Windows Server 2008 r2, работа, служба терминалов, служба удаленных рабочих столов
Установка сервера удалённых рабочих столов
Входим на сервер с правами администратора.
Открывем «Дисппетчер сервера» -> Роли -> Добавить роль:
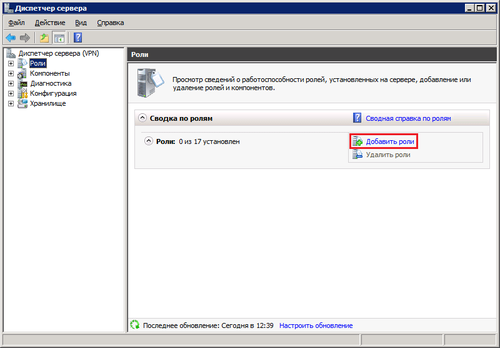
В списке доступных ролей сервера выбираем «Службы удалённых рабочих столов»:

В списке «Службы роли» отмечаем «Узел сеансов удалённых рабочих столов» и «Лицензирование удалённых рабочих столов». Этих служб достаточно для поддержания базовой функциональности.

Желательно устанавливать сервер терминалов до установки пользовательских приложений.
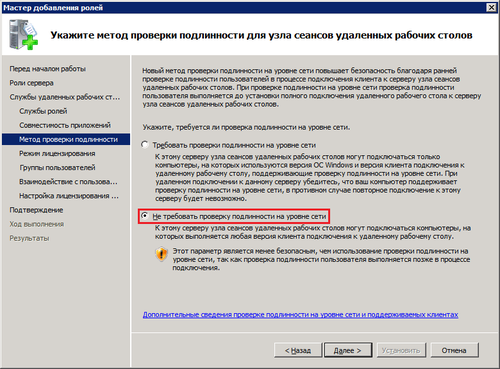
Метод проверки подлинности. «Требовать проверку подлинности на уровне сети» — эта опция обеспечивает повышенную безопасность, но в этом режиме к серверу не смогут подключаться пользователи с устаревшими клиентами (rdp 5.х и ниже), а также пользователи подключающиеся через Эксплорер (remote desktop web connection). Чтобы обеспечить поддержку клиентов всех версий, выбирайте опцию «Не требовать проверку подлинности на уровне сети».
Режим лицензирования. Желательно заранее определиться с режимом лицензирования: «на пользователя» или «на устройство». Лицензии «на пользователя» эффективны, если в организации большое количество мобильных пользователей, которым требуется доступ к серверу как из корпоративной сети, так и из удаленной (дом, другой офис). Лицензии «на устройство» эффективны, если пользователи жестко привязаны к своим рабочим местам.

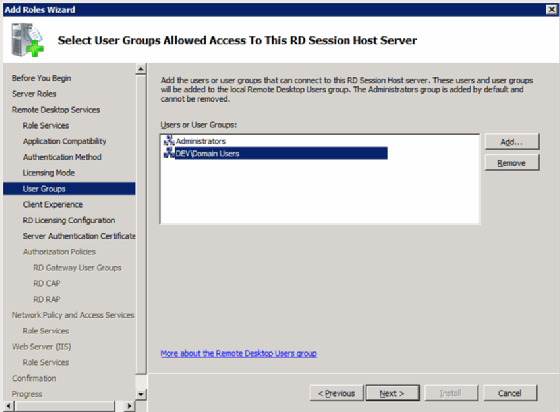
Группы пользователей. Здесь вы можете сразу указать группы или отдельных пользователей, которым будет разрешен доступ к серверу терминалов. Это можно будет сделать и позднее, просто добавив нужных пользователей в группу «Пользователи удаленного рабочего стола».

Настройка сервера лицензий Windows Server 2008 r2. Если сервер не входит в домен, то вариантов особо нет:

Обзор выбранных опций перед установкой.
Далее нажимаем кнопку Установить. Система один раз перезагрузится, после чего установка будет продолжена. В итоге вы должны увидеть жизнеутверждающий экран «Установка прошла успешно»
Активация сервера терминалов
Открываем Пуск -> Администрирование -> Службы удалённых рабочих столов -> «Диспетчер лицензирования удалённых рабочих столов». В списке выбираем сервер лицензий. Делаем правый клик, и в меню выбираем пункт «Активировать сервер»:

Запускается мастер активации сервера Windows Server 2008 r2
На следующем шаге выбираем метод подключения. Можно смело выбирать «Автоподключение»:
Сведения об организации. Вводим имя, фамилию и название организации
Дополнительные сведения. Можно заполнить, а можно и проигнорировать
Через несколько секунд ваш сервер будет успешно активирован
Теперь можно преступить к установке лицензий. Следует отметить, что после активации сервера лицензий нет необходимости сразу покупать и устанавливать лицензии. При отсутствии полноценных лицензий сервер работает в демо-режиме. Пользователям выдаются временные лицензии на 120 дней.
Установка лицензий
Запускаем мастер установки лицензий. Это можно сделать сразу после активации сервера лицензий, выбрав соответствующую опцию
Далее выбираем тип соглашения. В моем случае это «Enterprise Agreement». Номер соглашения можно найти в поисковике по запросу «Enrollment Number». Например, работают: 4965437 (3325596;6565792;4526017;5296992)

Выбираем версию продукта, тип лицензии (должен совпадать с ранее выбранным типом лицензий сервера лицензий), количество лицензий

Нажимаем Далее. Если данные верны, лицензии будут успешно установлены.
Попутные вопросы:
Как разрешить новому пользователю доступ к удаленному рабочему столу?
Откройте Диспетчер сервера -> Конфигурация -> Локальные пользователи -> Пользователи. Откройте свойства пользователя, которому необходим доступ, закладка «Членство в группах». Добавьте группу «Пользователи удаленного рабочего стола»:

Можно ли под одним аккаунтом создать несколько независимых сеансов подключения?
Можно, но по умолчанию эта опция отключена (для экономии ресурсов). Откройте Диспетчер сервера -> Роли -> Конфигурация служб терминалов -> Изменить настройки (на той же странице). Двойной клик на опции открывает окно, где можно выполнить изменения:

Какой порт использует RDP по умолчанию и как его изменить?>
По умолчанию используется порт TCP 3389. Изменить его можно отредактировав реестр. Откройте ветку
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\WinStations\RDP-tcp
и измените параметр PortNumber.
Взято отсюда
На нашем сайте Вы можете взять в аренду Windows VPS.
Вы можете включить удаленный рабочий стол, выполнив следующие действия:
-
Подключиться к VPS через VNC клиент (Для этого перейдите в панели управления VMmanager на страницу «Виртуальные машины» (категория «Управления» левого меню), выберите необходимую вам VPS и нажмите кнопку «VNC» в центральном верхнем меню).
-
Нажать Start(Пуск), щелкнуть правой кнопкой по Computer (Мой компьютер) и в выпадающем меню выбрать Properties (Свойства):
-
В появившемся окне выбрать вкладку Remote Settings:
-
В появившемся окне выбрать пункт Allow connections from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure):
-
Нажать «OK» в информационном окне, которое предупреждает, что исключения для удаленного рабочего стола в firewall включены и вы можете поменять настройки firewall, используя Firewall tool:
-
Нажать «Appaly» для применения настроек:
Теперь вы можете подключиться к VPS через удаленный рабочий стол.
Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Services Virtual Desktop Infrastructure product offers a lot of benefits, but not every IT administrator knows where to start.
As a virtual desktop administrator, you should learn the ins and outs of this VDI product to make the most of it. Learn step by step how to get Remote Desktop Services (RDS) and some of the basic RDS components up and running.
Step 1: Begin the installation
Launch Server Manager and select Server Roles. Once the roles manager screen is up, check the box for Remote Desktop Services. Some other boxes may already be checked, but this is fine — the only box you need to worry about for this step is the Remote Desktop Services box. Click the next button in the bottom right corner to proceed.
Now you should see an introduction to RDS. Select the next button at the bottom of the page.
Step 2: Select Remote Desktop Services roles you want to install
RDS includes several components and settings (Figure 1). These components can be on one machine or many.
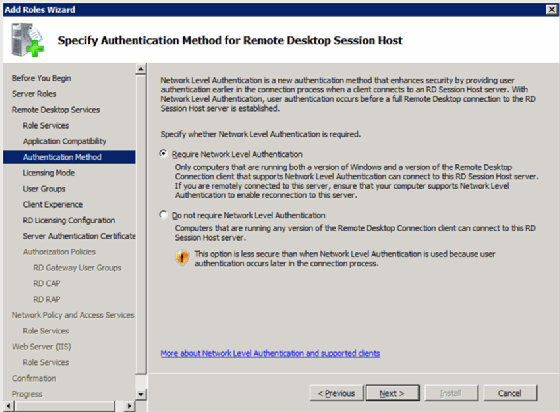
- Remote Desktop Session Host. This is the name for Terminal Server.
- Remote Desktop Virtualization Host. This component integrates with Microsoft Client Hyper-V. This allows for the pooling of virtual machines on Hyper-V so they can serve as virtual desktops.
- Remote Desktop Connection Broker. This component bridges the user with a virtual Windows desktop, remote application or Remote Desktop Session Host session.
- Remote Desktop Licensing. This is the modern name of Terminal Server licensing server that also includes licensing for Windows Server.
- Remote Desktop Gateway. This provides a single connection point for clients to connect to a specific virtual desktop, remote app or Remote Desktop Session Host session.
- Remote Desktop Web Access. This provides clients an interface to access their virtual desktop, remote app or Remote Desktop Session Host sessions.
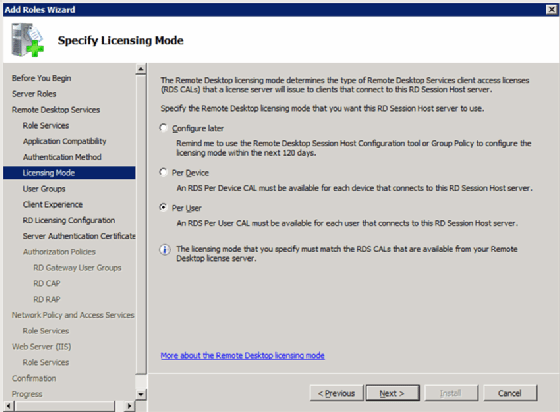
Step 3: Pick the license mode
As with past Terminal Server licensing, there are two license options: per-device and per-user (Figure 2).
Step 4: Allow access to Remote Desktop Session Host (not required)
Select which users to grant access to the local Remote Desktop Session Host. This server component is not required for RDS to work. If you choose to install the Remote Desktop Session Host, you will get this prompt (Figure 3).
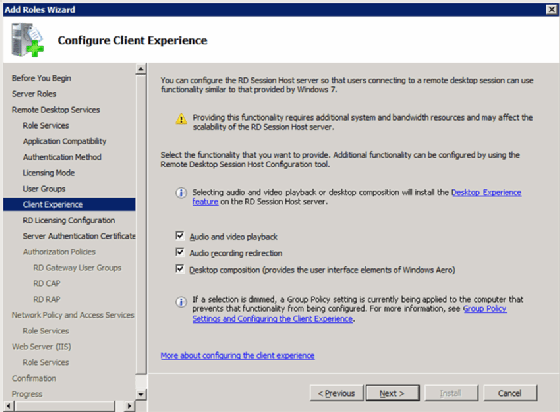
Step 5: Configure the client experience
The next screen is called Configure Client Experience (Figure 4). This is where you set the defaults for the end-user experience with the VDI system and remote desktop.
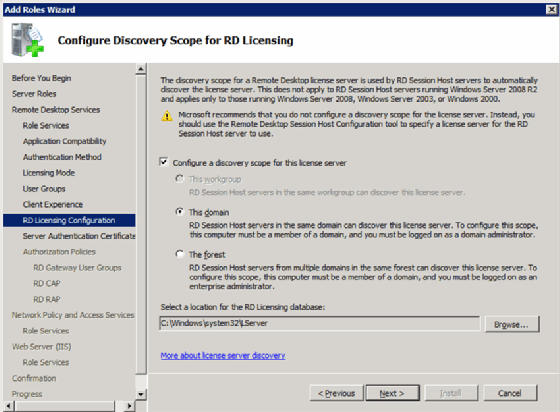
Step 6: Configure license scope
Just as with Terminal Server of the past, you can configure the scope of the Remote Desktop Session Host license server. You have the following two options:
- Domain. This limits the licensing to only servers in the domain (Figure 5).
- Active Directory Forest. This allows any Remote Desktop Session Host server in the Active Directory Forest — the highest-level container in a set of servers — to attain a license.
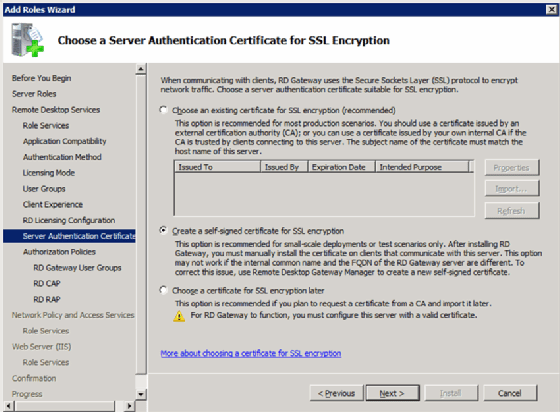
Step 7: Assigning the SSL certificate for Remote Desktop Gateway
The Remote Desktop Gateway uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to tunnel and encrypt traffic from the client. This functionality requires a certificate. There are two options for certificates:
- Specify a certificate from the certificate store.
- Produce a self-signed certificate.
In either case, the client must trust the certificate (Figure 6).
Step 8: Configure network access protection (optional)
These next few screens go beyond the scope of RDS but are related, so this article will just cover the basics.
Create authorization policies
This is where you would configure a policy that states who is allowed to establish a desktop connection to the Remote Desktop Gateway
(Figure 7).
Install and configure network access and protection policies
You can use this to configure and enforce network access policies such as Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) and network access protection from the client (Figure 8).
You can also use this feature to define different policies based on users’ connectivity (Figure 9).
Step 9: Install IIS and Remote Desktop Web Access
Remote Desktop Web Access requires Internet Information Services (IIS), so the next two screens are for installing and configuring IIS. First, there is the overview screen (Figure 10).
The second screen is the configuration screen (Figure 11).
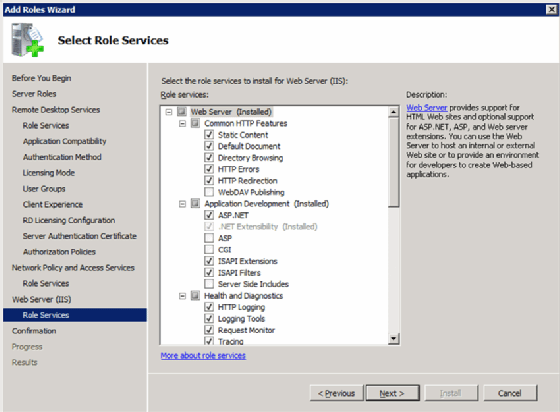
Step 10: The final steps
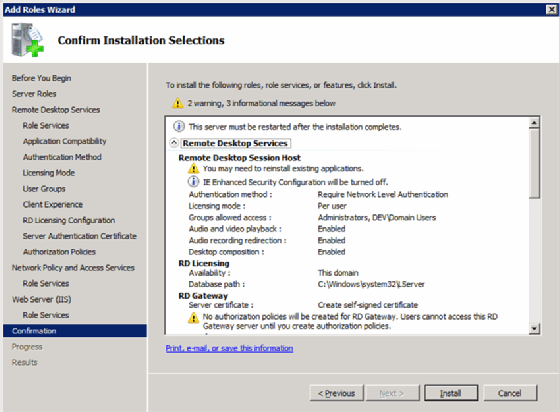
At this point, you’re done. The last two screens just let you know what you’re installing (Figure 12).
There is also the final screen that lets you know whether any additional steps like rebooting are required (Figure 13).
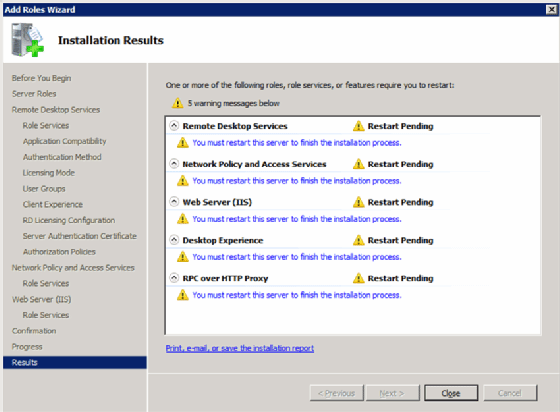
Now that you have installed and configured RDS, you can start using Remote Desktop Session Host and Remote Desktop Gateway Manager.
Remote Desktop is a useful feature that allows users to access their Windows Server 2008 R2 system from another computer. This can be particularly helpful for IT administrators or individuals who need to manage their server remotely. If you’re wondering how to enable Remote Desktop on your Windows Server 2008 R2, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open the Start menu on your server and click on «Control Panel.«
Step 2: In the Control Panel window, select «System and Security.«
Step 3: Under the System and Security section, click on «System.«
Step 4: In the System window, select «Remote settings» from the left sidebar.
Step 5: In the System Properties window that opens, navigate to the «Remote» tab.
Step 6: In the Remote tab, you will find two options: «Allow connections from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)» and «Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (more secure).» Choose the option that best suits your security requirements.
Step 7: Click on «Apply» and then «OK» to save your changes.
Now that you have enabled Remote Desktop on your Windows Server 2008 R2, you can access it remotely using a Remote Desktop client from another computer on the same network or through the internet. Simply launch the Remote Desktop client, enter the IP address or hostname of the server, and provide your credentials to establish a connection.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. Allows remote management of Windows Server 2008 R2, providing flexibility and convenience. | 1. Potential security risks if not configured properly or accessed from untrusted devices. |
| 2. Provides access to server resources and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. | 2. Requires a stable and reliable network connection for optimal performance. |
| 3. Helps streamline server administration and troubleshooting tasks. | 3. May require additional configuration and firewall settings to allow remote connections. |
Enabling Remote Desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 can greatly enhance your ability to manage and access your server remotely. However, it is important to ensure that proper security measures are in place to protect your system from unauthorized access. Consider configuring firewall settings and utilizing strong passwords to maintain the security of your remote connections.
Video Tutorial:How to enable RDP via command line?
How to install RSAT on Windows Server 2008 R2?
Installing RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tools) on Windows Server 2008 R2 is a straightforward process. Here are the steps:
1. Verify the compatibility: Before proceeding with the installation, ensure that your system meets the requirements to run RSAT. Make sure you have administrative rights and that your server is running Windows Server 2008 R2.
2. Download RSAT: Visit the Microsoft Download Center website and search for «Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows Server 2008 R2.» Locate the appropriate version, either 32-bit or 64-bit, depending on your system architecture. Download the RSAT package.
3. Run the installer: Once the download is complete, navigate to the download location and run the installer. The installation wizard will open.
4. Select the desired tools: In the installation wizard, you’ll be presented with a list of available tools. Choose the specific tools within RSAT that you want to install. You can select multiple tools by holding the Ctrl key while clicking.
5. Complete the installation: After selecting the desired tools, click on the «Install» button to begin the installation process. The installer will extract and install the selected tools on your system.
6. Configure RSAT: Once the installation is complete, you need to configure RSAT to enable and access the installed tools. This involves navigating to the «Control Panel» and finding the «Programs» section. Locate the «Turn Windows features on or off» option and click on it.
7. Enable RSAT features: In the «Windows Features» dialog box, scroll down to find the «Remote Server Administration Tools» section. Expand it to reveal more options. Check the box corresponding to the specific tools you installed in step 4. Click «OK.«
8. Restart if necessary: In some cases, enabling or disabling certain Windows features may prompt a system restart. If required, restart your server to apply the changes and make the RSAT tools accessible.
9. Access RSAT: Once the server restarts (if necessary), you can access the RSAT tools by searching for them in the Start Menu or from the Administrative Tools folder. Each tool will have its own interface and usage instructions.
Remember to refer to official documentation, such as Microsoft’s documentation for RSAT, for more detailed steps or troubleshooting guidance if needed.
To enable Windows Server Remote Desktop, follow these steps:
1. Log in to your Windows Server using an administrative account.
2. Click on the «Start» menu and type «Remote Desktop» in the search bar.
3. In the search results, click on the «Remote Desktop Connection» application to open it.
4. In the Remote Desktop Connection window, type the name or IP address of the server you want to connect to in the «Computer» field.
5. Click on the «Show Options» button to expand additional settings.
6. In the expanded options, you can configure settings like display, local resources, and experience. Make the necessary adjustments based on your preferences or requirements.
7. Once you’ve made the appropriate settings, click on the «Connect» button to start the remote desktop session.
8. If it’s your first time connecting to the server, you may be prompted to verify the server’s identity or enter your credentials. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the connection.
9. After successful authentication, you should now have remote access to the Windows Server desktop.
Please note that enabling Remote Desktop on a Windows Server may have security implications, so it’s vital to ensure proper security measures are in place, such as strong passwords, firewall configurations, and limiting access to authorized users. It’s also recommended to keep your server and Remote Desktop client software up to date to mitigate potential risks.
How to run as administrator command line Windows Server 2008 R2?
Running commands as an administrator on Windows Server 2008 R2 allows users to perform administrative tasks and make system-level changes. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Launch the Command Prompt: Click on the «Start» button, type «cmd» in the search box, and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
2. Run as administrator: Right-click on the Command Prompt icon in the search results and select «Run as administrator.» If prompted for permission, click «Yes.«
3. User Account Control (UAC) prompt: If UAC is enabled, a prompt may appear asking for confirmation to run the Command Prompt as an administrator. Click «Yes» to continue.
4. Elevated Command Prompt: After successfully running Command Prompt as an administrator, the title bar of the Command Prompt window should display «Administrator: Command Prompt» to indicate that you have elevated privileges.
5. Execute commands: You can now run any command that requires administrative privileges. Simply type the desired command and press Enter to execute it.
Note: Exercise caution while running commands as an administrator, as system-level changes can affect the stability and performance of the Windows Server if not executed correctly. It’s advisable to have a good understanding of the commands you intend to run and their potential impact on the system.
It’s important to keep in mind that this answer is written as a tech blogger and not as an technical blogger.
How to check Remote Desktop users in Windows Server 2008?
To check Remote Desktop users in Windows Server 2008, you can follow these steps:
1. Open the «Start» menu and go to «Administrative Tools» and then select «Remote Desktop Services.«
2. Under «Remote Desktop Services,» choose «Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration.«
3. In the console tree, expand the «Connections» folder.
4. Right-click on the name of your RDP connection (e.g., «RDP-Tcp«) and select «Properties.«
5. In the «Properties» window, go to the «Permissions» tab.
6. Here, you can see the list of users who have permissions to connect through Remote Desktop to your Windows Server 2008.
7. You can further modify the permissions by clicking the «Advanced» button and selecting «Advanced Permissions.«
Please note that these steps are specifically for Windows Server 2008, and the process may vary slightly on different Windows Server versions.
How to enable Remote Desktop in Windows Server 2008?
To enable Remote Desktop in Windows Server 2008, you can follow the steps below:
1. Open the Start menu and go to «Control Panel«.
2. In the Control Panel, click on «System and Security» or «System and Maintenance» depending on your Control Panel view.
3. In the new window, find and click on «System«. This will open the System Properties.
4. In the System Properties window, click on the «Remote settings» link on the left-hand side. This will open the Remote tab.
5. Under the Remote Desktop section, you will see two options: «Don’t allow connections to this computer» and «Allow connections from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)«. Select the second option if you want to allow remote connections.
6. If you want to restrict remote connections to specific users, click on the «Select Users» button and add the desired users to the list.
7. Click «OK» to save the changes.
8. If you have a firewall enabled, make sure to allow Remote Desktop connections through the firewall. Check your firewall settings or consult the Windows Server 2008 documentation for specific instructions on how to do this.
After applying these steps, Remote Desktop should be enabled on your Windows Server 2008. You can now access the server remotely using a Remote Desktop client.
How do I enable remote management in Windows Server 2008 R2?
Enabling remote management in Windows Server 2008 R2 involves several steps. Here’s how you can accomplish it:
1. Launch Server Manager: Log in to the Windows Server 2008 R2 machine, click on the Start button, and open the Server Manager console.
2. Add the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) feature: In the Server Manager window, click on the «Features» section in the left-hand pane. Then, click on the «Add Features» link in the main pane. A new window will open, and you need to select the «Remote Server Administration Tools» checkbox. Click «Next» to proceed.
3. Select the desired remote management tools: In the Remote Server Administration Tools window, expand the «Role Administration Tools» section and then expand the «AD DS and AD LDS Tools» option. Here, you can select the specific tools you want to enable for remote management, such as «Active Directory Administrative Center» or «Group Policy Management.» Once you’ve made your selections, click «Next.«
4. Confirm the installation selections: Review the summary of your installation selections and click «Install» to begin the installation process. The required files and features will be downloaded and installed on your Windows Server machine.
5. Enable remote management: After the installation completes, return to the Server Manager window, and in the left-hand pane, expand the «Configuration» section and select «Local Server.» In the main pane, locate the «Remote Management» option and click on the disabled status.
6. Configure remote management settings: A new window called «System Properties» will open. Click on the «Remote» tab and select the checkbox labeled «Allow remote connections to this computer.» You can also choose to enable remote management settings for specific users or groups by clicking on the «Select Users» button.
7. Firewall configuration: By default, the Windows Firewall blocks remote management connections. To allow remote management connections, you need to configure the firewall to permit them. In the Server Manager window, click on «Configuration» in the left-hand pane, and then select «Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.» From there, you can create inbound and outbound rules to allow remote management traffic.
8. Test remote management: Once you’ve completed the above steps, you can test remote management by connecting to the Windows Server 2008 R2 machine from another computer using remote management tools like Windows PowerShell or Remote Desktop.
It’s important to note that these instructions assume you have administrative access to the Windows Server 2008 R2 machine and are familiar with basic Windows Server administration concepts. Additionally, ensure that remote management is in compliance with your organization’s security policies and guidelines.
В данной статье мы рассмотрим самые начальные настройки Windows Server 2008 R2, данные настройки подходят для любой редакции (Standard, Enterprise и т.п). Мы рассмотрим самые популярные настройки, которые подходят для большинства задач, для которых устанавливают Windows Server. Это настройка сети, DNS, DHCP, настройка удаленных рабочих столов (RDP) и добавление пользователей.
Ознакомиться с процессом установки и активации Windows Server 2008 R2 можете в нашей прошлой статье.
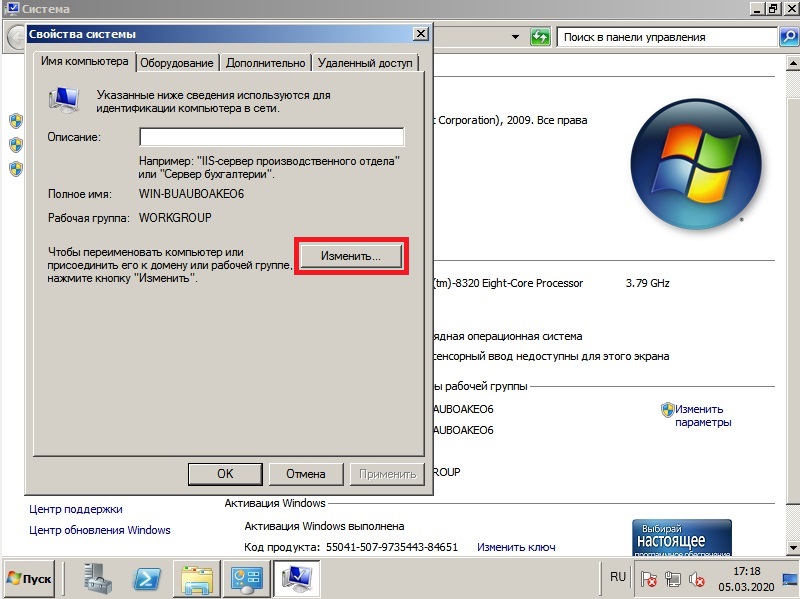
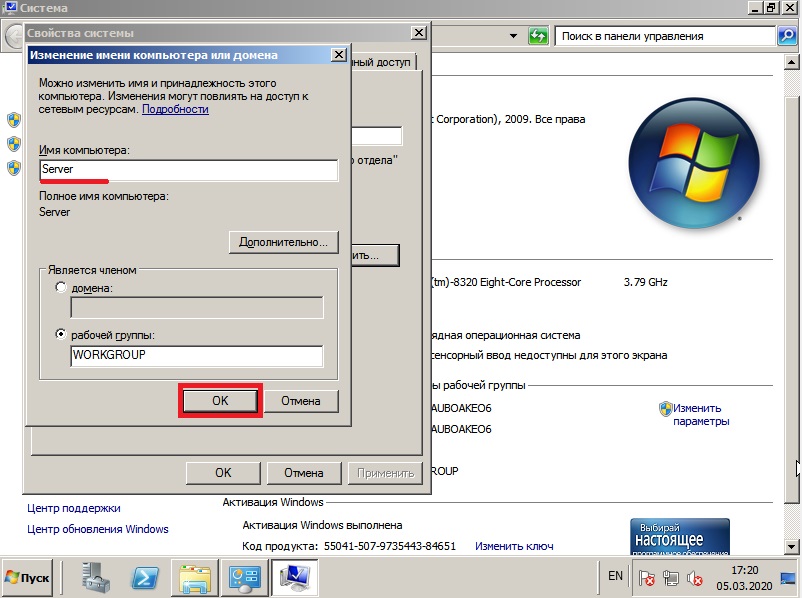
1) Итак, первым делом, нам нужно сменить имя сервера на свой, для более удобного его обозначения. Заходим в меню «Свойства» компьютера => Изменить параметры => В меню «Свойства системы» нажимаем кнопку «Изменить». Далее вводим в поле «Имя компьютера» свое желаемое наименование Вашего сервера. И нажимаем «ОК», Ваш компьютер должен перезагрузиться для применения параметров.
2) Теперь нам нужно задать серверу статический локальный IP адрес. К примеру если у Вас сервер присоединен к маршрутизатору (роутеру), то IP адрес выданный Вашим роутером можете проверить через терминал, путем нажатия кнопки «Выполнить» => CMD => В в ответе командной строки можете посмотреть Ваш локальный IP.
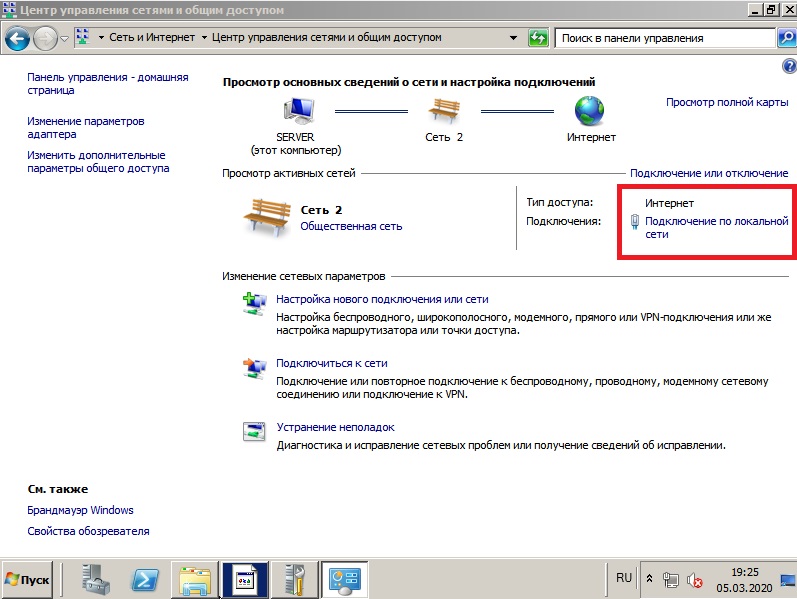
Далее заходим в «Панель управления» => Сеть и интернет => Центр управления сетями и общим доступом => Подключение по локальной сети.
Выбираете Вашу сетевую карту => Свойства.
IPv4 => Свойства
Теперь задаете Ваш локальный IP адрес. После применения настроек проверьте доступ в интернет, чтобы убедиться, что все сделано правильно.

3) Теперь приступим к установке ролей. Заходим в диспетчер серверов, нажимаем на пункт «Роли» => Добавить роли.
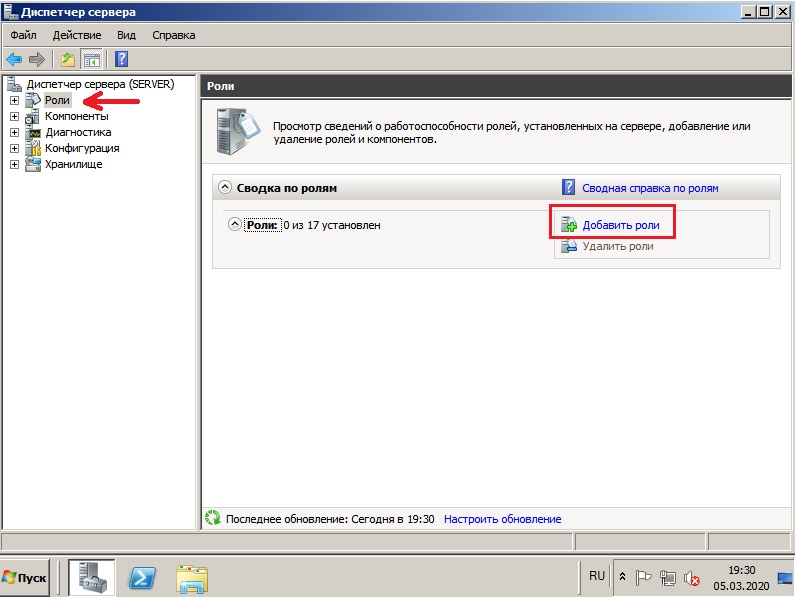
Здесь выбираем то, что для Вас нужно именно в работе сервера, большинство настроек ролей задаются сразу из установки роли. Поэтому мы рассмотрим варианты в случае когда определенная роль устанавливается, или пропускается. На примере мы установим DHCP сервер и зададим ему диапазон IP адресов для раздачи в локальную сеть, зададим домен и службы удаленных рабочих столов.
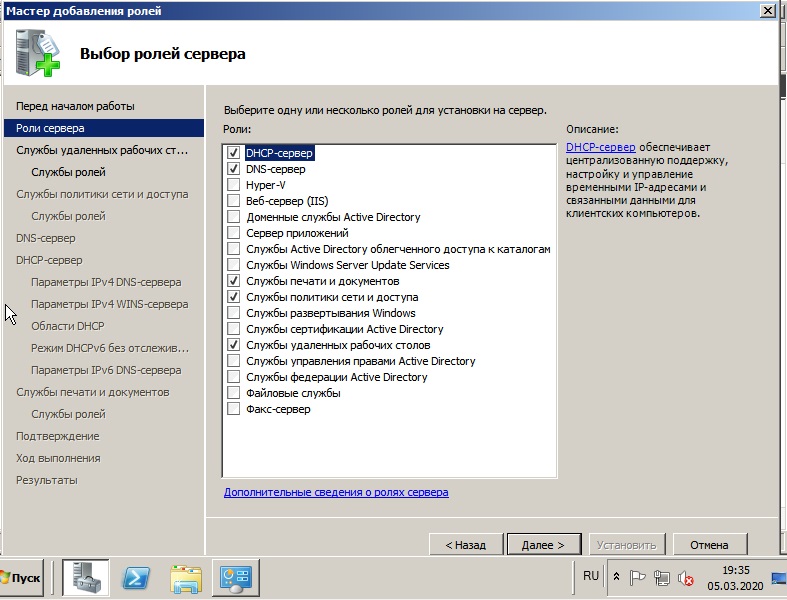
В службах ролей выбираем пункты для работоспособности RDP.
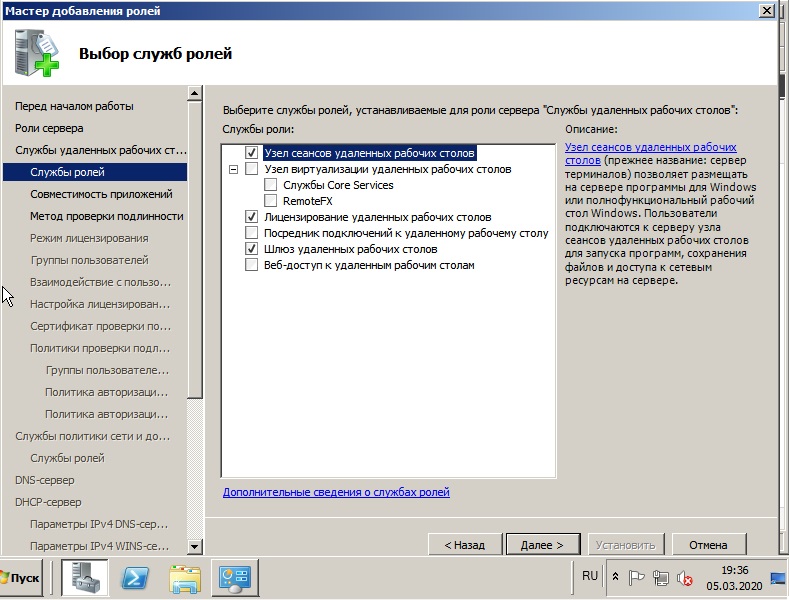
Если у Вас нет SSL сертификата, нажимаете «Не требовать проверку …».
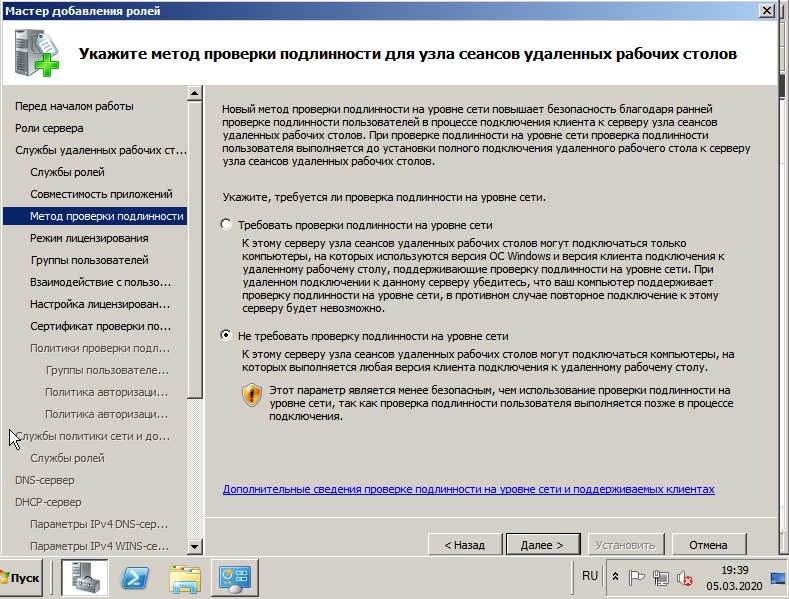
Здесь нужно выбрать пункт в зависимости от Вашего ключа активации для лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов. На устройство, или на пользователя. Их настройка ничем не отличается друг от друга, разница лишь в том, какой ключ Вы будете вводить. Если Вы пока не уверены в способе лицензирования можете выбрать «Настроить позже» к настройкам RDP мы вернемся чуть позже. А так же, если у Вас нет ключа для лицензирования RDP, то приобрести ключ активации Windows Server CAL на 20 пользователей можете в нашем каталоге.
Пропускаем пункт сертификатов.
В меню «Взаимодействие с пользователями разрешаем аудио и видео.
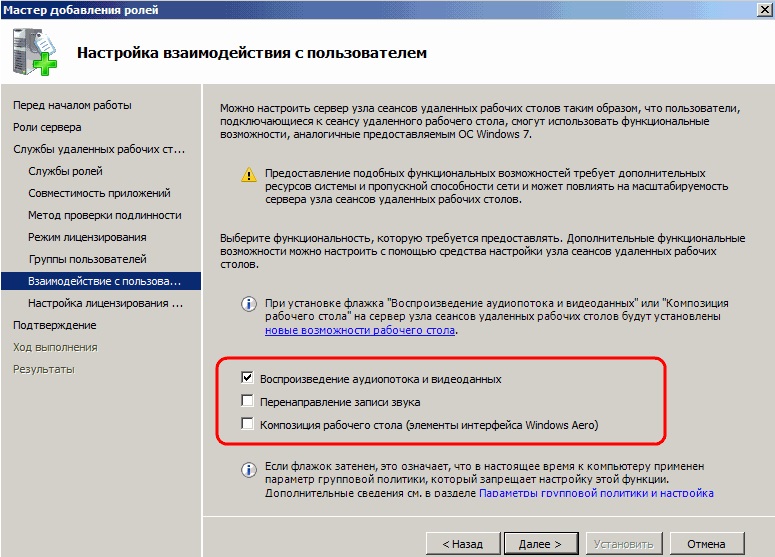
Доходим до параметров DHCP, указываете в нем названием Вашего домена, и Ваш локальный IP адрес для подключениям к данному DNS.
Теперь добавим области (диапазоны) DHCP.
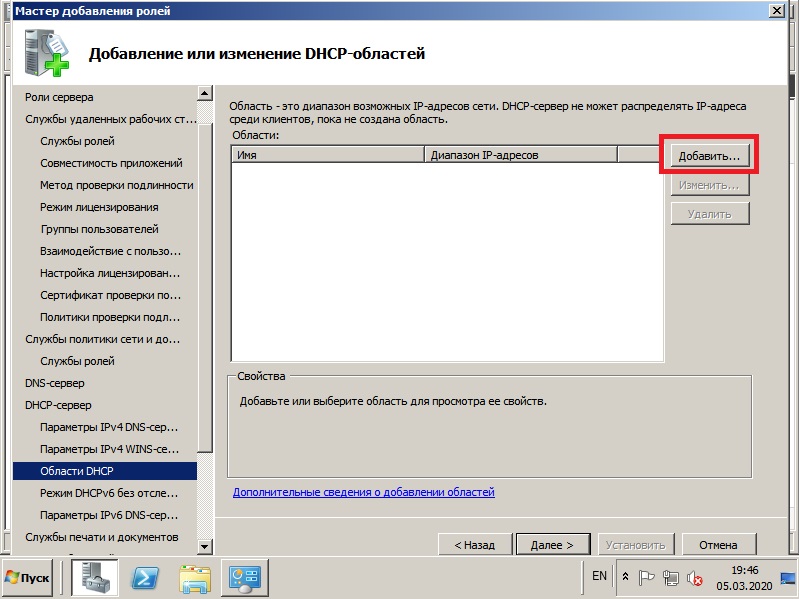
Задайте имя для Вашего DHCP сервера, начальный IP адрес и конечный, который будет раздавать Ваш сервер.
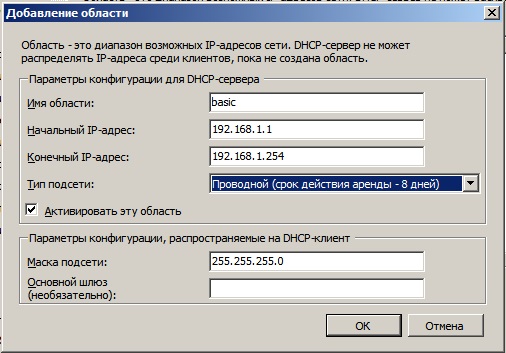
Отключаем IPv6
Если Вы в установке ролей выбрали службу печати (если она Вам нужна), то установке служб так же выбираете «Сервер печати».
Доходим до подтверждения и устанавливаем роли.
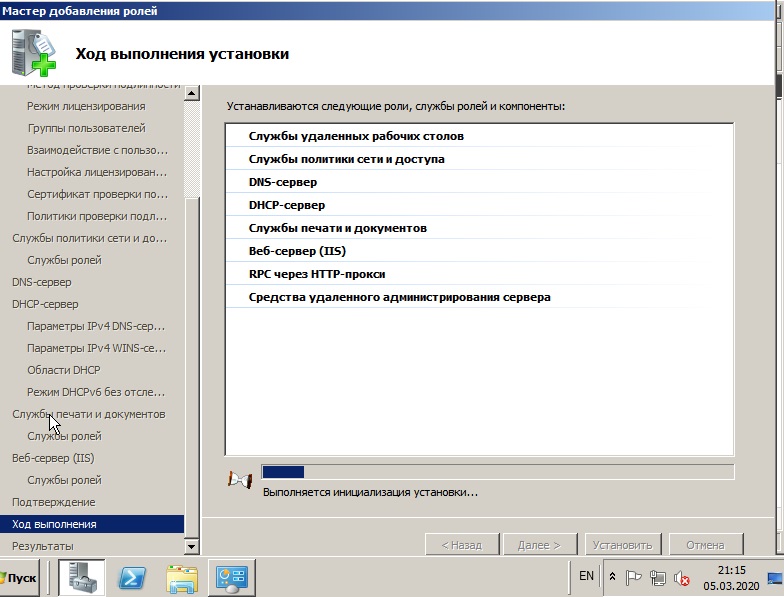
После установки ролей необходимо перезагрузиться.
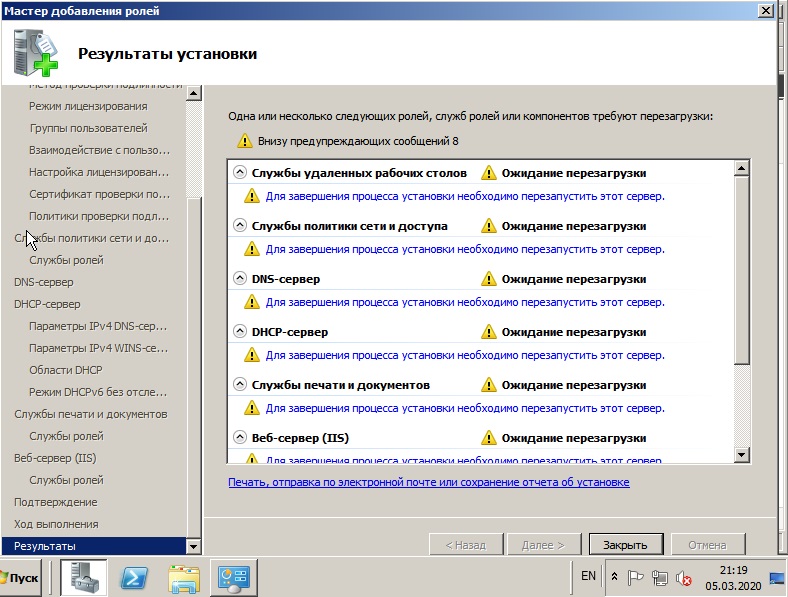
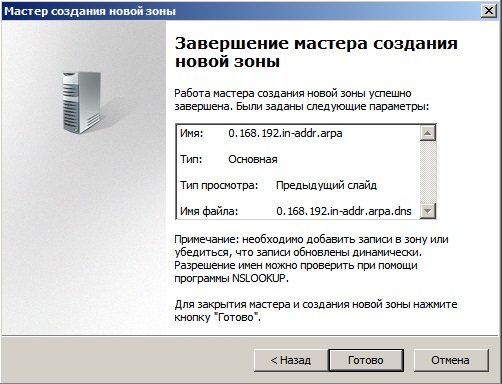
4) Теперь настроим DNS (домен). Открываем дерево «Диспетчер сервера» => DNS-сервер => DNS => Ваше имя сервера (в нашем случае «Server») => Глобальные журналы => Зоны обратного просмотра => Создать новую зону.
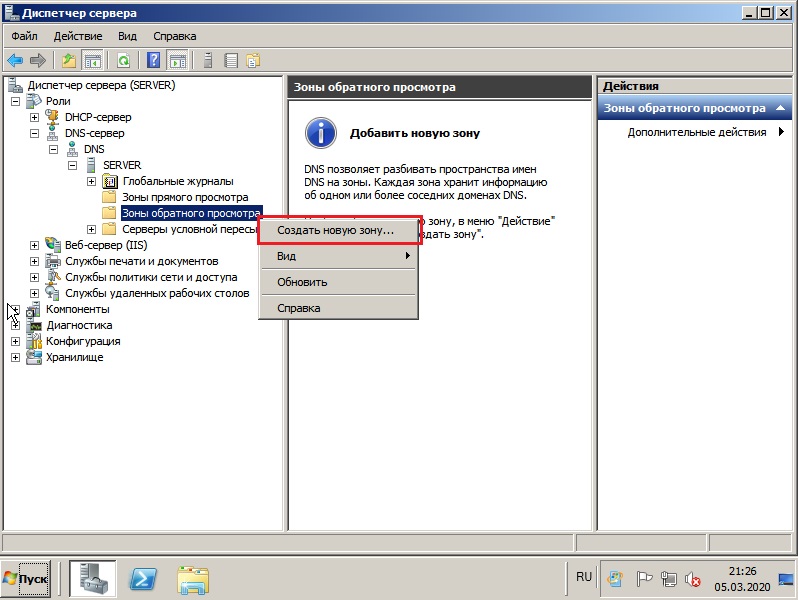
Выбираем пункт «Основная зона».
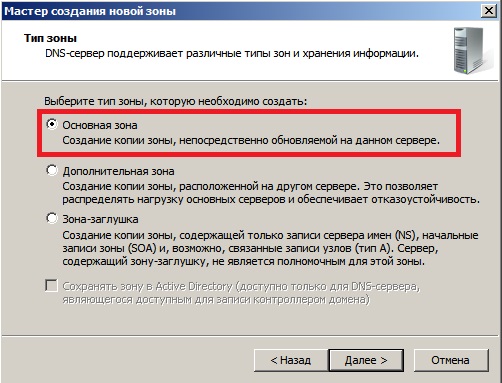
Зона обратного просмотра IPv4.
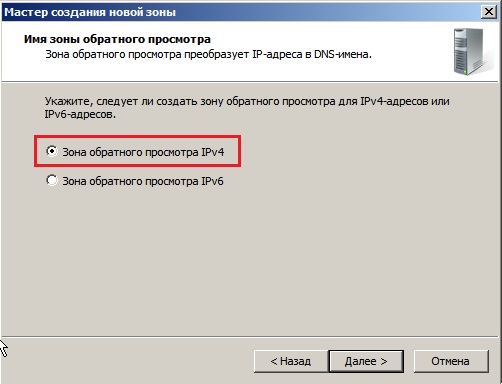
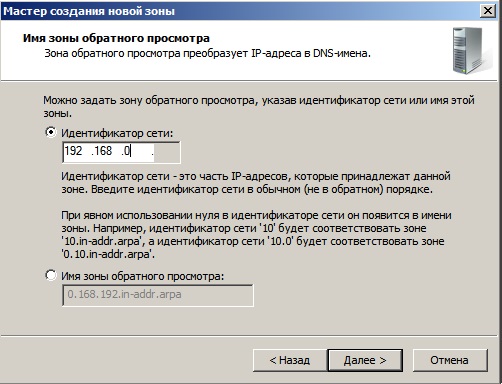
Выбираете Ваш идентификатор сети, под которым будет работать данный домен.
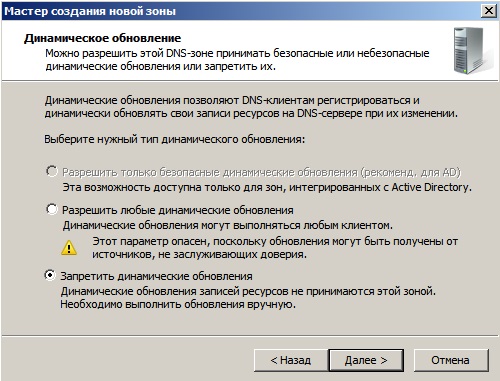
Для Windows Server 2008r2 рекомендуем отключать динамические обновления, лучше делать обновления в ручную.
5) Приступим к настройкам удаленных рабочих столов (RDP) Windows Server 2008 R2. Не важно, задали ли вы тип лицензирования (на устройство или на пользователя) в процессе установки, мы пройдемся по всем настройкам и определим тип уже в них.
Заходим в меню «Пуск» => Администрирование => Службы удаленных рабочих столов => Конфигурация узла сеансов удаленных рабочих столов.
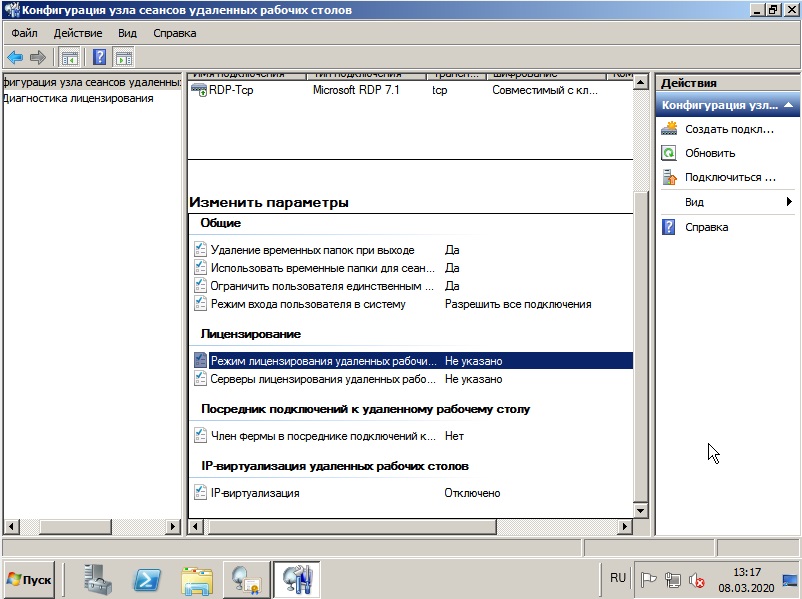
Внизу будет выбор параметров, из пункта «Лицензирование» выбираем пункт «Режим лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов».
Теперь здесь уже выбираем Ваш тип лицензирования в зависимости от Вашего ключа активации RDS User или Device CAL. Если у Вас нет ключа активации, приобрести его можете в нашем каталоге. Настройки «на пользователя», или «на устройство» ничем не отличаются друг от друга, кроме выбора непосредственно самого пункта лицензирования и Вашего ключа активации.
На примере выберем «На устройство» и нажимаем «Добавить».
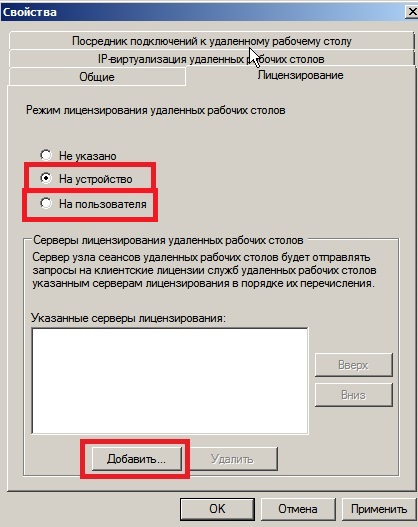
Добавляем Ваш сервер из «Известных» в «Указанные», после нажимаем «ОК».
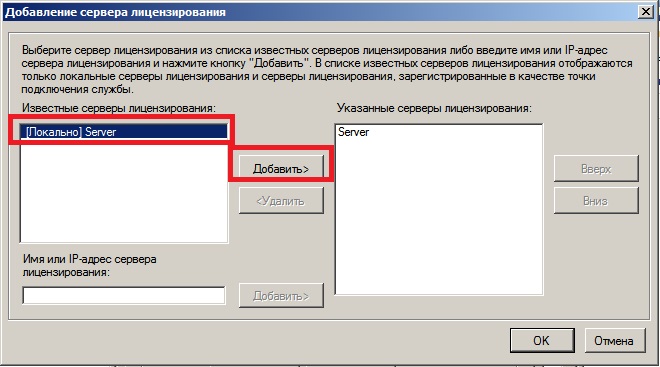
После, видим, что сервер добавлен, но не лицензирован. И находится пока в режиме ожидания.
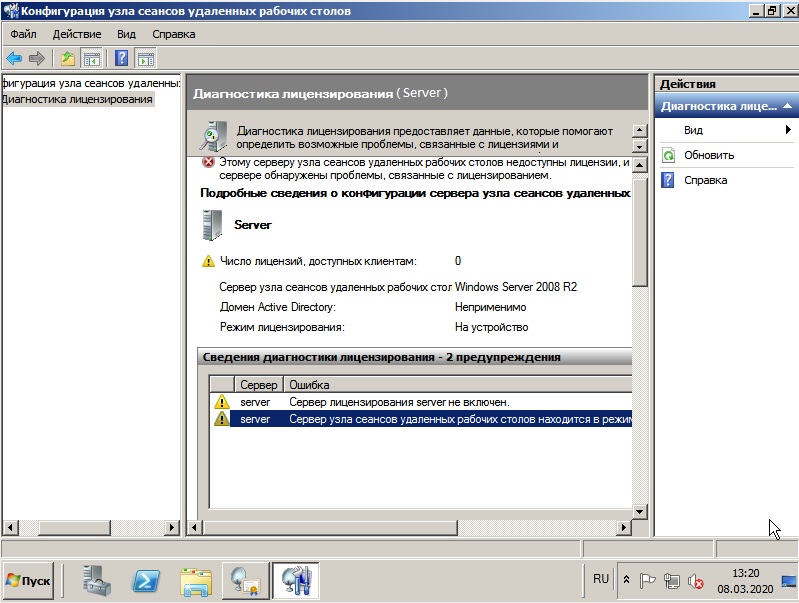
Заходим в меню «Пуск» => Администрирование => Службы удаленных рабочих столов => Диспетчер лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов.
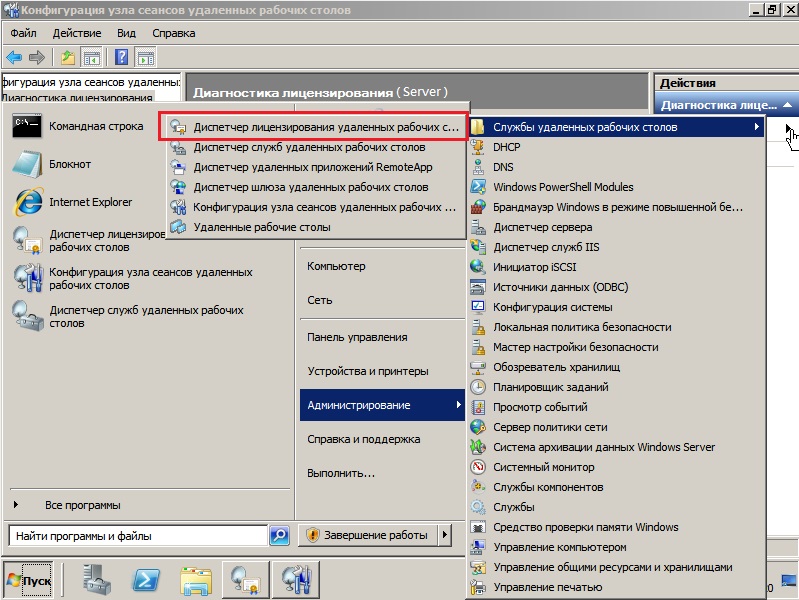
В новом окне у Вас будет Ваш сервер, на котором будет указано состояние активации — «Не активирован». Нажимаете правой кнопкой мыши => Активировать сервер.
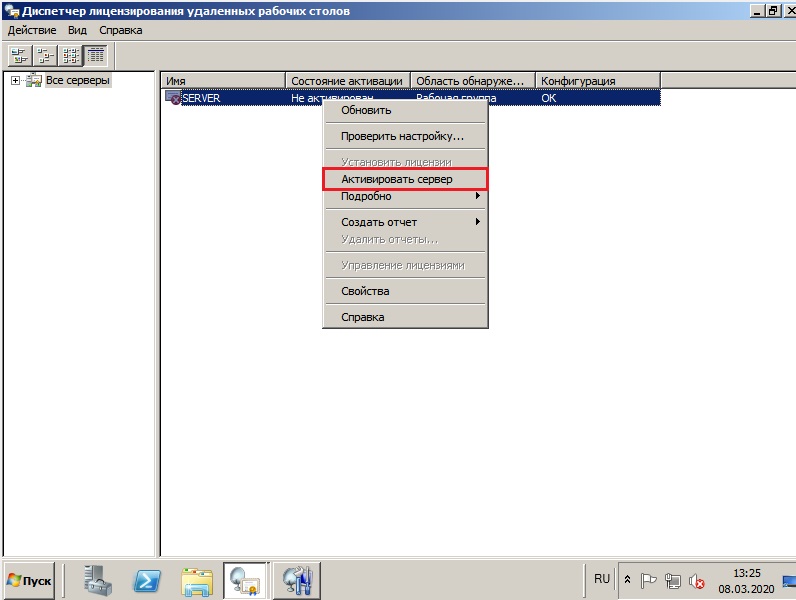
Рекомендуем выбрать «Автоматический режим».

Вводите данные Вашей организации. (Можно вводить любые данные, они не требуют проверки).
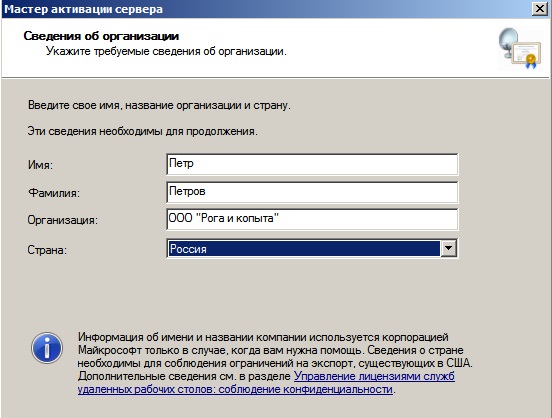
Запускаем мастер установки лицензий.
При лицензировании — выбираем «Пакет лицензий в розницу» => Далее.
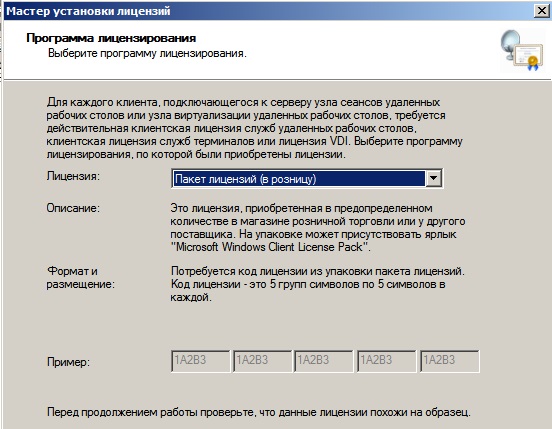
И теперь вводите Ваш ключ активации для лицензирования RDP (удаленных рабочих столов).
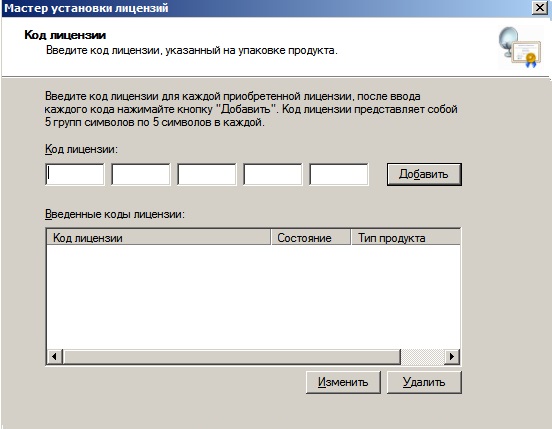
В зависимости от типа лицензирования у Вас может выйти следующее окно, в нем нужно будет ввести количество пользователей или устройств, которое указано в Вашей лицензии.
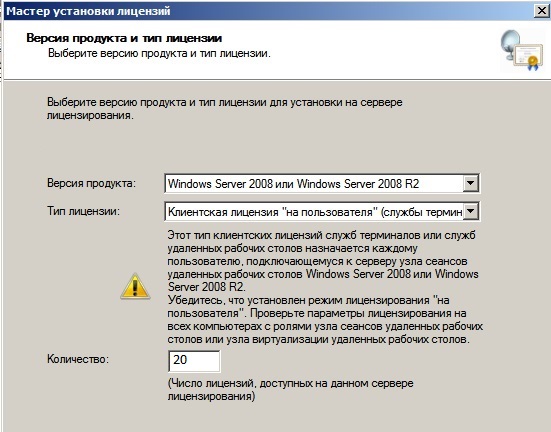
Завершаем работу мастера установки лицензий. Если все прошло успешно, то у Вас выйдет следующее окно.

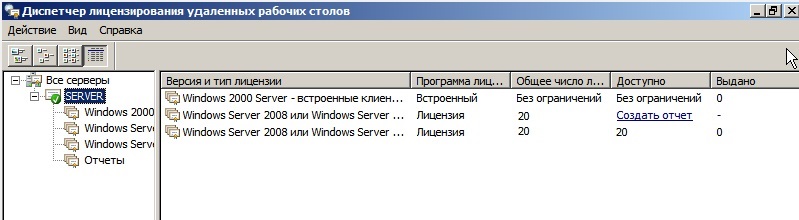
Теперь Вы можете увидеть, что Ваш сервер настроен на определенное число подключений, в заивимости от Вашего сервера.
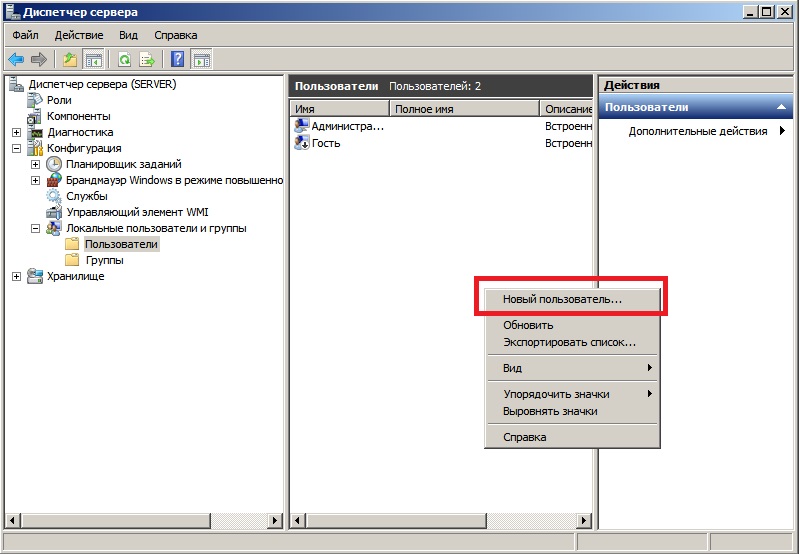
6) Но чтобы подключаться по RDP нам нужны пользователи, а точнее, нам нужно их завести. Заходим в «Диспетчер серверов» => Открываем дерево «Конфигурация» => Локальные пользователи и группы => Выбираем «Пользователи», далее в окне пользователей нажимаем правой кнопкой мыши => Новый пользователь.
Заполняем карточку пользователя и задаем ему пароль.
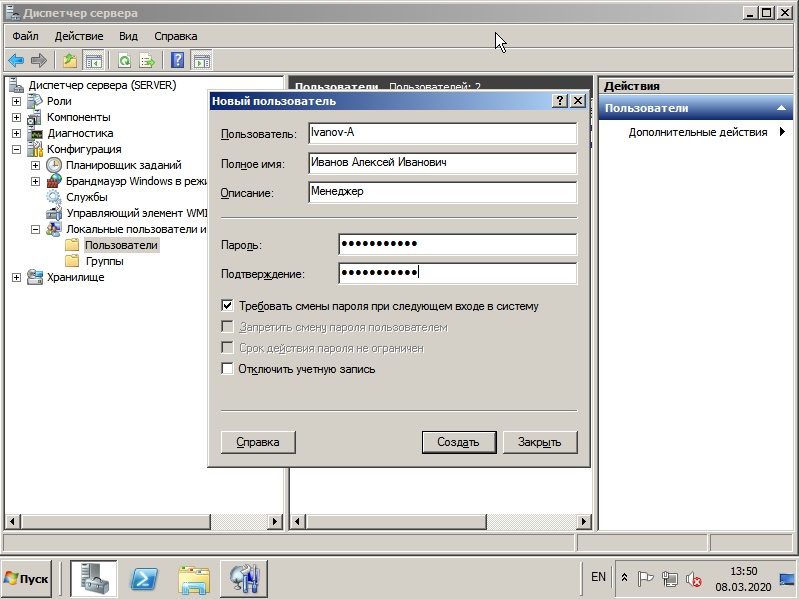
На этом все. Теперь Вы можете подключить первого клиента к серверу Windows Server 2008 R2.





