| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
| Configuring BitLocker Drive Encryption on Windows Server 2008 R2 | Adding New GPT and MBR Disks to Windows Server 2008 R2 Systems |
<google>BUY_WINSERV_2008R2</google>
Windows Server 2008 R2 is, as the name suggests, a server operating system. In the real world this means that systems running Windows Server 2008 R2 will most likely be located in large rack systems in a server room. As such, it is highly unlikely that system administrators are going to want to have to physically visit each of these servers to perform routine administrative tasks such as system configuration and monitoring. A far preferable scenario involves these administrators remotely logging into the servers from their own desktop systems to perform administrative tasks. Fortunately Windows Server 2008 R2 provides precisely this functionality through Remote Desktop and the remote administration features of the Server Manager. In this chapter we will look at the steps necessary to remotely administer Windows Server 2008 R2 systems using each of these approaches.
Contents
Contents
|
||
Remote Administration Using Server Manager
The Windows Server 2008 R2 Server Manager tool provides the ability to perform some administrative tasks on a remote server. Unfortunately, the administrative tasks that can be performed using this approach are quite restrictive and, as such, the following activities are disabled:
- Addition or removal of roles
- Addition or removal of features
- Modification of Windows Update settings
- Modification of network configuration
- Modification of domain settings
- Alteration of computer name
- Configuration of Internet Explorer security settings
- Execution of Security configuration wizard
- Management of Remote Desktop configuration settings
- System Properties configuration
In order to enable remote administration using the Server Manager, remote administration must first be enabled on the remote server. This can be achieved by launching Server Manager on the remote server and selecting the Configure Server Manager Remote Management link located in the Server Summary section. Within the resulting dialog, ensure that the option to Enable remote management of this server from other computers check box is selected before clicking on the OK button:
Once remote administration using Server Manager has been enabled, launch Server Manager on another computer located on the same domain or workgroup as the remote server, launch Server Manager and select the Action -> Connect to Another Computer menu option. Within the resulting dialog box, enter the name of the remote server to which you wish to connect and click on the OK button. A progress dialog will be displayed as the connection to the remote server is established. After a short delay the name of the current computer in the left hand pane of the Server Manager will change from the local computer to the remote server. Once the connection has been established, all the information displayed by Server Manager relates to the remote system. As you explore the various options you will begin to notice that a number of options are missing. For example, in the following figure there are no options listed to add or remove roles from the remote server:
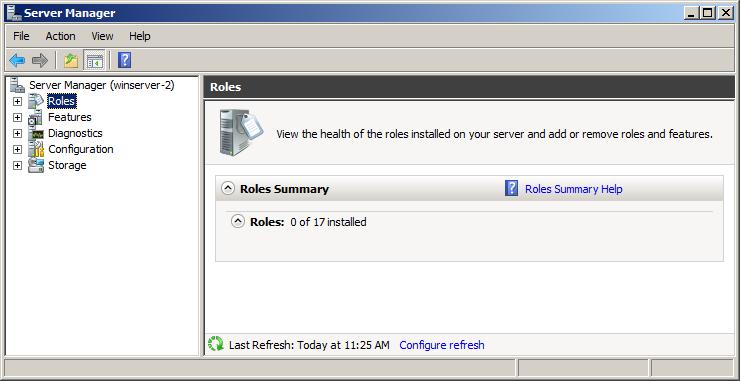
In order to perform a wider range of remote administrative tasks than those provided by the Server Manager, it is necessary to use Remote Desktop access.
What is Remote Desktop?
Remote Desktop allows the graphical interface of a remote Windows system to be displayed over a network onto a local system. In addition, keyboard and mouse events on the local system are transmitted to the remote system enabling the local user to perform tasks on the remote system as if they were physically sitting at the remote system. Conversely, resources (such as printers and disk drives) on the local system can be made available to the remote system for the duration of the connection. This remote control can be established in a number of ways, including over wide area networks (WAN), local area networks (LAN) or over the internet.
In the case of Windows Server 2008 R2, this service is provided by Remote Desktop Services (known as Terminal Services in previous versions of Windows Server) running on the remote system and the Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) client on the local system.
Remote Desktop Services run in two different modes, Administration and Virtual Session. Remote Desktop for Administration provides full administration functionality to the remote administrator (including access to the console session and visibility of notification messages). Remote Desktop for Administration is the equivalent to working directly at the remote system’s console. In virtual session mode the user is subject to some limitations such as the ability to install applications and view console notification messages.
Windows Server 2008 R2 imposes some administrator logon restrictions. Specifically, a maximum of two administrators may be logged on at any one time, either two logged on remotely, or one local and one remote administrator. This assumes, however, that different accounts are being used to log on. In other words, the same user may not log on locally and remotely simultaneously.
Enabling Remote Desktop Administration on the Remote Server
As mentioned previously, remote desktop functionality on the server is provided by Remote Desktop Services. It is important to note, however, that Remote Desktop Services do not have to be explicitly enabled on the server in order to support Remote Desktop Administration. In fact, all that needs to be done is to enable Remote Desktop Administration. This is configured by opening the Control Panel from the Start menu and selecting the System and Security icon followed by the System icon. In the section in the top left hand corner of the System page select Remote settings to display the following properties window:
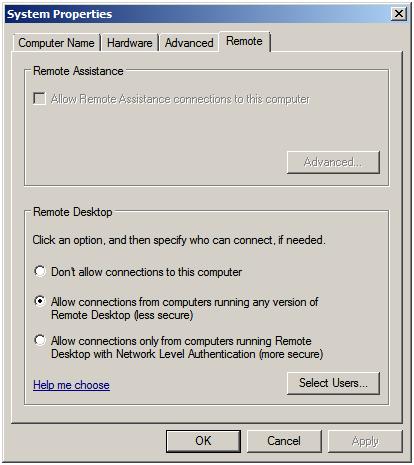
The Remote properties dialog provides a number of options. The default setting is to disallow remote connections to the computer system. The second option allows remote desktop connections from any version of the Remote Desktop client. The third, and most secure option, will only allow connections from Remote Desktop clients with Network Level Authentication support. This typically will only allow access to systems providing secure network authentication such as Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008.
If the Windows Firewall is active, the act of enabling Remote Desktop administration also results in the creation of a firewall exception allowing Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) traffic to pass through on TCP port 3389. This default port can be changed by changing this setting in the Registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\WinStations\RDP-tcp\PortNumber.
The easiest way to locate this registry key value is to execute regedit from the Run window or a command prompt, select Edit — > Find and enter RDP-tcp. In the resulting list, scroll down until you reach the PortNumber entry and double click on it to change the current value.
Controlling Remote Desktop Access
<google>WIN28BOX</google>
The default configuration for Remote Desktop is to allow all members of the Administration group to connect remotely. Active Directory also contains a Remote Desktop Users group to which users may be added to provide Remote Desktop access privileges. To provide users with remote desktop access, open the Control Panel -> System and Security -> System -> Remote settings panel and click on the Select Users button to invoke the Remote Desktop Users dialog illustrated in the following figure:
Note that users with administrative privileges do not need to be added to this list; by default they already have Remote Desktop access. To add additional users click on the Add… button to display the Select Users dialog. Enter the name of the user in the text box entitled Enter object names to select and click on Check names to list names that match the name entered. Select the appropriate name from the list. The following example shows user Bill on server winserver-2:

Click on OK to apply the change. The new user will now appear in the list of users with Remote Desktop access on the Remote Users screen. Click OK to close this screen and click on Apply in the System Settings screen. The specified user will now have remote desktop access to the system.
Starting the Remote Desktop Client
With the appropriate configuration tasks completed on the remote system the next step is to launch the Remote Desktop Client on the local system. The client can be run in either administration mode which provides full integration with the console of the remote server, or virtual session mode which provides some administrative privileges but does not provide console access or allow applications to be installed.
To invoke the Remote Desktop Client in virtual session mode either select Start -> All Programs -> Accessories -> Remote Desktop Connection or enter the following in the Run dialog or at a command prompt:
mstsc
To start the Remote Desktop Client in administrator mode run the following command:
mstsc /admin
In either case the following initial screen will appear requesting details of computer to which the client is to connect:

This can either be an IP address or a computer name. If previous connections have been established the User name field will be populated with the user name used in the preceding session. If you need to log in as a different user this option will be provided on the next screen which appears after the Connect button is pressed:
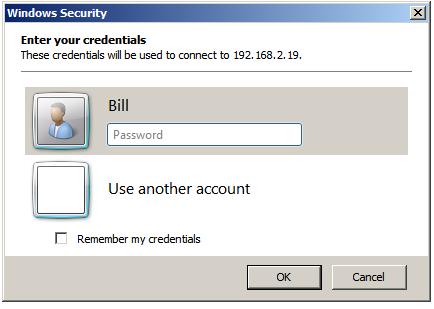
In this screen enter the password for the selected user (note that remote desktop access is only available for user accounts which are password protected). If a user other than the one displayed is required, simply click on the Use another account link and enter the necessary details. Click on OK to establish the connection. After a short delay the remote desktop will appear on the local computer screen.
Remote Desktop Client Configuration Options
The Options>> button displayed on the initial screen of the Remote Desktop Client provides six tabs, each containing a range of configuration options:
- General — Allows login credentials to be configured and session information to be saved.
- Display — Configures the resolution and color settings to be used when displaying the remote desktop on the local system.
- Local Resources — Specifies which local resources (sound, disk drives, printers etc) are to be made accessible to the remote system during the Remote Desktop session. This page also provides options to control the situations under which special key combinations such as Ctrl-Alt-Del are interpreted by the local or remote systems.
- Programs — Allows specified programs to be automatically invoked each time a remote sessions is established.
- Experience — Controls which desktop features are enabled or disabled for the Remote Desktop session. For example, over a slow dial-up connection it is unwise to have the desktop background displayed and font smoothing enabled. Either select the connection type and speed to see recommended settings, or use Custom to configure your own settings. This particular screen also provides the option to have the connection automatically re-established in the event that a session is dropped.
- Advanced — Enables and disables remote server verification. This ensures that the remote server to which you are connected is indeed the server you wanted. Also available are TS Gateway settings. By default the Remote Desktop Client is configured to automatically detect TS Gateway settings.
Remote Session Tracking
With Remote Desktop access implemented it is often useful to find out at times who is logged into a system. This can be achieved using the quser command-line tool. To obtain details of logged in users on a local system simply run quser at a command prompt or in a Run dialog:
C:Users\Administrator> quser USERNAME SESSIONNAME ID STATE IDLE TIME LOGON TIME administrator 1 Disc 3:18 7/11/2008 12:36 PM bill rdp-tcp#0 2 Active . 7/14/2008 9:11 AM nas console 3 Active none 7/11/2008 12:58 PM
To obtain information for a remote system simply run quser with the /server:<hostname> command-line option. For example:
C:\Users\Administrator> quser /server:winserver-2 USERNAME SESSIONNAME ID STATE IDLE TIME LOGON TIME administrator 1 Disc 3:22 7/11/2008 12:36 PM bill rdp-tcp#0 2 Active . 7/14/2008 9:11 AM nas console 3 Active none 7/11/2008 12:58 PM
Logging out from a Remote Desktop Session
When the Remote Desktop Client is exited by pressing the ‘X’ on the control panel the remote session continues to run on the server even though no client is connected. Next time the user connects the desktop session will appear exactly as it was left before.
To end the session select Start in the remote desktop session, click on the right arrow button in the bottom right hand corner of the menu and select Log Off. This will close down the remote desktop session and close the remote desktop client.
Running Multiple Remote Desktops
Multiple concurrent remote desktops can be run and managed within a single window using the MMC Remote Desktops snap-in. This may either be snapped into the MMC or launched from the command-line or a Run dialog by typing:
tsmmc.msc
Once launched, right click on the Remote desktops item in the tree in the left hand panel and select Add a new connection from the menu. Once selected the Add New Connection dialog will appear as follows:
In this dialog enter the IP address or computer name of the remote system together with the User name and the name to be assigned to this connection (this is essentially the name by which this connection will be listed and administered inside the Remote Desktops snap-in). For an administrative session (as opposed to a virtual session) set the Connect with /admin box. Click OK to add the session to the snap-in. Once added, the session will appear in the left hand panel under Remote Desktops. Repeat these steps to add connections to any additional remote systems required.
To establish a remote desktop connection, right click on the name of the session from the left hand panel and select Connect from the menu. The remote session will appear in the window. To start another session simply right click on the session name and once again select Connect. To switch between sessions simply click on the name of the session in the left hand panel and the corresponding desktop will be displayed. The following figure illustrates two sessions running in Remote Desktops:
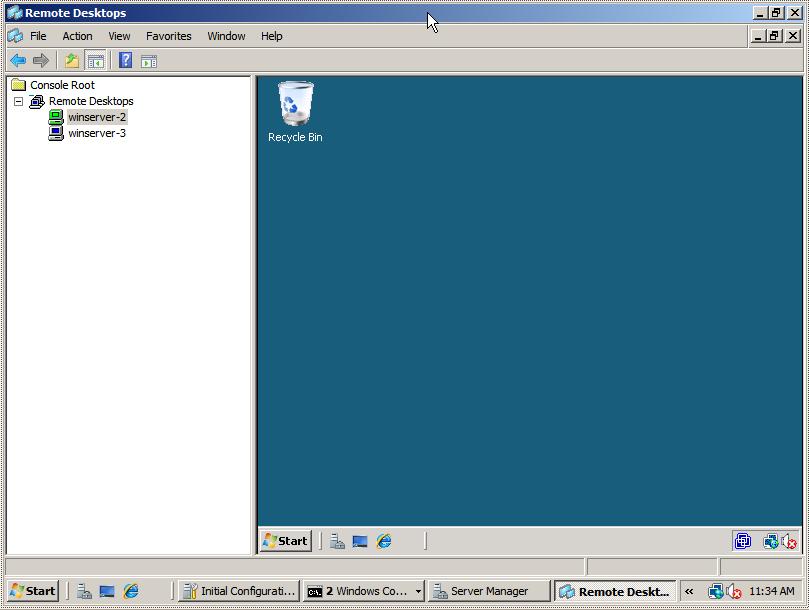
To change configuration options for each session right click on the desired session in the left hand panel and select Properties. This panel has a number of tabs which enable credentials, screen size and program start properties to be defined.
<google>BUY_WINSERV_2008R2_BOTTOM</google>
As a system administrator I have seen the time when despite the availability of 3-5 system admins at the same time, the management of end user issues can still become difficult to entertain. This is particularly true in the case of managing hundreds of users. In my previous job, me and my fellow admins used to resolve issues after receiving a ticket in our ticketing portal. Sometimes there were 15 tickets open at the same time, ranging from problems caused due to an unplugged power cable, to entire system crashes. In such a scenario it is not possible to run over to the server room each time you have to reset a password or unlock a locked account. To save time and resolve issues on the fly, we used to remotely login to the DC (Domain Controller), ADC (Additional Domain Controller), ISA (Internet Security and Acceleration) and Exchange (mail) Servers to resolve such issues. In many cases, we used the system of end users to complete these tasks with our DC admin accounts.
Now that we have talked about the basic scenario. In this post, we will tell you how to use Remote Desktop in Windows Server 2008 for remote management.
To make sure that your system can remotely connect, go to Computer (My Computer) Properties from the right-click context menu to enable incoming remote desktop connections.
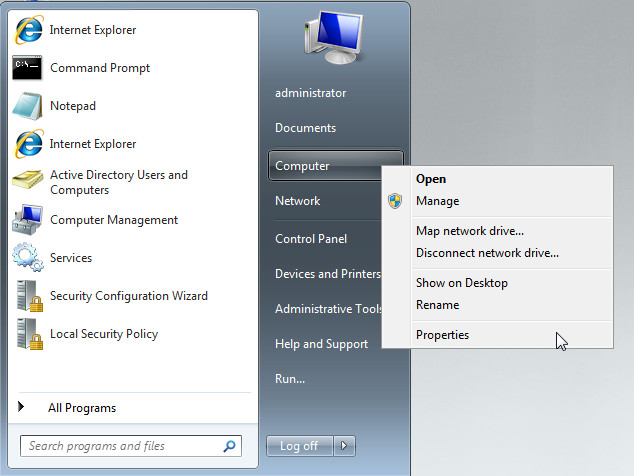
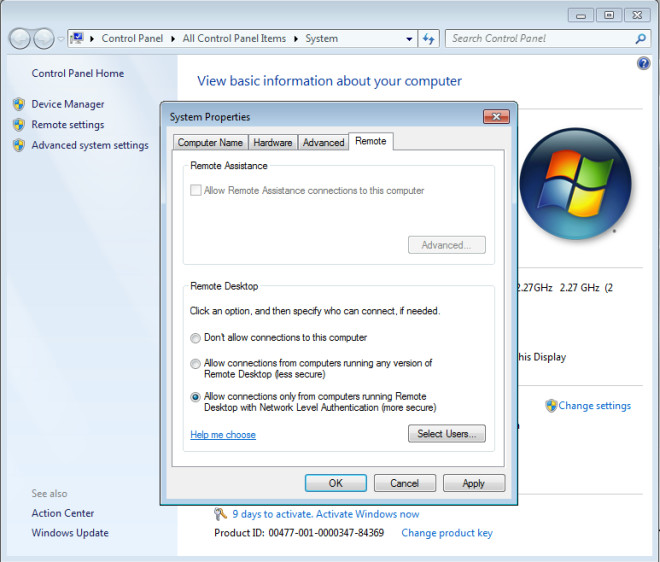
Click on Advanced System Settings and move over to the Remote tab. From here select Allow Connections Running Remote Desktop With Network Level Authentication (for a more secure environment). Alternatively, you can also choose Allow Connections From Computers Running Any Version Of Remote Desktop (for allowing remote desktop connection sessions with pre Windows Server 2008 systems). Once done, click OK. Note: make sure to do this on systems that you wish to remotely make connections to and from.
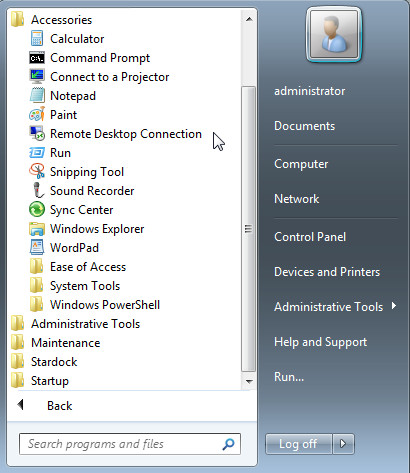
Now open Remote Desktop Connection via Start Search or go to Run > type mstsc > hit Enter.
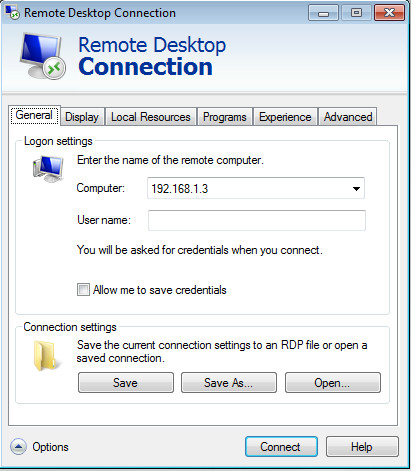
You can simply enter the IP of the system that you wish to connect remotely to and hit Connect or configure advanced options for managing your connection. For instance, in the General tab, login credentials can be entered to automatically login to the system that you are connecting to (e.g. Domain admin credentials). To visit Advanced Options, click Options button to expand the interface.
Reducing display quality can also help in a faster remote connection. This can be particularly helpful for low bandwidth connections.
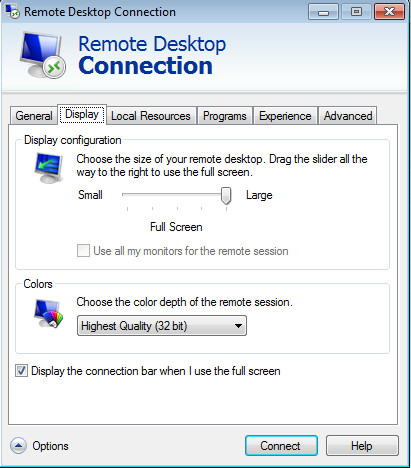
From the Local Resources tab, you can set the devices and resources that you wish to utilize during your remote session. Similarly, the Programs tab allows starting of selected programs as the remote session starts.
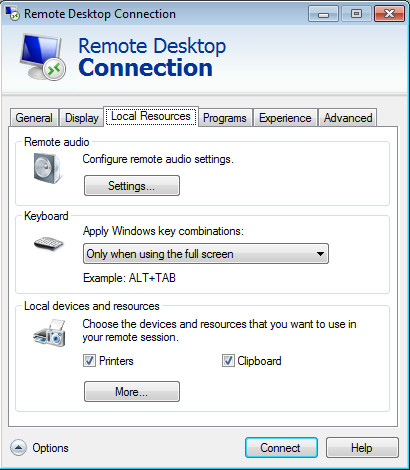
Bandwidth consumption can also be reduced by de-selecting unwanted features from the Experience tab.
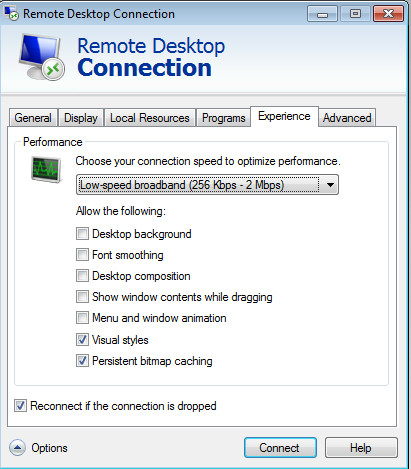
In the Advanced tab, you can set a warning message regarding authentication failure (e.g. when server authentication fails).
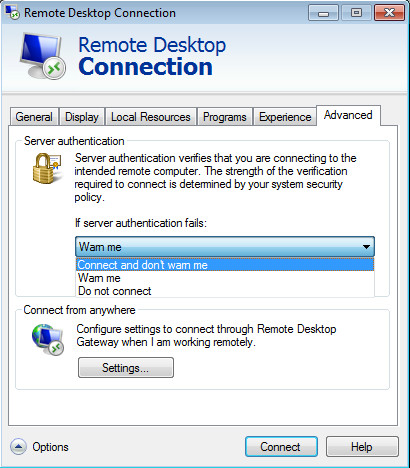
After configuring the desired settings, you can click on Connect to start your Remote Desktop Session.

Enabling remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 allows you to access and manage your server remotely from any location. This can be particularly useful if you need to make changes to your server’s settings or troubleshoot issues without physically being in front of the machine. In this blog post, we will guide you through the steps to enable remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 and provide some additional tips to enhance your remote desktop experience.
Video Tutorial:
There are several reasons why you would want to enable remote desktop on your Windows Server 2008 R2. Here are a few:
1. Remote management: Enabling remote desktop allows you to manage your server from anywhere with a network connection. This can save you time and effort by eliminating the need to physically be present at the server location.
2. Troubleshooting: If you encounter any issues with your server, enabling remote desktop allows you to troubleshoot and resolve the problem remotely. This can be particularly useful if the server is in a remote or hard-to-reach location.
3. Flexibility: Enabling remote desktop gives you the flexibility to work on your server from any device with a remote desktop client. This means you can use your laptop, tablet, or even your smartphone to access and manage your server.
Now that we understand why enabling remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 is important, let’s explore how to do it.
Method 1: Enabling Remote Desktop via the GUI
Enabling remote desktop using the graphical user interface (GUI) is the easiest way to do it. Here are the steps:
1. Open the “Start” menu and go to “Control Panel”.
2. Click on “System and Security”, then “System”.
3. In the left-hand pane, click on “Remote settings”.
4. In the “System Properties” window, go to the “Remote” tab.
5. Under the “Remote Desktop” section, select the option “Allow connections from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)”.
6. Click on “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
Pros:
1. Easy and straightforward process to enable remote desktop.
2. Allows for remote management and troubleshooting of the server.
3. Provides flexibility to work on the server from various devices with a remote desktop client.
Cons:
1. Selecting the less secure option may pose a slight security risk.
2. Limited control over user access and permissions.
Method 2: Enabling Remote Desktop via Group Policy
If you have a group of servers that need remote desktop enabled, using group policy is an efficient way to do it. Here’s how:
1. Open the “Group Policy Management” console.
2. Create a new GPO or select an existing one.
3. Right-click on the GPO and choose “Edit”.
4. Navigate to “Computer Configuration” > “Policies” > “Administrative Templates” > “Windows Components” > “Remote Desktop Services” > “Remote Desktop Session Host” > “Connections”.
5. Locate the policy setting called “Allow users to connect remotely using Remote Desktop Services” and double-click on it.
6. Select the “Enabled” option and click on “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
Pros:
1. Allows for centralized management of remote desktop settings.
2. Enables consistent configuration across multiple servers.
3. Provides granular control over user access and permissions.
Cons:
1. Requires advanced knowledge of group policy management.
2. May require additional configuration and troubleshooting if the policy is not applied correctly.
Method 3: Enabling Remote Desktop via Command Line
If you prefer using the command line, you can enable remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 using the “reg” command. Here’s how:
1. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator.
2. Type the following command and press Enter: reg add “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal Server” /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
3. Type the following command and press Enter: netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group=”Remote Desktop” new enable=Yes
4. Close the Command Prompt.
Pros:
1. Provides a quick way to enable remote desktop without using the GUI.
2. Allows for automation and scripting.
Cons:
1. Requires familiarity with the command line interface.
2. Limited visibility of other remote desktop settings.
Method 4: Enabling Remote Desktop via PowerShell
PowerShell is a powerful scripting language that can be used to enable remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2. Here’s an example of how to do it:
1. Open PowerShell as an administrator.
2. Type the following command and press Enter: Set-ItemProperty -Path ‘HKLM:SystemCurrentControlSetControlTerminal Server’ -name “fDenyTSConnections” -Value 0
3. Type the following command and press Enter: Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup “Remote Desktop”
4. Close PowerShell.
Pros:
1. Offers automation capabilities for remote desktop enablement.
2. Can be combined with other PowerShell scripts for advanced configuration.
Cons:
1. Requires familiarity with PowerShell scripting.
2. Limited visibility of other remote desktop settings.
What to Do If You Can’t Enable Remote Desktop
If you encounter any issues while trying to enable remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2, here are some potential fixes:
1. Check firewall settings: Ensure that the necessary firewall rules are in place to allow remote desktop connections.
2. Verify network connectivity: Make sure that the server has a stable network connection and can communicate with other devices on the network.
3. Check group policy settings: Confirm that the group policy settings are applied correctly and not blocking remote desktop connections.
4. Restart the Remote Desktop Services: Restarting the Remote Desktop Services can sometimes resolve issues with remote desktop connectivity.
Bonus Tips
Here are three bonus tips to enhance your remote desktop experience on Windows Server 2008 R2:
1. Use strong passwords: Ensure that you have strong passwords in place for all user accounts on the server to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Enable network-level authentication: Network-level authentication provides an additional layer of security by requiring users to authenticate before establishing a remote desktop session.
3. Use Remote Desktop Gateway: If your server is behind a firewall or requires access over the internet, consider setting up a Remote Desktop Gateway for secure remote access.
5 FAQs
Q1: How do I access a remote desktop session on Windows Server 2008 R2?
A: To access a remote desktop session on Windows Server 2008 R2, you will need a remote desktop client such as Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) or a third-party remote desktop application.
Q2: Can I connect to Windows Server 2008 R2 from a Mac?
A: Yes, you can connect to Windows Server 2008 R2 from a Mac using the Microsoft Remote Desktop application available in the Mac App Store.
Q3: Can multiple users connect simultaneously to a Windows Server 2008 R2 using remote desktop?
A: Yes, Windows Server 2008 R2 supports multiple concurrent remote desktop sessions, depending on the licensing and configuration of the server.
Q4: How can I improve the performance of a remote desktop session?
A: To improve the performance of a remote desktop session, you can reduce the display settings, disable unnecessary visual effects, and optimize your network connection.
Q5: Can I copy files between my local machine and the remote desktop session?
A: Yes, you can copy files between your local machine and the remote desktop session by using the clipboard or the shared drives feature in the remote desktop client.
Final Thoughts
Enabling remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 is a valuable capability that allows you to manage your server from anywhere, improve troubleshooting efficiency, and increase flexibility in server management. Whether you choose to enable remote desktop via the GUI, group policy, command line, or PowerShell, following the steps outlined in this blog post will help you achieve your desired remote desktop configuration. Don’t forget to implement the bonus tips and refer to the FAQs for additional guidance.{“@context”:”https://schema.org”,”@type”:”FAQPage”,”mainEntity”:[{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:” How do I access a remote desktop session on Windows Server 2008 R2?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:” To access a remote desktop session on Windows Server 2008 R2, you will need a remote desktop client such as Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) or a third-party remote desktop application.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:” Can I connect to Windows Server 2008 R2 from a Mac?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:” Yes, you can connect to Windows Server 2008 R2 from a Mac using the Microsoft Remote Desktop application available in the Mac App Store.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:” Can multiple users connect simultaneously to a Windows Server 2008 R2 using remote desktop?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:” Yes, Windows Server 2008 R2 supports multiple concurrent remote desktop sessions, depending on the licensing and configuration of the server.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:” How can I improve the performance of a remote desktop session?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:” To improve the performance of a remote desktop session, you can reduce the display settings, disable unnecessary visual effects, and optimize your network connection.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:” Can I copy files between my local machine and the remote desktop session?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:” Yes, you can copy files between your local machine and the remote desktop session by using the clipboard or the shared drives feature in the remote desktop client.”}}]}
Remote Desktop is a useful feature that allows users to access their Windows Server 2008 R2 system from another computer. This can be particularly helpful for IT administrators or individuals who need to manage their server remotely. If you’re wondering how to enable Remote Desktop on your Windows Server 2008 R2, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open the Start menu on your server and click on «Control Panel.«
Step 2: In the Control Panel window, select «System and Security.«
Step 3: Under the System and Security section, click on «System.«
Step 4: In the System window, select «Remote settings» from the left sidebar.
Step 5: In the System Properties window that opens, navigate to the «Remote» tab.
Step 6: In the Remote tab, you will find two options: «Allow connections from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)» and «Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (more secure).» Choose the option that best suits your security requirements.
Step 7: Click on «Apply» and then «OK» to save your changes.
Now that you have enabled Remote Desktop on your Windows Server 2008 R2, you can access it remotely using a Remote Desktop client from another computer on the same network or through the internet. Simply launch the Remote Desktop client, enter the IP address or hostname of the server, and provide your credentials to establish a connection.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. Allows remote management of Windows Server 2008 R2, providing flexibility and convenience. | 1. Potential security risks if not configured properly or accessed from untrusted devices. |
| 2. Provides access to server resources and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. | 2. Requires a stable and reliable network connection for optimal performance. |
| 3. Helps streamline server administration and troubleshooting tasks. | 3. May require additional configuration and firewall settings to allow remote connections. |
Enabling Remote Desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 can greatly enhance your ability to manage and access your server remotely. However, it is important to ensure that proper security measures are in place to protect your system from unauthorized access. Consider configuring firewall settings and utilizing strong passwords to maintain the security of your remote connections.
Video Tutorial:How to enable RDP via command line?
How to install RSAT on Windows Server 2008 R2?
Installing RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tools) on Windows Server 2008 R2 is a straightforward process. Here are the steps:
1. Verify the compatibility: Before proceeding with the installation, ensure that your system meets the requirements to run RSAT. Make sure you have administrative rights and that your server is running Windows Server 2008 R2.
2. Download RSAT: Visit the Microsoft Download Center website and search for «Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows Server 2008 R2.» Locate the appropriate version, either 32-bit or 64-bit, depending on your system architecture. Download the RSAT package.
3. Run the installer: Once the download is complete, navigate to the download location and run the installer. The installation wizard will open.
4. Select the desired tools: In the installation wizard, you’ll be presented with a list of available tools. Choose the specific tools within RSAT that you want to install. You can select multiple tools by holding the Ctrl key while clicking.
5. Complete the installation: After selecting the desired tools, click on the «Install» button to begin the installation process. The installer will extract and install the selected tools on your system.
6. Configure RSAT: Once the installation is complete, you need to configure RSAT to enable and access the installed tools. This involves navigating to the «Control Panel» and finding the «Programs» section. Locate the «Turn Windows features on or off» option and click on it.
7. Enable RSAT features: In the «Windows Features» dialog box, scroll down to find the «Remote Server Administration Tools» section. Expand it to reveal more options. Check the box corresponding to the specific tools you installed in step 4. Click «OK.«
8. Restart if necessary: In some cases, enabling or disabling certain Windows features may prompt a system restart. If required, restart your server to apply the changes and make the RSAT tools accessible.
9. Access RSAT: Once the server restarts (if necessary), you can access the RSAT tools by searching for them in the Start Menu or from the Administrative Tools folder. Each tool will have its own interface and usage instructions.
Remember to refer to official documentation, such as Microsoft’s documentation for RSAT, for more detailed steps or troubleshooting guidance if needed.
To enable Windows Server Remote Desktop, follow these steps:
1. Log in to your Windows Server using an administrative account.
2. Click on the «Start» menu and type «Remote Desktop» in the search bar.
3. In the search results, click on the «Remote Desktop Connection» application to open it.
4. In the Remote Desktop Connection window, type the name or IP address of the server you want to connect to in the «Computer» field.
5. Click on the «Show Options» button to expand additional settings.
6. In the expanded options, you can configure settings like display, local resources, and experience. Make the necessary adjustments based on your preferences or requirements.
7. Once you’ve made the appropriate settings, click on the «Connect» button to start the remote desktop session.
8. If it’s your first time connecting to the server, you may be prompted to verify the server’s identity or enter your credentials. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the connection.
9. After successful authentication, you should now have remote access to the Windows Server desktop.
Please note that enabling Remote Desktop on a Windows Server may have security implications, so it’s vital to ensure proper security measures are in place, such as strong passwords, firewall configurations, and limiting access to authorized users. It’s also recommended to keep your server and Remote Desktop client software up to date to mitigate potential risks.
How to run as administrator command line Windows Server 2008 R2?
Running commands as an administrator on Windows Server 2008 R2 allows users to perform administrative tasks and make system-level changes. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Launch the Command Prompt: Click on the «Start» button, type «cmd» in the search box, and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
2. Run as administrator: Right-click on the Command Prompt icon in the search results and select «Run as administrator.» If prompted for permission, click «Yes.«
3. User Account Control (UAC) prompt: If UAC is enabled, a prompt may appear asking for confirmation to run the Command Prompt as an administrator. Click «Yes» to continue.
4. Elevated Command Prompt: After successfully running Command Prompt as an administrator, the title bar of the Command Prompt window should display «Administrator: Command Prompt» to indicate that you have elevated privileges.
5. Execute commands: You can now run any command that requires administrative privileges. Simply type the desired command and press Enter to execute it.
Note: Exercise caution while running commands as an administrator, as system-level changes can affect the stability and performance of the Windows Server if not executed correctly. It’s advisable to have a good understanding of the commands you intend to run and their potential impact on the system.
It’s important to keep in mind that this answer is written as a tech blogger and not as an technical blogger.
How to check Remote Desktop users in Windows Server 2008?
To check Remote Desktop users in Windows Server 2008, you can follow these steps:
1. Open the «Start» menu and go to «Administrative Tools» and then select «Remote Desktop Services.«
2. Under «Remote Desktop Services,» choose «Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration.«
3. In the console tree, expand the «Connections» folder.
4. Right-click on the name of your RDP connection (e.g., «RDP-Tcp«) and select «Properties.«
5. In the «Properties» window, go to the «Permissions» tab.
6. Here, you can see the list of users who have permissions to connect through Remote Desktop to your Windows Server 2008.
7. You can further modify the permissions by clicking the «Advanced» button and selecting «Advanced Permissions.«
Please note that these steps are specifically for Windows Server 2008, and the process may vary slightly on different Windows Server versions.
How to enable Remote Desktop in Windows Server 2008?
To enable Remote Desktop in Windows Server 2008, you can follow the steps below:
1. Open the Start menu and go to «Control Panel«.
2. In the Control Panel, click on «System and Security» or «System and Maintenance» depending on your Control Panel view.
3. In the new window, find and click on «System«. This will open the System Properties.
4. In the System Properties window, click on the «Remote settings» link on the left-hand side. This will open the Remote tab.
5. Under the Remote Desktop section, you will see two options: «Don’t allow connections to this computer» and «Allow connections from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)«. Select the second option if you want to allow remote connections.
6. If you want to restrict remote connections to specific users, click on the «Select Users» button and add the desired users to the list.
7. Click «OK» to save the changes.
8. If you have a firewall enabled, make sure to allow Remote Desktop connections through the firewall. Check your firewall settings or consult the Windows Server 2008 documentation for specific instructions on how to do this.
After applying these steps, Remote Desktop should be enabled on your Windows Server 2008. You can now access the server remotely using a Remote Desktop client.
How do I enable remote management in Windows Server 2008 R2?
Enabling remote management in Windows Server 2008 R2 involves several steps. Here’s how you can accomplish it:
1. Launch Server Manager: Log in to the Windows Server 2008 R2 machine, click on the Start button, and open the Server Manager console.
2. Add the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) feature: In the Server Manager window, click on the «Features» section in the left-hand pane. Then, click on the «Add Features» link in the main pane. A new window will open, and you need to select the «Remote Server Administration Tools» checkbox. Click «Next» to proceed.
3. Select the desired remote management tools: In the Remote Server Administration Tools window, expand the «Role Administration Tools» section and then expand the «AD DS and AD LDS Tools» option. Here, you can select the specific tools you want to enable for remote management, such as «Active Directory Administrative Center» or «Group Policy Management.» Once you’ve made your selections, click «Next.«
4. Confirm the installation selections: Review the summary of your installation selections and click «Install» to begin the installation process. The required files and features will be downloaded and installed on your Windows Server machine.
5. Enable remote management: After the installation completes, return to the Server Manager window, and in the left-hand pane, expand the «Configuration» section and select «Local Server.» In the main pane, locate the «Remote Management» option and click on the disabled status.
6. Configure remote management settings: A new window called «System Properties» will open. Click on the «Remote» tab and select the checkbox labeled «Allow remote connections to this computer.» You can also choose to enable remote management settings for specific users or groups by clicking on the «Select Users» button.
7. Firewall configuration: By default, the Windows Firewall blocks remote management connections. To allow remote management connections, you need to configure the firewall to permit them. In the Server Manager window, click on «Configuration» in the left-hand pane, and then select «Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.» From there, you can create inbound and outbound rules to allow remote management traffic.
8. Test remote management: Once you’ve completed the above steps, you can test remote management by connecting to the Windows Server 2008 R2 machine from another computer using remote management tools like Windows PowerShell or Remote Desktop.
It’s important to note that these instructions assume you have administrative access to the Windows Server 2008 R2 machine and are familiar with basic Windows Server administration concepts. Additionally, ensure that remote management is in compliance with your organization’s security policies and guidelines.
TipsMake.com — Unlike Windows Server 2008 RTM, Windows Server 2008 R2 has a feature that allows you to remotely manage using Server Manager.
Note : Windows Server 2008 RTM can also be managed remotely. You can easily manage these servers with MMC Snap-In. However, using Server Manager in R2 is new .
By using Server Manager to remotely manage Windows Server 2008 R2 servers, you can manage:
Server to server : Fully installed Server Manager in Windows Server 2008 R2 can be used to manage the roles and features installed on another server running Windows Server 2008 R2.
Server to Server Core — Server Manager in a fully installed Windows Server 2008 R2 can be used to manage the roles and features installed on a Server Core of Windows Server 2008 R2.
Client to server — Server Manager is installed as part of the Remote Server Administration Tools — RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tool Group) on a computer running Windows 7 operating system. It is used to manage roles. and feature on a computer that runs Server Core of Windows Server 2008 R2. To install Server Manager on Windows 7 operating system, you need to install RSAT.
Things you can do remotely with Server Manager include:
• Display Windows auto update status.
• Run Best Practices Analyzer.
• Display or change information of Windows Firewall.
• Display and manage roles.
• Manage installed service roles
• Display Internet Explorer Advanced Security Configuration (IE ESC) settings
• Configure Windows Error Reporting
• Display or change the Windows Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP) status.
However, since this feature is still not 100% complete, you can’t control everything. Here’s what you can’t do with Server Manager.
• Add or remove remove roles, roles services, and features
• Configure Remote Desktop settings
• Configure System Properties
• Check the new role
• Change Windows auto update settings
• Change network settings
• Change the computer name or domain member
• Change Internet Explorer Advanced Security Configuration settings
• Run the Security Configuration Wizard, if the source computer is a server running Windows Server 2008 R2
How to turn on remote management:
Suppose the remote management server is fully installed and ready to operate. First, open Server Manager on the control server
Click the Configure Server Manager for Remote Management link
Select Enable remote management of this server from other computers
Click OK .

The server’s firewall will automatically configure to allow relevant information.
How do you connect to the control server?
On the server (running Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows with RSAT), open Server Manager
Right-click Server Manager and select Connect to Another Computer

In the Connect to Another Computer window, type the name or browse to the server you want to connect to.

If you want to keep the remote connection and do not want to reconfigure the admin server name after each time, you can open a new MMC window, add the Server Manager snap-in, connect to the administrative server and save Repeat this snap-in.
