Root certificates are public-key certificates that help your system determine if a website or program is genuine and is based on whether the licensing authority is trusted and whether the digital certificate remains valid.
If the digital certificate does not belong to a trusted authority, you will receive an error message in the form “There is a problem with the security certificate”, and the system may block the connection to the website or the launch of the program for your safety.
There are many certificate authorities, among which the most famous are Symantec® and Comodo®. And their root certificates are always freely available for download.
Windows has built-in certificates and automatically renews them. However, you can still optionally manually add additional root certificates to Windows from trusted certificate authorities (CAs).
This is just done in a few steps. The method is suitable for all versions of Windows.
-
On the downloaded root certificate file, right-click and select the ‘Install Certificate’. In the window that opens, the installation wizard press ‘Next’.
-
Next, you need to choose the right place to import – Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
-
Then just continue the proposed steps of the wizard.
-
As a result, you need to confirm the installation of our certificate.
Now all is done. Websites and programs authenticated by this root certificate will now work fine.
Root Certificates are embedded within our operating system all around. These are also known as Trusted Root Certificates, created by the Certificate Authority (CA), accrediting that a website or software is who they claim they are. It is more like a digital certificate of authentication
By default, Windows 11 updates its root certificate over the internet through Windows Update at least once a week through a Trusted Root Certificate List (CTL). However, if your device is not connected to the internet, certificates will likely expire over time, thus causing certain scripts and applications to not function properly, or experience problems while browsing the internet.
Let us help you avoid this problem by showing you how to update your system’s Root Certificates.
Before we begin, let us guide you on how to see and manage the Root Certificates on Windows 11 and find out which certificates are expired or about to expire.
Table of Contents
View trusted root certificates using the Certificate MMC
Windows comes with various Management Consoles that are used for managing different aspects of the operating system. One of these consoles is the Certificate Management Console.
This is a convenient way to view and manage Root Certificates if you prefer the Graphical User Interface (GUI). Otherwise, you can also obtain the relevant information through Windows PowerShell, which we have discussed in the next section.
Follow the steps below to launch the Certificate Management Console:
- Start by typing in mmc.exe in Run to launch Microsoft Management Console.
- From the top menu, click File and then click Add/remove snap-in.
- From the pop-up window, select Certificates under “Available Snap-ins” and then click Add.
- In the next window, select Computer account and click Next.
- Leave the default setting on the next page and click Finish.
- Back in the Add/Remove Snap-in window, click OK.
- Now, on the console, navigate to the following using the left pane:
Certificates (Local Computer) >> Trusted Root Certification Authorities >> Certificates
Here, you can view all the active and expired Root Certificates on your machine in the middle pane. It also states CA under the “Issued by” column, as well as the expiry date in another column.
View trusted root certificates using Windows PowerShell
Another way to obtain the information on the Root Certificates is through PowerShell. Run the following command in Windows PowerShell with administrative privileges to obtain the details:
Get-Childitem cert:\LocalMachine\root |format-list
As you may notice, this command provides the details on all Root Certificates, which may be a bit overwhelming for some. If you want the details on the expired certificates, use the following command:
Get-ChildItem cert:\LocalMachine\root | Where {$_.NotAfter -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(40)}
Now that you know how to manage the Root Certificates, let us update them.
Update root certificates from a remote computer
One way to update the Root Certificate(s) is to copy a valid certificate from another computer that is already installed, and then re-install it on your device. The process is simple as Windows is already equipped to export and import Root Certificates. However, to do this, make sure that both the source and the destination operating systems are the same.
We have divided this method into “Exporting a Root Certificate” and “Importing a Root Certificate” for your convenience.
Export Root Certificates
You need to begin by identifying the certificate that you need to update. Once done, follow the steps below to export the certificate:
- Open the Certificate Management Console on the source computer (as discussed earlier in this post).
- From there, right-click on the certificate that you want to move to another device, expand All Tasks from the context menu, and then click Export.
- The Certificate Export Wizard will now be open. On the welcome screen, click Next.
- Click Next on the next screen while leaving the default settings.
- On the next screen, click Browse and save the .cer file with a name of your choice, then click Next.
- On the final screen, confirm the settings and click Finish. Then click Ok on the confirmation dialog box.
You will now see the exported .cer file at the destination you chose in step 5. Copy this file onto a USB flash drive and plug it into the target system for the Root Certificate to be installed.
Import Root Certificates
Now paste the .cer file from the flash drive to anywhere with the OS and follow the steps below to import it.
- Open the Certificate Management Console on the source computer and navigate to the Certificates folder from the left pane.
- Right-click Certificates, expand All Tasks, and click Import from the context menu.
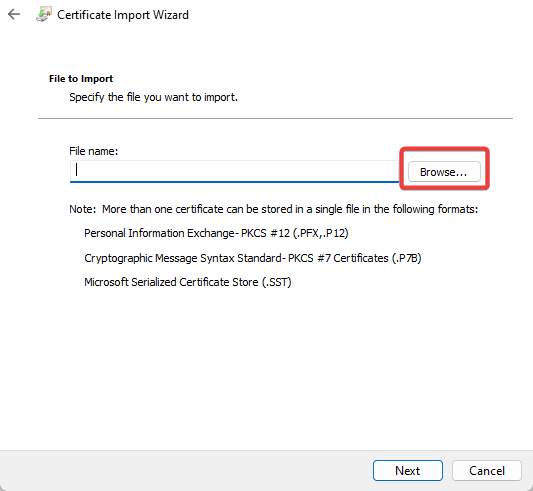
- On the welcome screen of Certificate Import Wizard, click Next.
- Click Browse on the next screen and select the .cer file which has been exported from another computer, then click Next.
- Now select “Automatically select the certificate store based on the type of certificate” and click Next.
- On the final screen of the wizard, click Finish.
The certificate will now be updated on your computer which you can see through the Certificate Management Console.
Another way to install this exported certificate is directly through the .cer file. Double-click the .cer file to launch it. From the certificate, click Install Certificate.

The Certificate Import Wizard will now be launched. From there, select Local Machine as the Store Location and then click Next.

The remaining steps for importing the certificate are the same as we had discussed above.
From an SST File
Serialized Certificate Store Format (SST) files are certificates created directly from a CA. An SST file contains certificates used to authenticate the identities of websites, apps, and programs.
The SST file can be downloaded on demand from Microsoft using Windows Update so you may have all the latest certificates at once.
Let us show you how to download the file, and then discuss different methods to install it.
Download Latest Root Certificates for Windows
Downloading the latest SST file with the latest Root Certificates is easy. Begin by creating a new folder using File Explorer where the SST file will be stored. Then, launch the Command prompt with administrative privileges and navigate to the empty folder you have created using the command below.
cd /d "PathToFolder"This is where the SST file will be downloaded. Replace PathToFolder with the complete path of the empty folder, as in the example below.

Now run the following command to download the latest certificates in an SST file:
certutil.exe -generateSSTFromWU roots.sst
You will now find that the SST file has been downloaded. This file contains all the latest Root Certificates. You can now install them all at once, or one-by-one (only the ones that are required).
Install All Certificates using SST File
Once you open the downloaded roots.sst file, you will see that it holds many certificates. In our case, it holds 436 files. These can all be installed instantly using Windows PowerShell. Here is how:
- Open PowerShell with administrative privileges.
- Now run the following command while replacing CertPath with the complete path to the downloaded SST file:
$sstStore = ( Get-ChildItem -Path <em>CertPath</em>\roots.sst) - Next, paste the following command to import all the certificates on your PC:
$sstStore | Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\Root
You will now find that the certificates have been imported to your machine from the downloaded SST file. You can verify this through the Certificate Management Console.
Install Individual Root Certificates using SST File
Another method to install the Root Certificates from an SST file is one-by-one. This may take a while, but the method can only be used when you wish to install specific certificates.
To do so, run the SST file by double-clicking on it. It will open in an identical console to MMC. From there, you can export a certificate and then import it on the local machine using the method we have already discussed above.
Alternatively, you can also double-click on the certificate and install it directly.

From an STL File
Serialized Certificate Trust List (STL) files also contain Root Certificates, but the file formatting is different than an SST file. Microsoft maintains an STL file you can download to obtain the latest Root Certificates for your Windows. The STL is updated twice a month.
Download Latest STL File
Once downloaded, extract its content using a third-party compression/decompression tool. The extracted folder should now contain only one STL file. You may then proceed to import the file using Command Line Interface (CLI).
Launch the Command Prompt with administrative privileges and navigate to the extracted folder using the Change Directory command:
cd /d "PathToExtracted"Replace PathToExtracted with the complete path to the extracted folder, as in the following example:

Now paste the following command to import the certificates within the STL file.
certutil -addstore -f root authroot.stl
You can now confirm that the latest certificates have been installed using the Certificate Management Console.
Final Thoughts
Although it may not seem like it, a Root Certificate is essential for your daily work on a PC, as it is making authorization handshakes and trust with other components in the background while you continue with your work.
However, once a certificate has expired, it can be safely deleted, as it is no longer valid. That said, we recommend that you install a new, valid certificate in its place before removing the old one.
Download Windows Speedup Tool to fix errors and make PC run faster
In one of our earlier posts, we have seen what Root Certificates are. There may be times, when some companies or users may feel the need to manage and configure Trusted Root Certificates, to prevent other users in the domain from configuring their own set. In this post, we will see how to manage Trusted Root Certificates & add certificates to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store in Windows 11/10.
To add certificates to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store for a local computer, from the WinX Menu in Windows 11/10, open Run box, type mmc, and hit Enter to open the Microsoft Management Control.
Press the File menu link and select Add/Remove Snap-in. Now under Available snap-ins, click Certificates, and then click Add.
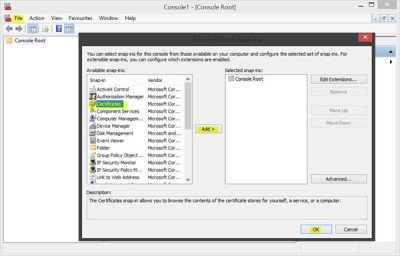
Click OK. In the next dialog box, select Computer account and then on Next.
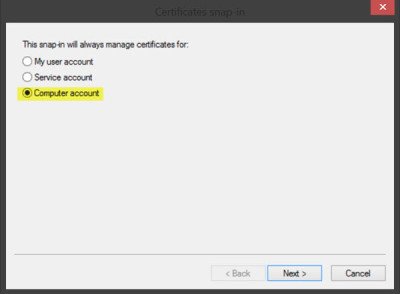
Now select Local computer and click on Finish.
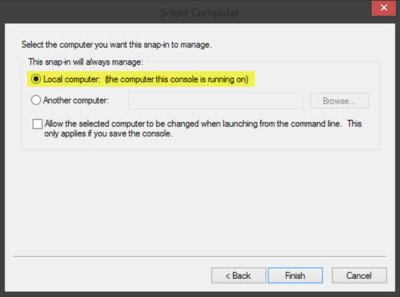
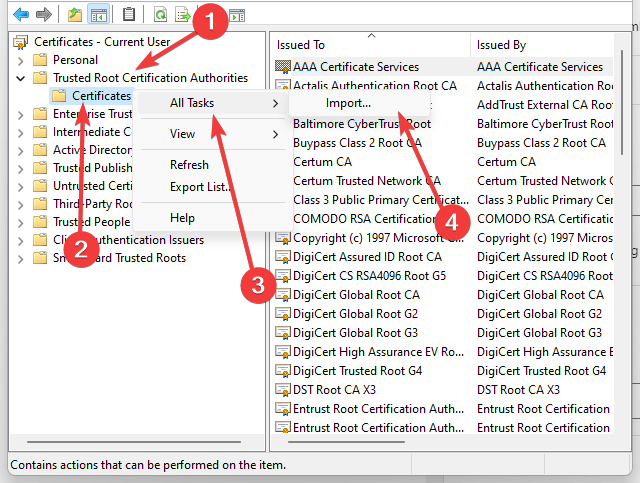
Now, back in MMC, in the console tree, double-click on Certificates and then right-click on Trusted Root Certification Authorities Store. Under All tasks, select Import.
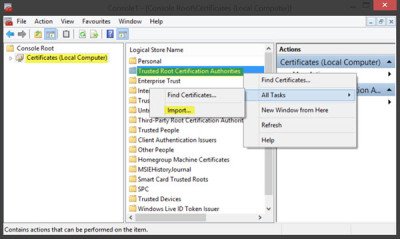
The Certificate Import Wizard will open.
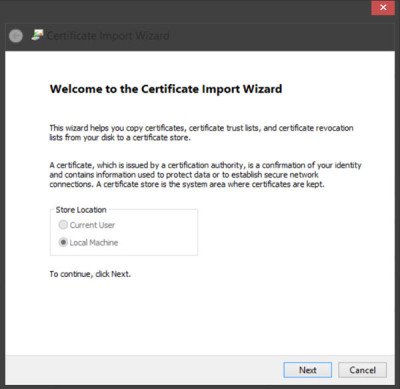
Follow the instructions in the wizard to complete the process.
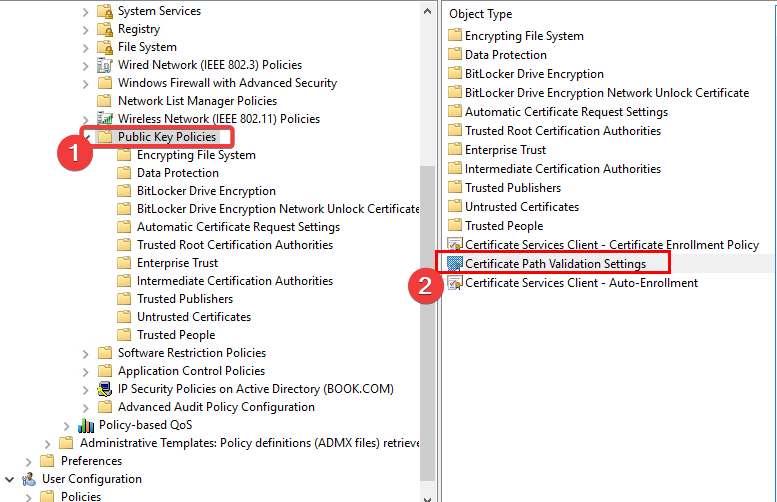
Now let us see how to configure and manage trusted root certificates for a local computer. Open MMC and press the File menu link and select Add/Remove Snap-in. Now under Available snap-ins, click Group Policy Object Editor, and then click Add. Select the computer whose local GPO you want to edit, and click Finish / OK.
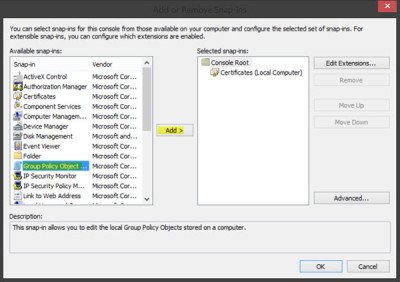
Now, back in the MMC console tree, navigate to Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings. Next Public Key Policies. Double-click Certificate Path Validation Settings, and then select the Stores tab.
Read: Manage certificates using Certificate Manager or Certmgr.msc.
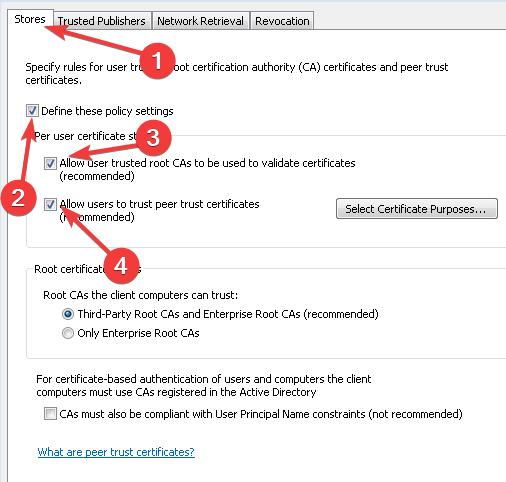
Here, select the Define these policy settings, Allow user trusted root CAs to be used to validate certificates and Allow users to trust peer trust certificates checkboxes.
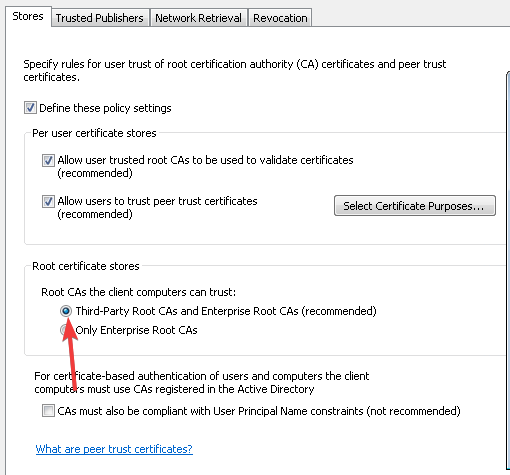
Finally, under Stores tab > Root certificate stores, select one option under Root CAs that the client computers can trust and click OK. If in doubt, go with the recommended option.
To see how you can manage trusted root certificates for a domain and how to add certificates to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store for a domain, visit Microsoft.
RCC is a free Root Certificates Scanner that can help you scan Windows Root Certificates for untrusted ones.
Anand Khanse is the Admin of TheWindowsClub.com, a 10-year Microsoft MVP (2006-16) & a Windows Insider MVP (2016-2022). Please read the entire post & the comments first, create a System Restore Point before making any changes to your system & be careful about any 3rd-party offers while installing freeware.
Reader Interactions
Since the web is moving towards to HTTPS, there is a increase in number of security certificate authorities (CAs) and variety of certificates issued. Windows 10 comes with some built-in certificates installed from leading CAs. But if you’re going to visit a website/app whose root certificate is not pre-installed on your machine (due to its vendor, type or format), you might get following prompt in the browser, where you need to trust the CA on your own. It might be possible you need to do this every-time you visit the website/app.
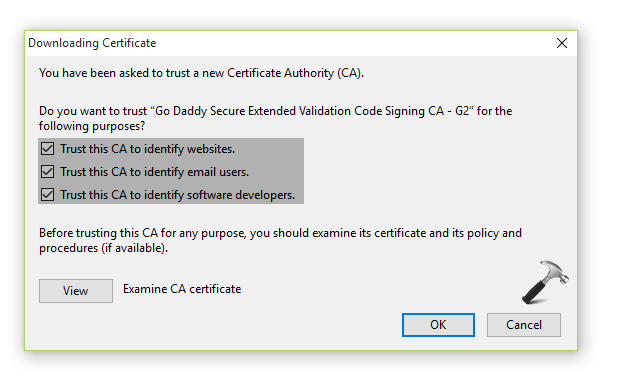
To avoid this, you can install the root certificate to your machine from the CA. All CAs publicly and freely allows the download of their root certificate through repository. Root certificate is top-most security certificate issued by a CA and all other intermediate certificates follows a tree-structure analogy starting from root certificate. So if root certificate is present on your machine, all the certificate issued in hierarchical order after it, will be automatically trusted by your system.
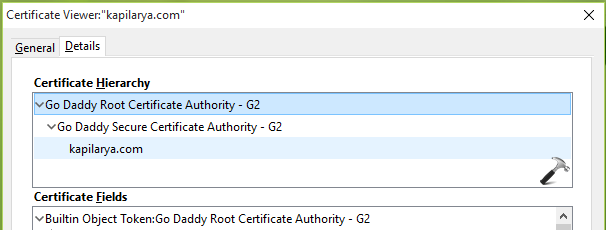
In this article, we’ll see the steps to manually add a trusted root certificate to your Windows 10 machine.
How To Install Trusted Root Certificate In Windows 10
FYI: You must be the administrator of your system to follow these steps.
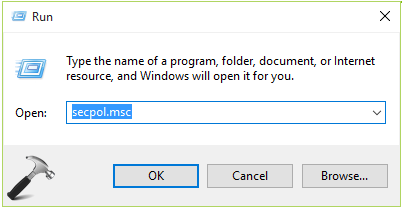
1. Press + R and put secpol.msc in Run dialog box. Click OK to open Security Policy snap-in.
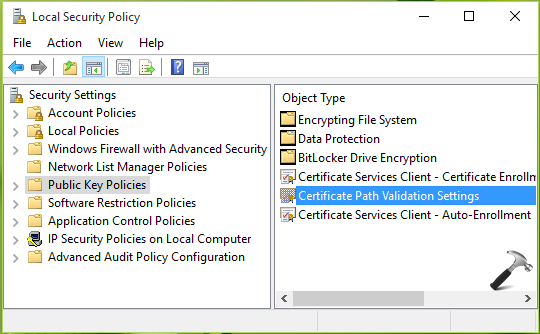
2. In Local Security Policy snap-in, click Public Key Policies > Certificate Path Validation Settings.
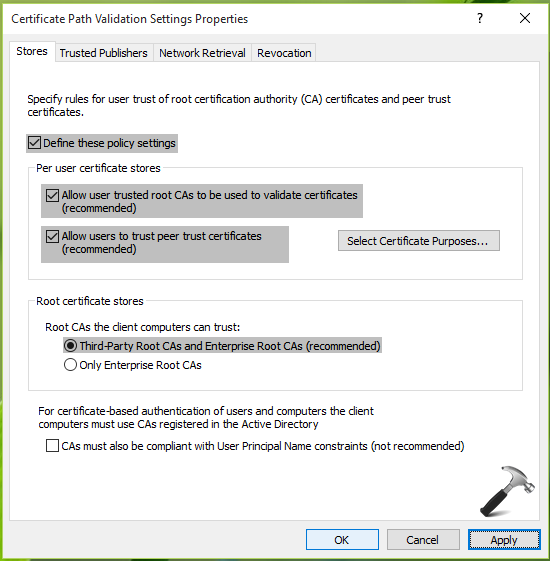
3. Then in Certificate Path Validation Settings Properties, under Store tab, check Define these policy settings. Make sure you check Allow user trusted root CAs to be used to validate certificates and Allow users to trust peer trust certificates options here. Under Root certificates stores, select Third-Party Root CAs and Enterprise Root CAs option. Click Apply followed by OK.
Close Local Security Policy snap-in.
4. Press + R and put certmgr.msc in Run dialog box. Click OK to open Certificate Manager snap-in.
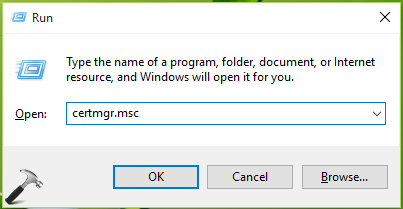
5. In Certificate Manager window, click Trusted Root Certification Authorities > Certificates. Right click on Certificates and select All Tasks > Import.
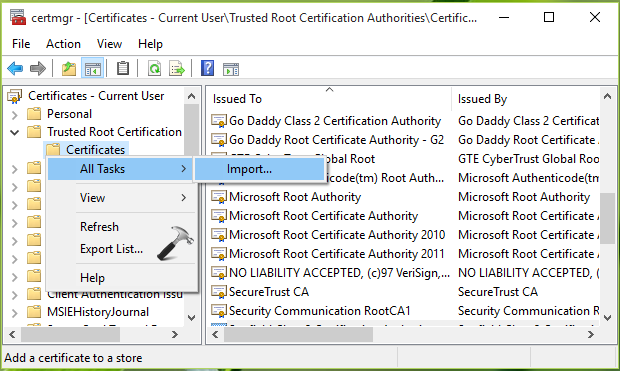
6. Now in Certificate Import Wizard, click Next.
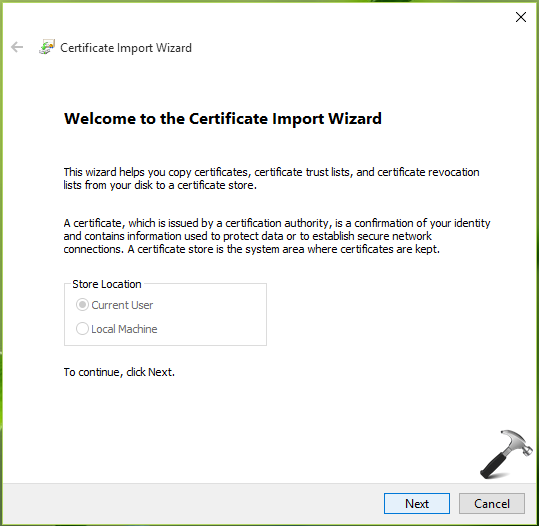
7. Then browse the certificate root file (make sure to select correct file format such .crt/.cer, .p7b/.spc etc.) which you got from your CA. Click Next.
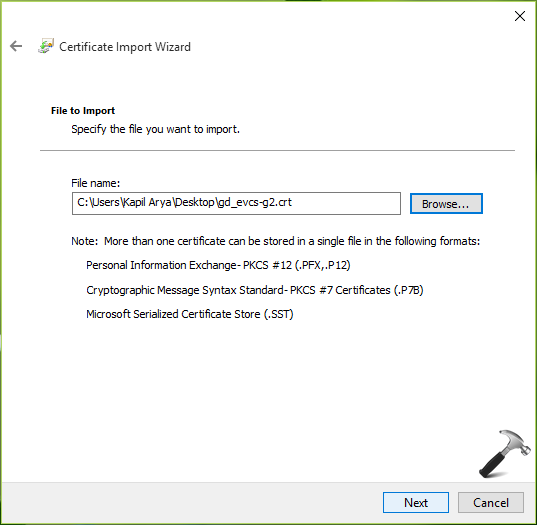
8. On the next screen, choose Automatically select the certificate store based on the type of certificate option. Hit Next.
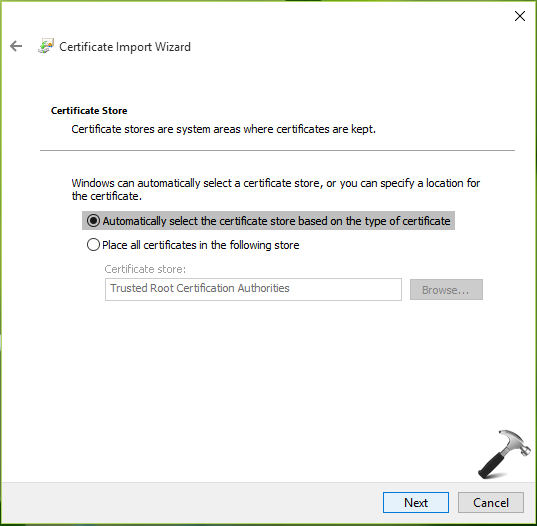
9. Click Finish to finally import the certificate to Trusted Root Certification Authorities store.
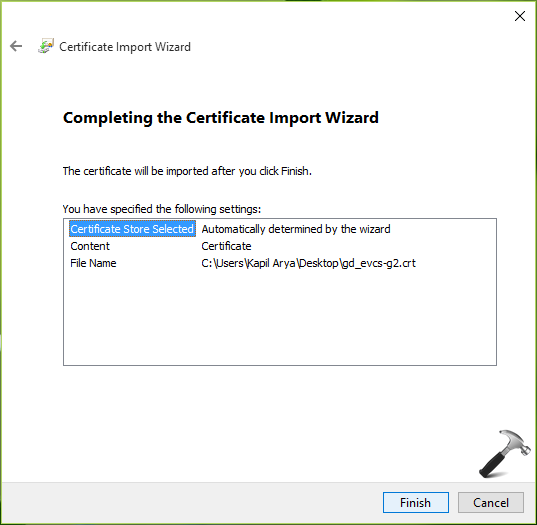
In few seconds, you’ll receive the confirmation saying ‘The import was successful‘ which means the new certificate is installed and ready for use.
In this way, you can install new trusted root certificates to Windows 10.
That’s it!
RELATED ARTICLES
Readers help support Windows Report. We may get a commission if you buy through our links.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
Root certificates are public key certificates that help your browser determine whether communication with a website is genuine and is based upon whether the issuing authority is trusted and if the digital certificate remains valid.
Suppose a digital certificate is not from a trusted authority. In that case, you’ll get an error message like There is a problem with this website’s security certificate, and the browser might block communication with the website.
Windows 10 has built-in certificates and automatically updates them. However, you can manually add more root certificates to Windows 10 from certificate authorities (CAs).
Where is the Trusted Root Certificate Store in Windows 10?
The Trusted Root Certificate store in Windows 10 is a collection of root certificates for Certificate Authorities (CAs) considered trustworthy by the operating system.
This store is used to validate digital certificates and establish secure connections over the internet.
You must access the Microsoft Management Console to access the Trusted Root Certificate store in Windows 10.
The trusted Root Certificate store is, however, located in the root of the Registry path below:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
How do I add a certificate to the trusted root on Windows 10?
- Install certificates from trusted CAs
- Install Trusted Root Certificates with the Microsoft Management Console
1. Install certificates from trusted CAs
- First, you’ll need to download a root certificate from a CA. For example, you could download one from the GeoTrust site.
- Next, press Win key + R, enter secpol.msc in Run’s text box, and hit Enter (Windows 10 Home edition doesn’t include the Local Security Policy editor. If your Windows key doesn’t work, check our quick guide to fix it).
- Then, click Public Key Policies and Certificate Path Validation Settings to open a Certificate Path Validation Settings Properties window.
- Click the Stores tab and select the Define these policy settings check box, then tick its two checkboxes.
- Select the Third-Party Root CAs and Enterprise Root CAs checkboxes and press the Apply then OK buttons to confirm.
- Press the Win key + R hotkey, type certmgr.msc in Run’s text box, and hit Enter.
- Click Trusted Root Certification Authorities, right-click Certificates, select All Tasks, and Import.
- Press the Next button, click Browse, and select the digital certificate root file saved to your HDD.
- Press Next again to select Automatically select the certificate store based on the type of certificate option.
- Then you can press Next and Finish to wrap up the import wizard. A window will open, confirming that the import was successful.
Most Windows 10 users have no idea how to edit the Group Policy. Learn how you can do it by reading our simple article.
If you don’t have the Group Policy Editor on your Windows PC, get it right now in just a couple of easy steps with our guide on installing the Group Policy Editor on Windows 10.
2. Install Trusted Root Certificates with the Microsoft Management Console
-
1. Press the Win key + R hotkey to open the Run dialog.
-
2. Input mmc in Run and press Enter to open the window below.
-
3. Click File and then select Add/Remove Snap-ins to open the window in the snapshot below.
-
4. Next, you should select Certificates and press the Add button.
-
5. A Certificates Snap-in window opens from which you can select Computer account >Local Account, and press the Finish button to close the window.
-
6. Then press the OK button in the Add or Remove Snap-in window.
-
7. Now you can select Certificates and right-click Trusted Root Certification Authorities on the MMC console window as below.
-
8. Then you can click All Tasks > Import to open the Certificate Import Wizard window.
-
9. From the Certificate Import Wizard window, you can add the digital certificate to Windows.
You can also install root certificates on Windows 10/11 with the Microsoft Management Console. The process is easy and simple, and the console can be accessed via the Run dialog.
If Microsoft Management Console can’t create a new document, follow our guide’s easy steps to solve the issue.
Can’t load the Microsoft Management Console? Our step-by-step guide will help you sort things out.
How to add the certificate to Trusted Root Certification Authorities store using the command line?
- Press Windows + R, type cmd, and hit Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
- Type the script below and hit Enter (Substitute your certificate’s path for C:\Users\Downloads and your certificate’s name for mycertificate):
certutil -addstore root C:\Users\\Downloads\mycertificate.cer
Now you’ve installed a new trusted root certificate in Windows 10. Similarly, you can add many more digital certificates to that OS and other Windows platforms.
Ensure that the third-party digital certificates come from trusted CAs, such as GoDaddy, DigiCert, Comodo, GlobalSign, Entrust, and Symantec.
If you have any more suggestions or questions, leave them in the comments section below, and we’ll certainly check them out.
Matthew Adams
Windows Hardware Expert
Matthew is a freelancer who has produced a variety of articles on various topics related to technology. His main focus is the Windows OS and all the things surrounding it.
He is passionate about the tech world, always staying up-to-date with the latest and greatest. With an analytical view, he likes problem-solving, focusing on errors and their causes.
In his free time, he likes to read and write about history and tries to always develop new skills.