Ping — утилита командной строки для проверки соединений в сетях TCP/IP. Она является одним из основных средств диагностики сети и входит в состав всех современных сетевых операционных систем. Принцип ее работы заключается в том, что она отправляет запросы (ICMP Echo-Request) протокола ICMP указаному узлу и фиксирует поступающие ответы (ICMP Echo-Reply).
Время между отправкой запроса и получением ответа позволяет определить задержки при передаче и частоту потери пакетов, а также оценить загруженность канала передачи данных. Полное отсутствие ICMP-ответов может означать, что удалённый узел неисправен.
В серверных ОС начиная с Windows Server 2008 входящие эхо-запросы по умолчанию запрещены и блокируются брандмауэром Windows. Сделано это скорее всего с целью предотвратить сетевые атаки типа ICMP Flooding (затопление атакуемого узла пакетами ICMP), которые могут вызвать отказ в обслуживании (Denial of Service, DoS). Безопасность конечно важна, однако в результате при попытке проверить доступность сервера мы получаем ошибку.
Для разрешения входящих эхо-запросов необходимо активировать соответствующее правило брандмауэра Windows. Вот несколько вариантов того, как это сделать.
Оснастка Windows Firewall with Adwanced Security
Самый простой способ разрешить ping — воспользоваться оснасткой «Windows Firewall with Adwanced Security». Для ее запуска нажимаем клавиши Win+R и вводим команду wf.msc.
Заходим в раздел входящих правил (Inbound Rules). Здесь нас интересует предопределенное правило для IPV4 — ″File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request — ICMPv4-In)″. Обратите внимание, что в таблице присутствуют два правила с одинаковым названием. На самом деле это одно и то же правило, просто настроенное для разных профилей — одно для доменного профиля, второе для общего и частного.
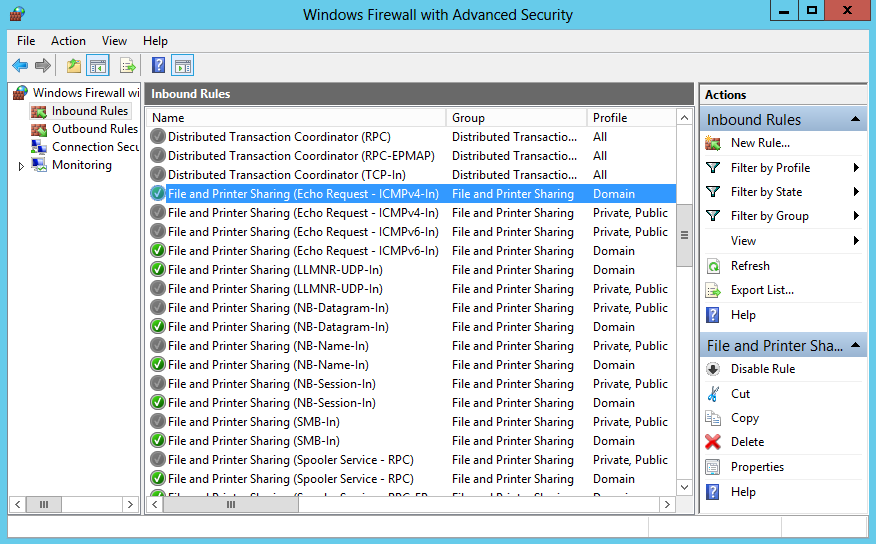
Активируем правило, отметив галочкой чекбокс Enabled и проверяем, чтобы в поле Action был выбран пункт ″Allow the connection″.
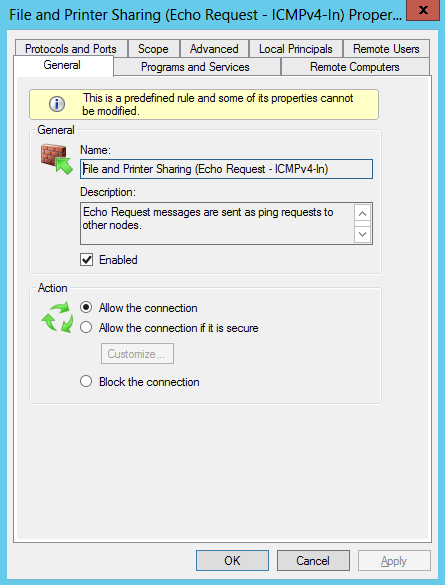
Переходим на вкладку Advanced и выбираем профили, для которых это правило будет действовать. Сохраняем правило и жмем OK. Теперь сервер можно пинговать.
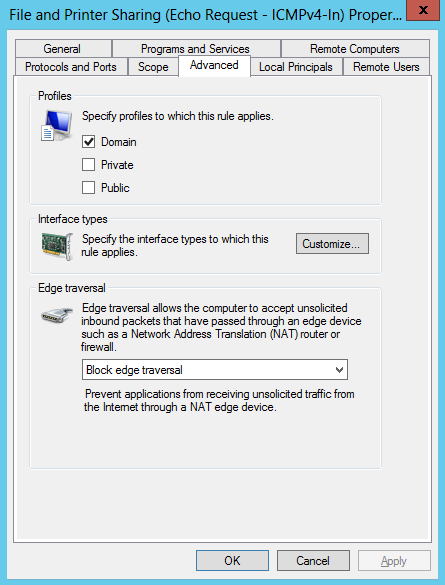
При необходимости в дополнительных мерах безопасности произведем еще несколько настроек, которые защитят сервер от атак и позволят вам спокойно пользоваться Ping-ом.
Переходим на вкладку Scope и в поле Remote IP address указываем, с каких адресов разрешено принимать входящие запросы. Здесь можно указать один адрес, диапазон адресов либо целиком подсеть.
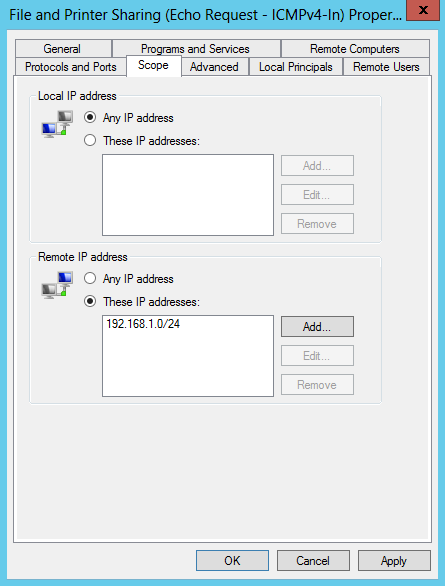
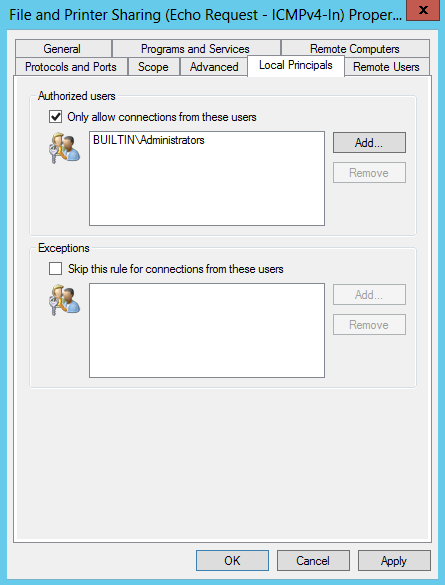
На вкладке Local Principals указываем локальных пользователей или группы, которым разрешается пинговать данный сервер. Как вариант, можно дать разрешение только группе локальных администраторов.
Групповые политики
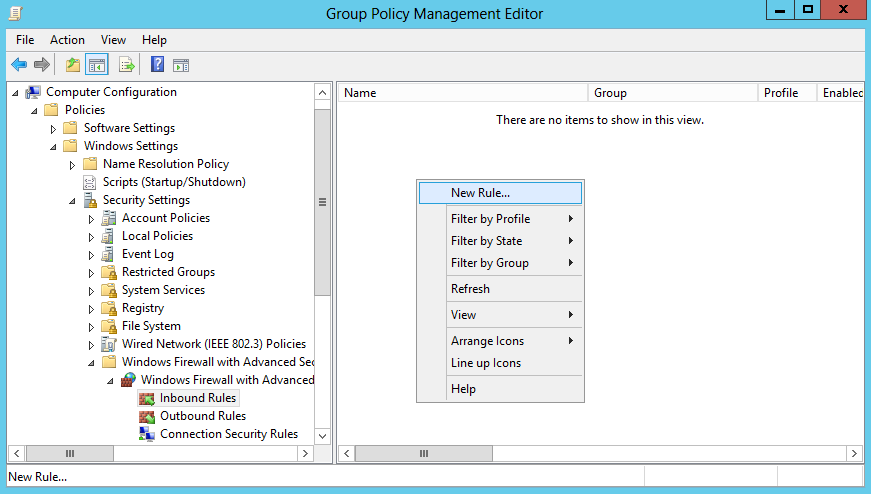
В доменной среде разрешить Ping можно централизованно, через групповые политики. Открываем в редакторе групповых политик соответствующую GPO и переходим в раздел Computer Configuration–Policies–Windows Settings–Windows Firewall with Adwanced Security. Раскрываем дерево поддразделов и переходим на вкладку Inbound Rule. Кликаем правой клавишей мыши и в контекстном меню выбираем New Rule.
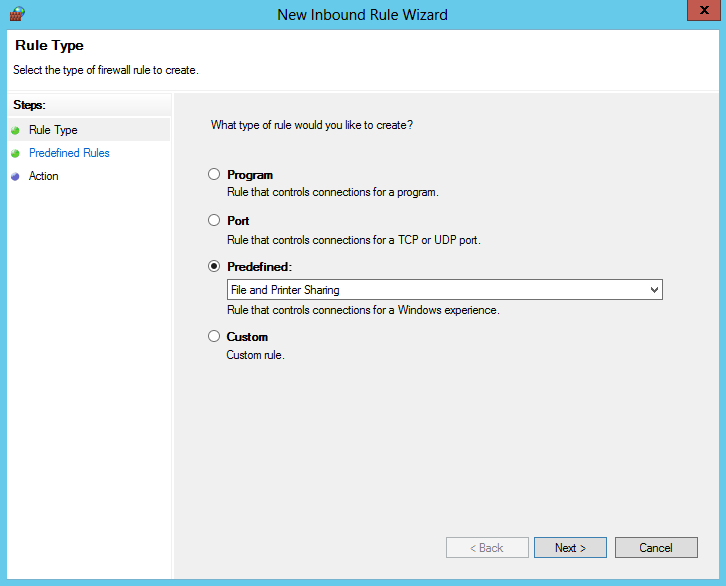
Выбираем Predefined (предопределенные правила) и находим в списке группу правил «File and Printer Sharing».
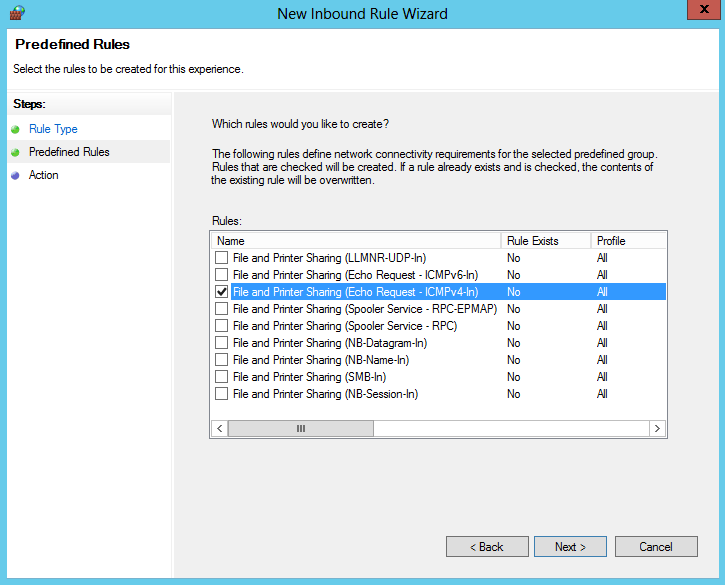
Находим правило ICMPv4-In и убираем выделение с остальных.
Выбираем для правила действие Allow the connection (разрешить подключениe) и жмем Finish, сохраняя правило.
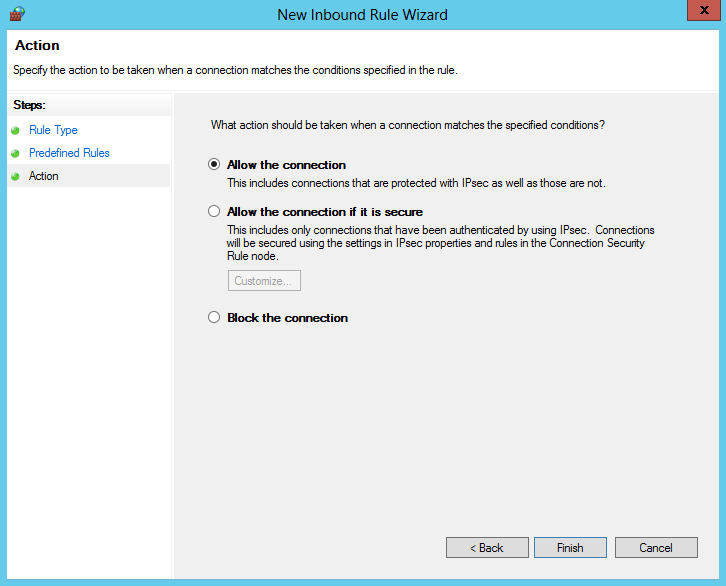
После того как правило создано, его можно открыть и отредактировать, точно так же как и в локальной оснастке брандмауэра.
Утилита Netsh
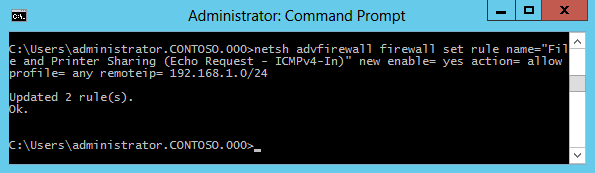
Кроме графических средств для управления правилами можно воспользоваться утилитой командной строки netsh. В качестве примера активируем правило ICMPv4-In для всех профилей брандмауэра и ограничим удаленные IP подсетью 192.168.1.0/24:
netsh adwfirewall firewall set rule name= ″File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request — ICMPv4-In)″ new enable= yes action= allow profile= any remoteip= 192.168.1.0/24
Если вы используете Windows Server 2008 (не R2), то команда будет выглядеть немного по другому. Для включения правила:
netsh firewall set icmpsetting 8
И для отключения:
netsh firewall set icmpsetting 8 disable
PowerShell
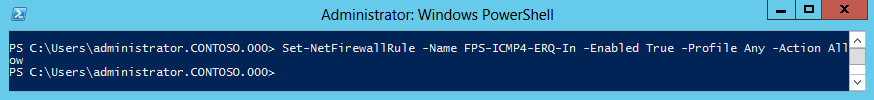
Также разрешить эхо-запросы можно с помощью PowerShell. Правда воспользоваться этим способом можно только в Windows Server 2012, в остальных ОС отсутствует соответствующий PowerShell модуль. Для активации правила воспользуемся следующей командой:
Set-NetFirewallRule -Name FPS-ICMP-ERQ-In -Enabled True -Profile Any -Action Allow
Вроде бы все. Хотя нет, вспомнил еще один интересный момент. Для нормальной работы службы каталогов Active Directory необходимо, чтобы брандмауэр пропускал ICMP пакеты от клиентских компьютеров к контроллеру домена. Это нужно для получения клиентами сведений групповой политики. Поэтому на контроллерах домена есть отдельное правило брандмауэра, разрешающее входящий ping — ″Active Directory Domain Controller — Echo Request (ICMPv4-In)″. Это правило активно по умолчанию.
Раздел: Windows
Написано: 13.09.2011
Автор: Antonio
Установили Windows Server 2008 и он не пингуется из сети?
Не беда!
Включить ping в Windows 2008 можно несколькими способами.
1. Простой
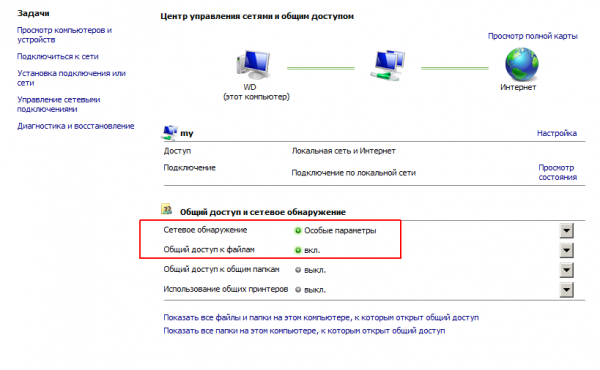
Пуск — Настройка — Панель управления — Центр управления сетями — Общий доступ и сетевое обнаружение
Включаем Сетевое обнаружение и Общий доступ к файлам
2. Используя расширенный режим брандмауэра
Пуск — Настройка — Панель управления — Администрирование — Брандмауэр Windows в режиме повышенной безопасности — находим и включаем в правилах для входящих подключений
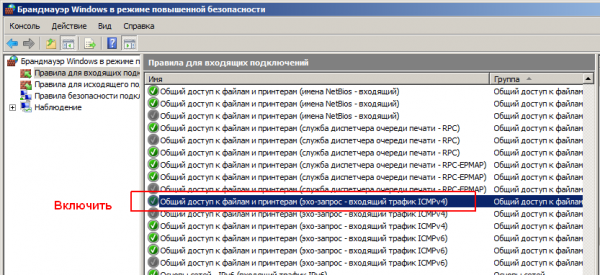
3. Как включить пинг компьютера в командной строке
Сделать чтобы ваш компьютер можно было пинговать, можно командой
netsh firewall set icmpsetting 8
В Windows Server 2008 R2
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="ICMP Allow incoming V4 echo request" protocol=icmpv4:8,any dir=in action=allow
Фразы: разрешить пинговать компьтер из сети, Windows 2008, Windows Server 2008, как включить пинг в фаерволле? расширенный режим брандмауэра как включить?
Windows · September 28, 2024
Configuring a firewall to allow ping requests on Windows Server 2008 is essential for network diagnostics and monitoring. The ping command is a useful tool for checking the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. However, by default, Windows Firewall blocks ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets, which are used by the ping command. This article will guide you through the steps to configure the Windows Firewall to allow ping requests.
Understanding ICMP and Ping
ICMP is a network layer protocol used by network devices to send error messages and operational information. The ping command utilizes ICMP Echo Request and Echo Reply messages to determine if a host is reachable. When a ping is sent, the target host responds with an Echo Reply if it is reachable. If the firewall blocks these messages, the ping will fail, leading to confusion during network troubleshooting.
Steps to Allow Ping on Windows Server 2008
To allow ping requests through the Windows Firewall on a Windows Server 2008 machine, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open Windows Firewall
- Click on the Start button.
- Navigate to Control Panel.
- Select System and Security.
- Click on Windows Firewall.
Step 2: Access Advanced Settings
- In the left pane, click on Advanced settings.
Step 3: Create a New Inbound Rule
- In the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security window, click on Inbound Rules in the left pane.
- In the right pane, click on New Rule….
Step 4: Select Rule Type
- Choose Custom and click Next.
Step 5: Specify Protocol and Ports
- In the Protocol type dropdown, select ICMPv4.
- Click on Next.
Step 6: Configure ICMP Settings
- Click on Customize… under the ICMP settings.
- Select Specific ICMP types.
- Check the box for Echo Request and click OK.
- Click Next.
Step 7: Specify Action
- Select Allow the connection and click Next.
Step 8: Specify Profile
- Select the profiles where you want the rule to apply (Domain, Private, Public) and click Next.
Step 9: Name the Rule
- Provide a name for the rule, such as Allow Ping, and click Finish.
Testing the Configuration
After configuring the firewall, it is essential to test whether the ping requests are now allowed. You can do this by opening the Command Prompt and typing:
ping [IP Address or Hostname]If the configuration is successful, you should receive replies from the target host. If not, double-check the firewall settings to ensure that the rule was created correctly.
Conclusion
Configuring the Windows Firewall to allow ping requests is a straightforward process that can significantly aid in network diagnostics. By following the steps outlined above, administrators can ensure that their servers are reachable for troubleshooting and monitoring purposes. Proper firewall configuration is crucial for maintaining network security while allowing necessary communication protocols.
For those looking for reliable USA VPS Hosting solutions, understanding firewall configurations is just one aspect of managing a secure and efficient server environment. Explore more about how to optimize your server settings with USAVPS.
Как настроить компьютер с операционной системой Windows Server 2008 Server Core для тестирования по ping?
Чтобы назначить исключение брандмауэра ддя пакетов ICMP, используемых во время операции Ping, выполните команду
netsh firewall set icmpsetting 8
Microsoft объявила, что данный синтаксис может оказаться устаревшим в будущих версиях Windows, и рекомендует новый синтаксис, netsh advfirewall. При использовании нового синтаксиса команда будет иметь вид
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name= «ICMP Allow incoming V4 echo request» protocol=icmpv4:8, any dir=in action=allow
Команда разбита на несколько строк для удобства чтения, но вводить ее следует в одной строке. Синтаксис advfirewall должен обеспечить более точный контроль над правилами брандмауэра. Дополнительные сведения о новом синтаксисе приведены в статье Microsoft «How to use the «netsh advfirewall firewall» context…»
One of the most valuable troubleshooting tools to check connectivity is ping.
It can quickly tell you whether systems are up and operational and if
you are able to resolve names to IP addresses. The basic syntax is
or
Tip
If the pinged system responds, you know the system
is operational. However, if the pinged system doesn’t respond, it
doesn’t necessarily mean that it is not operational. The remote
system’s firewall, or a firewall between your system and the remote
system, can block ICMP requests.
If you ping the hostname, the first thing that ping
does is resolve the name to an IP address. This can be valuable to
determine whether name resolution works. As an example, consider the
following ping command and its output:
C:\>ping dc1
pinging DC1.Pearson.pub [192.168.1.10] with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
ping statistics for 192.168.1.10:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
Note
Because the system is a member of the pearson.pub
domain, the pearson.pub suffix is appended to the hostname of dc1,
giving a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of dc1.pearson.pub.
Notice that the first line shows that
DC1.Pearson.pub has been resolved to 192.168.1.10. In this domain, it
is resolved by DNS, but it can also be resolved from the hosts file,
the lmhosts file, WINS, or a broadcast.
You can get a few different errors from ping, as shown in the following table.
| Error | Example | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Could not find host. |
C:\>ping dc99 |
Name resolution methods cannot resolve the name to an IP address. This commonly means that the name is not known by the DNS server. |
| Request timed out. |
C:\>ping 192.168.1.1 |
This indicates that the system is not responding. It can be because the system is not operational; however, the ping could also be blocked by a firewall. |
| Destination host unreachable. |
C:\>ping 192.168.3.10 |
This often indicates that the default gateway on the local system or the remote system is not configured correctly. The default gateway should be on the same subnet. |
Note
You might occasionally see the first reply timeout
but other replies succeed. This can be due to delays with routers and
the time it takes for ARP to get the MAC address.
Another error you might read about but rarely see is
TTL Expired in Transit. The TTL value determines the maximum amount of
time an IP packet can live in the network without reaching its
destination. If you have networking problems with routers and routes on
your network, a ping might get caught in a routing loop and expire on
the wire, causing this error.
It’s important to reiterate that a Request Timed Out
error doesn’t necessarily indicate the system is not operational. The
firewall setting might be preventing a ping. You can ensure that the
firewall is allowing ICMP ping requests with netsh, as shown in the following table.
| Enable and Disable ping in the Firewall | Comments |
|---|---|
C:\>netsh firewall set |
Enables echo requests.
Note The netsh firewall |
C:\>netsh firewall set |
Disables echo requests. |
C:\>netsh advfirewall |
You can use the netsh advfirewall firewall command to create a rule. This rule also enables echo requests.
Note This command works on both Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2. |
C:\>netsh advfirewall |
Deletes the advfirewall rule. |
ping supports several switches, many of which are shown in the following table.
| ping Switches | Comments |
|---|---|
-t |
You can use the -t switch to have ping continue pinging the specified host until you stop it. You can stop it by pressing Ctrl+C. While it’s running, you can press the Ctrl+Break keys to view statistics. |
-n |
You can specify the number of echo requests to send with the -n switch. By default, four ping echo requests are sent, but you can give a number such as 10 to send 10 instead. |
-a |
The -a switch can be used to resolve addresses to hostnames. This requires a reverse lookup zone and an associated PTR (pointer) record on the DNS server, so it won’t always work. |
-l |
You can change the size of the ping packet with -l (a lowercase “el,” not the number 1). The size is specified in bytes and the default size is 32 bytes. |
-i |
You can modify the TTL with the -i switch. The default is 128. |
-4 |
You can use the -4 switch to force ping to use IPv4. |
-6 |
You can use the -6 switch to force ping to use IPv6. |
You can also ping using the IPv6 address. For
example, the following listing shows the output when pinging the IPv6
link-local address of another computer:
C:\>ping fe80::c065:e623:4104:1469Pinging fe80::c065:e623:4104:1469 from fe80::84e0:3272:e623:21c6%10 with
32 bytes of data:
Reply from fe80::c065:e623:4104:1469: time=7ms
Reply from fe80::c065:e623:4104:1469: time=2ms
Reply from fe80::c065:e623:4104:1469: time=1ms
Reply from fe80::c065:e623:4104:1469: time=3msPing statistics for fe80::c065:e623:4104:1469:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 7ms, Average = 3ms
Tip
You can verify the operation of IPv6 on a remote computer by pinging its link-local address. You can use ipconfig /all on any computer to identify its link-local IPv6 address.
