
Доменом в Windows Server называют отдельную область безопасности компьютерной сети.
В домене может быть один или несколько серверов выполняющих различные роли. Разрешения, применяемые администратором, распространяются на все компьютеры в домене.
Пользователь, имеющий учетную запись в домене, может войти в систему на любом компьютере, иметь учетную запись на локальном компьютере не требуется.
В домене могут работать несколько тысяч пользователей, при этом компьютеры могут принадлежать к разным локальным сетям.
Несколько доменов имеющих одну и ту же конфигурацию и глобальный каталог называют деревом доменов. Несколько деревьев могут быть объединены в лес.
В домене есть такое понятие как групповая политика. Под групповой политикой понимают настройки системы, которые применяются к группе пользователей. Изменения групповой политики затрагивают всех пользователей входящих в эту политику.
Параметры групповой политики хранятся в виде объектов групповой политики (Group Policy Object, GPO). Эти объекты хранятся в каталоге подобно другим объектам. Различают два вида объектов групповой политики – объекты групповой политики, создаваемые в контексте службы каталога, и локальные объекты групповой политики.
Не будем подробно вдаваться в теорию и перейдем к практике.
Запускаем Диспетчер серверов -> «Добавить роли и компоненты».

На первой странице мастер напоминает, что необходимо сделать перед началом добавления роли на сервер. Нажмите «Далее».
На втором шаге нужно выбрать «Установка ролей и компонентов» и нажать «Далее».

Выбираем сервер, на который нужно установить Active Directory (он у нас один), «Далее».

Теперь нужно выбрать роль, которую нужно добавить. Выбираем «Доменные службы Active Directory». После чего откроется окно, в котором будет предложено установить службы ролей или компоненты, необходимые для установки роли Active Directory, нажмите кнопку «Добавить компоненты», после чего кликните «Далее».

PЗатем нажимайте «Далее», «Далее» и «Установить».

Перезапустите компьютер.
После того, как роль была добавлена на сервер, необходимо настроить доменную службу, то есть установить и настроить контроллер домена.
Настройка контроллера домена Windows Server
Запустите «Мастер настройки доменных служб Active Directory», для чего нажмите на иконку «Уведомления» в диспетчере сервера, затем нажмите «Повысить роль этого сервера до уровня контроллера домена».

Выберите пункт «Добавить новый лес», затем введите имя домена в поле «Имя корневого домена». Домены в сети Windows имеют аналогичные названия с доменами в интернете. Я ввел имя домена buzov.com. Нажимаем «Далее».

На этом шаге можно изменить совместимость режима работы леса и корневого домена. Оставьте настройки по умолчанию. Задайте пароль для DSRM (Directory Service Restore Mode – режим восстановления службы каталога) и нажмите «Далее».
Затем нажимайте «Далее» несколько раз до процесса установки.
Когда контроллер домена установиться компьютер будет перезагружен.
Добавление и настройка групп и пользователей в домене Windows Server
Теперь нужно добавить пользователей домена, что бы присоединить к сети рабочие места сотрудников.
Отроем «Пользователи и компьютеры Active Directory». Для этого перейдите в Пуск –> Панель управления –> Система и безопасность –> Администрирование –> Пользователи и компьютеры Active Directory.

Создадим отдел «Бухгалтерия», для этого выделите название домена и вызовите контекстное меню, в котором выберите (Создать – Подразделение). Введите имя отдела (бухгалтерия) и нажмите «OK»

Подразделения служат для управления группами компьютеров пользователей. Как правило их именуют в соответствии с подразделениями организации.
Создайте учетную запись пользователя в новом подразделении. Для этого в контекстном меню нового подразделения выберите пункт Создать –> Пользователь. Пусть первым пользователем будет Бухгалтер.

После ввода имени пользователя и учетной записи нажмите «Далее». Теперь нужно ввести пароль. По умолчанию пароль должен соответствовать требованиям сложности, то есть содержать три из четырех групп символов: заглавные буквы, строчные буквы, цифры, специальные знаки ( . , + – = ? № $ и так далее). Установите параметр «Требовать смену пароля при следующем входе в систему».
Создайте учетную запись группы безопасности. Для этого в контекстном меню нового подразделения (бухгалтерия) выберите пункт (Создать – Группа). При создании новой группы безопасности необходимо ввести имя, область действия и тип группы. Область действия определяет видимость данной группы в службе каталога. Глобальная группа видна в любом домене службы каталога и ей могут назначаться привилегии доступа к ресурсам других доменов. Локальная группа видна только в своем домене, то есть ей будут доступны ресурсы только ее домена. Группы безопасности позволяют
объединять пользователей и другие группы для назначения им одинаковых привилегий на различные объекты. Группы распространения используются для рассылки сообщений, они не участвуют в разграничении прав доступа.

Теперь нужно ввести компьютер в домен и зайти под новым пользователем. Для этого на клиентском компьютере нужно указать DNS-адрес. Для этого откройте «Свойства сетевого подключения» (Пуск –> Панель управления –> Сеть и Интернет – >Центр управления сетями и общим доступом – Изменение параметров адаптера), вызовите контекстное меню подключения и выберите «Свойства».
Выделите «Протокол Интернета версии 4 (TCP/IPv4)», нажмите кнопку «Свойства», выберите «Использовать следующие адреса DNS-серверов» и в поле «Предпочитаемый DNS-сервер» укажите адрес вашего DNS-сервера. Проверьте, что задан IP-адрес и маска той же подсети, в которой находится сервер.
Присоединение компьютера к домену
Откройте свойства системы (Пуск –> Панель управления –> Система и безопасность –> Система –> Дополнительные параметры системы). Выберите вкладку «Имя компьютера» и нажмите «Изменить». Выберите «Компьютер является членом домена» и введите имя домена.

После этого необходимо ввести логин и пароль пользователя с правами присоединения к домену (обычно администратора домена). Если вы всё указали правильно, то появиться приветственное сообщение «Добро пожаловать в домен …».
Для того чтобы завершить присоединение, необходима перезагрузка.
После перезагрузки войдите в систему под доменной учётной записью пользователя, которая была создана ранее

После ввода пароля операционная система попросит вас сменить пароль.
Вернемся на сервер. Нажмите «Пуск» -> Администрирование и перейдите в окно Управления групповой политикой. Выбираем наш лес, домен, Объекты групповой политики, щелкаем правой кнопкой мыши -> создать. Называем его buh (это объект групповой политики для группы Бухгалтерия).
Теперь необходимо привязать данный объект групповой политики к созданной группе. Для этого нажмите правой кнопкой на созданное подразделение (Бухгалтерия) и выберите «Связать существующий объект групповой политики…», затем выберите созданный ранее объект в списке и нажмите «ОК».

Далее выбираем созданный объект.

Выбранный объект должен появиться в списке связанных объектов групповой политики. Для редактирования параметров, определяемых данным объектом, нажмите на него правой кнопкой и выберите «Изменить».
Установка параметров безопасности
Установка параметров безопасности — завершающий этап настройка домена и групповых политик в Windows Server.
Ограничения парольной защиты
Ограничение на параметры парольной системы защиты задаются в контексте «Конфигурация компьютера». Выберите Конфигурация Windows –> Параметры безопасности –> Политики учетных записей –> Политика паролей.

В данном разделе объекта групповой политики определяются следующие параметры:
- «Минимальный срок действия пароля» задает периодичность смены пароля.
- «Минимальная длина пароля» определяет минимальное количество знаков пароля.
- «Максимальный срок действия пароля» определяет интервал времени, через который разрешается менять пароль.
- «Пароль должен отвечать требованиям сложности» определяет требования к составу групп знаков, которые должен включать пароль.
- «Хранить пароли, используя обратимое шифрование» задает способ хранения пароля в базе данных учетных записей.
- «Вести журнал паролей» определяет количество хранимых устаревших паролей пользователя.
Тут нужно указать необходимые параметры (определите самостоятельно).
Политика ограниченного использования программ
Объекты групповой политики позволяют запретить запуск определенных программ на всех компьютерах, на которые распространяется действие политики. Для этого необходимо в объекте групповой политики создать политику ограниченного использования программ и создать необходимые правила. Как это сделать.
Выберите раздел Конфигурация пользователя –> Политики –> Конфигурация Windows –> Параметры безопасности –> Политики ограниченного использования программ. Нажмите правой кнопкой на «Политики ограниченного использования программ», далее заходим в «Дополнительные правила» и жмем правой кнопкой мыши, затем выбираем «Создать правило для пути».
После обновления объекта групповой политики на рабочей станции, политика ограниченного использования программ вступит в действие и запуск программ, соответствующих правилам, будет невозможен.
Давайте запретим использовать командную строку на клиентском компьютере.

Запрет запуска командной строки (cmd.exe).

На этом все. Если у вас остались вопросы, обязательно задайте их в комментариях.
При попытке запустить командную строку на клиентской машине вы получите сообщение.

This article explains what Group Policies are and shows how to configure Windows Server 2012 Active Directory Group Policies. Our next article will cover how to properly enforce Group Policies (Group Policy Link Enforcement, Inheritance and Block Inheritance) on computers and users that a part of the company’s Active Directory.
FREE Hyper-V & VMware Backup: Easy to use — Powerful features — Just works, no hassle: It’s FREE for Firewall.cx readers! Download Now!
Before we dive into Group Policy configuration, let’s explain what exactly Group Policies are and how they can help an administrator control its users and computers.
A Group Policy is a computer or user setting that can be configured by administrators to apply various computer specific or user specific registry settings to computers that have joined the domain (active directory). A simple example of a group policy is the user password expiration policy which forces users to change their password on a regular basis. Another example of a group policy would be the enforcement of a specific desktop background picture on every workstation or restricting users from accessing their Local Network Connection properties so they cannot change their IP address.
A Group Policy Object (GPO) contains one or more group policy settings that can be applied to domain computers, users, or both. GPO objects are stored in active directory. You can open and configure GPO objects by using the GPMC (Group Policy Management Console) in Windows Server 2012:
Figure 1. GPO Objects
Group Policy Settings are the actual configuration settings that can be applied to a domain computer or user. Most of the settings have three states, Enabled, Disabled and Not Configured. Group Policy Management Editor provides access to hundreds of computer and user settings that can be applied to make many system changes to the desktop and server environment.
Group Policy Settings
Group Policy Settings are divided into Computer Settings and User Settings. Computer Settings are applied to computer when the system starts and this modifies the HKEY Local Machine hive of registry. User Settings are applied when the users log in to the computer and this modifies the HKEY Local Machine hive.
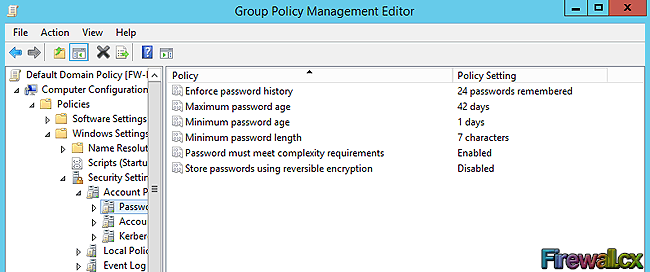
Figure 2. Group Policy Settings
Computer Settings and User Settings both have policies and preferences.
These policies are:
Software Settings: Software can be deployed to users or computer by the administrator. The software deployed to users will be available only to those specific users whereas software deployed to a computer will be available to any user that on the specific computer where the GPO is applied.
Windows Settings: Windows settings can be applied to a user or a computer in order to modify the windows environment. Examples are: password policies, firewall policy, account lockout policy, scripts and so on.
Administrative Templates: Contains a number of user and computer settings that can be applied to control the windows environment of users or computers. For example, specifying the desktop wallpaper, disabling access to non-essential areas of the computers (e.g Network desktop icon, control panel etc), folder redirection and many more.
Preferences are a group policy extension that does the work which would otherwise require scripts. Preferences are used for both users and computers. You can use preferences to map network drives for users, map printers, configure internet options and more.
Next, let’s take a look at how we can create and apply a Group Policy.
FREE Hyper-V & VMware Backup: Easy to use — Powerful features — Just works, no hassle: It’s FREE for Firewall.cx readers! Download Now!
Creating & Applying Group Policy Objects
By default, GPOs can be created and applied by Domain Admins, Enterprise Admins and Group Policy Creator Owner user groups. After creating the GPO, you can apply or link the GPOs to sites, domains or Organizational Units (OUs), however you cannot apply GPO to users, groups, or computers. GPOs are processed in following top to bottom order:
- Local Group Policy: Every windows operating system has local group policy installed by default. So this local group policy of the computer is applied at first.
- Site GPO: The GPOs linked to the Site is then processed. By default, there is no site level group policy configured.
- Domain GPO: Next, the GPO configured at domain level is processed. By default, GPO named default domain policy is applied at the domain level. This applies to all the objects of the domain. If there is policy conflict between domain and site level GPOs, then GPO applied to domain level takes the precedence.
- Organizational Unit GPO: — In the end, GPO configured at OU is applied. If there is any conflict between previously applied GPOs, the GPO applied to OU takes the most precedence over Domain, Site and Local Group Policy.
Let’s now take a look at a scenario to apply a group policy to domain joined computers to change the desktop background. We have a domain controller named FW-DC01 and two clients FW-CL1 and FW-CL2 as shown in the diagram below. The goal here is to set the desktop wallpaper for these two clients from a group policy:
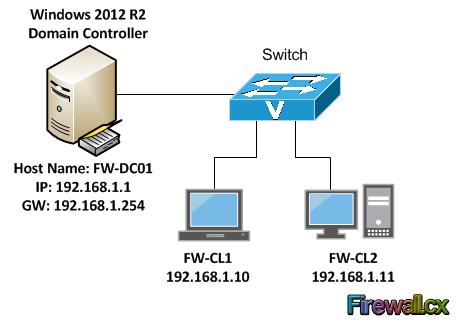
Figure 3. GPO Scenario
In our earlier articles we showed how Windows 8 / Windows 8.1 join an Active Directory domain, FW-CL1 and FW-CL2 are workstations that have previously joined our domain – Active Directory. We have two users MJackson and PWall in the FW Users OU.
Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) by going into Server Manager>Tools and select Group Policy Management as shown below:
Figure 4. Open GPMC
As the GPMC opens up, you will see the tree hierarchy of the domain. Now expand the domain, firewall.local in our case, and you will see the FW Users OU which is where our users reside. From here, right-click this OU and select the first option Create a GPO in this domain and Link it here:
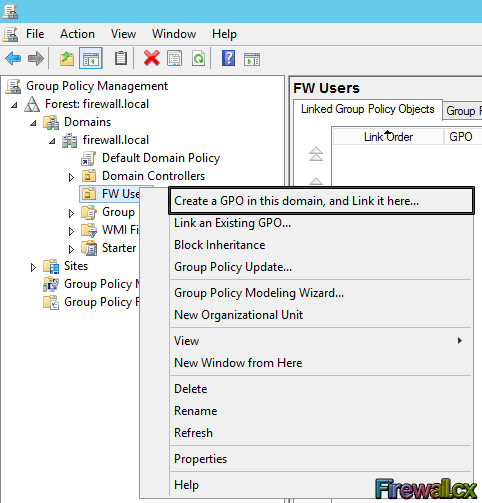
Figure 5. Select FW Users and Create a GPO
Now type the Name for this GPO object and click the OK button. We selected WallPaper GPO:
Figure 6. Creating our Wallpaper Group Policy Object
Next, right-click the GPO object and click edit:
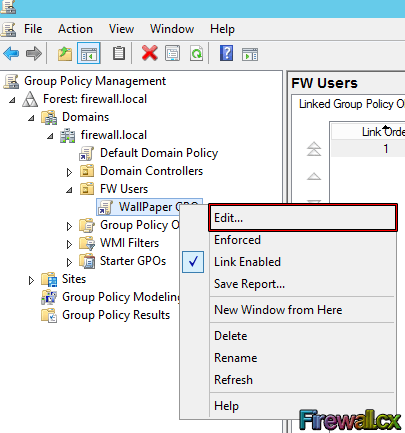
Figure 7. Editing a Group Policy Object
At this point we get to see and configure the policy that deals with the Desktop Wallpaper, however notice the number of different policies that allow us to configure and tweak various aspects of our domain users.
To find the Desktop Wallpaper, go to Expand User Configuration> Policies> Administrative Templates> Desktop> Desktop. At this point we should be able to see the setting in right window. Right-click the Desktop Wallpaper setting and select Edit:
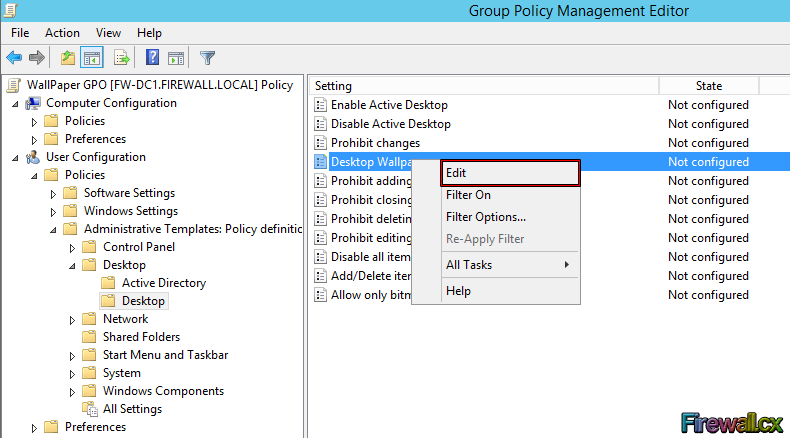
Figure 8. Selecting and editing Desktop Wallpaper policy
The settings of Desktop Wallpaper will now open. First we need to activate the policy by selecting the Enabled option on the left. Next, type the UNC path of shared wallpaper. Remember that we must share the folder that contains the wallpaper \\FW-DC1\WallPaper\ and configure the share permission so that users can access it. Notice that we can even select to center our wallpaper (Wallpaper Style). When ready click Apply and then OK:
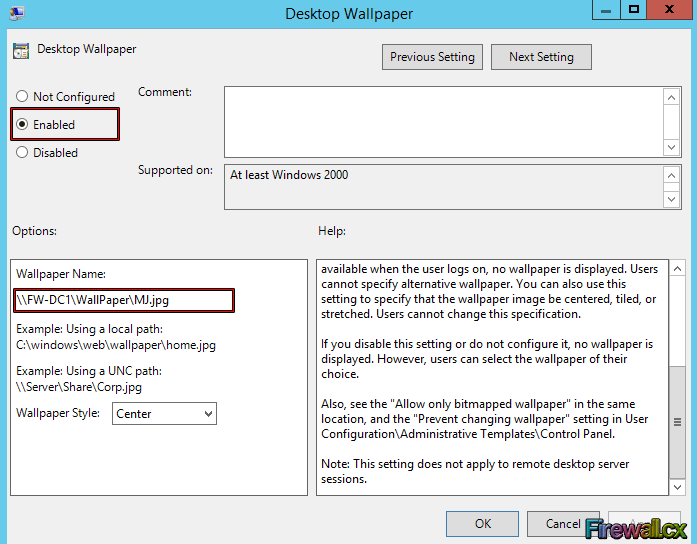
Figure 9. Configure Desktop Wallpaper
Now that we’ve configured our GPO, we need to apply it. To do so, we can simply log off and log back in the client computer or type following command in domain controller’s command prompt to apply the settings immediately:
C:\> gpupdate /force
Once our domain user logs in to their computer (FW-CL1), the new wallpaper policy will be applied and loaded on to the computer’s desktop.
Figure 10. User Login
As we can see below, our user’s desktop now has the background image configured in the group policy we created:

Figure 11. Computer Desktop Wallpaper Changed
This example shows how one small configuration setting can be applied to all computers inside an organization. The power and flexibility of Group Policy Objects is truly unbelievable and as we’ve shown, it’s even easier to configure and apply them with just a few clicks on the domain controller!
FREE Hyper-V & VMware Backup: Easy to use — Powerful features — Just works, no hassle: It’s FREE for Firewall.cx readers! Download Now!
This article explained what Group Policies Objects are and showed how to Configure Windows 2012 Active Directory Group Policies to control our Active Directory users and computers. We also highly recommend our article on Group Policy Enforcement, Inheritance throughout the Active Directory structure. More articles on Windows 2012 & Hyper-V can be found at our Windows 2012 Server section.
Group Policies are computer or user settings that can be defined to control or secure the Windows server and client infrastructure. Understanding GPO in Windows Server 2012 before actually configuring and applying policy settings is very important. It is easy to understand GPO in Windows Server 2012. There are some new features of GPO in Windows Server 2012.
Two main components of GPO are, GPO Object and GPO Policy Settings.
GPO Object: – GPO Object is an active directory object that has various group policy settings. These policy settings can be user settings or computer settings and can be applied to user or computers. GPO objects are stored in GPO container. The GPO object is stored in active directory database and each object has its own unique GUID (Globally Unique Identifier).
GPO Policy Settings: – GPO policy settings are the real settings within GPO object that defines particular action. GPO policy settings comes from GPO templates which are stored in SYSVOL folder of each domain controller. For example, Prohibit Access to Control Panel is a GPO policy setting that will simply disable access to control panel. Most of the GPO settings can be enabled, disabled or not configured. The example is shown below,

When you create a group policy, the GPO object is created and stored in GPO container in active directory and at the same time, GPO template is created and stored in SYSVOL folder. After creating a group policy, it can be linked to Sites, Domains and OUs. Group policy is process in the order of LSDOU: –
- Local Group Policy
- Sites
- Domains
- Organizational OUs
There are certain things that you should remember while creating and applying GPO settings. As stated earlier there are computer settings and user settings of each GPO object. Computer settings are applied at startup of the client machine. User settings are applied at use logon. Policies refresh can be initiated manually by using, C:\> gpupdate /force command or C:\> Invoke-Gpupdate powerShell cmdlet.
In fresh domain controller there are two default group policy settings configured. They are: –
- Default Domain Policy: – This policy is linked to the entire domain and has policies like password policies, account lockout policies and kerberos protocol policies. It is recommended that not to edit this policy. If you want to link new group policy then create new GPO and link to the domain.
- Default Domain Controller Policy: – This policy setting is applied to domain controllers and is linked to domain controllers OU. This policy affects domain controllers only.
The following two tabs change content below.
- Bio
- Latest Posts
Bipin is a freelance Network and System Engineer with expertise on Cisco, Juniper, Microsoft, VMware, and other technologies. You can hire him on UpWork. Bipin enjoys writing articles and tutorials related to Network technologies. Some of his certifications are, MCSE:Messaging, JNCIP-SEC, JNCIS-ENT, and others.
Group Policy Configuration on Windows Server 2012
This article explains how to setup and configure Group Policy on Microsoft Windows Server 2012. Free step by step guide for Group Policy configuration on Windows Server 2012
By default this feature enabled and installed automatically while installing Active directory Role on a server. You cannot remove this Role and cannot install this role individually on Windows 2012 Server.
1. Login to the Test Server
2. Now let’s start with login onto the server as shown below.

3. Give username & password (abc\administrator) & click on ok as shown below.
4. On the certificate verification window click on Yes button.
5. The Next windows will show the Server Desktop.

6. Open Server Manager from the Left down corner of server Desktop as shown below
7. Click on Group Policy Management from Tool Tab given in the Top right corner in Server Manager Dashboard.

8. The Group Policy Management window will open of ABC.com domain as shown.
9. Right Click on Group Policy Abject & click on New to create new group policy.

10. Give name to the Policy “Software Deployment policy” as shown below & click on ok button.

11. Right click on Software Deployment & click on Edit button as shown
12. Group Policy Management editor will open , Expand Policy Software Settings Software Installation Right Click & Select New Package
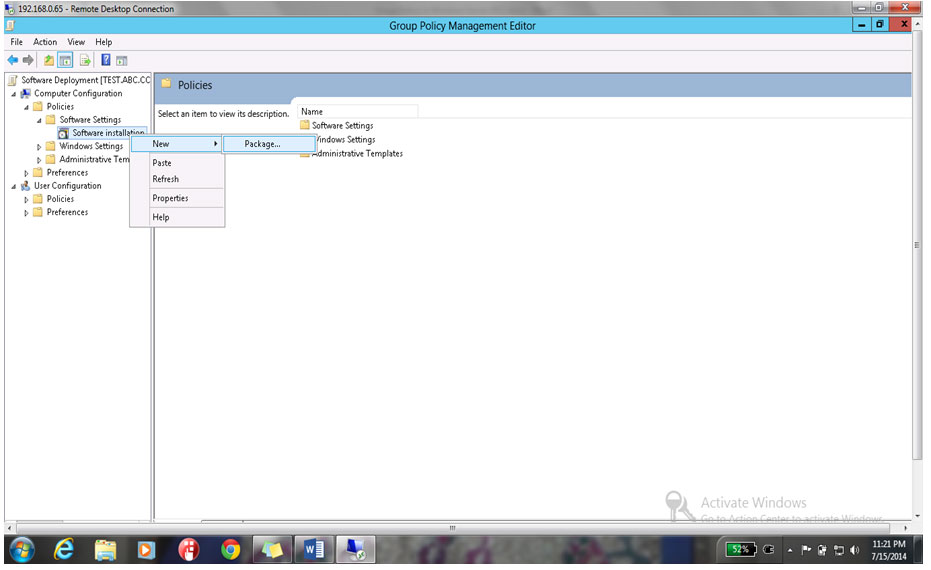
13. Before creating any package go to c drive & create a folder & copy the software installer file in to that folder as shown below
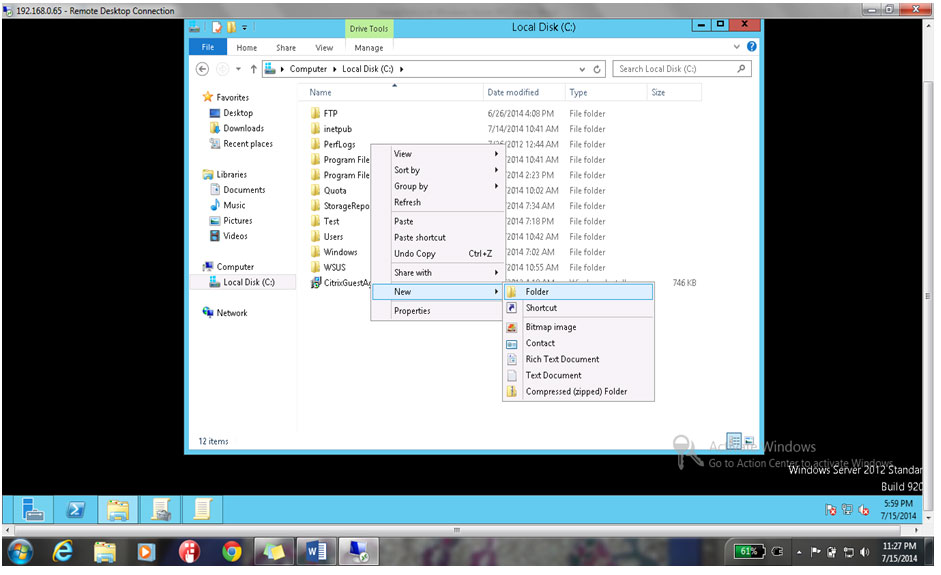
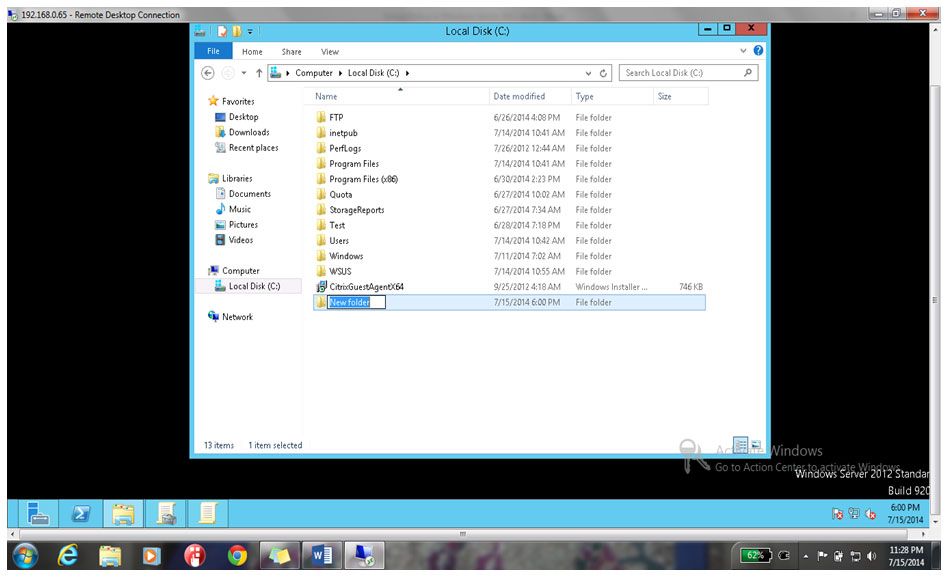
14. Rename it Software as shown below
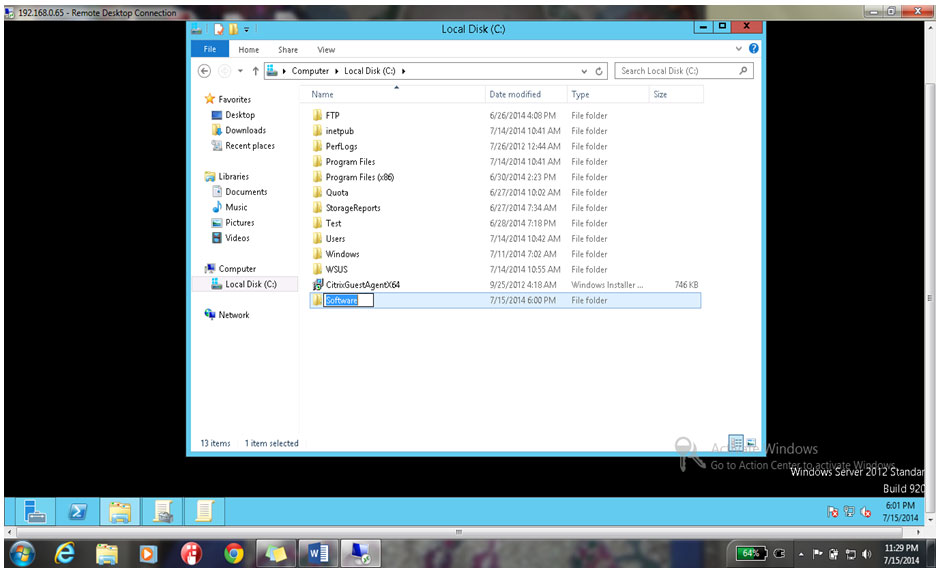
15. Place software into the directory as shown below

16. Right click on Software & click on properties
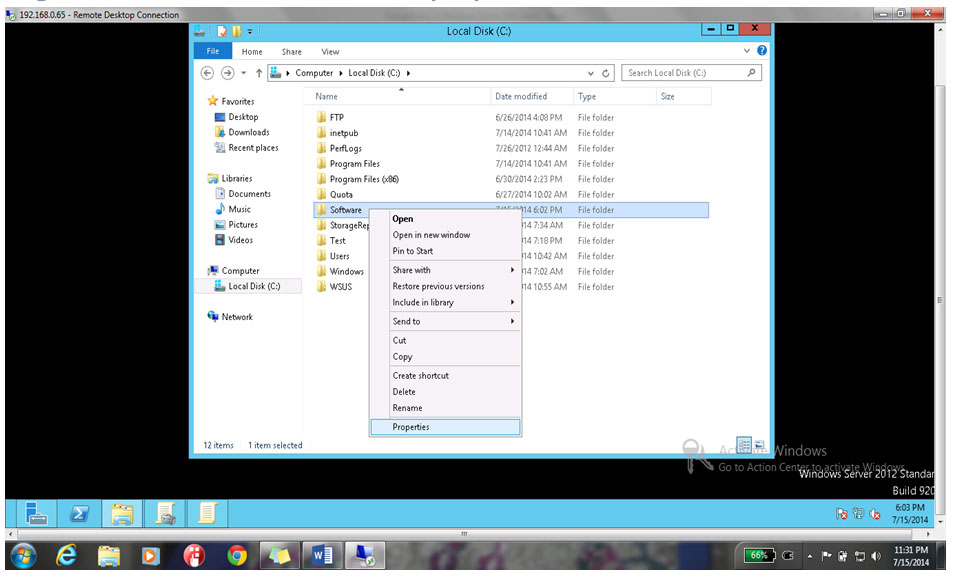
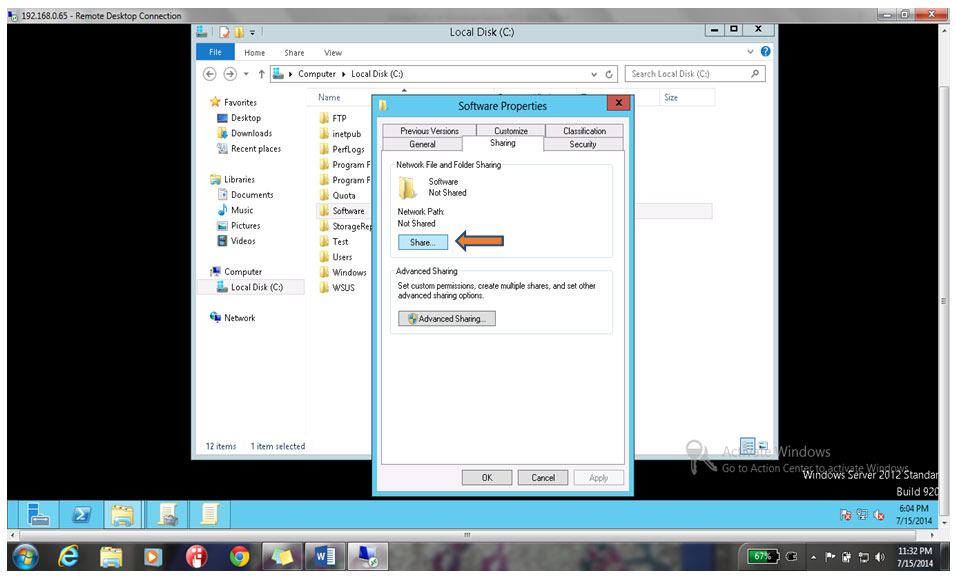
17. Click on Sharing Tab & click on Share button as shown below
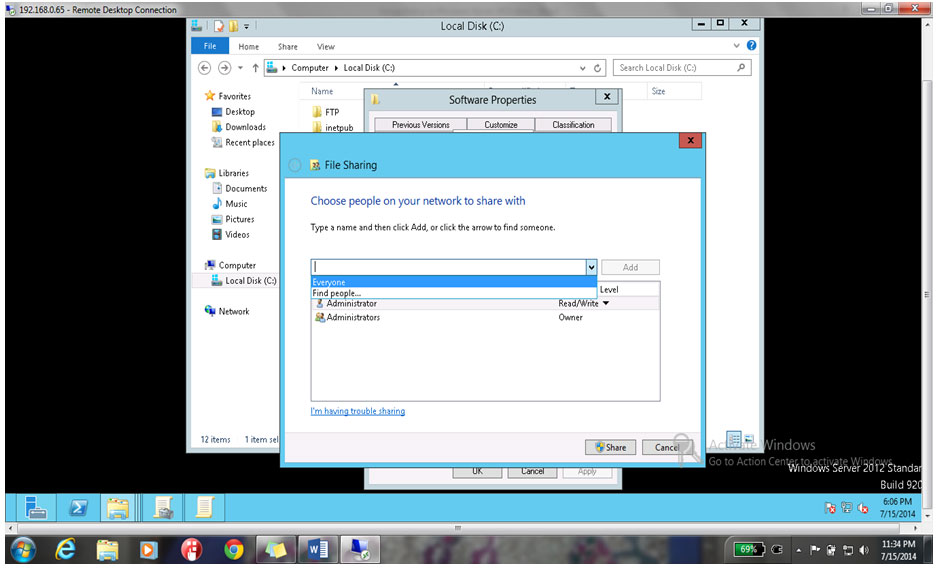
18. Select Everyone from the drop down menu as shown below
19. Click on Add button as shown below
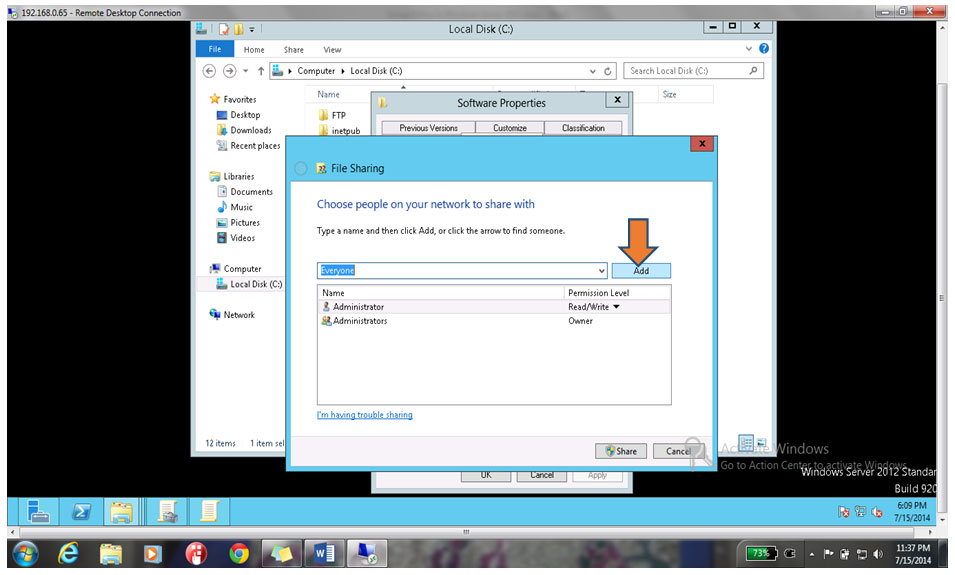
20. Select Read & Write Rights for all users as shown below

21. Click on Share button to finish the Sharing configuration a shown below
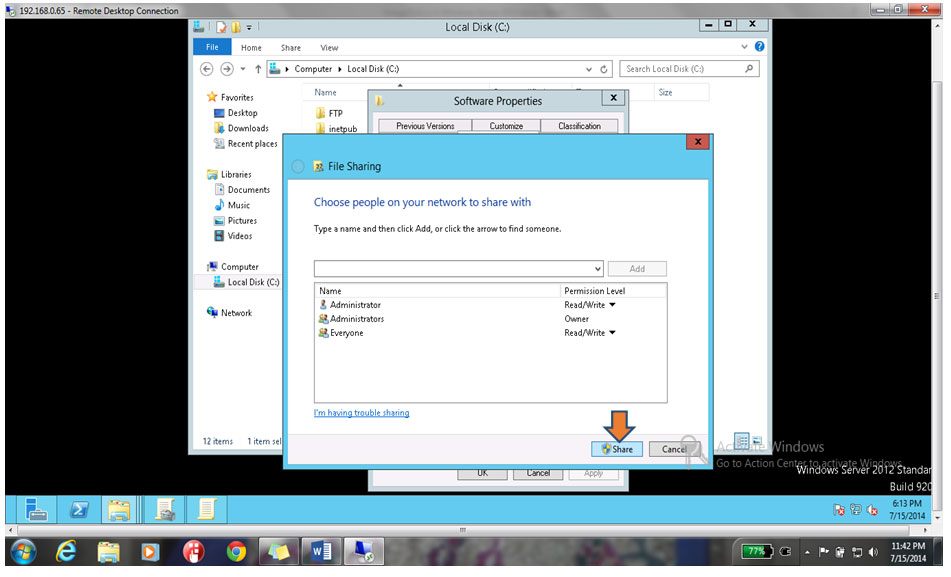
22. Click on Done
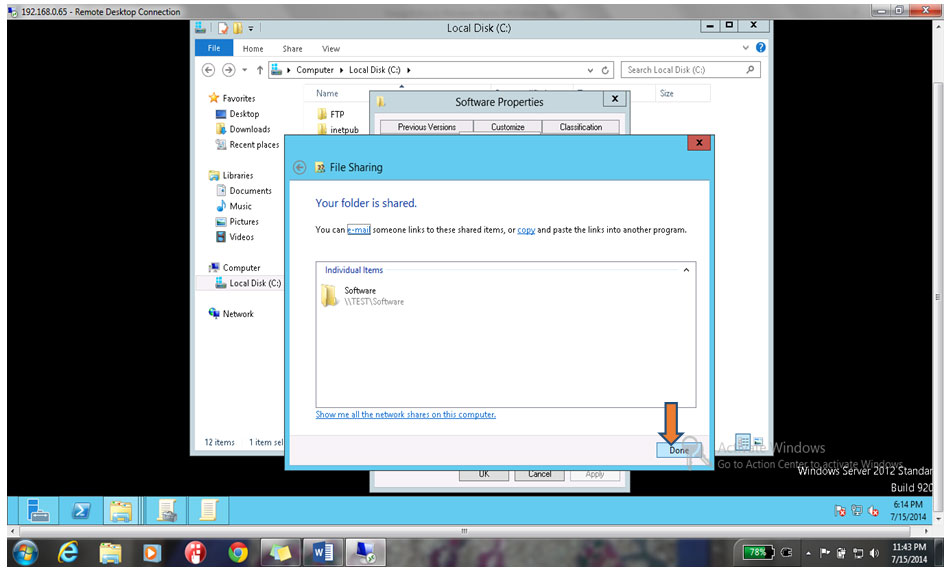
23. Then click on Close button

24. Come back to Group Policy Management Editor & select the Policy Right Click New Package
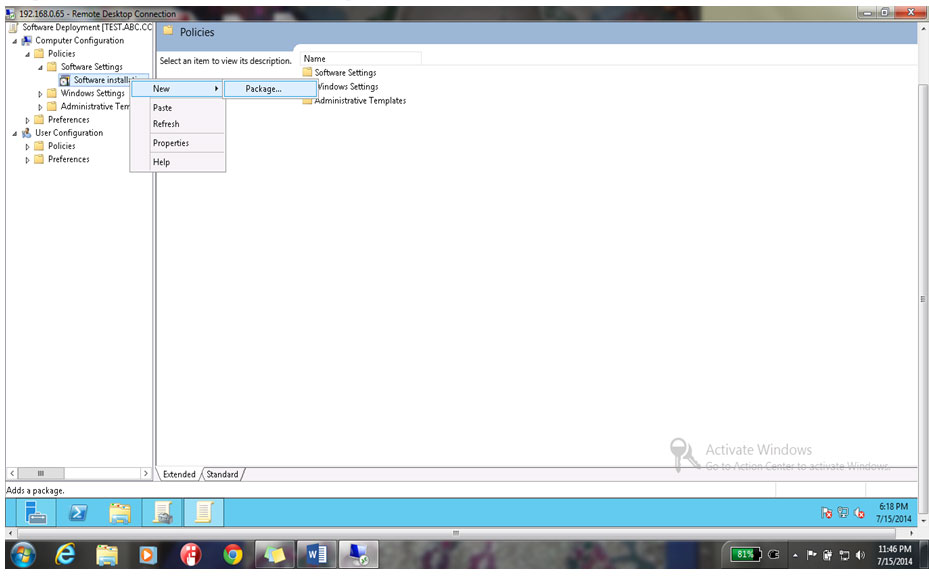
25. Select the Software by going to the location C:\ Software, Select the Software & Click on open button as shown below.
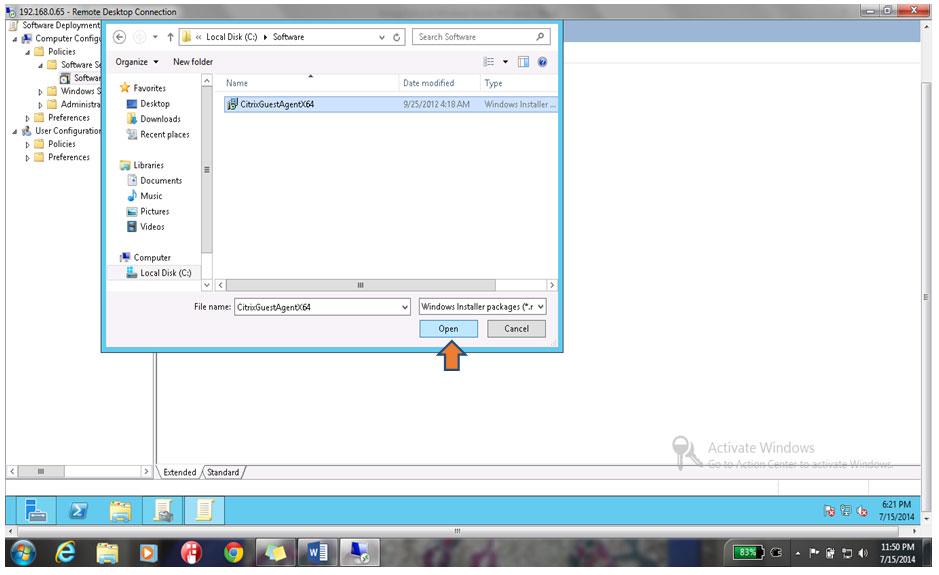
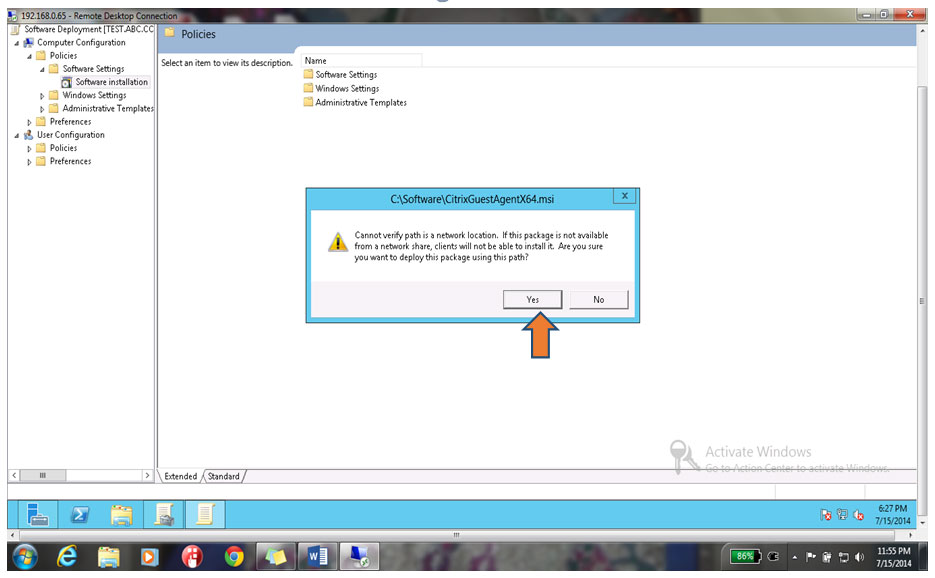
26. Click on Yes button on the Warning as shown below
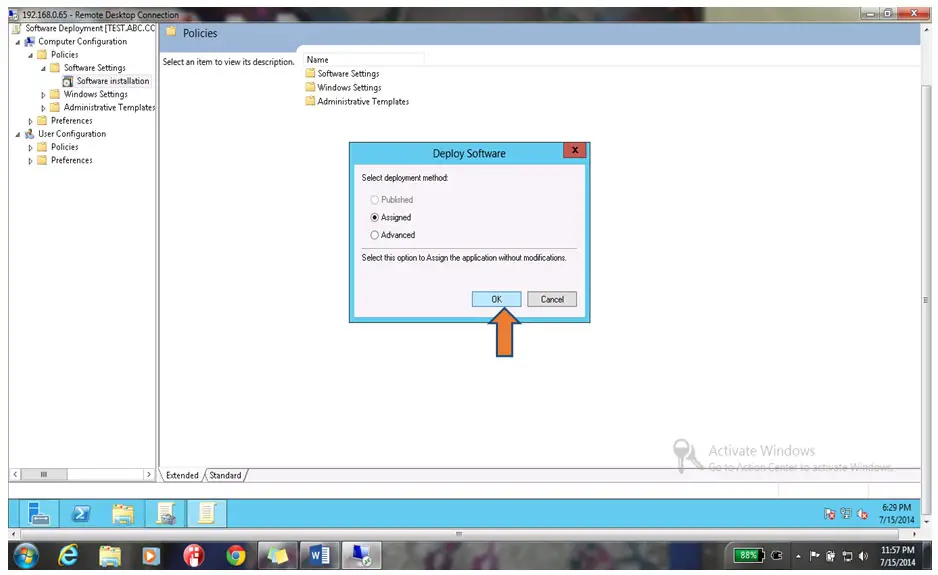
27. Select Assigned & click on Ok button as shown
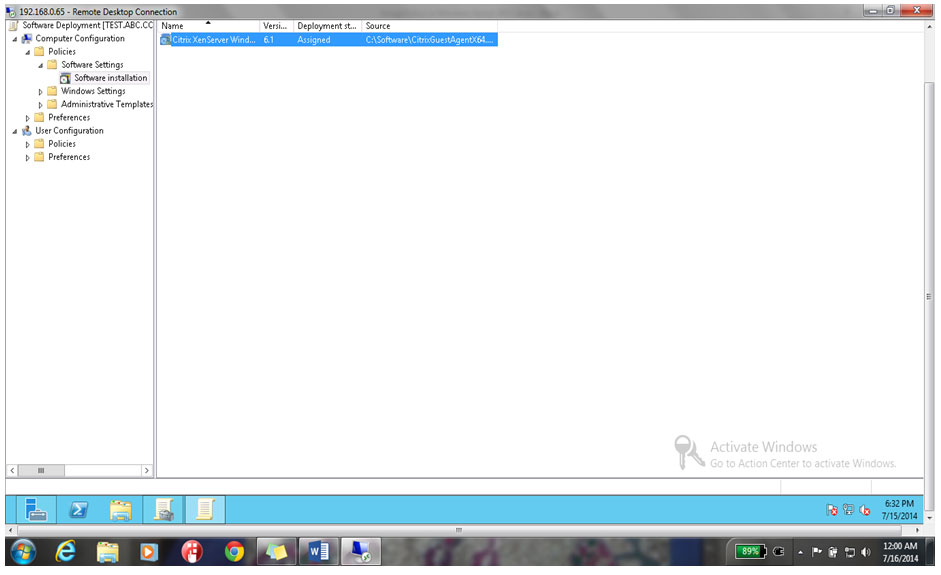
28. You can see Software Deployment Group policy has been configured on windows server 2012.
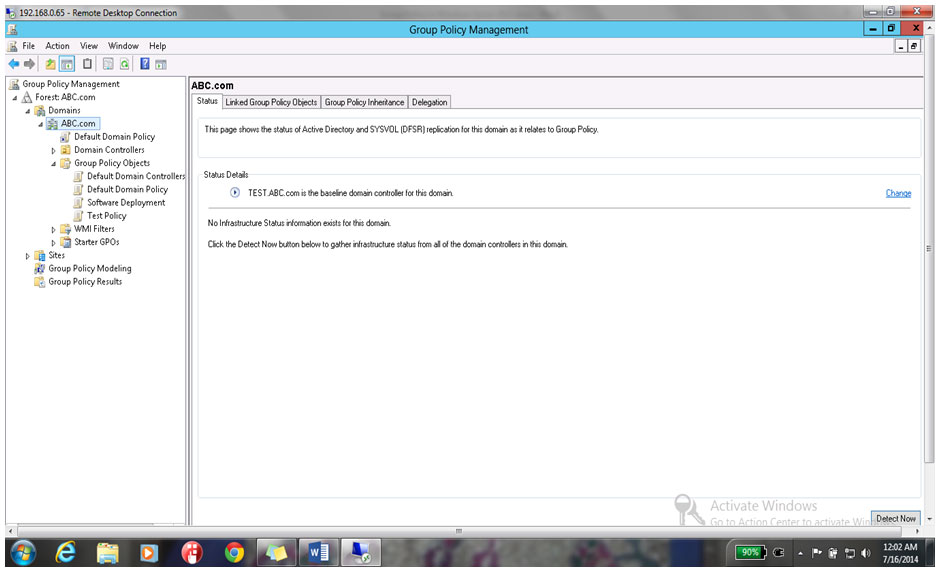
29. Close Group Policy Management editor & come back to Group Policy management Console.
30. Right Click on ABC.com & click on Linked in Exiting GPO
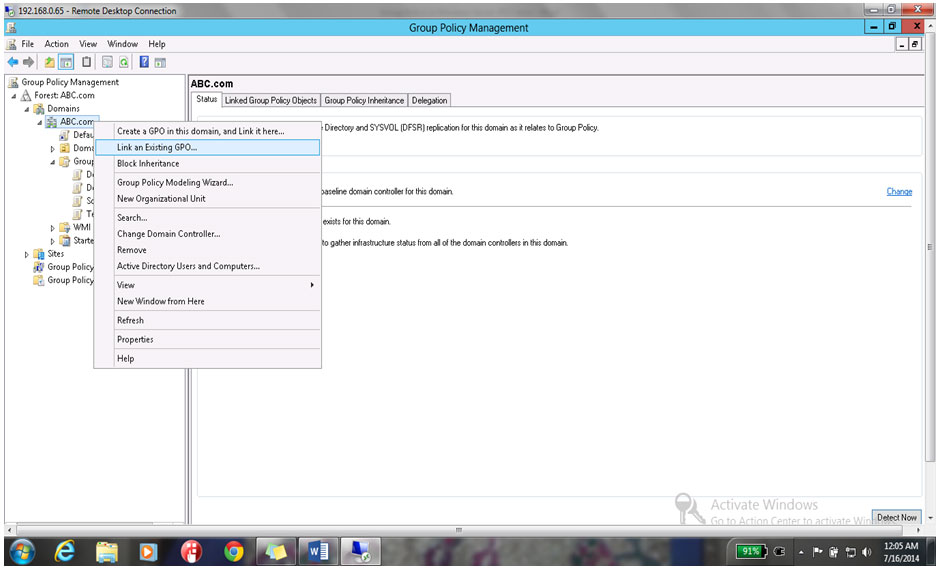
31. Select Software Deployment & click on ok as shown below
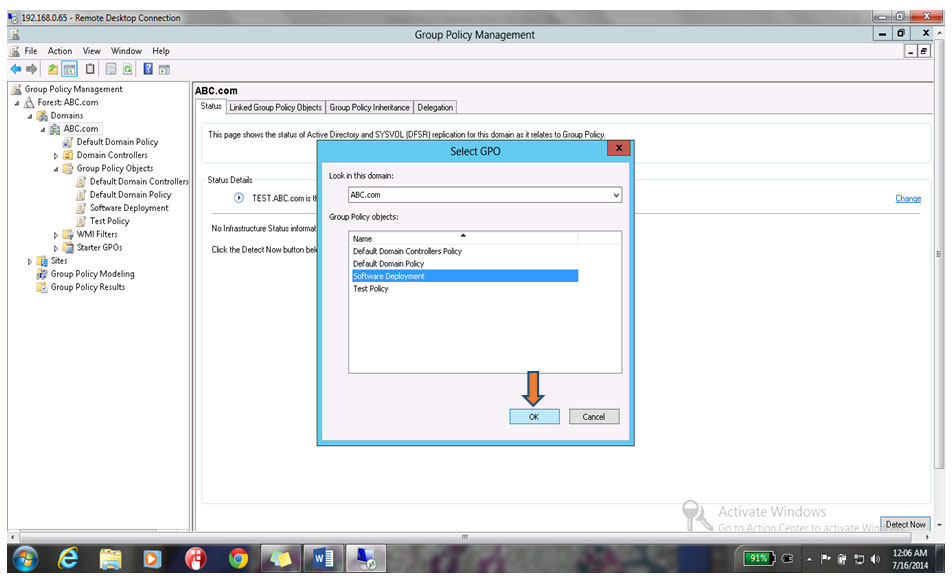
Now, close the Group policy management Console.
Read more
- Windows Server 2012 System Requirements
- Windows 2012 Server Versions
- Installing Windows Server 2012 on Virtual Cloud
- File server configuration on Windows Server 2012
- Installing Active Directory in Windows 2012 Server
- Installation and configuration of printer server and network printer on Windows 2012 Server
- How to join Computers to a Domain in Windows Server 2012
- User Creation in Active Directory Windows 2012 Server
- FTP Server Installation and Configuration on Windows Server 2012
- Disk Quota Management and Configuration on Windows Server 2012
- IIS Server Installation and Configuration on Windows Server 2012
- DHCP Server Configuration in Windows Server 2012
- VPN Server Installation and Configuration on Windows Server 2012
- DNS Server Installation and Configuration on Windows Server 2012
- Setup Shared Folder Permissions on Windows Server 2012
- WSUS Server Configuration on Windows Server 2012
Practice Exams
- MTA Practice Test
- MCSA, MCSE Practice Test
Tutorial
- MCSE Tutorial
Study Guide
- MCSE, MCSA Study Guide
Interview Questions
- MCSE and MCSA Interview Questions
- Networking Interview Questions
Resume
- MCSE Resume
- Network Administrator Resume
Microsoft provides several different tools
administrators can use to create and manage local and domain-based group
policies. The OS version the administrator is using to manage policies
determines the functionality the tools provide. As an example, when new
group policies are created using the Windows Server 2008 or greater
Group Policy Management Console, the GPO folder utilizes the new
ADMX/ADML templates, whereas the Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 tool
uploads the original ADM template files into the GPO folder.
This section details the
tools provided with Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 and later OSs to
manage local and group policies.
Group Policy Management Console
The most functional and useful tool provided
to create and manage Active Directory group policies is the Group Policy
Management Console (GPMC). The GPMC was introduced after the release of
Windows Server 2003; the functionality included with different OSs
produces different options and resulting operations when creating and
managing Active Directory group policies. This is the main tool for
managing the Group Policy infrastructure.
The GPMC is a Microsoft Management Console
(MMC) snap-in and can be added to a custom console. The GPMC snap-in
provides the most functionality for administrators who want to manage
domain group policies. The GPMC provided with Windows Server 2012 can
perform the following Group Policy administrative functions:
• Enable starter GPO functionality and create new starter GPOs
• Create new domain group policies
• Create new group policies using starter GPOs as templates
• Create and configure GPO links to sites, domains, and OUs
• View and manage GPOs in domains in the local and trusted Active Directory forests
• Back up and restore a single or all GPOs in a domain
• Back up and restore a single or all starter GPOs in a domain
• Import group policies from external
domains and migrate security settings using migration tables to ensure
proper import functionality
• Manage GPO link enforcement, enable links, and disable links
• Configure the block inheritance settings for sites, domains, and OUs
• Manage GPO status to control which nodes in a GPO are enabled or disabled
• Create and link WMI filters for GPOs
• Manage GPO security filtering
• Manage GPO delegation and administrative security
• Manage the GPO order of processing on containers with multiple GPO links
• View all configured settings of
existing group policies and any additional information, such as the
revision number, filtering, delegation, and create exported reports of
the configuration
• Check the replication status of the GPO infrastructure
• Generate HTML reports used to summarize Group Policy configurations and settings
• Run the Group
Policy Modeling Wizard to determine how group policies will be applied
to users or computers in specific containers
• Run the Group Policy Results Wizard to investigate how policies have been applied to specific computer/user objects
Group Policy Object Editor
The Group Policy Object Editor (GPOE), is the
tool used to edit local group computer and user policies. Each server
and workstation computer has a default local security policy. This
policy is accessed through the shortcut to the specific Local Security
Policy MMC snap-in located in the Administrative Tools program folder.
Now that Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and later OSs support
multiple local group policies, the GPOE must be used to manage or create
any local group policies other than the default.
The GPOE is used to edit all the configuration
settings of a policy. This includes configuring security settings,
installing software packages, creating restriction policies, defining
the scripts used by computers and users, and many other functions.
Group Policy Management Editor
To manage domain group policies, the Group
Policy Management Editor (GPME) is used and provides the same
functionality as the GPOE plus additional functionality only available
with this tool. One of the biggest differences is that the GPME includes
not only the Policy Settings node, but also the Preferences Settings
node, which is only available in domains. GPME is installed on Windows
Vista and later by downloading and installing the Remote Server
Administration Tools (RSAT) tools for the particular service pack and
OS. On Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, and Windows Server
2012 OSs, you can install the Group Policy tools from the Add Features
applet of Server Manager.
Group Policy Starter GPO Editor
The Group Policy Starter GPO Editor is used to
edit starter GPOs created by Group Policy administrators. This console
only shows the Administrative Templates nodes under the Computer
Configuration and User Configuration sections of a starter GPO. By
default, the settings available in the Administrative Templates sections
are all that can be set in a starter GPO; however, Microsoft provides
read-only starter GPOs for Windows Vista and Windows XP, but the Windows
Vista policy best practices still apply to Windows Server 2012 and
Windows 8. The Group Policy Starter GPO Editor is included with the
Windows Server 2012 Remote Server Administration Tools.
Print Management Console
First introduced with Windows Server 2003 R2,
the Print Management console is used to manage Active Directory and
local server and workstation printers. The Print Management console, shown in Figure 1,
can be used to view settings, configure drivers and options, and manage
printer and print jobs on a particular system or Active Directory-wide.
The Print Management console can also be used to deploy printers to
computers or users using the Deployed Printers node. Deploying printers
is a function that extends Group Policy functionality to allow printers
to be deployed to a predetermined set of users or computer objects to
which a GPO is linked.
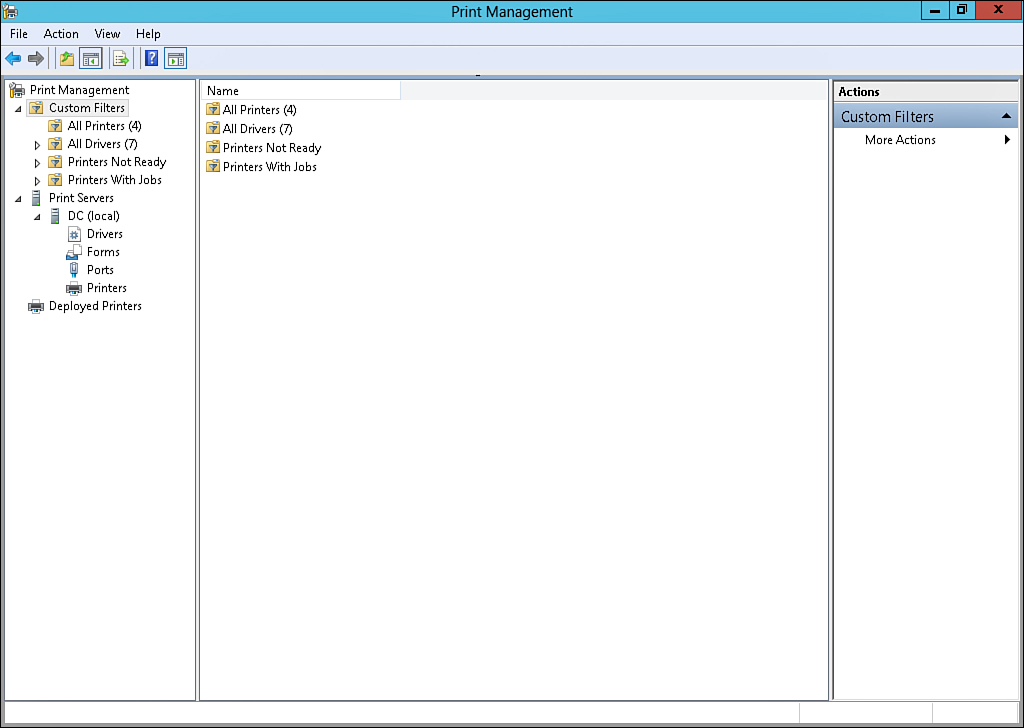
Figure 1. PRINT Management console.
The GPOE and the GPME on Windows Vista and
later include the Deployed Printers node beneath the Windows Settings
node in both the Computer Configuration and User Configuration settings
nodes. On Windows Server 2008 and later server OSs, the Print Management
console must be installed from the Server Manager Features, Add
Features link before the Deployed Printers node will be available in the
Group Policy Editor consoles. If a policy contains printers defined in
the Deployed Printers nodes, and the policy is viewed using the GPMC or
GPME on Windows XP, the deployed printers will not be viewed.
Furthermore, if the policy is opened on a Windows Server 2003 R2 server,
and if the Print Management console is not installed from Windows
components, the Deployed Printers node will not be shown. As a best
practice, only create GPOs to deploy printers using the GPMC and GPME on
Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and later OSs. To install the Print
Management console on Windows Server 2012, run the Add Features applet
from Server Manager and select the Print and Document Services Tools
from the Remote Administration Tools submenu.
Gpupdate.exe
The gpupdate.exe tool is a command-line tool
that assists administrators in troubleshooting GPO processing and
initiating GPO processing on demand. Certain sections of group policies
will only be applied at computer startup and user logon, whereas others
will be applied during these intervals and during the periodic refresh
interval. For the settings that apply during the computer startup and
user logon intervals, if network connectivity to the domain controllers
is not available during this interval, these settings might not ever be
applied. Also, remote or mobile workstations, systems that are put to
sleep or hibernated, and users logging on using cached credentials
usually do not get these policies applied. This is where the new Network
Location Awareness service for Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and
later OSs come into play; it will notify the system that a domain
controller is available and that will trigger a Group Policy refresh
cycle.
The gpupdate.exe tool enables you to apply
user and computer policies immediately. One common use of this tool is
to add the gpupdate.exe to a VPN post-connection script to allow these
settings to be applied to remote workstations that belong to the Active
Directory infrastructure. This tool provides the following options:
• gpupdate.exe /Target:{Computer | user}—This function allows the tool to process only the specified node of the group policy.
• gpupdate.exe /Force—This option reapplies all policy settings. This option does not automatically reboot the computer or log off the users.
• gpupdate.exe /Wait—This option defines how many seconds to allow GPO processing to complete. The default is 600 seconds, or 10 minutes.
• gpupdate.exe /Logoff—This option logs off the user account after GPO processing has completed.
• gpupdate.exe /Boot—This
option reboots the computer after Group Policy processing completes.
This is to apply the GPO settings that are only applied during computer
startup.
• gpupdate.exe /Sync—This
option processes GPO settings that normally only occur during computer
startup and user logon. This option requires that the administrator
designate whether the system can restart the computer or log off the
user.
