How to connect, delete and manage WiFi networks using command prompt (cmd) in your Windows PC/laptop using netsh wlan commands
Nowadays internet connectivity is everything. For the Internet, we have Wi-Fi connections that we manage and use through the network settings on Windows 7/8.1/10 computers.
You can also connect, manage, and delete your WiFi networks using the command prompt.
In fact, the command prompt offers many more features than the standard network connection settings in Windows 10.
Also Read- A-Z Windows CMD Commands List
To do this we only require a CMD(Command Prompt) with Administrator privileges and will have to use netsh wlan commands.
Table Of Contents
- How to connect to wifi using cmd with netsh wlan commands-
- 1# View various wireless network profiles saved on your PC
- 2# View WiFi adapter driver information
- 3# View wireless adapter settings
- 4# Recover your WiFi password from any of the WiFi connection profiles saved on your PC
- 5# Connecting to a WiFi network using command prompt
- 6# Stop your PC connecting automatically to a wireless network out of range
- 7# Delete wireless network profile stored on your PC
- 8# Export and import wireless network profiles
- 9# Generate a complete report of the wireless adapters on your PC/laptop
How to connect to wifi using cmd with netsh wlan commands-
Before we dive into the guide. You’ll need to open the Command Prompt with administrator rights to perform most of the commands. To do this, use the Windows key + X keyboard shortcut, and select Command Prompt (Admin).
Or search cmd and right click run as administrator
1# View various wireless network profiles saved on your PC
Command > Netsh WLAN show profiles
Every time you connect to a wireless access point, the operating system creates a “wireless network profile”, and it’s stored on your computer, you can view all these profiles using the following command line on the Command Prompt Netsh WLAN show profiles.
Alternatively, you can use the “interface” parameter to show the list of profiles for a particular wireless adapter:
Netsh WLAN show profiles interface=”your WiFi interface name”
2# View WiFi adapter driver information
Command > Netsh WLAN show drivers
When you need to get driver information about your computer’s wireless adapter, you can use the the above command. The result will show the exact drivers being used, the WiFi radios on your PC/laptop alongwith driver version number.
You can further use this command to check your WiFi capabilities. Type in the following command
C:\Netsh WLAN show wirelesscapabilities
The results will show you exactly what your WiFi connection is capable of including WiFi Direct service capabilities.
3# View wireless adapter settings
Command > Netsh WLAN show interfaces
You can see the details of your WiFi interfaces using above command. The results will show you description of the interface, SSID, BSSID, Cipher, authentication type, channel, average receive and transmit rate and radio type.
If you have multiple WiFi connections saved on your PC, the “Show interfaces” command will display the information for all the wireless adapters on your computer. If you only need to see the information for one adapter, you can use the following command:
Netsh WLAN show interface name=”your wifi connection name”
4# Recover your WiFi password from any of the WiFi connection profiles saved on your PC
Command > Netsh WLAN show profile name=”your WiFi connection name” key=clear
If you lost and cannot remember your network security key to connect another device to a particular Wi-Fi access point, you can use the above command to view your WiFi password. You can also use this command to see the data limits if you have set them.
5# Connecting to a WiFi network using command prompt
Command > netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=”your WiFi connection name” key=”your WiFi connection password”
You can use the above command to sign into your WiFi network. The above command is particularly useful if your WiFi settings in Windows 10 is not visible/cannot be connected due to some reasons. The additional commands are C:\netsh wlan start hostednet and C:\netsh wlan stop hostednetwork These two commands will start and stop your WiFi hotspot connection.
6# Stop your PC connecting automatically to a wireless network out of range
Command > Netsh WLAN set profileparameter name=”your WiFi connection name” connectionmode=manual
Normally, you would have configured your Windows 10 PC to connect to different WiFi networks automatically. While this is the best way to connect, sometimes notice that your laptop connects automatically to a WiFi connection that has zero or poor connectivity instead of an available full network WiFi connection. In such a case you can use the above command to prevent your computer from connecting to different networks automatically. If you want to move again to the automatic mode use the following command C:\Netsh WLAN set profileparameter name=” your WiFi connection name” connectionmode=auto
7# Delete wireless network profile stored on your PC
Command > Netsh WLAN delete profile name=”the WiFi connection you want to delete”
When you no longer need to connect to a particular wireless network, the access point is no longer available, or you need to reset the network profile settings, you can also use Netsh WLAN to delete any profile stored on your computer using the above command. If you can’t remember the name of the network profile, you can use the C:\Netsh WLAN show profiles command to list all the available profiles and select the one you want to delete.
8# Export and import wireless network profiles
Command > Netsh WLAN export profile key=clear folder=”the folder you want to save this report”
Sometimes you need to export and import wireless profiles. The above command exports all your wireless network profiles available on your PC. If you want to export a specific WiFi connection profile to a specific location, use this command > C:\Netsh WLAN export profile name=”your WiFi connection name” key=clear folder=”the folder you want to save this report”
9# Generate a complete report of the wireless adapters on your PC/laptop
Command > Netsh WLAN show WLANreport
Trouble shooting WiFi connection problems is very difficult as Internet has lots of conflicting tutorials and troubleshooting guide. Also you should know the exact problem you are facing while connecting to WiFi.
Using the above command will generate a full detailed WiFi networks report to the following location > C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\WLANReport\WLAN-report-latest.html.
Once the WLAN report has been created, copy and paste the path into your web browser’s address bar to open the report.
You can use this report to troubleshoot the problems, ask help on tech forums. The WLAN reports contain a graph with details of the connectivity status, including information, such as when the connection started, when it got disconnected, errors, and more.
The report also summarizes network adapters information configured on your system, session success/failures, disconnect reasons, and a lot more. It’s a very detailed report that can help you to ping point many Wi-Fi connectivity issues.
ALSO READ:
- How to Hack WiFi Password Using New WPA/WPA2 flaw
- How To Find WiFi Password When Forgot It
CONCLUSION:
So this was how to connect to wifi using cmd (command prompt) with netsh wlan commands
Узнаем список доступных интерфейсов сети
netsh wlan show interface
Выводим список Wifi сетей
netsh wlan show networks
Для подключения к WiFi сети служит команда
netsh wlan connect name=ИмяПрофиляСети
Можно указать конкретный интерфейс, при помощи которого выполнять подключение. Синтаксис таков: netsh wlan connect name=ИмяПрофиляСети interface=ИмяИнтерфейса
У меня бы это выглядело так:
netsh wlan connect name=TRENDnet interface=»Wireless Network Connection 3″
Отключение от WiFi сети Чтобы отключиться от WiFi сети, необходимо выполнить следующую команду
netsh wlan disconnect
Или указать конкретный интерфейс
netsh wlan disconnect interface=ИмяИнтерфейса
При помощи netsh можно просмотреть все доступные профили:
netsh wlan show profile
И, собственно, подключиться к сети с выбранным профилем:
netsh wlan connect ssid=ИмяСети name=ИмяПрофиляСети
A Wi-Fi adapter eases the process of connecting your Windows 10 laptop or desktop to the network and internet without dealing with cables. However, it’s only convenient if you know where to find the settings.
Whether setting up a device for the first time, connecting in a new place, or looking for an efficient method to connect multiple computers to the same network, Windows 10 offers multiple ways to connect to the internet using a Wi-Fi connection quickly.
In this Windows 10 guide, we will walk you through the steps to connect to a Wi-Fi network using the network flyout in Taskbar, Settings, Control Panel, and command lines with Command Prompt.
How to connect to Wi-Fi network using Taskbar
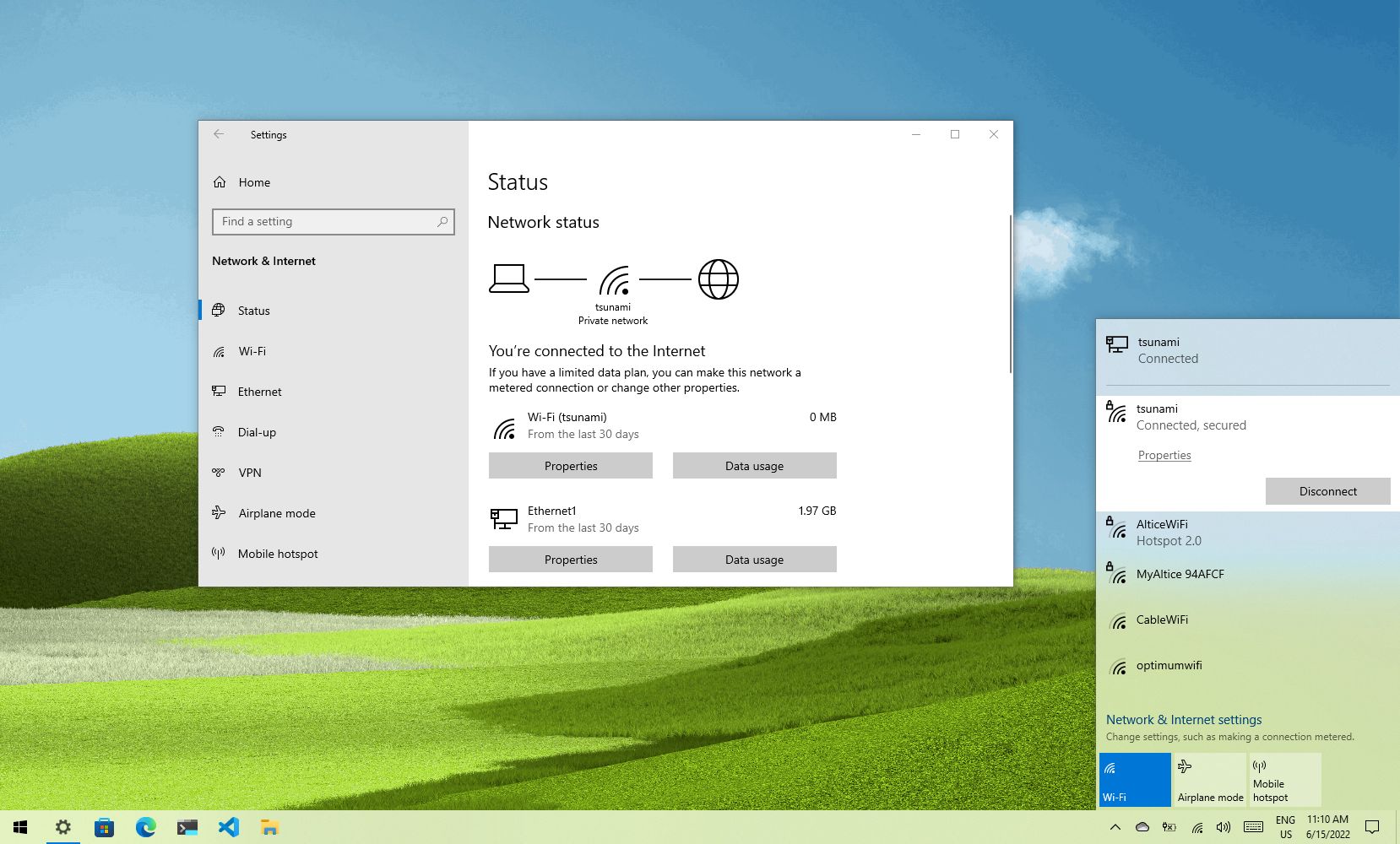
To connect to a Wi-Fi network through the taskbar on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Click the Network icon in the bottom-right corner of the taskbar.
- Quick note: Alternatively, you can open Action Center (Windows key + A), and then click the Network button in the «Quick actions» section to access the network flyout. If you don’t see the button, click the up arrow button on the left.
- Select the wireless network to connect.
- (Optional) Check the Connect automatically option.
- Click the Connect button.
- Quick tip: If you do not see any wireless access point in the list, click the Wi-Fi button to turn on the adapter.
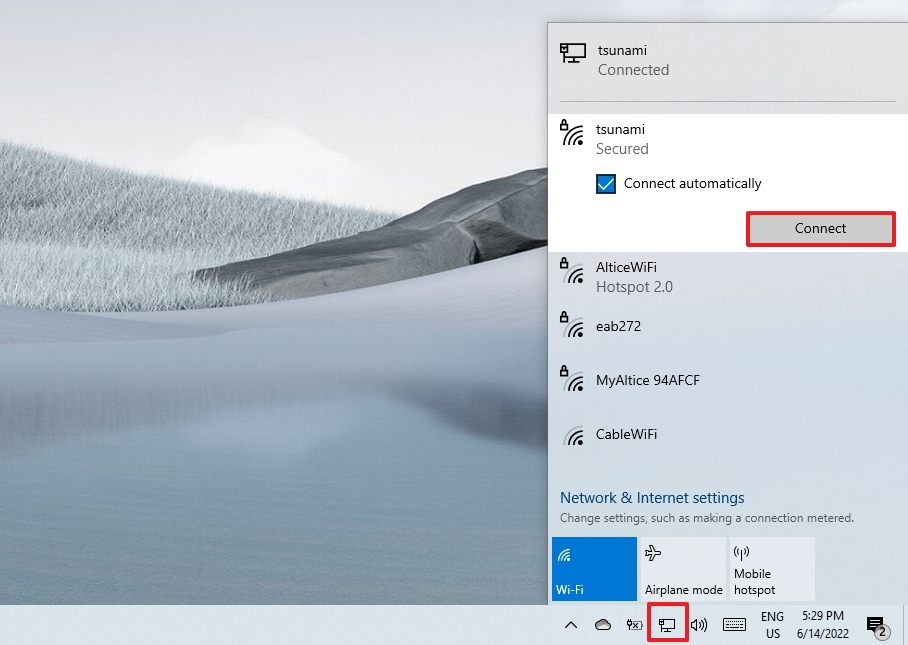
- Confirm the network security key (password).
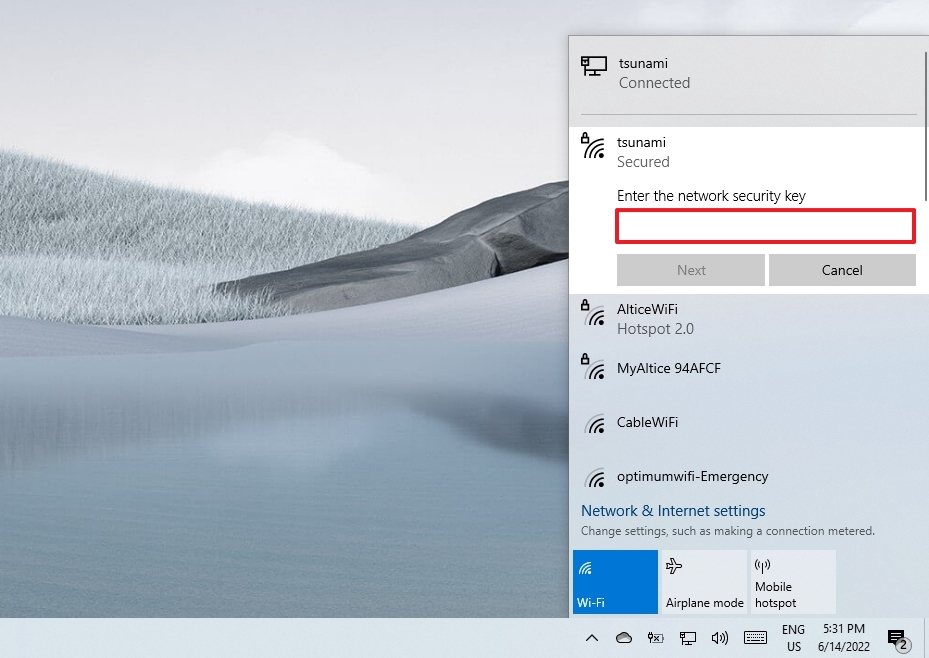
- Click the Next button.
- Confirm whether the device should be discoverable in the network by other PCs.
Once you complete the steps, the laptop will connect to the network using the Wi-Fi connection.
Reconnect automatically
In addition, Windows 10 also offers an option to reconnect the device automatically after disconnecting the adapter manually.
To set the Wi-Fi adapter to reconnect automatically, use these steps:
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Click the network icon in the system tray.
- Click the Wi-Fi button to turn off wireless connectivity.
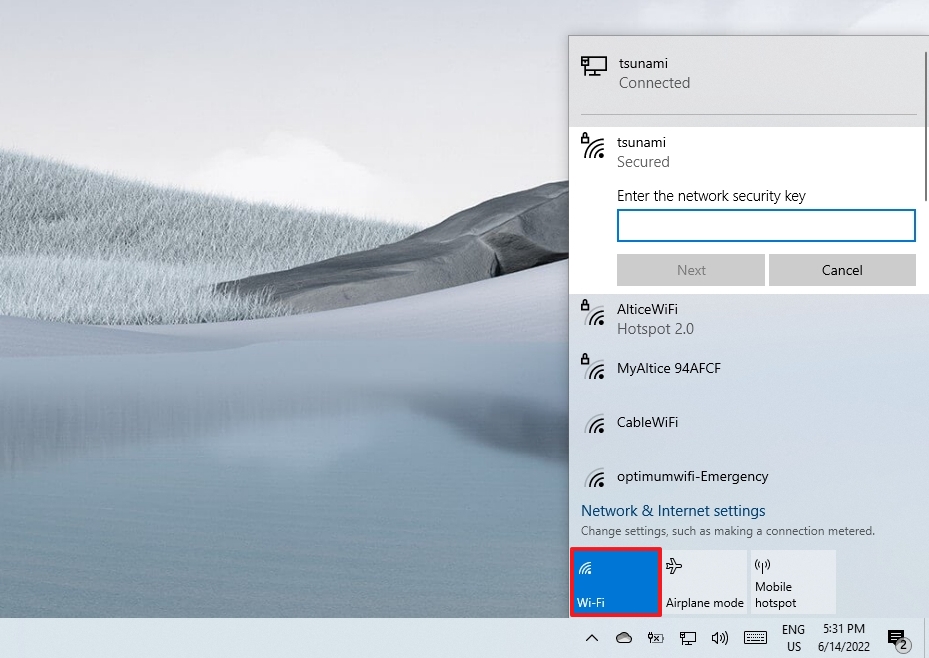
- Use the drop-down menu and select when to re-connect automatically:
- Manually.
- In one hour.
- In four hours.
- In one day.
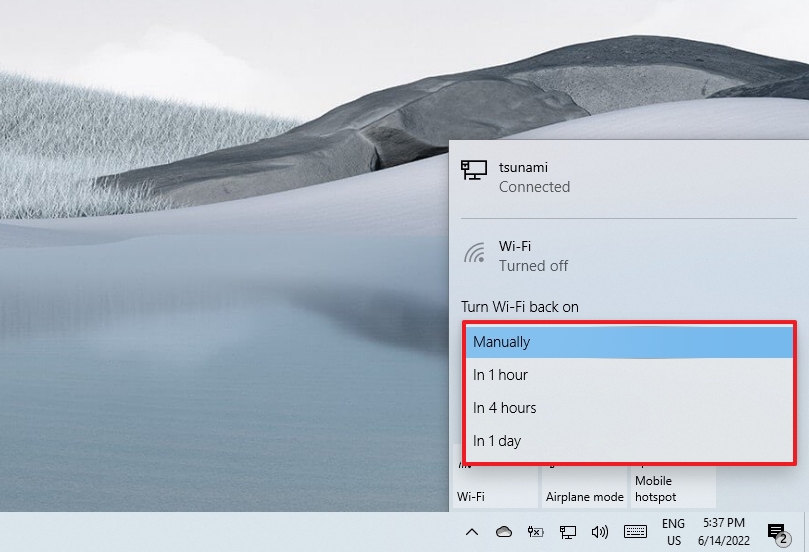
After you complete the steps, Windows 10 won’t try to connect to a wireless connection until the time you selected. When using this functionality, the device will only connect automatically to previously known networks.
How to connect to Wi-Fi network using Settings
Using «Network & Security» settings, you can also add wireless connections manually, and then when the network is in range, the laptop will connect automatically.
To prevision a Wi-Fi connection on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Network & Security.
- Click on Wi-Fi.
- Click the Manage known networks option.
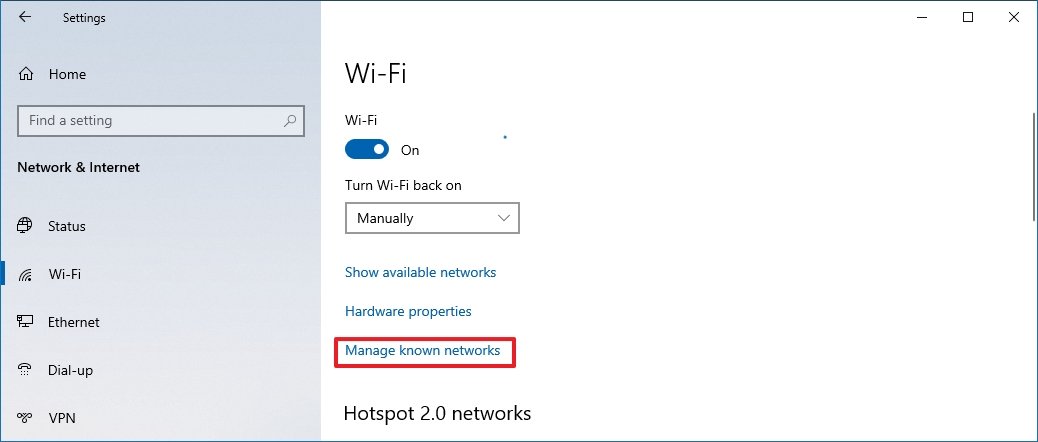
- Click the Add a new network button.
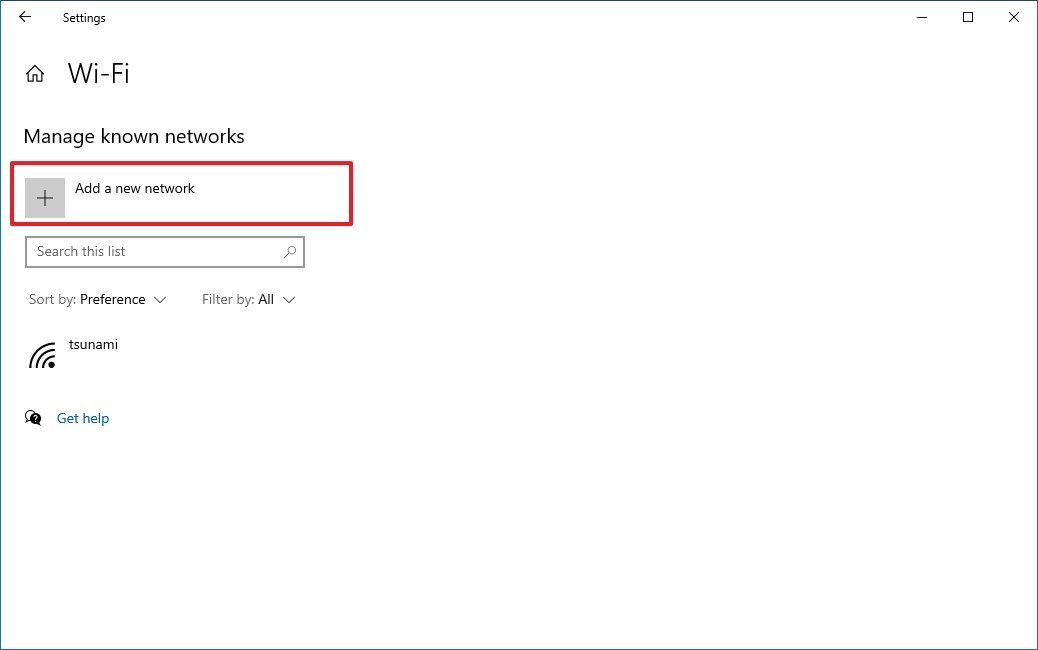
- Confirm the name of the network.
- Use the drop-down menu to select the Security type — for example, WPA2-Personal AES.
- Confirm the network security key (password).
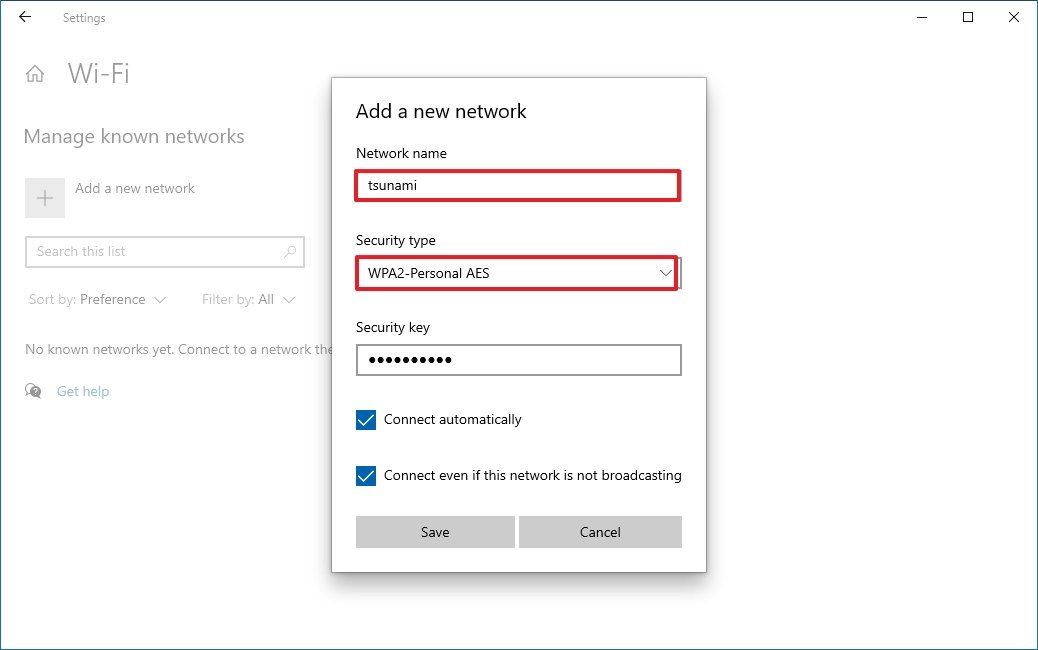
- Check the Connect automatically option.
- Check the Connect even if this network is not broadcasting option (if required).
- Click the Save button.
Once you complete the steps, the device will connect automatically when the wireless network is in range.
How to connect to Wi-Fi network using Control Panel
To connect to a Wi-Fi network with Control Panel, use these steps:
- Open Control Panel.
- Click on Network and Internet.
- Click on Network and Sharing Center.
- Under the «Change your networking settings» section, click the Set up a new connection or network option.
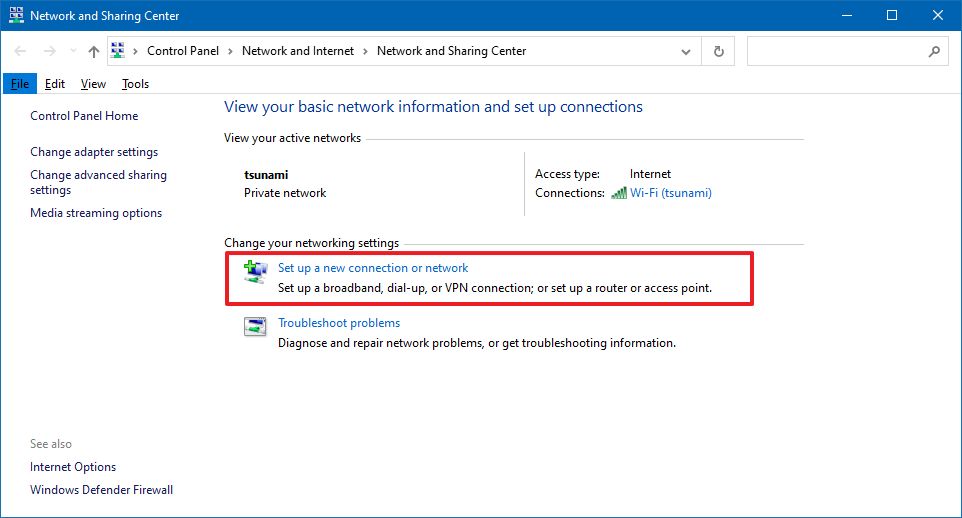
- Select the Manually connect to a wireless network option.
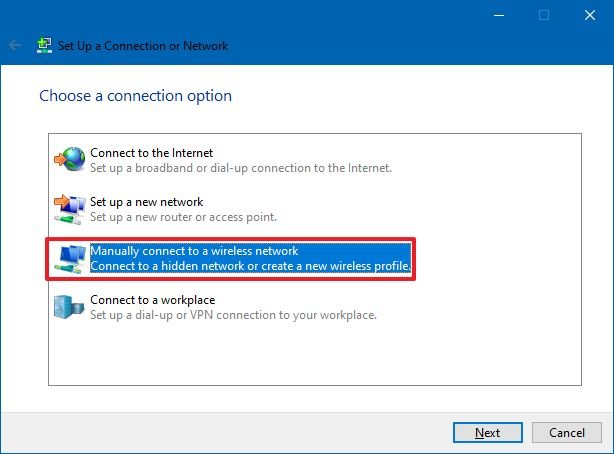
- Click the Next button.
- Confirm the network name.
- Use the drop-down menu to select the Security type — for example, WPA2-Personal.
- Confirm the network security key (password).
- Check the Start this connection automatically option.
- (Optional) Check the Connect even if the network is not broadcasting option.
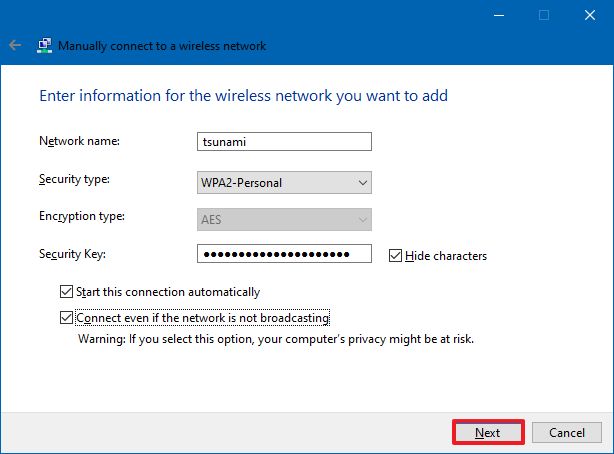
- Click the Next button.
- Click the Close button.
Once you complete the steps, the computer will automatically connect to the Wi-Fi network.
How to connect to Wi-Fi network using Command Prompt
How to connect to Wi-Fi network using Command Prompt
Alternatively, you can also use the netsh command-line tool in Command Prompt to connect to a Wi-Fi network.
To connect to a Wi-Fi access point with commands, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to view the available network profiles and press Enter: netsh wlan show profile
- Confirm the Wi-Fi network profile with your preferred settings.
- Type the following command to connect to the wireless network on Windows 10 and press Enter: netsh wlan connect ssid=YOUR-WIFI-SSID name=PROFILE-NAME
In the command, remember to specify the name (SSID) of the network and profile name with your network settings. For example, this command connects to the «tsunami» network using the «tsunami» profile: netsh wlan connect ssid=tsunami name=tsunami.
- Quick tip: On devices with more than one wireless adapter, you must also specify which adapter you want to use in the command. For example: netsh wlan connect ssid=YOUR-WIFI-SSID name=PROFILE-NAME interface=Wi-Fi.
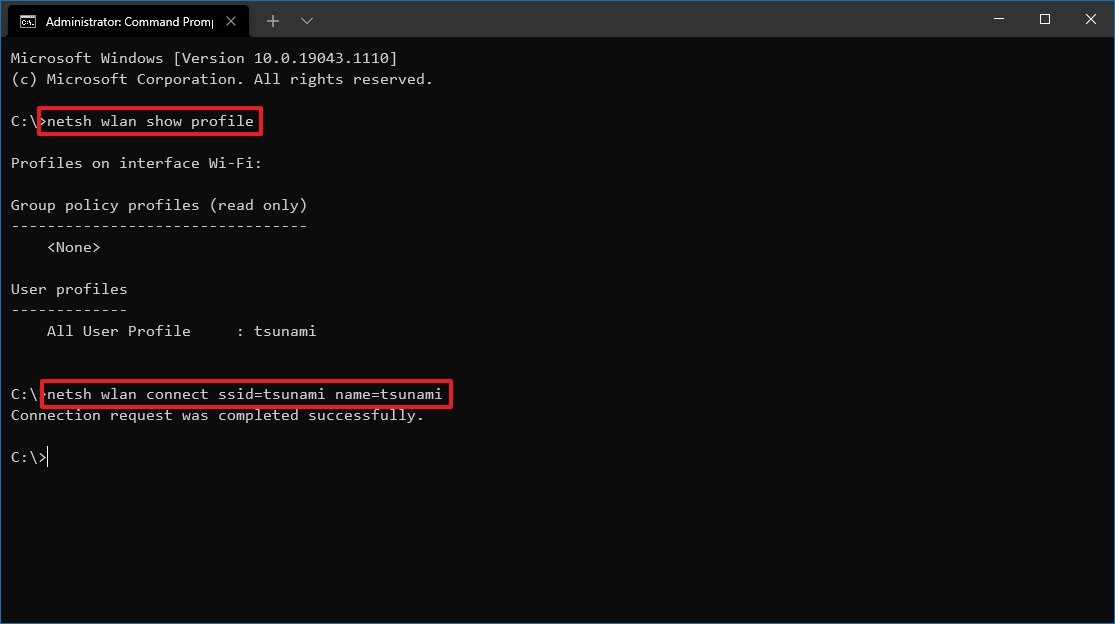
After you complete the steps, the device will connect to the wireless network.
New network connection
The netsh tool also lets you manage Wi-Fi adapters and networks. The only caveat is that you can only manage previously known networks since you cannot create new network profiles with this tool.
When you need to use Command Prompt to connect one or multiple computers to the same wireless network, you can export the network profile created automatically during the first connection. Then you can import it using the netsh tool to connect using the command-line tool.
Export Wi-Fi profile
To export a Wi-Fi profile with commands, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to view the available network profiles and press Enter: netsh wlan show profile
- Type the following command to export a profile and press Enter: netsh wlan export profile PROFILE-NAME key=clear folder=PATH\TO\EXPORT\FOLDER
For example, this command exports the tsunami profile to the «Documents» folder: netsh wlan export profile tsunami key=clear folder=C:\Users\m\Documents.
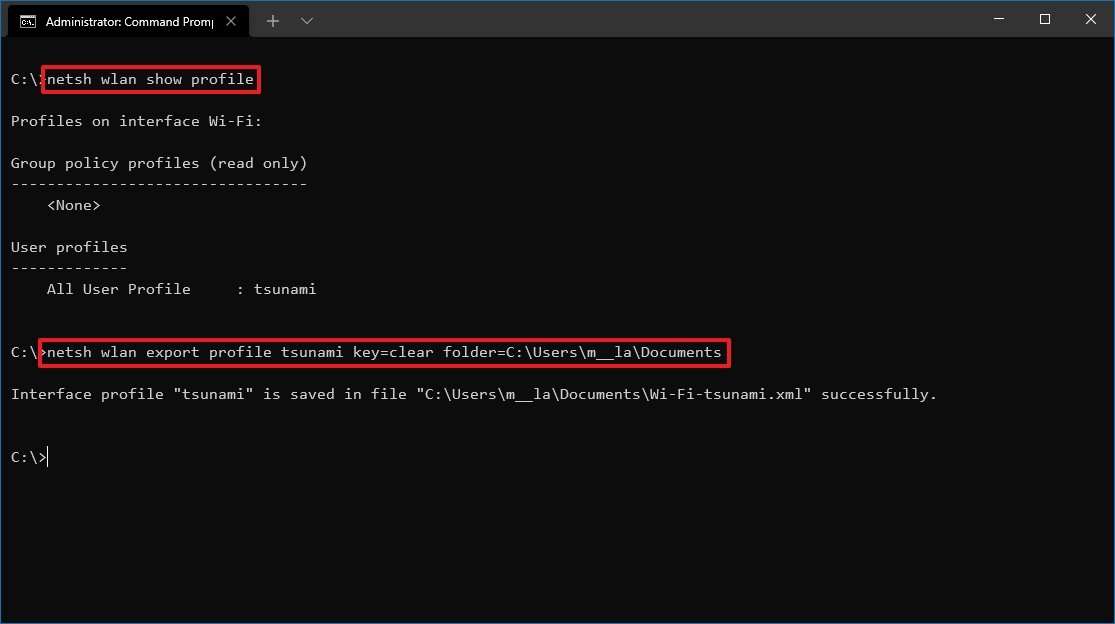
Once you complete the steps, you can import the same XML file to connect other devices to the same network.
Import Wi-Fi profile
To import a Wi-Fi profile on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to determine the name of the network adapter and press Enter: netsh wlan show interfaces
- Confirm the name of the adapter that will connect to the network.
- Type the following command to import the network profile and press Enter: netsh wlan add profile filename=»PATH\TO\PROFILE.XML» Interface=»YOUR-WIFI-ADAPTER-NAME» user=current
In the command, make sure to specify the location of the XML file and network interface name. For example, this command imports the xml profile located in the «Documents» folder to the Wi-Fi adapter: netsh wlan add profile filename=»C:\Users\m\Documents\wi-fi-tsunami.xml» Interface=»WI-FI» user=current.
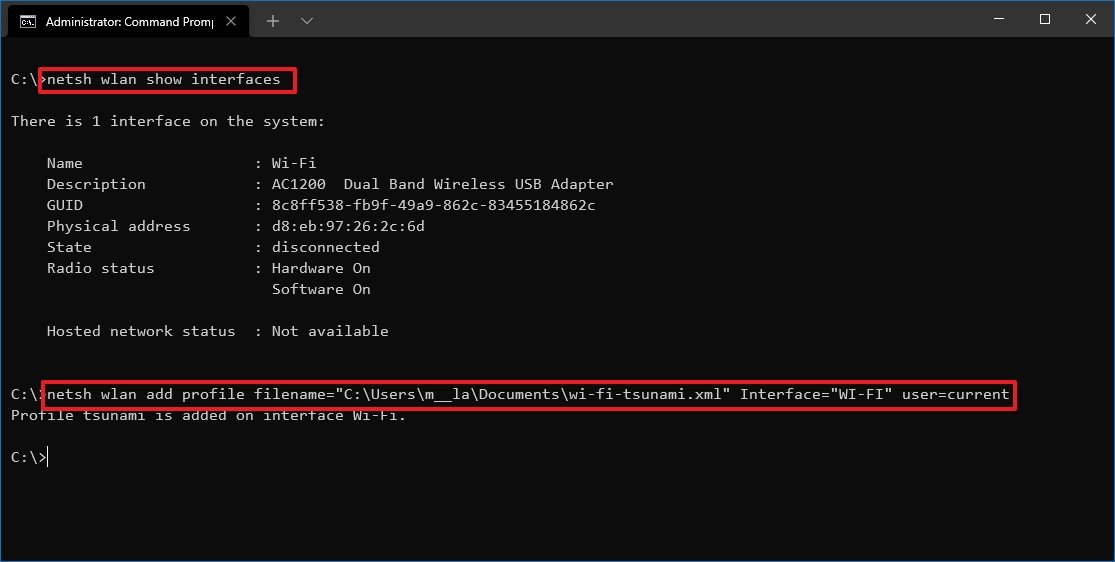
- Type the following command to connect to the wireless network and press Enter: netsh wlan connect ssid=YOUR-WIFI-SSID name=PROFILE-NAME
In the command, specify the SSID and profile name that corresponds to your network. For example, this command connects to an access point using the «tsunami» SSID and «tsunami» profile name: netsh wlan connect ssid=tsunami name=tsunami.
- Quick tip: If you have multiple wireless interfaces, you must also specify in the command which adapter you want to use. For example, netsh wlan connect ssid=YOUR-WIFI-SSID name=PROFILE-NAME interface=Wi-Fi.
After you complete the steps, the computer should connect to the wireless network automatically.
More Windows resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
ServerWatch content and product recommendations are editorially independent. We may make money when you click on links to our partners. Learn More.
Netsh is a command-line utility for configuring and monitoring the status of various network communication server roles and components on Windows Server computers. It helps users interact with the networking stack in Windows and control various network aspects, including Wi-Fi.
This article will demonstrate the usage of netsh commands for managing wireless networks in Windows 11. While some basic settings and functionalities can be managed using the Windows Network or the Control Panel, some tasks may require alternative steps. For such situations, Windows 11 users can use the netsh CLI to manage Wi-Fi settings and configurations.
How to Manage Wi-Fi Networks in Windows 11
To manage Wi-Fi networks in Windows 11, you first need to open the command prompt. Windows 11 provides two ways to use the netsh commands. You can either open the command prompt or netsh run command to initiate the netsh commands for wireless management.
The only difference between these two approaches is that you’ll have to use “netsh” before every command when using the command prompt.
Follow these steps to open the netsh run command.
- Click the search icon in the taskbar and enter “netsh” (without quotation marks) in the search box.
- Select Run as administrator, and the netsh command prompt will open.
To start managing Wi-Fi settings, you’ll want to get a clear view of the wireless profiles in Windows.
To do this, run the following netsh command to show the wireless network profiles.
wlan show profilesIf you’re using the command prompt, run the following command:
netsh wlan show profilesNow that you know how to view saved network profiles using the netsh command, let’s explore other commands to manage wireless networks in Windows 11.
Connect to the Wireless Network
To connect to the wireless network in Windows 11, run the following command:
wlan connect ssid=YOUR-WIFI-SSID name=PROFILE-NAMEFind the Security Key of the Network
If you want to retrieve the security key of your network, run this command:
wlan show profiles name=profile name key=clearCheck Network Interface Status
Here’s the command to check the network interface status of your wireless network:
interface show interfaceCheck All Available Wireless Connections
Run the following command to check all the available Wi-Fi connections:
wlan show networksDisconnect from the Connected Wireless Device
Run the following command to disconnected from the wireless device:
wlan disconnectDelete Wi-Fi Network Profiles
To delete a network profile, you can run the following command:
wlan delete profile name=profile nameAnalyze the Wireless Network Report
To analyze the wireless network report, you’ll need to run this command from the command prompt with administrator privileges:
Netsh wlan show wlanreportImport and Export Wi-Fi Network Files
You can’t modify network profiles in Windows directly. However, the wireless settings allow you to export a profile, make changes to its XML file, and then import it back to modify the profile settings without directly modifying the profile itself.
Export Wireless Network Files
Here’s the command to export wireless network files:
wlan export profile name=profile nameImport Wireless Network Files
You can then import them back in with this command:
wlan add profile filename=path_and_filename.xml interface=interface-nameStop Automatically Connecting to a Wi-Fi Network
Here’s the command to stop a device from automatically connecting to a network:
wlan set profileparameter name=profile name connectionmode=manualChange the Priority of Wi-Fi Networks
This command can rearrange connection priorities:
wlan set profileorder name=profile name interface=interface_name priority=1How to Create an Ad Hoc Wi-Fi Connection in Windows 11
A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) is a local area network (LAN) that can be established without traditional network infrastructure equipment such as a wireless access point or a router. It allows multiple wireless devices connecting each other instantly.
Windows 7, 8, 10, and 11 enable you to create WANETs. They are usually created temporarily to share files, presentations, or an internet connection among multiple devices. However, saving an ad hoc network profile for frequent use is also possible.
For this, your computer or laptop should have a wireless network adapter installed to create or join a WANET. Also, WANETs are wireless only, and devices connected to the network must be within 30 feet of range.
There are different ways to set up an ad hoc network in Windows 11. You can either create an ad hoc network through the Windows control panel or use the command prompt to run netsh commands.
Here, we will use the command prompt to create an ad hoc network on Windows 11.
Set the Ad Hoc Connection
Open the command prompt with administrator privilege and type the following command to configure your ad hoc network:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=network_name key=passwordReplace network_name with your desired ad hoc network and password with a secure password.
Start the Network
Once the network is created, run the following command to start the network:
netsh wlan start hostednetworkStop the Network
To stop the ad hoc network, run the following command:
netsh wlan stop hostednetworkRetrieve the Network
You can get the details of your ad hoc network by running the following command:
netsh wlan show hostednetworkModify the Network Details
To change the network details of the hosted wireless network, you can run this command:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork parameter parameter_name valueModify the Hosted Wireless Network’s Password
Run the following command to change the password of your wireless hosted network:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork key=new_passwordIf you want to check the new password, use this command for retrieving the wireless-hosted network mentioned above.
netsh wlan show profile name="Wi-Fi-Profile" key=clearTo enable internet access for users on this network via the Wireless Hosted Network, activate Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) first.
3 Top Tools for Network Configuration Management in Windows
Network configuration involves managing network settings, policies, and controls for devices connected to the network, as well as installing software and sharing internet connectivity.
In addition, network configuration management involves keeping track of any changes made to the configuration that may pose a security risk, system failure, or operational disruption. Network administrators use specialized software for network configuration management to mitigate these risks and to make bulk changes efficiently while minimizing the likelihood of errors.
Here are three of the top tools for network configuration management in Windows.
1. SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager
Best for customizability
SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager (NCM) is a very useful network configuration management tool for network administrators that enhances network reliability and security while saving time. The software manages changes, configurations, and compliance for various network devices from industry-leading manufacturers such as Cisco, HP, Dell, F5, Rukus, and others.
It’s an industry-leading solution for bulk configurations in mid-to-large businesses. It automates configuration backup and restores points, has multi-vendor capabilities, and has an automated alert system.
Pricing
Subscription-based pricing for SolarWinds NCM starts at $1,894, with a perpetual license starting at $3,671. You can get a quote for your particular use case. Subscription and perpetual licensing are available with a 30-day free trial option.
Pros
● Decreased troubleshooting time
● Software and hardware inventory tracking
● Easy-to-use dashboard
● Availability of audit module highlighting security compliance
Cons
● Administrators may face a learning curve
● High cost compared to other tools
2. ManageEngine NCM
Best for ease of use
ManageEngine NCM provides a comprehensive set of basic and advanced features that cater to organizations’ NCM needs. This tool facilitates efficient management of network devices and configurations while offering capabilities such as automated configuration backup, compliance management, and enhanced network security.
With its robust reporting capabilities, the tool helps companies generate insightful reports on changes, compliances, and inventory. Moreover, the monitoring and assessment capabilities of this tool allow businesses to track current changes, predict future changes, and prevent unexpected changes in the future.
Pricing
There is a free personal-use edition for two devices, a professional edition starting at $595 for 10 devices, and an enterprise edition starting at $8,395 for 250 devices. Custom-designed quoting options are available with a 30-day free trial period.
Pros
● Automated configuration backup is available
● Automatic scanning to detect unauthorized changes made
● Scalable platform
● Enhanced network stability
Cons
● The free version is limited to two devices only
3. Kiwi CatTools
Best for small businesses
SolarWinds Kiwi CatTools is a cost-effective yet robust network automation and configuration management tool designed to cater to the needs of small businesses. This tool provides a range of features that simplify device management, including a built-in Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server for scheduling backups, automated configuration change alerts and reports for analysis, and bulk configuration change capabilities that can be easily performed or reversed. Kiwi CatTools also offers the convenience of automated settings for a hassle-free experience.
In addition to these key features, Kiwi CatTools generates comprehensive HTML and text-based reports on basic configuration changes related to port, MAC, ARP, and other critical network parameters. These reports can be directly emailed to key stakeholders, facilitating streamlined communication and decision-making processes.
Pricing
A perpetual license costs $947 for unlimited devices after a 14-day trial.
Pros
● Reduced network downtime
● Execute bulk configuration reports
● Automated network backup
● Enhanced security
Cons
● Limited scripting capability
● Very basic UI
Bottom Line: Using Netsh Commands for Wi-Fi Management in Windows 11
Effective wireless network management is crucial for ensuring seamless connectivity and optimal performance of devices. With netsh commands, Windows 11 users can easily troubleshoot and manage their wireless network connections.
For IT departments needing greater depth and granularity, NCM tools like ManageEngine NCM and SolarWinds NCM provide powerful features that simplify device management, automate configuration changes, and generate detailed reports for analysis.
Take a deep dive into configuration management with our complete guide.

Максим aka WisH
Высшее образование по специальности «Информационные системы». Опыт работы системным администратором — 5 лет.
Задать вопрос
Через беспроводные сети работает много разного оборудования. К вайфаю подключаются компьютеры, телефоны, телевизоры и даже некоторая бытовая техника. Проблемы возникают в том случае, когда перестает работать роутер и нет возможности его быстро починить. В качестве временного решения создать беспроводную сеть на основе компьютера, всего одна команда «netsh wlan start hostednetwork» позволит запустить раздачу вайфай, а дальше её потребуется настроить.
Содержание
- Немного о наборе команд netsh
- Правильный запуск командной строки
- Проверка беспроводного адаптера
- Настройка точки доступа средствами Windows
- Создание
- Запуск сети и остановка
- Раздача интернета
- Автоматизация ввода
- Другие полезные способы применения команд netsh
- Решение проблем
Немного о наборе команд netsh
Утилита сетевой оболочки NETSH (NETwork SHell) появилась еще в Windows XP и с того времени этот набор команд переходит из системы в систему с некоторыми изменениями синтаксиса. Сама утилита является одним из лучших инструментов управления сетью и сетевыми адаптерами, которые только доступны в Windows 10 или Windows 7.
При использовании утилиты не придется использовать приложения из неизвестного источника. Это повышает вероятность правильной работы точки доступа и убирает шанс на получение вируса.
С помощью утилиты NETSH можно раздать Wi-Fi, настроить интернет, управлять сетевым адаптером, задавая для него несколько пакетов сетевых настроек. Доступно создание своей точки доступа и её настройка, управление фаерволлом и многое другое. Только обычный пользователь редко сталкивается с командной строкой, а еще реже использует встроенные утилиты из неё. Сегодня поговорим о настройке беспроводной сети и о самой утилите NETSH.
Правильный запуск командной строки
Перед работой с утилитой следует запустить командную строку. Некоторые путают стандартную консоль с PowerShell, который тоже активно начал использоваться, начиная с семерки. В десятке же вообще большинство работы ведется через него. В нем тоже можно запускать подобные команды, но мы остановимся на работе с консолью. Для того, чтобы устранить все недопонимания, расскажем как правильно открыть командную строку для настройки сети.
Командную строку запускайте от имени администратора, чтобы избежать проблем с применением команд.

Для разных версий виндовс алгоритм действий различается, но есть способ, подходящий для всех систем, начиная с семерки. Нажмите на меню Пуск, щелкните по нижней строке, которая служит для поиска информации. Напишите в ней «cmd», подождите, пока компьютер найдет требуемую программу и покажет её в списке. Теперь нажмите на неё правой кнопкой мыши и выберите из выпавшего меню «Запустить от имени администратора».
Запуск консоли с соответствующими правами позволит избежать проблем в будущем. Иногда для применения команд требуется изменение каких-то системных настроек или файлов, без разрешения администратора это сделать не получится. Будет обидно, если на середине настройки консоль начнет писать ошибки и отказы из-за недостатка прав.
Проверка беспроводного адаптера
Теперь перейдем к проверке возможностей вашего компьютера. Запустите консоль так, как рассказывали выше, а потом начинайте печатать команды по одной. Сначала вводите «ipconfig /all». В этом же окне отобразится информация о всех интерфейсах подключения и о том, активны они или нет. Здесь будет и кабельное подключение, и другие, если они есть.

Вторая команда звучит так: netsh wlan show interface. Эта команда покажет только беспроводной интерфейс. В этом окне узнаете его название, подключенную беспроводную сеть, скорость и некоторую другую информацию.

Теперь пишем третью команду: netsh wlan show driver. С помощью этой команды получится узнать установленный драйвер у беспроводного модуля, а также поддерживаемые им стандарты. Лучше проверьте на сайте разработчика, нет ли новых драйверов. Это важно при создании точки доступа из компьютера.

Посмотрите на раздел «Поддержка размещенной сети», если там стоит «Нет», то адаптер не поддерживает создание точки доступа. Попробуйте обновить драйвер, если не получилось, то остается использовать другой адаптер.
Настройка точки доступа средствами Windows
Теперь перейдем к самой настройке будущей беспроводной сети. Создать точку доступа из компьютера или ноутбука можно несколькими способами. Есть сторонние программы, которые почти всю работу сделают за вас, потребуется только ввести имя и пароль. С ними просто работать, но они отнимают много ресурсов от компьютера. Это заметно на слабых системах, из которых обычно и создают локальные точки доступа.
Второй способ заключается в использовании стандартных средств системы. Как раз мы разобрались, как можно запустить консоль, чтобы она правильно работала. Этот способ потребует чуть больше времени на настройку, а также некоторое время на то, чтобы разобраться с тем, как все это работает. Зато он менее затратен по системным ресурсам.
Создание
Не забудьте открыть консоль, перед тем как начинать настройку. Первым делом набирайте: «netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=”Имя сети” key=”Пароль” keyUsage=persisten». Только укажите свое название сети и пароль. Выставьте те, которые вам удобнее запоминать или вводить. Если поставите mode=disallow, то это отключит поддержку размещенной сети.

Теперь вводим «netsh wlan start hostednetwork», она запустит сеть в работу. После этого можно будет перейти к настройке самой сети. Полностью настройку выполнить через консоль не получится, некоторые вещи потребуется сделать из панели управления.
Запуск сети и остановка
Запуск и остановка сети выполняются через консоль. Хотя, иногда можно использовать стандартные средства, доступные в панели управления для включения и отключения адаптера. Команда для включения уже известна – это «netsh wlan start hostednetwork».
Для отключения стоит поменять одно слово, получится «netsh wlan stop hostednetwork». Введите команду, дождитесь окончания её применения, в самой консоли текстом отобразится результат выполнения операции. В случае проблем сможете узнать из-за чего возникла ошибка.
Еще пара слов про команды, которые могут потребоваться для включения и отключения точки доступа. Ввод команды «netsh wlan set hostednetwork allow» позволит включить поддержку размещенной сети, а «netsh wlan set hostednetwork disallow» послужит для отключения. Такие команды пригодятся, если потребуется отключить всех остальных абонентов от раздаваемой сети, чтобы что-то сделать на самом компьютере.
Раздача интернета
Сейчас у нас имеется созданная и включенная сеть, но сама она к интернету не подключена. Дальнейшие действия будут совершаться с помощью системных средств, но уже не в командной строке. Сначала потребуется перейти в настройки сети. Перейдите в Панель управления, далее в «Сеть и интернет», выберите “Центр управления сетями и общим доступом”, выберите «Изменение параметров адаптера». Откроется окно со всеми доступными подключениями.

Найдите то подключение, которое используется для доступа в интернет. Обычно это кабельное соединение. Щелкните по нему правой кнопкой мыши, выберите из выпавшего меню «Свойства». Открывается новое окно, в верхней части которого есть две вкладки, выберите вкладку с названием «Доступ». Поставьте галку в верхнем пункте «Разрешить другим пользователям использовать подключение к интернету данного компьютера».
Внизу откроется еще одна строка, в которой вам нужно указать ваш созданный адаптер. Также еще ниже поставьте галку, в которой другим подключениям разрешается управлять этим подключением. Далее нажмите на «Ок» и подождите завершения применения настроек. Теперь перезагрузите компьютер или перезапустите созданную виртуальную сеть.
Автоматизация ввода
Сеть придется запускать после каждого выключения компьютера или его перезагрузки. В некоторых случаях это потребуется для нормальной работы устройств, а в других случаях причиной будет зависание самой раздачи. Все действия совершаются через командную строку, что не очень удобно. Если вы поняли, что придется часть использовать какую-то команду или же потребуется часто регулировать настройки, то создайте файл для автоматизации процесса.
Если запускать точки доступа нужно всегда после включения компьютера, то добавьте созданный файл в автозагрузку. Нажмите клавишу с логотипом Windows + R, напечатайте shell:startup, кликните по «Ок». Откроется папка, в неё переместите созданный файл, отвечающий за запуск точки доступа.

Откройте блокнот. Наберите в блокноте те команды, какие хотите применить. Например, для включения сети достаточно команды «netsh wlan start hostednetwork». Введите её, нажмите на «Файл», потом на «Сохранить как». Откроется окно с сохранением. Введите имя файла, а после имени не забудьте приписать расширение .bat.
После этого переместите файл в любое удобное место. Кликните по нему два раза, чтобы запустить команду. После открытия файла появится командная строка, в которой будет прописана команда. В ней же покажут результат выполнения, после чего она автоматически закроется. Для всех созданных файлов проделайте следующую процедуру: кликните по ним правой кнопкой, выберите «Свойства», откройте вкладу «Совместимость» и поставьте галку о запуске от имени администратора.
Другие полезные способы применения команд netsh
Теперь поговорим еще о нескольких полезных возможностях утилиты netsh:
- netsh interface tcp show global. Показывает список параметров TCP, в котором узнаете включенные и отключенные функции. Например, здесь можно посмотреть включена или отключена функция автотюнинга. Она отвечает за повышение скорости обмена информацией, но иногда из-за сбоев начинает наоборот замедлять работу.
- netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled. Отключается функцию автотюнинга, используйте для проверки корректности её работы. Для включения опции поменяйте последнее слово на normal.
- Netsh wlan disconnect – отключает компьютер от текущего беспроводного подключения.
- netsh winhttp set proxy proxy-server=”адрес прокси:порт” – устанавливать прокси в указанное значение для подключения.
Далее перечислим все возможные команды для этой утилиты.
| Команда | Отображение списка команд | Пример ввода | Что делает команда |
| add | Добавление нового пункта | netsh add sslcert [ ipport= ] | Добавляет SSL-сертификат |
| advfirewall | Уровень настройки и изменения фаерволла в новом синтаксисе | netsh advfirewall firewall add rule | Добавление нового правила |
| branchcache | Настройка branchcache, отвечающего за пропускную способность | netsh exportkey branchcache [ outputfile = ] FilePath [ парольная фраза = ] | Экспорт файла ключа |
| bridge | Уровень настройки моста | netsh bridge show adapter | Показывает адаптеры, задействованный в организации моста |
| delete | Используется для удаления | netsh delete sslcert [ ipport= ] | Удаляет ssl-сертификат |
| dhcpclient | Используется для настройки DHCP | netsh DHCP client Enable | Включает DHCP |
| dnsclient | Позволяет задать параметры DNS | netsh dnsclient set dnsservers [name=] [source=]dhcp|static | Устанавливает указанные dns сервера |
| dump | Создает сценарий в конфигурации | netsh dump | |
| exec | Позволяет запустить на выполнение сценарий | netsh exec | Укажите путь до файла сценария утилита выполнит его |
| firewall | Вторая команда для настройки фаерволла, в разных версиях утилиты используются разные команды уровня | netsh firewall firewall add rule | Команда для добавления правилф фаерволла с устаревшим синтаксисом. Использовалась до Windows Server 2012 |
| help | Показывает полный список доступных команд | netsh help | |
| http | Для настройки http | netsh http add urlacl url=http://server1:1234/ | Добавление адреса в файл http.sys |
| interface | Для настройки одного из интерфейсов, людям привычнее называть это «портом» или «адаптером» | netsh interface ip set address local static | Устанавливает указанный статический адрес для порта |
| ipsec | Используется для настройки ipsec | netsh ipsec show all | Показывает все установленные политики |
| lan | Служит для настройки проводной сети | netsh lan add profile filename=путь до файла профиля interface=Имя интерфейса | Добавляет новый интерфейс для LAN |
| mbn | Настройка на уровне ‘netsh mbn’ | netsh mbn add dmprofile [interface=] [name=] | Добавление нового подключения через широкополосный мобильный интернет |
| namespace | Настройка пространства имен и связанных объектов | Netsh namespace SampleNamespace; class{} | Позволяет создавать и настраивать классы |
| nap | Настройка клиента защиты доступа к сети | netsh nap reset | Сбрасывает текущую конфигурацию |
| p2p | Настройка p2p(peer-to-peer) | netsh p2p group | Группировка пиров, для их последующей настройки |
| ras | Настройка ras(маршрутизация и удаленный доступ) | netsh ras show client | Показывает список клиентов, удаленно подключенных к этому компьютеру |
| rpc | Настройка rpc(удаленный вызов процедур) | netsh rpc add filter | Добавляет новый фильтр для вызова процедур |
| set | Установка параметров и их обновление | netsh interface ipv4 set address name=”LAN” static 10.253.0.35 | Используется в других командах для установки каких-то параметров |
| show | Отображение данных о подключении | В разных командах для отображения списка каких-то значений | |
| trace | Служит для анализа сетевого трафика | netsh trace start | Начинает анализ сетевого траффика |
| wfp | Диагностика подключения | netsh wfp show netevents | Показывает недавние события в сети |
| winhttp | Настройка winhttp, трафика, идущего через это протокол | netsh winhttp set proxy proxy-server | Установка прокси-сервера |
| winsock | Настройка способов взаимодействия приложений, работающих через один из интерфейсов | netsh winsock reset | Сбрасывает все текущие протоколы взаимодействия |
| wlan | Настройка беспроводного подключения | netsh wlan start hostednetwork | Запуск сети вай фай |
Решение проблем
При настройке сети могут возникать проблемы. Обычно они бывают следующие:
- Проблемы с созданием сети. Проверьте версию драйвера вашего адаптера, посмотрите, что он вообще может работать на передачу. Проверьте, что при настройке запустили консоль от имени админа.
- Сеть получилось создать, но команда запуска выдает ошибку. Перезагрузите компьютер. Проверьте, что консоль запускаете так, как рассказывали.
- Не получается подключится к созданному и запущенному вайфай. Проверьте правильность введенного пароля. Проверьте, что установили то, что хотели при настройке точки доступа. Можно попробовать вручную прописать клиента на сервере и наоборот, но в этой ситуации это не лучший выход.
- Есть подключение к вайфай, а интернет не работает. Проверьте, что вы сделали доступным для всех то подключение, через которое идет интернет к ноутбуку или компьютеру. Проверьте, что вписали имя DNS-сервера в своем подключении.
Попробуйте использовать следующие команды:
- netsh int ip reset c:\reset.log – сбросит все настройки TCP/IP будьте готовы ввести их заново.
- netsh advfirewall reset – сбросит настройки фаерволла до стандартных. Поможет, если что-то накрутили в самом фаерволле.
- ipconfig /flushdns;
- ipconfig /registerdns;
- ipconfig /release;
- ipconfig /renew;
- netsh winsock reset.
Последний набор команд почистит кэш и сбросит все возможные настройки. Если и это не поможет, то останется только задуматься о том, чтобы использовать какую-то стороннюю программу. Или о том, что у вас неисправен сам модуль беспроводной связи из-за чего к нему никто не может подключиться.
На этом разбор способа создания точки доступа из компьютера закончен. Помните, что беспроводные модули не предназначены для создания таких точек, из-за чего их радиус покрытия будет невелик, а скорость может оказаться меньше заявленной. Тем не менее, создание такой точки решит проблему отсутствия маршрутизатора и позволит протянуть какое-то время. Использовать для создания точек сторонние программы или консольные команды, решать вам. Помните о преимуществах и недостатках обоих методов.

