Home HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE Работа с веткой HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE Где в реестре находится информация о профилях пользователей?
Где в реестре находится информация о профилях пользователей?
03.06.2015 11:00
Администратор
Информация о профилях пользователей зашедших в систему находится в разделе
Раздел [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList]
Интересная статья? Поделись ей с другими:
Системный реестр
- Главная
- HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- Работа с веткой HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- HKEY_USERS
- HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG
- Автоматизация установки приложений / Silent installation of applications
- Remote Install Application
Операционные системы
- Windows
- FreeBSD
- Командная строка / Command prompt
Сообщество в VK / COMMUNITY in VK
http://www.regedit.su/
- Вопросы по поводу написанных статей можно обсудить в нашем сообществе в Вконтакте / Questions about written articles can be discussed in our community in Vkontakte
Администраторы время от времени должны удалять старые профили пользователей (уволенные пользователи, неактивные пользователи, и т.д.) в каталоге C:\Users на рабочих станциях и серверах Windows. Чаще всего с задачей очисткой профилей пользователей Windows сталкиваются на терминальных серверах RDS (Remote Desktop Services).
Основная проблема терминальных серверов – постоянный рост размеров каталогов профилей пользователей на диске. Частично эта проблема решается политиками квотирования размера профиля пользователя с помощью FSRM или NTFS квот, использованием профилей типа FSLogix или User Profile Disk, перемещаемыми папками и т.д. Но при большом количестве RDS пользователей в папке C:\Users со временем накапливается огромное количество каталогов с неиспользуемыми профилями пользователей.
Содержание:
- Как вручную удалить профиль пользователя в Windows?
- Групповая политика для автоматической очистки старых профилей
- PowerShell скрипт для удаления старых профилей пользователей в Windows
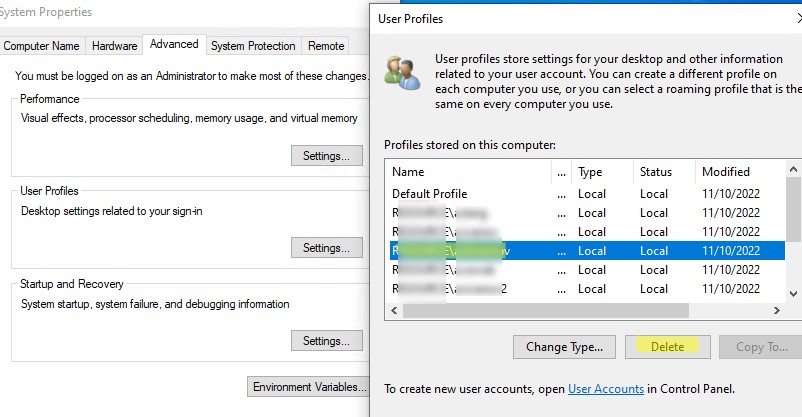
Как вручную удалить профиль пользователя в Windows?
В Windows вы можете вручную удалить профиль пользователя через панель управления.
- Откройте Advanced System Settings (команда
SystemPropertiesAdvanced
) -> User Profiles -> Settings; - В этом окне перечислен список всех профилей пользователей (локальных и доменных), которые хранятся на этом компьютере. Размер каждого профиля пользователя на диске указан в столбце Size.
- Выберите пользователя, чей профиль нужно удалить и нажмите кнопку Delete.
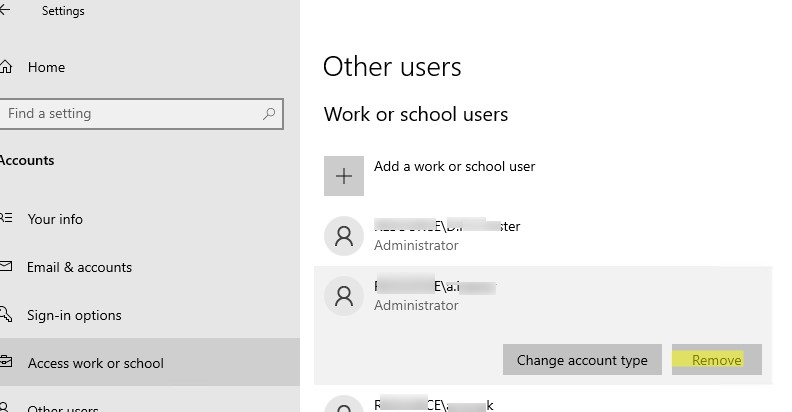
В Windows 11/10 и Windows Server 2022/2019 вы можете удалить профили пользователей с диска через приложение Settings. Перейдите в раздел Accounts -> Access work and school (или выполните команду быстрого доступа
ms-settings:otherusers
). Выберите пользователя и нажмите Remove чтобы удалить его данные с компьютера.
При корректном удалении профиля пользователя с диска будет удален каталог профиля в C:\Users и запись о пользователе в реестре.
Многие начинающиеся администраторы пытаются вручную удалить каталог с профилем пользователя из папки C:\Users. В этом случае нужно обязательно вручную удалить информацию о профиле из реестра Windows:
- Откройте редактор реестра
regedit.exe
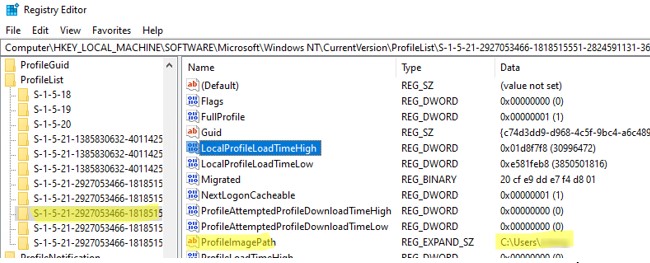
; - Перейдите в ветку HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
- Для каждого пользователя, выполнившего локальный вход в систему (этот метод входа должен быть разрешен пользователю настройками параметра Allow log on locally в GPO), создается отдельная ветка с SID пользователя в качестве имени;
- Вы можете найти раздел реестра, соответствующий пользователю по SID, или можете вручную просмотреть содержимое всех вложенных разделв, пока не найдете раздел, в котором значение ProfileImagePath указывает на каталог с профилем пользователя на диске (например,
C:\Users\kbuldogov
); - Удалите данный раздел реестра, чтобы завершить корректное удаление профиля.
Также вы можете удалить профиль конкретного пользователя с помощью PowerShell:
Get-CimInstance -Class Win32_UserProfile | Where-Object { $_.LocalPath.split(‘\’)[-1] -eq 'kbuldogov' } | Remove-CimInstance
Эта команда удалит как каталог на диске, так и ссылку на профиль пользователя kbuldogov в реестре HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList.
Эта команда будет работать как в Windows PowerShell, так и в новых версиях PowerShell Core 6.x,7.x
Можно удалить профиль пользователя на удаленном компьютере с помощью PowerShell Remoting и командлета Invoke-Command:
$compname="wks21s32"
$user = "kbuldogov"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $compname -ScriptBlock {
param($user)
Get-CimInstance -Class Win32_UserProfile | Where-Object { $_.LocalPath.split(‘\’)[-1] -eq $user } | Remove-CimInstance
} -ArgumentList $user
Групповая политика для автоматической очистки старых профилей
В Windows есть специальный параметр групповой политики для автоматического удаления старых профилей пользователей старше xx дней. Вы можете включить этот параметр с помощью локального редактора GPO (
gpedit.msc
) или с помощью консоли управления доменными GPO (
gpmc.msc
). В этом примере на назначим политику автоматической очистки профилей на хосты в ферме RDS, которые вынесены в отдельный контейнер (Organizational Unit) Active Directory.
Прежде чем применять политику удаления старых профилей ко всем хостам, настоятельно рекомендуем проверить ее на тестовом сервере. Выведите один из серверов RDSH в режим обслуживания и протестируйте политику на нем.
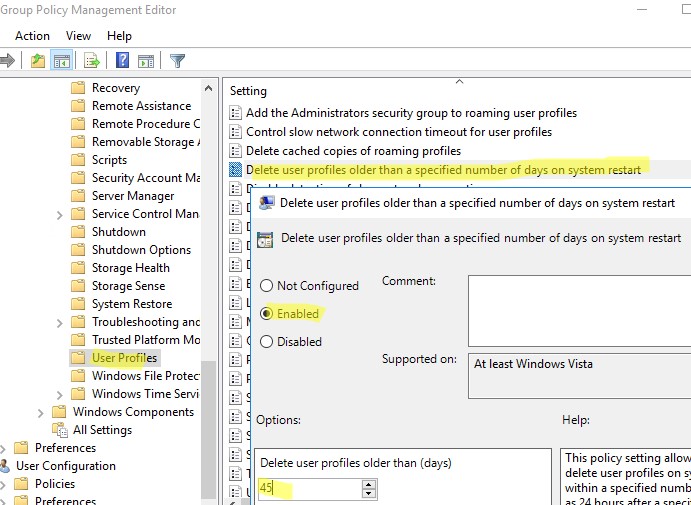
- Найдите OU с компьютерами/серверами, на который вы хотите применить политику очистки старых профилей пользователей. Щелкните по OU и выберите Create a GPO in this domain and Link it here;
- Укажите имя политики и отредактируйте GPO;
- Перейдите в раздел Конфигурация компьютера -> Административные шаблоны -> Система -> Профили пользователей (Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> User Profiles);
- Откройте параметр “Удалять при перезагрузке системы профили пользователей по истечении указанного числа дней” (Delete user profiles older than a specified number days on system restart);
- Включите политику и укажите через сколько дней профиль пользователя считается неактивным и “Служба профилей пользователей Windows” можно автоматически удалить такой профиль при следующей перезагрузке. Обычно тут стоит указать не менее 45-90 дней;
- После применения новых настроек групповых политк, служба User Profile Services на ваших серверах Windows будет автоматически удалять старые профили пользователей. Удаление выполняется при перезагрузке сервера.
При использовании этой политики нужно быть уверенным, что при выключении/перезагрузке сервера нет проблем с системным временем (время не сбивается), иначе могут быть удалены профили активных пользователей.
Другой недостаток — вы не можете запретить удаление определенных профилей, например, локальных учетных записей, администраторов и т.д.
В версиях до Windows 11/10 и Windows Server 2022/2019 эта политика работала некорректно. Дело в том, что неактивноть профиля пользователя ранее определялась по дате именения файла NTUSER.dat. При установке обновлений Windows, служба Trusted Installer может менять дату изменения файла NTUSER.dat в профиле каждого пользователя. В результате служба Win32_UserProfile считает, что профиль использовался недавно.
В современных версиях Windows эта политика проверяет активность профиля пользователей по параметрам LocalProfileUnloadTimeLow и LocalProfileUnloadTimeHigh в ветке
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList\<User Sid>
.
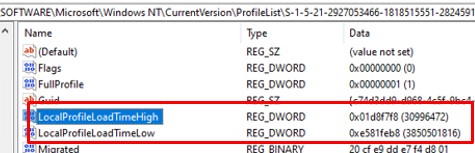
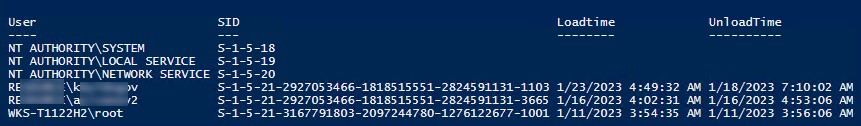
Вы можете получить значения параметров реестра LocalProfileLoadTimeLow и LocalProfileUnloadTimeHigh в привычном формате времени с помощью скрипта:
$profilelist = Get-ChildItem "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList"
foreach ($p in $profilelist) {
try {
$objUser = (New-Object System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier($p.PSChildName)).Translate([System.Security.Principal.NTAccount]).value
} catch {
$objUser = "[UNKNOWN]"
}
Remove-Variable -Force LTH,LTL,UTH,UTL -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
$LTH = '{0:X8}' -f (Get-ItemProperty -Path $p.PSPath -Name LocalProfileLoadTimeHigh -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue).LocalProfileLoadTimeHigh
$LTL = '{0:X8}' -f (Get-ItemProperty -Path $p.PSPath -Name LocalProfileLoadTimeLow -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue).LocalProfileLoadTimeLow
$UTH = '{0:X8}' -f (Get-ItemProperty -Path $p.PSPath -Name LocalProfileUnloadTimeHigh -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue).LocalProfileUnloadTimeHigh
$UTL = '{0:X8}' -f (Get-ItemProperty -Path $p.PSPath -Name LocalProfileUnloadTimeLow -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue).LocalProfileUnloadTimeLow
$LoadTime = if ($LTH -and $LTL) {
[datetime]::FromFileTime("0x$LTH$LTL")
} else {
$null
}
$UnloadTime = if ($UTH -and $UTL) {
[datetime]::FromFileTime("0x$UTH$UTL")
} else {
$null
}
[pscustomobject][ordered]@{
User = $objUser
SID = $p.PSChildName
Loadtime = $LoadTime
UnloadTime = $UnloadTime
}
}
PowerShell скрипт для удаления старых профилей пользователей в Windows
Вы можете удалять профили неактивных или заблокированных пользователей с помощью скрипта PowerShell.
Сначала попробуем подсчитать размер профиля каждого пользователя в папке C:\Users c помощью простого скрипта из статьи “Вывести размер папок с помощью PowerShell”:
gci -force ‘C:\Users\’-ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Where { !($_.Attributes -match " ReparsePoint") }| ? { $_ -is [io.directoryinfo] } | % {
$len = 0
gci -recurse -force $_.fullname -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | % { $len += $_.length }
$_.fullname, ‘{0:N2} GB’ -f ($len / 1Gb)
$sum = $sum + $len
}
“Общий размер профилей”,'{0:N2} GB’ -f ($sum / 1Gb)
Итого суммарный размер всех профилей пользователей в каталоге C:\Users около 22 Гб.
Теперь выведем список пользователей, профиль которых не использовался более 60 дней. Для поиска можно использовать значение атрибута профиля LastUseTime.
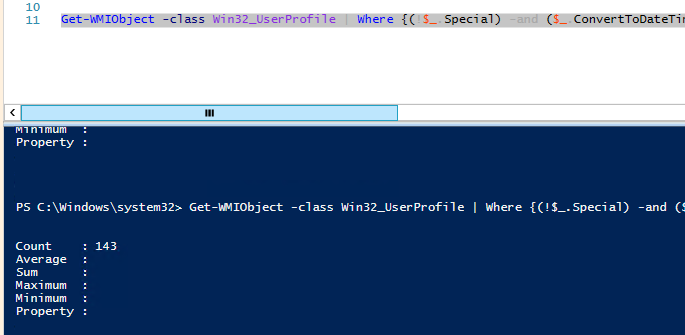
Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))}| Measure-Object
У меня на терминальном сервере оказалось 143 профиля неактивных пользователей (общим размером около 10 Гб).
Следующий PowerShell скрипт выведет список подробную информацию о профилях пользователей, которые не обновлялись более 60 дней. Скрипт сконвертирует SID пользователя в имя, посчитает размер профиля каждого пользователя и выведет все в таблице:
$allprofilesinfo = @()
$OldProfiles=Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))}
Foreach ($OldProfile in $OldProfiles)
{$objSID = New-Object System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier ($OldProfile.SID)
$objUser = $objSID.Translate( [System.Security.Principal.NTAccount])
$userinfo = New-Object PSObject -Property @{
userName = $objUser.Value
ProfilePath = $OldProfile.localpath
LastUsedDate = $OldProfile.ConvertToDateTime($OldProfile.LastUseTime)
FolderSize = "{0:N2} GB" -f ((gci –force $OldProfile.localpath –Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue| measure Length -s).sum / 1Gb)
}
$allprofilesinfo += $userinfo
}
$allprofilesinfo
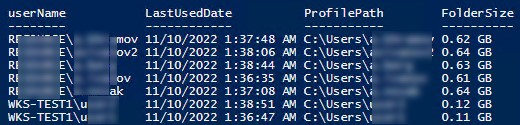
Чтобы удалить все эти профили достаточно добавить перенаправить список на команду Remove-WmiObject (перед использование скрипта удаления желательно несколько раз перепроверить его вывод с помощью параметра –WhatIf ):
Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and (!$_.Loaded) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-30))} | Remove-WmiObject –WhatIf
Как мы уже упомянули выше, при установке некоторых обновлений Windows, служба Trusted installer может менять дату изменения файла NTUSER.dat в профиле каждого пользователя.
На скриншоте выше видно, что все профили были изменены примерно в одно и тоже время. Проверьте дату последней установки обновлений в Windows:
gwmi win32_quickfixengineering |sort installedon |select InstalledOn -Last 1
Или с помощью модуля PSWindowsUpdate:
Get-WUHistory | Select-Object -First 20
Скорее всего она совпадет с датой изменения профилей. Поэтому в старых версиях Windows можно получить список неактивных профилей с помощью другого скрипта, который проверяет атрибуту lastwritetime каталога пользователя:
$USERS= (Get-ChildItem -directory -force 'C:\Users' | Where { ((Get-Date) — $_.lastwritetime).days -ge 60 } | % {'c:\users\' + $_.Name})
foreach ($User in $USERS) {
Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and (!$_.Loaded) -and ($_.LocalPath -eq $User)} | Remove-WmiObject WhatIf }
Чтобы не удалять профили некоторых пользователей, например, специальные аккаунты System и Network Service, учетную запись локального администратора, пользователей с активными сессиями, список аккаунтов-исключений), нужно модифицировать скрипт следующим образом:
#Список аккаунтов, чьи профили нельзя удалять
$ExcludedUsers ="Public","zenoss","svc",”user_1”,”user_2”
$LocalProfiles=Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and (!$_.Loaded) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))}
foreach ($LocalProfile in $LocalProfiles)
{
if (!($ExcludedUsers -like $LocalProfile.LocalPath.Replace("C:\Users\","")))
{
$LocalProfile | Remove-WmiObject
Write-host $LocalProfile.LocalPath, "профиль удален” -ForegroundColor Magenta
}
}
Вы можете настроить запуск этого скрипта через shutdown скрипт групповой политики или по расписанию заданием планировщика. (перед настройкой автоматического удаления профилей внимательно протестируйте скрипт в своей среде!).
Можно модифицировать скрипт, чтобы автоматически удалять пользователи всех пользователей, которые добавлены в определенную группу AD. Например, вы хотите автоматически удалять профили уволившихся пользователей. Просто добавьте такие учетные записи в группу DisabledUsers и выполните на сервере скрипт:
$users = Get-ADGroupMember -Identity DisabledUsers | Foreach {$_.Sid.Value}
$profiles = Get-WmiObject Win32_UserProfile
$profiles | Where {$users -eq $_.Sid} | Foreach {$_.Delete()}

Introduction
The user profile in Windows 10 contains all the personalized settings and preferences for an individual user. It includes information such as desktop settings, program data, app configurations, and more. There might be instances where you need to rename a user profile, whether it’s to fix a system issue or to accommodate a user’s request.
Renaming a user profile in Windows 10 requires modifying the Windows Registry, a database that stores system settings, configurations, and user profiles. It’s important to proceed with caution and follow the necessary steps to ensure the process is done correctly and without any errors.
Step 1: Backup Your Data
Before making any changes to the Windows Registry, it’s crucial to back up your data. This serves as a safety net in case anything goes wrong during the renaming process. Here’s how you can back up your data:
- Create a new folder on an external drive or a different partition of your computer’s hard drive.
- Copy all the important files and folders from your user profile directory to the newly created folder.
- Ensure that all the necessary data is successfully copied and stored in the backup folder.
By creating a backup of your data, you can easily restore your files in case of any unforeseen issues that may arise during the renaming process.
Step 2: Create a New User Account
Before renaming a user profile, it’s recommended to create a new user account with administrative privileges. This allows you to continue using your computer while performing the necessary changes. Here’s how you can create a new user account:
- Open the Start menu and go to the Settings app.
- Click on «Accounts» and navigate to the «Family & other users» section.
- Under «Other users,» click on «Add someone else to this PC.»
- Follow the on-screen instructions to create a new user account with administrative privileges.
Once you have successfully created a new user account, you can proceed with renaming the old user profile.
Step 3: Modify the Windows Registry
Modifying the Windows Registry is a sensitive process, and any mistakes can cause system instability or data loss. It’s crucial to carefully follow the steps outlined below to ensure a successful user profile rename:
1. Log in to the New User Account
Switch to the newly created user account with administrative privileges:
- Sign out of your current user account.
- On the login screen, select the newly created user account.
- Enter the password for the new user account and log in.
2. Open the Registry Editor
The Registry Editor allows you to make changes to the Windows Registry. Follow these steps to open the Registry Editor:
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type «regedit» in the Run dialog box and press Enter.
- Click «Yes» if prompted by the User Account Control.
3. Locate the User Profile in the Registry
Navigate to the user profile you want to rename:
- In the Registry Editor, expand the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList. - Under the ProfileList key, you will find a list of subkeys. Each subkey represents a user profile on your computer.
- Identify the correct subkey by checking the ProfileImagePath value, which contains the path to the user profile directory.
4. Rename the Profile
Now that you have located the correct subkey for the user profile, follow these steps to rename it:
- Right-click on the subkey representing the user profile and select «Rename».
- Enter the new name for the user profile and press Enter.
- Make sure to only modify the last part of the ProfileImagePath value, which corresponds to the username.
- Close the Registry Editor.
After renaming the user profile in the Registry, you can proceed with restarting your computer to apply the changes.
Step 4: Verify the Renamed User Profile
After restarting your computer, log in with the new user account to ensure that the user profile has been successfully renamed. Here are a few steps to verify the renamed user profile:
- After logging in to the new user account, go to the «C:\Users» directory in File Explorer.
- You should see the renamed user profile folder.
- Open the renamed user profile folder to confirm that all the data and settings are intact.
If everything appears to be in order, you have successfully renamed the user profile in the Windows 10 Registry.
Exploring a Different Dimension
Renaming a user profile in the Windows 10 Registry can be approached from another perspective to ensure a smooth process. Let’s explore a different dimension to rename a user profile:
Using a Third-Party Tool
In addition to the manual method discussed earlier, there are third-party tools available that can simplify the process of renaming a user profile. These tools provide a user-friendly interface and automate the necessary steps. Here are a few popular options:
1. Transwiz
Transwiz is a free utility that allows you to transfer user profiles, including renaming, between different computers or domains. It provides a simple and efficient way to rename user profiles without directly modifying the Windows Registry. Here’s how you can use Transwiz to rename a user profile:
- Download and install Transwiz from the official website.
- Launch Transwiz and follow the on-screen instructions to backup the existing profile and create a new profile with the desired name.
- Transwiz will handle all the necessary changes in the Windows Registry and ensure a seamless profile rename.
2. ForensiT User Profile Wizard
ForensiT User Profile Wizard is another powerful tool that simplifies the process of renaming user profiles. It can be used to migrate profiles between computers or domains, as well as to rename existing profiles. Here’s how you can use ForensiT User Profile Wizard:
- Download and install ForensiT User Profile Wizard from the official website.
- Launch the User Profile Wizard and select the option to rename an existing user profile.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to specify the current profile and the desired new name.
- The User Profile Wizard will handle the necessary changes in the Windows Registry and ensure a successful profile rename.
Using a third-party tool like Transwiz or ForensiT User Profile Wizard can provide a simpler and more streamlined approach for renaming user profiles, especially for those who are less familiar with manual Registry modifications.
Considering the Implications
When renaming a user profile, it’s important to consider the implications it may have on various elements within the operating system:
1. File Associations
Renaming a user profile may cause file associations to break, as the operating system relies on the original file paths stored in the Registry. When renaming a user profile, it’s a good idea to review and update any affected file associations to ensure they continue to work correctly.
2. Program Configurations
Certain programs or applications may have specific configurations tied to a user profile’s name. Renaming a user profile might require reconfiguring those programs or transferring the settings from the old profile to the new one.
3. Permissions and Security Settings
When renaming a user profile, it’s essential to verify that the new profile has the necessary permissions and security settings. Some settings and permissions may be specific to the old profile name and may not carry over automatically to the new profile.
Considering these implications before renaming a user profile can help minimize any potential issues and ensure a smooth transition to the new profile name.
Conclusion
Renaming a user profile in the Windows 10 Registry can be achieved through manual modification or by utilizing third-party tools. Both approaches involve precautions and considerations to ensure a successful profile rename. By following the necessary steps outlined in this article, you can confidently rename a user profile while preserving your data and settings. Remember to create a backup, proceed with caution, and be aware of any implications that may arise from the rename process. With diligence and care, you can rename a user profile in the Windows 10 Registry effectively.

Renaming User Profile in Windows 10 Registry
If you need to change a user profile name in Windows 10, you can do so by modifying the Windows Registry. Here are the steps to follow:
- Press Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type in regedit and click OK to open the Registry Editor.
- In the Registry Editor, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList.
- Expand the ProfileList folder and locate the folder with the name of the user profile you want to rename.
- Right-click on the folder and select Rename.
- Enter the new name for the user profile and press Enter.
- Close the Registry Editor and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
It’s important to note that modifying the Windows Registry should be done with caution, as any incorrect changes can have serious consequences on your system’s stability. Make sure to create a backup of the Registry before making any modifications.
Key Takeaways — How to Rename User Profile in Windows 10 Registry
- To rename a user profile in Windows 10, you can use the Registry Editor.
- Before proceeding, it is essential to create a backup of your registry.
- In the Registry Editor, navigate to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList folder.
- Find the profile that you want to rename by looking at the ProfileImagePath value.
- Right-click on the profile key and choose «Rename» to change the profile name.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about renaming user profiles in the Windows 10 Registry:
1. How can I rename a user profile in Windows 10 Registry?
To rename a user profile in Windows 10 Registry, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type «regedit» and press Enter to open the Registry Editor.
3. Navigate to the following path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList.
4. Look for the profile you want to rename in the list of keys on the left side of the Registry Editor.
5. Right-click on the profile key and select Rename.
6. Enter the new name for the profile and press Enter to save the changes.
7. Close the Registry Editor and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
2. Will renaming a user profile in Windows 10 Registry affect my files and settings?
Renaming a user profile in Windows 10 Registry does not affect your files and settings. The profile name is just a reference and changing it in the Registry does not modify the actual user folder or any of its contents.
However, it’s important to note that improper editing of the Registry can cause system instability or other issues, so always be cautious and make a backup before making any changes.
3. Can I rename the Administrator profile in Windows 10 Registry?
No, you cannot rename the Administrator profile in Windows 10 Registry. The Administrator account is a built-in system account with specific privileges and it cannot be renamed using the Registry Editor.
If you need to change the display name of the Administrator account, you can do so through the Command Prompt or Local Users and Groups in the Computer Management console.
4. What should I do if I encounter errors after renaming a user profile in Windows 10 Registry?
If you encounter errors after renaming a user profile in Windows 10 Registry, you can try the following solutions:
1. Restart your computer and check if the issue persists.
2. Use the Registry Editor to change the profile name back to its original name and see if the errors disappear.
3. If the errors continue, you can try creating a new user profile and transferring your files and settings to the new profile.
If none of these solutions work, it’s recommended to seek assistance from a technical expert to resolve the issue.
5. Is it possible to rename a user profile without using the Windows 10 Registry?
Yes, it is possible to rename a user profile in Windows 10 without using the Registry Editor. You can rename a user profile through the Control Panel or the User Accounts settings in the Settings app.
However, renaming a user profile this way only changes the display name, not the actual profile folder name or the profile key in the Registry. If you want to change the profile folder name or the profile key, you will need to use the Registry Editor.
In summary, renaming a user profile in Windows 10 Registry can be a useful solution for users who want to personalize their device or troubleshoot issues with their accounts. By following the steps outlined in this article, users can safely modify the necessary Registry keys to change their profile name.
It’s important to note that making changes to the Windows Registry should be done with caution, as any incorrect modifications can cause system instability or even data loss. It’s always recommended to create a backup of the Registry before making any changes.
Not being able to login to computer due to Corrupted User Profile can be quite frustrating. Hence, we are providing below two different methods to Fix Corrupt User Profile on a Windows computer.
According to Microsoft, User Profile an get corrupted if the Antivirus program on the computer was busy scanning the PC for malware, while you were trying to Login to the User Account.
In our testing, it was possible to repair the corrupted user profile and gain access to the User Account by using registry editor.
Another way to deal with a corrupt user profile is to create a new user account and transfer all your files from the corrupted User Account to New User Account.
Advertisement
Method 1. Fix Corrupt User Profile Using Registry Editor
Login to your main Admin Account or another User Account with admin previlages and follow the steps below to identify and fix the corrupted user profile.
1. Right-click on the Start button and click on Run.
2. In the Run Command window, type regedit and click on OK.
3. On the Registry Editor screen, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList.
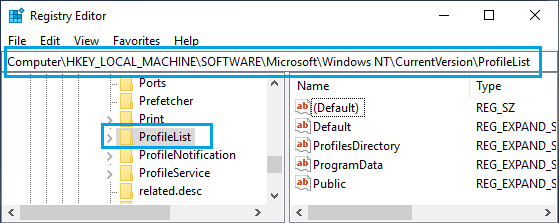
4. Open ProfileList Folder and you will see Folders starting with S-1-5. Each of these Folders represents a User Profile linked to User Account that was created on your computer.
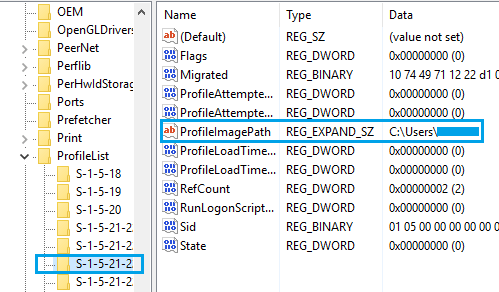
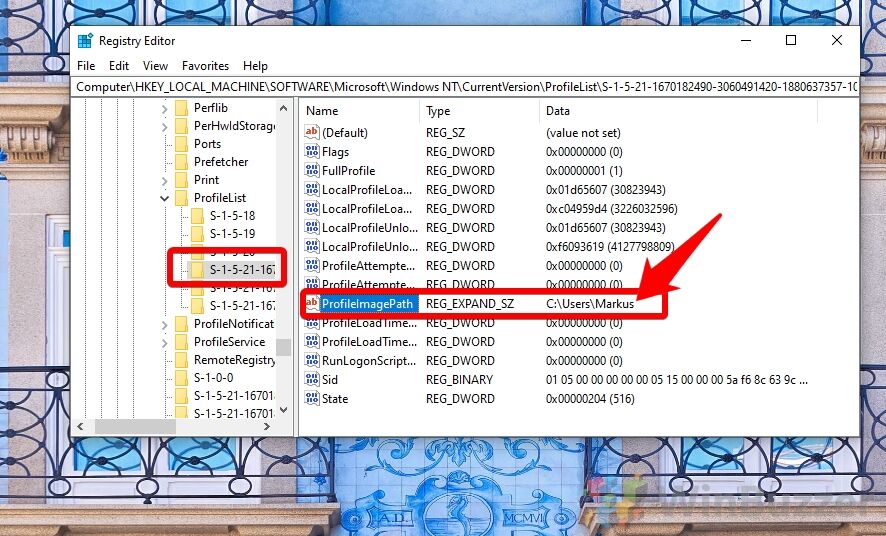
Now, the difficult task is to identify the S-1-5 Folder that belongs to the Corrupted User Profile. You can do this by clicking on each S-1-5 Entry and taking a look at ProfileImagePath in “Data” Column.
As you can see in above image, the “User Name” is clearly visible in ProfileImagePath Entry for the selected S-1-5 entry in the ProfileList Registry.
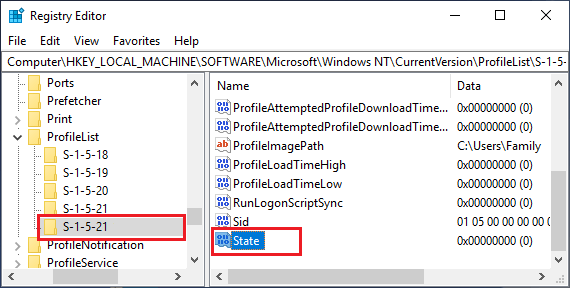
5. Once you find the right S-1-5 Folder, double-click on the State Field in right-pane.
Advertisement
6. In the Edit DWORD Window that appears, change the Value Data from 1 to 0 and click on the OK button.
7. Similarly, double-click on RefCount entry and change the Value Data from 1 to 0. If you cannot find “RefCount”, you need to create a New RefCount.
Right-click anywhere (blank space) in the right pane > click on New > DWORD (32 bit) Value and type RefCount as the Name for this New DWORD.
8. Close the Registry Editor and Restart the computer.
After this, you should be able to login to the user account and gain access to all your files.
Method 2. Transfer Files from Corrupted User Account to New Account
Create a New User Account by logging into your admin account and follow the steps below to transfer files from corrupted user account to new user account.
1. Open File Explorer > select Local Disc (C:) in the left-pane and double-click on Users Folder in the right-pane.
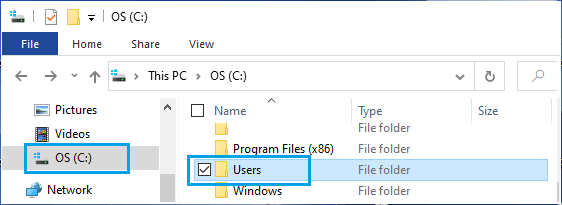
2. Once you are in Users Folder, open the Corrupted User Account by double-clicking on it.
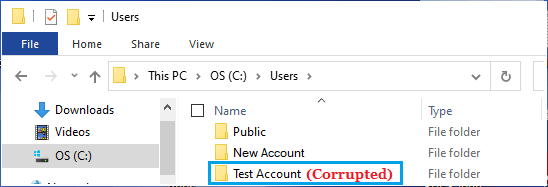
3. Individually select Desktop, Documents, Pictures and other Files/Folders that you want to transfer to New User Account.
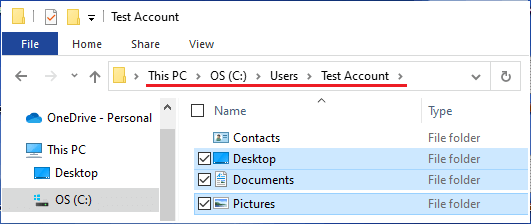
Important: Do not right-click and select all Files/Folders in the corrupted user account, as you will also end up copying hidden system files (Ntuser.dat, Ntuser.dat.log and Ntuser.ini) linked to the corrupted user profile.
4. Once Files/Folders are selected, right-click and select the Copy option to copy the files to clipboard.
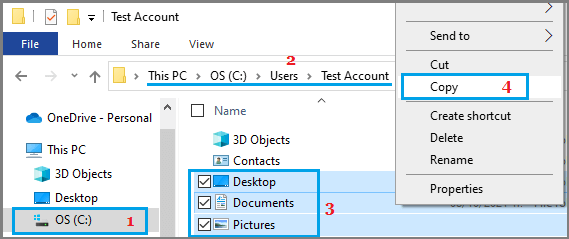
5. Once files are copied to the clipboard, open the New User Account that you created and Paste copied files into the New User Folder.
After this, login to New User Account and you will be able gain access to files that were transferred from the corrupted user account.
What to Do If the Admin Account is Corrupted?
If the Admin account is corrupted, you can activate or enable the Hidden Admin Account that Microsoft makes available on Windows computers for such rare occasions.
After logging in to the hidden admin account, you can try to repair the corrupted user profile on your computer by using steps as provided in the first method.
The other option is to create a new user account and transfer files from corrupted user account to new user account by using the second method as provided above.
Important: The name of the new user account needs to be different from that of the corrupted user account.
After deleting the corrupted user account, you can rename the new user account to the original user account name (if you want to maintain the same user name).
Adding a new account in Windows 11 / Windows 10 creates a user profile, a collection of settings, and folders that ensure each person on the PC has a unique, customized experience. This also contains their documents, saved games, videos, and more. This can take up some space, but fortunately, Windows lets you delete a user profile if you no longer need it or it gets corrupted.
The Difference Between User Profiles and User Accounts in Windows
Managing user data and settings on Windows 10 and 11 systems involves understanding the distinction between a user account and a user profile. While often used interchangeably, these two components serve different yet complementary roles in the Windows operating environment.
A user account is essentially the gateway to accessing a Windows system, acting as the user’s identity for system access. It consists of a username and, optionally, a password, which are required to log into Windows. User accounts can be associated with different levels of privileges, such as standard user rights or administrative permissions, determining what the user can and cannot do on the system.
In contrast, a user profile is a personalized environment linked to a user account. Once a user logs in, the system loads a unique user profile containing personal settings, configurations, desktop backgrounds, application settings, and files stored in the user’s personal folders. This profile ensures that each user’s experience is tailored to their preferences and saved from session to session.
Deleting a Windows User Profile vs. Deleting a Windows User Account
Deleting a user profile is a process distinct from deleting a user account. When you delete a user profile in Windows 10 or 11, you’re removing all the personalized settings and files associated with that profile, effectively resetting the user’s environment to a default state. However, the user account itself may remain intact, allowing for the creation of a new profile when the user logs in again. This process can be essential for troubleshooting, such as when a profile becomes corrupted, or for removing the data of users who no longer need access to the system.
There are multiple methods to delete a user profile in Windows, each suitable for different scenarios and user preferences. The Settings app offers a straightforward approach for those seeking simplicity, while the Control Panel and User Accounts Wizard provide more granular control over the deletion process. For a comprehensive removal, especially to address deeper system-level issues or ensure the complete clearance of all profile remnants, Advanced System Properties might be the preferred method.
⚠️ Please note: The process described below is the same in Windows 11 as it is in Windows 10. However, bear in mind that we’ll be using screenshots from Windows 10, so your UI may look a little different. We’ll point out any changes you need to be aware of as they come up.
How to Delete a Windows User Profile via System Properties
Before you start this process, make sure the user account you wish to delete is signed out.
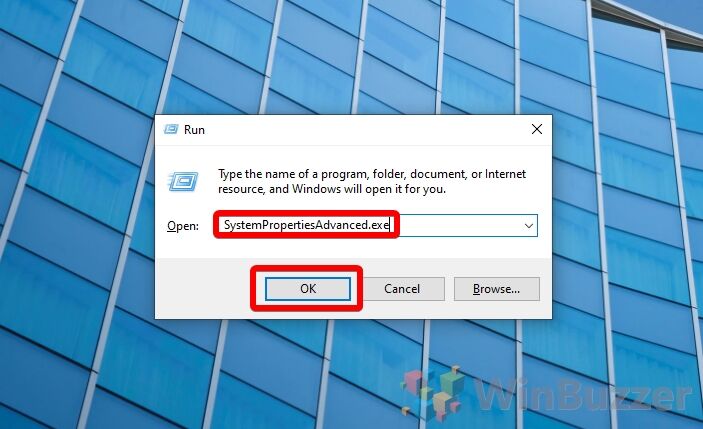
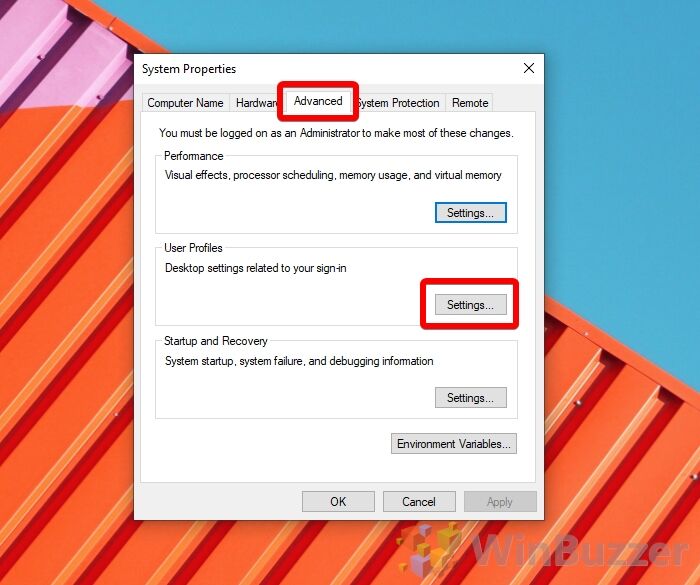
- Open System Properties
Press “Windows + R” to open the Run dialog, type “systempropertiesadvanced.exe”, and click “OK”.
- Open the Windows 11 / Windows 10 user profile settings
In the “Advanced” tab, look for the “User Profiles” heading and click “Settings…”.
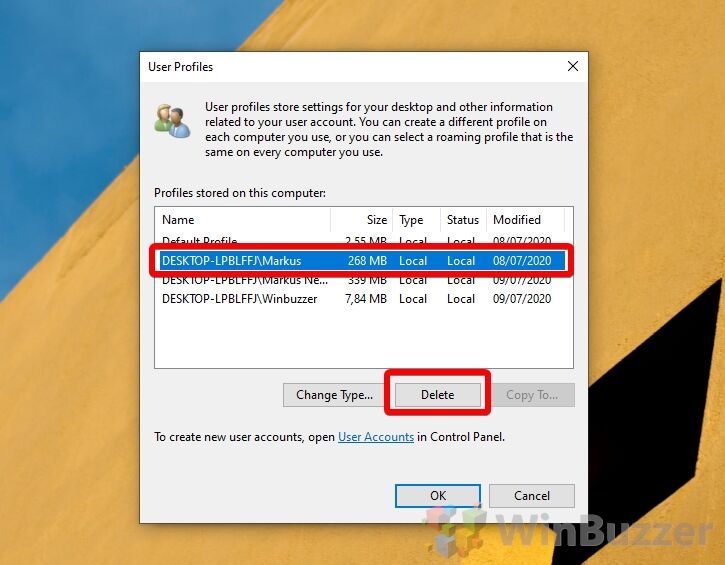
- Delete the Windows 11 / Windows 10 user profile
Windows 11 / Windows 10 will now return a list of user profiles linked to certain accounts. You’ll be able to see the name of the account after the PC identifier. Click the account, then press “Delete”.
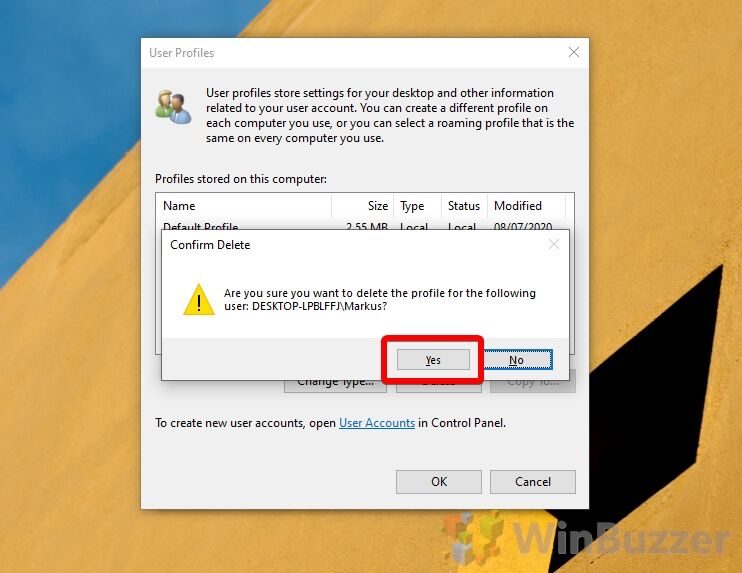
- Confirm the Windows 11 / Windows 10 delete user profile action
Microsoft will then make sure you really want to remove the user profile. You should make sure there are no files or settings you need on that account before you continue. When ready, click “Yes”.
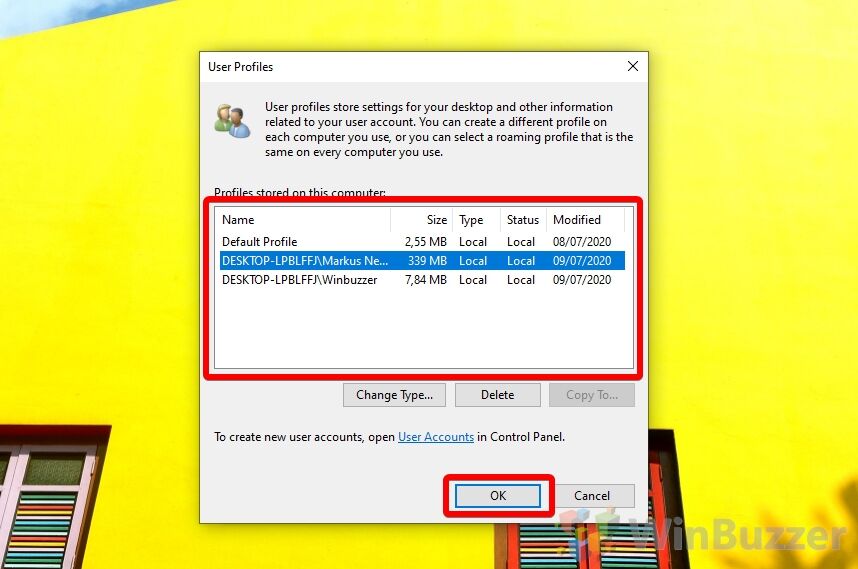
- Check the profile is removed from the User Profiles window
After pressing yes, you should note that the user profile is gone from the “Profiles stored on this computer:” list. Press “OK” to close it.
- Log back in to the user account to create a new user profile
You can create a new user profile for that account at any time by simply logging into it again. When you do so, Windows 10 will show a “This might take several minutes” prompt.
How to Delete a Windows User Profile from the Registry
If the above method doesn’t work, you can delete a user profile from the registry and via Windows 11 / Windows 10 File Explorer. First, though, sign out of the user and read up on how to safely edit the registry.
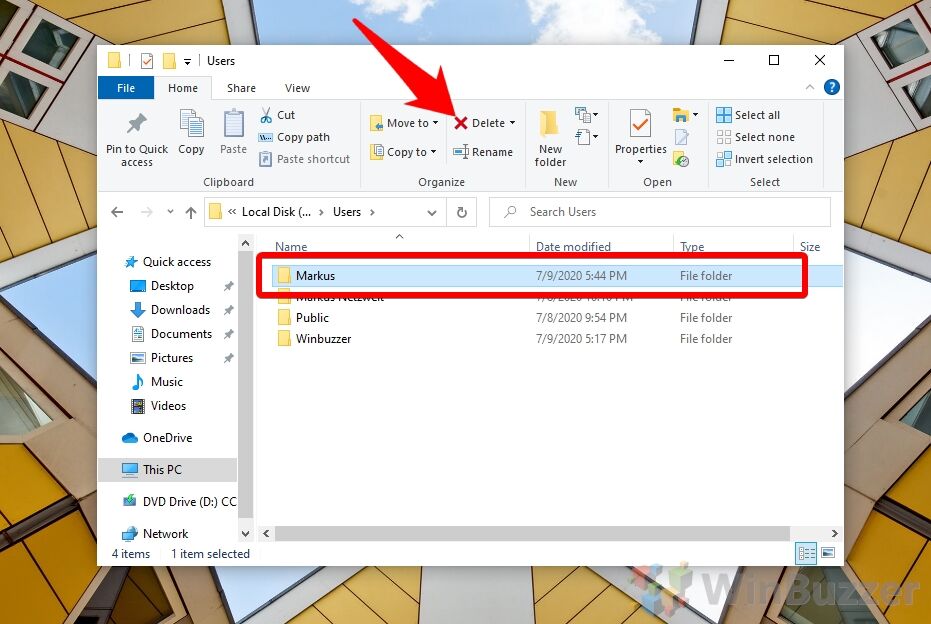
- Delete the Windows 11 / Windows 10 user profile via File Explorer
Head to the
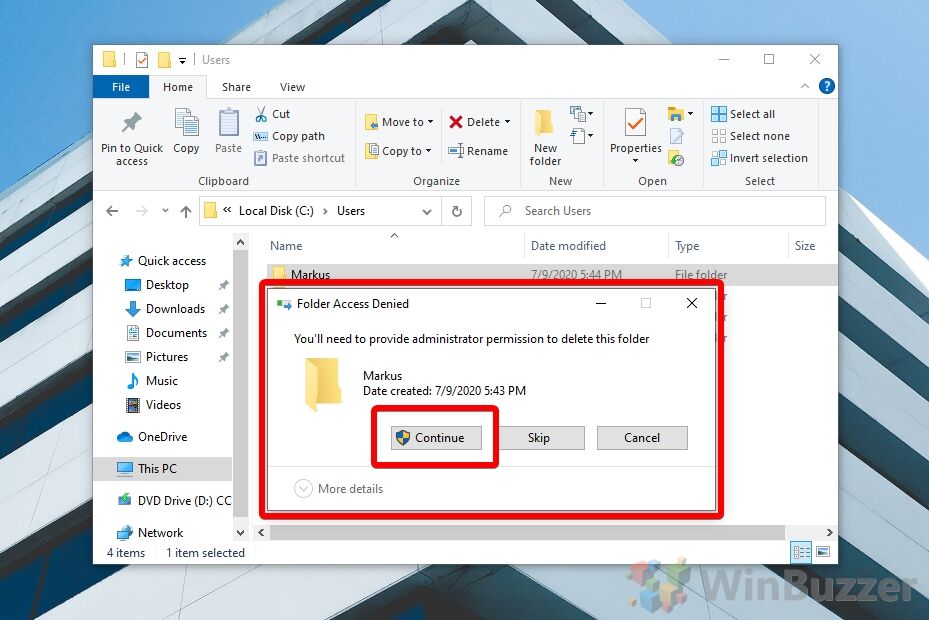
C:\Usersfolder and look for the user profile you want to remove. Click it, then press “Delete”. - Press “Continue” on UAC prompt
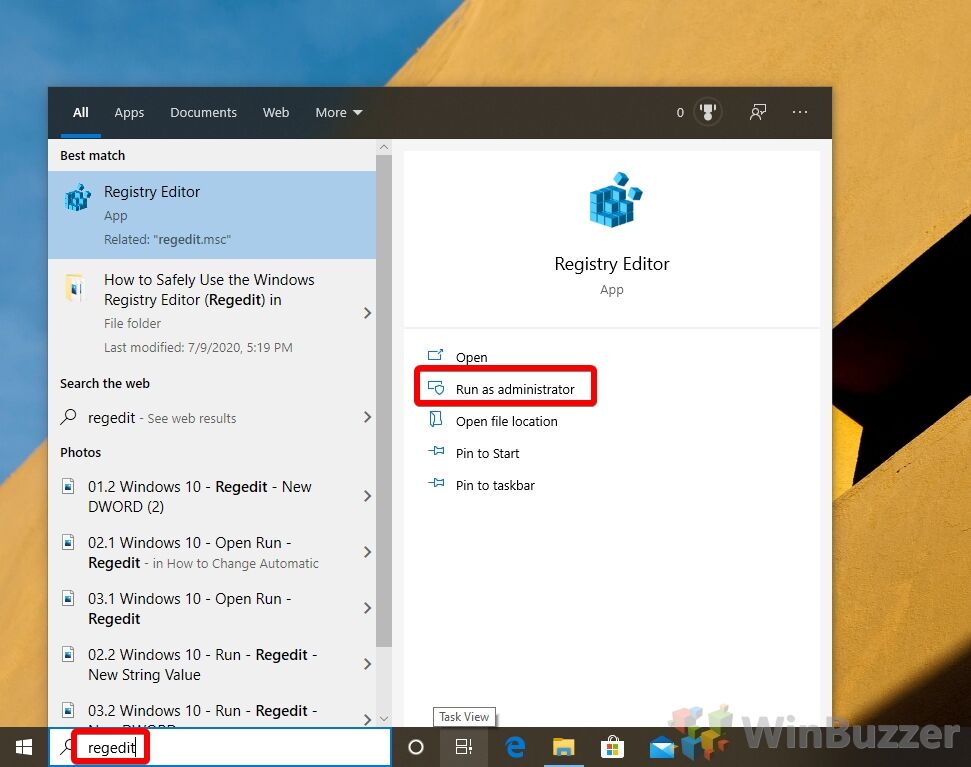
- Open the Registry editor
Press the “Start” button and type “regedit”, then click “Run as administrator”.
- Navigate to the profile list in registry editor
In the search bar or side menu, navigate to the profile list in registry editor, which is found at:
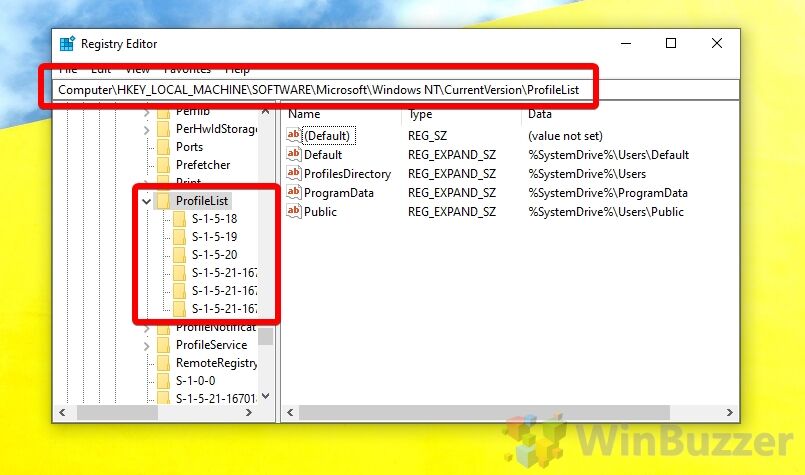
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\ProfileList - Find the account in the profile list registry key
The profile list registry key will have several SID keys for each user. To find the one you’re looking for, click on each and check the “Data” field next to the “ProfileImagePath” entry.
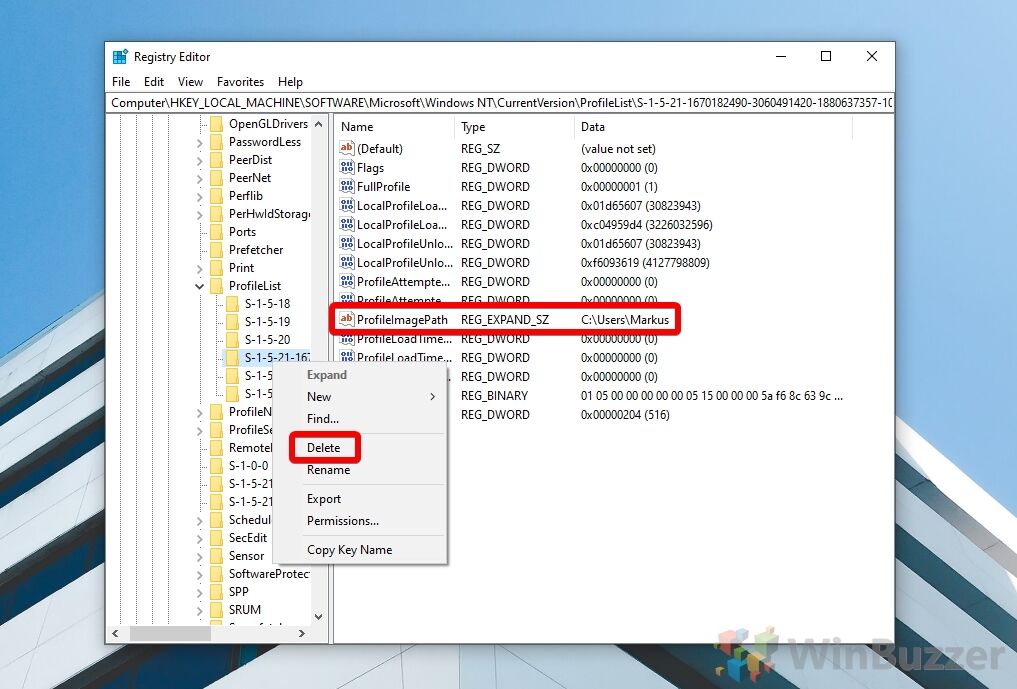
- Delete the user profile registry key
In the left-hand side menu, right-click the correct user SID and press “Delete”.
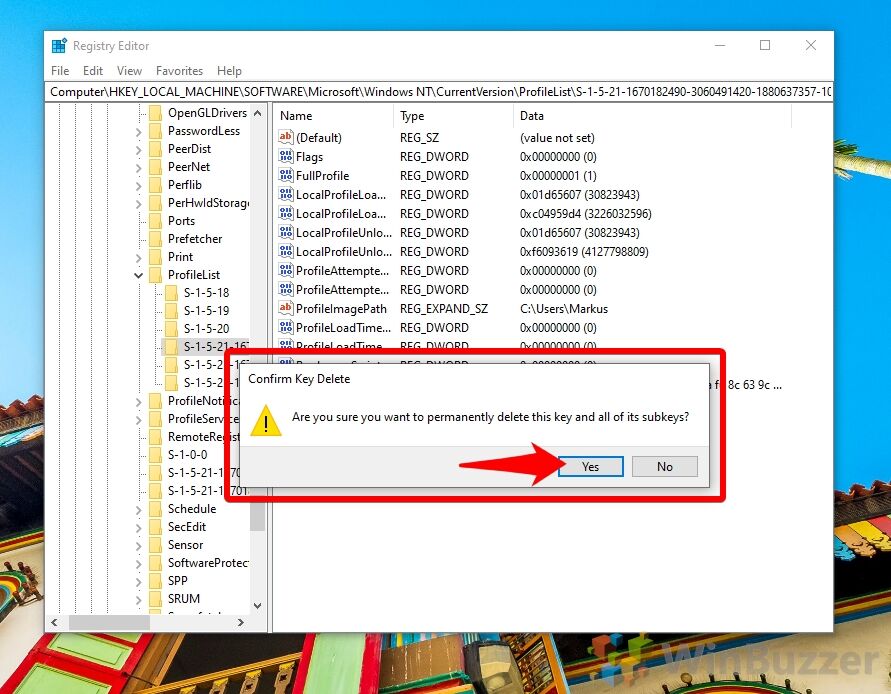
- Confirm the user profile registry key deletion
Make sure you’re deleting the key for the correct user before clicking “Yes”.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Windows User Profiles
How can I back up a user profile before deleting it in Windows 10 or 11?
Use Windows Backup and Restore feature to create a system image or manually copy the user folder from C:\Users\ to another location. Ensure all necessary files are included in the backup.
What are the implications of deleting a user profile on shared documents and desktop items?
Items stored in a user’s profile, including documents and desktop items, will be permanently deleted. Shared items located in public folders or other user profiles won’t be affected.
Can I delete a user profile to fix a login issue without deleting the account?
Yes, deleting just the profile can often resolve login problems by allowing Windows to create a fresh profile on the next login, without affecting the user’s account.
How do I manage user accounts and profiles in a family or shared computer setup?
Use Windows Settings to create separate accounts for each user, allowing for individual profiles, settings, and parental controls if necessary. This ensures a personalized and secure environment for each user.
What steps should I take if I’m unable to delete a user profile through the usual methods?
Restart your computer in Safe Mode and try deleting the profile again, or use a third-party software designed to clean up user profiles and registry entries.
How do I restore a user profile that was accidentally deleted?
If you have a backup, you can restore the user’s data by copying it back to the C:\Users\ directory. Restoring the profile settings exactly as they were might not be possible without a system restore point.
Can I delete a user profile to free up disk space?
Yes, deleting user profiles can free up disk space, especially if the profiles contain large files or have accumulated a lot of data over time.
How do I change the default location of user profiles in Windows 10 or Windows 11?
This involves editing the registry or using Group Policy, and it’s a complex process that can affect system stability. It’s typically recommended only for advanced users or IT professionals.
What should I do if a user profile deletion fails due to file permission issues?
Ensure you have administrative rights, take ownership of the files or folders in question, or check for any open files and applications that might be using the profile.
How does deleting a user profile affect cloud-synced data, like OneDrive or Dropbox?
Data synced with cloud services like OneDrive or Dropbox is not lost when a user profile is deleted, but you’ll need to reconfigure the sync settings when you log in again or set up a new profile.
Can I delete all user profiles at once in Windows 10 or Windows 11?
While technically possible, it’s risky and not recommended because it includes deleting the default and system profiles, which can render the system unusable or unstable.
How can I ensure that all traces of a user profile are removed from the system?
After deleting the profile via System Properties, manually check the C:\Users\ directory and the registry to ensure all related data and settings are removed.
What are the best practices for managing multiple user profiles on a shared computer?
Regularly back up important data, set clear storage and privacy guidelines, periodically review and clean up unused profiles, and ensure each user logs out after their session.
How can I prevent users from creating new profiles on a Windows 10 or Windows 11 PC?
This can be controlled through Group Policy settings by disabling the “Add or remove user accounts” option and other related settings under User Rights Assignment.
Is it possible to convert a local user profile to a Microsoft account profile without losing data?
Yes, you can link a local account to a Microsoft account through the Settings app under Accounts > Your info. This retains the profile data while enabling sync features and other Microsoft account benefits.
Related: How to Delete a Windows User Account
There are various reasons you might need to delete a user account: maybe the account is no longer needed, you’re preparing to give the computer to someone else, or you simply want to clean up old accounts that are no longer in use. Regardless of the reason, Windows 11 offers several ways to remove user accounts, which we explain in detail in our other guide.

Related: How to Enable the Hidden Administrator Account in Windows 11 and Windows 10
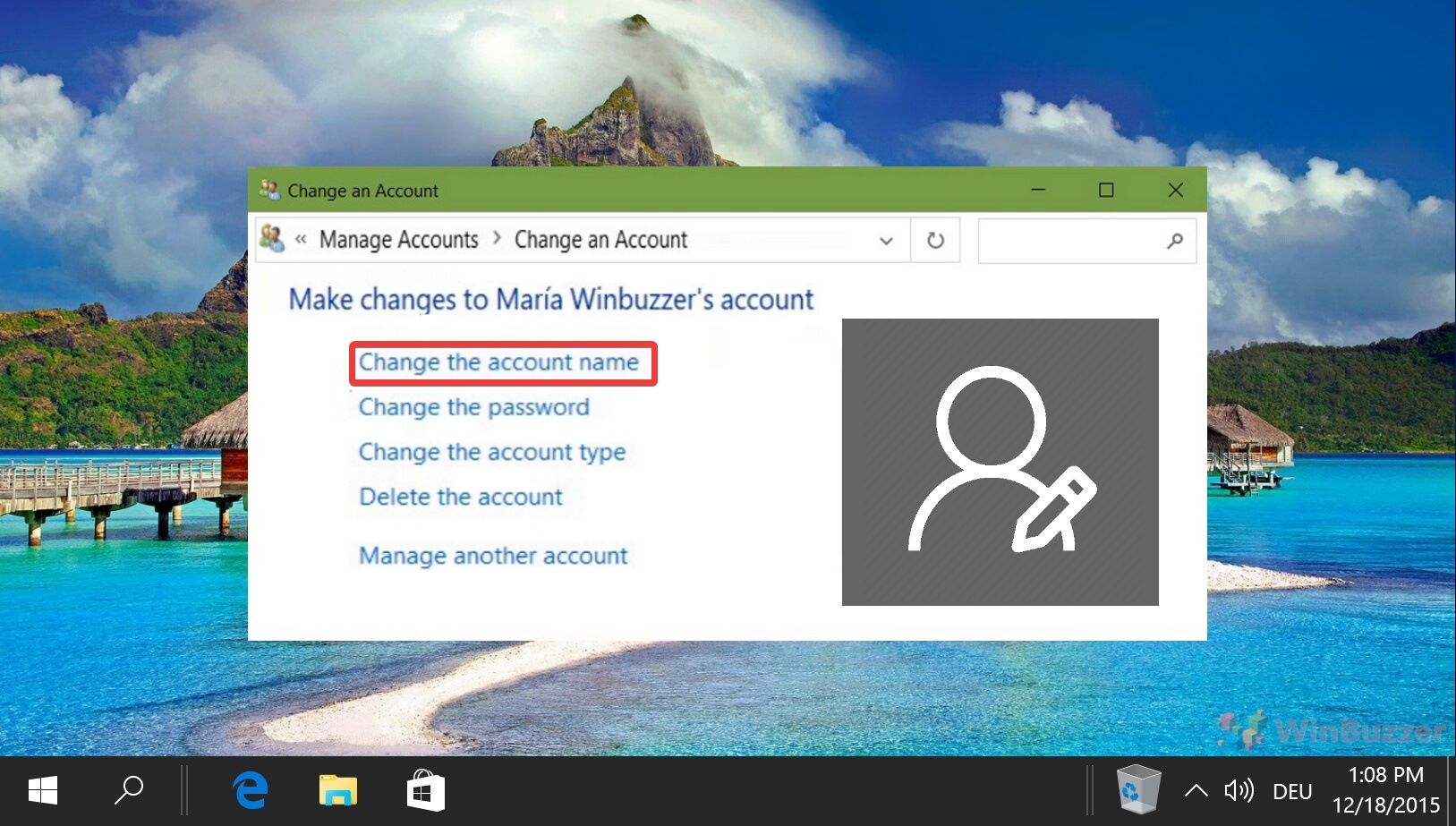
Related: How to Change a Windows Username / Account Name
There are different reasons why you might want to change a username in Windows 11 or Windows 10. Maybe your real name has changed and you need to reflect this change in Windows as well. Or you have been using a nickname and want to do a username change to your real name. In our other guide, we show you how to change a username / account name in Windows.
Last Updated on November 7, 2024 10:44 pm CET