Are you experiencing network connectivity issues on your Windows device? A simple restart of the Windows Network service might be all you need to resolve the problem. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of Windows Network service, exploring what it is, why you might need to restart it, and providing a comprehensive guide on how to do so.
Understanding Windows Network Service
Before we dive into the process of restarting the Windows Network service, it’s essential to understand what it is and its role in your device’s connectivity. The Windows Network service, also known as the Network Location Awareness (NLA) service, is a critical component of the Windows operating system. Its primary function is to manage your device’s network connections, ensuring that you can access the internet, local networks, and other network resources.
The Windows Network service is responsible for:
- Detecting and connecting to available networks
- Managing network adapter settings
- Resolving DNS queries
- Maintaining network security and firewall settings
Why Restart the Windows Network Service?
There are several scenarios where restarting the Windows Network service might be necessary:
- Network connectivity issues: If you’re experiencing problems connecting to a network, restarting the Windows Network service can often resolve the issue.
- Slow network speeds: A restart can help improve network performance and speeds.
- Network adapter issues: If your network adapter is malfunctioning or not recognized by Windows, restarting the Windows Network service can help resolve the problem.
- After installing new network drivers: Restarting the Windows Network service can ensure that the new drivers are properly loaded and functioning.
Methods to Restart Windows Network Service
There are several ways to restart the Windows Network service, and we’ll explore each method in detail.
Method 1: Restarting via Services Console
This is the most common method to restart the Windows Network service.
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type services.msc and press Enter.
- In the Services console, scroll down and find the Network Location Awareness (NLA) service.
- Right-click on the service and select Restart.
- Alternatively, you can also stop the service and then start it again.
Method 2: Restarting via Command Prompt
You can also restart the Windows Network service using the Command Prompt.
- Press the Windows key + X and select Command Prompt (Admin).
- Type the following command and press Enter: net stop nlasvc
- Wait for the service to stop, then type the following command and press Enter: net start nlasvc
Method 3: Restarting via PowerShell
If you’re comfortable using PowerShell, you can restart the Windows Network service using the following command:
- Press the Windows key + X and select Windows PowerShell (Admin).
- Type the following command and press Enter: Restart-Service -Name NlaSvc -Force
Method 4: Restarting via Windows Settings
In Windows 10 and later versions, you can also restart the Windows Network service via the Windows Settings app.
- Press the Windows key + I to open the Settings app.
- Click on Update & Security.
- Click on Troubleshoot.
- Click on Additional troubleshooters.
- Click on Network Adapter.
- Click on Run the troubleshooter.
- Follow the prompts to restart the Windows Network service.
Troubleshooting Tips
If restarting the Windows Network service doesn’t resolve your connectivity issues, here are some additional troubleshooting tips:
- Check your network adapter settings: Ensure that your network adapter is enabled and configured correctly.
- Update your network drivers: Outdated network drivers can cause connectivity issues. Update your drivers to the latest version.
- Disable and re-enable your network adapter: Sometimes, disabling and re-enabling your network adapter can resolve connectivity issues.
- Reset TCP/IP stack: Resetting the TCP/IP stack can resolve issues related to network connectivity.
Common Errors and Solutions
Here are some common errors you might encounter when restarting the Windows Network service, along with their solutions:
- Error 1061: The service cannot accept control messages at this time: This error occurs when the service is not responding. Try stopping the service and then starting it again.
- Error 1068: The dependency service or group failed to start: This error occurs when a dependent service is not running. Try starting the dependent service and then restarting the Windows Network service.
Conclusion
Restarting the Windows Network service can often resolve connectivity issues and improve network performance. By following the methods outlined in this article, you should be able to restart the Windows Network service and get your device connected to the internet or local networks. Remember to troubleshoot further if restarting the service doesn’t resolve your issues, and don’t hesitate to seek help if you’re unsure about any of the steps.
What is the Windows Network Service and why is it important?
The Windows Network Service is a crucial component of the Windows operating system that manages network connections and allows devices to communicate with each other. It is responsible for establishing and maintaining network connections, resolving hostnames, and managing network protocols. The Windows Network Service is essential for accessing the internet, sharing files, and communicating with other devices on a network.
If the Windows Network Service is not functioning correctly, it can cause a range of problems, including lost internet connections, inability to access shared files, and difficulty communicating with other devices. Restarting the Windows Network Service can often resolve these issues and restore network connectivity.
Why do I need to restart the Windows Network Service?
You may need to restart the Windows Network Service if you are experiencing network connectivity issues, such as a lost internet connection or inability to access shared files. Restarting the service can help to resolve these issues by resetting the network connections and re-establishing communication with other devices. Additionally, restarting the Windows Network Service can help to resolve issues with network protocols, such as DNS resolution problems.
Restarting the Windows Network Service is a relatively simple process that can be completed in a few steps. It is a non-invasive process that does not require any technical expertise or specialized tools. By restarting the Windows Network Service, you can quickly and easily resolve network connectivity issues and get back online.
How do I know if the Windows Network Service is not working correctly?
If the Windows Network Service is not working correctly, you may experience a range of symptoms, including lost internet connections, inability to access shared files, and difficulty communicating with other devices. You may also see error messages, such as “No internet connection” or “Unable to connect to network.” Additionally, you may notice that your network icon in the system tray is showing a red X or a yellow exclamation mark.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is likely that the Windows Network Service is not working correctly. In this case, restarting the service may help to resolve the issue. You can also try troubleshooting the problem by checking your network cables, restarting your router, and running a network diagnostic test.
Will restarting the Windows Network Service affect my internet connection?
Restarting the Windows Network Service will temporarily disconnect you from the internet. However, once the service has been restarted, your internet connection should be restored. You may need to wait a few seconds for the service to restart and for your internet connection to be re-established.
It is worth noting that restarting the Windows Network Service will not affect your internet service provider (ISP) or your internet plan. Your internet connection will be restored as soon as the service has been restarted, and you will be able to access the internet as usual.
Can I restart the Windows Network Service remotely?
Yes, it is possible to restart the Windows Network Service remotely using Remote Desktop or other remote access tools. This can be useful if you need to restart the service on a remote computer or if you are unable to access the computer physically.
To restart the Windows Network Service remotely, you will need to have remote access to the computer and the necessary permissions to restart the service. You can use Remote Desktop or other remote access tools to connect to the computer and restart the service.
How often should I restart the Windows Network Service?
You should only need to restart the Windows Network Service occasionally, such as when you are experiencing network connectivity issues. Restarting the service too frequently can cause unnecessary disruptions to your network connections and may not resolve the underlying issue.
It is recommended to restart the Windows Network Service only when necessary, such as when you are experiencing network connectivity issues or when troubleshooting a network problem. If you are experiencing frequent network connectivity issues, it may be worth investigating the underlying cause of the problem rather than simply restarting the service.
Are there any risks associated with restarting the Windows Network Service?
Restarting the Windows Network Service is a relatively safe process that does not pose any significant risks to your computer or network. However, as with any system service, there is a small risk of data loss or corruption if the service is restarted while files are being transferred or if there are unsaved changes.
To minimize the risk of data loss or corruption, it is recommended to save any open files and close any network-dependent applications before restarting the Windows Network Service. Additionally, you should ensure that you have the necessary permissions and follow the correct procedures for restarting the service.
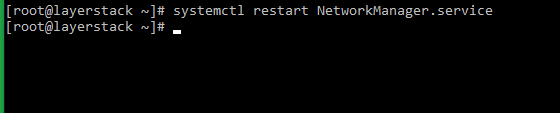
Once you make changes in the server network configuration file, then require to restart the server networking service in order to reflect the changes.
This guide will describe the steps to restart the network interface or network adapter in the Linux and Windows servers.
Restarting Network interface/adapter in Linux OS
Ubuntu / Debian
-
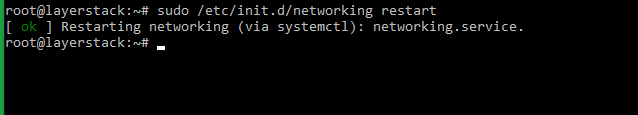
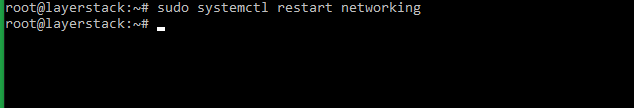
Use the following command to restart the server networking service.
# sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart or # sudo /etc/init.d/networking stop # sudo /etc/init.d/networking start else # sudo systemctl restart networking -
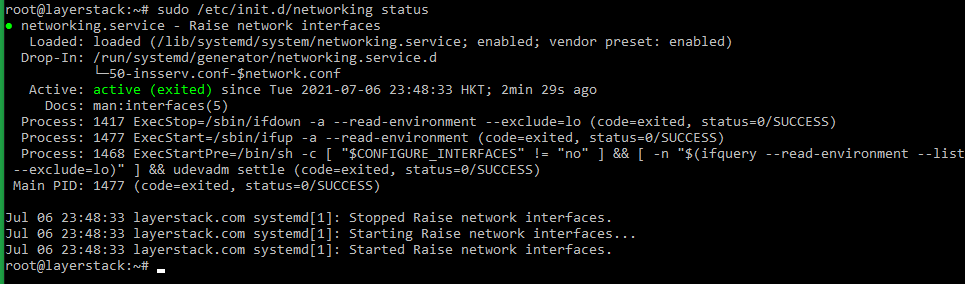
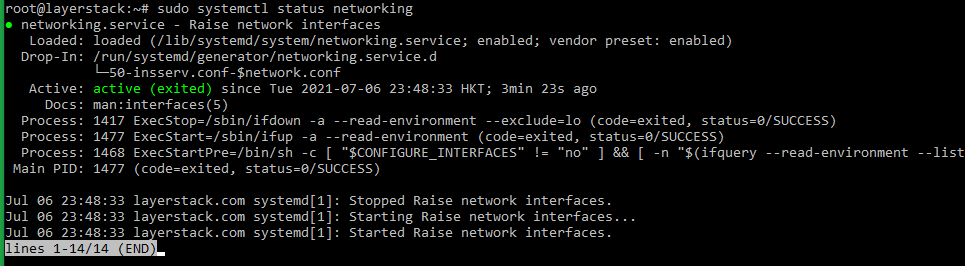
Once this is done, use the following command to check the server network status.
# sudo /etc/init.d/networking status or # sudo systemctl status networking
Ubuntu 17.10 and higher versions use NetPlan as the default network management tool and its configuration files are written in YAML syntax with a .yaml file extension.
Run the below command to update networking and then any changes that have been made to the network will take effect:
# netplan apply

AlmaLinux
-
Use the following command to restart the server networking service.
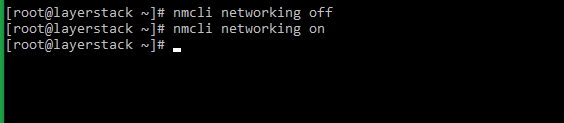
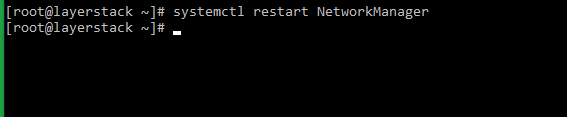
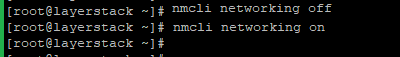
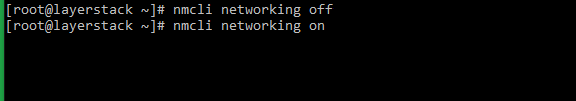
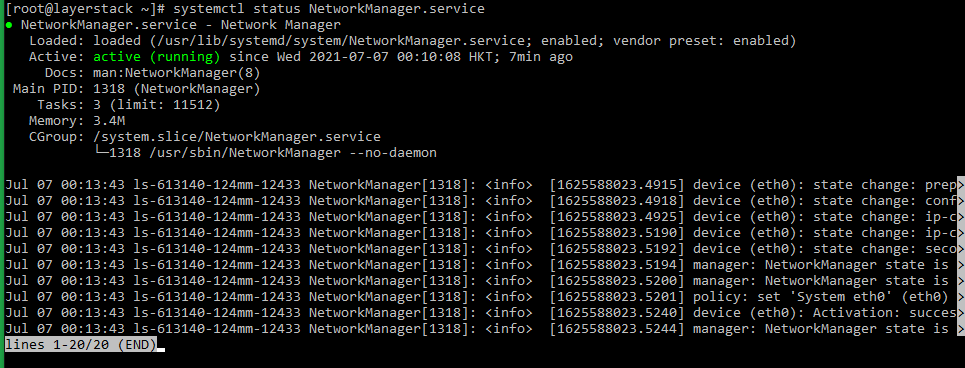
# nmcli networking off # nmcli networking on or # systemctl restart NetworkManager -
Once this is done, use the following command to check the server network status.
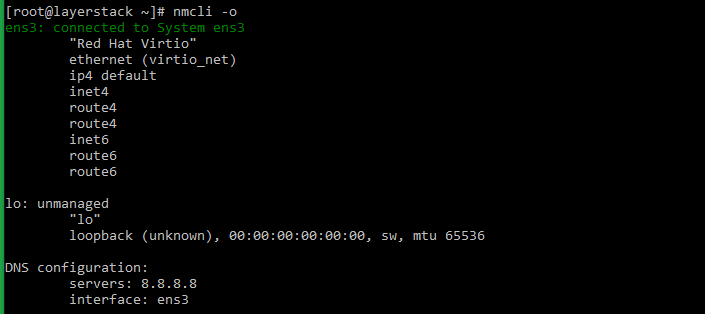
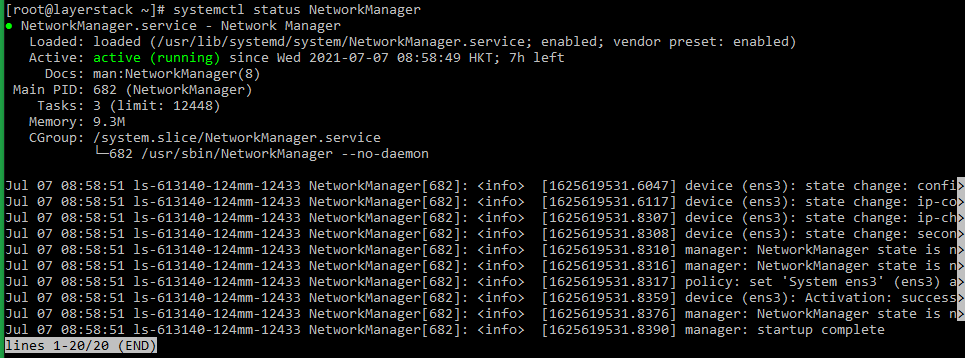
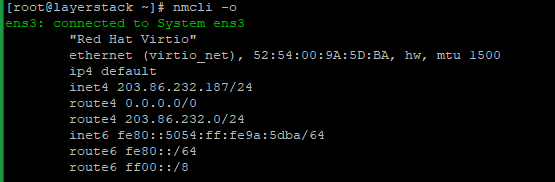
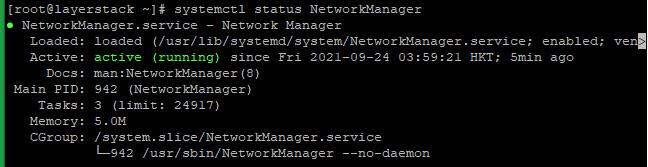
# nmcli -o or # systemctl status NetworkManager
Rocky Linux
-
Use the following command to restart the server networking service.
# nmcli networking off # nmcli networking on or # systemctl restart NetworkManager -
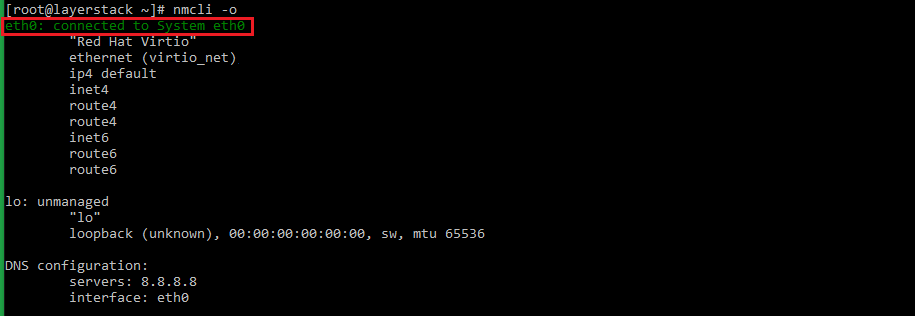
Either of the below commands can be executed to check the status of the networking service.
# nmcli -o or # systemctl status NetworkManager
CentOS 8
-
Use the following command to restart the server networking service.
# nmcli networking off # nmcli networking on or # systemctl restart NetworkManager.service -
Either of the below commands can be executed to check the status of the networking service.
# systemctl status NetworkManager.service or # nmcli -o
CentOS 7
-
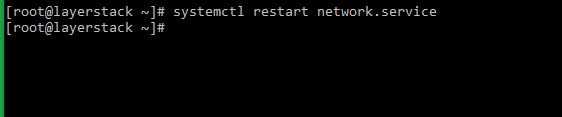
Use the following command to restart the server networking service.
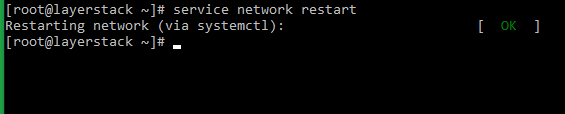
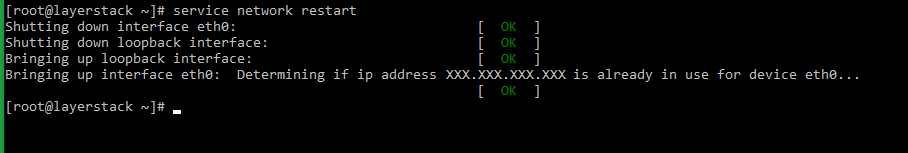
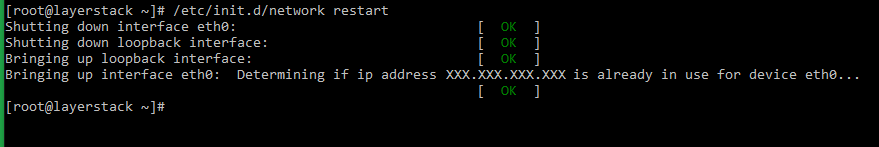
# systemctl restart network.service or # service network restart or # /etc/init.d/network restart -
The status of the networking service can be checked by making use of any of the below commands.
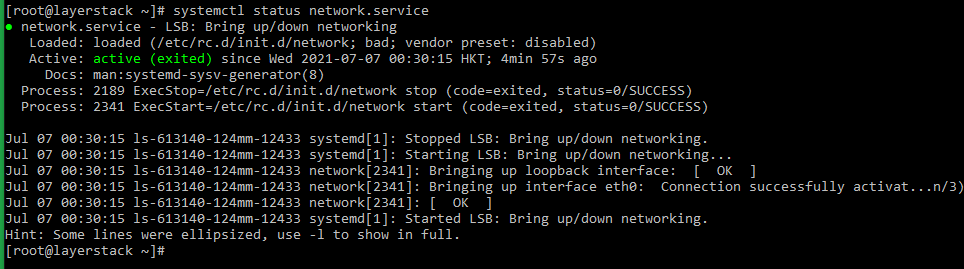
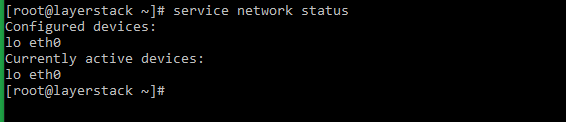
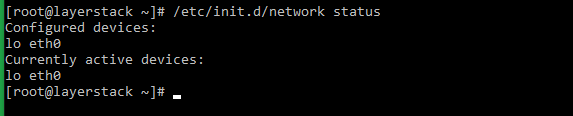
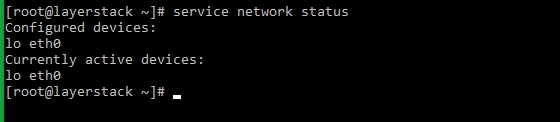
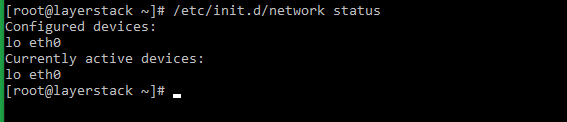
# systemctl status network.service or # service network status or # /etc/init.d/network status
CentOS 6
-
Use the following command to restart the server networking service.
# service network restart or # /etc/init.d/network restart -
Once this is done, use the following command to check the server network status.
# service network status or # /etc/init.d/network status
Windows OS
Using the Enable/Disable mode of network adapter
-
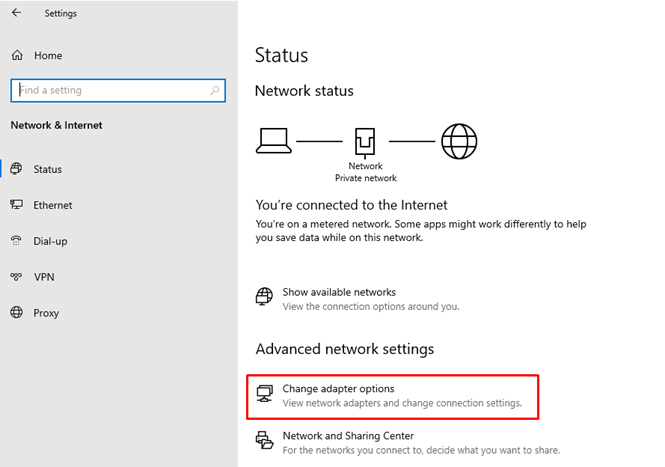
Click on the Windows key to open start and search
Settingsand go to theNetwork and Internetthen click onChange adapter optionwhich is shown in the below image.Then will get the below page:
-
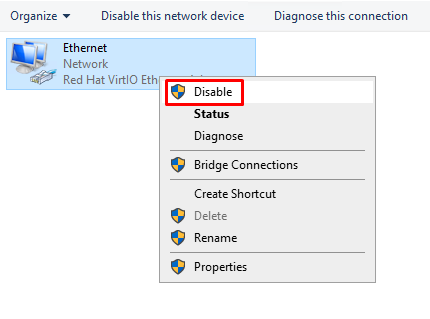
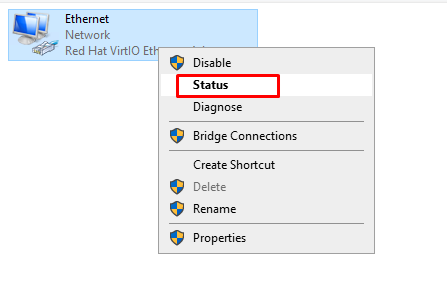
Right-click the
Ethernet deviceand click onDisableoption. -
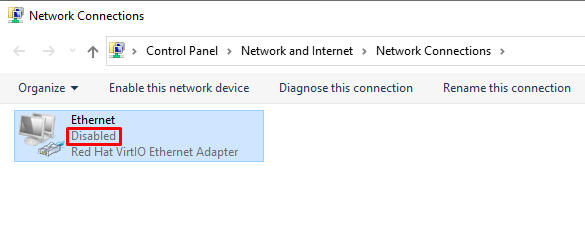
Again, Right-click the
Ethernet deviceand click onenableoption. -
Once this is done, Right-click the
Ethernet deviceand click onstatus.
Using the netsh command
In Windows OS, the command line method involves using the netsh command for resetting the network and TCP/IP stack.
-
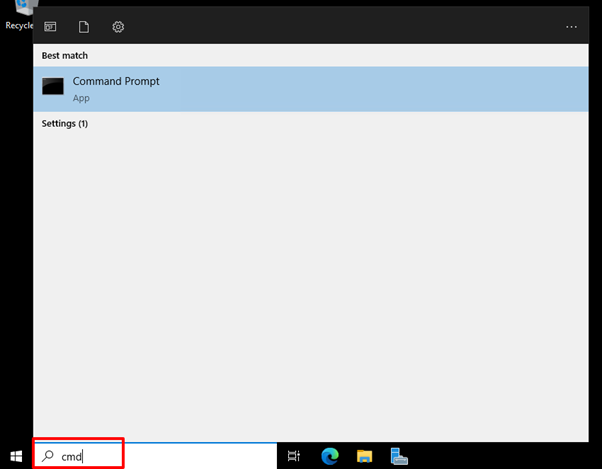
Go to
Startand typeCMDin the search window. -
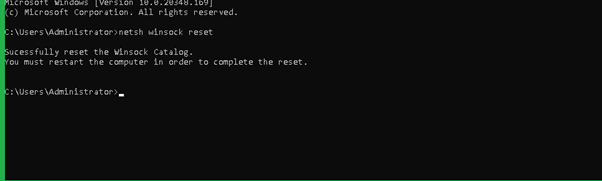
Once opened the
Command Prompt, the command for restarting the network interface, as provided below, can be executed.> netsh winsock reset -
Regularize the networking process as indicated in the message after restarting the server.
-
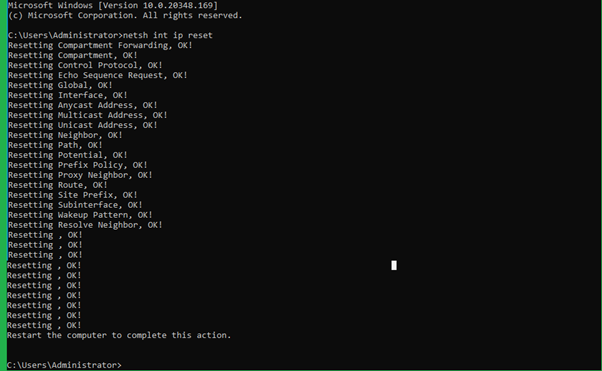
In addition to the above command, may also use the command which resets the TCP/IP stack. The command is as follows.
> netsh int ip resetThe output will be as follows:
Using the Network Reset option (Windows 10/11)
The reset button method can be used in Windows 10 & 11 versions by which the user can restart the Network interface. The steps for this are given below.
-
Click on Windows
Start Menubutton and then selectSettings. -
From the
Settingsoption, selectNetwork & Internetoption. -
Here you would be able to see the adapter options i.e
Advanced Network Settings, from which you can click onNetwork Resetoption. -
Click on the
Reset Nowbutton on the right side ofNetwork resetoption and you will be prompted for the confirmation. ChooseYesfor proceeding with resetting the network settings.Once clicked on
Yes, the network adapter will start to reset and you will be able to restart the network interface.
Related Tutorials
-
How to check if TCP / UDP port is open on Linux & Windows Cloud Servers
-
Installing telnet client on Linux and Windows Cloud Servers
-
How to check TCP/IP configuration with ipconfig on Windows Cloud Servers
-
How to check TCP/IP configuration with ifconfig on Linux Cloud Servers
-
How to configure the Static IP Address & Network Card for Linux & Windows Cloud Servers
- To disable, enable, and restart a network adapter on Windows 11, go to Settings > Network & internet > Advanced network settings.
- You can also disable, enable, or restart a network adapter from the Command Prompt, PowerShell, Device Manager, and the Control Panel on Windows 10 and 11.
All modern computers come with network adapters today so you can connect to the internet and communicate with other devices. However, even the most sophisticated network adapters, whether wired (ethernet) or wireless (wi-fi), can run into issues and not perform as they are supposed to. At this point, a simple restart of the network adapter usually fixes the issues.
By restarting the network adapter, you avoid rebooting the complete computer, and the basic connectivity issues are also resolved.
You may want to restart your network adapter if your computer hasn’t had downtime in quite some time and the internet speed isn’t optimized when you are having trouble connecting to the wireless SSID, or if you are experiencing any sort of issues with network connectivity. Restarting the network adapter should be the first of many steps for troubleshooting.
On Windows 11, restarting the ethernet, wi-fi, or virtual network adapter involves turning it off and then on again. Therefore, the methods discussed in this post to restart any network adapter first let you disable the adapter, and then re-enable it. In case you want to simply disable or enable a network adapter on your Windows PC, you can use the same methods discussed below.
Note: Restarting and resetting the network adapter are two different things. When you reset the network settings, all configurations are lost and need to be redone.
Table of Contents
Restart the network adapter from Settings in Windows 11
Microsoft has introduced the ability to disable and enable any network adapter on your computer directly from the Settings app. You no longer have to open the Control Panel to do it.
Unfortunately, this option is not available in Windows 10.
Use the following steps to restart the ethernet or the Wi-Fi network adapter from the Windows 11 Settings app:
-
Press the Windows Key + i to open the Settings app.
-
Switch to the “Network & internet” tab from the left.
-
Scroll down and click “Advanced network settings.”
Open advanced network settings -
Click Disable in front of the network adapter that you want to disable or restart.
Disable the network adapter from Settings -
In case you want to restart the adapter, click Enable in front of it.
Enable the network adapter from Settings
If you re-enable the network adapter, you have successfully restarted it. If you were encountering issues with the adapter, check to see if they have been resolved.
Restart the network adapter from Control Panel
Traditionally, you can also restart the network adapter from the Control Panel. This method (and the methods below) also works for Windows 10.
-
Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run Command box.
-
Type in “ncpa.cpl” and press Enter to open the Network Connections applet.
-
Right-click on the adapter that you want to disable/restart and click Disable.
Disable network adapter from the Control Panel -
To re-enable the adapter, right-click the adapter again and click Enable.
Re-enable the network adapter from the Control Panel
Restart the network adapter from Device Manager
To enable, disable, or restart any network adapter of your computer from the Device Manager, use these steps:
-
Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run Command box.
-
Type in “devmgmt.msc” and press Enter to open the Device Manager.
-
Click on “Network adapters” to expand it.
Expand Network Adapters in the Device Manager -
Right-click on the adapter that you want to disable/restart and click “Disable device.”
Disable network adapter from the Device Manager -
If asked for a confirmation, click Yes.
Confirm action -
To re-enable the adapter, right-click the adapter again and click “Enable device.”
Enable the network adapter from the Device Manager
After performing the steps above, the selected network adapter will be restarted and should perform optimally now.
Restart the network adapter from PowerShell
If you prefer using the Windows command line instead, then you can use the steps below to disable, enable, or restart the ethernet or the wireless network adapter using Windows PowerShell:
-
Open an elevated PowerShell instance.
-
Run the following command to list all the network adapters:
Get-NetAdapter | format-tableList all network adapter details in PowerShell -
Note down the name of the network adapter that you want to restart/disable.
-
Now use this command while entering your adapter’s name in place of [NetworkAdapterName] to disable it:
Disable-NetAdapter -Name “[NetworkAdapterName]” -Confirm:$falseDisable network adapter from PowerShell -
To re-enable the adapter, use this command:
Enable-NetAdapter -Name “[NetworkAdapterName]” -Confirm:$falseEnable/restart network adapter from PowerShell
Restart the network adapter from Command Prompt
You can also use the Command Prompt to restart any connected network adapter. Here is how:
-
Run the Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
-
List all the network adapter details with this command:
netsh interface show interfaceList all network adapter details in Command Prompt -
Note down the name of the network adapter that you want to restart/disable.
-
Now use this command while entering your adapter’s name in place of [NetworkAdapterName] to disable it:
netsh interface set interface “[NetworkAdapterName]” disableDisable network adapter from Command Prompt -
To re-enable the adapter, use this command:
netsh interface set interface “[NetworkAdapterName]” enableEnable/restart network adapter from Command Prompt
Ending words
Restarting the network adapters on Windows was already an easy task. However, Windows 11 has made it even more convenient.
Although the Settings app was supposed to replace the Control Panel, Microsoft still hasn’t entirely accomplished the task. They are gradually shifting the controls from the Control Panel over to the Settings app, and the addition of the ability to disable and enable the network adapters from the Settings app is part of that ongoing agenda.
- SS64
- CMD
- How-to
The NET command is used to manage services
as follows:
Syntax
NET START [service]
NET STOP [service]
NET PAUSE [service]
NET CONTINUE [service]
Key
service : The service name as shown in Control Panel, Services
Examples
List the basic Services:
NET HELP SERVICES
List the running Services:
NET START
Stop the print spooler service and if sucessful restart it again:
NET STOP spooler && NET START spooler
To use a long service name, surround it with quotes:
NET STOP «HomeGroup Listener»
Error/return codes
Unlike SC, the NET command does not return the documented Win32_Service class return codes (Service Not Active,Service Request Timeout, etc) and for many errors will return Errorlevel 2.
It will however echo its own errors on screen:
«The service table is locked. More help is available
by typing NET HELPMSG 2180»
«The service table is full. More help is available
by typing NET HELPMSG 2181»
«The requested service has already been started. More help is available
by typing NET HELPMSG 2182»
«The service name is invalid. More help is available
by typing NET HELPMSG 2185»
«The service is not responding to the control function.
NET HELPMSG 2186»
«The service control is busy.
NET HELPMSG 2187»
«Invalid service program name.
NET HELPMSG 2188»
«The service could not be controlled in its present state. More help is available
by typing NET HELPMSG 2189»
«The service ended abnormally. More help is available
by typing NET HELPMSG 2190»
«The requested pause or stop is not valid for this service. More help is available
by typing NET HELPMSG 2191»
«could not find service name. More help is available
by typing NET HELPMSG 2192»
«service control dispatcher pipe read failed. More help is available
by typing NET HELPMSG 2193»
«A thread for the new service could not be created. More help is available
by typing NET HELPMSG 2194»You can detect these errors by searching the output text with the FIND command as follows:
NET START alerter 2>&1|FIND «2182»
IF errorlevel 1 goto :sub_already_started
Related commands
Copyright © 1999-2025 SS64.com
Some rights reserved
Once in a while, the network operating system (NOS) service which supports the task that’s causing you trouble inexplicably stops or gets stuck. If users can’t access a server, it may be because one of the key network services has stopped or is stuck.
You can review the status of services by using the Services tool, as shown in Figure 19-1. To display it, choose Services from the Administrative Tools menu. Review this list to make sure that all key services are running. If a key service is paused or stopped, restart it.
Figure 19-1: The Services tool.
Which service qualifies as a key service depends on which roles you defined for the server. Table 19-1 lists a few key services that are common to most Windows network operating systems. However, many servers require other services.
Table 19-1: Key Windows Services
Open table as spreadsheet
|
Service |
What It Does |
|---|---|
|
Computer Browser |
Maintains a list of computers on the network that can be accessed. If this service is disabled, the computer cannot use browsing services, such as My Network Places. |
|
DHCP Client |
Enables the computer to obtain its IP address from a DHCP server. If this service is disabled, the computer’s IP address isn’t configured properly. |
|
DNS Client |
Allows the computer to access a DNS server to resolve DNS names. If this service is disabled, the computer cannot handle DNS names, including Internet addresses and Active Directory names. |
|
Server |
Provides basic file and printer sharing services for the server. If this service is stopped, clients cannot connect to the server to access files or printers. |
|
Workstation |
Enables the computer to establish client connections with other servers. If this service is disabled, the computer cannot connect to other servers. |
| Warning |
Key services usually stop for a reason, so simply restarting a stopped service probably won’t solve your network’s problem-at least, not for long. Review the system log to look for any error messages that may explain why the service stopped in the first place. |
If you’re using Windows 2000 Server or Windows Server 2003, you can double-click a service to display a dialog box that describes the service. This information can come in handy if you’re not certain what a particular service does.