Сетевой протокол SMB (Server Message Block) используется для предоставления совместного удаленного доступа к файлам, принтерам и другим устройствам через порт TCP 445. В этой статье мы рассмотрим: какие версии (диалекты) протокола SMB доступны в различных версиях Windows (и как они соотносятся с версиями samba в Linux); как определить версию SMB на вашем компьютере; и как включить/отключить клиент и сервер SMBv1, SMBv2 и SMBv3.
Содержание:
- Версии протокола SMB в Windows
- Как проверить поддерживаемые версии SMB в Windows?
- Вывести используемые версии SMB с помощью Get-SMBConnection
- Об опасности использования SMBv1
- Включение и отключение SMBv1, SMBv2 и SMBv3 в Windows
Версии протокола SMB в Windows
Есть несколько версии протокола SMB (диалектов), которые последовательно появлялись в новых версиях Windows:
Для реализации протокола SMB в Linux/Unix системах используется samba. В скобках мы указали в каких версиях samba поддерживается каждый диалект SMB.
- CIFS — Windows NT 4.0;
- SMB 1.0 — Windows 2000;
- SMB 2.0 — Windows Server 2008 и Windows Vista SP1 (поддерживается в Samba 3.6);
- SMB 2.1 — Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7 (поддерживается в Samba 4.0);
- SMB 3.0 — Windows Server 2012 и Windows 8 (поддерживается в Samba 4.2);
- SMB 3.02 — Windows Server 2012 R2 и Windows 8. 1 (не поддерживается в Samba);
- SMB 3.1.1 – Windows Server 2016 и Windows 10 (не поддерживается в Samba).
Начиная с версии Samba 4.14, по умолчанию используется SMB2.1.
При сетевом взаимодействии по протоколу SMB между клиентом и сервером используется максимальная версия протокола, поддерживаемая одновременно и клиентом, и сервером.
Ниже представлена сводная таблица, по которой можно определить версию протокола SMB, которая выбирается при взаимодействии разных версий Windows:
| Операционная система | Win 10, Server 2016 | Windows 8.1, Server 2012 R2 |
Windows 8, Server 2012 |
Windows 7, Server 2008 R2 |
Windows Vista, Server 2008 |
Windows XP, Server 2003 и ниже |
| Windows 10 ,
Windows Server 2016 |
SMB 3.1.1 | SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 8.1 , Server 2012 R2 |
SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 8 , Server 2012 |
SMB 3.0 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 7, Server 2008 R2 |
SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows Vista, Server 2008 |
SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows XP, 2003 и ниже | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 |
К примеру, при подключении клиентского компьютера с Windows 8.1 к файловому серверу с Windows Server 2016 будет использоваться протокол SMB 3.0.2.
Согласно таблице Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 для доступа к общим файлам и папкам на сервере могут использовать только SMB 1.0, который в новых версиях Windows Server (2012 R2 / 2016) может быть отключен. Таким образом, если в вашей инфраструктуре одновременно используются компьютеры с Windows XP (снятой с поддержки), Windows Server 2003/R2 и сервера с Windows Server 2012 R2/2016/2019, устаревшие клиенты не смогут получить доступ к файлам и папкам на файловом сервере с новой ОС.
Если Windows Server 2016/2012 R2 с отключенным SMB v1.0 используется в качестве контроллера домена, значить клиенты на Windows XP/Server 2003 не смогут получить доступ к каталогам SYSVOL и NETLOGON на контроллерах домена и авторизоваться в AD.
На старых клиентах при попытке подключиться к ресурсу на файловом сервере с отключенным SMB v1 появляется ошибка:
The specified network name is no longer available
Как проверить поддерживаемые версии SMB в Windows?
Рассмотрим, как определить, какие версии протокола SMB поддерживаются на вашем компьютере Windows.
В Windows 10, 8.1 и Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2 вы можете проверить состояние различных диалектов SMB протокола с помощью PowerShell:
Get-SmbServerConfiguration | select EnableSMB1Protocol,EnableSMB2Protocol
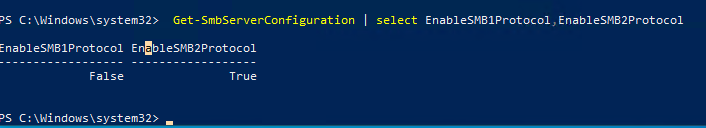
Данная команда вернула, что протокол SMB1 отключен (
EnableSMB1Protocol=False
), а протоколы SMB2 и SMB3 включены (
EnableSMB1Protocol=True
).
Обратите внимание, что протоколы SMBv3 и SMBv2 тесно связаны между собой. Нельзя отключить или включить отдельно SMBv3 или SMBv2. Они всегда включаются/отключаются только совместно, т.к. используют один стек.
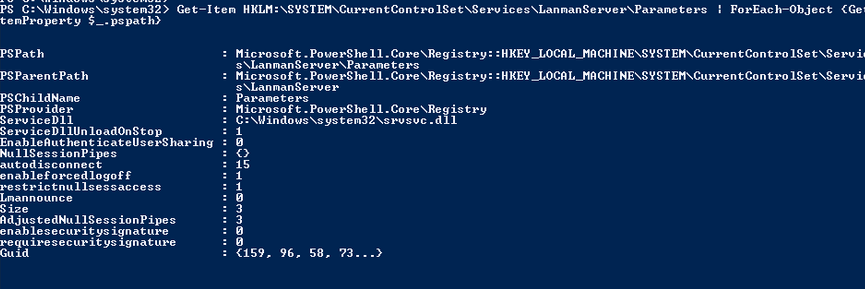
В Windows 7, Vista, Windows Server 2008 R2/2008:
Get-Item HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath}
Если в данной ветке реестра нет параметров с именами SMB1 или SMB2, значить протоколы SMB1 и SMB2 по умолчанию включены.
Также в этих версиях Windows вы можете проверить, какие диалекты SMB разрешено использовать в качестве клиентов с помощью команд:
sc.exe query mrxsmb10
SERVICE_NAME: mrxsmb10 TYPE : 2 FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0
sc.exe query mrxsmb20
SERVICE_NAME: mrxsmb20 TYPE : 2 FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0
В обоих случаях службы запущены (
STATE=4 Running
). Значит Windows может подключаться как к SMBv1, так и к SMBv2 серверам.
Вывести используемые версии SMB с помощью Get-SMBConnection
Как мы говорили раньше, компьютеры при взаимодействии по протоколу SMB используют максимальную версию, поддерживаемую как клиентом, так и сервером. Для определения версии SMB, используемой для доступа к удаленному компьютеру можно использовать командлет PowerShell
Get-SMBConnection
:
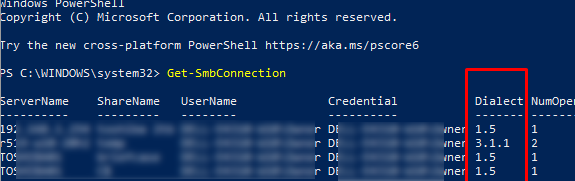
Версия SMB, используемая для подключения к удаленному серверу (ServerName) указана в столбце Dialect.
Можно вывести информацию о версиях SMB, используемых для доступа к конкретному серверу:
Get-SmbConnection -ServerName servername
Если нужно отобразить, используется ли SMB шифрование (появилось в SMB 3.0), выполните:
Get-SmbConnection | ft ServerName,ShareName,Dialect,Encrypted,UserName
В Linux вывести список SMB подключения и используемые диалекты в samba можно командой:
$ sudo smbstatus
Чтобы на стороне сервера вывести список используемых клиентами версий протокола SMB и количество клиентов, используемых ту или иную версию протокола SMB, выполните команду:
Get-SmbSession | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Dialect | Sort-Object -Unique
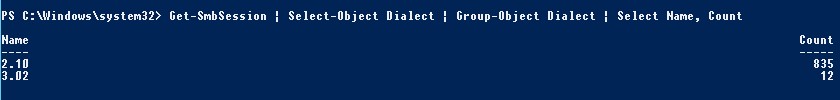
В нашем примере имеется 825 клиентов, подключенных к серверу с помощью SMB 2.1 (Windows 7/Windows Server 2008 R2) и 12 клиентов SMB 3.02.
С помощью PowerShell можно включить аудит версий SMB, используемых для подключения:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration –AuditSmb1Access $true
События подключения затем можно извлечь из журналов Event Viewer с помощью PowerShell:
Get-WinEvent -LogName Microsoft-Windows-SMBServer/Audit
Об опасности использования SMBv1
Последние несколько лет Microsoft из соображений безопасности планомерно отключает устаревший протокол SMB 1.0. Связано это с большим количеством критических уязвимостей в этом протоколе (вспомните историю с эпидемиями вирусов-шифровальщиков wannacrypt и petya, которые использовали уязвимость именно в протоколе SMBv1). Microsoft и другие IT компании настоятельно рекомендуют отказаться от его использования.
Однако отключение SMBv1 может вызвать проблемы с доступом к общий файлам и папкам на новых версиях Windows 10 (Windows Server 2016/2019) с устаревших версий клиентов (Windows XP, Server 2003), сторонних ОС (Mac OSX 10.8 Mountain Lion, Snow Leopard, Mavericks, старые версии Linux), различных старых NAS устройствах.
Если в вашей сети не осталось legacy устройств с поддержкой только SMBv1, обязательно отключайте эту версию диалекта в Windows.
В том случае, если в вашей сети остались клиенты с Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 или другие устройства, которые поддерживают только SMBv1, их нужно как можно скорее обновить или тщательно изолировать.
Включение и отключение SMBv1, SMBv2 и SMBv3 в Windows
Рассмотрим способы включения, отключения различных версий SMB в Windows. Мы рассматриваем отдельно включение клиента и сервера SMB (это разные компоненты).
Windows 10, 8.1, Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2:
Отключить клиент и сервер SMBv1:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName smb1protocol
Отключить только SMBv1 сервер:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $false
Включить клиент и сервер SMBv1:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName smb1protocol
Включить только SMBv1 сервер:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $true
Отключить сервер SMBv2 и SMBv3:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $false
Включить сервер SMBv2 и SMBv3:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $true
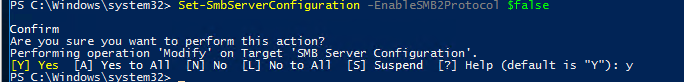
Windows 7, Vista, Windows Server 2008 R2/2008:
Отключить SMBv1 сервер:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 0 –Force

Включить SMBv1 сервер:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 1 –Force
Отключить SMBv1 клиент:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= disabled
Включить SMBv1 клиент:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= auto
Отключить SMBv2 сервер:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -Force
Включить SMBv2 сервер
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 1 –Force
Отключить SMBv2 клиент:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= disabled
Включить SMBv2 клиент:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= auto
Для отключения сервера SMBv1 на всех компьютерах независимо от версии Windows можно распространить параметр реестра типа REG_DWORD с именем SMB1 и значением 0 (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters)на через GPO.
Для отключения SMBv2 нужно в этой же ветке установить параметр SMB2=0.
Для отключения SMBv1 клиента нужно распространить такой параметр реестра:
- Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\mrxsmb10
- Name: Start
- Type: REG_DWORD
- Value: 4
При отключении SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support в Windows вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой “0x80070035, не найден сетевой путь”, ошибкой при доступе к общим папкам, и проблемами обнаружения компьютеров в сетевом окружении. В этом случае вместо служба обозревателя компьютеров (Computer Browser) нужно использовать службы обнаружения (линк).
How to enable and disable SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 in Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, and Windows Server 2012
This article describes how to enable and disable Server Message Block (SMB) version 1 (SMBv1), SMB version 2 (SMBv2), and SMB version 3 (SMBv3) on the SMB client and server components.
Summary
In Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, disabling SMBv2 deactivates the following functionality:
- Request compounding — allows for sending multiple SMB 2 requests as a single network request
- Larger reads and writes — better use of faster networks
- Caching of folder and file properties — clients keep local copies of folders and files
- Durable handles — allow for connection to transparently reconnect to the server if there is a temporary disconnection
- Improved message signing — HMAC SHA-256 replaces MD5 as hashing algorithm
- Improved scalability for file sharing — number of users, shares, and open files per server greatly increased
- Support for symbolic links
- Client oplock leasing model — limits the data transferred between the client and server, improving performance on high-latency networks and increasing SMB server scalability
- Large MTU support — for full use of 10-gigabye (GB) Ethernet
- Improved energy efficiency — clients that have open files to a server can sleep
In Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, disabling SMBv3 deactivates the following functionality (and also the SMBv2 functionality that is described in the previous list):
- Transparent Failover — clients reconnect without interruption to cluster nodes during maintenance or failover
- Scale Out concurrent access to shared data on all file cluster nodes
- Multichannel — aggregation of network bandwidth and fault tolerance if multiple paths are available between client and server
- SMB Direct adds RDMA networking support for very high performance, with low latency and low CPU utilization
- Encryption Provides end-to-end encryption and protects from eavesdropping on untrustworthy networks
- Directory Leasing — Improves application response times in branch offices through caching
- Performance Optimizations — optimizations for small random read/write I/O
More information
The SMBv2 protocol was introduced in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.
The SMBv3 protocol was introduced in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012.
For more information about the capabilities of SMBv2 and SMBv3 capabilities, go to the following Microsoft TechNet websites:
Server Message Block overview
What’s New in SMB
-
How to enable or disable SMB protocols on the SMB server
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 introduce the new Set-SMBServerConfiguration Windows PowerShell cmdlet. The cmdlet enables you to enable or disable the SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 protocols on the server component.
Notes When you enable or disable SMBv2 in Windows 8 or in Windows Server 2012, SMBv3 is also enabled or disabled. This behavior occurs because these protocols share the same stack.
You do not have to restart the computer after you run the Set-SMBServerConfiguration cmdlet.
- To obtain the current state of the SMB server protocol configuration, run the following cmdlet:
Get-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB1Protocol, EnableSMB2Protocol
- To disable SMBv1 on the SMB server, run the following cmdlet:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $false
- To disable SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB server, run the following cmdlet:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $false
- To enable SMBv1 on the SMB server, run the following cmdlet:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $true
- To enable SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB server, run the following cmdlet:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $true
Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008
To enable or disable SMB protocols on an SMB Server that is runningWindows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista, or Windows Server 2008, use Windows PowerShell or Registry Editor.
Windows PowerShell 2.0 or a later version of PowerShell
- To disable SMBv1 on the SMB server, run the following cmdlet:
Set-ItemProperty -Path «HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters» SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -Force
- To disable SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB server, run the following cmdlet:
Set-ItemProperty -Path «HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters» SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -Force
- To enable SMBv1 on the SMB server, run the following cmdlet:
Set-ItemProperty -Path «HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters» SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 1 -Force
- To enable SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB server, run the following cmdlet:
Set-ItemProperty -Path «HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters» SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 1 -Force
Note You must restart the computer after you make these changes.
Registry Editor
Important This article contains information about how to modify the registry. Make sure that you back up the registry before you modify it. Make sure that you know how to restore the registry if a problem occurs. For more information about how to back up, restore, and modify the registry, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
322756 How to back up and restore the registry in Windows
To enable or disable SMBv1 on the SMB server, configure the following registry key:
Registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\ParametersRegistry entry: SMB1
REG_DWORD: 0 = Disabled
REG_DWORD: 1 = Enabled
Default: 1 = Enabled To enable or disable SMBv2 on the SMB server, configure the following registry key:Registry subkey:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
Registry entry: SMB2
REG_DWORD: 0 = Disabled
REG_DWORD: 1 = Enabled
Default: 1 = EnabledHow to enable or disable SMB protocols on the SMB client
Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, and Windows Server 2012
Note When you enable or disable SMBv2 in Windows 8 or in Windows Server 2012, SMBv3 is also enabled or disabled. This behavior occurs because these protocols share the same stack.
- To disable SMBv1 on the SMB client, run the following commands:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb20/nsisc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= disabled
- To enable SMBv1 on the SMB client, run the following commands:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= auto
- To disable SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB client, run the following commands:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/nsi sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= disabled
- To enable SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB client, run the following commands:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= auto
Notes
- You must run these commands at an elevated command prompt.
- You must restart the computer after you make these changes.
- To obtain the current state of the SMB server protocol configuration, run the following cmdlet:
Published: 21/10/16 — 08:51:30 (Amanda Higgins)
Related Articles
Running DE8 on Windows Servers, do and dont’s (SMB1,SMB2,SMB3 and OpLocks)
With the release of DataEase 8.0, 8.1, 8.2 and Windows 7, 8 , 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2, we are frequently asked about how new versions of DataEase work when connecting to old versions of Windows servers and old versions of DataEase connecting to new…
Other sources of Network problems
This is a little old, but it is still useful. If you have switched off SMB2 and SMB3 on your networ as well as disabled OpLocks for SMB1 and still have problems with corruption, have a look below and see if some of these things might apply to your network…
Environment Variables in Windows XP, WIndows 7 and 8 (Complete List)
Environment variables is very useful to make general code. You can include them in paths directly to access files native to an active user/workstation/profile/session etc….
The following post shows detailed steps to enable and disable the Server Message Block (SMB) versions SMBv1, SMBv2 & SMBv3 on the SMB server and SMB client. The SMBv2 protocol was introduced in Windows Vista & Windows Server 2008 and the SMBv3 was introduced in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012.
The steps apply only to the following Windows versions:
• Windows Vista Enterprise
• Windows Vista Business
• Windows Vista Home Basic
• Windows Vista Home Premium
• Windows Vista Ultimate
• Windows 7 Enterprise
• Windows 7 Home Basic
• Windows 7 Home Premium
• Windows 7 Professional
• Windows 7 Ultimate
• Windows Server 2008 Datacenter
• Windows Server 2008 Enterprise
• Windows Server 2008 Standard
• Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter
• Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise
• Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard
• Windows 8
• Windows 8 Enterprise
• Windows 8 Pro
• Windows Server 2012 Datacenter
• Windows Server 2012 Essentials
• Windows Server 2012 Foundation
• Windows Server 2012 Standard
Important to Note:
It is recommended not to keep the SMBv2 or SMBv3 disabled. It should only be disabled for temporary troubleshooting. Keeping it disabled may deactivate various functions of the Windows server. The features which might get deactivated due to disabling SMBv2 & SMBv3 are mentioned below:
Disabling SMBv2 on Windows 7 & Windows Server 2008 R2 will deactivate the below functions:
• Request compounding – it enables users to send multiple SMB 2 requests as a single network request
• Larger reads and writes – better use of faster networks
• Caching of folder and file properties – clients keep local copies of folders and files
• Durable handles – when a temporary disconnection is there, it enables for connection to transparently rejoin to the server
• Improved message signing – HMAC SHA-256 replaces MD5 as hashing algorithm
• Improved scalability for file sharing – increases the no. of users, shares, and open files per server
• Support for symbolic links
• Client oplock leasing model – it automatically limits the volume of data transferred between the client and server, resulting in improved performance on high-latency networks and increasing the scalability of SMB server
• Large MTU support – for full use of 10-gigabyte (GB) Ethernet
• Enhanced energy efficiency – clients that have open files to a server can sleep
Disabling SMBv3 on Windows 8 & Windows Server 2012 will deactivate the below as well as above mentioned functions:
• Transparent Failover – it enables clients to rejoin the cluster nodes during the maintenance or failover without any interruption
• Scale Out – it allows concurrent access to shared data on all file cluster nodes
• Multichannel – aggregation of network bandwidth and fault tolerance if multiple paths are available between client and server
• SMB Direct – adds RDMA networking support for very high performance, with low latency and low CPU utilization
• Encryption – offers end-to-end encryption and completely defends from snooping on untrustworthy networks
• Directory Leasing – its caching functionality helps in improving the application response times in branch offices
• Performance Optimizations – optimizations for small random read/write I/O
Steps to Enable and Disable SMB Protocols on the SMB Server
Microsoft Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 have introduced a new cmdlet [Set-SMBServerConfiguration] in the Windows PowerShell which allows you to enable and disable the SMBv1, SMBv2 & SMBv3 protocols on the server. When you enable or disable the Server Message Block version 2 (SMBv2) in Windows 8 or in Windows Server 2012, automatically the SMBv3 is enabled or disabled, as the same stack is shared by the SMB protocols. Also, there is no need to restart your system once you run the Set-SMBServerConfiguration cmdlet.
Get the current state of the configuration of the SMB server protocol by running the below command:
Get-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB1Protocol, EnableSMB2Protocol
Disables the SMBv1 on the SMB server by running the below command:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $false
Disables the SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB server by running the below command:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $false
Enables the SMBv1 on the SMB server by running the below command:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $true
Enables the SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB server by running the below command:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $true
Steps to Enable and Disable the SMB protocols on SMB Server running Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista, or Windows Server 2008.
Using the Windows PowerShell 2.0 or later version:
Disables the SMBv1 on the SMB server by running the below command:
Set-ItemProperty -Path “HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters” SMB1 -Value 0 –Force
Disables the SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB server by running the below command:
Set-ItemProperty –Path “HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters” SMB2 –Value 0 –Force
Enables the SMBv1 on the SMB server by running the below command:
Set-ItemProperty –Path “HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters” SMB1 –Value 1 –Force
Enables the SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB server by running the below command:
Set-ItemProperty -Path “HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters” SMB2 -Value 1 -Force
Note that you need to restart your system after making changes to the SMB server.
Using Registry Editor:
Important to Note:
• Before making any changes to the registry, make sure to back up it.
Steps to enable and disable the SMBv1 on the SMB server using the registry:
Registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
Registry entry: SMB1
REG_DWORD: 0 = Disabled
REG_DWORD: 1 = Enabled
Default: 1 = Enabled
Steps to enable and disable SMBv2 on the SMB server using the registry:
Registry subkey:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
Registry entry: SMB2
REG_DWORD: 0 = Disabled
REG_DWORD: 1 = Enabled
Default: 1 = Enabled
Steps to Enable and Disable SMB protocols on the SMB client
The below steps apply to Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, and Windows Server 2012.
Disables the SMBv1 on the SMB client by running the below commands:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= disabled
Enables the SMBv1 on the SMB client by running the below commands:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= auto
Disables the SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB client by running the below commands:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= disabled
Enables the SMBv2 and SMBv3 on the SMB client by running the below commands:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= auto
Important to Note:
• The commands be run at a raised command prompt.
• The system must be restarted once you make these changes.
The Server Message Block (SMB) network protocol is used to share and access folders, files, printers, and other devices over network (TCP port 445). In this article, we will look at which versions (dialects) of SMB are available in different versions of Windows (and how they relate to samba versions on Linux); how to check the SMB version in use on your computer; and how to enable or disable the SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 dialects.
Contents:
- SMB Protocol Versions in Windows
- How to Check SMB Version on Windows?
- Checking Used SMB Dialects with Get-SMBConnection
- Stop Using the Insecure SMBv1 Protocol
- How to Enable and Disable SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 on Windows?
SMB Protocol Versions in Windows
There are several versions of the SMB protocol (dialects) that have consistently appeared in new Windows versions (and samba) :
- CIFS – Windows NT 4.0
- SMB 1.0 – Windows 2000
- SMB 2.0 – Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista SP1 (supported in Samba 3.6)
- SMB 2.1 – Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 (Samba 4.0)
- SMB 3.0 – Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8 (Samba 4.2)
- SMB 3.02 – Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1 (not supported in Samba)
- SMB 3.1.1 – Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10 (not supported in Samba)
Samba is used to implement the SMB protocol in Linux/Unix . Samba 4.14 and newer uses SMB 2.1 by default.
In SMB network communication, the client and server use the maximum SMB protocol version supported by both the client and the server.
The summary table of SMB version compatibility looks like this. Using this table, you can determine the version of the SMB protocol that is selected when different versions of Windows interact:
| Operating System | Windows 10, Win Server 2016 | Windows 8.1, Win Server 2012 R2 | Windows 8,Server 2012 | Windows 7,Server 2008 R2 | Windows Vista,Server 2008 | Windows XP, Server 2003 and earlier |
| Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 | SMB 3.1.1 | SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 8.1, Server 2012 R2 | SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.02 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 8, Server 2012 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 3.0 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows 7, Server 2008 R2 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.1 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows Vista, Server 2008 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 2.0 | SMB 1.0 |
| Windows XP, 2003 and earlier | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 | SMB 1.0 |
For example, if a client computer running Windows 8.1 connects to a file server with Windows Server 2016, the SMB 3.0.2 protocol will be used.
According to the table, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 can use only SMB 1.0 to access shared folders and files. The SMBv1 is disabled in newer versions of Windows Server (2012 R2/2016). So, if you are still using Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 devices on your network, they won’t be able to access shared folders on the file server running Windows Server 2016.
If Windows Server 2019/2016 with disabled SMB v1.0 is used as a domain controller, then Windows XP/Server 2003 clients won’t be able to access the SYSVOL and NETLOGON folders on domain controllers and authenticate with AD.
You may receive the following error when trying to connect to a shared folder on a file server with SMBv1 disabled:
The specified network name is no longer available
How to Check SMB Version on Windows?
Let’s look on how to find out which versions of the SMB are enabled on your Windows device.
On Windows 10/8.1 and Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2, you can check the status of various dialects of the SMB protocol using PowerShell:
Get-SmbServerConfiguration | select EnableSMB1Protocol,EnableSMB2Protocol
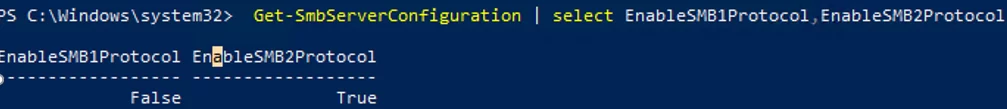
This command returned that the SMB1 protocol is disabled (EnableSMB1Protocol = True), and the SMB2 and SMB3 protocols are enabled (EnableSMB1Protocol = False).
Note that the SMBv3 and SMBv2 protocols are closely related. You cannot disable or enable SMBv3 or SMBv2 separately. They are always enabled/disabled only together because they share the same stack.
On Windows 7, Vista, and Windows Server 2008 R2/2008:
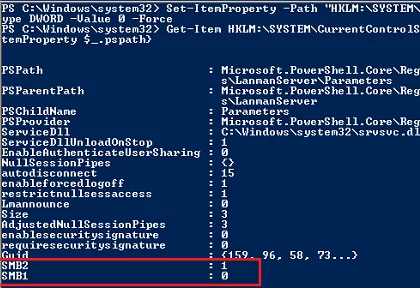
Get-Item HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath}
If there are no parameters named SMB1 or SMB2 in this registry key, then the SMBv1 and SMBv2 protocols are enabled by default.
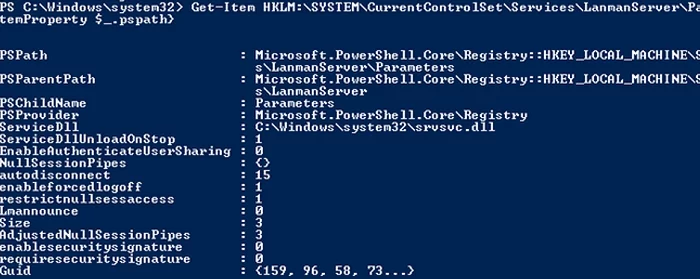
Also on these Windows versions, you can check which SMB client dialects are allowed to connect to remote hosts:
sc.exe query mrxsmb10
SERVICE_NAME: mrxsmb10 TYPE : 2 FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0
sc.exe query mrxsmb20
SERVICE_NAME: mrxsmb20 TYPE : 2 FILE_SYSTEM_DRIVER STATE : 4 RUNNING (STOPPABLE, NOT_PAUSABLE, IGNORES_SHUTDOWN) WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) SERVICE_EXIT_CODE : 0 (0x0) CHECKPOINT : 0x0 WAIT_HINT : 0x0
In both cases, the services are running (STATE = 4 Running). This means that the current Windows device can connect to both SMBv1 and SMBv2 hosts.
Checking Used SMB Dialects with Get-SMBConnection
When communicating over SMB, computers use the maximum SMB version supported by both the client and the server. The Get-SMBConnection PowerShell cmdlet can be used to check the SMB version used to access a remote computer:
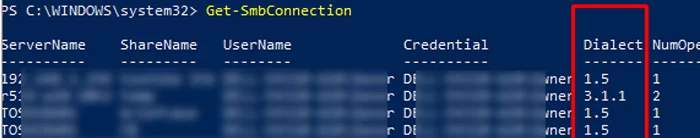
The SMB version used to connect to the remote server (ServerName) is listed in the Dialect column.
You can display information about the SMB versions used to access a specific server:
Get-SmbConnection -ServerName srvfs01
If you want to display if SMB encryption is in use (introduced in SMB 3.0):
Get-SmbConnection | ft ServerName,ShareName,Dialect,Encrypted,UserName
On Linux, you can display a list of SMB connections and used dialects in samba using the command:
$ sudo smbstatus
On the Windows SMB server side, you can display a list of the versions of the SMB protocols that the clients are currently using. Run the command:
Get-SmbSession | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Dialect | Sort-Object -Unique
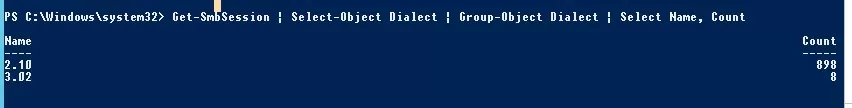
In this example, there are 898 clients connected to the server using SMB 2.1 (Windows 7/ Windows 2008 R2) and 8 SMB 3.02 clients.
You can use PowerShell to enable auditing of the SMB versions used for the connection:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration –AuditSmb1Access $true
SMB connection events can then be exported from Event Viewer logs:
Get-WinEvent -LogName Microsoft-Windows-SMBServer/Audit
Stop Using the Insecure SMBv1 Protocol
Over the past few years, Microsoft has systematically disabled the legacy SMB 1.0 protocol in all products for security reasons. This is due to the large number of critical vulnerabilities in this protocol (remember the incidents with wannacrypt and petya ransomware, which exploited a vulnerability in the SMBv1 protocol). Microsoft and other IT companies strongly recommend that you stop using SMBv1 in your network.
However, disabling SMBv1 can cause problems with accessing shared files and folders on newer versions of Windows 10 (Windows Server 2016/2019) from legacy clients (Windows XP, Windows Server 2003), third-party OS (Mac OSX 10.8 Mountain Lion, Snow Leopard, Mavericks, old Linux distros), old NAS devices.
If there are no legacy devices left on your network that support only SMBv1, be sure to disable this SMB dialect in Windows.
If you have clients running Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, or other devices that only support SMBv1, they should be updated or isolated.
How to Enable and Disable SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 on Windows?
Let’s look at ways to enable and disable different SMB versions on Windows. We’ll cover SMB client and server management (they are different Windows components).
Windows 10, 8.1, and Windows Server 2019/2016/2012R2:
Disable SMBv1 client and server:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName smb1protocol
Disable SMBv1 server only:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $false
Enable SMBv1 client and server:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName smb1protocol
Enable only SMBv1 server:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $true
Disable SMBv2 and SMBv3 server:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $false
Enable SMBv2 and SMBv3 server:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $true
Windows 7, Vista, and Windows Server 2008 R2/2008:
Disable SMBv1 server:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 0 –Force
Enable SMBv1 server:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 1 –Force
Disable SMBv1 client:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= disabled
Enable SMBv1 client:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= auto
Disable SMBv2 server:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -Force
Enable SMBv2 server:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 1 –Force
Disable SMBv2 client:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= disabled
Enable SMBv2 client:
sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= auto
You can disable SMBv1 server on domain joined computers by deploying the following registry parameter through the GPO:
- Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
- Name: SMB1
- Type: REG_DWORD
- Value: 0
Set the registry parameter SMB2=0 in order to disable the SMBv2 server.
To disable the SMBv1 client, you need to propagate the following registry setting:
- Key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\mrxsmb10
- Name: Start
- Type: REG_DWORD
- Value: 4
Server Message Block (SMB) is a networking file share protocol included in Windows workstation and Windows server that provides the ability to read and write files and perform other service requests to network devices on a share.
Windows supports file and printer sharing traffic by using the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol directly hosted on TCP. This differs from earlier operating systems, in which SMB traffic requires the NetBIOS over TCP (NBT) protocol to work on a TCP/IP transport. Removing the NetBIOS transport has several advantages, including:
- Simplifying the transport of SMB traffic.
- Removing WINS and NetBIOS broadcast as a means of name resolution.
- Standardizing name resolution on DNS for file and printer sharing.
NetBIOS over TCP traditionally uses the following ports:
| nbname | 137/UDP |
| nbname | 137/TCP |
| nbdatagram | 138/UDP |
| nbsession | 139/TCP |
Usually, you’ll be using SMB to connect to devices that don’t run Windows and Windows machines, such as a router with file sharing capabilities, Network-Attached Storage (NAS), or other computers running Linux.
Windows SMB versions
- SMB 1 – Windows 2000
- SMB 2 – Windows Server 2008 and WIndows Vista SP1
- SMB 2.1 – Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7
- SMB 3.0 – Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8 / 10
SMBv1 has been in use since Windows 95, and in 2019, it’s still often found and abused in networks. If you have SMB v1 enabled in your network, it can be used in blended attacks that might include ransomware and other malware. Recommendation is to use SMB3
Features of SMB3
- Pre-authentication Integrity (SMB 3.1.1+). Protects against security downgrade attacks.
- Secure Dialect Negotiation (SMB 3.0, 3.02). Protects against security downgrade attacks.
- Encryption (SMB 3.0+). Prevents inspection of data on the wire, MiTM attacks. In SMB 3.1.1 encryption performance is even better than signing!
- Insecure guest auth blocking (SMB 3.0+ on Windows 10+) . Protects against MiTM attacks.
- Better message signing (SMB 2.02+). HMAC SHA-256 replaces MD5 as the hashing algorithm in SMB 2.02, SMB 2.1 and AES-CMAC replaces that in SMB 3.0+. Signing performance increases in SMB2 and 3.
Windows documentation
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/file-server/troubleshoot/detect-enable-and-disable-smbv1-v2-v3
Enable The service
Windows 10
1. Enable, go to
- Control Panel – Network and Sharing Center – Change advanced sharing settings

Turn the options on depending on your needs
- Private Network
- Public Network
- All Networks
In this case I would do it for the private network

2. In all Networks there are some security setting to take into consideration
Public folder sharing
- Turn off
File sharing connections
- Strongest encryption in this case 128-bit encryption
Password protected sharing
- Turn on password protected sharing

3. Access the Network share
- Win key + e
- Network

Windows Server 2008
Same procedure just that in 2008 We get different options in Change advanced sharing settings
- Home or work
- Public
In this case I will enable Home or work

Click on save changes, and then, access the Network
Access the Network share
- Win key + e
- Network

Methods to check what version of SMB is installed on the Server (enable, disable & detect)
We will be using the following methods to check what version of SMB is installed on your computer:
- The PowerShell Method.
- The Registry Editor Method.
How to enable, disable & detect SMB1 (Powershell)
Windows 10, Windows 8.1
Detect
- Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol
- Get-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB1Protocol

Enable
- Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol

- Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol

Disable
- Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol

- Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol

Alternative way
1. Go to
- Control Panel – Programs and Features – Turn Windows features on or off

2. This pop up will show, disable SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support, uncheck the boxes under “SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support”, including the top folder

Windows Server 2008 & 2008 R2, Windows 7, Windows Vista (Powershell)
Detect
- Get-Item HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath}

Enable
- Set-ItemProperty -Path “HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters” SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 1 -Force

Disable
- Set-ItemProperty -Path “HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters” SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -Force

How to enable, disable & Detect SMB3 (Powershell)
Windows 10
Detect
- Get-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB2Protocol
- Get-SmbServerConfiguration

Enable
- Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $true

Disable
- Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $false

Windows Server 2008 (Powershell)
Detect
- Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath}

Enable
- Set-ItemProperty -Path “HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters” SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 1 -Force

Disable

Check the version of SMB using the registry
1. execute regedit from “ run” utility. Win key + r
2. Now visit the following path
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters

3. Now if you have the DWORDs named as SMB1 or SMB2, check their Value Data. If it is set to 0, it is disabled, 1 means enabled. Default 1

Methods to check what version of SMB is installed on the Clients
This method will work on Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, and Windows Server 2012
- The PowerShell Method.
- You must run these commands at an elevated command prompt.
- You must restart the computer after you make these changes.
SMB v1 on SMB Client
Detect
- sc.exe qc lanmanworkstation

Enable
- sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
- sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= auto

Disable
- sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb20/nsi
- sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= disabled
SMB v2/v3 on SMB Client
Detect
- sc.exe qc lanmanworkstation

Enable
- sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi
- sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= auto

Disable
- sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/nsi
- sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= disabled

Securing SMB
1. The first step is to disable SMB1 using the previous examples according to the type of OS, and, only use SMB3 if possible. Check if the protocol is enabled, if so, disable it, and enable a newer version.
Disabling SMBv1 is very complicated as many applications, platforms, printers, etc., are heavily dependent on it. SMBv1 should be carefully examined on an OS basis before hardening is performed.
You should make sure that any new software and hardware that requires the SMB protocol is able to negotiate newer versions (at least SMBv2, preferably SMBv3). For existing devices and software that only support SMBv1, you should contact the manufacturer for updates to support the newer dialects.
Be careful when you make these changes on domain controllers on which legacy Windows XP or older Linux and third-party systems (that do not support SMBv2 or SMBv3) require access to SYSVOL or other file shares where SMB v1 is being disabled.
Windows 10 example
- Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol

2. You might find that older copiers and printers or older network-accessible storage still depends on SMB v1 to be functional. You need to determine if the risk of SMB v1 is acceptable, or you can contact the vendors on your impacting devices to determine if you can get a firmware update to support SMB v2 and SMB v3 on these older devices.
3. Block SMB at the firewall level to prevent access from outside. It would do so by blocking TCP port 445 with related protocols on UDP ports 137-138 and TCP port 139, for all boundary devices.
- Avoid exposing SMB ports: Ports 135-139 and 445 are not safe to publicly expose and have not been for a decade.
4. Use the following steps to disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP; this procedure forces all SMB traffic to be direct hosted using only port 445. Take care in implementing this setting because it causes the Windows-based computer to be unable to communicate with earlier operating systems using SMB traffic due to the lack of ports 139 as an example:
- Click Start, Control Panel – Network and Internet – Network Connections
- Right-click Local Area Connection, or the adapter network card, and then click Properties.

- Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.

- Click Advanced.
- Click the WINS tab, and then click Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP.
If NetBIOS over TCP/IP is disabled, only port 445 will be used. You can also disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP by using a DHCP server with Microsoft vendor-specific option code 1, (“Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP”). Setting this option to a value of 2 disables NBT.

To determine if NetBIOS over TCP/IP is enabled on a Windows-based computer, issue a net config redirector or net config server command at a command prompt. The output shows bindings for:
NetbiosSmb device (which is the “NetBIOS-less” transport)
- NetBT_Tcpip is bound to each adapter individually; an instance of NetBT_Tcpip is shown for each network adapter that it is bound to.
NetBT_Tcpip device (which is the NetBIOS over TCP transport).
- NetbiosSmb is a global device, and is not bound on a per-adapter basis.
Command output when NetBIOS over TCP/IP is enabled
- net config server

NetBT_Tcpip device (which is the NetBIOS over TCP transport)
- net config redirector

5. Disable null session
A well-known vulnerability within Windows can map an anonymous connection (or null session) to a hidden share called IPC$ (which stands for interprocess communication).
- Open “Run” & run regedit
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\LsaInformation
- Set the value to 0 (restrictanonymous, restrictanonymoussam)
0 – None. Rely on default permissions
1 – Do not allow enumeration of Security Accounts Manager (SAM) accounts and names
2 – No access without explicit anonymous permissions (not available on Windows NT 4.0)

To confirm we can check “Local Security Policy”
- Go to Local Policies – Security Options
- Look for status on Network access (Network access allow anonymous SID/Name translation)
- Should be disabled

6. General Recommendations
- Patch everything: Keep your systems up-to-date to avoid exploits of known vulnerabilities.
- No single point of failure: Whether it’s ransomware, malware, hardware failure, database error, or something else. If your data is important, then it should be backed up, at least one other secure location.
- Use a firewall or endpoint protection: Most solutions will include a blacklist of known attacker IP addresses.
- Use a virtual private network (VPN): VPNs encypt and protect network traffic.
- Implement virtual local area networks (VLANs): VLANs can be used to isolate internal network traffic
- Use MAC address filtering: This can prevent unknown systems from accessing your network.
