что делает его идеальной платформой для работы с современными технологиями облачных вычислений. Эта интеграция создает гибкие и эффективные решения, которые позволяют организациям использовать облачные ресурсы для увеличения производительности, снижения затрат и улучшения безопасности.
С помощью Windows Server 2012 можно легко интегрировать свои собственные службы с публичными и частными облачными платформами. Например, можно создать гибридное облако, которое объединяет ресурсы вашей внутренней инфраструктуры с облачными службами, такими как Azure. Это позволяет расширить возможности вашей организации, предоставляя эластичные вычислительные ресурсы и возможность масштабирования в соответствии с потребностями.
Windows Server 2012 также предоставляет интеграцию с облачными службами через сервисы Active Directory. С помощью Windows Azure Active Directory вы можете синхронизировать учетные записи пользователей и групп с облачной платформой Azure. Это обеспечивает единый и централизованный контроль доступа к облачным и внутренним ресурсам, упрощает управление пользователями и повышает безопасность.
- Windows Server 2012 также предоставляет интеграцию с облачными службами через сервисы Active Directory. С помощью Windows Azure Active Directory вы можете синхронизировать учетные записи пользователей и групп с облачной платформой Azure. Это обеспечивает единый и централизованный контроль доступа к облачным и внутренним ресурсам, упрощает управление пользователями и повышает безопасность.
- Windows Server 2012 также предоставляет готовые инструменты для интеграции с популярными облачными службами, такими как Microsoft Office 365. Это позволяет пользователям управлять своими почтовыми ящиками и документами из одного места, а также обмениваться информацией с коллегами и партнерами.
- Windows Server 2012 также предоставляет возможность создания собственных облачных служб с использованием Hyper-V и Virtual Machine Manager. Это позволяет организациям развертывать и управлять виртуальными машинами в облаке с помощью знакомых инструментов и снижать свои затраты на оборудование и обслуживание.
Интеграция с облачными службами на Windows Server 2012 открывает организациям новые возможности для оптимизации своей инфраструктуры и повышения эффективности бизнес-процессов. Она позволяет объединить облачные и внутренние ресурсы, повысить безопасность и упростить управление пользователями. Благодаря этой интеграции компании могут получить максимальную выгоду от использования облачных вычислений и стать более гибкими и конкурентоспособными на рынке.
Windows operating system provides services in order to complete tasks in the foreground. There may become different types of job services in order to accomplish tasks like printing, network authentication, encryption, etc. Windows provides a lot of services by default. But more services can be added by third-party applications or other tools. services.msc is a shortcut to the service management console. In this tutorial, we will look at how to open and manage services with services.msc.
Open Windows Services Manager
Services Manager is used to managing operating systems services. There are different ways to open the Services Manager.
By writing Services to the search we will be listed the Services Manager. This will work with Recent Windows Operating systems like Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2016.

More compatible way to open Service Manager is running services.msc command in the Run . This will work all windows versions like Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2016.

Show/Display Service Status
After opening the Services Manager panel we will see a lot of services that are in a different states. There is two basic services status type
- Running means services is running as expected
- Stopped means services is not running and active.

We can see from screenshot that Service like Application Information is running without a problem. but service BranchCache is stopped and not running.
Change Service Status with GUI
We can change the service status. We can start or stop a service with net command which is provided by the operating system. But as you expect we need Administrator privileges in order to start and stop the service. We can use GUI too in order to manage Windows services with related buttons like start, stop, resume, etc. after select relevant service from the list.
For command line we need open a Administrator pribileged MSDOS or Powershell. Just right click to the opened box and Run as administrator.

Show Windows Service Status In Command Line
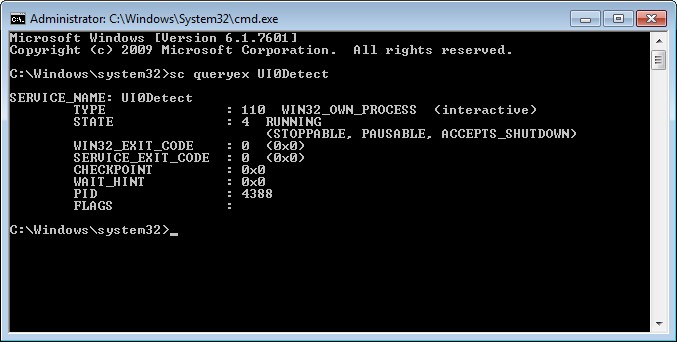
We will use sc command which is the main tool used to manage windows service. We will use query parameter in order to list given service status. We will list service named Application Info which is named as Appinfo in windows services.
> sc query Appinfo
As we can see from screenshot it has type 30 which is a Win32 service.
Start Windows Service In Command Line
We will use sc command with start parameter and service name in order to start the service named Appinfo .
> sc start AppinfoStop Windows Service In Command Line
We can stop the service with stop parameter. But keep in mind that some services may take some time to stop. After stopped the related session state of the session will be lost.
> sc stop AppinfoPause windows Server In Command Line
Another state of windows service is pause state which is rarely used. We can pause service for a short time.
> sc pause AppinfoResume Windows Service In Command Line
We need also resume paused windows service. We can use resume paramter for this.
> sc resume AppinfoStart Service On Boot
Services are started after a reboot automatically if they are set enabled. If not and set to Manual start we need to start them manually. We can enable auto service to start after a reboot with config command like below.
> sc config "Appinfo" start=enabledWindows Server 2012 предоставляет различные инструменты и функции для управления службами, что обеспечивает эффективное функционирование вашего сервера. Управление службами является одной из ключевых задач администратора сервера, ведь именно от них зависит работоспособность и безопасность вашей системы.
Что такое службы?
Службы в Windows Server 2012 — это программы, которые работают в фоновом режиме и выполняют определенные задачи на сервере. Они могут быть автоматически запущены при старте системы или по запросу. Службы могут управляться и мониториться с помощью специальных инструментов и команд.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим основные способы управления службами в Windows Server 2012, а также предоставим несколько полезных советов и рекомендаций по их настройке и обслуживанию.
Важно помнить, что некорректное управление службами может привести к сбоям системы или нарушению безопасности. Поэтому перед внесением изменений на сервере, рекомендуется сохранить резервную копию и ознакомиться с документацией и руководствами, связанными с настройкой служб.
Содержание
- Управление службами в Windows Server 2012: советы и руководство
- Настройка служб Windows Server 2012
- Методы запуска и остановки служб на Windows Server 2012
- Управление зависимостями служб Windows Server 2012
- Контроль доступа к службам на Windows Server 2012
- Мониторинг и управление работой служб в Windows Server 2012
Одним из основных инструментов управления службами является консоль «Управление службами» (Services.msc). В данной консоли вы можете просмотреть список всех служб на сервере, запустить/остановить службу, изменить ее параметры и настроить автоматическое запускание службы при загрузке системы.
Также в Windows Server 2012 доступно командное управление службами с помощью утилиты sc. С помощью этой утилиты вы можете выполнить различные операции над службами, такие как запуск, остановка, приостановка или изменение параметров службы.
Кроме стандартных инструментов управления службами, в Windows Server 2012 также присутствуют дополнительные возможности, которые можно использовать для более гибкого и эффективного управления службами. Например, вы можете создать группы служб, чтобы сгруппировать службы с похожими функциями или требованиями. Это позволит легче управлять службами, например, одновременно запускать/останавливать группу служб.
| Операция | Команда | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| Запуск службы | sc start [имя службы] | Запустить службу |
| Остановка службы | sc stop [имя службы] | Остановить службу |
| Приостановка службы | sc pause [имя службы] | Приостановить службу |
| Возобновление службы | sc continue [имя службы] | Возобновить выполнение приостановленной службы |
Важно отметить, что при управлении службами необходимо быть осторожными, поскольку некорректные действия могут привести к неправильной работе сервера или потере данных. Перед выполнением любых операций с службами рекомендуется создать резервные копии и проверить работоспособность сервера после изменений.
В общем, управление службами в Windows Server 2012 требует знания основных инструментов и команд, а также осторожность и внимательность при выполнении операций. Если вы уверены в своих действиях, то с помощью этих инструментов и руководств вы сможете управлять службами сервера эффективно и безопасно.
Настройка служб Windows Server 2012
1. Определение важности службы
Перед настройкой службы необходимо определить ее важность для работы сервера. Некоторые службы являются обязательными и не должны быть отключены. Однако, есть службы, которые могут быть отключены или настроены для работы только по требованию.
2. Отключение ненужных служб
Чтобы улучшить производительность сервера и освободить ресурсы, рекомендуется отключить ненужные службы. Для этого откройте «Сервисы» через панель управления, найдите нужную службу и выберите «Остановить» или «Отключить». Однако, перед отключением службы важно убедиться, что она действительно не используется.
3. Настройка типа запуска службы
В Windows Server 2012 есть несколько типов запуска служб: автоматический, автоматический (задержка запуска), автоматический (отложенный запуск), ручной и отключенный. Различные службы требуют разных типов запуска. Например, службы, необходимые для основной работы сервера, следует настроить на автоматический запуск, чтобы они запускались при старте системы. С другой стороны, службы, которые используются редко или по требованию, можно настроить на ручной или отключенный запуск.
4. Настройка зависимостей служб
Некоторые службы в Windows Server 2012 зависят от других служб для своей работы. Если вы планируете изменять тип запуска или отключать какую-либо службу, убедитесь, что это не приведет к проблемам с другими службами. Важно понимать, какие службы зависят от выбранной службы и иметь это в виду при настройке.
5. Мониторинг служб
После настройки всех служб рекомендуется мониторить их работу. Для этого можно использовать средства мониторинга, такие как Windows Event Viewer или системные журналы. Мониторинг поможет выявить проблемы с работой служб и принять соответствующие меры.
Надеюсь, эти советы помогут вам настроить службы в Windows Server 2012 и обеспечить стабильную работу вашего сервера.
Методы запуска и остановки служб на Windows Server 2012
На Windows Server 2012 существует несколько способов запуска и остановки служб, что позволяет администраторам гибко управлять работой системы. Вот несколько наиболее распространенных методов:
1. Управление службами через консоль PowerShell:
PowerShell — это мощный инструмент командной строки, который может быть использован для запуска и остановки служб на сервере. Для этого необходимо открыть PowerShell и ввести следующую команду:
Start-Service -Name <имя службы> — для запуска службы.
Stop-Service -Name <имя службы> — для остановки службы.
2. Использование Панели управления:
Другим способом управления службами на сервере является использование Панели управления. Для этого необходимо перейти в раздел «Система и безопасность» и выбрать «Администрирование» -> «Службы». Затем вы можете щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши на службе и выбрать «Запустить» или «Остановить», чтобы выполнить нужное действие.
3. Использование командной строки:
Еще одним способом управления службами на Windows Server 2012 является использование командной строки. Для этого нужно открыть командную строку и ввести следующую команду:
sc start <имя службы> — для запуска службы.
sc stop <имя службы> — для остановки службы.
Важно отметить, что для запуска или остановки службы требуются административные права. Поэтому убедитесь, что вы выполняете эти команды от имени администратора.
Вы можете выбрать любой из перечисленных методов в зависимости от ваших предпочтений и задач. Важно помнить, что некоторые службы могут быть критическими для работы сервера, поэтому перед выполнением действий с ними рекомендуется ознакомиться с их функциональностью и последствиями.
Управление зависимостями служб Windows Server 2012
Службы в Windows Server 2012 могут иметь зависимости с другими службами. Зависимость позволяет службам работать совместно и взаимодействовать друг с другом. В случае если одна из зависимых служб остановлена или имеет проблемы, это может повлиять на работу других служб.
Для управления зависимостями служб в Windows Server 2012 доступна специальная утилита — Службы. Чтобы открыть эту утилиту, выполните следующие действия:
| Шаг | Действие |
|---|---|
| 1 | Нажмите клавишу Win на клавиатуре для открытия меню Пуск. |
| 2 | Начните вводить слово Службы в поле поиска. |
| 3 | Нажмите на результат поиска, чтобы открыть утилиту Службы. |
В окне утилиты Службы вы увидите список всех установленных служб на вашем сервере Windows Server 2012. Для просмотра зависимостей какой-либо службы, выделите ее в списке и нажмите правой кнопкой мыши. В контекстном меню выберите пункт Свойства.
В открывшемся окне свойств службы перейдите на вкладку Зависимости. Здесь вы увидите список всех служб, от которых зависит выбранная служба, а также список служб, которые зависят от выбранной службы.
Чтобы изменить зависимости службы, можно использовать кнопку Добавить или Удалить. Кнопка Добавить позволяет добавить новую зависимость для выбранной службы, а кнопка Удалить позволяет удалить существующую зависимость.
Управление зависимостями служб в Windows Server 2012 позволяет эффективно организовывать работу служб на вашем сервере. Вы можете настроить зависимости таким образом, чтобы службы запускались и останавливались в нужном порядке, а также установить различные действия для случаев сбоев или ошибок.
Контроль доступа к службам на Windows Server 2012
В операционной системе Windows Server 2012 доступ к службам может быть ограничен с помощью механизма контроля доступа. Контроль доступа позволяет администраторам определить, какие пользователи или группы могут запускать, останавливать или изменять параметры служб.
Для настройки контроля доступа к службам необходимо открыть консоль управления службами. Для этого щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на панели задач и выберите пункт «Управление». Затем выберите «Службы».
После открытия консоли управления службами найдите нужную службу в списке и дважды щелкните на ней. В открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку «Вход в систему».
На вкладке «Вход в систему» можно установить аккаунт, от имени которого будет запускаться служба. Также здесь можно настроить контроль доступа, выбрав пункт «Определенные пользователи». Это позволит указать, какие пользователи или группы смогут запускать или изменять службу.
Чтобы добавить пользователей или группы, нажмите кнопку «Добавить». В открывшемся окне вы можете выбрать пользователей или группы из домена или локальной системы.
Для установки прав доступа выберите пользователя или группу и укажите разрешенные операции, такие как запуск, остановка или изменение параметров службы. После выбора нажмите кнопку «ОК», чтобы сохранить изменения.
Также на вкладке «Вход в систему» можно настроить параметры службы, такие как автоматическое запускание при загрузке системы или зависимость от других служб. После внесения изменений не забудьте нажать «ОК», чтобы сохранить изменения.
Используя механизм контроля доступа в Windows Server 2012, вы можете предотвратить несанкционированный доступ к службам и обеспечить безопасность вашего сервера.
| Шаг | Действие |
|---|---|
| 1 | Откройте консоль управления службами |
| 2 | Выберите нужную службу и откройте ее свойства |
| 3 | Перейдите на вкладку «Вход в систему» |
| 4 | Установите аккаунт и настройте контроль доступа |
| 5 | Добавьте пользователей или группы |
| 6 | Установите права доступа для каждого пользователя или группы |
| 7 | Нажмите «ОК» для сохранения изменений |
Мониторинг и управление работой служб в Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 предоставляет мощные средства мониторинга и управления службами, которые обеспечивают стабильную и надежную работу сервера. В этом разделе рассмотрим основные инструменты и методы для контроля и управления службами в операционной системе Windows Server 2012.
1. Службы в диспетчере задач
Один из основных инструментов для мониторинга запущенных служб в Windows Server 2012 — это диспетчер задач. Чтобы открыть диспетчер задач, нажмите комбинацию клавиш Ctrl + Shift + Esc или выполните команду «taskmgr» в командной строке.
В диспетчере задач перейдите на вкладку «Службы», где будут отображены все текущие службы, работающие на сервере. Здесь вы можете просмотреть их состояние, запустить, остановить или перезагрузить службу, а также изменить их параметры и зависимости.
2. Консоль управления службами (Services)
Windows Server 2012 также предоставляет графический интерфейс для управления службами — консоль управления службами. Чтобы открыть эту консоль, перейдите в меню «Пуск», затем введите «services.msc» в поле поиска и нажмите клавишу Enter.
В консоли управления службами вы найдете список всех установленных служб, их состояние и запуск. Щелкнув правой кнопкой мыши на службе, вы можете изменить ее параметры, запустить или остановить службу, а также настроить ее автоматический запуск при загрузке операционной системы.
3. PowerShell
PowerShell — это мощная командная оболочка и сценарный язык, поставляемый с Windows Server 2012. Позволяет автоматизировать множество задач, включая управление службами. Чтобы открыть PowerShell, нажмите комбинацию клавиш Win + X и выберите «Windows PowerShell».
В PowerShell вы можете использовать команды, такие как «Get-Service», «Start-Service», «Stop-Service» и другие, для получения информации о службах, их запуска и остановки. Это особенно полезно, когда вам нужно выполнить операции сразу для нескольких служб.
4. Логи событий
Windows Server 2012 предоставляет механизм логирования событий, который позволяет получать информацию о работе служб и других компонентов. Эти события записываются в специальные журналы событий, которые могут быть изучены для обнаружения проблем и принятия соответствующих мер.
Чтобы открыть журнал событий, нажмите комбинацию клавиш Win + X и выберите «Просмотреть журнал событий». В левой панели выберите соответствующий журнал событий, например, «Журнал приложений и служб» или «Журнал системы». Здесь вы найдете информацию о работе служб и событиях, связанных с ними.
С помощью этих инструментов и методов вы можете эффективно контролировать и управлять работой служб в Windows Server 2012, обеспечивая надежность и безопасность сервера.
Windows Server 2012 предлагает широкий набор инструментов для управления терминальными службами, что позволяет упростить и улучшить процесс работы с удаленными рабочими станциями. Такие инструменты позволяют администраторам настраивать и контролировать доступ пользователей, а также обеспечивать безопасность и эффективность работы системы.
Функции управления терминальными службами в Windows Server 2012 включают в себя возможность создания виртуальных рабочих станций, управление пользователями и группами, динамическое управление реестром, а также возможность контролировать и ограничивать доступ к ресурсам системы.
Важной особенностью управления терминальными службами в Windows Server 2012 является возможность производить удаленные обновления и настройки через групповые политики. Таким образом, администраторам необходимо только один раз настроить параметры и политики, а затем они автоматически применятся к всем удаленным рабочим станциям, что существенно облегчает процесс управления и позволяет сохранить временные ресурсы.
Управление терминальными службами в Windows Server 2012 — это мощный и удобный инструмент, который позволяет администраторам эффективно управлять удаленными рабочими станциями и обеспечивать безопасность и работоспособность всей системы.
Содержание
- Управление терминальными службами в Windows Server 2012
- Основные функции терминальных служб
- Преимущества Windows Server 2012
Управление терминальными службами в Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 предлагает обширные возможности для управления терминальными службами, которые могут быть использованы для удаленного доступа к приложениям и рабочим столам.
Одна из основных функций терминальных служб в Windows Server 2012 — это возможность предоставления удаленного рабочего стола пользователям. Благодаря этому пользователи могут получить доступ к своему рабочему столу из любого устройства с подключением к сети, что повышает гибкость и удобство работы.
Для управления терминальными службами в Windows Server 2012 необходимо использовать соответствующий инструментарий, который включает в себя такие компоненты, как серверы удаленных рабочих столов (Remote Desktop Session Host), виртуальные рабочие столы (Remote Desktop Virtualization Host) и шлюзы удаленных рабочих столов (Remote Desktop Gateway). Каждый из этих компонентов имеет свои особенности и функциональные возможности.
С помощью серверов удаленных рабочих столов можно предоставлять доступ к приложениям и рабочим столам с использованием технологии RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol). Это позволяет централизованно управлять приложениями и данными, а также контролировать доступ пользователей к системе.
Виртуальные рабочие столы позволяют создавать и управлять виртуальными машинами, на которых будут выполняться удаленные сеансы пользователей. Это позволяет снизить затраты на аппаратное обеспечение и упростить администрирование удаленных рабочих столов.
Шлюзы удаленных рабочих столов обеспечивают безопасный доступ к внутренней сети из внешних сетей через интернет. Это позволяет пользователям удаленно работать с приложениями и данными, не нарушая каналы связи и соблюдая информационную безопасность.
Управление терминальными службами в Windows Server 2012 может быть произведено через графический интерфейс Windows Server Manager или с помощью командной строки и PowerShell. В зависимости от потребностей и предпочтений администратора, доступны различные способы управления терминальными службами.
В итоге, управление терминальными службами в Windows Server 2012 предоставляет обширные возможности для организации удаленного доступа к приложениям и рабочим столам, а также гибкое и эффективное управление данными и пользователями.
Основные функции терминальных служб
Терминальные службы в Windows Server 2012 предоставляют несколько основных функций, которые позволяют организовать удаленное управление и подключение к серверу. Вот некоторые из этих функций:
1. Удаленное рабочее место: Терминальные службы позволяют пользователям подключаться к серверу и работать с ним, будто они физически находятся рядом с ним. Это особенно полезно в ситуациях, когда требуется доступ к серверу из удаленного офиса или домашнего компьютера.
2. Виртуальные рабочие столы: С помощью терминальных служб можно создавать и управлять виртуальными рабочими столами. Виртуальный рабочий стол позволяет пользователям запускать приложения и работать с ними, не устанавливая их на свой локальный компьютер.
3. Масштабирование: Терминальные службы позволяют масштабировать доступ к серверу, что значительно упрощает управление большим количеством пользователей. С помощью терминальных служб можно настроить доступ только для определенных групп пользователей или ограничить количество одновременных подключений.
4. Централизованное управление: Терминальные службы позволяют администраторам централизованно управлять подключениями и настройками учетных записей пользователей. Это упрощает управление доступом и обеспечивает безопасность данных.
5. Потенциальная экономия затрат: Использование терминальных служб может привести к сокращению затрат на обновление и поддержку локальных компьютеров. Вместо того, чтобы обновлять каждый компьютер отдельно, администраторы могут обновлять всего один сервер, на который подключаются пользователи.
В целом, терминальные службы в Windows Server 2012 предоставляют широкий набор функций, которые позволяют организовать эффективное удаленное управление и работу с сервером.
Преимущества Windows Server 2012
1. Улучшенная безопасность:
Windows Server 2012 обеспечивает более высокий уровень безопасности данных и сетевых коммуникаций. Он имеет множество инновационных функций для защиты серверов и клиентов от различных угроз, включая вредоносное ПО и несанкционированный доступ.
2. Улучшенные возможности виртуализации:
С Windows Server 2012 появились новые инструменты и функции, позволяющие эффективно виртуализировать физические серверы. Он поддерживает горячую миграцию виртуальных машин, динамическое распределение ресурсов и управление облачными средами.
3. Увеличенная производительность:
Windows Server 2012 обеспечивает высокую производительность и быстродействие серверов благодаря оптимизации работы с процессорами и памятью, а также улучшению алгоритмов обработки данных. Он позволяет более эффективно использовать ресурсы сервера и обеспечивает быстрый отклик на запросы пользователей.
4. Удобное управление:
Windows Server 2012 предоставляет интуитивно понятный и удобный интерфейс управления. Он имеет множество инструментов и функций, упрощающих настройку и администрирование серверов. Пользователи могут легко настраивать и контролировать параметры сервера и его служб, а также выполнять мониторинг его состояния.
5. Надежность и отказоустойчивость:
Windows Server 2012 обладает высокой степенью надежности и отказоустойчивости, что позволяет минимизировать время простоя серверов и обеспечивать непрерывную работу приложений и служб. Он имеет механизмы автоматической репликации и резервного копирования данных, а также системы обнаружения и исправления ошибок.
6. Расширенные возможности хранения данных:
Windows Server 2012 предлагает широкий выбор опций хранения данных, включая встроенные технологии хранения виртуальных машин, поддержку технологии Storage Spaces для создания гибких хранилищ данных и возможность интеграции с облачными хранилищами.
В целом, Windows Server 2012 предоставляет множество преимуществ для организаций, позволяющих эффективно управлять серверами, повышать безопасность данных и сетевых коммуникаций, а также обеспечивать высокую производительность и надежность серверных приложений. Это является важной особенностью данной операционной системы и обеспечивает ее популярность среди IT-специалистов.
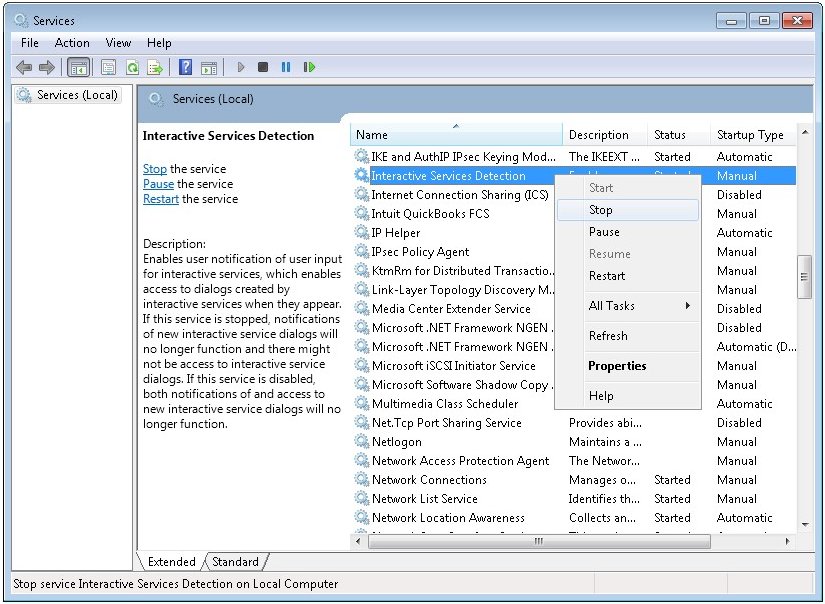
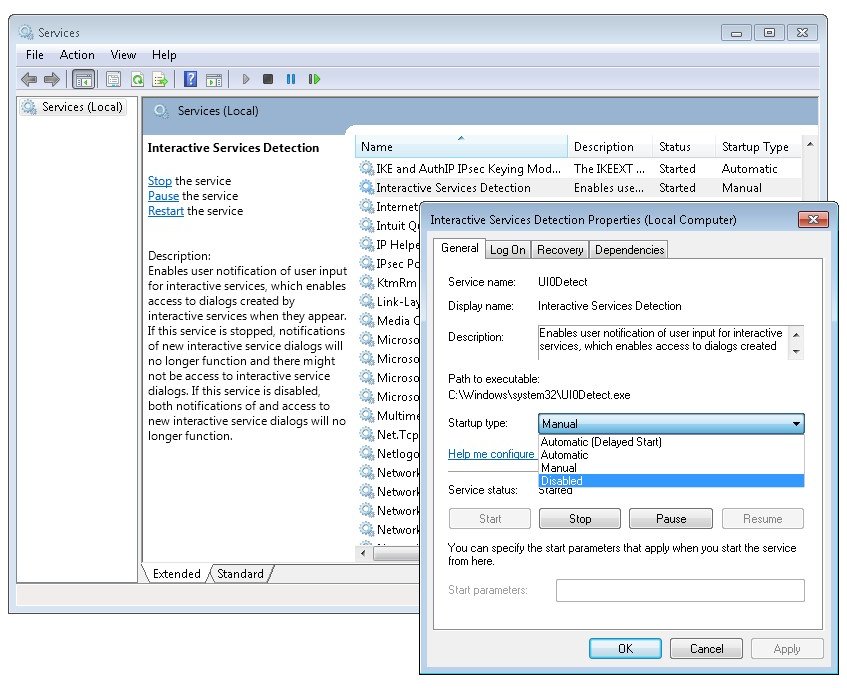
Большинство администраторов терминальных серверов Windows заметили, что начиная с Windows Server 2012, на RDS серверах пропали оснастки управления tsadmin.msc (Remote Desktop Services Manager — Диспетчер служб удаленных рабочих столов) и tsconfig.msc (Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration — Конфигурация узла сеансов удаленных рабочих столов). Разработчики Microsoft решили, что большинством параметров сервера RDS можно управлять через Server Manager, консоль редактора групповых политик (gpedit.msc) или в настройках RDS коллекций. Однако все эти инструменты не настолько просты и удобны как старые остатки.
Разберёмся, как можно вернуть оснастки tsadmin.msc и tsconfig.msc на RDS серверах под управлением Windows Server 2016 (инструкция также к Windows Server 2019 и 2012 R2 окружению).
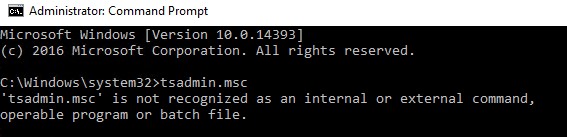
Для этого нам понадобится скопировать 6 файлов и 2 ветки реестра с любого сервера под управлением Windows Server 2008 R2 в аналогичный каталог C:\Windows\System32 на Windows Server 2016. Скопируйте следующие 7 файлов:
- c:\windows\system32\tsadmin.dll
- c:\windows\system32\tsconfig.dll
- c:\windows\system32\wts.dll
- c:\windows\system32\tsconfig.msc
- c:\windows\system32\tsadmin.msc
- c:\windows\system32\en\tsconfig.resources.dll
- c:\windows\system32\en\tsadmin.resources.dll
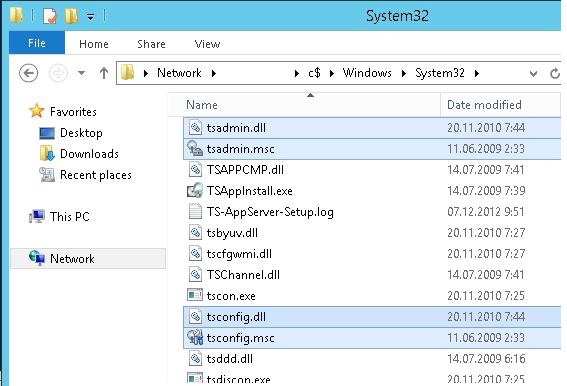
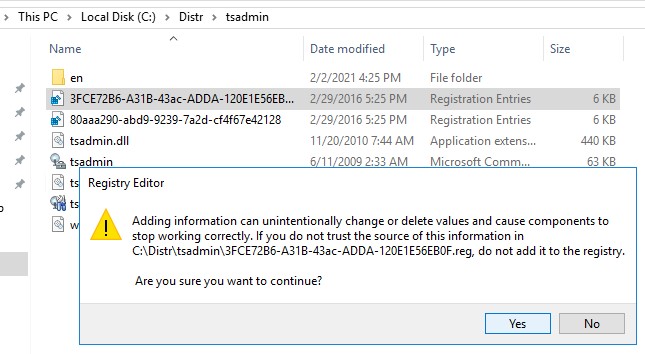
Затем на Windows Server 2008 R2 с помощью редактора regedit нужно экспортировать в файлы reg две ветки реестра:
- [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MMC\SnapIns\FX:{80aaa290-abd9-9239-7a2d-cf4f67e42128}]
- [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MMC\SnapIns\FX:{3FCE72B6-A31B-43ac-ADDA-120E1E56EB0F}]
И по очереди импортировать эти ветки в реестр Windows Server 2016. Достаточно дважды щелкнуть по reg файлу и согласится с внесением изменений в реестр.
Осталось скопировать dll и msc файлы в каталог C:\Windows\System32 на хосте с Windows Server 2016. Регистрировать файлы dll библиотек не обязательно.
Примечание. Если у вас нет под рукой развернутого сервера с Windows Server 2008 R2 (их сейчас сложно найти в связи с окончанием поддержки), вы можете скачать архив с необходимыми файлами с нашего сайта.
- Комплект файлов с английской версии ОС — tsadmin-winsrv.zip
- с русской версии — tsadmin-winsrv_ru.zip
После этого попробуйте запустить нужную оснастку командами
tsadmin.msc
:
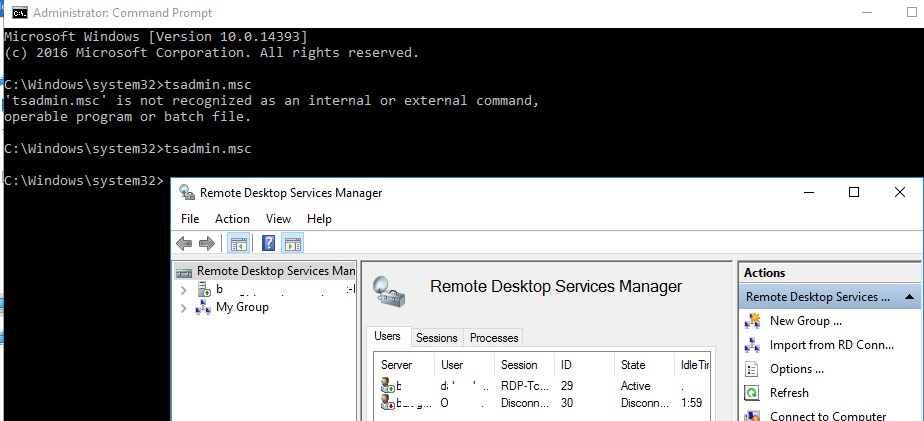
В этой консоли вы можете удобно управлять сессиями пользователей – можно отключить нужную сессию, отправить сообщение, инициировать корректный logoff и т.д. Оснастка tsadmin позволяет выбрать сразу нескольких пользователей и выполнить нужное действие сразу со всеми.
Можно запустить консоль
tsconfig.msc
:
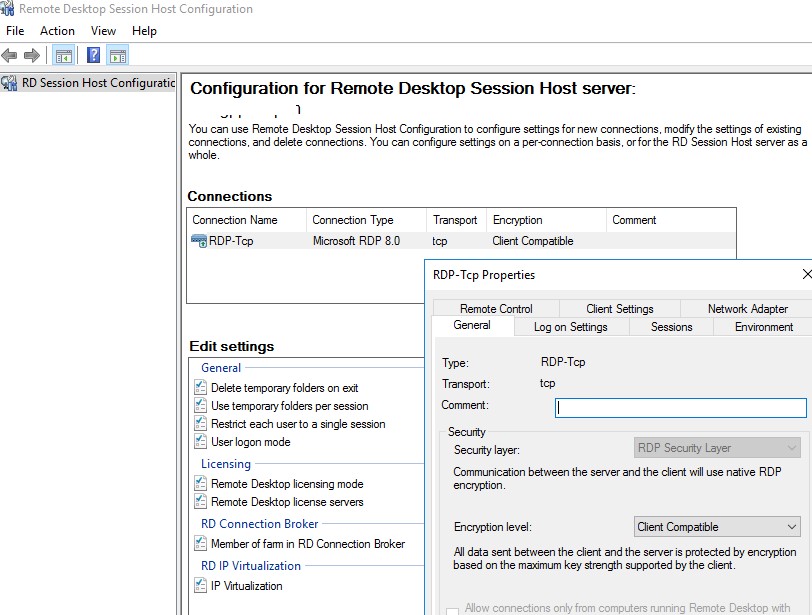
В консоли tsconfig.msc можно гораздо проще и удобнее настроить базовые параметры RDS хоста: задать сервер лицензирования и тип RDS лицензий, добавить хост в ферму RD Connection Broker (настроить вес хоста в ферме), настроить уровни шифрования RDP, настроить автозапуск программы при входе пользователя в сеанс, настроить таймауты отключения неактивных сессий пользователей на отдельно стоящем RDS хосте и т.д.
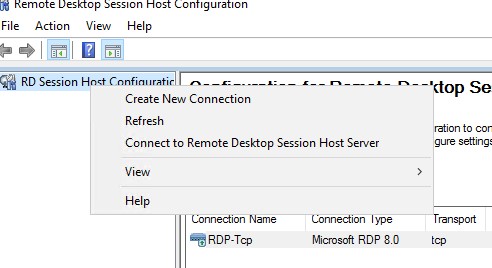
Обратите внимание, что не обязательно ставить эти консоли на все RDS хосты. С помощью опции Connect to Remote Desktop Session Host Server вы можете подключится к любому другому RDS хосту в вашей сети.
Примечание. Естественно, что использование старых консолей в новых версиях Windows Server это не поддерживаемое MS решение и вы можете использовать его на свой риск. ИМХО, проблем быть не должно.
Отметим, что с помощью консоли tsadmin.msc не получится подключиться к терминальной сессии пользователя (Ошибка: Access is denied). Подключение к RDS сессиям пользователей возможно по сценарию, описанному в статье RDS Shadow в Windows Server. Также в консоли tsconfig.msc в свойствах подключения RDP-Tcp отсутствует вкладка Security, через которую было удобно раздавать права группам сопровождения (без права администраторов) на подключение и управление RDP сессиями пользователей. Я использую следующую команду для предоставления определенной группе полные права на управления сессиями на сервере:
wmic /namespace:\\root\CIMV2\TerminalServices PATH Win32_TSPermissionsSetting WHERE (TerminalName ="RDP-Tcp") CALL AddAccount "domain\support_rds",2
Для просмотра текущий разрешений можно использовать PowerShell:
get-WmiObject -Namespace "root/cimv2/terminalservices" -Class win32_tspermissionssetting
- Home
- Windows Services FAQ
Helpful tips for managing your Microsoft Windows 11/10 & Server 2025/2022/2019/2016 Services
GENERAL
-
What is a Windows Service?
-
How do I manage a Windows Service?
-
Where are Windows Services stored/located?
-
How do I find the name of a Windows Service?
-
Where can I find the logs for a Windows Service?
-
How do I start/stop a Windows Service from the command line?
-
How do I disable a Windows Service from the command line?
-
How do I remove/delete a Windows Service?
-
How do I prevent a Windows Service from running?
-
How do I start (or stop) my Windows Service at a particular time?
-
How do I grant an account the «Log on as a service» right?
-
How can I grant a user the right to start/stop/restart a service?
-
How do I add a dependency to a service?
-
How do I set the description of a service?
-
How do I set the executable of a service?
-
How do I export a list of the Windows Services installed on my server?
-
Can a Windows Service access a mapped drive?
-
When should I use a scheduled task instead of a Windows Service?
-
Can I use SC to install my executable to run as a Windows Service?
-
How can my Windows Service access an ODBC connection?
-
Are Windows Services available on UNIX/Linux?
-
What is an elevated/administrative command prompt? How do I start one?
TROUBLESHOOTING
-
My service is stuck in the «Stop Pending» (or «Start Pending») state. How do I stop it?
-
My Windows Service fails to start (or stops working unexpectedly). How do I figure out what’s wrong?
-
My application works when I run it normally but it fails when started from a Windows Service. What is the problem?
-
Why doesn’t my Windows Service start automatically after a reboot?
-
The Stop button is greyed out. How do I stop the service?
-
My service is disabled. How do I start it?
EVOLUTION
-
What changed in Windows Vista (2006)?
-
What changed in Windows Server 2008?
-
What changed in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009)?
-
What changed in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012?
-
What is Session 0 Isolation?
-
How do I switch to Session 0 from the Command Line?
-
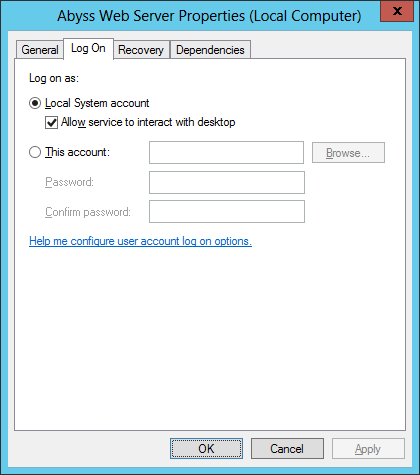
Why doesn’t «Allow service to interact with desktop» work on Windows 11/10 or Server 2025/2022/2019/2016?
-
How can I start my non-service application in Session 0?
-
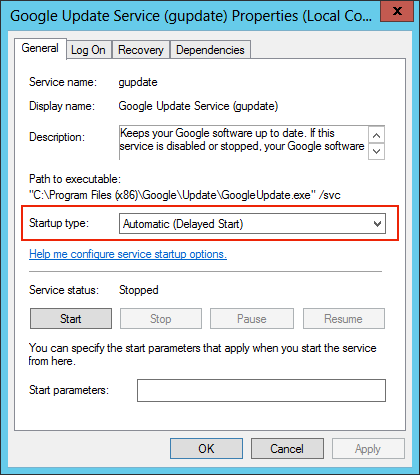
What does it mean to start my service Automatic (Delayed Start)?
-
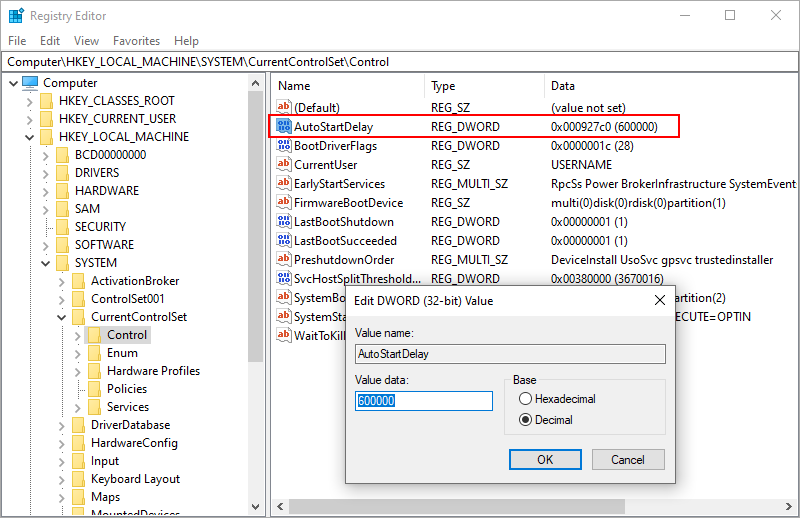
How do I adjust when «Automatic (Delayed start)» start?
-
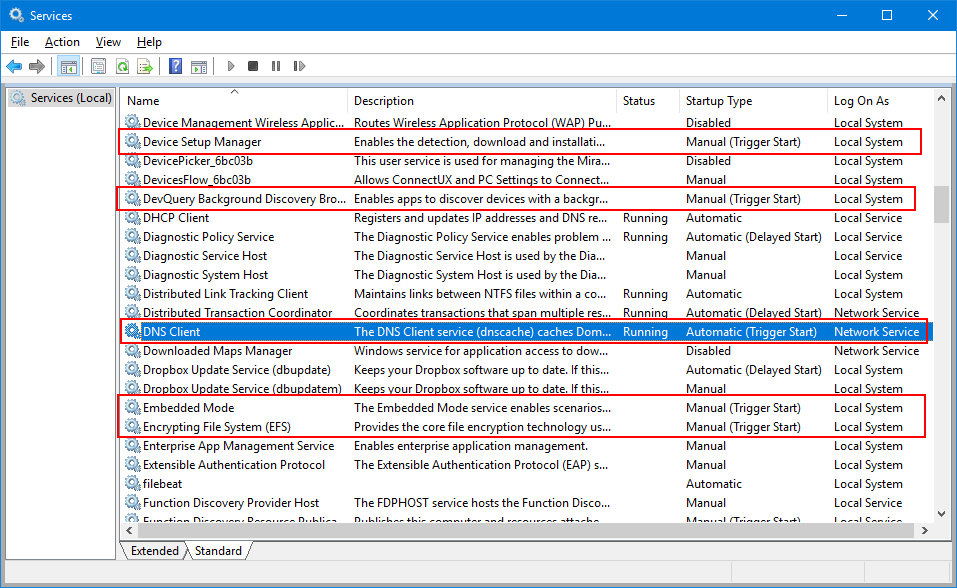
What are «Trigger Start Services»?
ERRORS
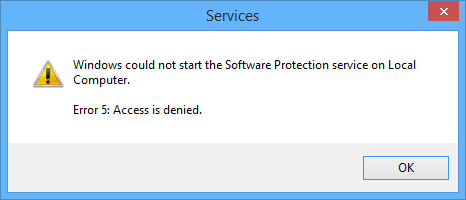
-
Windows Service Error 5: Access is denied
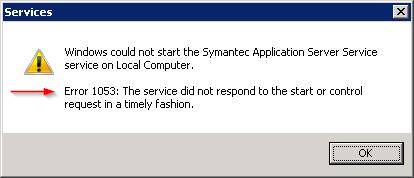
-
Windows Service Error 1053: The service did not respond to the start or control request in a
timely fashion -
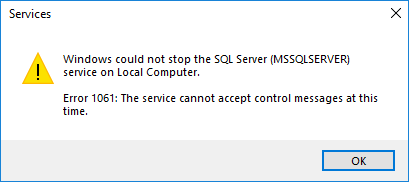
Windows Service Error 1061: The service cannot accept control messages at this time
-
Windows Service Error 1067: The process terminated unexpectedly
-
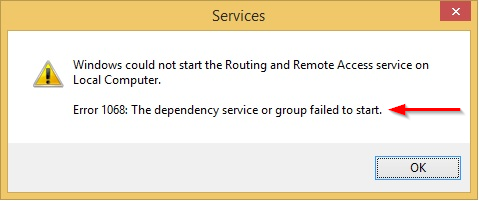
Windows Service Error 1068: The dependency service or group failed to start
-
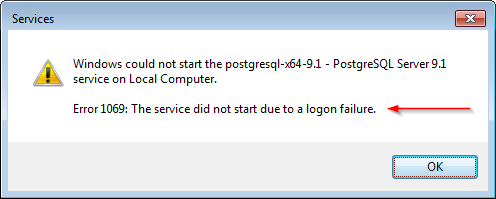
Windows Service Error 1069: The service did not start due to a logon failure
-
Windows Service Error 1072: The specified service has been marked for deletion
MICROSOFT SRVANY
-
What is Srvany?
-
What is Instsrv?
-
Where can I download Srvany and Instsrv?
-
How do I use Srvany to run my application as a service?
-
Is there a new version of Srvany for Windows Server 2008? For Windows 7?
-
Is Srvany supported on Windows Server 2008? Windows 7?
-
Is Srvany supported on Windows Server 2012? Windows 8/8.1?
-
Is Srvany supported on Windows 10? Windows Server 2019?
-
Is Srvany supported on 64-bit Windows?
-
Will Srvany close my application when I stop the service?
-
How do I remove a Srvany service?
-
If my program crashes, will Srvany start it again?
-
Can I use Srvany to run multiple applications on a single server?
-
Why can’t my application access mapped drives when run with Srvany?
INTERACTIVE / GUI SERVICES
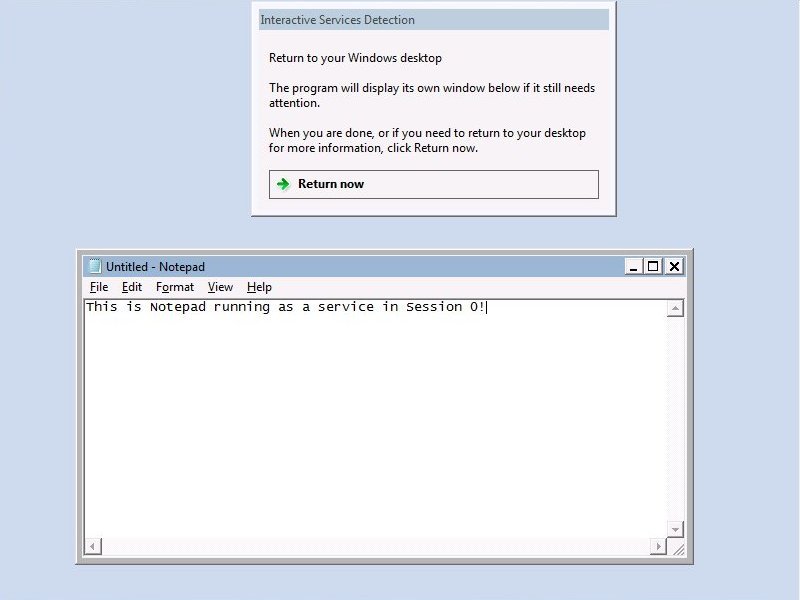
-
Can a Windows Service have a GUI? Should a Windows Service have a GUI?
-
Can a Windows Service start a GUI application?
-
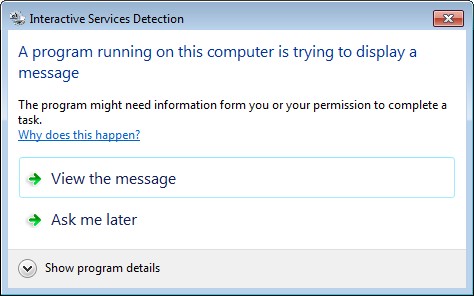
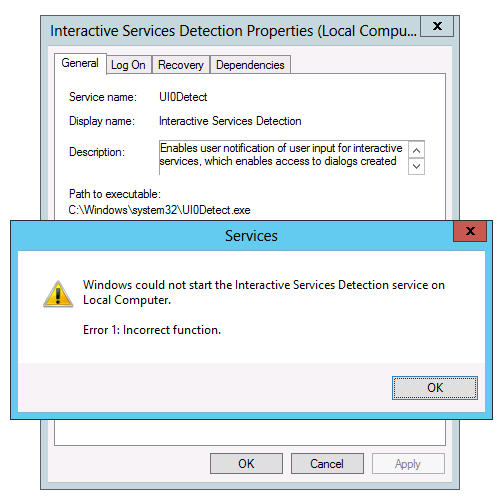
Why won’t the Interactive Service Detection service start on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012?
-
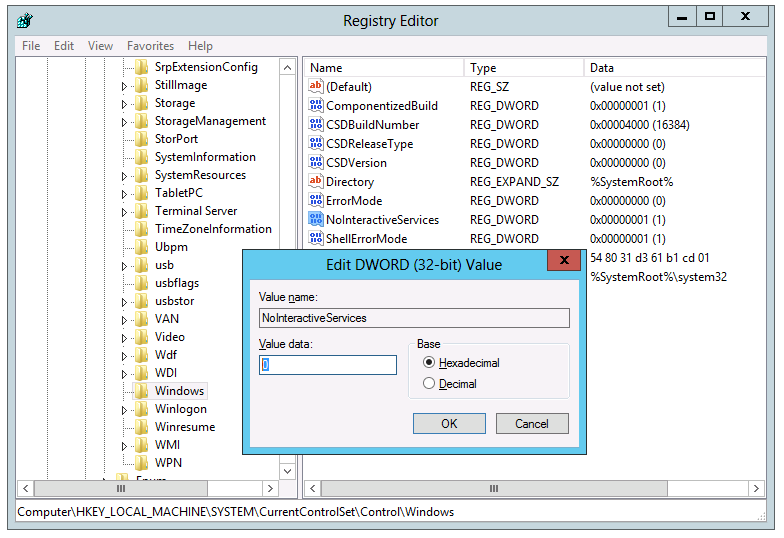
How do I disable/suppress the Interactive Services Detection Dialog?
-
Why can’t I switch to Session 0 on Windows 10?
ADDITIONAL HELP
-
My question has not been answered here. Can you please help?
-
What is a Windows Service?
A Windows Service is an advanced component/feature of Microsoft Windows that supports the management of
long running, background processes and applications.Unlike regular programs that are started by a user and run only while that user is logged on,
a Windows Service can start before any user logs on and can continue to run even after all users have logged off.Windows Services are ideal for software that must start automatically when the computer boots.
A Windows Service is conceptually similar to a
UNIX daemon. -
How do I manage a Windows Service?
You can manage Windows Services using the Windows Services control panel applet. To start the applet, either:
- Choose Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services; or
- Run «services.msc» from Start > Run…
The applet lists the Windows Services installed on your computer:
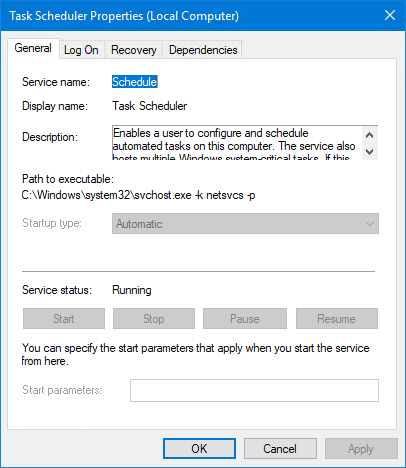
Double-click an entry to reveal its specific properties. Here’s the «Schedule» service (which operates the Windows Task Scheduler):
You can start, stop, pause or resume the service as appropriate.
You can also change the settings, such as the startup type (Automatic or Manual) or the log on account (on the Log On tab), etc. -
Where are Windows Services stored/located?
Services are stored in the
Windows Registry
— a hierarchical key-value database that’s an integral part of the operating system.
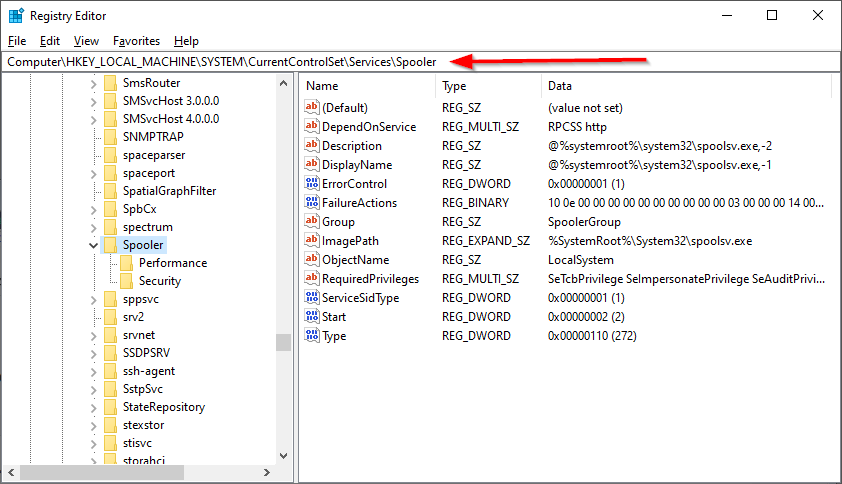
You can access the registry using the Registry Editor (started by running the regedit command).In the Registry Editor, you will find services under this key:
\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services
And each service will reside in a sub-key with its name.
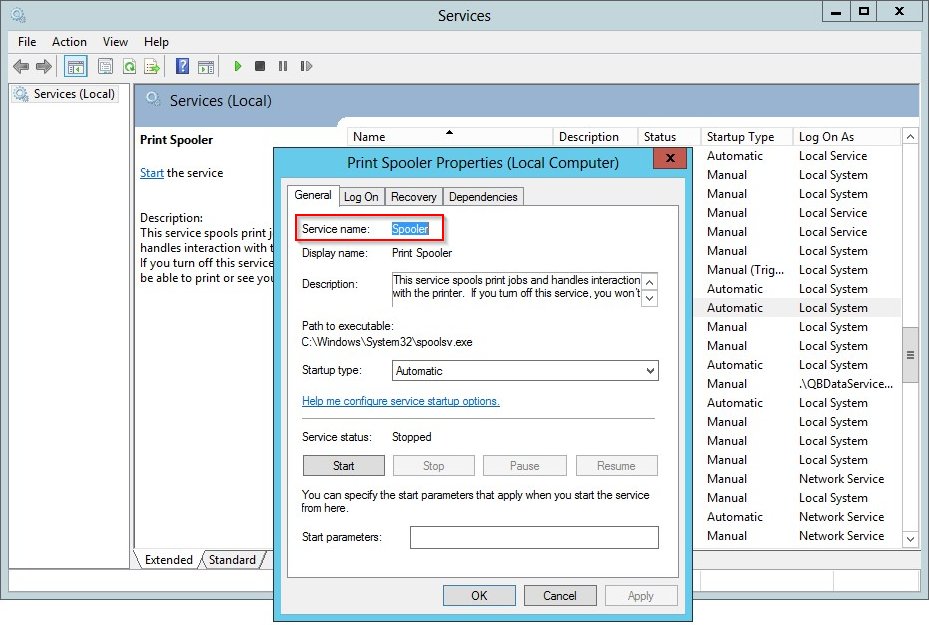
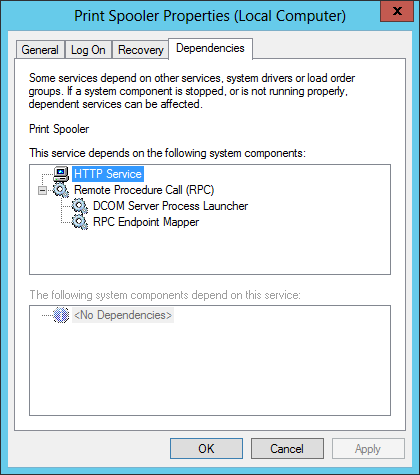
For example, here are the settings for the Print Spooler service (which is named «Spooler»):
-
How do I find the name of a Windows Service?
This 50-second video shows how to find the name of a Windows Service:
You can find the name of your service using the Windows Services control panel applet. To start the applet, either:
- Choose Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services; or
- Run «services.msc» from Start > Run…
The window that comes up lists all the Windows Services installed on your PC:
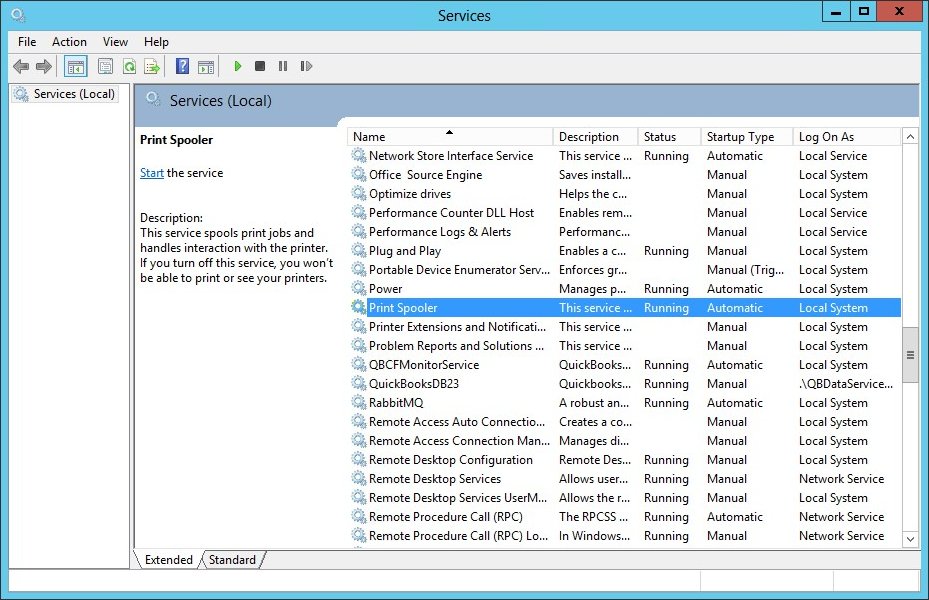
Find the service you’re interested in and double-click the entry to open its specific properties.
The service’s name will be shown near the top of the Properties window.
Here we can see that the name of the Print Spooler Windows Service is actually «Spooler»: -
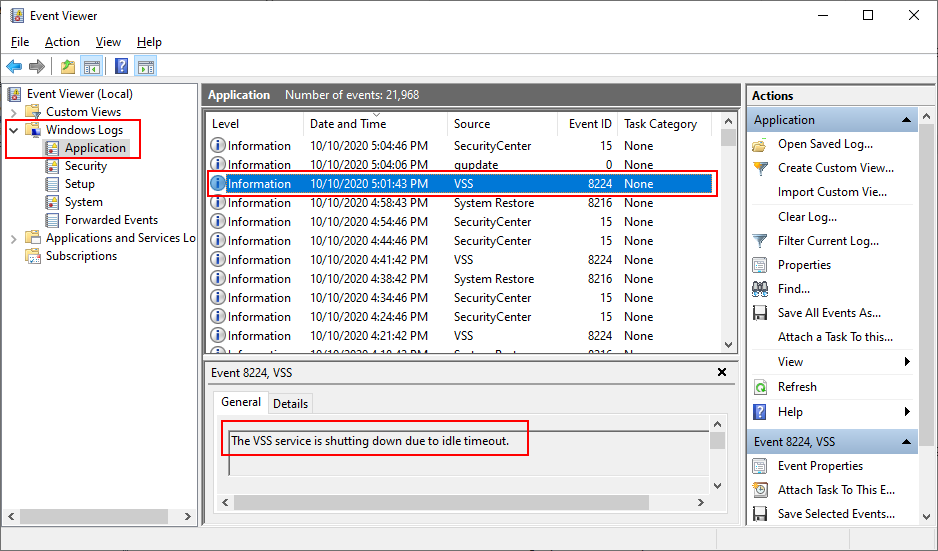
Where can I find the logs for a Windows Service?
Much like a regular application, a Windows Service can write its logs anywhere. Or it can choose not to write logs at all!
However, the convention is for services is to report errors, warnings and pertinent information to the Windows Event Logs.
You can inspect those entries using the
Windows Event Viewer.To find the messages reported by a particular service:
-
Start the Event Viewer (from the Control Panel, or by running eventvwr.msc)
-
Navigate to the Windows Logs > Application section (on the left)
-
In the center panel, look for entries where the Source is the name of your service
For example, here is a message from the Volume Shadow Copy (VSS) service:
-
-
How do I start/stop a Windows Service from the command line?
You can use the NET command to start and stop any Windows Service from a DOS prompt.
To start a service named «MyService», you would execute:
NET START MyService
To stop the same service, run:
NET STOP MyService
Be sure to enclose the service name in quotes if it contains spaces.
Note that only users with administrative privileges will be able to run the NET command.
-
How do I disable a Windows Service from the command line?
To disable a service, use the
SC command.Run it like this:
SC config <Service-Name> start= disabled
where <Service-Name> is the name of the service.
Be sure to enclose the name in quotes if it contains a space!For example, to disable the Bluetooth Support Service (whose name is «bthserv»), run:
SC config bthserv start= disabled
Note that space after the «start=» is important. The command will fail if you omit it.
Also note that disabling a service will not stop it.
Issue a NET STOP, either before or after disabling, to shut down the service.Note: If you’re not comfortable working from the command prompt, this short video shows how to disable a Windows Service using the Services GUI application:
-
How do I remove/delete a Windows Service?
You can delete a service with the
SC command.
Use it like this to remove a service called «MyService»:SC delete MyService
Enclose the service name in quotes if it contains spaces.
Beware: You can do serious damage to your operating system if you delete a critical service. Proceed with caution!
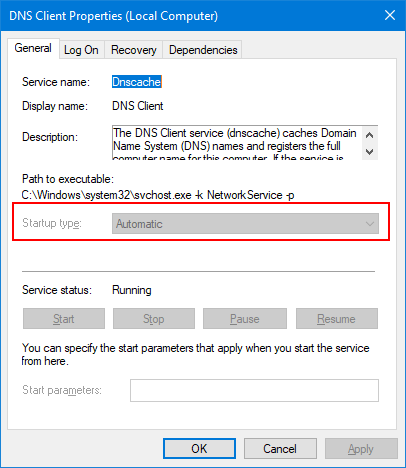
-
How do I prevent a Windows Service from running?
Most services are set to start automatically when Windows boots. These will show up with a Startup type of Automatic (or Automatic (Delayed Start))
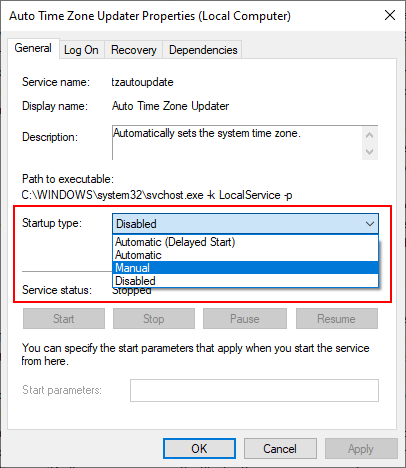
in the Services application:If starting at boot is not acceptable, you can change the Startup type to one of the following:
- Manual — The service should only start on demand, when explicitly requested to do so by a user (or by an application).
This is the appropriate choice when you want to start and stop the service yourself. - Disabled — The service cannot be started by any user or program. Choose this option to totally disallow the service from running.
But be sure not to disable any important Windows Services!
Of course, deleting a service
is another way to prevent it from running. But that’s only recommended if you know what you’re doing and can take full responsibility for the consequences! - Manual — The service should only start on demand, when explicitly requested to do so by a user (or by an application).
-
How do I start (or stop) my Windows Service at a particular time?
Use the
Windows Task Scheduler
to create a scheduled task running the
NET command
to start/stop the service at a time of your choosing.For example, suppose you have a backup that runs every Saturday from 8-10 PM and you wish to stop your service during that period.
You would create two scheduled tasks — one to stop the service at 8 and another to start it at 10.The task to stop the service would run this command:
NET STOP «service-name»
The task to start it up again would execute:
NET START «service-name»
In both cases, «service-name» is the name of your service as shown in the Control Panel Services application.
Follow this tutorial to create a scheduled task.
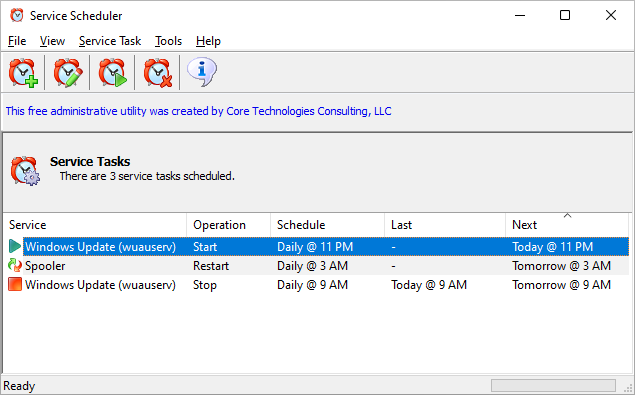
September 2022: Our new (and completely free) Service Scheduler utility
will help you start, stop or restart your service whenever you like.Simply choose your service, select the operation and set your time — that’s it:
-
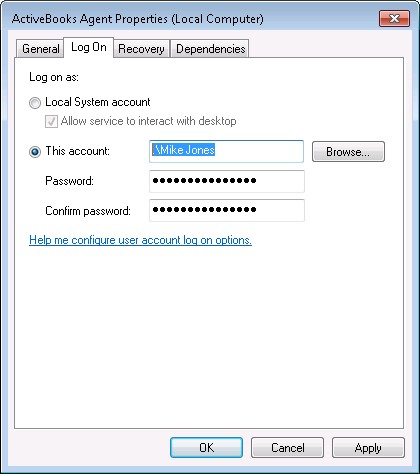
How do I grant an account the «Log on as a service» right?
If you want to run a Windows Service in a user account — by specifying the account on the service’s Log on tab —
you should make sure that the account has the «Log on as a service» right. If not, the service will fail to start with a
cryptic error like this:To ensure that your user/account has the «Log on as a service» security policy enabled:
-
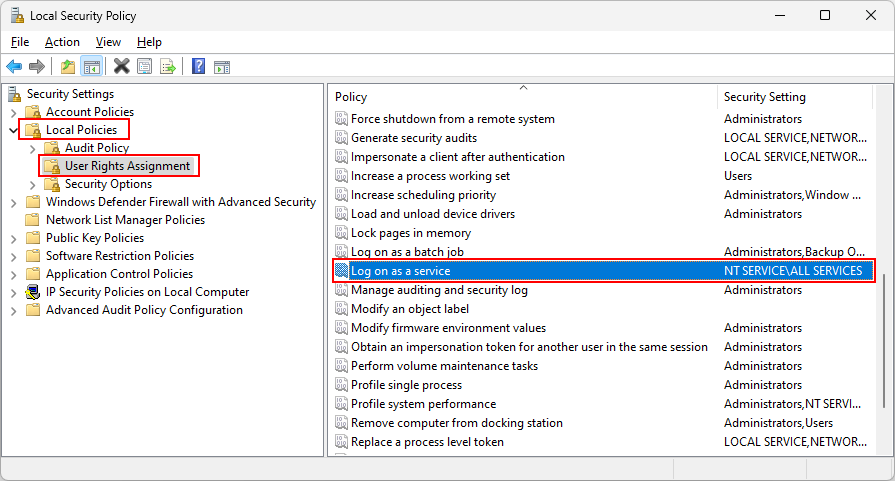
Run «secpol.msc» to start the Local Security Policy application.
-
In the left panel, navigate to Local Policies > User Rights Assignment.
-
You’ll see the list of policies on the right sorted by name.
Scroll down to find Log on as a service and double-click the entry to open its properties: -
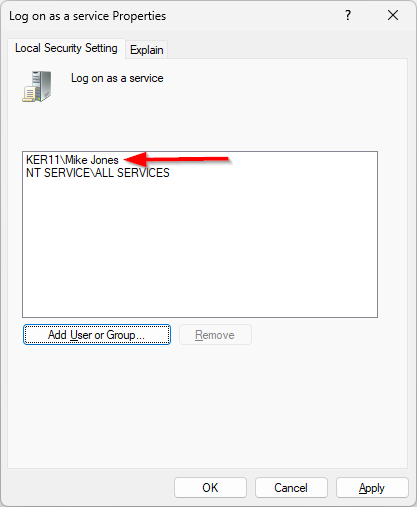
In the Log on as a service Properties window, click the Add User or Group button and enter your user account.
We added Mike, who’s an administrator on our machine:
-
Click OK to save your changes. You can close the Local Security Policy application as well.
For domain accounts, update the Group Policy too
Do you want your service to run in a domain account? Then you should grant the «Log on as a service» right in the
Group Policy application as well.
If not, you’ll encounter the
login failed
error sometime in the future — after the group policy overwrites the local policy.Follow the step-by-step instructions in this article
to update the group policy. -
-
How can I grant a user the right to start/stop/restart a service?
Every Windows Service has an
Access Control List (ACL)
recording who’s allowed to start, stop or restart it.
Here are three ways to manipulate a service’s ACL to grant or deny specific rights:-
Use Service Security Editor
a free point-and-click GUI tool for adjusting any service’s rights. Simply select the service, identify the user, and specify the operations that he is allowed to perform. -
Use the SC command line tool, as described in
this tutorial.
However working with SC can be very complicated, involving the composition of lengthy, hand-crafted command lines. It’s not recommended for the faint-hearted! -
Use the SubInACL command line utility, available for
download from Microsoft
and
documented in Method 3 on this Windows Support page.
It’s easier to use than SC but still requires careful attention.For example, if you have a user called «MikeJones» in the «SANFRAN» domain that you want to start and stop the «Print Spooler» service, you would run:
SubInACL.exe /service Spooler /GRANT=SANFRAN\MikeJones=TO
-
-
How do I add a dependency to a service?
The SC command can set the dependencies on a given service. Use it like this:
SC CONFIG <service-name> depend= <service-1>[/<service-2>/…/<service-N>]
where <service-name> is the
name of the service
you wish to change, and <service-1> to <service-N> are the names of the dependent services.
Note: The space after «depend=» is required, so don’t forget it.For example, to add the Windows Firewall as a dependency of the Google Update Service (so that the firewall is always running when updating Google’s software), you would:
-
Open services.msc and find the service name of the Google Update Service. It’s «gupdate».
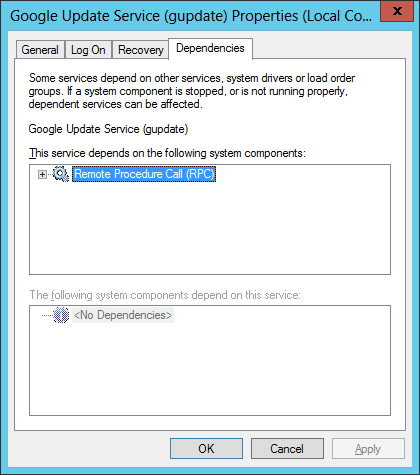
-
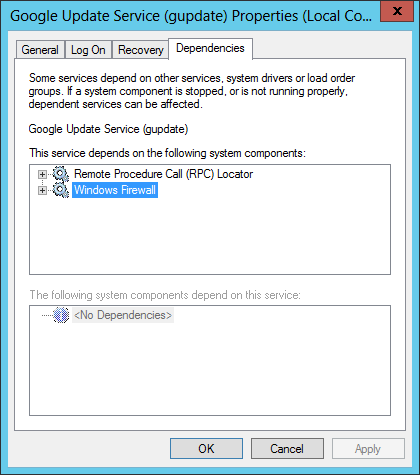
Switch to the Dependencies tab and make a note of the services already there. Find their names. There is only one, the Remote Procedure Call service, named «RpcLocator».
This is necessary because we don’t want to lose the existing dependencies. -
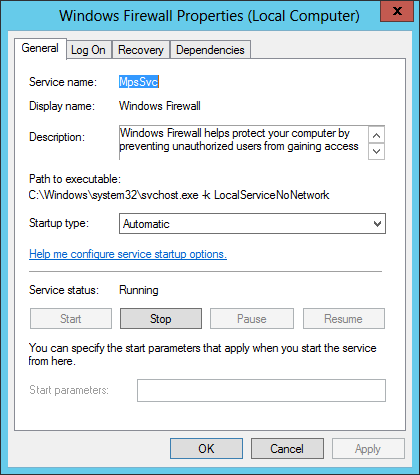
Find the name of the Windows Firewall service. It’s «MpsSvc».
-
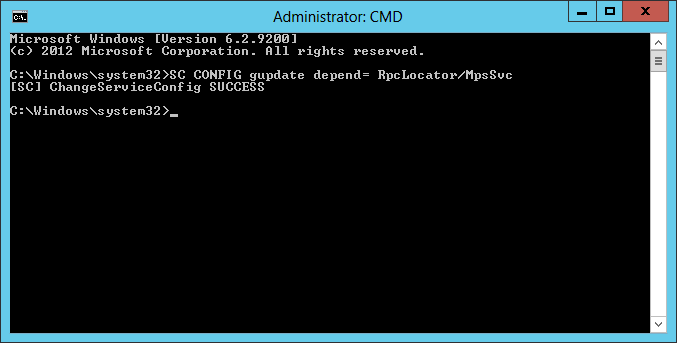
Use the SC command to update the dependencies of the Google Update Service to include the Windows Firewall service. The command line is:
SC CONFIG gupdate depend= RpcLocator/MpsSvc
Be sure to run it from an elevated command prompt:
-
Open the Google Update Service in services.msc and confirm that the dependencies have been updated:
-
-
How do I set the description of a service?
You can change a service’s description using the
SC command. Call it like this:SC DESCRIPTION [service-name] [new-description]
For example, to update the description of the
Apache Windows Service (named «Apache2.4»), run:SC DESCRIPTION Apache2.4 «An excellent open-source HTTP web server»
Administrative privileges are required to make this change so be sure to run the command from an elevated prompt.
-
How do I set the executable of a service?
While it may be tempting to fire up regedit.exe and directly modify the registry keys recording the service under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services,
it’s safer to use the
SC command
to change the executable invoked by the service.To set the executable for a service named «MyService», you would run:
SC CONFIG MyService binPath= «<The full path to your executable>»
Note that the oddly placed space separating binPath= from the executable’s path is actually required. Don’t eliminate it!
And be sure to enclose the path in quotes if it contains a space.
-
How do I export a list of the Windows Services installed on my server?
There are a couple of options for exporting your services:
Option #1: Export to Text or CSV from the Services application
-
Start the services application (from the Control Panel or by running «services.msc»);
-
Select Export List from the Action menu;
-
Specify a file name (and choose Text or CSV format) for the exported services.
The report will include the following values for each service: Name, Description, Status, Startup Type, Log On As.
Here’s what a CSV export looks like in Excel:Option #2: Export to XML with Windows Service Auditor
-
Download Windows Service Auditor (it’s free);
-
Start Windows Service Auditor;
-
Select Export (XML) from the All Services menu;
-
Specify a file name for the exported services.
The file will be in XML format, with a detailed record per service (including dependencies, recovery/failure options, triggers and more):
-
-
Can a Windows Service access a mapped drive?
Yes, but not without employing the proper configuration and doing some extra work.
A mapped drive exists only in the account in which the mapping was created. Thus the LocalSystem account, the default for all window services, will not «see» any drives mapped into a regular, interactive user account.
Configuring your service to run in a specific user’s account (via the
Log On
setting) has the potential to overcome the problem, but unfortunately persistent network connections are not restored by the service’s non-interactive login.
To access the drive by letter, your service must explicitly map the network drive by either:-
Running the
NET USE command (something like «NET USE W: \\server\folder» — no password should be necessary), or -
Calling the
WNetAddConnection2 API function if you can modify the code.
Note that a service can access the drive’s underlying UNC path («\\server\folder») without having to perform the steps above. Consider having your service work with the UNC path instead of the drive letter if you can.
-
-
When should I use a scheduled task instead of a Windows Service?
Using a scheduled task to run your application or batch file may be superior to a Windows Service when:
- You want to run at a few, fixed times each day, week or month.
For example, a batch file that periodically deletes the contents of a temporary folder would be perfect as a scheduled task.
Services are better suited for running 24/7. - You want to run whenever a user logs in, potentially bypassing the UAC prompt.
A Windows Service doesn’t provide that capability.
-
You don’t need error reporting when your application or batch file fails to start.
Errors from a Windows Service are reported to the Windows Event Log. Scheduled tasks aren’t as good at capturing and reporting errors.
- You don’t need to start or stop your application manually.
Services are easily started and stopped from the services control panel (or from the command line), but there is no such «console» to manage the ad-hoc execution of a scheduled task.
- You don’t need to start or stop your task from a remote machine.
There is no equivalent of «SC \\Server START» and «SC \\Server START STOP» for a scheduled task.
- You don’t care about automatically restarting (or taking more elaborate actions) when your application crashes.
The Task Scheduler doesn’t offer any of the recovery options available to Windows Services.
In summary, a scheduled task is often better for periodic, maintenance-type chores that don’t demand sophisticated control.
- You want to run at a few, fixed times each day, week or month.
-
Can I use SC to install my executable to run as a Windows Service?
Yes, SC will happily install any exe file as a service. However, the executable will only start if it
is a «true» Windows Service — one explicitly constructed to interface with the Windows Service
Control Manager (SCM).Regular, non-service executables will fail with
error 1053
when you try to start them from the Services Control Panel. -
How can my Windows Service access an ODBC connection?
If you want your service to access a user-specific ODBC data source (a «user DSN»), set the
user’s account on the service’s Log On tab: -
Are Windows Services available on UNIX/Linux?
No. Windows Services can only exist on Windows operating systems.
UNIX implements long running daemons in a very different way.
-
What is an elevated/administrative command prompt? How do I start one?
The command prompt is a Windows application that accepts textual commands to control your computer.
It’s typically used by administrators and other technical users who are comfortable typing instructions instead of manipulating graphical applications.You can start the command prompt by running CMD.EXE. Its distinctive window looks like this:
An elevated command prompt is a command prompt started with administrative rights.
With full rights, an elevated command prompt can run many administrative tasks, such as installing software, updating system files and manipulating Windows Services.
A normal («unelevated») command prompt cannot perform those privileged operations.How to start an elevated command prompt
-
Click the Start button.
-
Type cmd.
-
After a few seconds, an entry for the command prompt (or cmd) should appear in the list of results. Right-click that entry and select Run as administrator:
-
Windows may prompt you to confirm that you want to run as an administrator. Click Yes to proceed:
The elevated command prompt window will appear on your desktop.
-
-
My service is stuck in the «Stop Pending» (or «Start Pending») state. How do I stop it?
This short video shows you how to forcibly stop a stuck service:
A pending state usually means one of two things. Either:
- the service is working normally and is just taking a long time to complete a necessary operation, or
- the service has hung and is not interacting normally with the Windows Services Control Manager.
If you’ve waited long enough to rule out the first situation, then we have the second, and the only way to stop the service
is to reboot the machine or end its underlying process.
To terminate the process:-
Find the process identifier (PID) of the Service’s process using the SC command. For a Service named MyService, run:
sc queryex MyService
(Be sure to enclose the service name in quotes if it contains spaces.)
Here’s the result for the UI0Detect Service:
Make a note of the number on the PID line (4388 in the screenshot above).
-
Run the taskkill command to forcibly terminate the process. For PID 4338, use:
taskkill /F /T /PID 4388
You should see a SUCCESS message if all went well:
If you get «Access Denied», please ensure that you have the necessary administrative privileges by running the Command Prompt as an Administrator.
(Darn UAC!)
-
My Windows Service fails to start (or stops working unexpectedly). How do I figure out what’s wrong?
Most Windows Services report information, warnings and errors to the Windows Event Logs, so start there.
You can review those messages using the
Windows Event Viewer
Control panel application.Windows Services will place their messages in the Windows Logs > Application section (on the left hand side). The Source column in the central window contains the name of the service reporting the event.
Here’s an information event reported by the Avira AntiVir service:When a Service encounters a problem and cannot create a log entry, the Service Control Manager (SCM)
will write an entry in the Windows Logs > System section.
For example, here is the SCM telling us why the ActiveBooks service failed to start:Hopefully the Event Log messages will shed some light on what is going wrong.
-
My application works when I run it normally but it fails when started from a Windows Service. What is the problem?
You probably need to specify an account that can run the application normally on the service’s Log On tab:
By default, Windows runs your service in the LocalSystem account which may be very different from the account that you log in to.
Your application will encounter trouble if it:- Uses a printer or a network drive and LocalSystem doesn’t have sufficient rights to use those devices;
- Has never been installed in the LocalSystem account and so cannot find its settings there;
- Needs to access registry values or environment variables in your «normal» account.
Specifying your normal account on the Log On tab should solve those kind of problems.
-
Why doesn’t my Windows Service start automatically after a reboot?
There can be many reasons why a service doesn’t start automatically as expected.
Check the Windows Event Log
to see if you can find out what happened as the OS booted up.The most common problems include:
-
The service has the wrong password. Update the password on the service’s
Log On tab
and you should be good to go. -
A dependent service fails to start. Determine why the dependent service is failing and resolve the issue. Or if that doesn’t work, try to
remove the dependency — as long that won’t compromise your system. -
The service logs on as a domain user and it’s starting before Active Directory is ready. Set your service’s Startup type to
Automatic (Delayed Start) to give AD time to spin up and log you into the account you’ve specified. -
A required resource is unavailable at boot.
For example, if your service uses a database but the database is not yet fully initialized when your service starts, the service may quickly shut down.
Check your service’s log files for errors and add dependencies on any other critical services that are needed for support. Setting your service to start
Automatic (Delayed Start) to give other components more time to start up
in advance may also resolve the issue. -
The service is missing its executable or important DLLs.
Check that the service’s executable is present and that all necessary DLLs and other files are in place. Use the excellent
Dependency Walker utility
to identify missing components, and keep mind that re-running your service’s installer may help by restoring missing files.
-
-
The Stop button is greyed out. How do I stop the service?
The Stop button is unavailable when the service is busy and unable to accept a request to stop.
If the service is off doing its work, simply waiting some time for it to complete its pending tasks may resolve the situation.
As they say, patience is a virtue.However, if you’ve waited a while and the problem persists, your service may be stuck.
You can try to forcibly
terminate the service’s underlying executable using TASKKILL
(or via the Task Manager), but this may not be a viable option when the process
is hosting many services (like Microsoft’s svchost). In that second situation a reboot
may be your only recourse. -
My service is disabled. How do I start it?
You cannot start a disabled service. Not with NET START, SC START or even via the Services application.
To start the service, you must «un-disable» it first. That is, you must set its Startup type to Manual, Automatic or Automatic (Delayed). That is best done via the
Services application (services.msc):You should be able to start the service once you’ve made that change.
Note that you can also re-enable your service from the command line using the
SC command.
Run:SC config <Service-Name> start= demand
where <Service-Name> is the name of the service.
Replace «demand» with «auto» to have Windows start the service automatically at boot (instead of manually, on demand).
-
What changed in Windows Server 2008?
Nothing. No new features were introduced in the original release of Windows Server 2008.
There were a few changes for Server 2008 R2 though. -
What changed in Windows Vista (2006)?
Microsoft made significant adjustments to Windows Services in Vista. The main changes are:
-
Session 0 is now «isolated» and no user can log in there to interact with the GUI from a Service. This change — effected primarily for security concerns — makes it
much more difficult to work with GUI-based Windows Services. The situation is discussed in the
«Can a Windows Service have a GUI?» entry below. -
In an attempt to reduce resource contention as the computer boots, services that should be started at boot now have the option of being delayed and starting shortly after boot.
In practice, this means delaying service startup by 1-2 minutes — quite appropriate for some services.The new setting is available in the Startup type field — Automatic (Delayed Start):
The complete technical details are available in
this article from Microsoft Developer’s Network. -
-
What changed in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009)?
The adjustments made in 2009 were highly technical and not very visible to end users. Only the following is of note:
-
Services can be automatically started or stopped in response to one or more Trigger events. Trigger events include:
- A specific device (e.g. memory stick) arrives or is present when the system starts
- A given port is opened or closed
- A machine or user policy changes
- The first IP address becomes available or the last IP address becomes unavailable
Microsoft doesn’t provide a GUI for managing triggers so you must use the
SC command
(or the free
Service Trigger Editor).
The complete technical details are available in
this article from Microsoft Developer’s Network. -
-
What changed in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012?
Not much. The few,
highly technical adjustments
were entirely «under the hood»:- A service can retrieve information on how it was started
- Services can be notified when a user initiates a reboot
- Three new
service triggers
were introduced, but they are merely placeholders awaiting definition from Microsoft
There were no user interface changes.
-
What is Session 0 Isolation?
A Session (also known as a Logon Session) is created whenever a user logs in to Windows. Each session has a numeric identifier,
called a Session ID.Windows creates a single session when your PC boots and all the Windows Services (and many other administrative processes) will run in that session.
Since the ID of that session is 0, it’s been nicknamed Session 0.On legacy versions of Windows (NT, 2000, XP and Server 2003), the first user to log into the physical PC is automatically
placed into the already created Session 0.
An RDP/Terminal Services user can log in to Session 0 by specifying a special flag when opening the connection (/admin).
And once in Session 0, a user can see and interact with the graphical elements of any program running there, including those created by Windows Services.
In this way, Microsoft (perhaps inadvertently?) allowed users to freely interact with Windows Services that choose to display a user interface.Ultimately, Microsoft realized that allowing users to interact with Windows Services could lead to security problems.
Indeed, a virus installing itself as
a service running from a high privilege account could
easily wreak havoc on a user’s desktop.Microsoft’s solution is to prohibit users from logging in to Session 0.
Now, the first user creates Session 1, the second Session 2, etc., and there is simply no way to access Session 0 via login.
This policy — introduced in Windows Vista in 2006 — is known as Session 0 Isolation. It’s described in great detail in
this technical document from Microsoft.Session 0 Isolation is enforced in all current versions of Windows.
-
How do I switch to Session 0 from the Command Line?
Unfortunately switching to Session 0 is not possible in Windows 10/11 or Server 2019/2022 and later.
That’s because Microsoft removed all access to Session 0
in Windows 10 Version 1803 (April 2018).In earlier versions of Windows, you can switch to Session 0 from the command line by running:
rundll32.exe winsta.dll,WinStationSwitchToServicesSession
Save one of these files to your desktop to easily access Session 0 on demand:
- Batch file to switch to session 0
- Shortcut to switch to session 0
Note that the Interactive Services Detection service (UI0Detect) must be running for switching to work.
-
Why doesn’t «Allow service to interact with desktop» work on Windows 11/10 or Server 2025/2022/2019/2016?
In older versions of Windows (NT, 2000, XP and Server 2003), services are allowed to show their windows and tray icons on the desktop
of the user logged on to the PC. This ability was enabled by checking the
Allow service to interact with desktop
option in the service’s Log On properties:Although that setting still exists on Windows 11/10 or Server 2025/2022/2019/2016, it no longer has the desired effect.
That’s because Microsoft’s security-centric Session 0 Isolation
modifications ensure that no user can log on to Session 0 — the desktop where the windows created by a service are displayed.So while checking the Allow service to interact with desktop box still enables the service’s windows to be displayed in Session 0,
since no one can log in to Session 0 to see the service’s windows, the setting has been effectively marginalized. -
How can I start my non-service application in Session 0?
Sometimes it makes sense to launch an application on the isolated Session 0.
For example, does the application work properly when launched in the context of a Windows Service?Microsoft’s advanced «process-launcher» utility,
PsExec,
will start any program in Session 0. Use it like this:psexec -i 0 -s <executable>
where:
<executable> is the full path to the program to run,
-i 0 indicates to start the process interactively in Session 0, and
-s runs the process in the system account. (Optional — omit it to run the process with your own credentials.)For example, this line will start the command prompt in the system account in Session 0:
psexec -i 0 -s C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe
-
What does it mean to start my service Automatic (Delayed Start)?
Services configured to start Automatic will be immediately kicked off by Windows as the machine boots up. In contrast, those set
to Automatic (Delayed Start) will be held back from that first wave and will start
2 minutes after the last Automatic service is launched.The setting is most useful in two respects:
-
It can alleviate the «mad rush» at boot, when all services try to start simultaneously. By designating non-critical services
for a delayed start, the really important services can secure a larger slice of the machine’s precious resources and become available
sooner. -
It can delay a service from starting until other critical supporting services are operational. For example, without the delay it’s
possible for a service to start before the network is fully initialized, leading to very strange problems.
-
-
How do I adjust when «Automatic (Delayed start)» services start?
By default, services designated as «Automatic (Delayed start)» start 2 minutes after the last «Automatic» service is launched.
That delay can be adjusted for all services by changing (or adding) the AutoStartDelay (DWORD/REG_DWORD) value in the registry:HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\AutoStartDelay
The value is in milliseconds.
For example, this screenshot shows us setting a 10 minute (600000 millisecond) delay:
Please keep in mind that this setting applies to all delay-start services. Use it with caution!
-
What are «Trigger Start Services»?
Instead of starting automatically at boot or manually (on demand), a service can be configured to start (or stop)
in response to specific operating system events.
A service starting from an event is called a Trigger Start Service.Trigger Start Services were introduced in Windows 7 and Server 2008 R2 (in 2009).
They were created to improve efficiency and speed up the boot process after Microsoft realized that many of the 100+ services
set to start automatically at boot and run 24/7 in the background didn’t really need to be active all the time.
The trigger mechanism was put in place to encourage services to remain dormant until needed.Looking at the
Services application
on our Windows Server 2019 machine, there are more than 60 Trigger Start Services installed.
Each says Automatic (Trigger Start) or Manual (Trigger Start) in the Startup Type column. Here are a few:Strangely, you won’t see any mention of a trigger when you examine a Trigger Start Service’s properties.
The Startup type simply says «Automatic» or «Manual» and there are no trigger settings to be found anywhere (as seen with the DNS Client service):Use
Service Trigger Editor
to examine and manage Trigger Start Services.
Our free utility shows you what events start or stop the service, allow you to add other triggering events, and much more.Here’s Service Trigger Editor working with the DNS Client service:
-
Windows Service Error 5: Access is denied
Error 5 denotes a lack of permissions. Your Windows account doesn’t have the rights necessary to work with the service.
Windows will usually inform you where your account falls short. For example, you may not be able to start the service:
Or you may not be able to open the service:
In any case, your only recourse is to seek extra rights for your account.
Your systems administrator (or our free
Service Security Editor
utility) should be able to help. -
Windows Service Error 1053: The service did not respond to the start or control request in a timely fashion
This error comes up about 30 seconds after an attempt to start the service,
because the service fails to report to the Windows Service Control
Manager (SCM) that it’s started. You’re probably facing one of the following problems:-
The application being launched by the service is not a true Windows Service.
Only an executable specifically constructed to interact with the SCM can
signal that it’s started and is running properly. A non-service application — such as a
batch file or program you normally launch from a desktop icon — will not
send the required signal and eventually the SCM will give up waiting and declare that the service failed
to start.If you’re unable (or unwilling) to modify your application’s code to make it a true Windows Service, you can
use a «wrapper» to start your application as a service.
Microsoft’s Srvany will do the basic job for free but
more robust commercial alternatives are also available. -
Your Windows Service application is taking too long to start and report back to the SCM.
If you have access to the code, restructure the application logic to move expensive operations (such as accessing a database, web site or
other remote resource) outside of the startup sequence
(OnStart()
in C# programs). -
Your Windows Service application is getting hung during startup and never tells the SCM that it’s started.
If this is your own code, it’s time to debug! Either attach the debugger, or sprinkle your startup
code with print statements to see where your application is going astray. Watch out for calls to
MessageBox()
and other blocking functions!
-
-
Windows Service Error 1061: The service cannot accept control messages at this time
This mysterious message comes up when a service is unable to perform the operation you attempted.
Essentially, your request arrived at a «bad time», when the service is unable to fulfill it.At any given time, the operations a service can perform depend on its current state — what it’s doing.
For example, a running service may accept the Stop command but not the Pause or Resume commands.To determine what is allowed, Windows asks a service the following question: What operations can you currently perform?
The service responds with a list of what it can do.You encounter Error 1061 when you try to perform an action that’s not on the list of allowed operations.
-
Windows Service Error 1067: The process terminated unexpectedly
This error occurs when the process created by the service exits quickly, without notifying
the Windows Service Control Manager (SCM). It can happen for a variety of reasons, including:-
There is a configuration problem preventing the service application from starting properly. Check
that configuration files are in the expected locations with valid contents, and that startup options reflect reality. -
The process being launched by the service is missing a required component (DLL, library, or other file).
Re-installing the service may help here, but watch for dependencies as well.
For example, a C# service will fail with 1067 when the underlying .NET installation is corrupt and
should be re-installed.
If you remain in the dark after considering the above, examine the
Windows Event Logs.
Sometimes a failing service will leave an important clue there before it dies. -
-
Windows Service Error 1068: The dependency service or group failed to start
Apparently your service relies on other services to support its work, and one of those services is unable to start properly.
You can identify the dependent services in the Services Control panel:Rule out the ones already running; try to start each of the others in turn and identify the culprit.
-
Windows Service Error 1069: The service did not start due to a logon failure
This error happens when your service is configured to run in a specific user account but that
account’s password was recently changed.
The fix is simple; edit your service in
services.msc
and specify the new password on the service’s Log On tab: -
Windows Service Error 1072: The specified service has been marked for deletion
This error happens when your service has been uninstalled but Windows was unable to remove all its associated files because of a conflict.
Usually it’s caused by having the service open in a service-aware program, like the
Services Control Panel,
the Windows Event Viewer,
or even the Windows Task Manager.
Closing all those applications may be enough to have the service fully removed, but if that doesn’t work a reboot should do the trick. -
What is Srvany?
Srvany is a utility developed by Microsoft that can start almost any regular, non-service application as a Windows Service.
Since a Windows Service must be specially constructed to interface with the operating system
(to allow Windows to start, stop or pause it on demand),
a regular application without this interface will not function properly as a Service.
To solve the problem, Microsoft developed Srvany — an «adapter» (or «wrapper») that can accept the Windows Service
commands and translate those into actions that a regular executable can understand.Like any good adapter, Srvany is installed between Windows and the application and handles all interaction between them.
For example, when Windows says «Start the service», Srvany intercepts the request
and starts the application as if you had double-clicked on it yourself.Srvany was developed in the late 1990’s for Windows NT and remains mostly unchanged to this day. It’s available as part of the
Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit Tools package. -
What is Instsrv?
Instsrv is a Microsoft-developed utility used to install a Srvany Service.
It doesn’t take part in the actual running of an application as a service — it just helps with the installation. -
Where can I download Srvany and Instsrv?
-
How do I use Srvany to run my application as a service?
-
Is there a new version of Srvany for Windows Server 2008? For Windows 7?
No. Srvany and Instsrv were last released with Windows Server 2003 and no modifications have been made for
Windows 7, Vista, Server 2008 or Server 2008 R2.Note that these tools will work fine on Windows 2008 and Windows 7, but their lack of knowledge of recent developments in Windows Services
(Session Zero isolation, Service Triggers, etc.) can sometimes present problems. Please be cautions in a production environment! -
Is Srvany supported on Windows Server 2008? Windows 7?
No. While Srvany.exe runs fine on Windows Server 2008/R2, Srvany (and the rest of the
Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit Tools)
are only supported on Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP. And even then, the official documentation accompanying the resource kit cautions:The SOFTWARE supplied in the Windows Resource Kit Tools is not supported under any Microsoft standard support
program or service. -
Is Srvany supported on Windows Server 2012? Windows 8/8.1?
No. While Srvany.exe runs fine on Windows Server 2012 (and its R2 variant), Srvany (and the rest of the
Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit Tools)
are only supported on Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP. And even then, the official documentation accompanying the resource kit cautions:The SOFTWARE supplied in the Windows Resource Kit Tools is not supported under any Microsoft
standard support program or service. -
Is Srvany supported on Windows 10? Windows Server 2019?
No. While Srvany.exe runs fine on Windows 10 and Server 2019, Srvany (and the rest of the
Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit Tools)
are only supported on Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP. And even then, the official documentation accompanying the resource kit cautions:The SOFTWARE supplied in the Windows Resource Kit Tools is not supported under any Microsoft
standard support program or service. -
Is Srvany supported on 64-bit Windows?
No. Even though the 32-bit executable runs fine on 64-bit versions of Windows, Srvany (and the rest of the
Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit Tools)
are not officially supported on 64-bit platforms. There is no 64-bit version of Srvany.exe. -
Will Srvany close my application when I stop the service?
Yes, but somewhat abruptly.
Instead of sending the usual WM_CLOSE or WM_QUIT messages to gracefully shut down the application, Srvany will
forcibly terminate it. This can be quite disruptive, as highlighted in the
old Srvany documentation (Srvany.wri, included with the original Windows NT 4.0 resource kit):«WARNING: When the service is stopped, it terminates the application via the
WIN32 TerminateProcess() API:
this is a drastic way to end an application. For example, it would not allow the application to prompt the
user to save changes. Therefore, it’s recommended to close the application BEFORE stopping the service.» -
How do I remove a Srvany service?
A service created with Srvany is much like any other and you can
remove it using the SC command.The service can also be removed using the Instsrv utility. Run it like this:
Instsrv MyService remove
-
If my program crashes, will Srvany start it again?
Unfortunately, no. Srvany doesn’t monitor your application in any way and will not run a new copy if it fails.
Indeed, Srvany may continue to run even after your application exits! You can’t rely
on the service’s status to tell you if your application is up or not. -
Can I use Srvany to run multiple applications on a single server?
Yes, you can install as many Srvany-created services as you like — each with its own unique name of course!
Even though each service will reference the same Srvany.exe file, each service will run entirely independently
and can be managed as such. -
Why can’t my application access mapped drives when run with Srvany?
That’s not a «Srvany thing» — by default, Windows Services do not have access to mapped drive letters.
UNC paths (which look like «\\Server\Path») should be fully accessible, but if using them is not an option
this answer discusses some ways to make mapped drives available in the context of a
Windows Service. -
Can a Windows Service have a GUI? Should a Windows Service have a GUI?
Can it? Yes.
Should it? No.
But things are never that black and white…
First, realize that the Windows Services architecture doesn’t impose any GUI-related restrictions on a service.
Services are free to create windows, tray icons, alert boxes or any other GUI elements, just like conventional windows applications can.
The key question is this: When a service creates a window, where will it be shown?By default, the GUI elements from a Service appear in Session 0 — the session/desktop created by Windows when your PC boots.
A user logging in to Session 0 can see the windows from a Service and interact with them normally. Interactive services «just work» there.On Windows 2000, XP and Server 2003, the first non-remote user to log in to the PC was placed in Session 0.
If you walked up to the keyboard and mouse and logged in, you would almost surely end up in Session 0.
Remote users could log in to Session 0 by starting the Remote Desktop application with the «/admin» flag.
For those users, interactive services worked as expected and many Windows programs were architected to take advantage of that.However, Microsoft changed the playing field for interactive services in Windows Vista (2007).
Session 0 has been «isolated», and no user can log in there.
(This was done mainly for security concerns — a virus infecting a service could
force itself onto any user’s desktop,
which
the folks at Redmond recognized as a security risk.) The upshot is that the windows from a Service will no longer
show up on any user’s desktop, effectively dealing a death blow the entire notion of interactive services.Realizing that it would be difficult to do away with interactive services by decree however, Microsoft made several concessions
to keep interactive services on life support. The Interactive Services Detection Service (ISDS) was introduced to alert a
user whenever a service shows a window or message box on Session 0. After flashing a few times on the task bar, the window it displays looks like this:Clicking on the View the message button initiates a gut wrenching transition from the normal desktop to the very strange looking world of
Session 0 where the Service’s windows are running (Notepad.exe in this case):Despite the austere appearance, you can interact normally with your service’s windows in Session 0. And when you’re done,
clicking on the Return now button will magically transport you back you to your regular desktop.It’s easy to see that most users would be inconvenienced by always having to perform such an awkward
switch to Session 0 to interact with an application. This effectively limits the attractiveness of
an interactive service and any sane computer professional will certainly recommend against constructing
one today.Note: Unfortunately switching to Session 0 is no longer possible in Windows 10/11 or Server 2019/2022 and later.
That’s because Microsoft removed all access to Session 0
in Windows 10 Version 1803 (April 2018). -
Can a Windows Service start a GUI application?
Yes, a service can definitely launch a GUI application.
However, that application will run in Session 0 — the background desktop where services reside.
You won’t see the application on your desktop. -
Why won’t the Interactive Service Detection service start on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012?
Attempting to start the Interactive Service Detection (UI0Detect) service on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 can fail with the incomprehensible
«Error 1: Incorrect function» message:This is because Microsoft has disabled interactive services in these new operating systems!
Fortunately, it’s easy to re-enable interactive services by editing the registry:
- Start the registry editor («regedit.exe»)
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Windows on the left side
- On the right, double-click the NoInteractiveServices entry and change its value from 1 to 0
- Click OK to record your change
- Close the registry editor
The Interactive Service Detection service should start properly after this change.
-
How do I disable/suppress the Interactive Services Detection Dialog?
There are three ways to prevent the
Interactive Services Detection Dialog from alerting you of a GUI application running in Session 0.
All involve stopping the Interactive Services Detection (ISD) service, which runs in the background and summons the ISD dialog
whenever it detects activity in Session 0:-
Stop the Interactive Services Detection Service
Simply stopping the service will cause the dialog to disappear. This may not be a permanent fix though;
the dialog may return if someone else (or another application) restarts the service.To stop the service, run «services.msc», right-click on the Interactive Services Detection entry in the list and select Stop from the menu:
-
Disable the Interactive Services Detection Service
By changing the service’s startup type to Disabled, you will ensure that no person (or application) can start the service.
The dialog will never be shown.To disable the service, run «services.msc», double-click on the Interactive Services Detection entry in the list and
change the Startup type to Disabled: -
Set the NoInteractiveServices registry key
When it starts, The ISD service checks the NoInteractiveServices registry key. If the value is 1, the service will refuse to start,
and you will never see the ISD dialog.Follow these instructions to set the NoInteractiveServices registry key
— just set the DWORD value to 1 instead of 0.
Note that the Interactive Services Detection service also provides the ability to switch to Session 0 to view your Session 0 desktop.
Switching to Session 0 won’t be available when the ISD service is not running! -
-
Why can’t I switch to Session 0 on Windows 10?
Unfortunately access to Session 0 has been removed in Windows 10 and Server 2019. And it’s not coming back!
Note that services and applications continue to run as normal in Session 0 — you just can’t see them.
This article digs into the technical details.
-
My question has not been answered here. Can you please help?