From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) is a Microsoft API and server software that makes it possible to create applications to administer the routing and remote access service capabilities of the operating system, to function as a network router. Developers can also use RRAS to implement routing protocols. The RRAS server functionality follows and builds upon the Remote Access Service (RAS) in Windows NT 4.0.[1]
RRAS was introduced with Windows 2000 and offered as a download for Windows NT 4.0.
- Multiprotocol router — The computer running RRAS can route IP, IPX, and AppleTalk simultaneously. All routable protocols are configured from the same administrative utility. RRAS included two unicast routing protocols, Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) as well as IGMP routing and forwarding features for IP multicasting.
- Demand-dial router — IP and IPX can be routed over on-demand or persistent WAN links such as analog phone lines or ISDN, or over VPN connections.
- Remote access server — provides remote access connectivity to dial-up or VPN remote access clients that use IP, IPX, AppleTalk, or NetBEUI.
Routing services and remote access services used to work separately. Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), the protocol suite commonly used to negotiate point-to-point connections, has allowed them to be combined.
RRAS can be used to create client applications. These applications display RAS common dialog boxes, manage remote access connections and devices, and manipulate phone-book entries.[2]
Routing and Remote Access Service Management Pack
[edit]
The Routing and Remote Access Service Management Pack helps a network administrator monitor the status and availability of computers running Windows Server 2008 R2.[3]
Features introduced in Windows Server 2008
[edit]
- Server Manager – Application used to assist system administrators with installation, configuration, and management of other RRAS features.
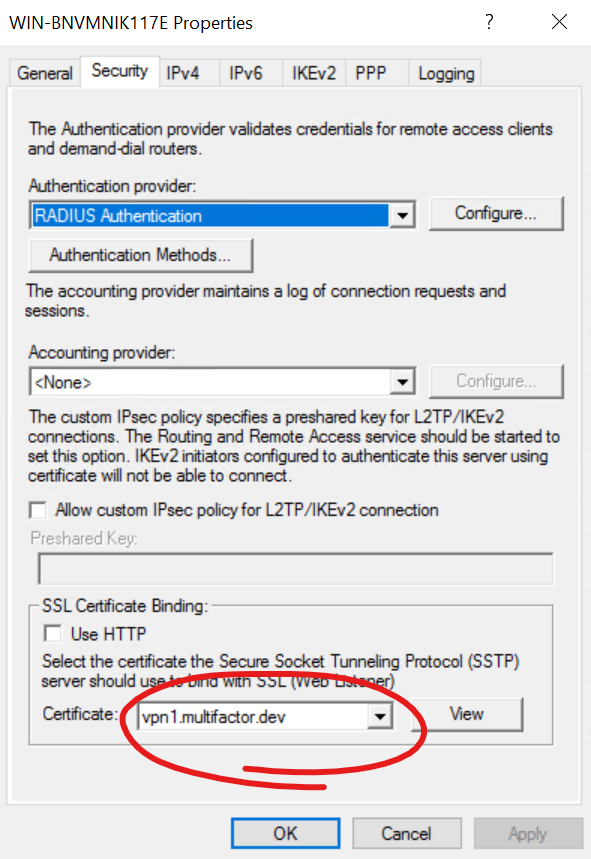
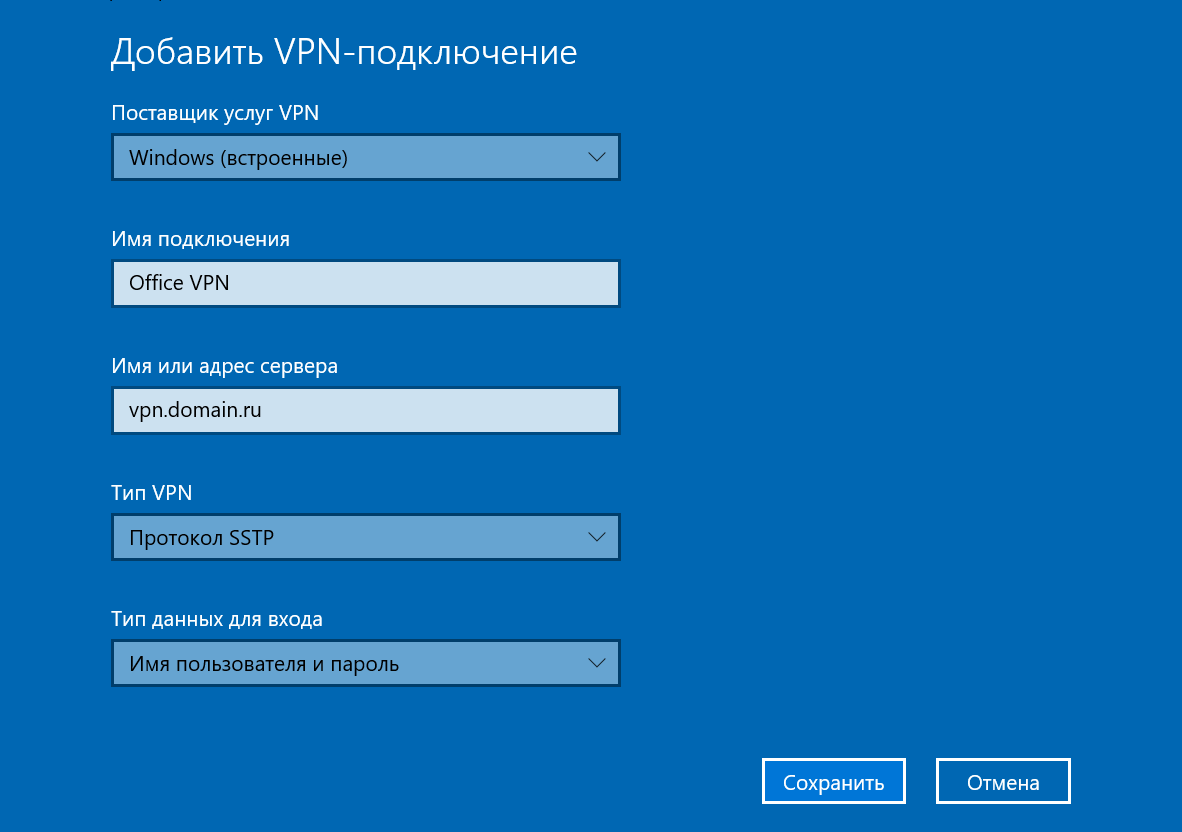
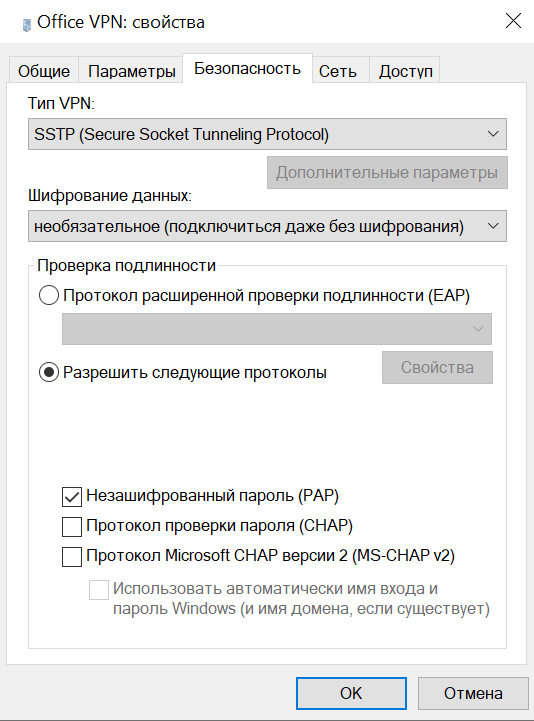
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol
- VPN enforcement for Network Access Protection – Limits VPN connections to defined network services.
- IPv6 support – added PPPv6, L2TP, DHCPv6, and RADIUS technologies allowing them to work over IPv6.
- New cryptographic support – strengthened encryption algorithms to comply with U.S. government security requirements, in addition to removing algorithms which could not be strengthened.[4]
Removed technologies
[edit]
- Bandwidth Allocation Protocol (BAP) was removed from Windows Vista, and disabled in Windows Server 2008.
- X.25.
- Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP). SLIP-based connections will automatically be updated to PPP-based connections.
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
- IP over IEEE 1394
- NWLink IPX/SPX/NetBIOS Compatible Transport Protocol
- Services for Macintosh
- Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol component in Routing and Remote Access
- Basic Firewall in RRAS (replaced with Windows Firewall)
- Static IP filter APIs for RRAS (replaced with Windows Filtering Platform APIs)
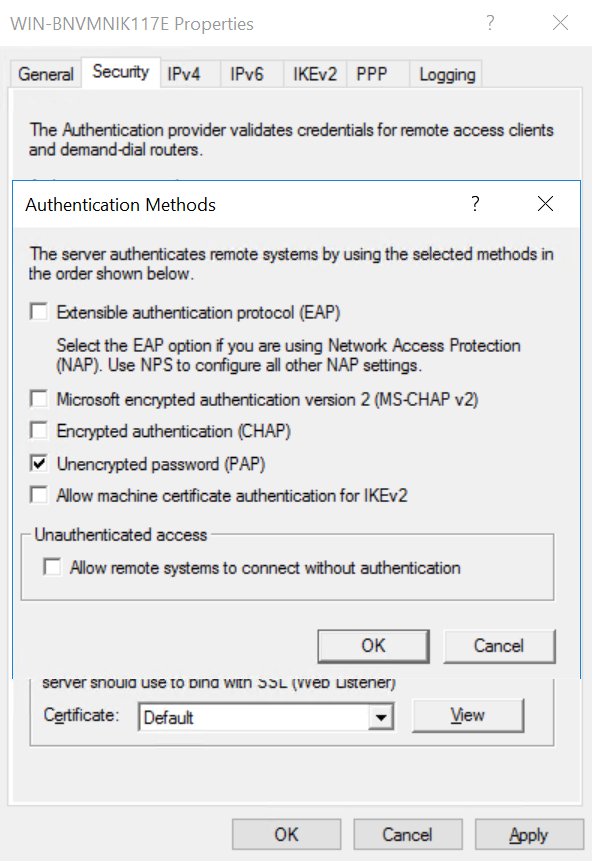
- The SPAP, EAP-MD5-CHAP, and MS-CHAP authentication protocols for PPP-based connections.[4]
- Remote Access Service
- ^ RRAS MSDN Library
- ^ Routing and Remote Access Service MSDN
- ^ RRAS Management Pack Guide for System Center Operations Manager 2007
- ^ a b What’s New in Routing and Remote Access in Windows Server 2008
- Tech FAQ
What changes in Routing and Remote Access Services and how to setup – Windows Server 2025
IT and Virtualization Consultant. Vladan is the founder, and executive editor of the ESX Virtualization Blog at vladan.fr. He is a VMware VCAP-DCA and VCAP-DCD, and has been a vExpert from 2009 to 2023.
IT and Virtualization Consultant. Vladan is the founder, and executive editor of the ESX Virtualization Blog at vladan.fr. He is a VMware VCAP-DCA and VCAP-DCD, and has been a vExpert from 2009 to 2023.
Windows Server 2025 is the latest Microsoft Server Operating system released recently. The OS brings many new features and additions while also improves security. Through the evolution of the product, Microsoft also phasing out certain elements and protocols. Today, we’ll explore what Microsoft has changed in Routing and Remote Access Services (RRAS) compared to previous releases of Windows Server 2025 and we’ll run the process of installation and configuration of the component.
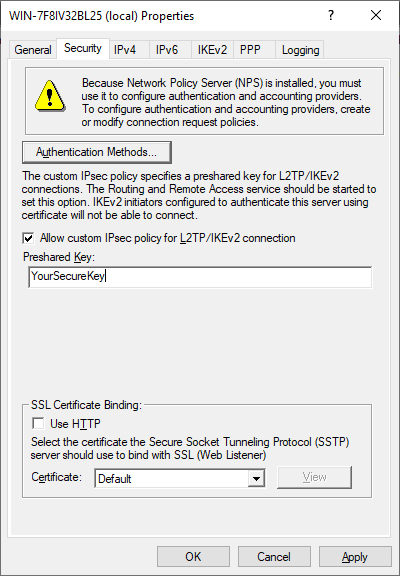
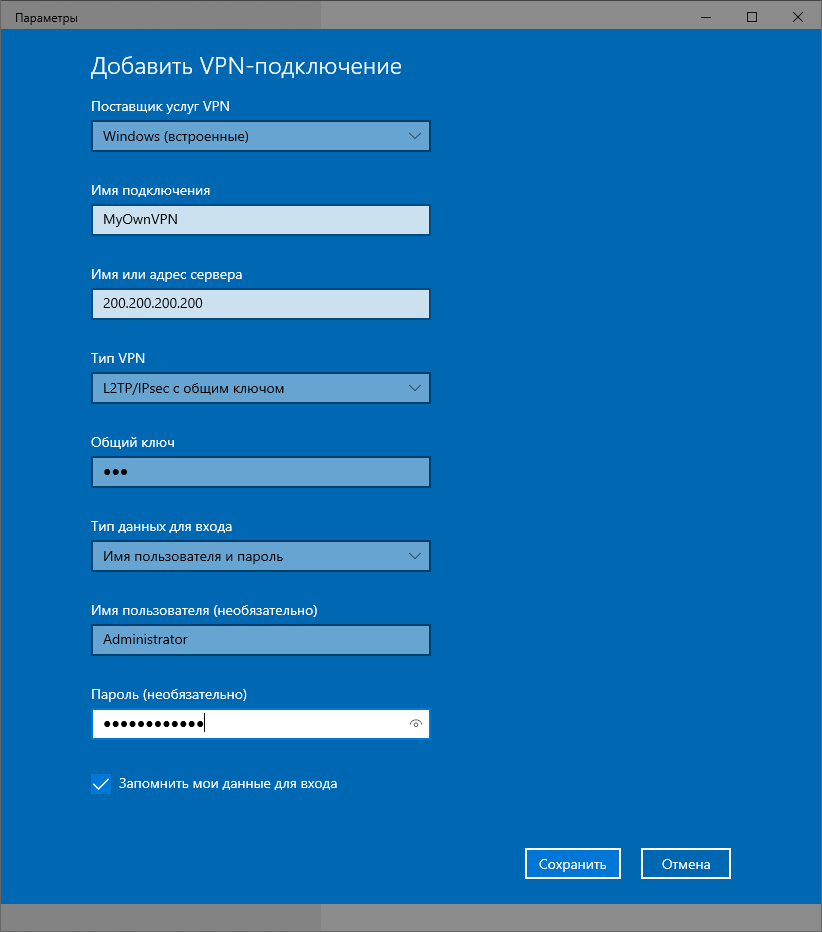
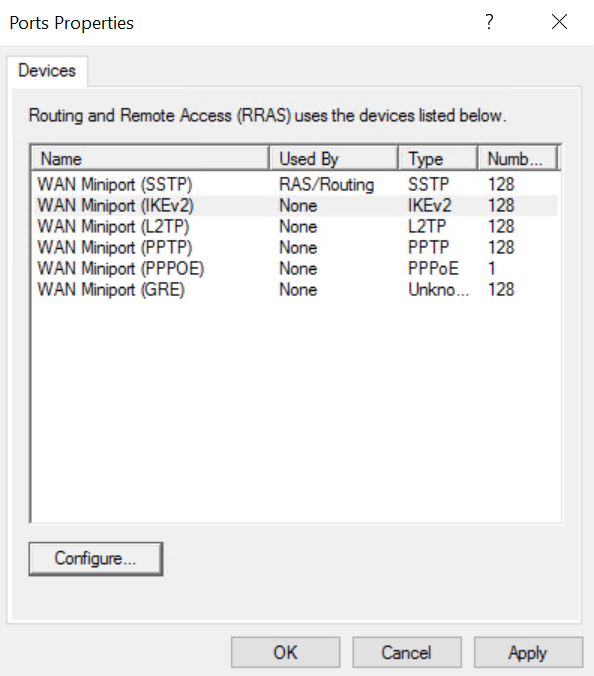
As you know, RRAS has been part of Windows Server family for a very long time. However, two of the protocols used, PPTP and L2TP, are not used by default for VPN connections, but rather the SSTP and IKEv2 connections are privileged. Yhe older PPTP and L2TP protocols can still be used, however, by default they are deactivated and rather the SSTP and IKEv2 connections are pre-configured for remote access.
If you do an in-place upgrade (yes, available for Windows Server 2025), the existing configurations keep its configuration and protocols for connections. For example, if you run Windows Server 2019 with PPTP and L2TP connections configured as VPN, then after upgrade to Windows Server 2025, those connections are still accepted.

Default configuration of RRAS protocols with Windows Server 2025
As you can see, the number of ports is zero for the L2TP and PPTP types of connections, meanings that the default, the number of ports is set to zero. It means that by default, RRAS setups don’t accept VPN connections based on PPTP and L2TP protocols. You can still use them if you want, but those type of connections aren’t secure and Microsoft is phasing out those two protocols. They are deprecated. Microsoft says that:
“Deprecation refers to the stage in the product lifecycle when a feature or functionality is no longer in active development and may be removed in future releases.”
What is RRAS good for?
RRAS with WS 2025 is good for remote administration and secure your remote VPNs, but many users prefer using dedicated hardware VPNs.
There might be use cases for both, hardware or software-based VPNs. Why not using the one provided by Microsoft while you already pay for CALs for your co-workers.
The Routing and Remote Access service (RRAS) supports remote user or site-to-site connectivity by using virtual private network (VPN) or dial-up connections.
When using a RRAS, you can deploy VPN connections and allow end users to connect your co-workers with remote access to your organization’s network. You can also create a site-to-site VPN connection between two servers at different locations.
If you’re using Hyper-V, you can also use RRAS as multitenant gateway where you have VMs Networks deployed with VLANs, then you can deploy RRAS in a VM which will be used as a software gateway and router that allows routing between cloud network traffic and virtual and physical networks.
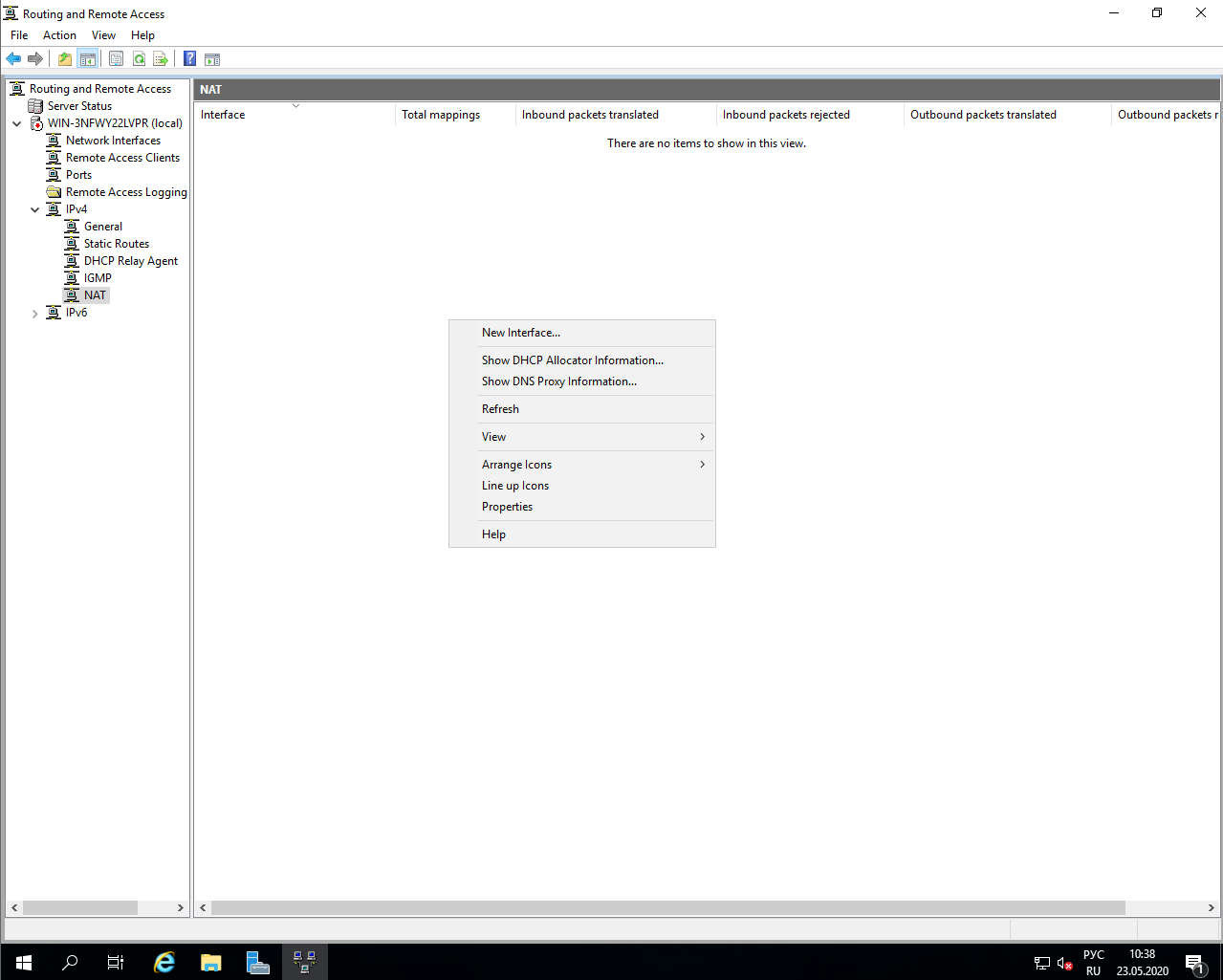
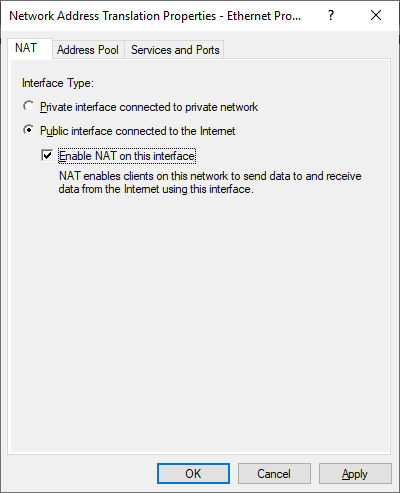
Lastly, you can configure the RRAS Multitenant Gateway with Border Gateway Protocol used for dynamic routing where you can enable Network Address Translation (NAT) to provide Internet access for VMs on your VM networks.
What are system requirements for RRAS in Windows Server 2025?
The system requirements are similar to what they were in 2022 or 2019:
- You’ll need to mee the hardware requirements (if you’re installing on physical box) first, then install WS 2025.
- You’ll need to use an account with enough privileges (account in the local administrator’s group if the system is outside of a MS domain, or an account with administrative rights on the system).
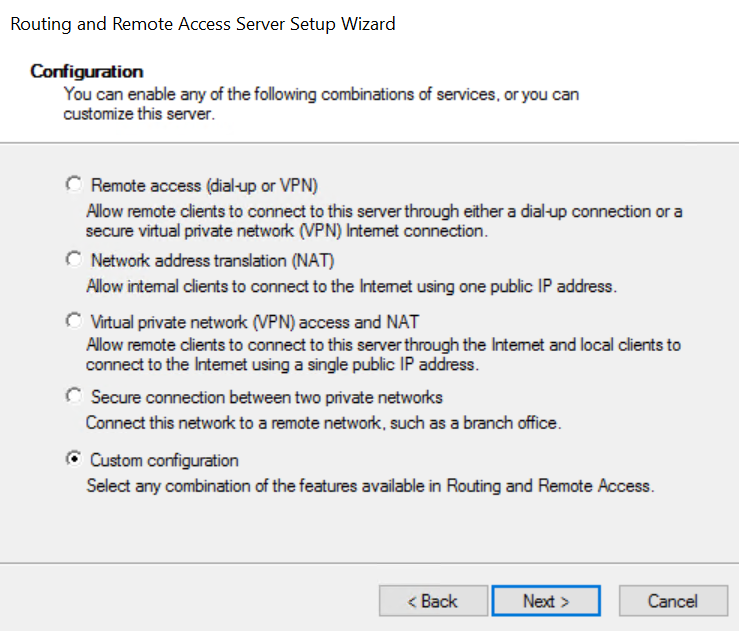
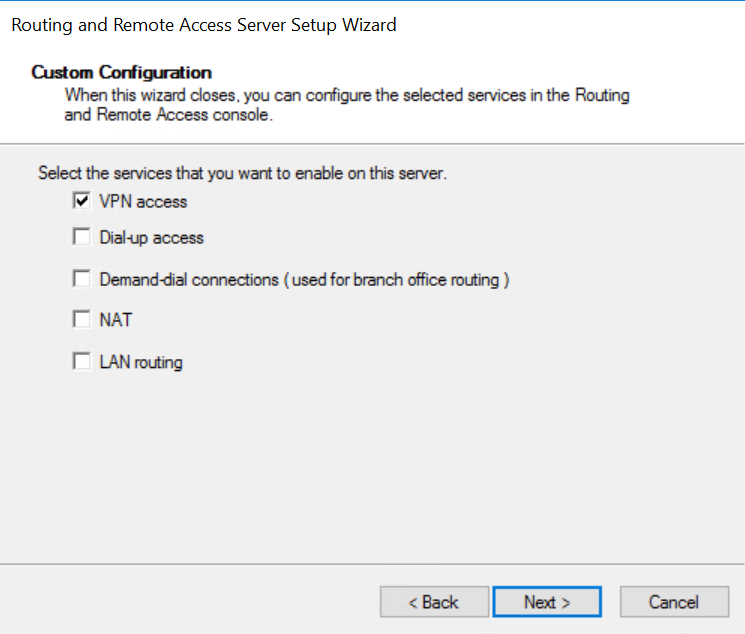
How to Install and configure RRAS on Windows Server 2025
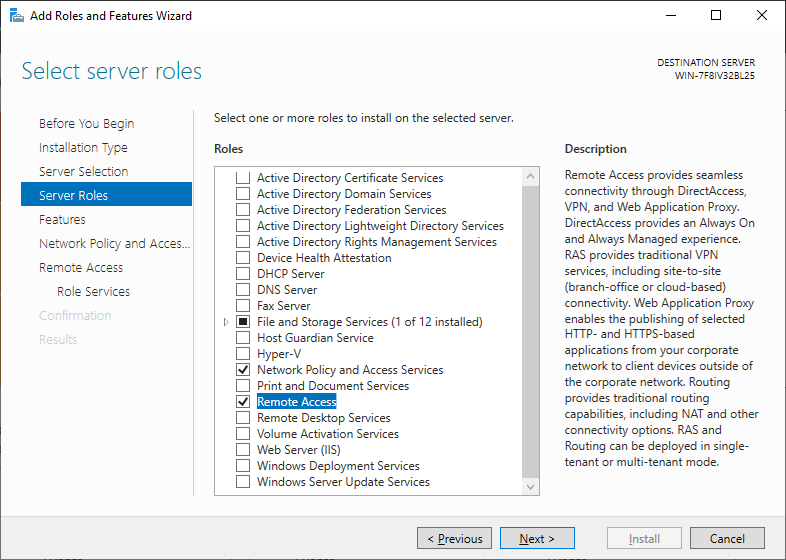
Open Server manager and start Add Roles and Features wizard. Then go ahead and:
- Select Remote Access > Check Remote access in the roles section
- Check the box DirectAccess and VPN (RAS) and click the Add features button, with then add all the necessary tools the systems ask you for.
- Follow the wizard and reboot the host at the end.
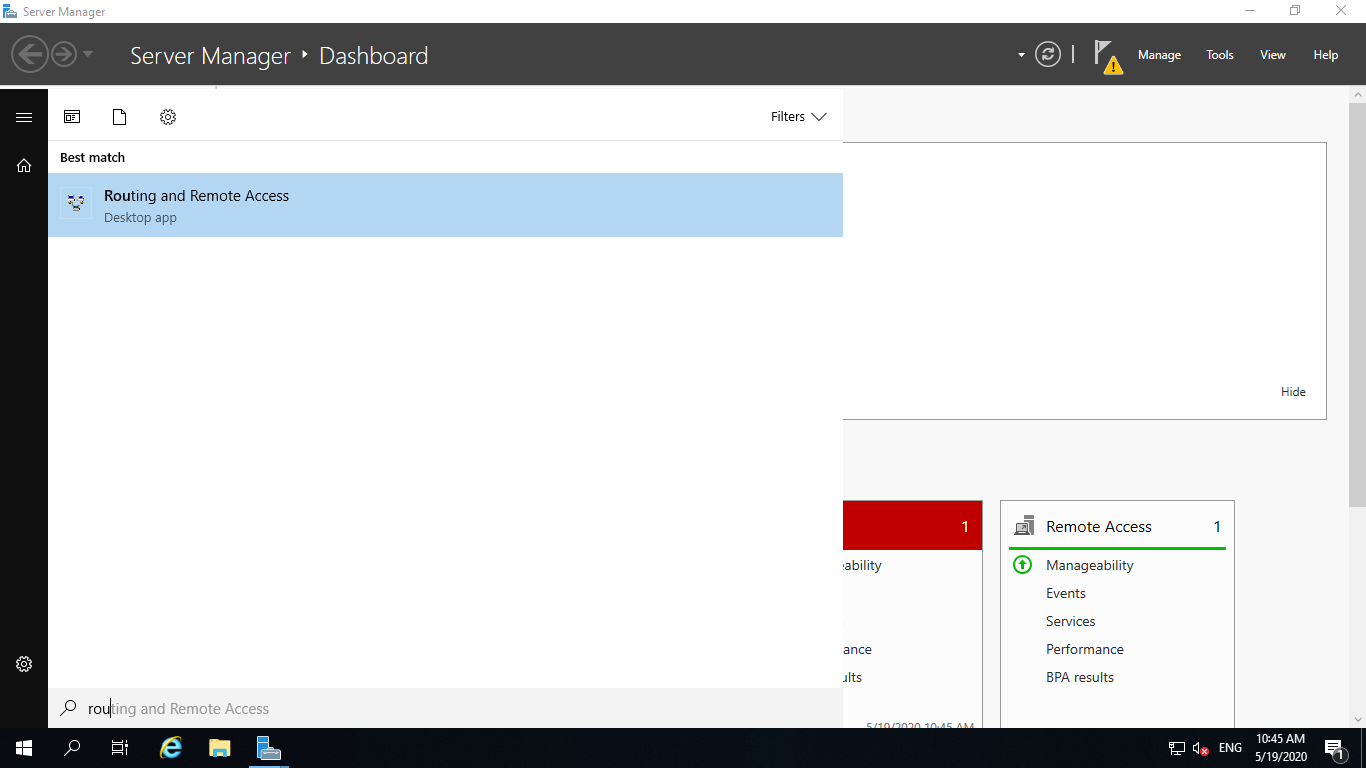
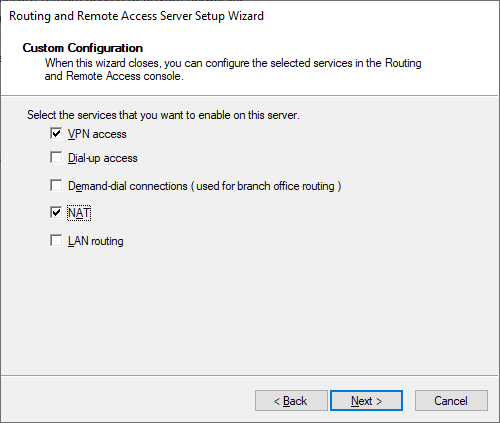
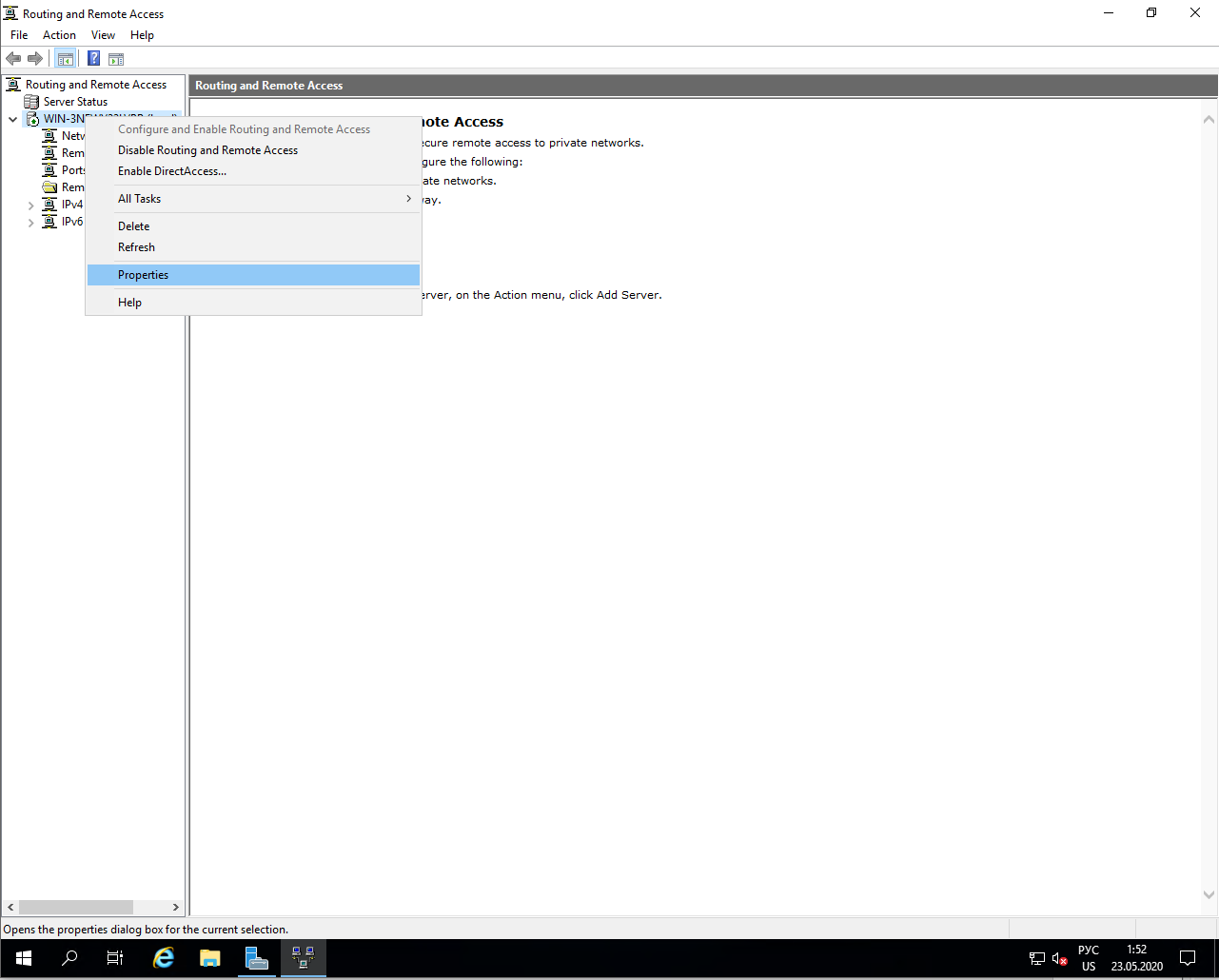
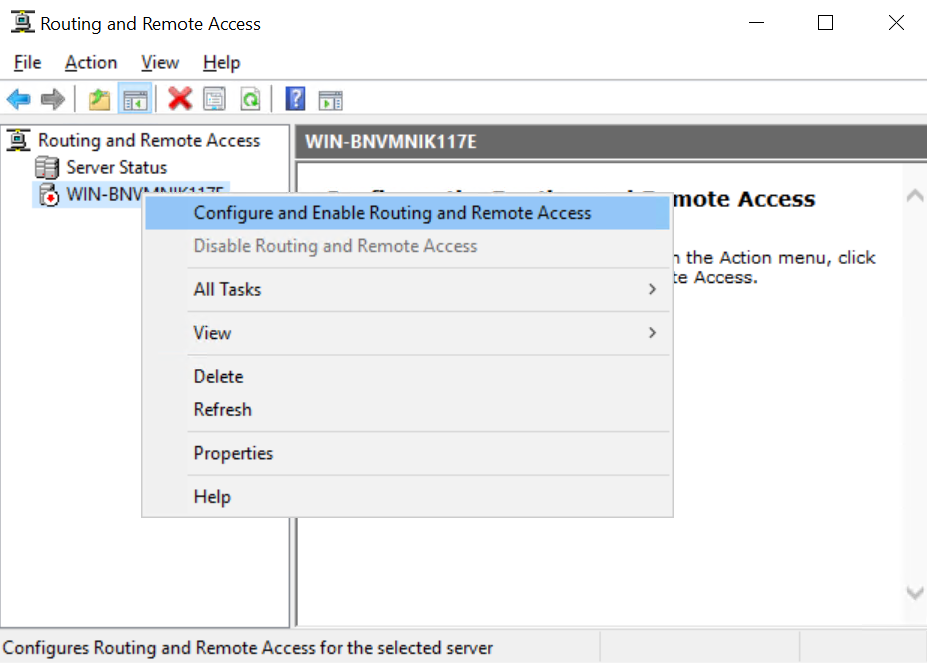
- Open the RRAS console by typing RRAS in the search box. Then right click the node and select Configure and Enable Routing and Remote Access.

Configuration of RRAS in Windows Server 2025
- After successful configuration, make sure that your firewall ports accept connections on 443 for SSTP and 500/4500 for IKEv2.
- Make sure that the host has at least 2 Network interface cards (NICs).
- Your host should not be a domain controller
For VPN access, your AD users should be configured with following:
Each user has to be enabled to use Dial-In. (In AD > User properties > Dial-In tab > Allow access under Network Access Permission).
Installation via PowerShell
Within the Microsoft documentation we can find that it is also possible to script the installation and there is a cmdlet.
Enter and run the following cmdlet:
Install-WindowsFeature DirectAccess-VPN -IncludeManagementTools

You should see the following output:

Now you’re done.
Final Words
By supporting modern VPN protocols like SSTP and IKEv2, RRAS ensures encrypted connections and reliable access to internal resources, making it ideal for hybrid and remote work environments.
When comparing software-based VPNs to hardware-based VPNs, several advantages become evident, such as that software-based solutions are generally cost-effective, easier to deploy and manage, and offer greater scalability. They also provide compatibility across various operating systems and devices. However, you should always proceed with some kind of proof of concept (POC) before implementing in production.
The choice between software and hardware VPNs depends also on the specific needs and resources of an organization. Microsoft RRAS and VPN is fairly popular between IT admins as it allows you to quickly setup a VPN without spending additional funds.