Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Running Python Scripts
Running a Python script is a fundamental task for any Python developer. You can execute a Python .py file through various methods depending on your environment and platform. On Windows, Linux, and macOS, use the command line by typing python script_name.py to run your script. You can also use the python command with the -m option to execute modules. This tutorial covers these methods and more, ensuring you can run Python scripts efficiently.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll understand that:
- Running a Python
.pyscript involves using thepythoncommand followed by the script’s filename in the terminal or command prompt. - Running Python from the command prompt requires you to open the command prompt, navigate to the script’s directory, and execute it using
python script_name.py. - Running a
.pyfile in Windows can be done directly from the command prompt or by double-clicking the file if Python is associated with.pyfiles. - Running a Python script without Python installed is possible by using online interpreters or converting scripts to executables, but it’s more flexible to install Python and run scripts natively.
To get the most out of this tutorial, you should know the basics of working with your operating system’s terminal and file manager. It’d also be beneficial for you to be familiar with a Python-friendly IDE or code editor and with the standard Python REPL (Read-Eval-Print Loop).
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “How to Run Your Python Scripts” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:
Interactive Quiz
How to Run Your Python Scripts
One of the most important skills you need to build as a Python developer is to be able to run Python scripts and code. Test your understanding on how good you are with running your code.
What Scripts and Modules Are
In computing, the term script refers to a text file containing a logical sequence of orders that you can run to accomplish a specific task. These orders are typically expressed in a scripting language, which is a programming language that allows you to manipulate, customize, and automate tasks.
Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled. So, scripts are typically run by some kind of interpreter, which is responsible for executing each order in a sequence.
Python is an interpreted language. Because of that, Python programs are commonly called scripts. However, this terminology isn’t completely accurate because Python programs can be way more complex than a simple, sequential script.
In general, a file containing executable Python code is called a script—or an entry-point script in more complex applications—which is a common term for a top-level program. On the other hand, a file containing Python code that’s designed to be imported and used from another Python file is called a module.
So, the main difference between a module and a script is that modules store importable code while scripts hold executable code.
In the following sections, you’ll learn how to run Python scripts, programs, and code in general. To kick things off, you’ll start by learning how to run them from your operating system’s command line or terminal.
How to Run Python Scripts From the Command Line
In Python programming, you’ll write programs in plain text files. By convention, files containing Python code use the .py extension, and there’s no distinction between scripts or executable programs and modules. All of them will use the same extension.
To create a Python script, you can use any Python-friendly code editor or IDE (integrated development environment). To keep moving forward in this tutorial, you’ll need to create a basic script, so fire up your favorite text editor and create a new hello.py file containing the following code:
This is the classic "Hello, World!" program in Python. The executable code consists of a call to the built-in print() function that displays the "Hello, World!" message on your screen.
With this small program ready, you’re ready to learn different ways to run it. You’ll start by running the program from your command line, which is arguably the most commonly used approach to running scripts.
Using the python Command
To run Python scripts with the python command, you need to open a command-line window and type in the word python followed by the path to your target script:
- Windows
- Linux + macOS
After you press Enter, you’ll see the phrase Hello, World! on your screen. If the previous command doesn’t work right, then you may need to check if Python is in your system’s PATH. You can also check where you saved hello.py.
That’s it! You’ve run your first script! Note that on Windows, you also have the option of using the py command, which triggers the py.exe launcher for console applications. This is the most basic and practical way to run Python scripts.
A cool feature of a terminal or shell application is that you can redirect the output of your commands using a straightforward syntax. This feature may be useful in those situations where you have a Python program that can generate a long output, and you’d like to save it to a file for later analysis.
In these situations, you can do something like the following:
In this command, the > symbol tells the shell to redirect the output of your command to the output.txt file, rather than to the standard system output, your screen. This process is commonly known as redirection, and it works on both Windows and Unix-like systems, such as Linux and macOS.
If the output file doesn’t exist, then the shell automatically creates it. On the other hand, if the file already exists, then the shell overwrites its old content with the new output.
Finally, if you want to add the output of consecutive executions to the end of output.txt, then you can use two angle brackets (>>) instead of one:
Now, the shell app will append the current output to the end of output.txt. You’ll end up with a file containing the phrase "Hello, World!" twice.
Using the Script’s Filename Directly
On Windows, you can also run Python scripts by simply entering the name of the file containing the executable code at the command line:
Once you’ve written the path to your script and pressed Enter, you’ll note that a new terminal window appears on your screen for a few seconds, showing the script output. This is possible because Windows associates .py and .pyw files to python.exe and pythonw.exe, respectively.
This way of running Python scripts on Windows may be annoying because the code runs in a new terminal window that automatically closes after the execution ends. In most cases, you won’t be able to check the program’s output.
On Linux and macOS, you can also run your scripts directly. However, things are a bit different here, and you need some setup steps. Go ahead and run the following command:
- Linux
- macOS
Unix systems prioritize security, which means that you can’t go around executing any file as a program. So, you get a permission denied error when you try to run hello.py directly. To fix this issue, you need to explicitly tell the system that the file is executable. To do this, you can use the chmod command:
After running this command, your hello.py file will be executable. However, that’s not enough for the script to run properly:
Why are you getting another error now? The problem is that your operating system (OS) doesn’t know which program to use for running your script and is trying to run it with the shell itself. You can fix that by making a small addition to your hello.py file:
You’ve added a new line at the beginning of hello.py. It now starts with a Unix-style shebang, which is a special kind of comment that you can include in your scripts to tell the operating system which program to use for running the content of this file. In this case, you tell the OS to use Python.
Now you can run the script directly from your command line:
Wow! That was a long road! However, the effort was worth it. Now when you create a Python script to automate tasks in a Unix operating system, you know how to make it executable and run it from your command line.
Running Modules With the -m Option
The python command has a series of command-line options that can be useful in specific situations. For example, if you want to run a Python module, then you can use the command python -m <module-name>. The -m option searches Python’s module search path, sys.path, for the module name and runs its content:
In this example, you run the hello.py file as a module. This is possible because Python automatically adds the current directory to its sys.path list. Note that the module-name argument needs to be the name of a module object, not a file name. In other words, you don’t include the .py suffix.
If the target module isn’t in sys.path, then you get an error:
In this example, the missing name isn’t in the sys.path list, so Python isn’t able to execute it, and therefore it returns an error.
How to Run Python Code Interactively
Running scripts isn’t the only way to run Python code. Because Python is an interpreted language, you can use the interpreter to run code interactively. When you run the python command without arguments, you start a new interactive session, or REPL (Read-Eval-Print Loop). In there, you can run any Python code and get immediate feedback about how the code works.
In the following sections, you’ll learn the basics of the Python interpreter and how to run code in it. This knowledge will be pretty valuable for you, especially in those situations where you need to quickly test a small piece of Python code.
Getting to Know the Python Interpreter
Python is a high-level programming language with a clean and readable syntax. Python and its wide ecosystem of packages and libraries can boost your productivity in a variety of fields. The name Python also refers to a piece of software called the interpreter, which is the program that allows you to run Python code.
The interpreter is a layer of software that works between your program and your computer hardware to get your code running. Depending on the Python implementation that you use, the interpreter can be a program written in:
- C, like CPython, which is the core implementation of the language
- Python itself, like PyPy, which is a fast implementation with a just-in-time (JIT) compiler
- Java, like Jython, which can take advantage of the Java ecosystem
- .NET, like IronPython, which uses the .NET ecosystem
Whatever interpreter you use, the code that you write will run in this program. Therefore, the first condition to be able to run scripts and code is to have the interpreter correctly installed on your operating system.
The Python interpreter can run code in two different modes:
- Script, or program
- Interactive, or REPL
In script mode, you use the interpreter to run a source file as an executable program, just like you learned in the previous section. In this case, Python loads the file content and runs the code line by line, following the program’s execution flow.
Alternatively, interactive mode is when you launch the interpreter and use it as a platform to run code that you type in directly. This mode is pretty useful for learning Python as well as for developing, testing, and debugging your applications.
Running Python Code Interactively
Interactive sessions are a widely used tool for running Python code. To start a Python interactive session, or REPL, open a command-line window, type in the python command, and then press Enter.
These steps will take you into the Python interpreter, which looks something like the following:
- Windows
- Linux
- macOS
The standard primary prompt for the interactive mode consists of three right angle brackets, >>>. So, as soon as you see these characters, you’ll know that you’re in.
The Python interpreter is an interactive way to talk to your computer using the language. It’s like live chat. It’s also known as the REPL because it goes through four steps that run under the hood:
- Reading your input, which consists of Python code as expressions and statements
- Evaluating your Python code, which generates a result or causes side effects
- Printing any output so that you can check your code’s results and get immediate feedback
- Looping back to step one to continue the interaction
This feature of Python is a powerful tool that you’ll wind up needing in your Python coding adventure, especially when you’re learning the language or when you’re in the early stages of a development process.
Once you’ve started a REPL session, you can write and run Python code as you wish. The only drawback is that when you close the session, your code will be gone. This is another difference between the script and interactive modes. Scripts are persistent.
When you work interactively, Python evaluates and executes every expression and statement immediately:
An interactive session will allow you to test every piece of code that you execute. That’s why this tool is an awesome development helper and an excellent space to experiment with the language and test ideas on the fly.
To leave interactive mode and jump back to the system shell, you can use one of the following options:
- Executing the built-in
quit()orexit()functions - Pressing the Ctrl+Z and Enter key combination on Windows, or the Ctrl+D combination on Unix systems, such as Linux and macOS
Go ahead and give the Python REPL a try. You’ll see that it’s a great development tool that you must keep in your tool kit.
How to Run Scripts From Python Code
You can also run Python scripts and modules from an interactive session or from a .py file. This option opens a variety of possibilities. In the following sections, you’ll explore a few tools and techniques that will allow you to run scripts and code from Python code.
Taking Advantage of import Statements
When you import a module from another module, script, or interactive session, what really happens is that Python loads its contents for later access and use. The interesting point is that the import statement runs any executable code in the imported module.
When the module contains only class, function, variable, and constant definitions, you probably won’t be aware that the code was run. However, when the module includes calls to functions, methods, or other statements that generate visible results, then you’ll witness its execution.
This provides you with another option to run scripts:
You’ll note that import runs the code only once per session. After you first import a module, successive imports do nothing, even if you modify the content of the module. This is because import operations are expensive, and Python takes some extra steps to optimize overall performance:
These two imports do nothing because Python knows that the hello module was already imported. Therefore, Python skips the import. This behavior may seem annoying, especially when you’re working on a module and trying to test your changes in an interactive session. However, it’s an intentional optimization.
Using the importlib Standard-Library Module
In the Python standard library, you can find the importlib module. This module provides the import_module() function, which allows you to programmatically import modules.
With import_module(), you can emulate an import operation and, therefore, execute any module or script. Take a look at this example:
The import_module() function imports a module, bringing its name to your current namespace. It also runs any executable code that the target module contains. That’s why you get Hello, World! on your screen.
You already know that once you’ve imported a module for the first time, you won’t be able to import it again using another import statement. If you want to reload the module and run it once again, then you can use the reload() function, which forces the interpreter to import the module again:
An important point to note here is that the argument of reload() has to be the name of a module object, not a string. So, to use reload() successfully, you need to provide a module that’s already imported.
Leveraging the Power of the Built-in exec() Function
So far, you’ve learned about some handy ways to run Python scripts. In this section, you’ll learn how to do that by using the built-in exec() function, which supports the dynamic execution of Python code.
The exec() function provides an alternative way to run your scripts from inside your code:
In this example, you use the with statement to open the hello.py file for reading. Then, you read the file’s content with the .read() method. This method returns a string that you pass to exec() for execution.
You must be careful when using the exec() function because it implies some important security risks, especially if you’re using it for running external code. To learn more about this function, check out Python’s exec(): Execute Dynamically Generated Code.
How to Run Python Scripts on IDEs and Code Editors
For developing a large and complex application, you should use an integrated development environment (IDE) or an advanced text editor that incorporates programmer-friendly features.
Most of these programs have options that allow you to run your programs from inside the environment itself. It’s common for them to include a Run or Build action, which is usually available from the toolbar or from the main menu.
Python’s standard distribution comes with IDLE as the default IDE. You can use this program to write, debug, modify, and run your modules and scripts. Other IDEs, such as PyCharm and Thonny, also allow you to run scripts from inside the environment. For example, in PyCharm, you can press Ctrl+R on your keyboard to quickly run your app’s entry-point script.
Advanced code editors like Visual Studio Code and Sublime Text also allow you to run your scripts. In Visual Studio Code, you can press Ctrl+F5 to run the file that’s currently active, for example.
To learn how to run Python scripts from your preferred IDE or code editor, check its specific documentation or take a quick look at the program’s GUI. You’ll quickly figure out the answer.
How to Run Python Scripts From a File Manager
Running a script by double-clicking on its icon in a file manager is another way to run your Python scripts. You probably won’t use this option much in the development stage, but you may use it when you release your code for production.
In order to run your scripts with a double click, you must satisfy some conditions that will depend on your operating system.
Windows, for example, associates the extensions .py and .pyw with the programs python.exe and pythonw.exe, respectively. This allows you to run your scripts by double-clicking on their icons.
On Unix systems, you’ll probably be able to run your scripts by double-clicking on them in your file manager. To achieve this, your script must have execution permissions, and you’ll need to use the shebang trick that you’ve already learned. Like on Windows, you may not see any output on-screen when it comes to command-line interface scripts.
The execution of scripts through a double click has several limitations and depends on many factors, such as the operating system, the file manager, execution permissions, and file associations. Still, you can consider this alternative a viable option for production-ready scripts and programs.
Conclusion
You’ve acquired the knowledge and skills that you need for running Python scripts and code in several ways and in a variety of situations and development environments. The command line will be your best friend when you need to run production-ready scripts. During development, your IDE or code editor will provide the right option to run your code.
In this tutorial, you’ve learned how to:
- Run Python scripts from the command line or terminal in your current OS
- Execute code in interactive mode using Python’s standard REPL
- Use your favorite IDE or code editor to run Python scripts during development
- Launch scripts and programs from your operating system’s file manager
These skills are essential for you as a Python developer. They’ll make your development process much faster, as well as more productive and flexible.
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “How to Run Your Python Scripts” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:

Interactive Quiz
How to Run Your Python Scripts
One of the most important skills you need to build as a Python developer is to be able to run Python scripts and code. Test your understanding on how good you are with running your code.
Frequently Asked Questions
Now that you have some experience with running Python scripts and code, you can use the questions and answers below to check your understanding and recap what you’ve learned.
These FAQs are related to the most important concepts you’ve covered in this tutorial. Click the Show/Hide toggle beside each question to reveal the answer.
To run a Python script from the command line, open a terminal or command prompt and type python followed by the path to your script file. For example, python hello.py. On Windows, you might also use py instead of python. If you see any errors, check that Python is added to your system’s PATH variable.
In script mode, you execute a file containing Python code using the Python interpreter, and the code runs sequentially. In interactive mode, you use the Python interpreter to run code directly, one statement at a time, often in a REPL (Read-Eval-Print Loop). This allows for immediate feedback and experimentation.
Yes. On Windows, you can double-click .py files to run them since they’re associated with python.exe. On Unix systems, you need to ensure that the script has execution permissions and includes a shebang (#!/usr/bin/env python) as the first line. However, this method may not display output for console applications.
You can execute a Python module using the command line with the -m option. For example, python -m module_name. This runs the module as a script, provided it’s available in the Python module search path.
Besides the command line, you can run Python scripts using an IDE (Integrated Development Environment) like PyCharm or Thonny, a code editor like Visual Studio Code, or from an interactive session using the Python REPL. Each environment provides additional features to aid development and debugging.
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Running Python Scripts
Пройдите тест, узнайте какой профессии подходите
Работать самостоятельно и не зависеть от других
Работать в команде и рассчитывать на помощь коллег
Организовывать и контролировать процесс работы
Введение
Python — один из самых популярных языков программирования в мире, и его скрипты часто запускаются через командную строку. В этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим, как установить Python, проверить его установку и запустить скрипт через командную строку. Эти шаги помогут вам начать работать с Python и использовать его для автоматизации задач, написания скриптов и многого другого. Мы также обсудим некоторые полезные советы и инструменты, которые могут облегчить вашу работу с Python.

Установка Python
Прежде чем запустить Python скрипт, необходимо установить сам Python. Процесс установки может немного отличаться в зависимости от операционной системы, которую вы используете. Давайте рассмотрим, как это сделать на разных платформах.
Windows
- Перейдите на официальный сайт Python: python.org.
- Скачайте последнюю версию Python для Windows. Обычно это будет установочный файл с расширением
.exe. - Запустите установочный файл и следуйте инструкциям на экране. Обязательно отметьте опцию «Add Python to PATH» перед началом установки. Это добавит Python в системные переменные PATH, что позволит запускать Python из любой директории через командную строку.
macOS
- Откройте терминал. Вы можете найти его в папке «Программы» -> «Утилиты» или воспользоваться поиском Spotlight.
- Введите команду
brew install python3. Homebrew — это популярный менеджер пакетов для macOS, который упрощает установку различных программ. - Если у вас не установлен Homebrew, сначала установите его, следуя инструкциям на официальном сайте Homebrew. Установка Homebrew также потребует установки Xcode Command Line Tools, если они еще не установлены.
Linux
- Откройте терминал. В зависимости от вашего дистрибутива, это может быть GNOME Terminal, Konsole или другой терминал.
-
Введите команду для установки Python. Для дистрибутивов на базе Debian (например, Ubuntu) используйте:
Для дистрибутивов на базе Red Hat (например, Fedora) используйте:
-
Убедитесь, что вы используете команду с правами суперпользователя (
sudo), так как установка программ требует административных прав.
Проверка установки Python
После установки Python важно убедиться, что он установлен правильно и доступен через командную строку. Это поможет избежать проблем при запуске скриптов в будущем.
Windows
- Откройте командную строку. Для этого нажмите Win + R, введите
cmdи нажмите Enter. - Введите команду
python --versionилиpython3 --version.
Если установка прошла успешно, вы увидите версию Python, например, Python 3.9.1. Если команда не распознается, возможно, Python не был добавлен в PATH. В этом случае вам нужно будет добавить его вручную через настройки системы.
macOS и Linux
- Откройте терминал.
- Введите команду
python3 --version.
Вы должны увидеть версию Python, например, Python 3.9.1. Если команда не распознается, убедитесь, что Python установлен правильно и доступен в PATH.
Запуск Python скрипта через командную строку
Теперь, когда Python установлен и проверен, можно запустить Python скрипт через командную строку. Давайте рассмотрим этот процесс более подробно.
Создание простого скрипта
Для начала создадим простой скрипт. Откройте текстовый редактор, такой как Notepad (Windows), TextEdit (macOS) или gedit (Linux), и введите следующий код:
Сохраните файл с расширением .py, например, hello.py. Убедитесь, что файл сохранен в директории, к которой у вас есть доступ через командную строку или терминал.
Запуск скрипта
Windows
- Откройте командную строку.
-
Перейдите в директорию, где сохранен ваш скрипт, используя команду
cd. Например, если скрипт находится на рабочем столе, введите: -
Введите команду для запуска скрипта:
Если все сделано правильно, вы увидите вывод Hello, World! в командной строке.
macOS и Linux
- Откройте терминал.
-
Перейдите в директорию, где сохранен ваш скрипт, используя команду
cd. Например, если скрипт находится в папке «Documents», введите: -
Введите команду для запуска скрипта:
Если все сделано правильно, вы увидите вывод Hello, World! в терминале.
Заключение и полезные советы
Запуск Python скриптов через командную строку — это базовый, но важный навык для любого программиста. Вот несколько полезных советов, которые помогут вам работать с Python более эффективно:
- 📝 Редактирование пути: Если вы часто работаете с Python, добавьте путь к Python в системные переменные PATH, чтобы не вводить полный путь к интерпретатору каждый раз. Это можно сделать через настройки системы (Windows) или файл
.bash_profile(macOS и Linux). - 🐍 Использование виртуальных окружений: Для управления зависимостями и изоляции проектов используйте виртуальные окружения. Создайте виртуальное окружение с помощью команды
python -m venv myenvи активируйте его перед запуском скриптов. Это поможет избежать конфликтов между различными версиями библиотек. - 🔄 Автоматизация задач: Используйте Python скрипты для автоматизации рутинных задач, таких как обработка файлов, работа с API и многое другое. Например, вы можете написать скрипт для автоматического резервного копирования важных файлов или для отправки уведомлений по электронной почте.
- 📚 Изучение документации: Официальная документация Python — это отличный ресурс для изучения языка и его возможностей. Посетите docs.python.org для получения подробной информации о стандартной библиотеке и различных модулях.
- 🛠 Использование IDE: Интегрированные среды разработки (IDE) могут значительно упростить процесс написания и отладки кода. Попробуйте использовать такие инструменты, как PyCharm, VS Code или Jupyter Notebook для работы с Python.
Теперь вы знаете, как установить Python, проверить его установку и запустить скрипт через командную строку. Эти знания помогут вам начать работу с Python и использовать его для решения различных задач. Удачи в ваших начинаниях с Python!
Читайте также
Last Updated :
21 Dec, 2023
Python scripts are Python code files saved with a .py extension. You can run these files on any device if it has Python installed on it. They are very versatile programs and can perform a variety of tasks like data analysis, web development, etc.
You might get these Python scripts if you are a beginner in Python so in this discussion, we will explore various techniques for executing a Python script.
What is Python Script?
Python is a well-known high-level programming language. The Python script is a file containing Python-written code. The file containing Python script has the extension ‘.py’ or can also have the extension ‘.pyw’ if it is being run on a Windows 10 machine.
To run a Python script, we need a Python interpreter installed on the device. In this article, we will learn how to run a Python script.
Methods to Run a Script in Python
There are various methods to Run a Python script, we will go through some generally used methods for running a Python script:
- Interactive Mode
- Command Line
- Text Editor (VS Code)
- IDE (PyCharm)
How to Run a Python Script?
Let’s go through the basic steps and understand how a script works.
Here is a simple code to print ‘Hello World!’.
Python3
To Execute this program, first we have to save it with the ‘.py’ extension. Then we can execute this file with the help of the terminal.
Here, the print() function is to print out any text written within the parenthesis. We can write the text that we want to be printed using either a single quote as shown in the above script or a double quote.
If you are coming from any other language then you will also notice that there is no semicolon at the end of the statement as, with Python, you do not need to specify a semicolon at the end of the line. And also we don’t need to include or import any files to run a simple Python script.
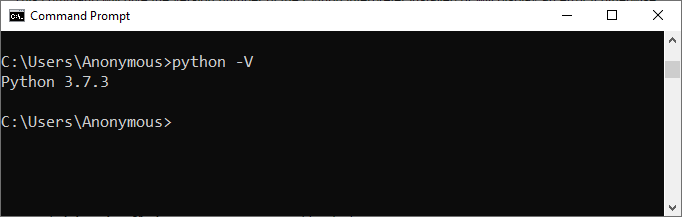
There are various ways to run a script in Python but before going toward the different ways to run a Python script, we first have to check whether a Python interpreter is installed on the system or not. So in Windows, open ‘cmd’ (Command Prompt) and type the following command.
python -V
This command will give the version number of the Python interpreter installed or will display an error if otherwise.
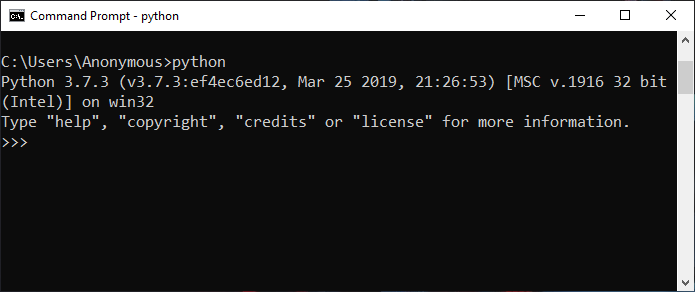
1. Run Python Script Interactively
In Python Interactive Mode, you can run your script line by line in a sequence. To enter an interactive mode, you will have to open Command Prompt on your Windows machine, type ‘python’ and press Enter.
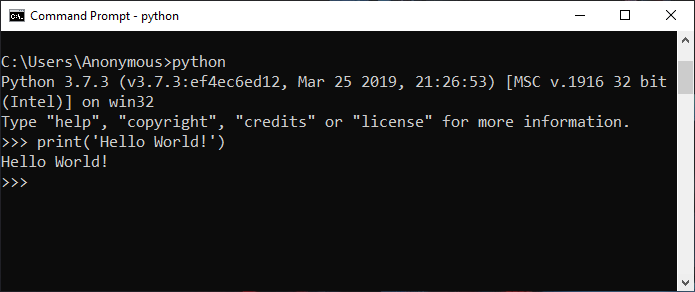
Example1: Using Print Function
Run the following line in the interactive mode:
print('Hello World !')
Output:
Example 2: Using Interactive Execution
Run the following lines one by one in the interactive mode.
name = "Aakash"
print("My name is " + name)
Output:
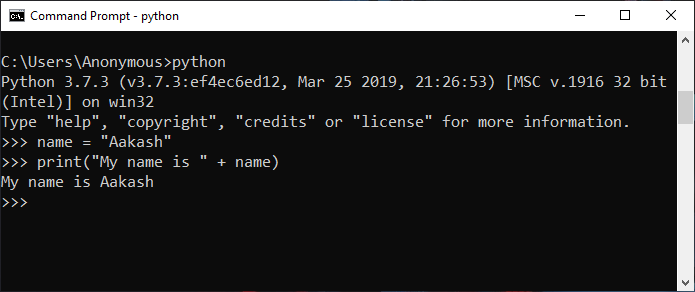
Example 3: Interactive Mode Comparison
Run the following lines one by one in the interactive mode.
a = 1
b = 3
if a > b:
print("a is Greater")
else:
print("b is Greater")
Output:
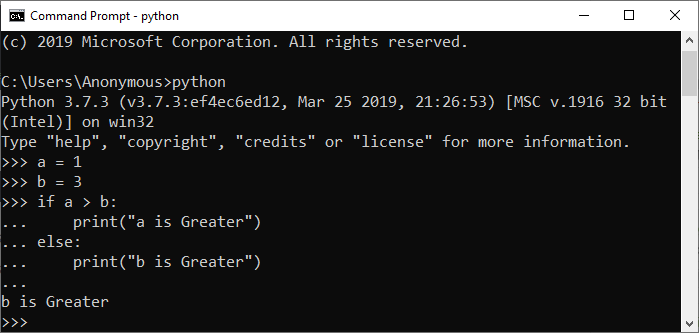
Note: To exit from this mode, press ‘Ctrl+Z’ and then press ‘Enter’ or type ‘exit()’ and then press Enter.
2. Run Python Script by the Command Line
Running Python scripts on Windows via the command line provides a direct and efficient way to execute code. It allows for easy navigation to the script’s directory and initiation, facilitating quick testing and automation.
Example 1: Using Script Filename
To run Python in the terminal, store it in a ‘.py’ file in the command line, we have to write the ‘python’ keyword before the file name in the command prompt. In this way we can run Python programs in cmd.
python hello.py
You can write your own file name in place of ‘hello.py’.
Output:
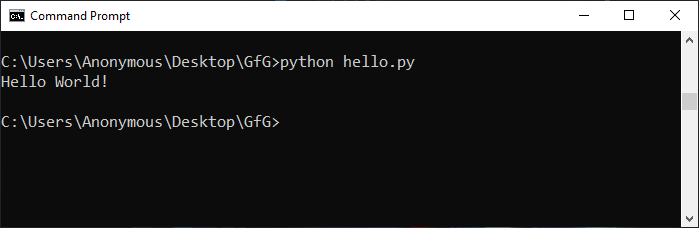
Example 2: Redirecting output
To run a Python script in Terminal from the command line, navigate to the script’s directory and use the python script_name.py command. Redirecting output involves using the > symbol followed by a file name to capture the script’s output in a file. For example, python script_name.py > output.txt redirects the standard output to a file named “output.txt.”
Output :

Output
3. Run a Script in Python using a Text Editor
To run Python script on a text editor like VS Code (Visual Studio Code) then you will have to do the following:
- Go to the extension section or press ‘Ctrl+Shift+X’ on Windows, then search and install the extension named ‘Python’ and ‘Code Runner’. Restart your vs code after that.
- Now, create a new file with the name ‘hello.py’ and write the below code in it:
print('Hello World!')
- Then, right-click anywhere in the text area and select the option that says ‘Run Code’ or press ‘Ctrl+Alt+N’ to run the code.
Output:
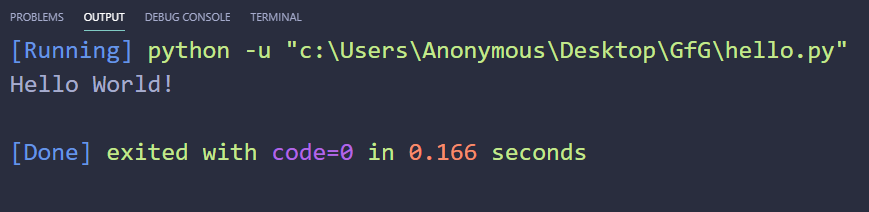
4. Run Python Scripts using an IDE
To run Python script on an IDE (Integrated Development Environment) like PyCharm, you will have to do the following:
- Create a new project.
- Give a name to that project as ‘GfG’ and click on Create.
- Select the root directory with the project name we specified in the last step. Right-click on it, go to New, anto, and click on the ‘Python file’ option. Then give the name of the file as ‘hello’ (you can specify any name as per your project requirement). This will create a ‘hello.py’ file in the project root directory.
Note: You don’t have to specify the extension as it will take it automatically.
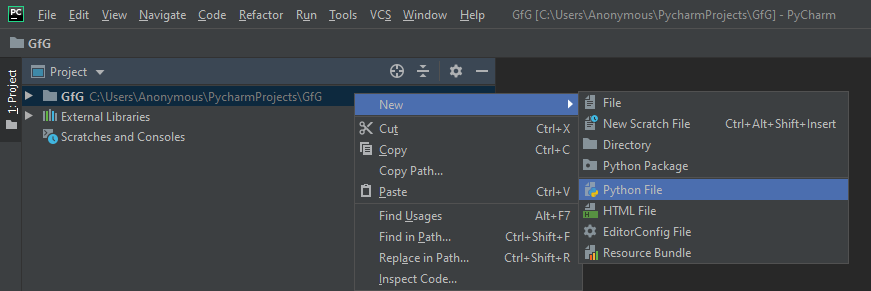
- Now write the below Python script to print the message:
print('Hello World !')
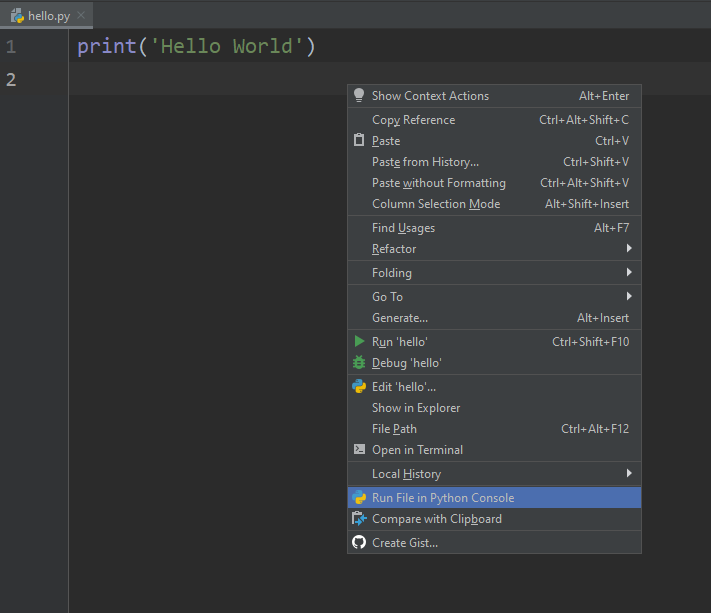
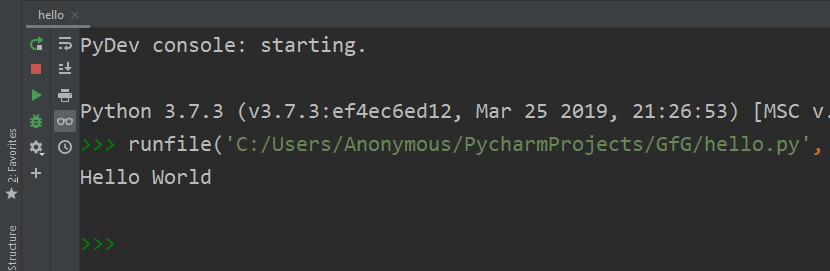
- To run this Python script, Right click and select the ‘Run File in Python Console’ option. This will open a console box at the bottom and show the output there. We can also run using the Green Play Button at the top right corner of the IDE.
Output:
We have covered 4 different methods to run Python scripts on your device. You can use any of the above methods depending on your device. Running Python scripts is a very basic and easy task. It helps you in sharing your work and accessing other source work for learning.
Similar Reads:
- Run Python script from anywhere in linux
- Run function from the command line In Python
- How to Run a Python Script using Docker?
- Schedule a Python Script to Run Daily
A crucial operation you need to be aware of when programming is to run a Python script.
Although this seems like a simple operation, most beginners often face difficulty when running scripts.
In this article, we will guide you through the process of running scripts in Python using different methods and environments.

To run a Python script, you must:
- Open a Terminal or Command Prompt Window
- Navigate to the directory where your Python script (.py file) is located using the ‘cd’ command
- Execute your script by typing ‘python’ followed by the name of your script

There are multiple ways to run a script, and by the end of this article, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to run Python scripts in different environments and operating systems.
Understanding each method can improve your programming experience and help you adapt to different scenarios.
Let’s get into it!
6 Methods to Run a Python Script
In this section, we will cover 6 ways of running a Python Script.
Specifically, we will go over the following:

- Running a Python Script From Command Line
- Running a Python Script From Python Interactive Shell
- Running a Python Script in IDE
- Running a Python Script in IDLE
- Running a Python Script Using Import
- Running a Python Script Using runpy.run_module() And runpy.run_path()

1) How to Run a Python Script From Command Line
The process of running a Python script from the command line is quite similar across different operating systems.
In this section, we will look at how you can:
- Run Python scripts from the command line on Windows
- Run Python scripts from the command line on Linux and MacOS
1) How to Run Python Scripts From The Command Line on Windows
You can use the following steps to run a Python program from the command line on Windows:
Step 1: Open the Command Line Interface. You can do this by searching for cmd in the start menu or by pressing Win+R, typing cmd, and then hitting Enter.
Step 2: Navigate to the directory containing your Python script using the cd command.
For example, if your script is in a directory on your local drive E in a folder named “PythonScripts”, you would type cd E\PythonScripts.
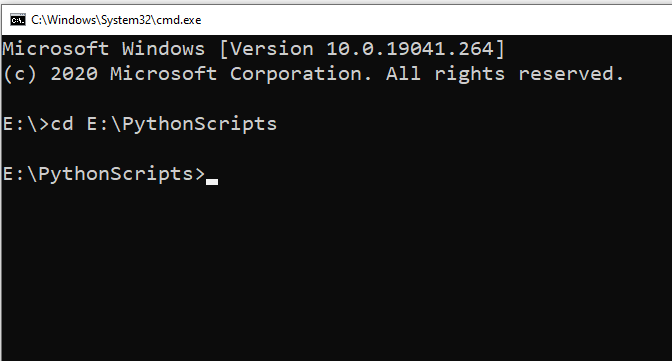
Step 3: Run the script by typing python script.py (replace script.py with the name of your script), and press Enter.
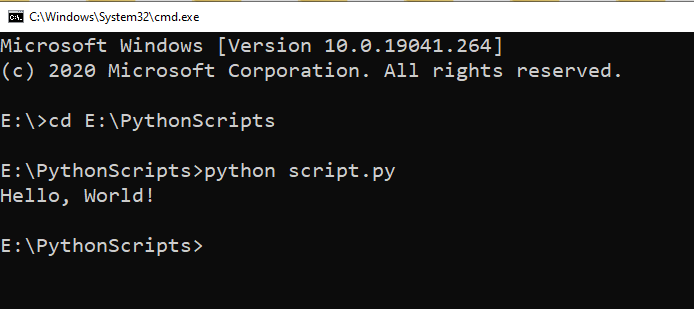
2) How to Run Python Scripts From The Command Line on Linux And MacOS
Follow the steps listed below to run Python scripts from the command line on Linux and MacOS:
Step 1: Open the terminal.
Step 2: Navigate to the directory containing your Python script using the cd command.
For example, if your script is in a directory in your home folder named “PythonScripts”, you would type cd ~/PythonScripts.
Step 3: To run your script, type python3 script.py (replace script.py with the name of your script), and press Enter.
2) How to Run Python Script From Python Interactive Shell
The Python Interactive Shell, also known as the Python Interpreter, is an excellent tool for trying out small snippets of Python code and doing simple calculations, but it’s not the best tool for running large, complex scripts.
However, if you want to run a Python script from the Python Interactive Shell, you can do so using Python’s built-in execfile() function in Python 2, or using the exec() function with open() in Python 3.

Running a Python Script in Python 2
Follow the steps below to run a script from the Python interactive shell in Python 2:

Step 1: Open the Python Interactive session by typing python into your terminal or command prompt and hitting Enter.
Step 2: Type execfile(‘script.py’), replacing ‘script.py’ with the path to your script.
For example:
>>> execfile('C:/Users/username/Desktop/script.py')Running a Python Script in Python 3
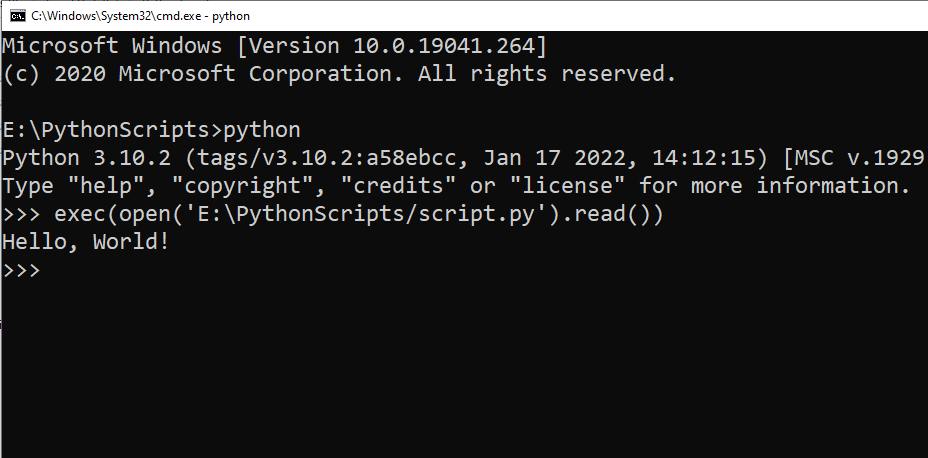
In Python 3, the execfile() function has been removed. Instead, you can use exec() with open() to achieve the same effect.
Follow the steps below to run a script in Python 3:
Step 1: Open the Python Interactive Shell by typing python3 (or python if Python 3 is your default Python) into your terminal or command prompt and hitting Enter.
Step 2: Type the following, replacing ‘script.py’ with the path to your script.
>>> exec(open('C:/Users/username/Desktop/script.py').read())The output for the above execution will be:
3) How to Run a Python Script in IDE
You can run Python scripts in different Integrated development environments, and each has its own way of executing scripts.
For instance, if you’d like to run a Python script in VS Code, you can follow the steps given below:
Step 1: Launch Visual Studio Code, and open your Python file (File > Open File…).
If you haven’t created a Python file yet, create a new file (File > New File), and make sure to save it with a .py extension.
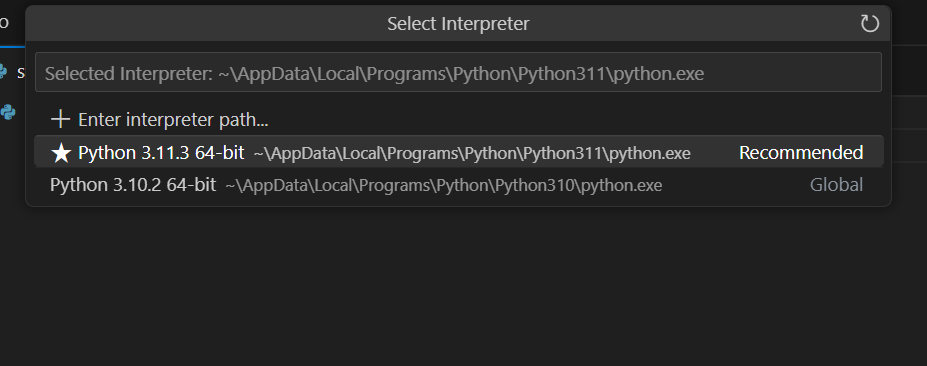
Step 2: Select a Python interpreter by clicking on the Python version in the bottom left of the status bar, or use the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P) and search for “Python: Select Interpreter”.
This will show a list of available interpreters that VS Code can find automatically, including virtual environment interpreters.
Step 3: Once you have written your Python script and selected the Python interpreter, you can open a new terminal in VS Code to execute the script.
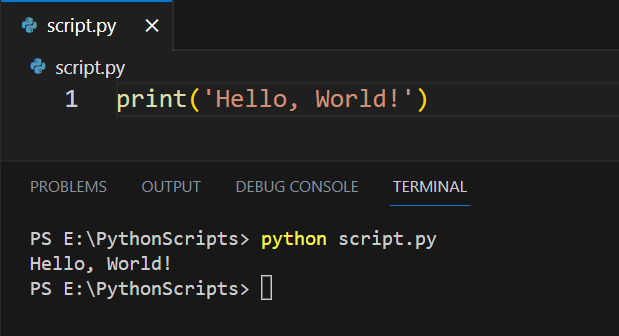
If you are using a Python virtual machine, you can use the same steps as discussed above after creating a virtual environment.
4) How to Run Python Script in Python’s IDLE
Python’s IDLE (Integrated Development and Learning Environment) is a simple IDE that comes with Python.
To run a Python script in IDLE, you can follow the steps given below:
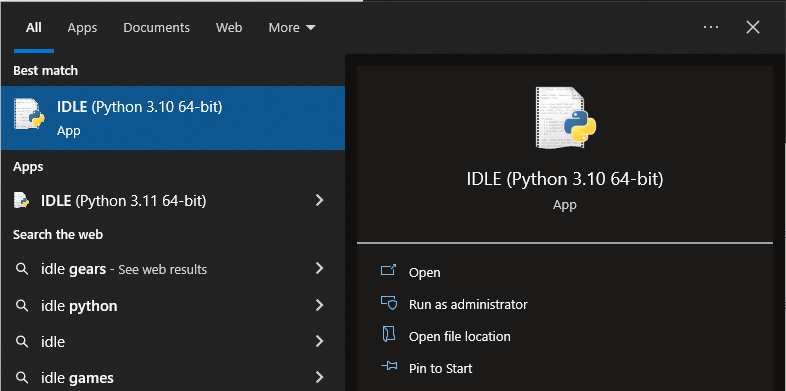
Step 1: You can launch Python IDLE from your Start Menu (Windows), Applications folder (macOS), or application launcher (Linux).
Simply search for IDLE and click on the icon.
Step 2: Once IDLE is open, you can load your Python script into the IDLE text editor. Go to File > Open… in the menu bar.
Navigate to your Python script in the file dialog, select it, and click Open.
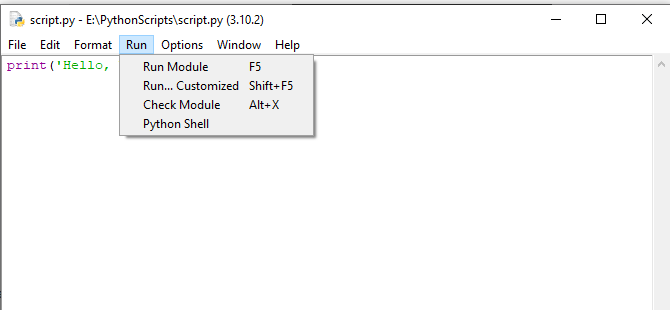
Step 3: After the script is loaded into the IDLE text editor, you can run it by going to Run > Run Module in the menu bar, or simply by pressing the F5 key.
Step 4: The output from your script will be displayed in the Python Shell window.
If your script includes input calls like input(), the shell will also provide a prompt for user input.
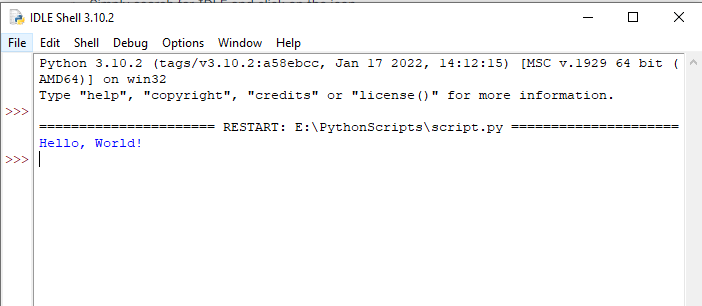
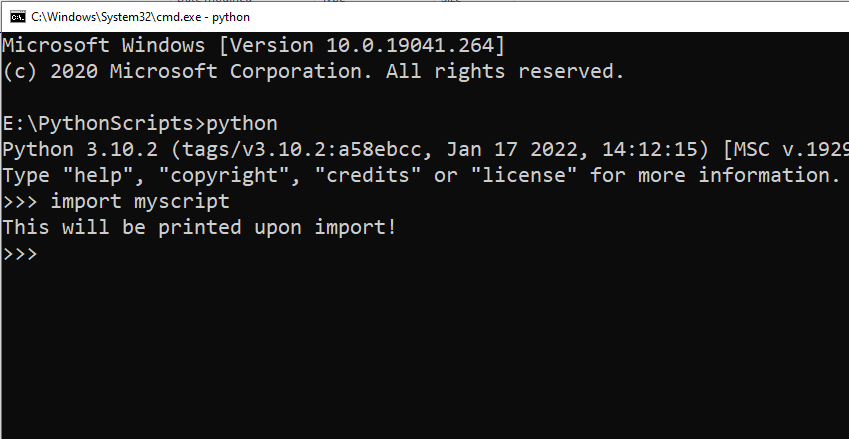
5) How to Run a Python Script Using Import
Running a Python script using import essentially involves treating the script as a module.
When you import the script, Python will execute it from top to bottom, just as if you’d run the script directly.
Suppose you have a Python script named myscript.py with the following content:
# myscript.py
def greet():
print("Hello from myscript!")
print("This will be printed upon import!")You can run the script by importing it.
Open the Python shell by typing python or python3 (depending on your installation) in the terminal. Navigate to the directory containing myscript.py or make sure myscript.py is in a directory that’s part of your PYTHONPATH.
Import myscript with the following code:
>>> import myscriptThe output of this execution will be:
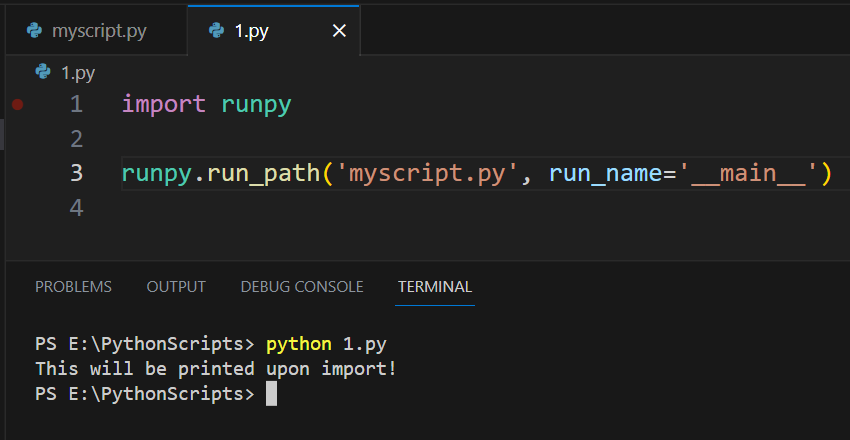
6) How to Run a Python Script Using runpy.run_module() And runpy.run_path()
The runpy module in Python allows you to execute Python code dynamically.
It contains two main functions, run_module() and run_path(), which can be used to run Python scripts.
1) runpy.run_module()
The run_module() function allows you to execute a Python module without importing it.
It runs the module as if it was invoked from the command line using the -m option.
The following is an example of this method:
import runpy
# Run a standard library module as a script
# Equivalent of running "python -m http.server" from the command line
runpy.run_module(mod_name='http.server', run_name='__main__', alter_sys=True)In this example, the http.server module from the Python standard library is being run, which will start a simple HTTP server.
2) runpy.run_path()
The run_path() function allows you to execute a Python script located at a specific path.
It reads and runs the Python file specified as the path.
The following is an example of run_path():
import runpy
# Run a script file as a standalone script
runpy.run_path('path_to_script.py', run_name='__main__')In this example, replace ‘path_to_script.py’ with the actual path to your Python script.
This will execute the script just like running python path_to_script.py from the command line.
Supercharge your analytics game with Code Interpreter by watching the following video:
Final Thoughts
Mastering the various ways to run a Python script is an invaluable skill for any programmer. It allows you to test and execute your code across diverse platforms and environments.
By learning these techniques, you’ll find that you have more flexibility and control in your development process, whether it’s running scripts from the command line, an IDE, or even using Python’s own tools like import and runpy.
Each method discussed offers unique benefits, be it the simplicity of running scripts in an IDE, the powerful control provided by command-line execution, or the dynamic capabilities of the import statement and runpy.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, you will find some frequently asked questions you may have when running Python scripts.

How do I execute a Python script in terminal?
To execute a Python script in the terminal, simply type python followed by the file name, including the “.py” extension.
For example, to run a script called “script.py”, you would type:
python script.py
What is the command to run a Python script from the command line?
The command to run a Python script from the command line is the same as executing it in the terminal.
Use python followed by the file name with the “.py” extension.
For instance:
python script.py
How can I run a .py file in Windows?
To run a .py file in Windows, open the Command Prompt and navigate to the directory containing the .py file.
Then, use the command python followed by the file name with the “.py” extension.
For example:
python script.py
What are the steps to run a Python script in a specific folder?
To run a Python script in a specific folder, follow these steps:
- Open the terminal or command prompt.
- Navigate to the folder containing the .py file using the cd command. For example:
cd path/to/your/script-folder
- Run the Python script using the python command followed by the file name:
python script.py
How can I execute Python code in Visual Studio Code?
To execute Python code in Visual Studio Code, follow these steps:
- Open the Python file in Visual Studio Code.
- Ensure that the Python extension is installed and correctly configured.
- Click the “Run” button in the top-right corner, or right-click in the editor and select “Run Python File in Terminal”.
Is it possible to run a Python script in the background?
Yes, it is possible to run a Python script in the background. This can be achieved using various methods, such as appending an ampersand (&) to the command in Unix-like systems or using the start command in Windows.
For example:
- On Unix-like systems:
python script.py &
- On Windows:
start python script.pyDownload Article
A quick guide to operating Python scripts in command prompt
Download Article
Whether you’re writing Python code on your Windows PC or just want to use existing Python scripts, it’ll be helpful to learn how to run code from the Command Prompt. Running Python code is easy—you’ll just need to have Python installed. This wikiHow article will walk you through opening a Python file from Command Prompt, and teach you how to fix the common «python is not recognized as an internal or external command» error.
Easy Way to Run a Python Script
To run a Python file, type “Python File.py” where “File” is your file’s name. For example, if your Python file is named “Script,” type “Python script.py” instead. Press enter to run the command and open the file.
-
Find the Python file that you want to open in Command Prompt.
- If you already know the folder path to the Python file you want to open, skip ahead to opening the file in Command Prompt.
-
Click once the Python file for which you want to see the folder path.
Advertisement
-
Doing so prompts a drop-down menu to appear.
-
It’s in the drop-down menu. The properties window will open.
-
The folder address (or «path») to the right of the «Location» heading is what you’ll need to enter into Command Prompt when switching to the directory in which your Python file is stored.
- You can copy the location by highlighting it (click and drag your mouse across the «Location» value) and then pressing Ctrl+C.
Advertisement
-
Click the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of the screen. The Start menu will pop up.
-
Type in cmd to do so.
-
It’s at the top of the Start menu. Doing so will open Command Prompt.
-
Type cd and a space, then type in the «Location» address for your Python file and press ↵ Enter.
- For example, to open a Python file in a folder named «Files» on your Desktop, you would enter cd desktop/Files here.
- If you copied the path to the file, you can type in cd and a space and then press Ctrl+V to paste in the path.
-
Type in python file.py where file is your Python file’s name.
- For example, if your Python file is named «script», you would type in python script.py here.
- If your Python file has one or more spaces in its name, you’ll place quotation marks around the file name and extension (e.g., python "my script.py").
-
Doing so runs your command and opens your Python file via your computer’s installed Python program.
- If you encounter an error that says
'python' is not recognized as an internal or external commandafter pressing Enter, you’ll need to add Python to the PATH list before retrying this part.
- If you encounter an error that says
Advertisement
-
Enable viewing for hidden folders. Since one of the folders that contains your Python installation folder is most likely hidden, you’ll have to unhide it before proceeding:
- Open File Explorer
.
- Click the View tab.
- Check the «Hidden items» box.
- Open File Explorer
-
In some cases, the Python path is «C:\Python27»; however, if you’ve installed the most recent version of Python using the default settings, it’s tucked away in a hidden folder. You can copy the proper file path by doing the following:
- Click This PC on the left side of the File Explorer.
- Double-click your hard drive in the «Devices and drives» section.
- Scroll down and double-click the «Users» folder.
- Double-click the folder with your username on it.
- Scroll down and double-click «AppData».
- Double-click «Local».
- Scroll down and double-click «Programs».
- Double-click the «Python» folder.
- Double-click the Python folder with your preferred version number (e.g., «Python36»).
-
Click once the address bar at the top of the File Explorer to highlight its contents, then press Ctrl+C to copy the highlighted address.
-
Right-click the Start
icon to do so. You should see a pop-up menu appear.
- You can also press ⊞ Win+X to open the Power User pop-up menu.
-
It’s in the pop-up menu. A new window will open.
-
This is a link in the upper-right corner of the window. Doing so opens the System Information window.
-
You’ll see this in the upper-left side of the System Information window. Yet another window will pop up.
-
It’s in the bottom-right corner of the pop-up window.
-
This window is at the top of the Environment Variables window.
- You may have to scroll up or down with your mouse cursor hovering over the «User variables» pane to find the «Path» variable.
-
Doing so opens a pop-up window.
-
It’s on the right side of the window. A text field will open in the middle of the window.
-
Press Ctrl+V to do so. Your copied path will appear in the text field in the middle of the window.
-
This will save your changes and close the «Path» window, the «Environmental Variables» window, and the «System Properties» window.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
I want to create a shortcut that executes the utility «ptpython,» running in the cmd prompt. The shortcut I have points to the directory containing «ptpython.exe» file but it does not execute it.
It sounds like ptpython.exe is a command-line utility, meaning it will only start if you execute it from a DOS window — you can’t create a shortcut for it directly. You can probably create a shortcut to cmd.exe, though (the DOS window) and pass it the ptpython.exe file as a parameter. Something like «cmd.exe /c ptpython.exe» should work, or if this disappears in the end, try with /k (instead of /c).
-
Question
Does this work on Windows 7?
Yes. The directions to access the environment variables would be slightly different, as there is no «Power User» menu in Windows 7. Instead: 1. Press the Windows key and R to open the Run dialog. 2. Enter «sysdm.cpl». 3. Click the «Advanced» tab of the System Properties Window. 4. Click the «Environmental variables». Most everything else would work as described even on Windows 95 (if there’s a version of Python for Windows 95).
-
Question
After opening the Command Prompt and navigation to the directory in which the py file exists and opening Python, not able to run the file using python file_name.py. It says that the syntax is wrong.
That sounds like a problem with the file you’re trying to run. Make sure you are using the right version of Python for it (version 2 or 3, usually).
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about programming languages, check out our in-depth interview with Kevin Burnett.
Video
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 997,376 times.


























