What Is Windows Security Center Service?
In the digital age, security has become an essential part of operating systems such as Microsoft Windows. Users are increasingly aware of threats from malware, viruses, and other forms of cyber-attacks. To address these concerns, Microsoft has integrated numerous security features into its Windows operating system, one of which is the Windows Security Center Service. This article aims to provide a detailed understanding of what the Windows Security Center Service is, its functionalities, how it enhances system security, and the implications for users today.
Overview of Windows Security Center Service
Windows Security Center, also known as Windows Security Center Service (WSC), is a component of the Windows operating system that monitors and manages the security status of various services and applications on a computer. Introduced in Windows XP and iteratively improved in subsequent versions, the Security Center aims to inform users about their security configurations and offer a centralized location for maintaining system security.
The core purpose of the Windows Security Center is to inform users about the status of their security solutions, including antivirus software, firewalls, and Windows Update. It consolidates information about the system’s security posture, ensuring that the computer is adequately protected against potential threats.
Key Features of Windows Security Center Service
-
Real-Time Monitoring:
The Windows Security Center Service continuously monitors the system for any potential security issues. It checks whether essential security features, like antivirus software and firewalls, are active and updated. If a user’s antivirus software is out of date or disabled, WSC generates alerts, prompting users to take action. -
Centralized Security Dashboard:
The Security Center provides a centralized dashboard where users can quickly view the status of their security settings. This dashboard includes comprehensive information about the operational state of antivirus programs, firewall protections, and automatic updates. -
User Notifications:
One of the most useful functions of the Windows Security Center is its ability to notify users of any security-related issues. This proactive notification mechanism helps users stay informed. Alerts may include requests to activate a firewall, reminders for antivirus updates, or warnings about potential vulnerabilities in the system. -
Integration with Third-Party Security Software:
Windows Security Center is designed to work not only with Microsoft’s security products (such as Windows Defender) but also with third-party antivirus and firewall software. This integration allows for a seamless user experience, as users can receive notifications about the status of their chosen security applications. -
Control over Security Settings:
Users can easily manage their security settings directly from the Windows Security Center. By providing a straightforward interface, users can easily navigate to relevant settings, modify configurations, or access links to repair or remove applications. -
Compliance with Security Requirements:
In organizational settings, the Security Center aids compliance with various security requirements by ensuring that recommended protections are enabled and operational. This helps in maintaining a secure environment within businesses and mitigating risks associated with external threats.
Components Monitored by Windows Security Center Service
The Windows Security Center Service monitors several critical components to ensure comprehensive protection. The following are the primary components that are under its surveillance:
-
Firewall:
The firewall acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks. Windows Security Center checks whether the Windows Firewall is turned on and whether it is configured to protect the system from unauthorized access. -
Antivirus Software:
The security center checks for the presence and functionality of antivirus software installed on the system. It verifies whether the antivirus is updated with the latest virus definitions and is actively scanning for threats. -
Automatic Updates:
Keeping a system updated is paramount for security. Windows Security Center ensures that automatic updates for Windows and security software are enabled, helping protect the system against newly discovered vulnerabilities. -
User Account Control (UAC):
User Account Control helps prevent unauthorized changes to a user’s operating system. The Security Center monitors the status and prompts users to adjust settings to enhance security further. -
Spyware Protection:
In addition to conventional viruses, spyware poses a significant threat. WSC monitors the system for spyware and provides alerts if potential spyware detection tools are inactive or absent.
How Windows Security Center Service Enhances User Security
The presence of the Windows Security Center Service enhances user security in several ways:
-
Informed Decision Making:
By providing users with clear information about their security status, the Security Center empowers them to make informed decisions about protective measures. Users can easily identify potential gaps in their defenses and address them proactively. -
Reduced Risk of Malware:
With its real-time monitoring capabilities, the Windows Security Center significantly reduces the risk of malware infections. By ensuring that security solutions are enabled and running, it serves as a frontline defense against threats. -
User Awareness:
Regular notifications and status updates foster a culture of security awareness among users. This increased vigilance can lead users to adopt safer practices, such as avoiding suspicious links and downloading content only from trusted sources. -
Accessibility of Security Tools:
The centralized nature of the Security Center simplifies access to security tools and settings. Users do not need to search through multiple menus and applications; they can manage security from one location. -
Enhanced Support for Third-Party Solutions:
By supporting various third-party security products, WSC allows users to customize their security experience according to their preferences without sacrificing awareness or reporting capabilities.
Challenges and Limitations
While the Windows Security Center Service offers many advantages, it is not without its challenges and limitations:
-
User Complacency:
One risk is that users might become complacent, relying solely on WSC for security without actively practicing safe online behavior. Awareness and education are essential in complementing the service’s capabilities. -
Compatibility Issues:
Occasionally, the integration with third-party security software can lead to compatibility issues. In some cases, certain security features may not function correctly, causing alerts that can be confusing or unnecessary. -
False Positives:
Windows Security Center may sometimes generate false positives, flagging software that users know to be secure as a potential threat. This can lead to unnecessary stress and confusion. -
Dependency on Antivirus Solutions:
Users who heavily rely on antivirus solutions might overlook other security measures. Relying on just one layer of defense can lead to vulnerabilities in cases where antivirus software fails to protect against new or sophisticated threats. -
Limited Capabilities:
The Security Center is primarily a monitoring tool and does not provide proactive threat remediation. Users must still manage their security threats by employing additional tools or following best practices in cybersecurity.
Best Practices for Leveraging Windows Security Center Service
To maximize the effectiveness of the Windows Security Center Service, users are encouraged to adopt several best practices:
-
Regularly Update Security Software:
Ensure that all installed security software is up to date. Schedule periodic checks to confirm that updates are automatically applied. -
Maintain Awareness of Security Alerts:
Pay attention to alerts and notifications from the Security Center, and take immediate action when recommended. -
Utilize Multiple Layers of Security:
Beyond relying on the Security Center, consider employing additional layers of security such as web filtering, anti-malware programs, and secure browsing extensions. -
Educate Yourself and Others:
Be proactive in learning about cybersecurity threats and best practices. Sharing this knowledge with family, friends, and colleagues can help create a safer digital environment. -
Regular System Checks:
Conduct routine checks of your system’s security settings and the status of your firewall and antivirus. Regularly review your online behaviors and adjust them as necessary for optimal protection. -
Backup Important Data:
Regularly back up important files to an external drive or cloud-based service. In the event of a security breach or malware attack, having backups ensures that data can be recovered. -
Be Cautious with Downloads and Links:
Exercise caution when downloading files or clicking links from unknown sources. This vigilance helps avoid potential encounters with malware or phishing attempts.
Conclusion
The Windows Security Center Service plays a vital role in maintaining the security posture of Windows-based systems. Its real-time monitoring, user notifications, and centralized dashboard empower users to stay informed and take proactive measures against various cybersecurity threats. While it has its limitations, by understanding how to leverage this service effectively, users can enhance their overall security strategy and contribute to a safer online environment.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, it is more important than ever for users to stay engaged and informed regarding their digital security. The Windows Security Center Service serves as a central hub in this endeavor, guiding users toward better security practices and vigilance in their online activities. By combining the functionalities offered by WSC with effective usage of additional cybersecurity measures, users can build a robust defense against potential threats and ensure a secure computing experience.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Security and Maintenance
|
Security and Maintenance in Windows 11 |
|
| Other names | Action Center (Windows 7 to Windows 8.1) Windows Health Center (Windows 7 RC build) Windows Solution Center (Windows 7 Beta build) Windows Security Center (Windows Vista & Windows XP SP2) |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Included with | Windows XP (Service Pack 2) and later Windows Server 2008 and later |
| Predecessor | Windows Security Center |
| Service name | wscsvc |
| Type | System monitor |
Security and Maintenance (formerly known as Action Center, and Security Center in earlier versions) is a component of the Windows NT family of operating systems that monitors the security and maintenance status of the computer. Its monitoring criteria includes optimal operation of antivirus software, personal firewall, as well as the working status of Backup and Restore, Network Access Protection (NAP), User Account Control (UAC), Windows Error Reporting (WER), and Windows Update. It notifies the user of any problem with the monitored criteria, such as when an antivirus program is not up-to-date or is offline.
Security and Maintenance consists of three major components: A control panel applet, a Windows service and an application programming interface (API) provided by Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI).
The control panel applet divides the monitored criteria into categories and color-codes them. Yellow indicates a non-critical warning, e.g. some settings are not being monitored or are not optimal. Red indicates a critical message, e.g. anti-virus program is offline.
A service, named «Security Center», determines the current state of the settings. The service, by default, starts when the computer starts; it continually monitors the system for changes, and notifies the user if it detects a problem. In versions of Windows prior to Windows 10, it adds a notification icon into the Windows Taskbar.
A WMI provider makes the settings available to the system. Third-party anti-virus, anti-spyware and personal firewall software vendors primarily register with Security and Maintenance through the WMI provider. Windows Vista added a new set of APIs that let programs retrieve the aggregate health status within Security and Maintenance, and to receive notifications when the health status changes. These APIs allow programs to confirm that the system is in a healthy state before engaging in certain actions. For example, a computer game can ensure that a firewall is running before connecting to an online game.
Security and Maintenance is in charge of the following:
- Querying the status of the personal firewall and turning it on
- Querying the status of the anti-malware program, turning it on and instructing it to update itself
- Querying the status of the Internet security settings and asking the user to change them if they are not optimal
- Querying the status of the User Account Control settings and asking the user to change it if it is not optimal
- Scheduling and executing automatic maintenance tasks, which includes a quick scan for malware, disk defragmentation, power efficiency diagnostics[1]
- Querying the status of Backup and Restore and prompting the user to schedule a backup if one is not in place (Windows 7 only)
- Querying the status of File History; however, the user is not alerted about it (Windows 8 and later only)
- Querying the status of HomeGroup; no alerts are issued about it
- Managing problems logged by Windows Error Reporting: The user can see their details, send them to Microsoft if they are not automatically sent, query a solution for them (although most of the times, there is none) or selectively delete them.
Microsoft learned from discussions with customers that there was confusion as to whether users were taking appropriate steps to protect their systems, or if the steps they were taking were effective.[2] From this research, Microsoft made the decision to include a visible control panel with Windows XP Service Pack 2 that would provide a consolidated view of the most important security features. Service Pack 2, released in August 2004, includes the first version of Windows Security Center (WSC). This version monitors Windows Update, Windows Firewall, and the availability of an anti-virus program. Third-party providers of personal firewall and anti-virus software packages were encouraged to use WSC API to register their products with WSC.
On August 25, 2004, PC Magazine published an article in their Security Watch newsletter titled «Windows XP SP2 Security Center Spoofing Threat» which outlined a design vulnerability which could allow malware to manipulate Security Center into displaying a false security status regardless of the true security status. To do so, the malware requires administrative privileges. Microsoft countered their claim by asserting that if a piece of malware gains administrative privileges, it need not spoof anything, as it can commit much nastier malicious actions.[3]
WSC in Windows Vista monitors new criteria, such as anti-spyware software, User Account Control, and Internet Explorer security settings. It can also display logos of third-party products that have been registered with the Security Center.
Unlike Windows XP, in the beta versions of Windows Vista, WSC could not be disabled or overridden. Security software maker Symantec spoke out against this, noting that it would cause a great deal of consumer confusion because any security problems would be reported by both WSC and Symantec’s tools at the same time.[4] McAfee, another large security software vendor, lodged similar complaints.[5] In the end, Microsoft allowed WSC to be disabled.[6]
In Windows 7, Windows Security Center has been renamed Action Center. It was designed to centralize and reduce the number of notifications about the system; as such, it encompasses both security and maintenance of the computer.[7] Its notification icon on Windows Taskbar only appears when there is a message for perusal and replaces five separate notification icons found in Windows Vista.[8] A «Troubleshooting» link was also added, providing a shortcut to Windows 7’s new Troubleshooting control panel.
In Windows 8, Action Center monitors 10 new items: Microsoft account, Windows activation, SmartScreen, automatic maintenance, drive status, device software, startup apps, HomeGroup, File History, and Storage Spaces.[9]
«Windows Defender Security Center» redirects here. For the anti-malware component of Microsoft Windows, see Windows Defender.
In Windows 10, the name «Action Center» is now used for application notifications and quick actions.[10] The Action Center from Windows 8.1 was renamed to Security and Maintenance, causing confusion for users and IT administrators.[11] It no longer displays an icon in the notification area, but otherwise retains all the features of the Windows 8.1 Action Center. The «Troubleshooting» link was removed in Windows 10 Fall Creators Update.
Starting with Windows 10 Creators Update, Microsoft has introduced a new component called Windows Defender Security Center (WDSC) that provides much of the same functionality. This new component is a Universal Windows Platform app and is also the default front-end for Windows Defender.[12][13] It relies on its own service, called «Windows Defender Security Center Service».
In comparison to Security and Maintenance, the WDSC:
- monitors antivirus and firewall software, device drivers, device security, storage capacity, account protection, parental control, SmartScreen and Windows Update[14]
- has its own distinct icon in the notification area (a black-and-white shield divided by a cross in four sectors)
- can fully control Windows Defender[12]
- recognizes and supports third-party antivirus and firewall (version 1709 and later):[14] upon detecting such software, it will automatically disable itself
In Windows 10 version 1809, the Windows Defender Security Center was renamed to Windows Security.[15]
- List of Microsoft Windows components
- Microsoft Defender Antivirus
- Microsoft Security Essentials
- ^ Stanek, William (February 15, 2014). Windows Server 2012 R2 Inside Out Volume 1: Configuration, Storage, & Essentials. Vol. 1. Microsoft Press (published 2014). ISBN 9780735685611.
In Task Scheduler, the following tasks are triggered by automated maintenance: […] Microsoft\Windows\Power Efficiency Diagnostics. Analyzes power usage
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Security Center: The Voice of Security for Windows Vista». Microsoft. October 6, 2006. Archived from the original on November 4, 2015. Retrieved November 16, 2009.
- ^ Munro, Jay (August 25, 2004). «Windows XP SP2 Security Center Spoofing Threat». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis.
- ^ Jeremy Reimer (September 27, 2006). «Symantec says Vista will «reduce consumer choice»«. Ars Technica. Retrieved October 14, 2006.
- ^ Hines, Matt (October 3, 2006). «McAfee Chides Microsoft Over Vista Security Policies». eWeek. Archived from the original on December 7, 2023.
- ^ Seltzer, Larry (October 16, 2006). «Microsoft Caves on Vista Security». eWeek. Archived from the original on January 2, 2013. Retrieved August 13, 2008.
- ^ Gilmour, Sean (November 11, 2008). Sinofsky, Steven (ed.). «Action Center». Engineering Windows 7. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 29, 2014. Retrieved October 29, 2014.
- ^ Rubenking, Neil J. (November 20, 2008). «Security in Windows 7: Getting Started». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on December 28, 2019.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (August 2, 2012). «Keep tabs on performance in Windows 8 with Action Center». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on October 29, 2014. Retrieved October 29, 2014.
- ^ «Find action center in Windows 10». Microsoft Support. Archived from the original on January 29, 2023.
- ^ Chen, Raymond (May 16, 2017). «There’s a group policy for Action Center, and another one for Action Center». The Old New Thing. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 13, 2019.
- ^ a b Lich, Brian (May 18, 2017). «Windows Defender Antivirus in the Windows Defender Security Center app». Microsoft Learn.
- ^ Popa, Bogdan (August 24, 2017). «Quick Tip: Use the Old Windows Defender in Windows 10 Creators Update». Softpedia. SoftNews.
- ^ a b Lich, Brian (October 17, 2017). «The Windows Defender Security Center app». Microsoft Learn.
In Windows 10, version 1709, we increased the scope of the app to also show information from third-party antivirus and firewall apps.
- ^ «What’s new in Windows 10, version 1809 for IT Pros». Microsoft Learn Archive. September 2018. Archived from the original on November 11, 2020. Retrieved December 19, 2020.
- MSDN: Windows Security Center API
Vista – Windows Security Center (WSC)
Vista – Windows Security Center (WSC)
The Windows Security Center (WSC) is a container object found in the Control Panel. WSC is growing in size, and in addition to Windows Update and Firewall, it now also contains Windows Defender. Like Microsoft’s XP version, WSC also has Internet Options, which is a link that takes you to the IE7 settings.
Contents of the Windows Security Center
- Windows Update
- Windows Defender
- Windows Firewall
- Internet Options
- Windows 8 Network Location
Windows Update
In Vista, Windows Update supports the full range of options. You can download and install security patches at a time, and in manner, to suit any machine. In a Domain environment, Windows Update is best configured via Group Policy. One useful feature of the WSC is the ability to double check that the machine is indeed up-to-date. I also like to review the history to see which patches my machine has downloaded.
♦
Windows Defender
Not only are Adware and Spyware annoying, research indicates that they cause a significant number of hangs and crashes. Less obvious are the numerous hesitations that you see when browsing or even typing.
Windows Defender is dedicated to blocking not only Adware and Spyware, but also keyloggers, bots and rootkits. However, to detect viruses and Trojan horses you still need additional anti-virus software. Norton has been around for long time and Microsoft are pushing their own product: OneCare security.
For a quick check, click on Scan and make sure that no malware has recently infected your machine.
Software Explorer
One interesting feature of Defender is the Software Explorer. This picture (right) is just a thumbnail, the full interface shows Startup, Network and Winsock problems.
The Software Explorer is Windows Vista’s troubleshooting center which links to the Task Manger, in addition, be aware that all significant Windows Defender actions are logged in the Application log.
Windows Firewall
In Windows Vista, one of the new capabilities of the Firewall is, filter outbound packets (as well as block incoming traffic). As a result, malware is easier to detect and block if it tries to send its nefarious results through a different port. On a corporate network most of the Windows Security Center features are controlled by other methods, but in the home network, a properly configured Firewall will thwart most of the common network attacks.
Recommended: Solarwinds’ Permissions Analyzer – Free Active Directory Tool
I like thePermissions Analyzer because it enables me to see WHO has permissions to do WHAT at a glance. When you launch this tool it analyzes a users effective NTFS permissions for a specific file or folder, and takes into account network share access, then displays the results in a nifty desktop dashboard!
Think of all the frustration that this free SolarWinds utility saves when you are troubleshooting authorization problems for user’s access to a resource. Give this permissions monitor a try – it’s free!
Download SolarWinds’ Free Permissions Analyser – Active Directory Tool
Internet Options
In Vista, Internet Options takes you to the properties of IE7. This entrance to the IE settings is an alternative if you are in security inspection mode, or if you cannot open IE7 because malware has take over the other route.
Summary of WSC
Windows Security Center (WSC) provides a focal point to review a machine’s security. WSC is useful for home machines, for example the Defender to check for Malware, and the Firewall to check that key ports are blocked.
If you like this page then please share it with your friends
Configuring Windows Vista Topics:
|
Vista Tools and Extras
|
|
Download Your Tweak the Registry Ebook for only $6.45 This ebook will explain the workings of the registry. I thoroughly enjoy tweaking the registry, and I want to distill the best of my experiences and pass them on to you. Each registry tweak has two aims; to solve a specific problem, and to provide general learning points, which help you to master regedit. Over 60 pages ebook and PDF format |
About The Author
Guy Thomas
The Windows Security Center was added to Windows XP in Service Pack 2. It has a front end for «Firewall, Automatic Updates, and Virus Protection. Windows Security Center, or WSC, monitors the activities or existence of Automatic Updates, Windows Firewall and virus protection provided by third party anti virus software.
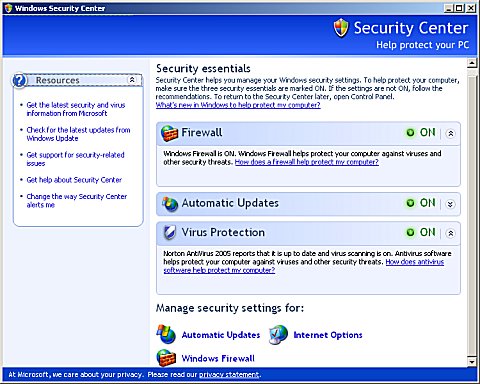
WSC is not necessarily a bad thing. Microsoft Windows security is bad, and Microsoft is embarrassed about it. It is up to the end user to keep the copy of Microsoft Windows up-to-date with the latest service packs and security updates. Keeping Windows current will eliminate some of the security vulnerabilities. Blocking unwanted Internet traffic with the built in firewall and adding third party anti virus software also help to tighten security. Some more advanced users would rather not have WSC nagging them about these things, because they feel they can manage these things on their own.
Security Center in Windows XP can be disabled or turned off. To disable WSC do the following:
- Click on Start button, then select Control Panel.
- Select “Administrator Tools” (if you don’t see it, double click on “Performance and Maintenance” first).
- Double click “Services”.
- Find and double click on the service named “Security Center”. Alternatively right click on “Security Center”, and select “Properties” on right click menu.
- In the “General” tab, beside the “Startup type:”, change the setting from Automatic to “Disabled”. This will permanently disable Security Center forever, even after you reboot and restart the computer system.
- The click on “Stop” button at the bottom of the dialog window to stop Security Center immediately during current log on session.
For general users, it is recommended that you keep WSC active.
If you have a firewall other than Windows firewall, check the information that came with the firewall or go to the manufacturer’s website to find out how to turn it on.
Windows does not detect all firewalls. If you are sure that you have a firewall installed and turned on, you can click Show me my available options to stop receiving notifications from Security Center about your firewall. If you do this, Windows will not monitor your firewall status or alert you if it is off.
When it comes to computer security, the Windows Security Center Service plays a crucial role in safeguarding your system. With its robust features and continuous monitoring, it ensures that your computer is protected from various threats and vulnerabilities.
Windows Security Center Service is a built-in feature in Microsoft Windows operating systems, designed to provide a centralized hub for managing and maintaining the security of your computer. It constantly monitors the status of your antivirus, firewall, and other security settings, and alerts you if any potential issues or risks are detected. With the Windows Security Center Service, you can take proactive steps to ensure the safety and integrity of your system.
The Windows Security Center Service is a built-in feature of the Windows operating system that monitors the security status of your computer. It checks for the presence of antivirus software, firewall protection, and the latest Windows updates. If any of these security features are missing or turned off, the Security Center will prompt you with alerts and notifications. It ensures that your computer is protected and helps you stay vigilant against potential security threats.

Understanding the Windows Security Center Service
The Windows Security Center Service, also known as WSCSVC, is an essential component of the Microsoft Windows operating system. It is designed to monitor and manage various security-related settings and features on a Windows computer. The primary function of the Windows Security Center Service is to ensure that the system is protected against potential security threats.
1. The Importance of Windows Security Center Service
The Windows Security Center Service is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of a Windows system. It provides a centralized location to monitor the status of essential security components such as antivirus software, firewall protection, and Windows Updates. By regularly checking these components, the Security Center Service ensures that they are up-to-date and functioning correctly.
Furthermore, the Windows Security Center Service provides real-time information about the security status of the system. It alerts users if there are any security-related issues that need attention, such as disabled firewall or outdated antivirus definitions. This proactive monitoring helps users take immediate action to address any vulnerabilities and prevent potential threats.
Overall, the Windows Security Center Service plays a vital role in protecting Windows users from various security risks. It serves as a valuable tool for both individual users and system administrators, providing them with the necessary information and control to maintain a secure computing environment.
2. Components Monitored by the Windows Security Center Service
The Windows Security Center Service monitors several key components to ensure the overall security of a Windows system. These components include:
- Antivirus software: The Security Center Service monitors the status and validity of the installed antivirus software. It checks if the antivirus software is up-to-date and active.
- Firewall protection: It verifies if the Windows Firewall or any third-party firewalls are enabled to provide protection against unauthorized access.
- Windows Updates: The Security Center Service ensures that the system is set up to receive and install the latest Windows updates, including security patches.
- Internet security settings: It evaluates the configuration of internet security settings, such as the security level of Internet Explorer and other browsers.
By actively monitoring these components, the Windows Security Center Service helps users maintain a secure computing environment and promptly address any potential vulnerabilities within the system.
3. Managing the Windows Security Center Service
The Windows Security Center Service can be managed through the Windows Security app, accessible from the Windows Start menu. This app provides users with an overview of their device’s security status and allows them to make necessary changes to security settings.
User intervention may be required in cases such as:
- Updating antivirus software: If the Security Center Service detects outdated antivirus software, it will prompt the user to update it. Users should follow the provided instructions to download and install the latest antivirus definitions.
- Configuring firewall settings: If the Security Center Service finds that the system’s firewall is turned off or if there is an issue with a third-party firewall, users may need to adjust the settings to enable proper protection.
- Checking for Windows Updates: Users should regularly check for and install Windows updates to ensure that their system has the latest security patches.
By actively managing the Windows Security Center Service, users can optimize their system’s security and stay protected against emerging threats.
4. Windows Security Center Service and Third-Party Security Software
The Windows Security Center Service allows integration with third-party security software. This means that if you have antivirus or firewall software installed from a different vendor, the Security Center Service can monitor their status as well.
When third-party security software is installed, the Security Center Service detects and recognizes it, providing information about its status alongside the built-in Windows security components. This integration enables users to have centralized visibility and control over all their security software from a single interface, making it easier to manage and ensure comprehensive protection.
It is worth noting that some third-party security software may disable the Windows Security Center Service notifications to avoid duplicate alerts. In this case, users should refer to the provided documentation or the vendor’s support for further instructions on how to manage the software effectively.
Exploring Windows Security Center Service Advanced Features
While the Windows Security Center Service primarily focuses on monitoring key security components, there are advanced features available for in-depth security management and customization. These features provide additional layers of protection and control for Windows users.
1. Windows Defender Firewall
Windows Defender Firewall is the built-in firewall protection included with Windows. It allows users to customize firewall settings, create inbound and outbound rules, and manage network security profiles. It works seamlessly with the Windows Security Center Service to provide comprehensive network protection against unauthorized access and malicious activities.
Windows Defender Firewall can be accessed through the Windows Security app or via the Control Panel. Users can configure advanced settings, such as specifying allowed and blocked apps, enabling logging and notifications, and adjusting network profiles.
By leveraging the advanced features of Windows Defender Firewall, users can tailor their network security based on their specific requirements and enhance the overall protection provided by the Windows Security Center Service.
2. Windows Defender Antivirus
Windows Defender Antivirus is the default antivirus software integrated into Windows 10 and later versions. It provides real-time protection against various types of malware, including viruses, ransomware, spyware, and more.
Users can utilize the advanced features of Windows Defender Antivirus to further optimize their security. This includes customizing the scanning options, configuring protection settings, managing quarantine files, and scheduling regular scans.
The integration of Windows Defender Antivirus with the Windows Security Center Service ensures that users have reliable antivirus protection and can easily manage their antivirus software’s various aspects.
3. Windows Update
Windows Update is a vital component of the Windows Security Center Service. It allows users to keep their operating system and other Microsoft software up-to-date with the latest security patches, bug fixes, and feature enhancements.
Users can access Windows Update settings through the Windows Security app or the Windows Settings menu. They can choose between automatic updates or manual installation of updates. Additionally, users can view update history and troubleshoot any issues that may arise during the update process.
By regularly updating the Windows operating system, users can ensure that their system is equipped with the latest security measures and patches, reducing the risk of exploitation by known vulnerabilities.
4. Windows Security App
The Windows Security app serves as a central hub for managing all aspects of security on a Windows system. It provides users with an intuitive interface to access and configure various security settings, including the Windows Security Center Service.
Through the Windows Security app, users can monitor the overall security status of their system, perform quick scans for malware, manage firewall and network settings, control device performance and health, and access other security-related tools and resources.
Having the Windows Security app ensures that users have a single point of control and easy access to all security features, simplifying the management and maintenance of a secure Windows environment.
In conclusion, the Windows Security Center Service is an integral part of the Windows operating system, aimed at monitoring and managing essential security components. By actively monitoring antivirus software, firewall protection, Windows Updates, and internet security settings, the Security Center Service helps users maintain a secure computing environment. Users can manage the Windows Security Center Service through the Windows Security app and integrate it with third-party security software for comprehensive protection. Additionally, advanced features such as Windows Defender Firewall, Windows Defender Antivirus, Windows Update, and the Windows Security app provide users with further control and customization options to enhance the security of their Windows system. It is recommended that users regularly review and update their security settings to ensure optimal protection against emerging threats.

Understanding Windows Security Center Service
The Windows Security Center Service is a built-in feature in the Windows operating system that helps to monitor and manage the security settings on your computer. It acts as a central hub for all security-related features and provides users with an overview of their system’s security status.
When you access the Windows Security Center Service, you can see important information about the status of your firewall, antivirus software, and Windows Updates. It also alerts you if any of these components are not functioning correctly or if there are any security threats detected on your system.
The Windows Security Center Service ensures that your computer is equipped with the necessary tools and updates to protect against malware, viruses, and other security risks. It provides recommendations for improving your system’s security and offers guidance on how to address any issues that may arise.
By regularly checking and updating the security settings through the Windows Security Center Service, you can ensure that your computer remains secure and protected from potential threats.
Key Takeaways — What Is Windows Security Center Service
- The Windows Security Center Service is a built-in feature in Windows operating systems.
- It monitors the security status of your computer and provides notifications and alerts.
- The Security Center Service checks if your antivirus software is up-to-date and running.
- It also monitors your firewall settings and checks for Windows updates.
- Windows Security Center Service helps protect your computer from malware and other security threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Windows Security Center Service is an essential component of the Windows operating system. It provides centralized management and monitoring of security settings and features on a Windows computer. Here are some frequently asked questions related to the Windows Security Center Service:
1. Why is the Windows Security Center Service important?
The Windows Security Center Service plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and protection of a Windows computer. It monitors the status of essential security features, such as antivirus software, firewall settings, and automatic Windows updates. By keeping these security settings up to date, the Windows Security Center Service helps to prevent and detect potential security threats, keeping the system and user data safe.
Additionally, the Windows Security Center Service provides users with a central location to manage their computer’s security settings, allowing them to easily enable or disable specific security features and access relevant security-related information.
2. How is the Windows Security Center Service accessed?
The Windows Security Center Service can be accessed through the Windows Security Center interface, which can be typically found in the Control Panel or Settings app, depending on the Windows version. This interface provides a comprehensive overview of the security status of the system, including antivirus protection, firewall settings, and Windows Update status.
Users can also access the Windows Security Center Service by opening the Windows Security app, which provides more detailed information about the security features and settings of the system.
3. Can the Windows Security Center Service be disabled?
The Windows Security Center Service is a critical component of the Windows operating system, and it is not recommended to disable it. Disabling the service may leave the system vulnerable to security threats, as it will no longer actively monitor and manage essential security settings.
However, in some cases, users may choose to disable specific security features through the Windows Security Center Service interface, such as disabling Windows Defender if they prefer to use a third-party antivirus software. It is important to carefully consider the potential risks and consequences before disabling any security feature.
4. What are the common issues with the Windows Security Center Service?
Some common issues with the Windows Security Center Service include:
— Antivirus software or firewall not being recognized by the service.
— Windows Security Center Service not starting or responding.
— Inaccurate or outdated security status information being displayed.
If you encounter any of these issues, it is recommended to troubleshoot the problem by updating the antivirus software, restarting the computer, or running the Windows Troubleshooter specifically designed for security-related issues.
5. Can the Windows Security Center Service be customized?
Yes, the Windows Security Center Service can be customized based on the user’s preferences and specific security requirements. Users can configure various security settings, such as enabling or disabling antivirus software, enabling or disabling the firewall, and managing Windows Update settings through the Windows Security Center interface.
Additionally, users can choose to receive security notifications and alerts, customize the frequency of automatic security scans, and specify actions to be taken when potential security threats are detected.
To sum up, the Windows Security Center Service is a crucial component of the Windows operating system that helps ensure the security of your computer. It acts as a central hub for monitoring and managing various security features to protect your system from threats, such as viruses, malware, and data breaches.
The Windows Security Center Service provides real-time monitoring and alerts for antivirus, firewall, and other security software installed on your computer. By keeping this service enabled and up-to-date, you can enhance the overall security of your system and enjoy a safer computing experience.
