From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This page provides details for the version history of the Microsoft’s Windows Phone branded mobile operating systems, from the release of Windows Phone 7 in October 2010, which was preceded by Windows Mobile version 6.x.
Windows Phone 7 was the first release of the Windows Phone mobile client operating system, released worldwide on October 21, 2010, and in the United States on November 8, 2010.
| Table of versions: Windows Phone 7 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Changes |
| 7.0.7004 | October 29, 2010 |
|
| 7.0.7008 | 2010 |
|
| 7.0.7390 (NoDo) | March 22, 2011[1] |
|
| 7.0.7392 | 2011 |
|
| 7.0.7403 | 2011 |
|
| Version | Release date | Changes |
Windows Phone 7.5 (Mango)
[edit]
At the 2011 Mobile World Congress, Steve Ballmer announced a major update to Windows Phone 7 due toward the end of the year, Windows Phone 7.5, codenamed Mango.[2] The new OS would address many of the platform’s shortcomings, including a mobile version of Internet Explorer 9 that supports the same web standards and graphical capability as the desktop version, multi-tasking of third-party apps,[3][4] Twitter integration for the People Hub,[5][6][7] and Windows Live SkyDrive access.[8] Although the OS internally identifies itself as version 7.1, it is marketed as version 7.5 in all published materials intended for end-users.[9][10]
Microsoft started rolling out Windows Phone 7.5 to both the United States[11] and International[12] markets on September 27, 2011. The first phones that came pre-loaded with Windows Phone 7.5 were released in the last quarter of 2011.
A minor update released in 2012 known as Tango, along with other bug fixes, would also lower the hardware requirements to allow for devices with 800 MHz CPUs and 256 MB of RAM to run Windows Phone. Certain resource-intensive features are also disabled on these phones, and the Windows Phone Store will also prevent the installation of apps that are considered to be too intensive for use on weaker hardware.[13] The lower requirements were adopted in order to allow the development of lower-cost devices, particularly to target emerging markets such as China.[14]
| Table of versions: Windows Phone 7.5 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Changes |
| 7.10.7720 (Mango) | September 27, 2011 |
|
| 7.10.7740 | 2011 |
|
| 7.10.8107 (Refresh) | 2011 |
|
| 7.10.8112 | 2012 |
|
| 7.10.8773.98 (Tango) | June 28, 2012 |
Also confirmed are 23 additional markets[35] including; Bahrain, Bulgaria, China, Costa Rica, Croatia, Estonia, Iceland, Iraq, Israel, Kazakhstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Qatar, Romania, Saudi Arabia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Thailand, Turkey, UAE, Ukraine, Venezuela and Vietnam. This update will also include a Skype application. |
| 7.10.8779.8 |
|
|
| 7.10.8783.12 |
|
|
| Version | Release date | Changes |
Windows Phone 7.8 is the final major release of Windows Phone 7. It consists exclusively of user interface improvements backported from Windows Phone 8, as existing Windows Phone 7 devices can not be upgraded to due to changes to its architecture and hardware requirements. These include a home screen with the ability to resize live tiles, new accent color options, and an updated lock screen with support for Bing wallpapers. Unlike Windows Phone 8, the lock screen does not allow third-party apps to display notifications on it.[37][38]
| Table of versions: Windows Phone 7.8 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Changes |
| 7.10.8858.136 | February 1–2, 2013 |
|
| 7.10.8860.142 | March 14, 2013 |
|
| 7.10.8862.144 | March 14, 2013 |
|
| Version | Release date | Changes |
General Distribution Release 1, a minor update known as Portico was rolled out in December 2012 that brought some improvements and bugfixes, including enhancements in Messaging, more efficient Bluetooth connectivity, and an «always-on» setting for WiFi connections, among other additional platform updates
Microsoft rolled out a package of minor updates called General Distribution Release 2, beginning in July 2013 and spanning the following months, depending on the manufacturer and carrier. Along with this update Nokia released its own update which updated the firmware of the user, namely Lumia Amber, which was available for only Lumia phones. The update brought many camera improvements and fixed some bugs in the cameras of existing Lumia phones.
On October 14, 2013, Microsoft released the third General Distribution Release update for Windows Phone 8, which would roll out to phones over the following months. Windows Phone Developers were among the first to receive the update under a new Developer Preview Program.
| Table of versions: Windows Phone 8 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Highlights |
| 8.0.9903.10 (Apollo) |
October 29, 2012 |
|
| 8.0.10211.204 (GDR1) |
December 11, 2012 |
|
| 8.0.10327.77
8.0.10328.78 |
July 12, 2013 |
|
| 8.0.10512.142 8.0.10501.127 8.0.10517.150 8.0.10521.155 (GDR3) [41][42] |
October 14, 2013[43] |
|
| 8.0.10532.166 | April 14, 2014 |
|
| Version | Release date | Highlights |
General Distribution Release 1 (GDR1; also referred to as Update 1) adds new language and region support for Cortana, the option to organize apps into folders on the Start Screen, SMS forwarding of multiple messages, improvements to Xbox Music, a live tile for the Windows Phone Store and an option for sandboxing applications. In addition, Update 1/GDR1 also includes new VPN and Bluetooth features for enterprise users, as well as support for interactive cases such as HTC’s «Dot View» case, larger «phablet» screen resolutions such as 1280×800, 540×960 qHD and 1280×768 and the Qualcomm QuickCharge 2.0 standard.[44][45]
Microsoft has made several changes to Internet Explorer Mobile that brings the browser experience closer in line with the experiences on Safari (iOS) and Chrome (Android). To accomplish this, Microsoft moved away from open standards and adopted non-standard features used in Safari and Chrome, implemented browser detection, improved page rendering by detecting legacy WebKit features, brought support for HTML5, and fixed interoperability issues with bad HTML code.[46]
- IE11 on Windows Phone 8.1:
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows Phone 8.1; ARM; Trident/7.0; Touch; rv:11; IEMobile/11.0; NOKIA; Lumia 928) like Gecko
- IE11 on Windows Phone 8.1 with Update 1/GDR1:
Mozilla/5.0 (Mobile; Windows Phone 8.1; Android 4.0; ARM; Trident/7.0; Touch; rv:11.0; IEMobile/11.0; NOKIA; Lumia 720) like iPhone OS 7_0_3 Mac OS X AppleWebKit/537 (KHTML, like Gecko) Mobile Safari/537
Information regarding GDR2 (also referred to as Update 2) was released in February 2015 it was revealed that Microsoft was working on a 2nd update for Windows Phone 8.1 that would provide increased security for OEM’s, add extra languages and additional technology support and is also reported to bring an anti-theft mode.[49]
| Table of versions: Windows Phone 8.1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Version | Release date | Highlights |
| 8.10.12359.845 (Blue) |
April 14, 2014 | User Interface
General user experience changes
New technology support
Internet Explorer 11
Apps
System
Enterprise
Developer features
|
| 8.10.12382.878 | May 14, 2014 |
|
| 8.10.12393.890 | June 2, 2014 |
|
| 8.10.12397.895 | June 12, 2014 |
|
| 8.10.12400.899 | July 16, 2014 | |
| 8.10.14141.167 | ||
| 8.10.14147.180 (GDR1) [54][55] |
August 4, 2014 | Apps
General user experience changes
New technology support
Enterprise
OEM
|
| 8.10.14157.200 | August 19, 2014 |
|
| 8.10.14176.243 | September 24, 2014 |
|
| 8.10.14192.280 | October 24, 2014 |
|
| 8.10.14203.306 | November 13, 2014 |
|
| 8.10.14219.341 | December 5, 2014 |
|
| 8.10.14226.359 | December 24, 2014 |
|
| 8.10.14234.375 | February 24, 2015 |
|
| 8.10.15116.125 (GDR2) [57] |
March 2, 2015 | General user experience changes
New technology support[61]
Security features
|
| 8.10.15127.138 | March 2015 |
|
| 8.10.15135.146 | March 2015 | |
| 8.10.15137.148 | March 2015 | |
| 8.10.15143.154 | April 2015 | |
| 8.10.15145.156 | April 2015 | |
| 8.10.15148.160 | May 2015 |
|
| 8.10.15153.165 | June 2015 | |
| 8.10.15155.167 | July 2015 | |
| 8.10.15156.168 | January 2016 | |
| 8.10.15165.177 | August 2016 | |
| 8.10.15172.184 | March 2017 |
|
| 8.10.15176.188 | December 2017 |
|
| 8.10.15185.197 | November 2018 |
|
| 8.10.15191.203 | June 2019 |
|
| Version | Release date | Highlights |
Windows 10 Mobile was announced on January 21, 2015, as a mobile operating system for smartphones and tablets with screens smaller than 8 inches, with the first build released on February 12, 2015.[66] It is the successor to Windows Phone 8.1[67] and replaced the Windows Phone brand, while Microsoft has since ceased active development of Windows 10 Mobile. Windows Phone 8.1 devices were eligible for upgrade to Windows 10, pursuant of manufacturer and carrier support.[68] Some features may have varied depending on hardware compatibility.[69]
- Android version history
- BlackBerry 10 version history
- Firefox OS version history
- iOS version history
- Palm OS version history
- Sailfish OS version history
- Symbian version history
- Tizen version history
- ^ Warren, Tom. «Windows Phone 7 «NoDo» update now available». WinRumors. Archived from the original on July 25, 2014. Retrieved April 5, 2014.
- ^ Shankland, Stephen (February 15, 2011). «Windows Phone 7 update to offer IE9». ZDNet. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on October 15, 2011. Retrieved March 24, 2011.
- ^ Stevens, Tim (February 14, 2011). «Windows Phone 7’s multitasking uses zoomed-out cards to check on your apps». Engadget. AOL. Archived from the original on February 17, 2011. Retrieved March 24, 2011.
- ^ Cha, Bonnie (February 14, 2011). «Multitasking, IE9 coming to Windows Phone». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on April 26, 2012. Retrieved March 24, 2011.
- ^ Bright, Peter (February 14, 2011). «Windows Phone 7’s future revealed: multitasking, IE9, Twitter». Ars Technica. Condé Nast Digital. Archived from the original on October 18, 2011. Retrieved October 27, 2011.
- ^ Mathews, Lee (February 14, 2011). «Windows Phone 7 update to bring Twitter and SkyDrive integration, webOS style multitasking». Switched. AOL. Archived from the original on July 7, 2012. Retrieved October 27, 2011.
- ^ Stevens, Tim (February 14, 2011). «Windows Phone 7’s multitasking uses zoomed-out cards to check on your apps». Engadget. AOL. Archived from the original on February 17, 2011. Retrieved March 24, 2011.
- ^ Ponder, George (February 14, 2011). «New features heading to Windows Phone 7: Multi-tasking, IE9, Skydrive and more». WPCentral.com. Mobile Nations. Archived from the original on January 6, 2012. Retrieved October 27, 2011.
- ^ Devereux, William (July 27, 2011). «Windows Phone Mango officially branded 7.1, marketed as 7.5». Anything But iPhone. Archived from the original on October 16, 2011. Retrieved August 23, 2011.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (July 27, 2011). «Microsoft gives Windows Phone developers a refreshed (non-RTM) Mango build». ZDNet. Archived from the original on October 2, 2011. Retrieved August 23, 2011.
- ^ «The Smartphone Reinvented Around You — Windows Phone (USA)». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 30, 2011. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ «The Smartphone Reinvented Around You — Windows Phone (United States)». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 2, 2012. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ Warren, Tom (March 8, 2012). «Microsoft details full Windows Phone ‘Tango’ 256MB RAM device limitations». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on July 1, 2012. Retrieved June 20, 2012.
- ^ Warren, Tom (February 27, 2012). «Windows Phone 7.5 update will support 256MB RAM and slower processors in April». The Verge. Vox Media. Archived from the original on July 5, 2012. Retrieved June 21, 2012.
- ^ Miller, Matthew (June 20, 2011). «Hands-on with Windows Phone 7.5 Mango technical preview». zdNet. Archived from the original on June 23, 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ Adhikari, Richard (May 24, 2011). «WP7 Visual Voicemail». TechNewsWorld. Archived from the original on March 18, 2012. Retrieved June 14, 2011.
- ^ Devereux, William (May 24, 2011). «Bing on Windows Phone Mango Revolutionizes Mobile Search». Anything but iPhone. Archived from the original on February 16, 2015. Retrieved February 15, 2015.
- ^ Nguyen, Vincent (June 20, 2011). «Windows Phone 7.1 Mango Technical Preview». SlashGear. Archived from the original on June 22, 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ Lein, Adam Z (August 28, 2011). «Why Windows Phone Mango Can’t Edit Older Office Documents». Pocketnow. Archived from the original on January 26, 2012. Retrieved May 4, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k «What’s new in Pictures + Camera for Mango». Archived from the original on May 5, 2012. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ Toor, Amar (August 25, 2011). «Microsoft: front facing cameras, Skype integration coming with Mango update». Engadget. Archived from the original on September 25, 2011. Retrieved August 25, 2011.
- ^ Cha, Bonnie; Dolcourt, Jessica (June 20, 2011). «Hands-on with Windows Phone 7.5 Mango technical preview». cNet. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ Bishop, Todd (August 17, 2011). «Windows Phone games: Details on Microsoft’s ‘Fast Async’ service — GeekWire». GeekWire. Archived from the original on March 24, 2012. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ «Is Find on Page feature being removed from IE9 Mango?!». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 22, 2012. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ Buckley, Sean (August 24, 2011). «Mango teaches Windows Phone to share, probably still needs carrier permission». Engadget. Archived from the original on September 25, 2011. Retrieved August 24, 2011.
- ^ Lein, Adam Z (June 21, 2011). «The Ultimate Windows Phone 7.5 Mango Preview». PocketNow. Archived from the original on June 23, 2011. Retrieved June 23, 2011.
- ^ «Samsung Focus Alarm Now Too Loud?». October 5, 2011. Archived from the original on October 15, 2011. Retrieved October 26, 2011.
- ^ «Mango Changed my Alarm Snooze interval???». October 17, 2011. Archived from the original on February 27, 2012. Retrieved October 26, 2011.
- ^ «Additions in the Windows Phone SDK 7.1». Msdn.microsoft.com. March 23, 2012. Archived from the original on May 10, 2012. Retrieved May 30, 2012.
- ^ Warren, Tom (November 17, 2011). «Windows Phone Update». winrumors. Archived from the original on November 19, 2011. Retrieved November 17, 2011.
- ^ Warren, Tom (January 4, 2012). «Windows Phone update rolling out, fixes disappearing keyboard and location privacy bugs». The Verge. Archived from the original on January 8, 2012. Retrieved January 4, 2012.
- ^ Rubino, Daniel (April 2012). «Nokia readies Lumia 710 Mango OS update for China». WPcentral.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b Rubino, Daniel (July 2012). «Some new undocumented features of Windows Phone mango». WPcentral.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Ajgekar, Aviraj (May 2012). «HTC Mozart: Windows Phone Update from 7.10.8107 to 7.10.8112.7 to 7.10.8773.98 to 7.10.8779.8 !!». Aviraj Ajgekar Blog.
- ^ Belfiore, Joe (February 2012). «Get Ready for 60% More Potential Customers». Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 26, 2012. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ Myerson, Terry (February 2012). «Windows Phone at Mobile World Congress 2012». Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 15, 2012. Retrieved April 18, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Phone 7.8 hands-on: cosmetically yours». Engadget. February 3, 2013. Retrieved November 26, 2022.
- ^ Welch, Chris (November 28, 2012). «Microsoft says Windows Phone 7.8 update coming in ‘early 2013’«. The Verge. Retrieved November 26, 2022.
- ^ a b «Windows Phone 7.8 Problems: Data-Draining Live Tiles, Lumia Audio Issues | Pocketnow». Pocketnow. February 4, 2013. Archived from the original on February 8, 2013. Retrieved February 5, 2013.
- ^ «Windows Phone 8 update history». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 30, 2012. Retrieved December 20, 2012.
- ^ a b «Windows Phone 8 update history». windowsphone.com. Windows Phone How-to (United States). Archived from the original on December 30, 2012. Retrieved December 20, 2012.
- ^ «Introducing Windows Phone Preview for Developers». Building Apps for Windows. Archived from the original on October 15, 2013. Retrieved October 14, 2013.
- ^ «Announcing our third Windows Phone 8 update—plus a new developer preview program». Blogging Windows. Archived from the original on October 17, 2013. Retrieved October 14, 2013.
- ^ Rubino, Daniel (July 30, 2014). «Microsoft reveals Update 1/GDR1 for Windows Phone 8.1, due next week for Preview users | Windows Phone Central». Wpcentral.com. Archived from the original on August 25, 2014. Retrieved August 21, 2014.
- ^ Belfiore, Joe (July 30, 2014). «Windows Phone 8.1 Update brings Cortana to new markets + new featuresBlogging Windows». Blogs.windows.com. Archived from the original on July 30, 2014. Retrieved August 21, 2014.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (July 31, 2014). «Windows Phone 8.1 Update 1/GDR1: Internet Explorer | Windows Phone content from Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows». Winsupersite.com. Archived from the original on August 8, 2014. Retrieved August 21, 2014.
- ^ «The Mobile Web should just work for everyone». blogs.msdn.com. Microsoft. August 1, 2014. Archived from the original on August 4, 2014. Retrieved December 18, 2014.
- ^ «User-agent string changes». msdn.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 18, 2014. Retrieved December 18, 2014.
- ^ Surur, Suril (February 16, 2015). «Windows Phone 8.1 GDR2 goes to OEMs, may bring anti-theft mode». Windows Mobile PowerUser. Archived from the original on February 16, 2015. Retrieved February 15, 2015.
- ^ «Windows Phone 8.1 Review | Windows Phone Central». April 14, 2014. Archived from the original on April 18, 2014. Retrieved April 20, 2014.
- ^ «Cortana (yes!) and Many, Many Other Great Features coming in Windows Phone 8.1». Blogging Windows. Archived from the original on April 4, 2014. Retrieved April 20, 2014.
- ^ a b c «Windows Phone 8.1 Review | Windows Phone Central». April 14, 2014. Archived from the original on April 20, 2014. Retrieved April 20, 2014.
- ^ Molen, Brad (April 14, 2014). «Windows Phone 8.1 review: Microsoft’s mobile OS finally feels whole». Engadget. AOL. Archived from the original on July 24, 2017. Retrieved September 18, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Phone 8.1 Update brings Cortana to new markets + new features». Blogging Windows. Archived from the original on July 30, 2014. Retrieved July 30, 2014.
- ^ a b «2.9: Notification — Windows Phone Hardware Development». windowsphone.com. Archived from the original on August 26, 2014. Retrieved August 24, 2014.
- ^ «MSDN Blogs». msdn.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 4, 2014. Retrieved July 31, 2014.
- ^ «Windows Phone 8.1 GDR2 — Windows Phone Hardware Development». windowsphone.com. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 12, 2015.
- ^ «Here is another unannounced Windows Phone 8.1 Update 2 feature — WMPoweruser». WMPoweruser. March 31, 2015. Archived from the original on April 2, 2015. Retrieved March 31, 2015.
- ^ «Settings gets a visual refresh in Windows Phone 8.1 Update 2 | Windows Central». March 2, 2015. Archived from the original on March 3, 2015. Retrieved March 2, 2015.
- ^ a b «Hands on with Windows Phone 8.1 Update 2». WMPoweruser. March 2, 2015. Archived from the original on March 4, 2015. Retrieved March 2, 2015.
- ^ «The Official Bluetooth SIG Member Website». bluetooth.org. Archived from the original on February 7, 2015. Retrieved February 15, 2015.
- ^ Rubino, Daniel (April 20, 2015). «Windows Phone 8.1 Update 2 also brings MKV video support». Windows Central. Archived from the original on April 28, 2015. Retrieved April 29, 2015.
- ^ «Reset protection | Windows Phone Hardware Development». Archived from the original on April 16, 2015. Retrieved April 8, 2015.
- ^ «Protect my Windows Phone | Windows Phone How-to (United States)». Archived from the original on May 11, 2015. Retrieved May 6, 2015.
- ^ «New software update for Lumia 640 & Lumia 640 XL: — Microsoft Community». Archived from the original on October 2, 2016. Retrieved September 28, 2016.
- ^ «Announcing the first build of Windows 10 Technical Preview for Phones». blog.windows.com. Gabe Aul. February 12, 2015. Archived from the original on February 13, 2015. Retrieved February 12, 2015.
- ^ «Windows Phone 10 to be called just Windows 10». GSMArena. Archived from the original on February 14, 2015. Retrieved February 11, 2015.
- ^ Bright, Peter (January 24, 2015). «Every Windows Phone 8 phone will get Windows 10, except the ones that won’t». Ars Technica. Archived from the original on July 8, 2017. Retrieved June 15, 2017.
- ^ «Yes, Windows 10 is Coming to Low-End Windows Phones». thurrot.com. Petri. February 9, 2015. Archived from the original on February 11, 2015. Retrieved February 11, 2015.
Материал из РУВИКИ — свободной энциклопедии
| Windows Mobile | |
|---|---|
| Скриншот версии Windows Mobile 6.5.3 |
|
| Разработчик | Microsoft |
| Семейство ОС | Windows CE |
| Основана на | Windows CE |
| Исходный код | Закрытый |
| Первый выпуск | 19 апреля 2000 года[1] |
| Последняя версия | 6.5.3 (2 февраля 2010 года[2]) |
| Метод обновления | AKU, официальные прошивки |
| Поддерживаемые платформы |
Pocket PC смартфоны |
| Тип ядра | Гибридное |
| Интерфейс | Графический |
| Лицензия | Microsoft EULA |
| Состояние | Историческое; Поддержка прекращена в мае 2012 года |
| Предыдущая | Windows CE и Pocket PC |
| Следующая | Windows Phone |
| Веб-сайт | microsoft.com:80/windows… |
| Медиафайлы на РУВИКИ.Медиа |
Windows Mobile — мобильная операционная система, разработанная Microsoft для собственных аппаратных платформ Pocket PC (карманные персональные компьютеры, коммуникаторы) и Smartphone (смартфоны). В настоящий момент не разрабатывается и не поддерживается: в мае 2011 года стало известно о прекращении поддержки разработчиков приложений сервиса Windows Marketplace for Mobile[3]; в июле 2011 года компания сообщила своим клиентам о прекращении работы сервиса My Phone в октябре 2011 года[4]; в мае 2012 года Microsoft закрыла магазин приложений Windows Marketplace for Mobile для владельцев устройств[5].
Последняя версия — Windows Mobile 6.5 — основана на Windows CE 5.2, имеет базовый набор приложений, разработанных с использованием Microsoft Win32 API (программы могут приобретаться через сервис Windows Marketplace for Mobile или устанавливаться вручную пользователем; доступна свободная разработка программ для третьих лиц), функционально и визуально пытается быть похожим на настольную версию Windows. В отличие от Windows Mobile 6 и предыдущих версий, управляемых стилусом,[6][7] WM 6.5 для сенсорных устройств рассчитана на пальцевое управление.[8]
Доля Windows Mobile на рынке смартфонов с каждым годом снижается,[9] в третьем квартале 2009 года падение составило 20 %.[10][11] В США в 2008 году это была 3-я наиболее популярная операционная система для бизнес-пользователей (после BlackBerry OS и iOS), охватывающая ▼ 24 % корпоративных пользователей.[12] Среди общих продаж 2010 года — это 6-я наиболее популярная мобильная операционная система (после Android, bada, Symbian OS, BlackBerry OS и iOS), делящая ▼5 % доли мирового рынка смартфонов.
15 февраля 2010 года на выставке Mobile World Congress, проходившей в Барселоне, Microsoft анонсировала преемника Windows Mobile — Windows Phone. Новая ОС не совместима с предыдущей программно-аппаратной платформой и потому смартфоны с Windows Mobile 6.x не способны обновиться до Windows Phone.[13]
Windows Mobile для Pocket PC (сенсорных устройств) в стандартной поставке включает следующие особенности:
- начальный экран «Сегодня» (англ. Today) отображает текущую дату, информацию о владельце, предстоящие встречи, новые сообщения и задачи. Начиная с WM 6.5 экран имеет название «Home screen»;
- кнопка «Пуск», находящаяся в верхнем баре, раскрывает меню со списком программ и служебными ссылками, как в настольной версии Windows;
- панель задач отображает текущее время, вариант звукового профиля и заряд батареи;
- мобильная версия Microsoft Office — Office Mobile;
- пакет программ Outlook Mobile;
- мобильный браузер Internet Explorer Mobile, основанный на настольной версии IE[14];
- Windows Media Player для Windows Mobile;
- интеграция с сервисами Windows Live;
- клиент для PPTP VPN;
- функция Internet Connection Sharing (ICS), позволяющей делить подключение к Интернет с настольным компьютером через USB или Bluetooth;
- файловая система и структура папок аналогичны таковым в Windows 9x/Windows NT;
- многозадачность.
Основные отличия smartphone-версии от Pocket PC:
- интерфейс, адаптированный под телефонный форм-фактор, рассчитан на кнопочное управление устройством, из-за этого программы Pocket PC и Smartphone не совместимы друг с другом;
- начальный экран «Today» отображает (в порядке сверху вниз) ярлыки на недавно запущенные приложения, текущую дату, предстоящие встречи, звуковой профиль и новые сообщения;
- кнопка «Пуск» расположена в нижней панели;
- список программ отображается в отдельном экране;
- отсутствует экранная клавиатура, вследствие наличия штатной (как мобильной, так и QWERTY).
Qtek S100 — типичный представитель платформы Pocket PC
Существуют три версии операционной системы для различных программно-аппаратных платформ[15]:
- Windows Mobile Professional — для коммуникаторов с сенсорным экраном и функцией мобильного телефона (платформа Pocket PC)
- Windows Mobile Classic — для карманных персональных компьютеров (платформа Pocket PC)
- Windows Mobile Standard — для смартфонов с функцией мобильного телефона, но без сенсорного экрана (платформа Smartphone)
Классические WM-устройства[править | править код]
Изначально классические устройства Windows Mobile (англ. Windows Mobile Classic devices) были карманными персональными компьютерами без возможности подключения к сотовой сети и имели название Pocket PC (PPC). Наследниками Pocket PC являются операционные системы Windows Mobile Professional, кроме функций КПК поддерживающая ещё и функции телефона, и Windows Mobile Classic, тоже предназначенная для КПК, но построенная на более современных технологиях.
Smartphone[править | править код]
Платформа Smartphone («смартфон») вышла вместе с Pocket PC 2002 (по сути, она является его [PPC 2002] урезанной версией). Хотя в широком смысле термин «смартфон» включает как Pocket PC, так и телефоны с функциями КПК, следует отметить, что Microsoft использует термин для определения более конкретных аппаратных свойств устройств: smartphone-устройство должно быть оптимизировано для работы одной рукой и наделено экраном малой площади без сенсорных возможностей.
Pocket PC 2000 (Windows CE 3.0 Pocket PC Edition)[править | править код]
Pocket PC 2000 (первая версия Windows Mobile) — кодовое имя Rapier. Выпущена 19 апреля 2000 года на основе Windows CE 3.0. Это был дебют, впоследствии операционную систему назвали Windows Mobile. Также она призвана быть преемником операционной системы Palm-Size PC. Сохранена обратная совместимость с приложениями Palm-Size PC. Pocket PC 2000 предназначен в основном для КПК, однако для нескольких устройств Palm-Size PC есть возможность обновления. Кроме того, для Pocket PC 2000 были выпущены несколько телефонов, однако Smartphone Edition ещё не была создана. Поддерживалось только разрешение 240×320 (QVGA). Также поддерживались съемные карты памяти CompactFlash и Multimedia Card. В то время для устройств Pocket PC не была определена конкретная архитектура процессора. В результате Pocket PC 2000 была выпущена на нескольких архитектурах: SH-3, MIPS и ARM.
Первоначально Pocket PC была похожа на операционные системы Windows 98, Windows Me и Windows 2000.
Особенности / встроенные приложения для Pocket PC 2000, включали следующее:
- Pocket Office
- Pocket Word
- Pocket Excel
- Pocket Outlook
- Pocket Internet Explorer
- Windows Media Player
- Microsoft Reader
- Microsoft Money
- Заметки «от руки»
- Поддержка распознавания символов
- Инфракрасный (ИК) порт
Pocket PC 2002[править | править код]
Pocket PC 2002 (кодовое имя Merlin), основанная на Windows CE 3.0, — это первый выпуск под названием Pocket PC. Нацелена на бесклавиатурные устройства Pocket PC с разрешением QVGA (320×240). Впервые появляется поддержка устройств без сенсорного экрана, что рождает появление первых устройств типа «Смартфон» на Windows Mobile.
Windows Mobile 2003[править | править код]
23 июня 2003 года Microsoft представила следующее поколение операционной системы Pocket PC под названием Windows Mobile 2003 (кодовое имя Ozone, версия Windows CE — 4.20)[16][17][18].
В операционной системе появилось приложение для работы с графическими файлами (Pictures), доработан браузер Pocket Internet Explorer (более оптимизирован для просмотра больших страниц на маленьком экране, поддержка Java-скриптов)[19]. Система получила поддержку новых беспроводных стандартов — Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, IPSec/L2TP, IPv6[16].
Windows Mobile 2003 вышла в четырёх редакциях: Windows Mobile 2003 for Pocket PC Premium Edition, Windows Mobile 2003 for Pocket PC Professional Edition, в которой отсутствовал ряд программ, по сравнению с редакцией Premium, для создания более дешёвых устройств[19], Windows Mobile 2003 for Pocket PC Phone Edition и Windows Mobile 2003 for Smartphone[20].
Windows Mobile 2003 SE[править | править код]
24 марта 2004 года была представлена Windows Mobile 2003 Second Edition, кодовое имя Ozone Update[21]. Операционная система построена на ядре Windows CE 4.21[18]. Существенными новшествами обновления системы являются возможность изменения ориентации экрана с вертикальной на горизонтальную и поддержка разрешения экрана VGA (640×480), а также экранов с квадратным соотношением сторон[22]. Для защиты беспроводного соединения добавлена поддержка Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)[23].
Windows Mobile 5.0[править | править код]
Операционная система Windows Mobile 5.0 (кодовое имя Magneto, версия Windows CE — 5.1) была представлена 10 мая 2005 года на конференции Mobile and Embedded Developers Conference в Лас-Вегасе[24][25]. Изменения в интерфейсе направлены на улучшение навигацией джойстиком и управлением устройством одной рукой; офисный пакет переименован из Pocket Office в Office Mobile, в котором отказались от использования карманного формата документов в пользу оригинальных, а также добавилась новая программа в составе пакета — PowerPoint Mobile — для просмотра презентаций; новый подход к работе с памятью устройства, который отвечает за сохранность данных[24]. В операционную систему встроена поддержка клавиатуры QWERTY, USB 2.0, сотовых сетей класса 3G[25]. В Windows Mobile 5.0 используются Windows Media Player 10 Mobile, ActiveSync 4.0.
После установки пакета обновлений AKU 3 в системе появилась поддержка .NET Compact Framework 2, поддержка стандартов WPA2 и QoS, улучшены Internet Explorer Mobile (поддержка AJAX) и работа с Bluetooth (FTP-профиль, качество A2DP-профиля)[26].
Windows Mobile 6[править | править код]
Windows Mobile 6 была представлена 12 февраля 2007 года в Барселоне на выставке 3GSM World Congress 2007[27]. Версия построена на Windows CE 5.2[18] и имеет кодовое имя «Crossbow»[28]. Система вышла в трёх редакциях для КПК (Windows Mobile 6 Classic), для коммуникаторов (Windows Mobile 6 Professional) и для смартфонов (Windows Mobile 6 Standard).
В Windows Mobile 6 возросла производительность, появилась поддержка IP-телефонии, интегрировано приложение-оболочка Marketplace для построения магазина приложений, встроена интеграция с онлайн-сервисами Windows Live, встроено шифрование карты памяти, также шестая версия имеет немного обновлённые внешний вид и системные звуки[28]. Впервые в Windows Mobile 6 появилась функция автоматического обновления системы (Windows Update)[29].
Windows Mobile 6.1[править | править код]
В апреле 2008 года на выставке CTIA Wireless 2008 было представлено небольшое обновление операционной системы под номером 6.1[30]. В ней появились новые возможности браузера Internet Explorer Mobile («Масштаб», «Обзор страницы»), поддержка шифрования файлов на устройстве, новый режим для отображения смс-переписки, диспетчер задач, полезная для корпоративного сектора поддержка Mobile Device Manager[31]. Для операционной системы в редакции для смартфонов (Windows Mobile 6.1 Standard) появилась возможность заменить стандартный экран новым пользовательским «карусельным» интерфейсом[32]. Версия Windows CE — 5.2.19202[18].
Windows Mobile 6.5[править | править код]
Windows Mobile 6.5 анонсирована в феврале 2009 года на Mobile World Congress 2009 в Барселоне, официально новая версия операционной системы вышла в мае 2009 года[33][34]. С 6 октября 2009 года начали появляться устройства на новой системе[35]. Windows Mobile 6.5 построена на Windows CE 5.2.21234[18].
В Windows Mobile 6.5 — много изменений, касающихся интерфейса, направленного на пользование устройством с помощью пальцев: основное меню находится на рабочем столе с иконками в шестиугольниках, изменён экран «Сегодня» (пальцеориентированные элементы); также изменился экран блокировки, где появилась информация о событиях в системе с быстрым доступом к основным функциям устройства, обновился мобильный браузер Internet Explorer Mobile до шестой версии, доработан сервис Windows Marketplace for Mobile в качестве магазина приложений и появился новый онлайн-сервис — My Phone (синхронизация и хранение данных)[36].
В феврале 2010 года появилось первое устройство, работающее на обновлённой версии системы Windows Mobile 6.5.3, новшествами этого обновления стали поддержка ёмкостных экранов, поддержка мультитач, изменение кнопок в нижней части экрана на круглую форму, обновленный интерфейс операционной системы, ещё больше адаптированный под управление пальцами[37][38][39].
Таблица версий[править | править код]
| Название | Дата | Кодовое имя | Версия Windows CE | Версия Windows Mobile | ПО для синхронизации с ПК |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handheld PC 1.0 | 1996 | Pegasus | 1.0 Build 126-457 | 1.0 | H/PC Explorer 1.0 |
| Handheld PC 2.0 | 1997 | Mercury | 2.0 Build 7258-7260 | 2.0 | Windows CE Services 2.0 |
| Pocket PC 2000 | 19 апреля 2000 (CES 2000) | Rapier | 3.0.9348 Build 9351 | 3.0 | ActiveSync 3.1 |
| Pocket PC 2002 | 6 сентября 2001 | Merlin | 3.0.11171 Build 11178 | 3.1 | ActiveSync 3.5 |
| Windows Mobile 2003 | 23 июня 2003 | Ozone | 4.20.1081 Build 13100 | 4.2 | ActiveSync 3.7 |
| Windows Mobile 5.0 | 10 мая 2005 | Magneto | 5.1.1700 Build 14334-14397 | 5.0 | ActiveSync 4.0 |
| Windows Mobile 6 | 12 февраля 2007 | Crossbow | 5.2.318 Build 15341.0.0.0 | 6.0 | ActiveSync 4.5, Windows Mobile Device Center |
| Windows Mobile 6.1 | 4 января 2008 | Crossbow | 5.2.19202 Build 19202.1.0.0 | 6.1 | ActiveSync 4.5, Windows Mobile Device Center |
| Windows Mobile 6.1.4 | июль 2008 | Crossbow | 5.2.19588 Build 19588.1.1.4 | 6.1.4 | ActiveSync 4.5, Windows Mobile Device Center |
| Windows Mobile 6.5 | 11 мая 2009 | Titanium | 5.2.20757 Build 20757.1.4.0 | 6.5 | ActiveSync 4.5, Windows Mobile Device Center |
| Windows Mobile 6.5.1 | октябрь 2009 | Titanium | 5.2.23063 Build 23063.5.3.0 | 6.5.1 | ActiveSync 4.5, Windows Mobile Device Center |
| Windows Mobile 6.5.3 | 2 февраля 2010 | Titanium | 5.2.28008 Build 28008.5.3.0 | 6.5.3 | ActiveSync 4.5, Windows Mobile Device Center |
Windows Phone
[править | править код]
Windows Phone — мобильная операционная система, являющаяся преемником Windows Mobile, но несовместима с ней. С выходом Windows Mobile версии 6.5 компания Microsoft начала создавать бренд под названием Windows Phone[40][41]. Так стали именоваться все телефоны с этой операционной системой, но первая операционная система Windows Phone (сразу под номером 7 — как продолжение линейки мобильных систем от Microsoft[41]) вышла 11 октября 2010 года. 21 октября начались первые поставки устройств на новой платформе, среди которых были аппараты от HTC, LG, Samsung. В операционной системе использован новый интерфейс под названием «Metro», интегрированы социальные сети и сервисы Microsoft — Zune и Xbox Live.
Основными конкурентами платформы Windows Mobile были мобильные операционные системы Symbian, BlackBerry OS, iOS, Palm OS, Android и другие системы на базе ядра Linux (например, Palm webOS, Access Linux Platform, Maemo, Moblin, Openmoko). В 2007 году Windows Mobile занимала второе место среди мировых продаж мобильных операционных систем, следуя за операционной системой Symbian[42]. Доля мировых продаж в 2008 и 2009 годах составляла 11,8 % и 8,7 % соответственно, тем самым Windows Mobile занимала среди мобильных операционных систем третье место в 2008 году и четвёртое в 2009 году[43]. По результатам общих продаж смартфонов уже на 1 квартал 2010 года платформа Windows Mobile сместилась на пятое место среди мобильных операционных систем (после Symbian, BlackBerry OS, iOS и Android) с долей в 6,8 %[44].
Компания Microsoft, разрабатывающая Windows Mobile, получает лицензионные отчисления от производителей техники и ПО для Android. При этом доход компании Microsoft, получаемый таким образом, более чем в 2 раза выше, чем доход компании-разработчика, то есть Google[45].
Список мобильных операционных систем с открытым исходным кодом
- ↑ De Herrera, Chris. Windows CE/Windows Mobile Versions (англ.). pocketpcfaq.com (6 сентября 2007). Дата обращения: 18 октября 2010. Архивировано 4 сентября 2019 года.
- ↑ Microsoft introduces Windows Mobile 6.5.3 Professional for Windows Phones (англ.). unwired. Дата обращения: 18 октября 2010. Архивировано 31 мая 2012 года.
- ↑ Microsoft отказывается от Windows Mobile 6.x. Что станет со смартфонами на базе этой ОС. OSZone. Дата обращения: 16 апреля 2013. Архивировано 19 августа 2014 года.
- ↑ Новый шаг к сворачиванию Windows Mobile. OSZone. Дата обращения: 16 апреля 2013. Архивировано 23 марта 2012 года.
- ↑ Windows Mobile Marketplace закрывается. Mail.Ru. Дата обращения: 16 апреля 2013. Архивировано 17 апреля 2013 года.
- ↑ Charles Arthur. Windows Mobile: where’s the love? And where’s the sales figure? (англ.). The Guardian (20 октября 2009). Дата обращения: 17 октября 2010. Архивировано 5 февраля 2012 года.
- ↑ Виктор Дашкевич. Коммуникаторы Windows Mobile. Методы ввода и управления. Mobile-review.com (16 ноября 2007). Дата обращения: 18 октября 2010. Архивировано 10 марта 2010 года.
- ↑ Обзор операционной системы Windows Mobile 6.5: отличия от WM6.1. MForum.ru. Дата обращения: 18 октября 2010. Архивировано 13 мая 2012 года.
- ↑ Windows Mobile loses 2.7% of smartphone market in Q209 (англ.). Ars Technica (12 августа 2009). Дата обращения: 17 октября 2010. Архивировано 31 мая 2012 года.
- ↑ Продажи смартфонов с Windows Mobile упали. Лента.ру (13 ноября 2009). Дата обращения: 14 ноября 2009. Архивировано 7 февраля 2010 года.
- ↑ Windows Mobile smartphone sales plunge 20% in Q3 (англ.). ComputerWorld (12 ноября 2009). Дата обращения: 17 октября 2010. Архивировано 31 мая 2012 года.
- ↑ Air Pressure: Why IT Must Sort Out App Mobilization Challenges (англ.). InformationWeek (5 декабря 2009). Дата обращения: 17 октября 2010. Архивировано 31 мая 2012 года.
- ↑ Microsoft: «No Windows Phone 7 upgrade for Windows Mobile 6.x devices» (англ.). APC Magazine (1 марта 2010). Дата обращения: 24 ноября 2012. Архивировано 25 ноября 2012 года.
- ↑ Andy Lees. Worldwide Partner Conference 2008 (англ.). Microsoft (8 июля 2008). Дата обращения: 18 октября 2010. Архивировано 5 февраля 2012 года.
- ↑ Windows Mobile Editions Get Less Confusing Names: Professional, Standard and Classic (англ.). Gizmodo (29 января 2007). Дата обращения: 18 октября 2010. Архивировано 5 февраля 2012 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Жизнь после смерти: эволюция КПК. CNews. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 15 декабря 2013 года.
- ↑ Новая ОС Pocket PC — Windows Mobile 2003. Компьюлента. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 8 августа 2009 года.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 Operating System Version of Windows Mobile Devices (англ.). Microsoft. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 19 апреля 2013 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Обзор программного обеспечения Windows Mobile 2003. Mobile-review.com. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 6 января 2013 года.
- ↑ Windows Mobile: общие данные/Разнообразие версий и совместимость. Mobi. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 12 октября 2012 года.
- ↑ Исторический экскурс по Windows Mobile. 4PDA. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 4 марта 2016 года.
- ↑ Обзор операционной системы Windows Mobile 2003 Second Edition. Mobile-review.com. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 22 января 2013 года.
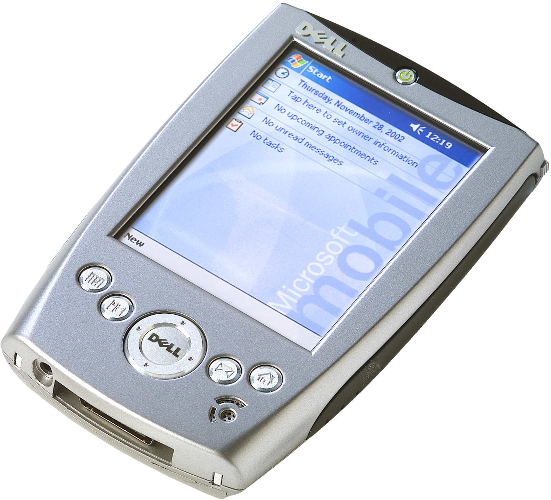
- ↑ Dell Axim X30 review (64MB, 624MHz processor). CNET. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 28 апреля 2013 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Обзор операционной системы Windows Mobile 5.0 (Magneto). Mobile-review.com. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 11 января 2013 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Смартфоны и КПК получили новую Windows. CNews. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 14 июля 2014 года.
- ↑ Обзор пакетов обновлений AKU для Windows Mobile 5.0. Mobile-review.com. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 2 февраля 2013 года.
- ↑ 3GSM World Congress 2007, часть III: шквал новинок Windows Mobile на Ferra.ru. Ferra. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 13 апреля 2014 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Обзор операционной системы Windows Mobile 6 Professional (Crossbow). Mobile-review.com. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 2 февраля 2013 года.
- ↑ Windows Mobile 6: обзор изменений по сравнению с Windows Mobile 5.0. Mobi. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 30 июля 2013 года.
- ↑ Windows Mobile 6.1 представлена официально. Mobi. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 30 июля 2013 года.
- ↑ Windows Mobile 6.1 – почти 6. Mobile-review.com. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 3 февраля 2013 года.
- ↑ Свежий взгляд на Windows Mobile 6.1. Открытые системы. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 19 апреля 2013 года.
- ↑ Microsoft Mobile Dev team: ‘Windows Mobile 6.5 is done’ (англ.). ZDNet. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 28 апреля 2013 года.
- ↑ Microsoft представила Windows Mobile 6.5. OSZone. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 17 ноября 2011 года.
- ↑ Microsoft: смартфоны и коммуникаторы с Windows Mobile 6.5 появятся 6 октября. Ferra. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 14 июля 2014 года.
- ↑ Windows Mobile 6.5: плюсы и минусы новой мобильной ОС. CNews. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 14 июля 2014 года.
- ↑ Windows Mobile 6.5.3 — начало multi-touch положено. Ferra. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 14 июля 2014 года.
- ↑ ОС Windows Mobile 6.5.3 показали без лишнего шума. Ferra. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 14 июля 2014 года.
- ↑ Microsoft рассказала о нововведениях в Windows Mobile. Клерк.Ру. Дата обращения: 18 января 2013. Архивировано 17 февраля 2015 года.
- ↑ WM 6.5: называйте меня Windows Phone. Компьютерра. Дата обращения: 29 июня 2012. Архивировано из оригинала 30 ноября 2012 года.
- ↑ 1 2 Q&A: Microsoft on Windows Phone 7 Series (англ.). CNET. Дата обращения: 29 июня 2012. Архивировано 5 августа 2012 года.
- ↑ Gartner posts worldwide mobile OS numbers for 2008 (англ.). Engadget. Дата обращения: 3 февраля 2013. Архивировано 19 апреля 2013 года.
- ↑ Россия держится за Windows Mobile. CNews. Дата обращения: 3 февраля 2013. Архивировано 5 сентября 2012 года.
- ↑ Android обошла Windows Mobile. CNews. Дата обращения: 3 февраля 2013. Архивировано из оригинала 14 июля 2014 года.
- ↑ CNews: В 2013 г. Microsoft заработает на Android в 2,6 раза больше, чем Google. Дата обращения: 13 мая 2013. Архивировано 11 июля 2013 года.
- Windows Mobile (англ.)
- Windows Mobile: общие данные/Разнообразие версий и совместимость
Windows Mobile OS, developed by Microsoft, was a significant player in the mobile operating system landscape, particularly in the early 2000s. Initially launched in 2000 as “Pocket PC 2000,” it evolved through various versions, each introducing new features and improvements. The OS was designed to offer a familiar Windows-like experience on handheld devices, catering to business professionals with productivity tools and enterprise features. Despite its early success, Windows Mobile struggled to compete with the rise of iOS and Android, leading to its eventual decline. Nonetheless, its impact on mobile computing and enterprise solutions remains notable.
The Early Days: Birth and Development
The early days of Windows Mobile OS trace back to its origins with the release of “Pocket PC 2000,” built on the Windows CE kernel. Designed for PDAs and smartphones, the OS featured a touch interface and stylus input, catering to business users seeking productivity tools. Early versions like Pocket PC 2002 and Windows Mobile 2003 brought incremental improvements, including better connectivity and multimedia capabilities. Initially, the market response was positive, as the OS provided a familiar Windows experience on mobile devices. However, adoption was limited by hardware constraints and competition from other emerging platforms.
Major Versions and Their Impact
Windows CE (Pocket PC 2000, Pocket PC 2002)

Introduction and Key Features: Windows CE, beginning with Pocket PC 2000 released in April 2000, laid the foundation for Microsoft’s mobile OS offerings. Pocket PC 2002 followed in October 2001, enhancing the user experience with more integrated applications and a familiar Windows interface.
Device Compatibility: Both versions were designed for a range of devices, including PDAs and early smartphones, making them accessible to a broad audience.
Windows Mobile 2003

New UI Elements and Media Support: Released in June 2003, Windows Mobile 2003 brought a refreshed UI and improved multimedia capabilities, catering to the growing need for media consumption on mobile devices.
Enhanced Connectivity Features: This version also featured better connectivity options, including enhanced Bluetooth support and improved network integration.
Windows Mobile 5.0

Persistent Storage and Enhanced Security: Launched in May 2005, Windows Mobile 5.0 introduced persistent storage, preventing data loss when power was lost, and included significant security enhancements.
Office Mobile Suite Introduction: This version marked the introduction of the Office Mobile Suite, providing users with access to Microsoft Office applications like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint on their mobile devices.
Windows Mobile 6.x Series

Versions: 6.0 (Standard, Professional), 6.1, and 6.5: The Windows Mobile 6.0 series was released in February 2007, with subsequent updates like 6.1 in April 2008 and 6.5 in October 2009. These versions offered tailored experiences for different user needs, including Standard and Professional editions.
Enhanced Business and Enterprise Features: These updates included improved email, calendar, and security features, catering to business and enterprise users.
Introduction of Windows Marketplace for Mobile: Windows Mobile 6.5 introduced the Windows Marketplace for Mobile, an app store launched in October 2009, allowing users to download applications directly to their devices.
Windows Mobile 7 (Canceled Project)

Overview of the Planned Features: Windows Mobile 7, planned as a significant overhaul, was expected to introduce a modernized UI and advanced features. However, the project was canceled before its release.
Transition to Windows Phone: The focus shifted to Windows Phone, with the first version, Windows Phone 7, launching in October 2010, representing a fresh start for Microsoft’s mobile OS efforts.
Key Features and Capabilities
User Interface and Experience

Windows Mobile OS offered a user interface that closely resembled the desktop Windows experience, providing familiarity for users. It featured a start menu, taskbar, and icons similar to its desktop counterpart. The UI was designed for touch input, primarily using a stylus, and later incorporated more finger-friendly elements in its later versions.
Multimedia and Entertainment
The OS supported a range of multimedia capabilities, including audio and video playback, as well as streaming services. Windows Media Player was integrated into the OS, allowing users to enjoy music, videos, and other media content. Windows Mobile supported various media formats, making it a versatile choice for entertainment on the go.
Productivity and Business Tools
Windows Mobile OS was known for its strong focus on productivity and business applications. It included the Office Mobile Suite, providing users with the ability to view and edit Word, Excel, and PowerPoint documents. The OS also supported synchronization with Microsoft Outlook, enabling users to manage emails, contacts, and calendars seamlessly.
Security and Privacy Features
Security was a key focus in Windows Mobile, especially in versions aimed at business and enterprise users. The OS included features such as encryption, password protection, and remote wipe capabilities, ensuring data security. It offered VPN support and secure access to corporate networks, making it suitable for business environments requiring robust security measures.
Hardware and Device Compatibility

Popular Devices Running Windows Mobile
Windows Mobile OS was featured on a variety of popular devices, including the HTC Touch series, Samsung Omnia, and the Motorola Q. These devices catered to different market segments, from business professionals to general consumers, and showcased the versatility of the OS.
Compatibility and Hardware Requirements
Windows Mobile was designed to be compatible with a wide range of hardware configurations, from PDAs to smartphones. The hardware requirements evolved over time, generally requiring a minimum of 32MB RAM and a 200MHz processor in earlier versions, with later versions requiring more advanced specifications to support new features and functionalities. The OS supported various screen resolutions and input methods, including touchscreens and physical keyboards.
Partnerships with Manufacturers
Microsoft established strong partnerships with several leading hardware manufacturers, including HTC, Samsung, LG, and Motorola. These partnerships allowed for a diverse range of devices running Windows Mobile, helping to expand its market reach. The collaboration between Microsoft and these manufacturers ensured that devices were optimized for the OS, offering a seamless user experience and leveraging the latest hardware innovations.
Challenges Faced by Windows Mobile OS
Market Competition
The Rise of iOS and Android: One of the significant challenges Windows Mobile faced was the rapid rise of Apple iOS and Android. These competing platforms offered more intuitive interfaces, a richer app ecosystem, and better user experiences, quickly gaining popularity among consumers and businesses alike.
Struggles to Maintain Market Share: As iOS and Android gained traction, Windows Mobile struggled to maintain its market share. The OS’s inability to keep up with the pace of innovation and consumer preferences led to a gradual decline in its user base.
Developer Support and App Ecosystem
Limited Number of Apps Compared to Competitors: Windows Mobile’s app ecosystem was limited compared to the vast offerings available on iOS and Android. The lack of apps made it less attractive to users who wanted a wide variety of applications for entertainment, productivity, and more.
Challenges in Attracting Developers: The OS struggled to attract developers, partly due to the perceived complexity of developing for the platform and the smaller user base. This further limited the availability of high-quality apps and updates.
User Interface and User Experience Issues
Criticisms of Outdated UI Design: The user interface of Windows Mobile was often criticized for being outdated and less user-friendly compared to the sleek, modern designs of its competitors. The reliance on stylus input and lack of touch-friendly elements were significant drawbacks as touchscreen devices became more prevalent.
Lack of Innovation in User Experience: Windows Mobile failed to innovate in terms of user experience, often lagging behind in introducing new features that resonated with users. This stagnation contributed to a perception of the OS being less dynamic and exciting.
Hardware Limitations

Inconsistent Performance Across Devices: The performance of Windows Mobile varied significantly across different devices, leading to an inconsistent user experience. This inconsistency was partly due to varying hardware specifications and optimization levels among different manufacturers.
Issues with Hardware Compatibility and Fragmentation: The wide range of devices running Windows Mobile often led to issues with hardware compatibility and fragmentation. Users faced challenges with software updates and compatibility with newer hardware features, which hindered the overall experience.
Marketing and Brand Perception
Lack of Clear Branding Strategy: Windows Mobile suffered from a lack of a clear and cohesive branding strategy. This made it difficult for the OS to establish a strong identity in the market, especially as other platforms had more defined brand personas.
Perception as a Business-Only OS: Despite efforts to appeal to a broader audience, Windows Mobile was often perceived as a business-only OS. This perception limited its appeal among general consumers who sought more versatile and entertainment-focused features.
Comparison with Other Operating Systems
Comparison with iOS
User Interface and User Experience: iOS offered a sleek and intuitive user interface, emphasizing ease of use and a polished design, which contrasted with Windows Mobile’s more traditional, desktop-like interface. The touch-centric UI of iOS, combined with multi-touch gestures, provided a more seamless and engaging experience compared to the stylus-dependent Windows Mobile.
App Ecosystem and Developer Support: iOS boasted a vibrant app ecosystem with a vast number of high-quality apps available on the App Store. The strong developer support for iOS, driven by a lucrative market and streamlined development tools, stood in stark contrast to Windows Mobile’s more limited app offerings and challenges in attracting developers.
Security and Privacy Features: Both iOS and Windows Mobile prioritized security and privacy, but iOS was generally considered more robust in this regard. Apple’s stringent app review process and consistent updates contributed to a more secure environment compared to the occasionally inconsistent security measures on Windows Mobile.
Comparison with Android
Customizability and Flexibility: Android’s open-source nature allowed for extensive customization and flexibility, enabling users and manufacturers to tailor the OS to specific needs. This stood in contrast to Windows Mobile’s more uniform and restrictive environment, which limited customization options.
Market Share and Device Range: Android’s rapid rise was fueled by a wide range of devices across various price points, capturing a significant market share. Windows Mobile, while present on a variety of devices, could not match the sheer volume and diversity of the Android ecosystem, which attracted a broader audience.
Integration with Google Services: Android’s deep integration with Google services, such as Gmail, Google Maps, and Google Play, provided a cohesive ecosystem that enhanced the user experience. Windows Mobile’s integration with Microsoft’s services, while useful, did not offer the same level of seamlessness and appeal, particularly to users who were not already embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem.
Comparison with BlackBerry OS and Symbian

Focus on Business and Enterprise Users: Like Windows Mobile, both BlackBerry OS and Symbian initially targeted business and enterprise users, offering features such as secure email and productivity tools. However, as the market evolved, all three OSs struggled to retain relevance against the more consumer-oriented iOS and Android platforms.
Market Share Decline and Legacy: Both BlackBerry OS and Symbian experienced significant market share declines, similar to Windows Mobile. They were unable to adapt quickly enough to the changing landscape dominated by touch-centric and app-rich ecosystems, leading to their eventual decline.
Key Differentiating Features: While BlackBerry OS was renowned for its secure messaging and robust hardware keyboards, Symbian was known for its energy efficiency and support for a wide range of hardware. Windows Mobile, meanwhile, focused on offering a familiar Windows experience on mobile devices, with strong integration of Microsoft Office and enterprise features. However, these differentiating features were not enough to sustain their positions in the rapidly evolving mobile market.
Conclusion
Windows Mobile OS played a pivotal role in the early days of mobile computing, offering a familiar Windows experience on handheld devices and paving the way for business-focused mobile solutions. Despite its initial success, the rise of iOS and Android overshadowed its contributions, leading to its decline. However, Windows Mobile’s emphasis on productivity, security, and integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem left a lasting legacy in the tech industry. Its evolution and eventual transition to Windows Phone mark an important chapter in the history of mobile operating systems.
Microsoft выпускала мобильные ОС задолго до того, как смартфоны прочно обосновались в карманах большинства людей. Усилия корпорации в данном направлении длились более двадцати лет. Итогом стали несколько интересных систем, которые мы сегодня и рассмотрим.
Windows CE 1.0 — компьютер в кармане
Содержание
- Windows CE 1.0 — компьютер в кармане
- Windows CE 2.0 — универсальная ОС для карманных, игровых и бытовых устройств
- Pocket PC 2000 (Rapier) c Office из коробки
- Pocket PC 2002 похожа на Windows XP
- Windows Mobile 2003 (Ozone) с корпоративными фишками
- Windows Mobile 5 (Magneto) для смартфонов и карманных компьютеров
- Windows Mobile 6 (Crossbow) — поддержка смартфонов с тачскринами
- Windows Mobile 6.1 была популярна
- Windows Mobile 6.5 (Titanium) принесла магазин приложений
- История Windows Phone
- Windows Phone 7 (Photon) для продвинутых коммуникаторов
- Windows Phone 8 (Apollo) запомнилась по смартфонам Lumia
- Windows Phone 8.1 (Blue) с Cortana
- Windows 10 Mobile (Threshold) — универсальные приложения
Операционная система была выпущена Биллом Гейтсом 17 ноября 1996 года. Была также известна под кодовым именем Pegasus. Заложила основание мобильных платформ Microsoft. Предназначалась для КПК — карманных персональных компьютеров, которые нередко называли наладонниками. Не были похожи на современный смартфон. Больше напоминали крошечный ноутбук. Легкие и компактные для своей эпохи устройства обычно весили менее 450 грамм. Базировались на процессорах с тактовой частотой 40–50 МГц. Дисплей чаще был монохромным («чёрно-белым»), а разрешение — порядка 480 х 240 пикселей.
С девайса на Windows CE 1.0 можно было заходить в интернет и читать сайты благодаря Pocket Internet Explorer. Карманная версия браузера не имела общего кода с настольной программой. Была написана с нуля, поскольку требовалось максимально легкое ПО — компьютерное оказалось бы слишком тяжелым. Из устройств с Windows CE 1.0 запомнился HP 320LX с монохромным экраном, разрешение которого составляло 640 х 240 пикселей. Весил 442 грамма. Был оснащен 79-клавишной клавиатурой и тачскрином, с которым работали с помощью стилуса. Базировался на 40-мегагерцевом процессоре, обладал 4 МБ ОЗУ и 5 МБ ПЗУ.
Windows CE 2.0 — универсальная ОС для карманных, игровых и бытовых устройств
Первую Windows CE многие всерьез не восприняли и считали бета-версией. С выходом CE 2.0 (Birch) платформа стала более зрелой. Платформа дебютировала 29 сентября 1997 года. Могла работать на устройствах разных типов, в том числе: игровых консолях, автомобилях и кухонных приборах. Совместима с архитектурами процессоров ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, StrongARM, SuperH и x86. Обладала поддержкой цветных дисплеев и сети. Получила 12 обновлений. На CE 2.0 работал целый ряд компьютеров, в том числе и довольно широко известный HP Jornada 820. Девайс получил экран с разрешением 640 х 480 пикселей, который отображал 256 цветов. Был оснащен клавиатурой и тачпадом. За вычисления отвечал 190 МГц процессор Intel StrongARM. Оперативной и постоянной памяти было по 16 МБ. Довольно массивный агрегат весом 1 кг. И габаритный: 24,6 х 3,3 х 17,8 см.

Pocket PC 2000 (Rapier) c Office из коробки
Дата выпуска системы: 19 апреля 2000 года. Единственным разрешением экрана, которое поддерживала данная версия, было 240 х 320 (QVGA). В предустановленное ПО входили карманные версии Microsoft Office, включая Pocket Word, Pocket Excel и Pocket Outlook. На борту присутствовала и Notes — программа для создания заметок с распознаванием рукописного ввода. Браузера Pocket Internet Explorer коснулись улучшения, в числе которых возможность менять размер веб-страниц под маленькие экраны. ОС поддерживала передачу файлов по воздуху через инфракрасный (ИК) порт. Типичное устройство на базе данной платформы — легкий 165-граммовый наладонник Compaq iPAQ H3100 с D-pad, тачскрином и настраиваемыми кнопками. Базировался на 206 МГц чипе Intel StrongARM. Обладал 16-мегабайтными ОЗУ и ПЗУ.

Pocket PC 2002 похожа на Windows XP
ОС увидела свет 4 октября 2001 года. Кодовое название платформы — Merlin. Преимущественно предназначалась для КПК. Но в версию Phone Edition разработчики добавили функциональность сотового телефона. В Pocket Internet Explorer добавили поддержку просмотра WAP. Визуально интерфейс был подобен Windows XP. Пример популярного компьютера на данной операционной системе — Dell Axim X5 с настраиваемыми кнопками, D-pad и сенсорным экраном под стилус. Весил КПК лишь 196 грамм. Базировался на 300 МГц процессоре Intel XScale. Обладал цветным дисплеем с разрешением 240 х 320 точек. Получил по 32 мегабайта ОЗУ и ПЗУ.

Windows Mobile 2003 (Ozone) с корпоративными фишками
ОС появилась 23 июня 2003 года. Выпускалась в нескольких редакциях, в том числе — Pocket PC Premium, Professional, Smartphone и Phone. Получила сильные по своим временам функции для бизнеса, среди которых: улучшенный Wi-Fi, поддержка VPN и API-интерфейсы SMS. Классикой устройства с Windows Mobile 2003 можно назвать, например, O2 XDA II с 400 МГц процессором Intel XScale. На борту 190-граммового гаджета — 128 МБ оперативной памяти и 64 МБ ПЗУ. Экран с разрешением 240 х 320 пикселей и 16-битной глубиной цвета.
Windows Mobile 5 (Magneto) для смартфонов и карманных компьютеров
Система дебютировала 9 мая 2005 года. Существовали две версии: для КПК и смартфонов. Первая с поддержкой сенсорного экрана и MS Office, а вторая — без. Из наладонников на базе данной платформы запомнился Palm Treo 750v с 300 МГц процессором Samsung, 16-битной глубиной цвета и разрешением дисплея 240 х 240 точек. Обладал 100 МБ RAM и 60 МБ ПЗУ.
Windows Mobile 6 (Crossbow) — поддержка смартфонов с тачскринами
Шестая версия вышла 12 февраля 2007 года. Принесла упрощенную схему именования: Classic , Standard и Professional. Профессиональная версия работала на смартфонах с сенсорными экранами, стандартная — на телефонах без тачскринов, а классическая — на наладонниках. Была добавлена поддержка новых разрешений экрана: 800 х 480 и 320 х 320 пикселей. Стала платформой ряда продвинутых девайсов, в том числе легендарного HTC Touch со 128 МБ оперативной памяти и 256 МБ ПЗУ. Легкое 112-граммовое устройство обладало 200 МГц процессором и сенсорным экраном под стилус.
Windows Mobile 6.1 была популярна
Появилась 1 апреля 2008 года. Получила переработанный плиточный интерфейс. Internet Explorer улучшили, в том числе добавили полностраничное масштабирование. Пользователи хорошо восприняли данную версию. Устанавливалась на довольно мощные девайсы. Например, на Sony Ericsson Xperia X1 с 528 МГц процессором и 256 МБ RAM. Гаджет был оснащен и полноценной клавиатурой и тачскрином, а весил лишь 145 грамм.

Windows Mobile 6.5 (Titanium) принесла магазин приложений
Версия выпущена 11 мая 2009 года. Принесла магазин мобильных приложений Windows Marketplace. Стала удобнее для управления пальцами, а не стилусом. Получила новый экран «Сегодня» с крупными элементами. Данный интерфейс потом частично перекочевал в новую Windows Phone. А меню «Пуск» на основе шестиугольной плитки испытания временем не выдержало. Применялась в популярных устройствах. Например, в Samsung Omnia Pro B7330 с 528 МГц процессором. Устройство обладало и сенсорным экраном и клавиатурой, а весило всего 111 грамм.

История Windows Phone
Эпоха смартфонов требовала новых подходов и на смену Windows Mobile пришла Windows Phone. Новое семейство мобильных ОС стало попыткой конкурировать с уже состоявшимися лидерами рынка: Android и iOS.
Windows Phone 7 (Photon) для продвинутых коммуникаторов
Релиз состоялся 21 октября 2010 года. Стала последней мобильной Windows на основе CE. Следующие версии Windows Phone базировались уже на ядре Windows NT. Запомнилась интерфейсом Metro, упрощенными значками и красочным домашним экраном. Нуждалась в пяти аппаратных кнопок: «Пуск», «Назад», «Поиск», «Камера» и «Питание». Возросли требования к процессору и экрану. Типичный девайс на базе данной ОС — коммуникатор HTC HD7. Получил мощный 1,0 ГГц чип Snapdragon S1. Обладал 4,3″ экраном-гигантом с разрешением 480 х 800 пикселей и 32-битной глубиной цвета. У модели были и тачскрин, и QWERTY-клавиатура. 576 МБ ОЗУ сочетались с 512 МБ ПЗУ.

Windows Phone 8 (Apollo) запомнилась по смартфонам Lumia
У Windows Phone 8, которая увидела свет 29 октября 2012 года, было немало общего с настольной ОС. Предполагалось, что единообразие интерфейса ПК и мобильного девайса будет удобным и пользователям и разработчикам. Можно было менять размеры плиток главного экрана. Поддерживались 720p дисплеи. Система поставлялась с Internet Explorer 10. Платформа стала итогом партнерства Microsoft и Nokia. На Windows Phone 8 работали смартфоны Lumia, в том числе достаточно популярный Nokia Lumia 920. Экран данного устройства отображал 16 млн цветов и обладал разрешением 1280 х 768 пикселей. Получил 2-ядерный процессор Qualcomm Krait с графикой Adreno 320 и 1 ГБ ОЗУ.

Windows Phone 8.1 (Blue) с Cortana
14 апреля 2014 года ОС была существенно улучшена. Добавлены голосовой помощник Cortana, голосовой поиск и удобный центр уведомлений. Браузер обновлен до Internet Explorer 11. Смартфоны под управлением данной системы были довольно мощными. Например, HTC One M8 базировался на флагманском чипсете Snapdragon 801 с четырехъядерным 2,45 ГГц ЦП и GPU Adreno 330. На борту 2 ГБ ОЗУ. Обладал тачскрином с разрешением 1280 х 768 пикселей.

Несмотря на усилия Microsoft, Windows так и не удалось стать массовой ОС для мобильных устройств. Зато сохранила абсолютное лидерство на рынке платформ для ПК. Читайте в «Блоге системного администратора» обзор десктопных версий Windows:
Windows 10 Mobile (Threshold) — универсальные приложения
Выпущена 20 ноября 2015 года и стала последней в череде мобильных платформ Microsoft. Ориентировалась на унификацию с настольной Windows 10. Принесла универсальную платформу UWP, которая позволяла создавать приложения для запуска на любых устройствах с Windows 10, в том числе мобильных и десктопных. Улучшила синхронизацию между девайми. Например, пользователь отклонял уведомление на ПК — автоматически отклонялось и на смартфоне. Стала операционной системой мощных устройств — например, Microsoft Lumia 950 XL с четырехъядерным ЦП и 3 ГБ оперативной памяти.

В октябре 2017 года Microsoft объявила, что больше не станет выпускать устройств на Windows 10 Mobile. Мобильная Windows была оригинальна, обладала интересным функционалом. Немало пользователей и сегодня сожалеют, что данная ОС не получила развития.
У вас было устройство с Windows Mobile или Windows Phone? Напишите в комментариях.
5
3
голоса
Рейтинг статьи
Windows Phone
A history
Microsoft is giving up on its mobile OS aspirations for now. In Windows Phone, it produced a unique mobile OS; arguably the most original of the mobile OSes. Let’s see how it got there.
The journey to Windows Phone 10 was a colourful one that spans three decades and includes many devices, and several different operating systems.
This story starts with the launch of Windows CE 1.0 in 1996.
Windows CE was launched in 1996 by Bill Gates, and laid the foundation for Microsoft’s future mobile operating systems.
Referred to as Handheld PCs, the form factor of these devices was that of a small, portable PC, resembling more a tiny laptop than the mobile devices we’re used to today.
But mobile they were, generally weighing less than 450 g. CPU speeds were in the 40-50 MHz range, and they usually came with monochrome screens with resolution of around 480×240 pixels.
Pocket Internet Explorer was also introduced with CE 1.0. It did not share a codebase with its desktop counterpart—instead it was written from scratch to be lightweight.
Device in class: HP 320LX

| Screen | Monochrome 640×240 |
| Input | 79 key keyboard Touchscreen Stylus |
| CPU | 40 MHz |
| RAM | 4 MB |
| ROM | 5 MB |
| Weight | 442 g |
Many regarded the first version of Windows CE to be a short-lived beta. With CE 2.0 Microsoft modularised the operating system, and expanded the number and types of device that could run it. Windows CE could now be used in diverse devices including cars, games consoles, and even kitchen utensils.
Supported architectures were ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, StrongARM, SuperH and x86.
Notably, Windows CE 2.0 added support for colour VGA screens, as well as built-in network support.
In all, there were 12 further updates to Windows CE 2.
Device in class: HP Jornada 820

| Screen | 256 colours 640×480 |
| Input | Keyboard Touchpad |
| CPU | Intel StrongARM 190 MHz |
| RAM | 16 MB |
| ROM | 16 MB |
| Weight | 1.1 kg |
| Size | 246×33×178 mm |
Based on Windows CE 3.0 which was launched in the same year, the only resolution supported by this release was 240×320 (QVGA).
Built-in apps included pocket versions of Microsoft’s Office suite, including Pocket Word, Pocket Excel, and Pocket Outlook, as well as Notes, a note taking app with handwriting recognition.
The Pocket Internet Explorer browser saw improvements too, with features like Shrink-to-fit which resized web pages for small screens.
Infrared (IR) file beaming was also supported.
Device in class: Compaq iPAQ H3100
| Screen | Monochrome 240×320 |
| Input | Stylus Touchscreen D-pad Customisable buttons |
| CPU | Intel StrongARM 206 MHz |
| RAM | 16 MB |
| ROM | 16 MB |
| Weight | 163 g |
| Size | 5×3×6 mm |
This release mainly targeted Pocket PC devices, although a Phone Edition of the OS included cell phone functionality in addition to the PDA abilities.
Aesthetically, Pocket PC 2002 was designed to look like Windows XP.
WAP browsing support was added to Pocket Internet Explorer.
Device in class: Dell Axim X5

| Screen | Colour 240×320 |
| Input | Stylus Touchscreen D-pad Customisable buttons |
| CPU | Intel XScale 300 MHz |
| RAM | 32 MB |
| ROM | 32 MB |
| Weight | 196 g |
| Size | 5×3×6 mm |
Windows Mobile 2003 came in a variety of editions, including Pocket PC Premium, Professional, Smartphone, and Pocket PC Phone.
It included a number of enterprise features such as VPN support, WiFi enhancements, and SMS APIs.
Device in class: O2 XDA II
| Screen | 16-bit colour 240×320 |
| Input | Touchscreen D-pad |
| CPU | Intel XScale 400 MHz |
| RAM | 128 MB |
| ROM | 64 MB |
| Weight | 190 g |
| Size | 5.117×3.28×6.2 mm |
Windows Mobile 5 was available in Pocket PC and Smartphone editions, the former including touchscreen and MS Office, and the latter without.
A new memory architecture was added for persistent storage: RAM was used for running programs, not for storage, so that no data would be lost under power failure.
Device in class: Palm Treo 750v
| Screen | 16-bit colour 240×240 |
| Input | Touchscreen Stylus D-pad Qwerty keyboard |
| CPU | Samsung 300 MHz |
| RAM | 100 MB |
| ROM | 60 MB |
| Weight | 154 g |
| Size | 111×58×22 mm |
Windows Mobile 6 introduced a new, simplified, naming scheme, with Classic, Standard, and Professional versions.
Professional ran on smartphones with touchscreens, Standard ran on mobile phones without touchscreens, and Classic which was for PDAs or Pocket PCs.
New screen sizes of 320×320 and 800×480 were supported.
Device in class: HTC Touch
| Screen | 16-bit colour 240×320 |
| Input | Touchscreen Stylus D-pad |
| CPU | ARM 200 MHz |
| RAM | 128 MB |
| ROM | 256 MB |
| Weight | 112 g |
| Size | 100×58×14 |
Although this was a minor update to Windows Mobile 6.0 it included some key features and was well received.
It included a redesigned home screen, with a tile-based UI, and threaded SMS conversations.
Internet Explorer saw some improvements too, with full-page zooming.
Device in class: Sony Ericsson Xperia X1

| Screen | 16-bit colour 480×800 |
| Input | QWERTY keyboard Touchscreen Optical trackpad Stylus |
| CPU | ARM 11 528 MHz |
| RAM | 256 MB |
| ROM | 512 MB |
| Weight | 145 g |
| Size | 110×53×17 mm |
Windows Mobile 6.5 was a stopgap update to Windows Mobile 6.1 intended to bridge the gap between version 6.1 and the then-to-be-released Windows Mobile 7.
This release was significant in that it saw the OS become more finger-friendly. It featured a slick new Today screen with large, clean, expanding, text elements—parts of this UI would carry over into Windows Phone.
It also included a hexagonal tile-based Start Menu, which was innovative, but ultimately didn’t stand the test of time.
Windows Marketplace for Mobile, an app store, was also launched with this release.
Device in class: Samsung Omnia Pro B7330

| Screen | 16-bit colour 320×320 |
| Input | QWERTY keyboard Touchscreen |
| CPU | ARM 11 528 MHz |
| RAM | 256 MB |
| ROM | 512 MB |
| Weight | 111 g |
| Size | 110×53×17 mm |
Windows Phone 7 was the only version of Windows Phone based on Windows CE, as future versions moved to the Windows NT kernel.
Windows Phone 7 employed Microsoft’s Metro UI, a design language focused on typography and simplified icons, as well as Live Tiles, a fresh, colourful, tile-based home screen, with fluid transitions between screens. It looked markedly different to its predecessors, and offered a unique alternative to Android and iOS.
Microsoft laid down minimum hardware specifications for Windows 7 handsets, which mandated 5 physical buttons, for Start, back, search, camera, and power., as well as CPU, GPU, screen, and connectivity requirements.
Device in class: HTC HD7

| Screen | 32-bit colour 480×800 |
| Input | QWERTY keyboard Touchscreen |
| CPU | Snapdragon S1 1.0 GHz |
| GPU | Adreno 200 |
| RAM | 576 MB |
| ROM | 512 MB |
| Weight | 162 g |
| Size | 122×68×11 mm |
Based on Windows NT kernel, and sharing Windows 8 code, Windows Phone 8 release saw a unification of Microsoft’s mobile and desktop offerings, resulting in a more consistent experience for developers and users across platforms.
Resizable home screen tiles, 720p HD screens, Internet Explorer 10
Introduced in November 2011, the line is the result of a long-term partnership between Nokia and Microsoft—as such, most Lumia smartphones run the Windows Phone operating system, excluding some later models which run the newer Windows 10 Mobile. The Lumia name is derived from the partitive plural form of the Finnish word lumi, meaning «snow»
Device in class: Nokia Lumia 920
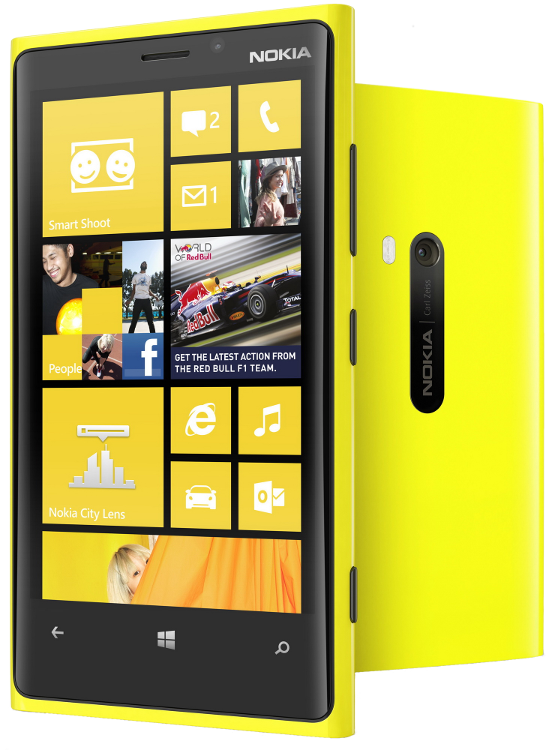

| Screen | 32-bit/16 M colours 1280×768 |
| Input | Touchscreen |
| CPU | Qualcomm Krait dual-core 1.5 GHz |
| GPU | Adreno 320 |
| RAM | 1 GB |
| Weight | 185 g |
| Size | 130×71×11 mm |
Windows Phone 8.1 saw significant upgrades to the Windows OS.
Cortana, Microsoft’s voice activated digital assistant, came to the platform, and brought voice-based search to Windows Phone.
A new notifications panel, called Action Center, was also introduced which vastly improved notifications in Windows Phone
Internet Explorer 11
Device in class: HTC One M8

| Screen | 32-bit/16 M colours 1280×768 |
| Input | Touchscreen |
| CPU | Qualcomm Snapdragon 801 2.45 GHz |
| GPU | Adreno 330 |
| RAM | 2 GB |
| Weight | 160 g |
| Size | 146×71×9 mm |
This was the last iteration of the Windows Phone OS. It aimed to unify and provide greater consistency with its Windows 10 desktop counterpart.
It provided the new Universal Windows Platform (UWP) which allowed apps to be built for and run across all Windows 10 devices, whether desktop, mobile, or console.
Syncing was also improved between devices. For example, a notification dismissed on desktop would automatically be dismissed on mobile too.
Device in class: Microsoft Lumia 950 XL

| Screen | 32-bit/16 M colours 1280×768 |
| Input | Touchscreen |
| CPU | 4×core Cortex A57 2GHz + 4×core Cortex A53 1.5 GHz |
| GPU | Adreno 430 |
| RAM | 3 GB |
| Weight | 165 g |
| Size | 152×79×8 |
In October 2017 Microsoft’s corporate vice president, Joe Belfiore, confirmed that, due to low market-share and lack of third-party development, Microsoft will no longer sell or manufacture new Windows 10 Mobile devices.
Existing devices will receive bug fixes and security updates only.
So long, Windows Phone. We will miss you.

 with Microsoft Account; sign in will persist across devices + apps with permissions prompt
with Microsoft Account; sign in will persist across devices + apps with permissions prompt