Непростые экономические условия, в которых вынужден существовать современный бизнес, вынуждают думать скорее не о развитии и расширении имеющейся ИТ-инфраструктуры, а о грамотном использовании базовых продуктов, без которых не обойтись. Одним из таких продуктов является Windows Server – популярная серверная операционная система, часто применяемая в крупных организациях. К сожалению, компании, относящиеся к малому и среднему бизнесу, от Windows Server часто отказываются, считая, что он:
• стоит дорого;
• предлагает слишком много всего ненужного.
Попробуем сегодня развеять эти заблуждения. Давайте вместе посмотрим, что из себя представляет Windows Server, и как его могут оптимально использовать небольшие организации.
Для чего нужен Windows Server 2012
Для начала поговорим о том, для чего нужен Windows Server.
В первую очередь это, конечно, построение единой инфраструктуры для организации любого размера. На основе такой инфраструктуры могут работать приложения различной сложности, разворачиваться дополнительные локальные и веб-службы.
Windows Server также успешно применяется для аутентификации и авторизации пользователей. Часто небольшие организации (от 25 ПК) отказываются использовать Windows Server, считая, что обойдутся ноутбуками, и никакое централизованное администрирование им ни к чему. А ведь здесь встает один из самых основных вопросов при управление компьютерными пользователями: предоставление доступа к конкретной информации. Безусловно, существуют случаи, когда организации нет нужды ограничивать доступ к информации (все живут в идеальном мире, никто ничего без спроса не правит, не удаляет, не передает конкурентам).
В реальности доступ к определенной информации все же нужно ограничивать (ну, как минимум, к бухгалтерской и финансовой отчетности). Второй момент: пользователю может понадобиться получить доступ к своим файлам с соседнего компьютера: чтобы их распечатать, показать руководству, представить потенциальным клиентам организации. Наконец, третье. Один из используемых компьютеров может просто выйти из строя. И если сам ноутбук заменить можно относительно безболезненно, то информация на нем может быть утеряна навсегда. Без Windows Server задачи аутентификации и авторизации пользователей, а также вопрос сохранения данных значительно затрудняется. Можно создавать рабочие группы, настраивать вручную все права. Но это занимает много времени. А потом всеми этими настройками очень сложно объективно и своевременно управлять.
Windows Server с помощью Active Directory, групповых политик и функции управления файлами позволяет в разы упростить эту задачу
Последняя версия
Последней версией на момент написания этой статьи является Windows Server 2012 R2. Несмотря на то, что система вышла в свет в октябре 2013 года, она не теряет своей актуальности.
По сравнению с предыдущими версиями, система претерпела ряд изменений для того, чтобы предоставить пользователям максимально востребованную функциональность. Среди основных нововведений представлено расширение возможностей виртуализации, хранение и обработки данных, репликации. Была расширена функция работы с сетевыми настройками, управление серверами и настройками автоматизации, повышены возможности обеспечения безопасности имеющейся инфраструктуры.
О том, какие функции были представлены в Windows Server 2012 R2, написано много статей, еще больше представлено материалов о том, как систему настраивать и эти функции использовать. Проблема заключается в применении знаний на практике. Причем дело не столько в технической настройке, сколько в необходимости выбора подходящей редакции Windows Server, которая будет максимально отвечать потребностям организации, и при этом не будет требовать лишней переплаты за ненужные возможности.
Есть еще один важный момент. Не обязательно приобретать самую дорогую редакцию Windows Server для того, чтобы настроить инфраструктуру своей сети. Вполне возможно, что вам подойдет более простая версия: получите весь нужный функционал и сможете сэкономить на лицензиях и внедрении. Поэтому основной вопрос, на который стоит обратить внимание – это редакции Windows Server и их лицензирование.
Лицензирование Windows Server 2012 R2
Windows Server 2012 R2 чаще всего предлагают приобрести в одной из двух редакций: Standard и Datacenter. Единственное их отличие заключается в том, что, имея лицензию Standard, можно бесплатно развернуть до двух виртуальных машин Windows. Если же вы приобрели лицензию Datacenter, то в количестве виртуальных машин, которые можно развернуть, вы не ограничены. При этом лицензирование Microsoft в редакциях Standard и Datacenter может потребовать дополнительных затрат.
С точки зрения правильного лицензирования необходимо также приобрести лицензии на клиентский доступ (Windows Server CAL) на количество пользователей (или устройств), которые в вашей организации используют компьютер. А если вы хотите предоставить своим сотрудникам возможность удаленного подключения к серверу, то необходимо также приобрести лицензии на удаленный доступ (Windows Server Remote Desktop CAL). Сумма набегает приличная. Особенно неприятно, когда не нужны даже те две виртуальные машины, которые позволяет без дополнительных лицензий стандарт.
Как итог, получаем значительные расходы на продукт, большая часть возможностей которого нам не нужны. В связи с этим обратите внимание на две редакции Windows Server 2012 R2, о которых рассказывают реже, но они намного привлекательнее для небольших организаций. Это редакции Windows Server 2012 R2 Foundation и Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials.
Windows Server 2012 R2 Foundation
Редакция Foundation оптимальная для организаций малого бизнеса, в которых число пользователей не превышает 15. Несмотря на то, что применять редакцию Foundation можно только на однопроцессорном сервере с оперативной памятью не больше 32 ГБ, приобретать дополнительные лицензии на клиентский доступ (Windows Server CAL) не нужно. Кроме того, важно учитывать, что Windows Server Foundation может быть запущен только в физической среде. Последнее, Foundation можно приобрести только вместе с сервером (тип лицензии OEM), он не предоставляется по корпоративным программам лицензирования.
Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials
Редакция Essentials подходит компаниям с численностью до 25 пользователей. Убирается одно из ограничений Foundation: использовать редакцию Essential можно на двухпроцессорном сервере, а размер оперативной памяти увеличен до 64 ГБ. Также Windows Server Essentail можно запускать в виртуальной среде, но в этом случае уже будет нельзя запустить в физической. Иными словами, Essential можно запустить либо в физической среде, либо в виртуальной. Лицензии для клиентского доступа также не требуются. Расширены также и каналы, по которым можно приобрести Essential: эта редакция доступна не только в одном комплекте с сервером, но также ее можно приобрести в рамках корпоративного приглашения.
Возвратимся теперь к одному из заблуждений, которое было обозначено в самом начале.
Очень часто небольшие компании не используют для администрирования сети именно серверную операционную систему из-за слишком высокой цены. Это справедливо, если вы выбираете между Windows Server Standard и Windows Server Datacenter. Их стоимость составляется из лицензии на сервер (в сервере не больше двух процессоров) плюс лицензии на клиентский доступ плюс лицензии на удаленное подключение. Такие затраты в большинстве случаев совершенно не вписываются в бюджет небольшой организации или стартапа, численность которых не превышает 25 пользователей.
Тем не менее, серверная система намного удобнее для реализации основных задач администрирования и управления системой, сетью, пользователями. Windows Server представлен в двух редакциях, которые отвечают этим требованиям – поддерживают необходимые функции и не бьют по бюджету: Windows Server Foundation и Windows Server Essentials.
Теперь, когда с лицензированием вопрос более или менее понятен, можно переходить к следующему шагу. А именно, решать, какие функции нам нужны, а какие нет. Это, например, касается такой функции, как Server Core – возможности устанавливать и использовать Windows Server в режиме консоли. Как показывает практика, такая возможность малым компаниям кажется слишком сложной.
А вот невозможность интеграции редакции Foundation с Office 365 может стать своеобразным камнем преткновения. В том случае, если интеграция с Office 365 критически важна, выбирать нужно Essentials.
Active Directory
Пожалуй, это один из основных компонентов, из-за которого Windows Server приобретается. Active Directory присутствует и в редакции Essentails, и в редакции Foundation, но их функциональность в корне отличается. Если вы используете редакцию Essentials, вы должны создать домен в процессе установки и при этом в дальнейшем у вас не будет возможности его изменить. Кроме того, в процессе установки Essentials будет установлена не только роль AD, но и DNS, File Service (файловые службы), IIS Web Service и Remote Desktop Service. А вот в редакции Foundation
дается более привычная всем гибкость настройки.
Администрирование
Для более комфортного управления в редакции Essentials вы получите специальный дэшборд, который предоставит комфортный интерфейс для начинающих пользователей.
В редакции Foundation управлять сервером вы можете через обычный Server Manager.
Сетевое взаимодействие
Для Foundation никаких ограничений нет, а вот для Essentials есть: установка Essentials возможна только через роутер, который поддерживает IPv4 NAT.
Апгрейд лицензии
Очень важный момент. Вы всегда можете сделать апгрейд Windows Server Foundation или Essentials до Standard (например, в случае расширения бизнеса и увеличения числа пользователей в организации).
Подводя итоги
Итак, Windows Server позволяет оптимизировать расходы на инфраструктуру. Широкий набор моделей лицензирования, а также вариантов приобретения лицензии позволяет подобрать тот вариант, который будет приносить организации пользу, при этом не переплачивать за неиспользуемые функции и ненужные нововведения.
Дешевые версии не означают, что они неприменимы в реальных условиях. Функциональность уменьшена обдуманно, при этом все нужные компоненты и даже некоторые встроенные дополнения присутствуют в редакции Foundation и Essentials. Пусть в Essentials нет роли Hyper-V; в то же время редакция поддерживает возможность интеграции с облачными приложениями и сервисами (Microsoft Azure и Office 365). Т.е. приобретая Essentials, вы получаете как качественно подготовленную инфраструктуру для вашей организации, так и возможность интеграции с ключевыми продуктами Microsoft, которые необходимы в повседневной современной работе – как на своем рабочем месте, так и удаленно.
В реальных рабочих условиях в каждой организации при построении инфраструктурных решений системные администраторы отдают предпочтения обкатанным и хорошо протестированным версиям. Поэтому Windows Server 2012 R2 своей актуальности еще долго не потеряет.
Наши партнёры
FREE Hyper-V & VMware Virtualization Backup: FREE for Firewall.cx readers for a Limited Time! Download Now!
Windows Server 2012 Editions
On the 1st of August, 2012 Microsoft released Windows Server 2012– the sixth release of the Windows Server product family. On May 21st 2013, Windows Server 2012 R2 was introduced and is now the latest version of Windows Server in the market. Microsoft has released four different editions of Windows Server 2012 varying in cost, licensing and features. These four editions of Windows Server 2012 R2 are: Windows 2012 Foundation edition, Windows 2012 Essentials edition, Windows 2012 Standard edition and Windows 2012 Datacenter edition.
Let’s take a closer look at each Windows Server 2012 edition and what they have to offer.
Users can also download the free Windows Server 2012 R2 Licensing Datasheet in our Windows Server Datasheets & Useful Resources download section, which provides a detailed overview of the Licensing for Windows Server 2012 and contains extremly useful information on the various Windows Server 2012 edition, examples on how to calculate your licensing needs, Virtualization instances supported by every edition, server roles, common questions & answers, plus much more.
More technical articles covering Windows 2012 Server and Hyper-V Virtualization are available in our Windows 2012 Server section.
Windows Server 2012 Foundation Edition
This edition of Windows Server 2012 is targeted towards small businesses of up to 15 users. The Windows Server 2012 R2 Foundation edition comes pre-installed on hardware server with single physical processor and up to 32GB of DRAM memory. Foundation edition can be implemented in environments where features such as file sharing, printer sharing, security and remote access are required. Advanced server features such as Hyper V, RODC (Read Only Domain Controller), data deduplication, dynamic memory, IPAM (IP Address Management), server core, certificate service role, hot add memory, windows update services and failover clustering are not available in the Foundation edition.
Windows Server 2012 Essentials Edition
The Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials edition is the next step up, also geared towards small businesses of up to 25 users. Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials edition is available in retail stores around the world making it easy for businesses to install the new operating system without necessarily purchasing new hardware. Similar to the Foundation edition, the Essentials edition does not support many advanced server features, however it does provide support of features like Hyper V, dynamic memory and hot add/remove RAM.
Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials edition can run a single instance of virtual machine on Hyper V, a feature that was not available in Windows Server 2012 Essentials (non-R2) edition. This single virtual machine instance can be Windows Server 2012 R2 Essential edition only, seriously limiting the virtualization options but allowing companies to begin exploring the benefits of the virtualization platform.
Windows Server 2012 Standard Edition
The Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard edition of windows server is used for medium to large businesses that require additional features not present in the Foundation & Essential edition. The Standard edition is able to support an unlimited amount of users, as long as the required user licenses have been purchased.
Advanced features such as certificate services role, Hyper V, RODC (Read Only Domain Controller), IPAM (IP Address Management), Data deduplication, server core, failover clustering and more, are available to Windows Server 2012 Standard edition. We should note that the Standard edition supports up to 2 Virtual Machines.
Windows Server 2012 Datacenter Edition
The Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter edition is the flagship product created to meet the needs of medium to large enterprises. The major difference between the Standard and Datacenter edition is that the Datacenter edition allows the creation of unlimited Virtual Machines and is therefore suitable for environments with extensive use of virtualization technology.
Before purchasing the Windows Server 2012 operating system, it is very important to understand the difference between various editions, the table below shows the difference between the four editions of Windows Server 2012:
FREE Hyper-V & VMware Virtualization Backup: FREE for Firewall.cx readers for a Limited Time! Download Now!
|
Editions |
Foundation |
Essentials |
Standard |
Datacenter |
|
Distribution |
OEM Only |
Retail, volume licensing, OEM |
Retail, volume licensing, OEM |
Volume licensing and OEM |
|
Licensing Model |
Per Server |
Per Server |
Per CPU pair + CAL/DAL |
Per CPU pair + CAL/DAL |
|
Processor Chip Limit |
1 |
2 |
64 |
64 |
|
Memory Limit |
32GB |
64GB |
4TB |
4TB |
|
User Limit |
15 |
25 |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
File Services limits |
1 standalone DFS root |
1 standalone DFS root |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
Network Policy & Access Services limits |
50 RRAS connections and 10 IAS connections |
250 RRAS connections, 50 IAS connections, and 2 IAS Server Groups |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
Remote Desktop Services limits |
50 Remote Desktop Services connections |
Gateway only |
Unlimited |
Unlimited |
|
Virtualization rights |
n/a |
Either in 1 VM or 1 physical server, but not both at once |
2 VMs |
Unlimited |
|
DHCP, DNS, Fax server, Printing, IIS Services |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows Server Update Services |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Active Directory Services |
Yes, Must be root of forest and domain |
Yes, Must be root of forest and domain |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Active Directory Certificate Services |
Certificate Authorities only |
Certificate Authorities only |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows Powershell |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Server Core mode |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Hyper-V |
No |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Windows Server 2012 Licensing — Understanding Client Access License (CAL) & Device Access License (DAL) Licensing Models
The standard and datacenter editions of Server 2012 support Client Access License (CAL) or Device Access License (DAL) licensing model. A CAL license is assigned to a user whereas a DAL license is assigned to device (computer). For example, a CAL assigned to a user, allows only that user to access the server via any device. Likewise, if a DAL is assigned to particular device, then any authenticated user using that device is allowed to access the server.
We can use a simple example to help highlight the practical differences between CAL and DAL licensing models and understand the most cost-effective approach:
Assume an environment with Windows Server 2012 R2 standard edition and a total of 50 users and 25 devices (workstations). In this case, we can purchase either 50 CAL licenses to cover the 50 users we have or alternatively 25 DAL licenses to cover the total amount of workstations that need to access the server. In this scenario, purchasing DALs is a more cost effective solution.
If however we had 10 users with a total of 20 devices , e.g 2 devices per user (workstation & laptop), then it more be more cost effective to purchase 10 CAL licenses.
Windows Server 2012 Foundation Edition Licensing Model
Windows Server 2012 Foundation is available to OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) only and therefore can only be purchased at the time of purchasing a n new hardware server. Windows 2012 Foundation edition supports up to 15 users. CALs or DALs are not required for the Foundation edition servers. In addition, Foundation edition owners cannot upgrade to other editions. The maximum number of SMB (Server Message Block or file sharing) connections to the server is 30. Similarly, maximum number of RRAS (Routing and Remote Access Service) and RDS (Remote Desktop Service) connections is 50.
Windows Server 2012 Essentials Edition Licensing Model
The Essential edition of server 2012 is available to OEMs (with the purchase of new hardware) and also at retail stores. The user limit of this server edition is 25 and device limit is 50. This means that a maximum of 25 users amongst 50 computers can access the Windows Server 2012 Essentials edition. For example, you have 20 users rotating randomly amongst 25 computers accessing the Server 2012 Essentials edition, without any problem. CALs or DALs are not required for Windows Server 2012 Essentials edition because no more than 25 users can access the server.
A common question at this point is what if the organization expands and increases its users and computers?
In these cases Microsoft provides an upgrade path allowing organizations to upgrade to the Windows Server 2012 Standard or Datacenter edition license and perform an in-place license transition. Once the transition is complete, the user limitation, and other features are unlocked without requiring migration or reinstallation of the server.
Companies upgrading to a higher edition of Windows 2012 Server should keep in mind that it will be necessary to purchase the required amount of CALs or DALs according to their users or devices.
Administrators will be happy to know that it is also possible to downgrade the Standard edition of Server 2012 to the Essentials edition. For example, it is possible to run Essential edition of Server 2012 as virtual machine utilizing one of two available virtual instances in Standard edition as shown in the figure below. This eliminates the needs to purchase Essential edition of Server 2012.
FREE Hyper-V & VMware Virtualization Backup: FREE for Firewall.cx readers for a Limited Time! Download Now!
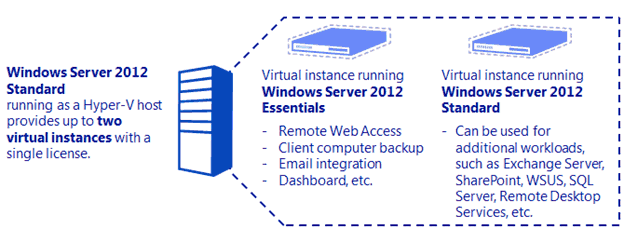
With the release of Windows Server 2012 Essentials R2, Microsoft has updated its licensing model. Unlike Windows Server 2012 Essentials (non-R2), you can now run a single instance of a virtual machine.
The Hyper-V role and Hyper-V Manager console are now included with Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials. The server licensing rights have been expanded, allowing you to install an instance of Essentials on your physical server to run the Hyper-V role (with none of the other roles and features of the Essentials Experience installed), and a second instance of Essentials as a virtual machine (VM) on that same server with all the Essentials Experience roles and features.
Windows Server 2012 Standard Edition & Datacenter Edition Licensing Model
The license of Standard and Datacenter edition is based on sockets (CPUs) and CAL or DAL. Definition of a socket is a CPU or physical processor. Logical cores are not counted as sockets. A single license of Standard and Datacenter edition covers up to two physical processors per physical server. CAL or DAL licenses are then required so that clients/devices can access the Windows server. Standard edition allows up to 2 virtual instances while the Datacenter edition allows unlimited number of virtual instances.
For example, a Windows 2012 Server R2 Standard edition installed on a physical server with one socket (CPU) can support up to two instances of virtual machines. These virtual machines can be Server 2012 R2 Standard or Essentials edition. Similarly, if you install a Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter edition, then you can install an unlimited number of virtual machines.
Let’s look at some examples on deploying Standard and Datacenter edition servers and calculating the licenses required:
Scenario 1: Install Server 2012 Standard/Datacenter Edition on a server box with four physical processors and 80 users.
In this scenario, we will be required to purchase two Standard/Datacenter Edition licenses because a single license covers up to two physical processors, plus 80 CAL licenses so our users can access the server resources.
Scenario 2: Install Server 2012 Standard Edition on a physical server with 1 physical processor, running 8 instances of virtual machines. A total of 50 users will be accessing the server.
Here, four Server 2012 Standard edition licenses are required and 50 CALs or DALs. Remember that a single Standard edition license covers up to two physical processors and up to two instances of virtual machines. Since the requirement is to run 8 instances of virtual machines, we need four Standard edition licenses.
If we decided to use the Datacenter edition in this scenario, a single license with 50 CAL would be enough to cover our needs, because the Datacenter edition license supports an unlimited number of virtual instances and up to two physical processors.
Summary
Microsoft’s Windows Server 2012 is an attractive server-based product designed to meet the demands of small to large enterprises and has a very flexible licensing model. It is very important to fully understand the licensing options and supported features on each of the 4 available editions, before proceeding with your purchase – a tactic that will help ensure costs are kept well within the allocated budget while the company’s needs are fully met.
Windows Server 2012 R2 Foundation разработан специально для небольших организаций, где рассматривается приобретение первого сервера или уже используется клиентская операционная система для обеспечения базовой инфраструктуры. Он основан на уже зарекомендовавшем себя Windows Server 2012 R2 и сможет обеспечить все ключевые элементы ИТ в небольшом бизнесе:
- совместная работа с файлами и принтерами
- удаленный доступ
- безопасность ИТ среды
Для чего нужен Windows Server 2012 R2 Foundation и что он может делать?
- Безопасная идентификация и доступ пользователей (служба каталогов Active Directory)
- Управление настройками компьютеров (Group Policy)
- Платформа для работы бизнес-приложений, например 1С
- Общий доступ к принтерам, сканерам, факсам
- Резервное копирование сервера полностью или выборочно
- Базовые сетевые службы (DHCP, DNS), удаленный доступ к сети (VPN)
- Удаленная работа с бизнес-приложениями с любого места и компьютера, где есть Интернет (терминальный сервер)
- Удаленный доступ к рабочим столам компьютеров (RD Gateway)
- Возможность размещения веб-сайта (веб-сервер IIS)
Подробнее…
Готовое решение на базе Windows Server 2012 R2 Foundation на нашем сайте.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Windows Server 2012
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
|
Screenshot of Windows Server 2012, showing the Server Manager application which is automatically opened when an administrator logs on, taskbar, and the blue color of Aero Lite |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Windows Server |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
August 1, 2012; 12 years ago[1] |
| General availability |
September 4, 2012; 12 years ago |
| Latest release | 6.2.9200 with May 2025 monthly update rollup / May 13, 2025; 0 days ago |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (GUI) |
| License | Commercial proprietary software |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2012 R2 (2013) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2012 (archived at Wayback Machine)) |
| Support status | |
|
Windows Server 2012, codenamed «Windows Server 8«, is the ninth major version of the Windows NT operating system produced by Microsoft to be released under the Windows Server brand name. It is the server version of Windows based on Windows 8 and succeeds the Windows 7-based Windows Server 2008 R2, released nearly three years earlier. Two pre-release versions, a developer preview and a beta version, were released during development. The software was officially launched on September 4, 2012, which was the month before the release of Windows 8.[3] It was succeeded by Windows Server 2012 R2 . Mainstream support ended on October 9, 2018, and extended support ended on October 10, 2023. It is eligible for the paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program, which offers continued security updates until October 13, 2026.
It removed support for Itanium and processors without PAE, SSE2 and NX.[4] Four editions were released. Various features were added or improved over Windows Server 2008 R2 (with many placing an emphasis on cloud computing), such as an updated version of Hyper-V, an IP address management role, a new version of Windows Task Manager, and ReFS, a new file system. Windows Server 2012 received generally good reviews in spite of having included the same controversial Metro-based user interface seen in Windows 8, which includes the Charms Bar for quick access to settings in the desktop environment.
It is the final version of Windows Server that supports processors without CMPXCHG16b, PrefetchW, LAHF and SAHF.
As of April 2017, 35% of servers were running Windows Server 2012, surpassing usage share of Windows Server 2008.[5]
Windows Server 2012, codenamed «Windows Server 8»,[6] is the fifth release of Windows Server family of operating systems developed concurrently with Windows 8.[7][8]
Microsoft introduced Windows Server 2012 and its developer preview in the BUILD 2011 conference on September 9, 2011.[9] However, unlike Windows 8, the developer preview of Windows Server 2012 was only made available to MSDN subscribers.[10] It included a graphical user interface (GUI) based on Metro design language and a new Server Manager, a graphical application used for server management.[11] On February 16, 2012, Microsoft released an update for developer preview build that extended its expiry date from April 8, 2012 to January 15, 2013.[12]
Before Windows Server 2012 was finalized, two test builds were made public. A public beta version of Windows Server 2012 was released along with the Windows 8 Consumer Preview on February 29, 2012.[7] On April 17, 2012, Microsoft revealed «Windows Server 2012» as the final name for the operating system.[6] The release candidate of Windows Server 2012 was released on May 31, 2012, along with the Windows 8 Release Preview.[8]
The product was released to manufacturing on August 1, 2012 (along with Windows 
Windows Server 2012 is based on Windows 8 and is the second version of Windows Server which runs only on 64-bit CPUs.[16] Coupled with fundamental changes in the structure of the client backups and the shared folders, there is no clear method for migrating from the previous version to Windows Server 2012.
Installation options
[edit]
Unlike its predecessor, Windows Server 2012 users can switch between «Server Core» and «Server with a GUI» installation options without a full re-installation. Server Core – an option with a command-line interface only – is now the recommended configuration. There is also a third installation option that allows some GUI elements such as MMC and Server Manager to run, but without the normal desktop, shell or default programs like File Explorer.[11]
Server Manager has been redesigned with an emphasis on easing management of multiple servers.[17] The operating system, like Windows 8, uses the Metro-based user interface unless installed in Server Core mode.[18] The Windows Store is available by installing the desktop experience feature from the server manager, but is not installed by default.[19] Windows PowerShell in this version has over 2300 commandlets, compared to around 200 in Windows Server 2008 R2.[20]
Windows Server 2012 includes a new version of Windows Task Manager together with the old version.[21] In the new version the tabs are hidden by default, showing applications only. In the new Processes tab, the processes are displayed in varying shades of yellow, with darker shades representing heavier resource use.[22] Information found in the older versions are now moved to the new Details tab. The Performance tab shows «CPU», «Memory», «Disk», «Wi-Fi» and «Ethernet» graphs. Unlike the Windows 8 version of Task Manager (which looks similar), the «Disk» activity graph is not enabled by default. The CPU tab no longer displays individual graphs for every logical processor on the system by default, although that remains an option. Additionally, it can display data for each non-uniform memory access (NUMA) node. When displaying data for each logical processor for machines with more than 64 logical processors, the CPU tab now displays simple utilization percentages on heat-mapping tiles.[23] The color used for these heat maps is blue, with darker shades again indicating heavier utilization. Hovering the cursor over any logical processor’s data now shows the NUMA node of that processor and its ID, if applicable. Additionally, a new Startup tab has been added that lists startup applications,[24] however this tab does not exist in Windows Server 2012.[25] The new task manager recognizes when a Windows Store app has the «Suspended» status.
IP address management (IPAM)
[edit]
Windows Server 2012 has an IP address management role for discovering, monitoring, auditing, and managing the IP address space used on a corporate network. The IPAM is used for the management and monitoring of Domain Name System (DNS) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers. Both IPv4 and IPv6 are fully supported.[26]
Windows Server 2012 has a number of changes to Active Directory from the version shipped with Windows Server 2008 R2. The Active Directory Domain Services installation wizard has been replaced by a new section in Server Manager, and a GUI has been added to the Active Directory Recycle Bin.[27] Multiple password policies can be set in the same domain.[28] Active Directory in Windows Server 2012 is now aware of any changes resulting from virtualization, and virtualized domain controllers can be safely cloned. Upgrades of the domain functional level to Windows Server 2012 are simplified; it can be performed entirely in Server Manager. Active Directory Federation Services is no longer required to be downloaded when installed as a role, and claims which can be used by the Active Directory Federation Services have been introduced into the Kerberos token. Windows Powershell commands used by Active Directory Administrative Center can be viewed in a «Powershell History Viewer».[29][30]
Windows Server 2012, along with Windows 8, includes a new version of Hyper-V,[31] as presented at the Microsoft BUILD event.[32] Many new features have been added to Hyper-V, including network virtualization, multi-tenancy, storage resource pools, cross-premises connectivity, and cloud backup. Additionally, many of the former restrictions on resource consumption have been greatly lifted. Each virtual machine in this version of Hyper-V can access up to 64 virtual processors, up to 1 terabyte of memory, and up to 64 terabytes of virtual disk space per virtual hard disk (using a new .vhdx format).[33][34] Up to 1024 virtual machines can be active per host, and up to 8000 can be active per failover cluster.[35] SLAT is a required processor feature for Hyper-V on Windows 8, while for Windows Server 2012 it is only required for the supplementary RemoteFX role.[36]
Main article: ReFS
Resilient File System (ReFS),[37] codenamed «Protogon»,[38] is a new file system in Windows Server 2012 initially intended for file servers that improves on NTFS in some respects. Major new features of ReFS include:[39][40]
- Improved reliability for on-disk structures
- ReFS uses B+ trees[39] for all on-disk structures including metadata and file data. Metadata and file data are organized into tables similar to a relational database. The file size, number of files in a folder, total volume size and number of folders in a volume are limited by 64-bit numbers; as a result ReFS supports a maximum file size of 16 exabytes, a maximum of 18.4 × 1018 folders and a maximum volume size of 1 yottabyte (with 64 KB clusters) which allows large scalability with no practical limits on file and folder size (hardware restrictions still apply). Free space is counted by a hierarchical allocator which includes three separate tables for large, medium, and small chunks. File names and file paths are each limited to a 32 KB Unicode text string.
- Built-in resilience
- ReFS employs an allocation-on-write update strategy for metadata,[39] which allocates new chunks for every update transaction and uses large IO batches. All ReFS metadata has built-in 64-bit checksums which are stored independently. The file data can have an optional checksum in a separate «integrity stream», in which case the file update strategy also implements allocation-on-write; this is controlled by a new «integrity» attribute applicable to both files and directories. If nevertheless file data or metadata becomes corrupt, the file can be deleted without taking the whole volume offline. As a result of built-in resiliency, administrators do not need to periodically run error-checking tools such as CHKDSK when using ReFS.
- Compatibility with existing APIs and technologies
- ReFS does not require new system APIs and most file system filters continue to work with ReFS volumes.[39] ReFS supports many existing Windows and NTFS features such as BitLocker encryption, Access Control Lists, USN Journal, change notifications,[41] symbolic links, junction points, mount points, reparse points, volume snapshots, file IDs, and oplock. ReFS seamlessly[39] integrates with Storage Spaces, a storage virtualization layer that allows data mirroring and striping, as well as sharing storage pools between machines.[42] ReFS resiliency features enhance the mirroring feature provided by Storage Spaces and can detect whether any mirrored copies of files become corrupt using background data scrubbing process, which periodically reads all mirror copies and verifies their checksums then replaces bad copies with good ones.
Some NTFS features are not supported in ReFS, including object IDs, short names, file compression, file level encryption (EFS), user data transactions, hard links, extended attributes, and disk quotas.[38][39] Sparse files are supported.[43][44] Support for named streams is not implemented in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, though it was later added in Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2.[45] ReFS does not itself offer data deduplication.[39] Dynamic disks with mirrored or striped volumes are replaced with mirrored or striped storage pools provided by Storage Spaces. In Windows Server 2012, automated error-correction with integrity streams is only supported on mirrored spaces; automatic recovery on parity spaces was added in Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2.[45] Booting from ReFS is not supported either.
Windows Server 2012 includes version 8.0 of Internet Information Services (IIS). The new version contains new features such as SNI, CPU usage caps for particular websites,[46] centralized management of SSL certificates, WebSocket support and improved support for NUMA, but few other substantial changes were made.[47]
Remote Desktop Protocol 8.0
[edit]
Remote Desktop Protocol has new functions such as Adaptive Graphics (progressive rendering and related techniques), automatic selection of TCP or UDP as transport protocol, multi touch support, DirectX 11 support for vGPU, USB redirection supported independently of vGPU support, etc.[48] A «connection quality» button is displayed in the RDP client connection bar for RDP 8.0 connections; clicking on it provides further information about connection, including whether UDP is in use or not.[49]
Windows Server 2012 supports the following maximum hardware specifications.[34][50] Windows Server 2012 improves over its predecessor Windows Server 2008 R2:
| Specification | Windows Server 2012 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Physical processors[a] | 64 | 64 |
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled |
640 | 256 |
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled |
320[b] | 64 |
| Memory | 4 TB | 2 TB |
| Failover cluster nodes (in any single cluster) | 64 | 16 |
System requirements
[edit]
Minimum system requirements for Windows Server 2012[52]
| Processor | 1.4 GHz, x64 |
|---|---|
| Memory | 512 MB |
| Free disk space | 32 GB (more if there is at least 16 GB of RAM) |
Windows Server 2012 runs only on x86-64 processors. Unlike older versions, Windows Server 2012 does not support Itanium.[4]
Upgrades from Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 are supported, although upgrades from prior releases are not.[52]
Windows Server 2012 has four editions: Foundation, Essentials, Standard and Datacenter.[53][54][55][56][50]
Reviews of Windows Server 2012 have been generally positive.[59][60][61] Simon Bisson of ZDNet described it as «ready for the datacenter, today,»[59] while Tim Anderson of The Register said that «The move towards greater modularity, stronger automation and improved virtualisation makes perfect sense in a world of public and private clouds» but remarked that «That said, the capability of Windows to deliver obscure and time-consuming errors is unchanged» and concluded that «Nevertheless, this is a strong upgrade overall.»[60]
InfoWorld noted that Server 2012’s use of Windows 8’s panned «Metro» user interface was countered by Microsoft’s increasing emphasis on the Server Core mode, which had been «fleshed out with new depth and ease-of-use features» and increased use of the «practically mandatory» PowerShell.[62] However, Michael Otey of Windows IT Pro expressed dislike with the new Metro interface and the lack of ability to use the older desktop interface alone, saying that most users of Windows Server manage their servers using the graphical user interface rather than PowerShell.[63]
Paul Ferrill wrote that «Windows Server 2012 Essentials provides all the pieces necessary to provide centralized file storage, client backups, and remote access,»[64] but Tim Anderson contended that «Many businesses that are using SBS2011 and earlier will want to stick with what they have», citing the absence of Exchange, the lack of ability to synchronize with Active Directory Federation Services and the 25-user limit,[65] while Paul Thurott wrote «you should choose Foundation only if you have at least some in-company IT staff and/or are comfortable outsourcing management to a Microsoft partner or solution provider» and «Essentials is, in my mind, ideal for any modern startup of just a few people.»[66]
Windows Server 2012 R2
[edit]
A second release, Windows Server 2012 R2, which is derived from the Windows 8.1 codebase, was released to manufacturing on August 27, 2013[67] and became generally available on October 18, 2013, by Microsoft.[68] An updated version, formally designated Windows Server 2012 R2 Update, was released in April 2014.[69][70]
Microsoft originally planned to end mainstream support for Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 on January 9, 2018, with extended support ending on January 10, 2023. In order to provide customers the standard transition lifecycle timeline, Microsoft extended Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2 support in March 2017 by 9 months. Windows Server 2012 reached the end of mainstream support on October 9, 2018 and entered the extended support phase, which ended on October 10, 2023.[71][72][73]
Microsoft announced in July 2021 that they will distribute paid Extended Security Updates for volume licensed editions of Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 for up to 3 years after the end of extended support.[74] For Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2, these updates will last until October 13, 2026. This will mark the final end of all security updates for the Windows NT 6.2 product line after 14 years, 2 months and 12 days and will also mark the final end of all security updates for the Windows NT 6.3 product line after 13 years, 1 month and 16 days.
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of Microsoft Windows
- List of operating systems
- Microsoft Servers
- ^ Applies to Windows Server 2008 R2 and 2012 Datacenter and Windows Server 2012 Standard only. Other editions support less.
- ^ Each virtualized partition, including the host itself, can use up to 64 processors.[51]
- ^ a b Each license of Windows Server 2012 Standard or Datacenter allows up to two processor chips. Each license of Windows Server 2012 Standard allows up to two virtual instances of Windows Server 2012 Standard on that physical server. If more virtual instances of Windows Server 2012 Standard are needed, each additional license of Windows Server 2012 allows up to two more virtual instances of Windows Server 2012 Standard, even though the physical server itself may have sufficient licenses for its processor chip count. Because Windows Server 2012 Datacenter has no limit on the number of virtual instances per licensed server, only enough licenses for the physical server are needed for any number of virtual instances of Windows Server 2012 Datacenter. If the number of processor chips or virtual instances is an odd number, the number of licenses required is the same as the next even number. For example, a single-processor-chip server would still require 1 license, the same as if the server were two-processor-chip and a five-processor-chip server would require 3 licenses, the same as if the server were six-processor-chip, and if 15 virtual instances of Windows Server 2012 Standard are needed on one server, 8 licenses of Windows Server 2012, which can cover up to 16 virtual instances, are needed (assuming, in this example, that the processor chip count does not exceed 16).
- ^ For the Standard and Datacenter editions, each user or device accessing the software must have a client access license (CAL) assigned (either per-user or per-device), so there may be no more simultaneous users than the number of client-access licenses, except up to 2 simultaneous users purely to administer the server software, or for running virtualization or web workloads. Remote Desktop Services requires an additional CAL separate from the aforementioned CAL.
- ^ If the number of physical processors in a particular server is under 64, the limit is determined by the quantity of licenses assigned to that server. In that case, the number of physical processors cannot exceed twice the number of licenses assigned to the server.
- ^ http://blogs.technet.com/b/windowsserver/archive/2012/08/01/windows-server-2012-released-to-manufacturing.aspx
- ^ a b «Microsoft Product Lifecycle». Microsoft Support. Microsoft. January 2012. Archived from the original on February 27, 2013. Retrieved October 10, 2012.
- ^ a b Snover, Jeffrey (August 1, 2012). «Windows Server 2012 released to manufacturing!». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. TechNet blogs. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved January 29, 2013.
- ^ a b Foley, Mary Jo (April 5, 2010). «Microsoft pulls the plug on future Itanium support». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on August 12, 2012. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 approximately equal to Windows Server 2008». SmartProfile. August 25, 2017.
- ^ a b Foley, Mary Jo (April 17, 2012). «Windows Server «8» officially dubbed Windows Server 2012″. ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on November 19, 2014. Retrieved April 17, 2012.
- ^ a b Savill, John (February 29, 2012). «Q: Where can I download and get more information on Windows Server «8» Beta and Windows 8 Consumer Preview?». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Retrieved February 29, 2012.
- ^ a b Snover, Jeffrey (April 24, 2012). «Windows Server 2012 Release Candidate Timing». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. TechNet blogs. Archived from the original on February 11, 2013. Retrieved January 21, 2013.
- ^ Laing, Bill (September 9, 2011). «Windows Server 8: An Introduction». Server & Cloud Blog. Microsoft. TechNet blogs. Archived from the original on October 28, 2012. Retrieved January 23, 2013.
- ^ «Download Windows Server 8 Developer Preview via MSDN». Softpedia. SoftNews SRL. September 14, 2011. Archived from the original on May 8, 2012. Retrieved January 25, 2013.
- ^ a b Bisson, Simon (September 14, 2011). «Windows 8 Server Developer Preview». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ Arghire, Ionut (February 18, 2012). «Windows 8 Developer Preview Expiration Date Gets Postponed». Softpedia. SoftNews SRL. Archived from the original on October 13, 2013. Retrieved July 15, 2013.
- ^ Snover, Jeffrey. «Windows Server 2012 Essentials released to manufacturing, available for evaluation today!». Windows Server Blog!. Microsoft. TechNet blogs. Archived from the original on January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 25, 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 Essentials reaches general availability!». Windows Server Blog!. Microsoft. TechNet blogs. Archived from the original on April 29, 2015. Retrieved January 25, 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012». Microsoft DreamSpark. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 19, 2016. Retrieved January 25, 2013.
- ^ Joel Hruska (May 18, 2007). «Windows Server 2008 declared 32-bit’s last hurrah». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on August 24, 2021. Retrieved August 24, 2021.
- ^ Callaham, John (September 9, 2011). «Windows Server 8 Screenshot Leak Shows New UI». Neowin.net. Neowin LLC. Archived from the original on February 27, 2013. Retrieved January 21, 2013.
- ^ Wilhelm, Alex (September 9, 2011). «Windows Server 8 Screenshot leaks». News. The Next Web. Archived from the original on August 28, 2012. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ «Managing Privacy: Windows Store and Resulting Internet Communication». TechNet. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 6, 2014. Retrieved January 30, 2014.
- ^ Thurott, Paul (November 2, 2011). «Windows Server «8» Preview (Unedited, Complete Version)». Paul Thurott’s Supersite for Windows. Penton Media. Archived from the original on March 20, 2012. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ Williams, Mike; Hanson, Matt (October 25, 2012). «Windows 8 tips: mastering the interface». Techradar. Future Publishing. Archived from the original on January 22, 2013. Retrieved January 22, 2013.
- ^ Haveson, Ryan (October 13, 2011). Sinofsky, Steven (ed.). «The Windows 8 Task Manager». Building Windows 8. Microsoft. MSDN blogs. Archived from the original on January 25, 2013. Retrieved January 31, 2013.
- ^ «Using Task Manager with 64+ logical processors». Building Windows 8. MSDN blogs. Archived from the original on November 6, 2015. Retrieved October 29, 2011.
- ^ «How to Get the Most out of New Windows 8 Task Manager?». October 24, 2011. Archived from the original on April 7, 2012. Retrieved October 29, 2011.
- ^ Hu, Aaron. «How to disable start-up items in windows server 2012». TechNet Forums. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 27, 2013. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
The Startup tab is not present on Windows Server 2012. It is only on Windows 8.
- ^ «IP Address Management (IPAM) Overview». TechNet Library. Microsoft. February 29, 2012. Archived from the original on May 2, 2013. Retrieved January 21, 2013.
- ^ Shields, Greg (July 3, 2012). «Quick Guide: What’s New in Windows Server 2012 Active Directory». Redmond magazine. 1105 Redmond Media. Archived from the original on January 21, 2013. Retrieved January 21, 2013.
- ^ Sherif Mahmoud, Tamer (May 29, 2012). «Creating fine grained password policies through GUI Windows server (sic) 2012 «Server 8 beta»«. Team blog of MCS @ Middle East and Africa. Microsoft. TechNet blogs. Archived from the original on March 7, 2013. Retrieved January 21, 2013.
- ^ Bruzzese, J. Peter (October 26, 2011). «Windows Server 8: The 4 best new Active Directory features». InfoWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on May 12, 2012. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ Deuby, Sean (September 14, 2011). «What’s New in Windows Server 2012 Active Directory». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Archived from the original on February 17, 2015. Retrieved July 16, 2013.
- ^ Herrmann, Max; Laing, Bill; Vecchiet, Manlio; Neil, Mike (September 14, 2011). «Day 2: Windows Server 8». Channel 9. Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 17, 2012. Retrieved February 2, 2013.
- ^ «BUILD2011: Windows Server 8». Channel 9. Anaheim, California: Microsoft. September 13–16, 2011. Archived from the original on October 7, 2012. Retrieved February 2, 2013.
- ^ «Server Virtualization Features». Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 4, 2012. Retrieved October 5, 2012.
- ^ a b Savill, John (October 28, 2011). «Q: What are Windows Server 8’s Scalability Numbers?». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ Garg, Pankaj; Tan, See-Mong (September 14, 2011). «Day 2: A deep dive into Hyper-V Networking». Channel 9. Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 10, 2012. Retrieved January 22, 2013.
- ^ Savil, John (October 21, 2011). «Q: Will Windows Server 8 require the processor to support SLAT?». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ Lucas, Martin (January 1, 2013). «Windows Server 2012: Does ReFS replace NTFS? When should I use it?». Ask Premier Field Engineering (PFE) Platforms. Microsoft. TechNet blogs. Archived from the original on June 2, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ a b Foley, Mary Jo (January 16, 2012). «Microsoft goes public with plans for its new Windows 8 file system». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on May 21, 2013. Retrieved January 21, 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g Verma, Surendra (January 16, 2012). Sinofsky, Steven (ed.). «Building the next generation file system for Windows: ReFS». Building Windows 8. Microsoft. MSDN blogs. Archived from the original on May 26, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ Meyer, David (January 17, 2012). «Microsoft takes wraps off new Windows file system». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on May 21, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ «ReadDirectoryChangesW function». MSDN Library. Microsoft. November 8, 2012. Archived from the original on May 4, 2013. Retrieved January 21, 2013.
- ^ Nagar, Rajeev (January 5, 2012). Sinofsky, Steven (ed.). «Virtualizing storage for scale, resiliency, and efficiency». Building Windows 8. Microsoft. MSDN blogs. Archived from the original on May 9, 2013. Retrieved January 18, 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012: Does ReFS replace NTFS? When should I use it?». January 2, 2013. Archived from the original on June 2, 2013. Retrieved March 31, 2013.
- ^ «ReFS (Resilient File System) supports sparse files». Archived from the original on March 15, 2013. Retrieved March 31, 2013.
- ^ a b «Resilient File System Overview». TechNet Library. Microsoft. February 29, 2012. Archived from the original on September 1, 2017. Retrieved December 25, 2013.
- ^ Mackie, Kurt. «Microsoft Touts IIS 8 Improvements». Redmond magazine. 1105 Redmond Media. Archived from the original on May 15, 2013. Retrieved August 17, 2012.
- ^ Anderson, Tim (September 4, 2012). «Windows Server 2012: inside Microsoft’s Enterprise Server OS». Computer Weekly. TechTarget. Archived from the original on January 22, 2013. Retrieved January 21, 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 Remote Desktop Services (RDS) – Windows Server Blog – Site Home – TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. May 8, 2012. Archived from the original on October 5, 2013. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ «Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) 8.0 update for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2». Support.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on October 25, 2012. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ a b c Seldam, Matthijs ten (October 13, 2012). «Windows Server — Sockets, Logical Processors, Symmetric Multi Threading». Matthijs’s blog. Microsoft. TechNet blogs. Archived from the original on November 2, 2012. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- ^ «Logical Processor count changes after enabling Hyper-V role on Windows Server 2012». March 28, 2013. Archived from the original on May 15, 2013. Retrieved April 1, 2013.
- ^ a b «Installing Windows Server 2012». TechNet Library. Microsoft. System requirements. Archived from the original on May 26, 2024. Retrieved June 10, 2012.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (July 5, 2012). «Microsoft goes public with Windows Server 2012 versions, licensing». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on November 9, 2012. Retrieved July 5, 2012.
- ^ «Purchasing Windows Server 2012». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 7, 2015. Retrieved December 8, 2015.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 Licensing and Pricing FAQ» (PDF). Microsoft. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 2, 2012. Retrieved July 5, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 Licensing Data Sheet» (PDF). Microsoft. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 22, 2012.
- ^ «Introduction to Windows Server 2012 Foundation». TechNet. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 5, 2012. Retrieved December 8, 2015.
- ^ «Introduction to Windows Server 2012 Foundation». TechNet Library. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 5, 2012. Retrieved November 4, 2012.
- ^ a b Bisson, Simon (September 13, 2012). «Windows Server 2012: RTM review». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved January 19, 2013.
- ^ a b Anderson, Tim (September 5, 2012). «Windows Server 2012: Smarter, stronger, frustrating». The Register. Situation Publishing. Archived from the original on December 26, 2012. Retrieved January 19, 2013.
- ^ Ferrill, Paul (October 3, 2012). «Windows Server 2012 Review: The Bottom Line». ServerWatch. QuinStreet. Archived from the original on January 15, 2013. Retrieved January 19, 2013.
- ^ Rist, Oliver (June 27, 2012). «Review: Weighing Windows Server 2012». InfoWorld. IDG. Archived from the original on March 10, 2013. Retrieved January 19, 2013.
- ^ Otey, Michael (July 25, 2012). «Is Microsoft Trying to Kill Windows Server?». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Archived from the original on January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 19, 2013.
- ^ Ferrill, Paul (December 16, 2012). «A Hands-on Look at Windows Server 2012 Essentials». ServerWatch. QuinStreet. Archived from the original on January 15, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ Anderson, Tim (December 21, 2012). «Windows Server 2012 Essentials review». PC Pro. Dennis Publishing. Archived from the original on January 6, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ Thurott, Paul (October 2, 2012). «Windows Server 2012: Foundation vs. Essentials». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Archived from the original on October 8, 2012. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 R2 Reaches the Release to Manufacturing (RTM) Milestone». Microsoft Docs. August 27, 2013. Archived from the original on January 14, 2020. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- ^ «Save the date: Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows System Center 2012 R2 and Windows Intune update coming Oct. 18 — The Official Microsoft Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Microsoft Docs. August 14, 2013. Archived from the original on April 1, 2014. Retrieved February 10, 2014.
- ^ «August updates for Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 | Blogging Windows». Archived from the original on September 6, 2015. Retrieved November 14, 2014.
- ^ Resseler, Mike (August 27, 2013). «eBook — What’s new in Windows Server 2012 R2 Preview». Veeam Software. Archived from the original on April 5, 2014. Retrieved September 3, 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012». Microsoft Docs. Archived from the original on July 28, 2021. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft Extends Windows Server 2012 Support — Redmondmag.com». Redmondmag. Archived from the original on July 28, 2021. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 Nears End of life». February 3, 2020. Archived from the original on January 26, 2021. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ «Product Lifecycle FAQ — Extended Security Updates». docs.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 29, 2021. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- Stanek, William (2013). Windows Server 2012 Inside Out. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-6631-3.
- Stanek, William (2014). Windows Server 2012 R2 Inside Out Volume 1: Configuration, Storage, & Essentials. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-8267-2.
- Stanek, William (2014). Windows Server 2012 R2 Inside Out Volume 2: Services, Security, & Infrastructure. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-8255-9.
- Official website
- Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2012 on TechNet
- Windows Server 2012 R2 on MSDN
- Windows Server 2012 on MSDN
- Tutorials and Lab Manual Articles of Windows Server 2012 R2
Affordable Digital Licences
By focusing exclusively on digital licences, we avoid the additional costs associated with physical packages. This means no boxes, discs, or other accessories that increase the manufacturing and shipping costs by Microsoft, allowing us to offer lower prices to our customers.
Certified Microsoft Partners
As official Microsoft partners, we have access to special prices on different products and regions. We take advantage of these opportunities to purchase large quantities at reduced prices, directly benefiting our customers.
Global Network of Partners and Deals
Our specialised team is constantly exploring global opportunities with Microsoft partners. This worldwide network allows us to access exclusive offers and buy products in large volumes. By leveraging these strategic opportunities, we can offer our customers exceptional prices without compromising on quality.
Pricing Strategy for Global Expansion
We are committed to expanding our presence worldwide. Therefore, we have adjusted our prices to leave a minimal profit margin, trusting that a higher volume of sales will compensate for this strategy. Our goal is to gain international recognition through accessible prices.
OEM and Volume Licences
Many of our licences are OEM or volume-based (MAK or KMS), which gives us additional discounts and allows us to offer even more competitive prices.
Our Commitment to Fair Prices and Quality
We are dedicated to providing you with the best possible value for your money. During our promotional period, you will find even greater discounts on our already low prices. We firmly believe that everyone should have access to the latest Microsoft products, regardless of their budget.
