Applies ToWindows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation Windows 7 Service Pack 1 Windows 7 Ultimate Windows 7 Enterprise Windows 7 Professional Windows 7 Home Premium Windows 7 Home Basic Windows 7 Starter
This article describes an issue that occurs when the wireless session times out in Windows 7 Service Pack 1 (SP1) or Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1. A hotfix is available to fix this issue. Before you install this hotfix, see the Prerequisites section.
Symptoms
This issue occurs when a Windows 7-based computer is connected to a wireless network by using the Wi-Fi Protected Access II (WPA2) protocol and the wireless access point (AP) starts a new exchange of WPA2 keys. In the four-way handshake, the Windows 7-based computer sends a Message 2 (M2) with an invalid message integrity check (MIC) and secure bit.
Note This issue may occur every 12 hours or more frequently, and it takes one minute to regain the network connectivity.
For more information about this issue, go to the Cisco website.
Cause
This issue occurs because the WPA2 key context is not set correctly before the four-way handshake rekeys. Certain variables are not reset after the previous four-way handshake. This causes the secure bit to be set incorrectly and the stale Pairwise Transient Key (PTK) to be used to calculate the MIC in the M2 key messages. Some (specifically but not limited to Cisco) APs reject the M2 messages because of these errors.
Hotfix information
Important If you install a language pack after you install this hotfix, you must reinstall this hotfix. Therefore, we recommend that you install any language packs that you need before you install this hotfix. For more information, see Add language packs to Windows.
A supported hotfix is available from Microsoft. However, this hotfix is intended to correct only the problem that’s described in this article. Apply this hotfix only to systems that are experiencing this specific problem.
If the hotfix is available for download, there’s a «Hotfix Download Available» section at the top of this Knowledge Base article. If this section doesn’t appear, submit a request to Microsoft Customer Service and Support to get the hotfix.
Note If additional issues occur or if any troubleshooting is required, you might have to create a separate service request. The usual support costs will apply to additional support questions and issues that don’t qualify for this specific hotfix. For a complete list of Microsoft Customer Service and Support telephone numbers or to create a separate service request, visit the following Microsoft website:
Prerequisites
To apply this hotfix, install Service Pack 1 in Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2.
Registry information
To use the hotfix in this package, you don’t have to make any changes to the registry.
Restart requirement
You may have to restart the computer after you apply this hotfix.
Hotfix replacement information
This hotfix doesn’t replace a previously released hotfix.
File Information
The English (United States) version of this software update installs files that have the attributes that are listed in the following tables. The dates and times for these files are listed in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Be aware that dates and times for these files on your local computer are displayed in your local time and with your current daylight saving time bias. The dates and times may also change when you perform certain operations on the files.
Notes
-
The files that apply to a specific product, milestone (RTM, SPn), and service branch (LDR, GDR) can be identified by examining the file version numbers as shown in the following table:
Version
Product
Milestone
Service branch
6.1.760 1.23 xxx
Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2
SP1
LDR
-
GDR service branches contain only those fixes that are widely released to address widespread, critical issues. LDR service branches contain hotfixes in addition to widely released fixes.
-
The MANIFEST files (.manifest) and the MUM files (.mum) that are installed for each environment are listed in the «Additional file information» section. MUM, MANIFEST, and the associated security catalog (.cat) files, are very important to maintain the state of the updated components. The security catalog files, for which the attributes are not listed, are signed with a Microsoft digital signature.
x64 Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Nwifi.sys |
6.1.7601.23207 |
324,096 |
11-Sep-2015 |
17:20 |
x64 |
x86 Windows 7
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Nwifi.sys |
6.1.7601.23207 |
270,848 |
11-Sep-2015 |
17:02 |
x86 |
x64 Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File property |
Value |
|---|---|
|
File name |
Amd64_87bc8280f965997a845adad7cf39a6ab_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.23207_none_1ab274d11e2d1647.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
704 |
|
Date (UTC) |
11-Sep-2015 |
|
Time (UTC) |
21:24 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-native-80211_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.23207_none_adc5e6ecbea51f05.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
65,699 |
|
Date (UTC) |
11-Sep-2015 |
|
Time (UTC) |
18:48 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Update.mum |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
1,843 |
|
Date (UTC) |
11-Sep-2015 |
|
Time (UTC) |
21:24 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
x86 Windows 7
|
File property |
Value |
|---|---|
|
File name |
Update.mum |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
1,625 |
|
Date (UTC) |
11-Sep-2015 |
|
Time (UTC) |
21:24 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
X86_532181f6d9549b37471d0be27cd1ccde_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.23207_none_91932b15bdebf270.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
700 |
|
Date (UTC) |
11-Sep-2015 |
|
Time (UTC) |
21:24 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
X86_microsoft-windows-native-80211_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.23207_none_51a74b690647adcf.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
65,695 |
|
Date (UTC) |
11-Sep-2015 |
|
Time (UTC) |
18:29 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
Status
Microsoft has confirmed that this is a problem in the Microsoft products that are listed in the «Applies to» section.
References
See the terminology that Microsoft uses to describe software updates.
More Information
What changes we have made to fix this issueThis fix addresses an incorrectly set security flag in the M2 message of the rekey handshake. This in turn produces an incorrectly calculated MIC. Some Cisco APs reject the M2 message because of these errors. The fix sets the M2 flag correctly during a rekey handshake.
The third-party products that this article discusses are manufactured by companies that are independent of Microsoft. Microsoft makes no warranty, implied or otherwise, about the performance or reliability of these products.
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Установил на Acer Aspire 5739g Windows Server 2008 R2.
Поставил драйвер на чипсет.
Через ethernet кабель интернет работает. WLAN адаптер (Intel WiFi Link 5100 ABG) тоже определяет, но ни одного wi-fi подключения не видит. В компонентах «службу беспроводной локальной сети» включил. Служба «автонастройки WLAN» работает. Службу пробовал перезапускать, ноут ребутал, драйвера на WLAN адаптер ставил (для Win Vista x64).
Подскажите в чем проблема?
UPD: Проблему решил. На ноуте есть сенсорные кнопки, которые вкл\откл wifi, bt, регулируют звук. Нажал на кнопку wifi и он стал искать сети. Только вот не могу понять 2 вещи:
1. Драйвера для этих кнопок не устанавливал, как они могут работать…
2. Как я понимаю, при отключении через эту кнопку wifi, в сетевых подключениях (изменение параметров адаптера) должен отключатся адаптер wifi.
Или я в чем то ошибаюсь…
Изменено пользователем Aries
After having installed Microsoft Windwos 2008 R2 Server and fully patched it to the latest and greatest service packs you can’t get the wireless network interface to work, you check and download the latest drivers for the wireless card but still that interface will not activate…..The interface is there but no one is home.
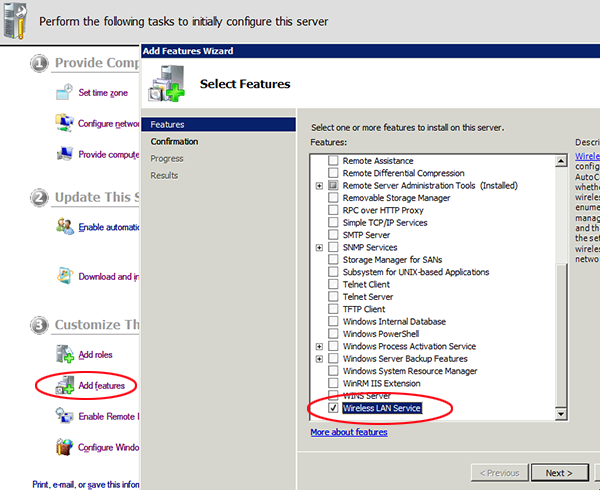
– the Wireless Service needs to be enabled as a feature out of the box!
Launch ‘Initial Configuration Tasks’ or ‘Server Manager’, click on Add Feature and enable the ‘Wireless Service Manager’, it is disabled by default as a security measure.
windows-2008-wireless-working-feature
Posted: August 24, 2009/Under: Operating Systems/By:
After installing Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2, the wireless adapter or WiFi adapter is not working or functioning. System cannot detect or see any wireless networks with no wireless networks available error message, and system cannot connect to Internet or wireless LAN.
To make matter worse, users have installed the proper signed driver for the wireless adapter, either through Windows Update, drivers CD from vendor or download latest and correct driver from OEM or manufacturer’s website. In Device Manager, the wireless or WiFi network adapter is working properly. And, when using Windows Server built-in diagnostics feature to troubleshoot the no wireless connection problem, it indicates that the wireless adapter is either having driver or hardware issue.
The cause of the no wireless connection is that Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 disables and turns off Wireless LAN service by default, which supports the wireless WLAN Auto Configuration service, and configures WLAN AutoConfig for automatic startup.
In order to turn on Wireless LAN and WLAN AutoConfig service in Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2, go to Server Manager (in Administrator Tools). Go to Features branch and click on Add Features. Click and tick the check box for Wireless LAN Service. Complete the installation wizard to install wireless support.
The Wireless LAN Service configures the WLAN AutoConfig service to start automatically, regardless of whether the computer has any IEEE 802.11 wireless adapters installed. When enabled, WLAN AutoConfig enumerates every wireless network adapter installed on the computer, manages IEEE 802.11 wireless connections, and manages the wireless connection profiles that contain the settings required to configure a wireless client to connect to a wireless network. WLAN AutoConfig allows user to connect to an existing wireless network (data encryption key or network key may be required), change wireless network connection settings, configure a connection to a new wireless network, and specify preferred wireless networks. WLAN AutoCofig also notifies user when new wireless networks are available. When switching wireless networks, WLAN AutoConfig dynamically updates your wireless network adapter settings to match the settings of that new network and a network connection attempt will be made.
Время от времени возникает необходимость подключения серверной операционной системы Windows к беспроводной сети. На первый взгляд задача элементарная: подключил адаптер, поставил драйвер… Однако ее практическая реализация способна вызвать нешуточные сложности. Мы уже готовы услышать привычные сетования в адрес компании Microsoft, но на самом деле все довольно просто и логично, единственное, что можно поставить в упрек разработчику, так это неинформативное поведение системы в данной ситуации, на наш взгляд вполне можно было бы добавить подсказки или отразить событие в логах.
Онлайн-курс по устройству компьютерных сетей
На углубленном курсе «Архитектура современных компьютерных сетей» вы с нуля научитесь работать с Wireshark и «под микроскопом» изучите работу сетевых протоколов. На протяжении курса надо будет выполнить более пятидесяти лабораторных работ в Wireshark.
Начнем с того, что обозначенная в заголовке задача для серверных систем довольно нетипична, но иногда такая потребность все-таки появляется. Решается она тоже просто, покупкой нужного беспроводного адаптера. В общем все идет достаточно привычно, до тех пор, пока вы не попытаетесь подключиться к беспроводной сети. В этот момент выяснится, что сервер не видит не одной сети, а сам адаптер находится в состоянии Отключено.
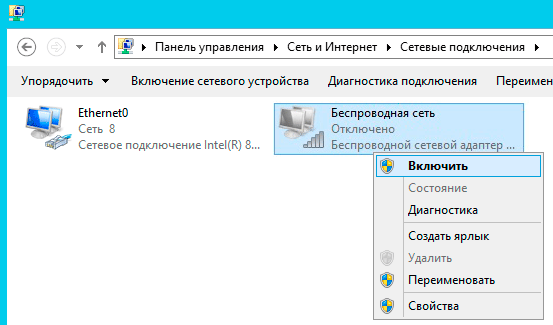
Попытка включить его не приводит к успеху, адаптер делает попытку включиться, но тут же снова переходит в отключенное состояние. При этом система не выдает никаких сообщений и не делает никаких записей в журналах событий.
Внешне ситуация выглядит как некая несовместимость и на поиск «подходящего» драйвера можно потратить достаточно много времени или, решив, что проблема с адаптером, даже купить новый, с таким же эффектом. Поэтому не спешите тратить время и деньги, давайте лучше разберемся в ситуации.
Как мы уже говорили, данная задача для серверного применения нетипична, поэтому, следуя общей тенденции развития серверных операционных систем Microsoft, данная возможность была оформлена в виде отдельной компоненты, которая по умолчанию не установлена.
В целом такое решение разработчиков логично и правильно, меньше неиспользуемых служб — меньше потребляемых ресурсов, меньше возможных уязвимостей. С другой стороны, добавить какие-либо подсказки или записывать в журнал событие с ошибкой все-таки стоило бы, иначе для неподготовленного пользователя ситуация выглядит достаточно неоднозначно.
Для того, чтобы Windows Server мог работать с беспроводными сетями следует установить компоненту Служба беспроводной локальной сети, после чего сервер потребуется перезагрузить.
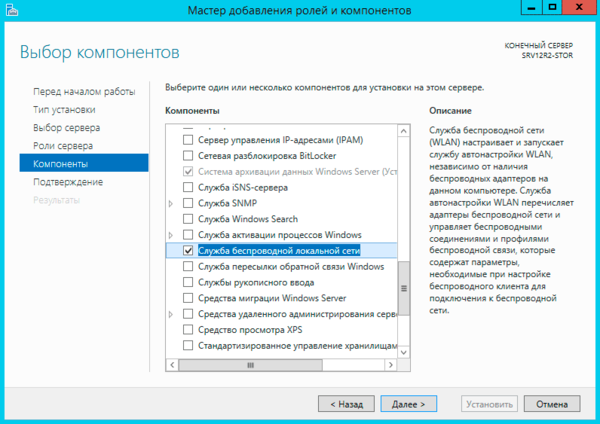
Казалось бы, проблема решена, но не стоит спешить. После перезагрузки Служба автонастройки WLAN автоматически не запускается, хотя в ее настройках установлен автоматический запуск.
Эта ситуация не является ошибкой и описана в документации, хотя такое поведение службы непонятно. Вам потребуется запустить службу вручную или еще раз перезагрузить сервер. После этого можно включить беспроводной адаптер и подключиться к нужной сети.
Интересно, что если после первой перезагрузки вы вставите новый адаптер, то по завершению установки драйвера служба автоматически запустится. Возможно в связи с этим в некоторых руководствах в сети присутствует рекомендация после добавления компоненты удалить и заново установить драйвер адаптера.
Такой же самый результат можно получить гораздо быстрее используя PowerShell, для этого выполните всего одну простую команду:
Add-WindowsFeature wireless-networking
После чего точно также потребуется перезагрузить сервер и запустить службу вручную. Быстро это сделать можно еще одной командой:
net start wlansvcКак видим, для успешного администрирования Windows Server, вопреки расхожему мнению, что в нем все делается интуитивно понятно и мышкой, все-таки желательно знать структуру и базовые принципы устройства системы, что избавит вас от возможных трат впустую времени и денег.
Онлайн-курс по устройству компьютерных сетей
На углубленном курсе «Архитектура современных компьютерных сетей» вы с нуля научитесь работать с Wireshark и «под микроскопом» изучите работу сетевых протоколов. На протяжении курса надо будет выполнить более пятидесяти лабораторных работ в Wireshark.
