Все способы:
- Используем команду netstat для просмотра открытых портов
- Отображение всех подключений и ожидающих портов
- Постраничное отображение открытых портов
- Запись результатов в текстовый файл
- Поиск по содержимому
- Вопросы и ответы: 2
Netstat — одна из встроенных команд операционной системы Windows. В ее функциональность входит отображение состояния сети со всеми требуемыми деталями. Пользователь задействует встроенный синтаксис, чтобы отфильтровать результаты или задать дополнительные действия для этой утилиты. В рамках сегодняшнего материала мы бы хотели рассказать о доступных методах просмотра открытых портов с помощью этого стандартного инструмента.
Используем команду netstat для просмотра открытых портов
Портами называют натуральные числа, которые записываются в заголовках протоколов передачи данных (TCP, UDP и так далее). Они определяют процесс получения и передачи информации в рамках одного хоста и в большинстве случаев используются онлайн-программами для установки соединения. Просмотр открытых портов может понадобиться в случае определения работоспособности приложений или при стандартном мониторинге сети. Лучше всего с этим справится команда netstat, а ее активация доступна с применением разных аргументов.
Отображение всех подключений и ожидающих портов
Самый простой аргумент, применяемый к утилите netstat, имеет обозначение -a, и отвечает за вывод сведений обо всех активных подключениях их портов, которые ожидают соединения. Такая информация доступна к просмотру без применения прав администратора и выводится на экран следующим образом:
- Поскольку рассматриваемая команда является консольной, потребуется запустить приложение, чтобы ее выполнить. Откройте меню «Пуск», найдите там «Командную строку» и запустите ее. О других методах перехода в консоль читайте в другом нашем материале по следующей ссылке.
- В поле ввода напечатайте
netstat -a, а затем нажмите на клавишу Enter. - На экране тут же начнет появляться список с доступными адресами.
Подробнее: Открытие командной строки в Windows 10
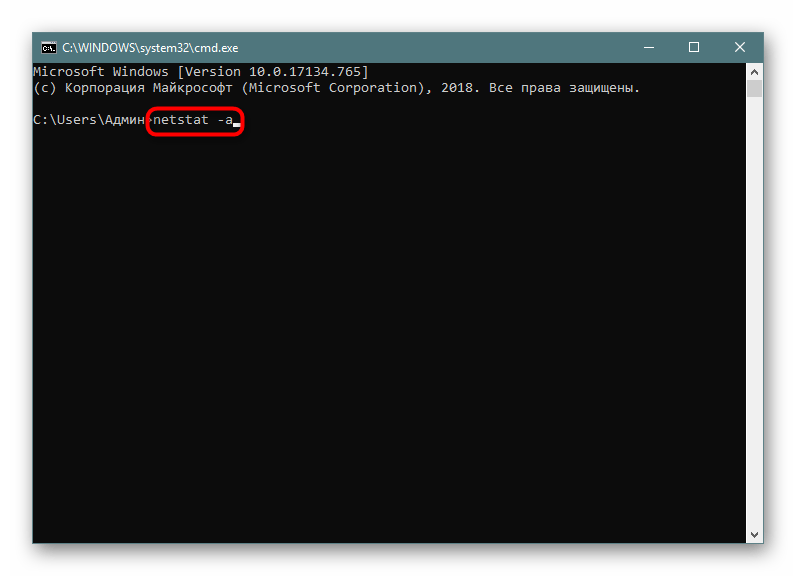
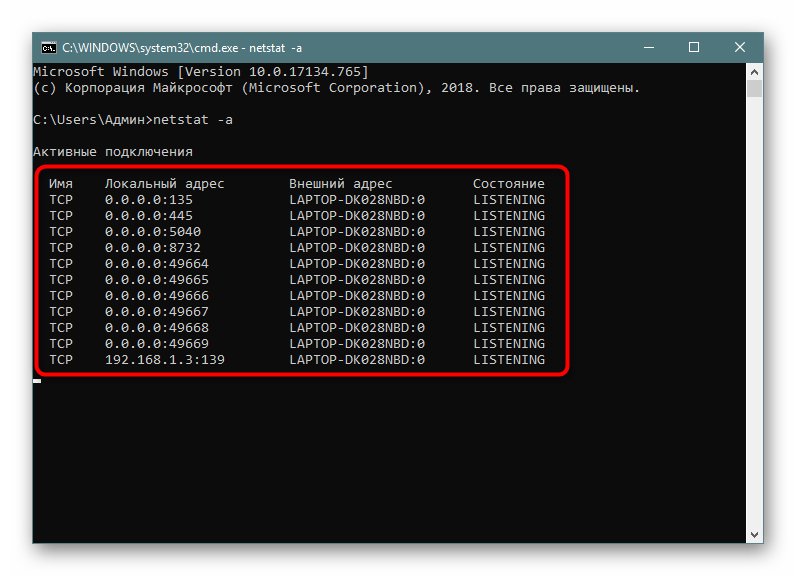
Мониторинг производится в режиме реального времени, поэтому не все результаты будут доступны к просмотру сразу. Придется подождать немного времени, чтобы все они могли прогрузиться. Во время этого не закрывайте консоль, если не хотите прервать процесс, ведь при повторном запуске команды все начнется заново.
Постраничное отображение открытых портов
К сожалению, приведенный выше вариант отображает не все необходимые данные об открытых портах, поскольку выводит он только те параметры, которые на текущий момент находятся в состоянии LISTENING. К тому же там не указывались уникальные идентификаторы процессов (PID), что тоже играет важную роль во время определенного мониторинга. Потому советуем обратить внимание немного на другие аргументы.
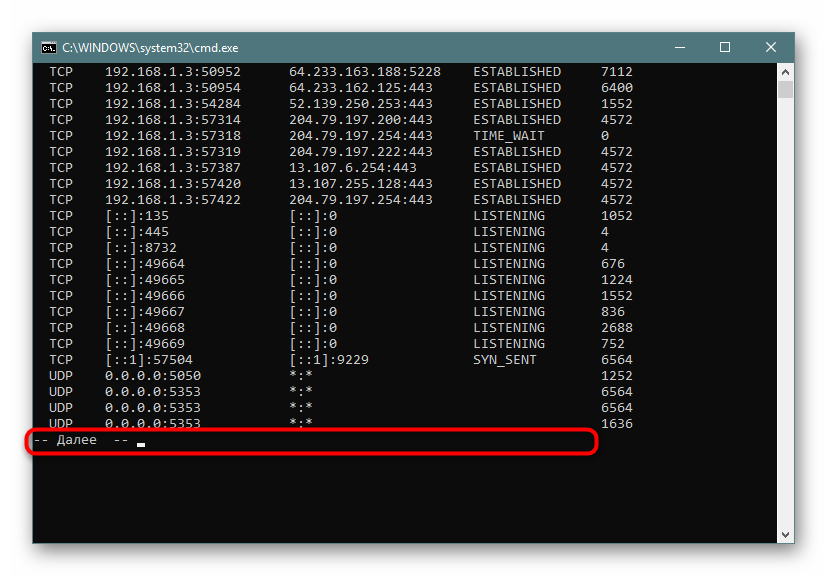
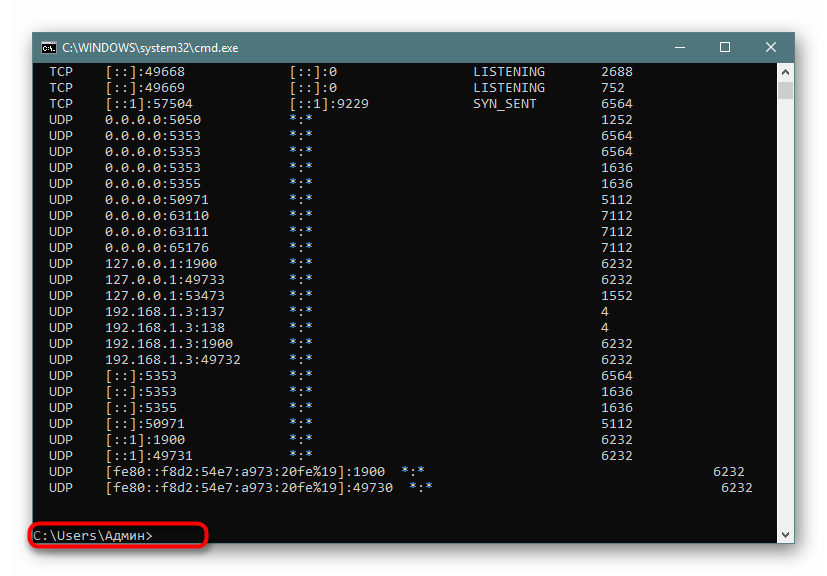
- В консоли пропишите
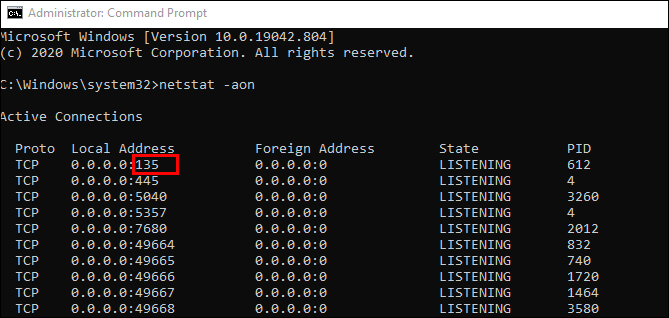
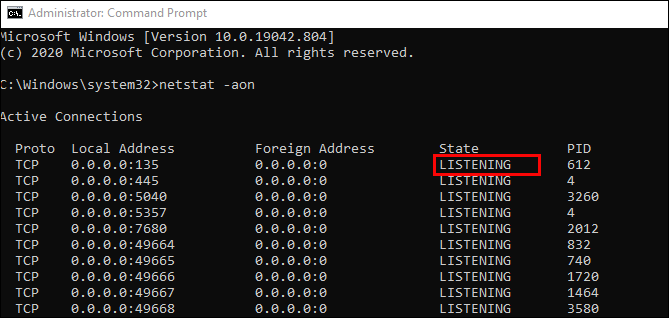
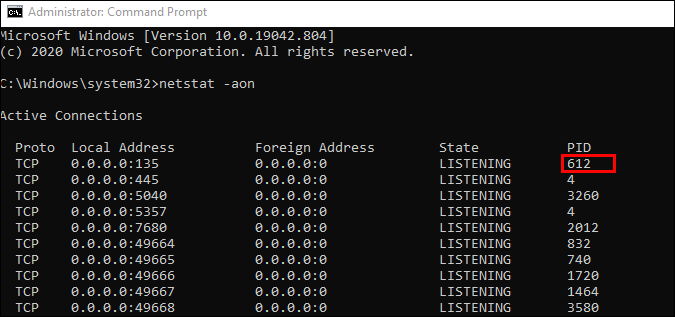
netstat -aon | moreи нажмите на Enter. - Здесь сразу же появится вся важная информация о портах, которые находятся в разных состояниях. В пятой колонке обозначаются идентификаторы.
- Не все порты выводятся сразу, поэтому нужно жать на Enter, чтобы каждый раз отображать еще по одной строке.
- Если вы увидите поле ввода, значит все страницы были успешно выведены на экран.
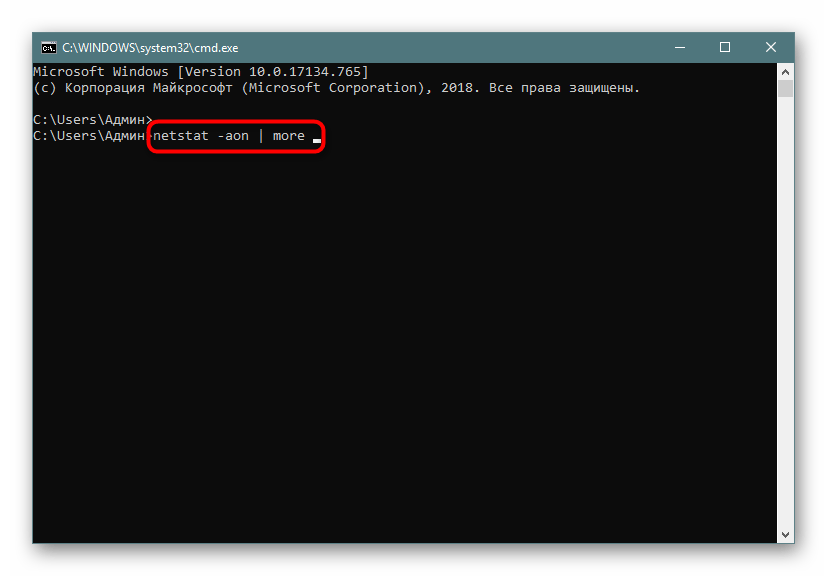
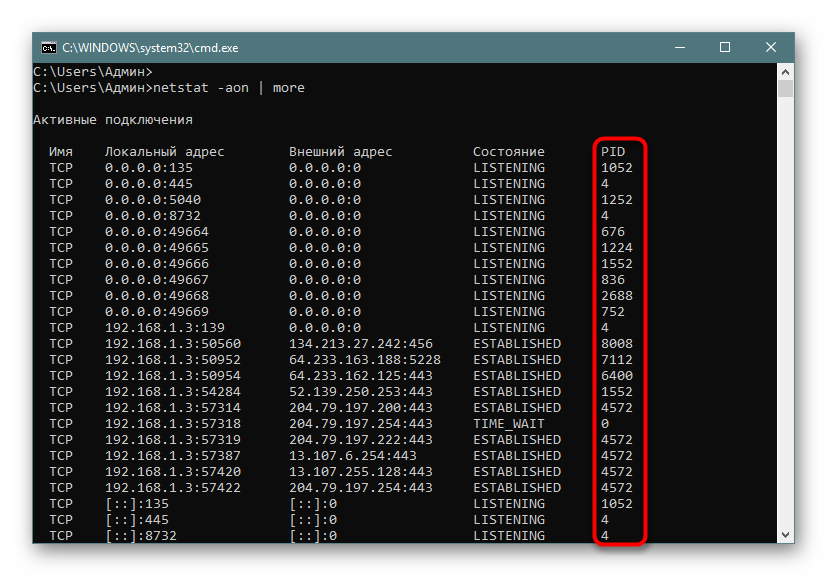
Теперь хотелось бы поговорить про используемые аргументы и значение увиденных параметров. Давайте сначала затронем знакомые буквы синтаксиса:
| Аргумент | Описание |
|---|---|
| -a | Отображает сведения обо всех подключениях |
| -o | Отвечает за включение колонки с идентификатором каждого адреса |
| -n | Переводит адреса портов и их номера в числовой формат |
| more | Постраничный вывод элементов |
Важно также уточнить и состояние портов, поскольку они могут являться открытыми, но на этот момент не использоваться или ожидать своего подключения. В колонке «Состояние» могут отображаться такие показатели:
| Показатель | Описание |
|---|---|
| CLOSE_WAIT | Подключение ожидает своего закрытия |
| CLOSED | Подключение было успешно закрыто |
| ESTABLISHED | Активная работа соединения |
| LISTENING | Ожидается соединение или еще говорят: «Слушается порт» |
| TIME_WAIT | Время ответа было превышено |
Эти объяснения должны разобраться помочь не только с составлением запросов для netstat, но и без проблем разобраться с полученной информацией.
Запись результатов в текстовый файл
Иногда требуется сохранить готовые результаты мониторинга в текстовый файл, чтобы выполнить дальнейшие действия, ведь копировать информацию прямо из консоли не всегда удобно, да и займет это намного больше времени, нежели просто указать дополнительный аргумент при вводе команды.
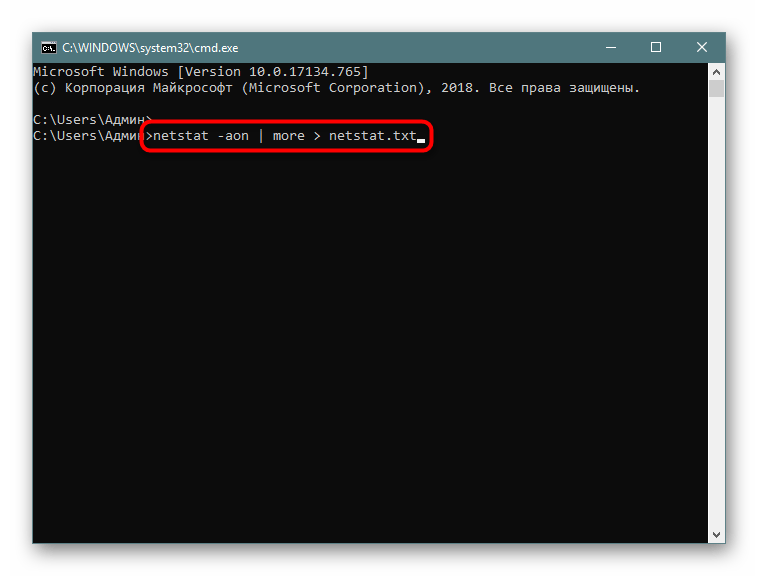
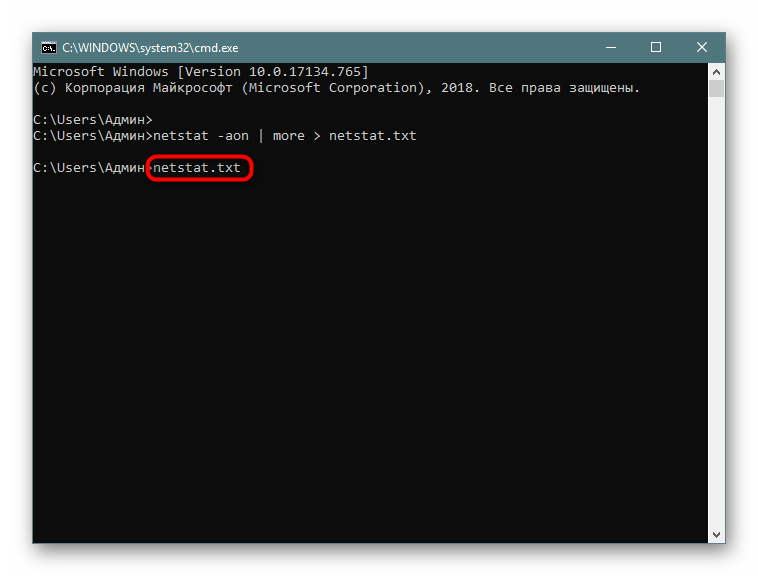
- Напишите, например,
netstat -aon | moreилиnetstat - a, а затем добавьте> netstat.txt, что означает запись результатов в указанный файл (он будет создан в пользовательской папке). После ввода нажмите на Enter. - Запустите файл, введя его название и формат в консоли.
- Теперь вы можете управлять содержимым и сохранить его в любом другом удобном месте.
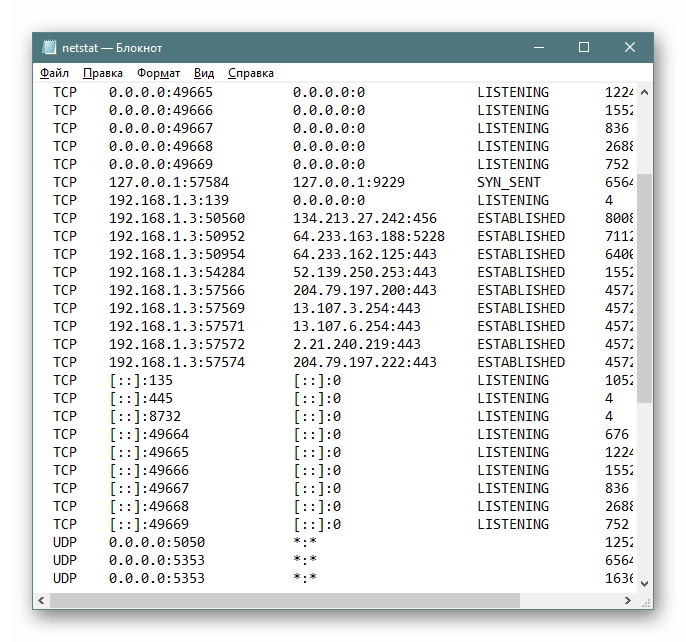
Поиск по содержимому
В случае необходимости отображения только подключений с определенными параметрами или адресами лучше всего использовать дополнительную команду find, которая перед выводом сведений произведет фильтрацию данных, и это освободит вас от надобности вручную искать каждый соответствующий пункт. Тогда полная консольная команда приобретает следующий вид:
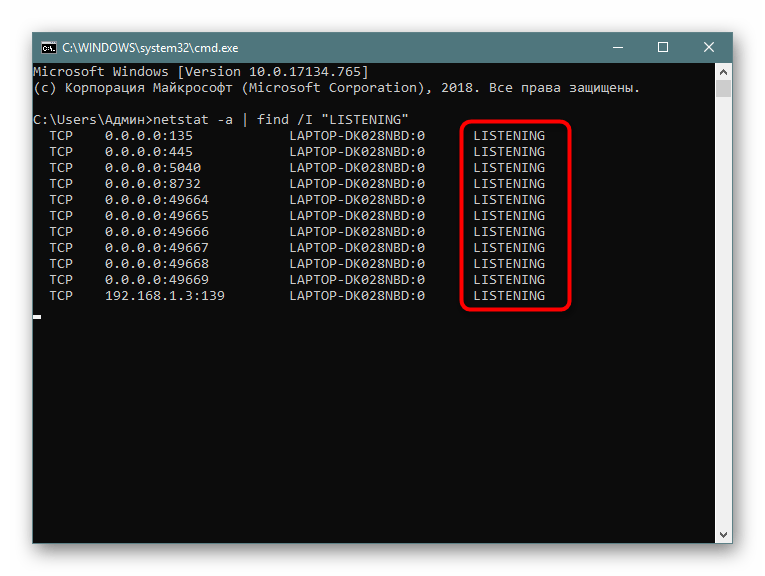
- Введите
netstat -a | find /I "LISTENING", что задаст параметр отображения только портов с состоянием LISTENING, аргумент /I при этом используется для отмены учета регистра символов. - В результатах отобразится только подходящая информация.
Выше вы узнали о методах определения открытых портов через встроенную команду netstat. После этого можете приступить к работе с программами или пробросу других портов в случае необходимости. К слову, этой теме посвящен отдельный материал на нашем сайте. Перейдите по указанным ниже ссылкам, чтобы ознакомиться с подробными инструкциями.
Читайте также:
Открываем порты на роутере
Открываем порты в брандмауэре Windows 10
Команда netstat всегда показывает правильные результаты, однако если хотите убедиться в открытости порта другим путем, рекомендуем задействовать специальные онлайн-сервисы, позволяющие справиться с поставленной задачей.
Читайте также: Сканирование портов онлайн
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь

In this tutorial, we will learn how to run the netstat command to check open ports in Windows Operating System. We will also look at command options and how to use the findstr command (similar to grep) to filter the netstat output.
To check open ports, open a command prompt (or PowerShell) as administrator and run the netstat command as follows:
netstat -aonThe command displays lots of information. What you should pay attention to are Local Addresses that are in the LISTENING state.

As you can see in the previous screenshot, In my Windows 10 computer, port 22 (SSH) is open.
Administrators can run the following command to show opened ports only without all other details:
netstat -aon | findstr /i listeningOne important point is that the Windows Firewall may block a port even if it is in the listening state. In the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security, there has to be a corresponding inbound firewall rule to match the listening port (Anything with a green checkmark is an open rule).

The Foreign Address column of the output shows the IP address and port of the computer/server at the remote end of the connection.
To check that the port is open from a remote computer, an administrator can run the telnet command from a remote computer against the IP address of the Windows computer.
For example, to check if port 22 is open, I will run the telnet command from a remote computer as follows:
telnet IP_ADDRESS 22Replace IP_ADDRESS with the actual IP Address of the Windows computer.

Filtering netstat using findstr
Administrators can use the findstr CMD command (which is similar to grep) to filter netstat command data based on string patterns.
For example, run the following command to check TCP connections in TIME_WAIT State.
netstat -a | findstr /i TIME_WAITThe /I option is for the case insensitive matching.

Command Options
Windows netstat command, without any command-line arguments, displays active TCP connections.
It also includes some useful command options to show network connections and ports in various forms, such as show connections and opened ports based on the protocol, find the process id of a connection/port, view network statics, and find the application that utilizes connections and ports.
| -a | displays all network connections and ports on which Windows is listening (include both IPv4 or IPv6 addresses). |
| -b | The output shows you which applications are using each active connection and ports (need administrative privileges). |
| -e | Displays network statistics, such as the Errors, the number of bytes, and packets sent and received. |
| -n | Displays addresses and ports in numerical format. |
| -f | When used, the output will contain Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) of IP addresses, if available. |
| -o | Displays an additional column that contains the Process ID (PID). |
| -p | Display data for a specific protocol (e.g., -p TCP). The Protocol can be one of the following: TCP, UDP, TCPv6, or UDPv6. If combined with the -s option, Protocol can be TCP, UDP, ICMP, IP, TCPv6, UDPv6, ICMPv6, or IPv6. |
| -r | Check Windows routing table. |
| -s | Displays detailed network statistics for each protocol (IPv4, IPv6, ICMPv4, ICMPv6, TCP, and UDP). |
| interval | Sets Time interval (in seconds) to automatically update the output. See examples to learn more. |
Examples: Using the netstat command
List all Active TCP connections:
netstatCheck open ports:
netstat -aon | findstr /i listeningOnly want to see information about TCP protocol:
netstat -a -p tcpShow network statistics:
netstat -sReal-time network monitoring — In the following example, we set a 5 second time interval to check active network connections in real-time. The number 5 causes the command to repeat every five seconds (Press CTRL+C to quit).
netstat -n 5If you need more information about the Windows netstat command, type netstat \? in the command prompt.
Last Updated :
09 Apr, 2025
Open ports on your Windows computer act like doors for data-letting information in and out. While necessary for apps and services, unprotected ports can become security risks. Checking which ports are open helps you spot vulnerabilities, fix connection issues, and keep your system safe.
Using Command Prompt (CMD), you can quickly see active ports with simple built-in commands—no extra tools needed. This guide walks you through the steps to check open ports in Windows, understand the results, and close any unnecessary ones.
Whether you’re troubleshooting a network problem or guarding against threats, these CMD techniques give you control over your system’s security.

How to Check Open Ports Using CMD in Windows
Make sure that the essential ports are allowed or blocked by your firewall system configuration. The Control Panel’s Windows Firewall settings allow you to control all the initial processes for system requirements. If you discover the open ports that ought to be closed within the system, you might want to halt the related service or change the in-build configuration of the program that opened the port manually.
Now, see the below-mentioned steps and implement them to Check Open Ports Using CMD in Windows.
Step 1: Open CMD or Command Prompt
- Press Win + R from your keyboard > Type cmd > Click on the Enter button
Step 2: Implement the «netstat» Command
An effective tool for keeping an eye on open ports within the system and configured network connections is the netstat command to simplify. It offers comprehensive details on all open connections and system servers, such as the protocol in use, and local and international addresses to control or verify all the connection’s status.
- Type the below command in the cmd to check the open port functions > Press Enter
netstat -an | find "LISTEN"
- See the output below
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:902 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
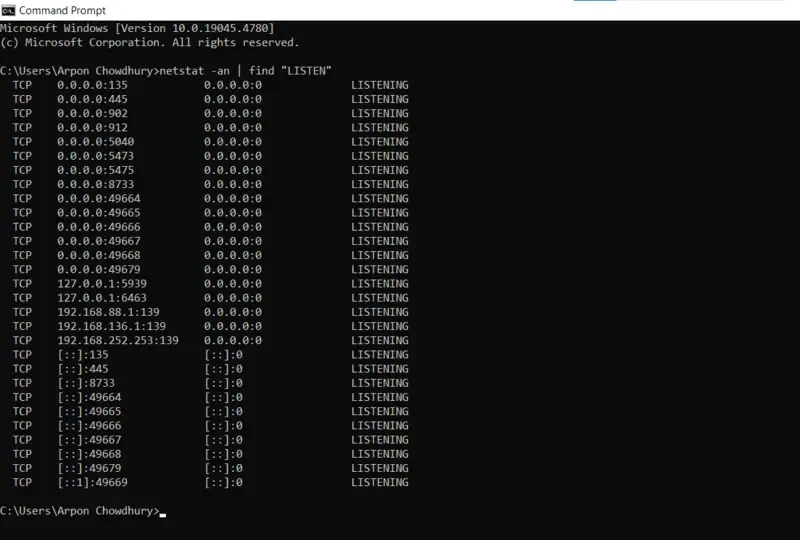
In this case, 0.0.0.0 designates that all pre-processed network interfaces are listening on the port, which is open for the internal system server. The port number is the number that comes after the colon of the system commands (e.g., 135, 445, 3389).
Step 3: Observe the functional Process Using the Port
- Write the following command to identify which application or process is using a specific port within the system.
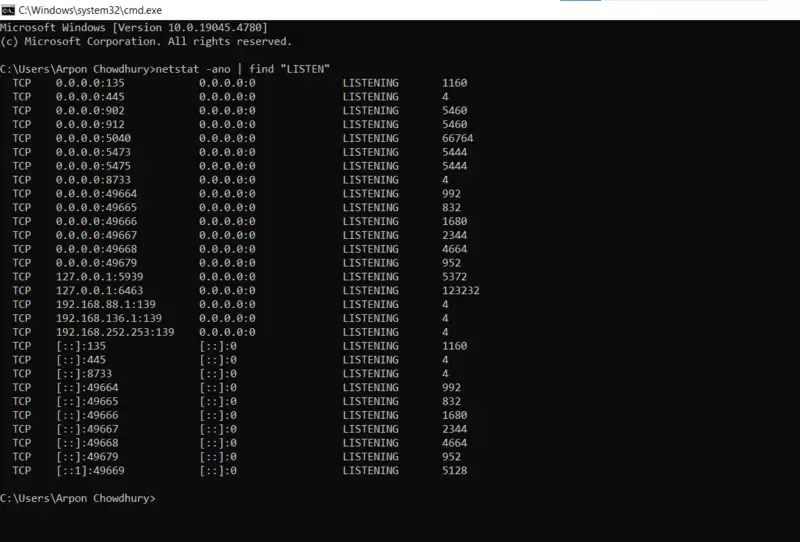
netstat -ano | find "LISTEN"
An extra -o flag is included with this command while processed, which shows the Process ID (PID) connected to each port manually.
- See the output within a PID column
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 1160
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4
- Search and Open Task Manager > Go to Details option > See the PID column
Step 4: Check Specific Port in cmd
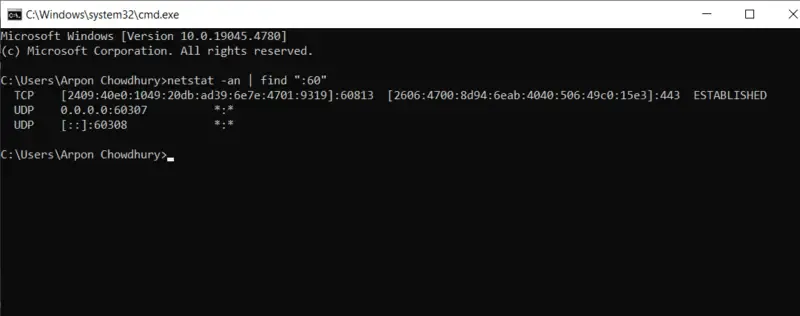
- You can change the implemented command to focus on a particular port if you want to see if it’s open or not within the system configuration. For instance, use this to see if port 60 is open to identify the process:
netstat -an | find ":60"
- See the final entry below —
TCP 0.0.0.0:40 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
Conclusion
Using Windows’ CMD to check all the internal open ports is a simple yet effective method for network management, security control, and troubleshooting issues identification. You can safeguard your system from external potential dangers and make sure your connected network is operating efficiently by routinely checking open ports within the system. The netstat command is an invaluable resource for any IT professional or developer toolset, especially when paired with a basic understanding of ports and processes of all the initial implementations.
Also Read
- How to check Active Network Connections in Windows?
- Ways to Find Out List of All Open Ports in Linux
Imagine you’re playing your favorite online game, but you’re experiencing lag and connection issues. Or perhaps you’re concerned about the security of your Windows system and want to ensure no unauthorized access points exist. The culprit behind these scenarios could be open ports on your system.
Open ports act as virtual doorways that allow your computer to communicate with other devices or servers across a network. They play a crucial role in facilitating various online activities, from web browsing and email to file sharing and online gaming. However, open ports can also pose security risks if not properly managed, potentially allowing malicious actors to gain access to your system.
Understanding how to check open ports Windows is essential for both troubleshooting network problems and maintaining optimal system security. This process, known as port scanning, allows you to identify which ports are open, the services or applications associated with them, and potential vulnerabilities that may need addressing. The article will guide you on how you can check Windows open ports.
What are Open Ports?
Open ports are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) or UDP (User Datagram Protocol) ports that are currently in use by a running process or service on your system. These ports are essential for network communication protocols, as they allow different applications and services to exchange data. For example, when you access a website, your web browser uses port 80 (HTTP) or port 443 (HTTPS) to communicate with the web server.
There are 65,535 available TCP and UDP ports, divided into three ranges:
- Well-known ports (0-1023): Assigned to common network services like FTP (21), SSH (22), and HTTP (80).
- Registered ports (1024-49151): Assigned to specific organizations or vendors for their products and services.
- Dynamic ports (49152-65535): Used for temporary or private connections, such as during a file transfer.
Explore the Blazing Fast Speed with Cheap Windows VPS!
With Ultahost, Hosting Windows VPS has never been easier or faster. Enjoy ultra-fast SSD NVME speeds with no dropouts and slowdowns.
Checking open ports is crucial for maintaining system security and preventing unauthorized access. Here are some reasons why:
- Malware and virus infections: Malware can use open ports to communicate with their command and control servers, stealing sensitive data or spreading further infections.
- Unauthorized access: Open ports can allow hackers to access your system remotely, potentially leading to data breaches or system compromise.
- Resource utilization: Unused open ports can consume system resources, slowing down your system’s performance.
Windows provides two built-in tools for port scanning: Netstat and PowerShell. Below we outline the basic guide on how to see open ports Windows.
Netstat
Netstat is a command-line utility that displays active network connections, routing tables, and interface statistics. To use netstat for port scanning, you need to open Command Prompt as an administrator use the following command and press Enter:
netstat -an
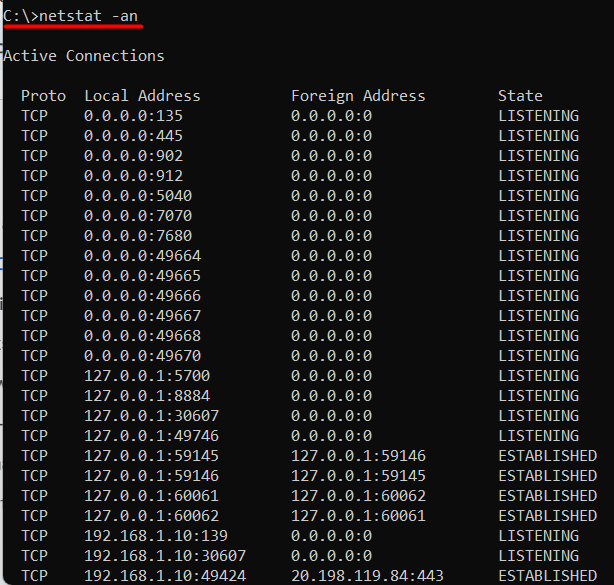
The -an option displays all active connections, including listening ports. Look for the “Local Address” column, which shows the IP address and port number of each connection.
PowerShell
PowerShell is a powerful task automation and configuration management framework from Microsoft. To use PowerShell for port scanning, you need to open it as an administrator and then execute the below command:
Get-NetTCPConnection
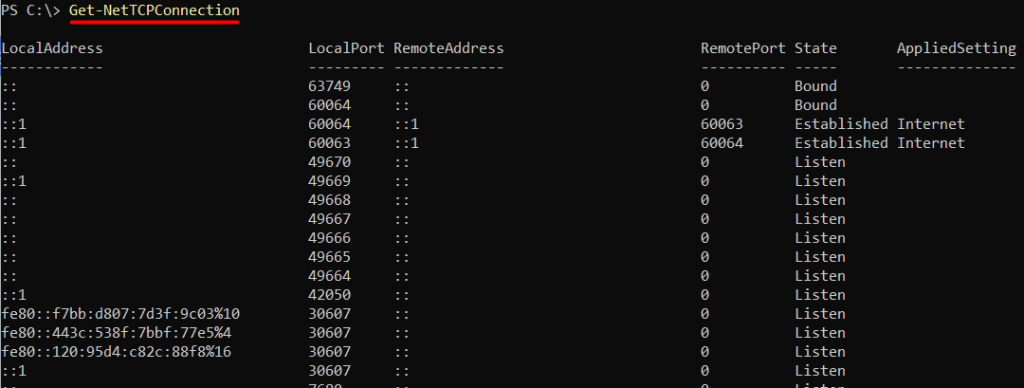
This cmdlet displays all list open ports Windows, including listening ports. Look for the “LocalAddress” property, which shows the IP address and port number of each connection.
Third-party software for Port Scanning
While built-in tools can provide basic port scanning capabilities, third-party software offers more advanced features and flexibility.
Nmap
Nmap is a popular, open-source port scanner that provides detailed information about network hosts and services. To use Nmap:
Download and install Nmap from the official website.
After installing it you need to open the open Command Prompt as an administrator and execute the below command:
Type nmap -p 1-65535 <IP address>
Replace <IP address> with the IP address of your system or a specific host. Nmap will scan all 65,535 ports and display the results, including open ports and services:
nmap -p 1-65535 192.168.10.1
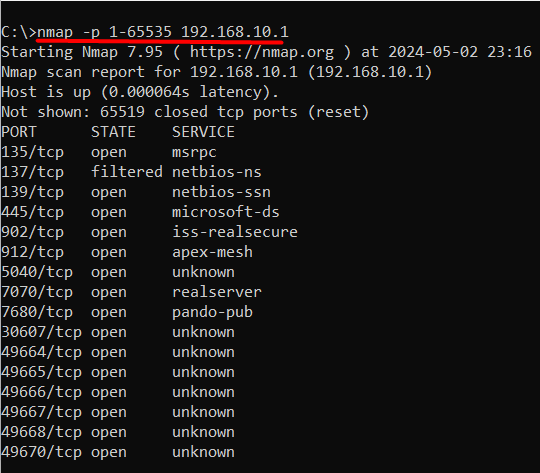
If you are unaware of your IP address then you can execute the ipconfig command on the command prompt to find it.
Conclusion
Open ports play a vital role in facilitating online activities, but they can also pose significant security risks if not properly managed. Understanding how to check open ports in Windows is essential for both troubleshooting network problems and maintaining optimal system security. By identifying open ports, users can determine which services or applications are associated with them and address potential vulnerabilities that may need attention.
By utilizing built-in tools like Netstat and PowerShell, or third-party software like Nmap, users can effectively scan for open ports and take necessary steps to ensure system security. Regular port scanning can help prevent malware infections, unauthorized access, and resource utilization, ultimately protecting sensitive data and system integrity. By grasping the importance of open ports and how to manage them, users can take a proactive approach to maintaining a secure and efficient Windows system.
While enabling open ports on your Windows machine can be useful for specific applications but it also introduces security risks. For a more secure and controlled environment rent a VPS from Ultahost. These VPS plans grant you root access and complete control over your server’s firewall configuration. This allows you to open ports with specific control ensuring only necessary ports are exposed.
FAQ
What are open ports in Windows?
Open ports are communication endpoints that allow data to be transmitted between a device and a network. In Windows, these ports can be in a listening state, waiting for incoming connections, or actively transmitting data.
Why is it important to check open ports in Windows?
Checking open ports can help you identify any potential security vulnerabilities on your Windows system. Unnecessary open ports could be exploited by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to your system or to launch attacks.
How can I check open ports in Windows?
You can check open ports in Windows using various methods, including using built-in command-line tools like Netstat or PowerShell, third-party software, or online port scanning tools.
How do I use the netstat command to check open ports?
To use the netstat command, open Command Prompt, and type netstat -an. This will display a list of all open ports and their respective states (listening, established, etc.).
Can PowerShell be used to check open ports in Windows?
Yes, PowerShell provides cmdlets such as Get-NetTCPConnection and Get-NetUDPEndpoint that allow you to check open TCP and UDP ports, respectively.
Maybe you’re troubleshooting a network connectivity issue for a specific program and need to check whether its port access is open. What if you need to confirm that your NAS device can communicate with your Windows 10 PC? Whatever reason you need to look for open ports, this article provides detailed steps to check them on Windows 10 using several available tools, either built-in or free to download and use.
There are a couple of handy tools in Windows to scan open ports. You’ll see how to do so on NetStat, PortQry.exe, and NirSoft CurrPorts.
Using NetStat to Check for Open Ports in Windows 10
One of the simplest ways to check for open ports is to use NetStat.exe. You can find this tool in the System32 folder on Windows 10. With NetStat, you can see open ports or ports that a specific host uses.
Netstat is short for network statistics. It shows protocol statistics and the current TCP and IP network connections. The two commands needed to identify open ports in netstat -ab and netstat -aon.
Here’s an explanation of what each letter from the commands means.
- “a” displays all connections and listening ports.
- “b” shows all executables involved in creating each listening port.
- “o” provides the owning process ID related to each connection.
- “n” shows the addresses and port numbers as numerals.
Two commands are helpful, depending on your needs. The second option (netstat -aon) additionally provides a process ID you can later search for in the Task Manager.
Using ‘netstat -ab’ to Identify Open Ports
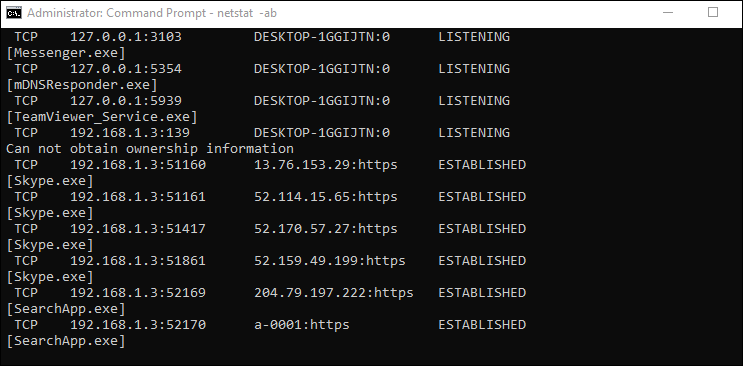
The first option you’ll use (netstat -ab) lists all active ports and the process that uses them.
- In the Cortana Search Bar, type the following:
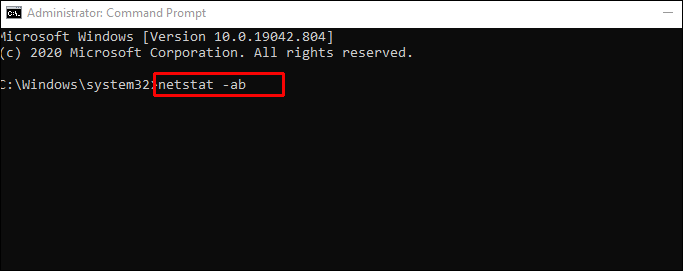
cmdthen select Run as administrator. - Now, type
netstat -ab, then press Enter. - Wait for the results to load. Port names get listed next to each local IP address.
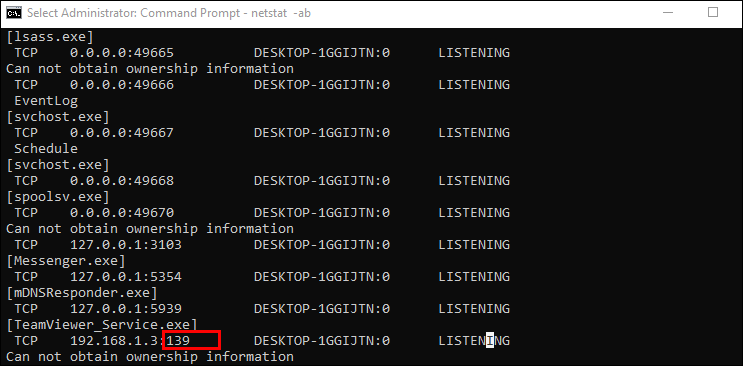
- Look for the port number you need; if it says LISTENING in the State column, it means your port is open.
Using ‘netstat -aon‘ to Identify Open Ports
The second option(netstat -aon) includes process IDs, which you’ll use to identify a task/application in the Task Manager. Some processes may be challenging to identify using netstat -ab, so netstat -aon gets used. As referenced above, “a” represents all connections and ports, “o” represents the owning process ID, and “n” represents the addresses and port numbers as numerals.
Using netstat -aon comes in handy when netstat -ab isn’t enough to identify what program has a specific port tied up. In that case, follow these steps:
- In the Cortana Search Bar, type “
cmd“ and choose “Run as administrator.” - Once inside, type the following command without quotes:
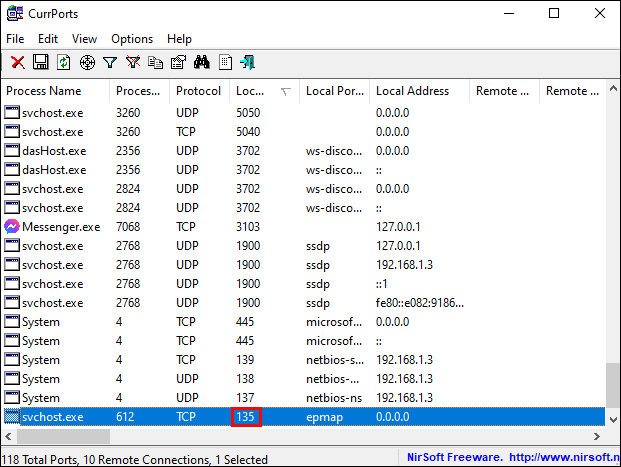
netstat -aonthen press Enter. - You will now see five columns: Protocols, Local Address, Foreign Address, State, and PID (Process ID). In the Local Address, you have a port number. For example: 0.0.0.0:135. Here, 135 is the port number.
- In the “State” column, you will see whether a specific port appears opened. For opened ports, it will say LISTENING.
- To verify which app uses a particular port, find the PID (the number from the last column) for a specific port.
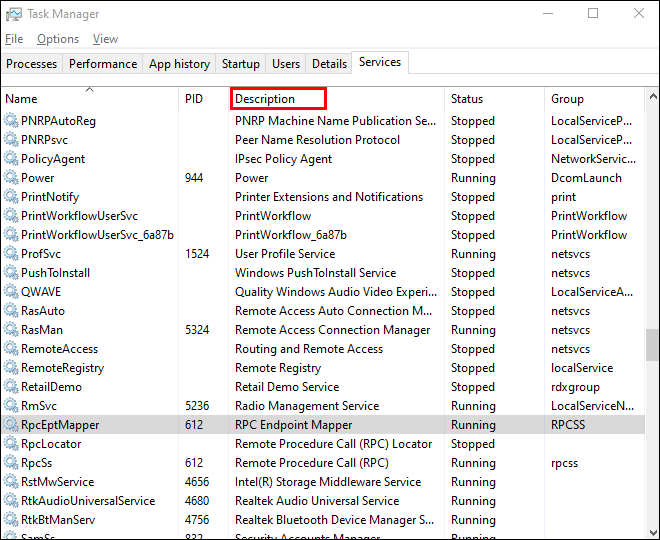
- Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc.
- Go to the Details or Services tab to see all processes on your Windows 10 system. Sort them by the PID column to find the PID for the port you’re trying to troubleshoot. You can see which app uses the port in the Description section.
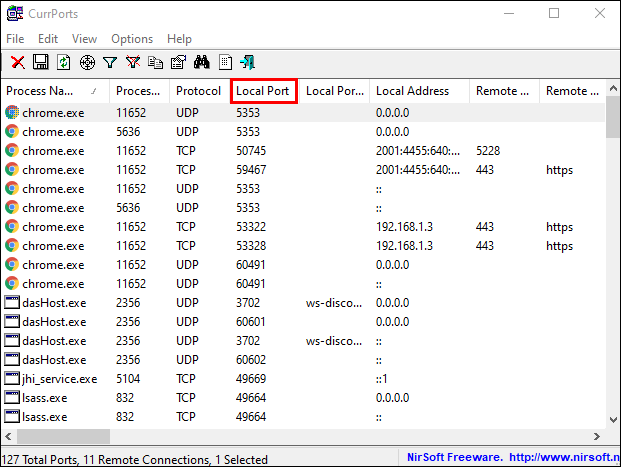
Checking for Open Ports with NirSoft CurrPorts
If you find the Command Prompt solution too tricky, a simpler alternative is to use NirSoft CurrPorts. This tool displays your currently opened ports (TCP, IP, and UDP). You’ll also see information about a specific process, such as name, path, version info, etc.
This tool has been around for quite a while and is available for Windows 10. You can find the NirSoft Currports download link at the bottom of Nirsoft’s website.
Note: Ensure you download the correct version. They have 32-bit and 64-bit releases. The app is portable. Unzip the folder, then run the executable file.
Once you have CurrPorts running, perform the following steps:
- You’ll see a list of your computer processes. Sort them by Local Port to search through them more easily.
- Now, find and select the port you are troubleshooting.
- You can now see all the process details, such as Process Name, Process ID, State, etc.
Another way is to double-click on a process to see its details in a single window.
Checking for Open Ports Using PortQry.exe
PortQry.exe is another handy tool that lets you scan open ports. You download PortQry (scroll down to see the download) and extract it to run it through the Command Prompt. You can also download PortQryUI, a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for PortQry (more on that below), as an add-on if you don’t want to use the command line.
With portqry.exe, you insert specific parameters that can be found in the executable’s folder.
How to Run PortQry.exe Using the Command Prompt
- Download PortQry, then unzip the files to your chosen location. The default is “C:\” but can be changed if desired.
- If in the default directory, type
cd c:\PortQryV2\in the Command Prompt to set the location of the executable file. - If in a custom directory, type
cd [drive letter]:\[folder1]\[folder2]\but replace all content in the square brackets with actual names. Include all folders needed. - Type
portqry.exe -localto launch it. This command displays the TCP and UDP ports the specified ‘localhost’ uses. - In addition to all the parameters NetStat displays, Portqry shows you several port mappings and the number of ports in each state.
- You can also check for open ports for a remote host. Run portqry.exe -n [hostname/IP] in the Command Prompt. Replace the hostname and IP sections with the remote host’s name and IP address. Add -e [port_number] to the command line to look for a specific port.
How to Run PortQry.exe using the UI Add-On
For those preferring to use a graphical interface instead of commands when using PortQry.exe, Microsoft offers an add-on named PortQryUI.
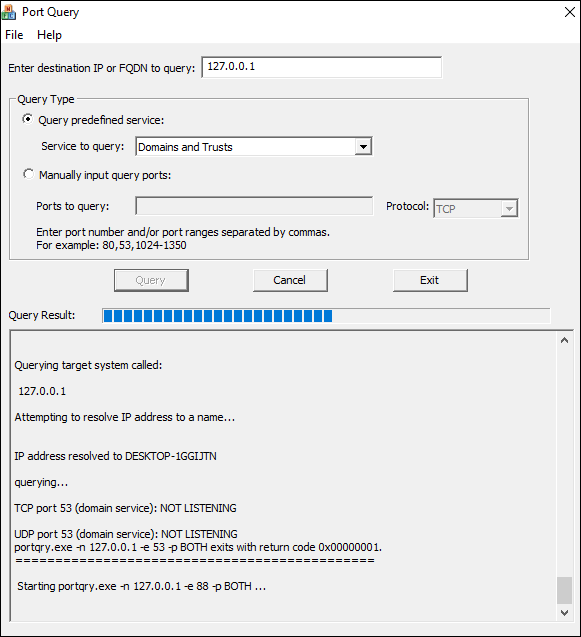
The PortQryUI add-on already includes the necessary version of PortQry, so you don’t need both downloads to use it.
- Download PortQryUI, then unzip the files to your chosen location. The default is “C:\” but can be changed if desired.
- Launch Windows Explorer, navigate to the PortQryUI.exe file location, then click it to launch the UI.
- To view TCP and UDP ports for the ‘localhost’ (your PC), leave the Destination IP as 127.0.0.1 so it passes through the network’s devices and configuration settings (network card, router’s config, etc.) and not just read from the local PC.
- To view all TCP and UDP ports, click on Manually input query ports, then type 1-65535 in the Ports to query section. Also, select TCP, UDP, or Both from the Protocol dropdown.
- To filter your TCP/UDP ports list, click Query predefined service, then choose which service to query. You can only select one at a time.
- You can also check a remote host by changing the FQDN or domain in the query box at the top.
- If you want to check a specific port, enter the number in Ports to query.
In closing, knowing how to check if a specific port is open is beneficial if you’re troubleshooting a program’s network connection or need a port for a particular game. Luckily, it’s not as challenging to do as it looks.
Out of all the options listed above, Netstat is recommended as it’s built into the OS and usually gives you all the details you need. There might be a few extra steps required compared to CurrPorts, but you don’t have to download anything, and there’s nothing to screw up.
How do I check if Port 3306 is open in Windows 10?
To verify if port 3306 is open, you can use NetStat, CurrPorts, or PortQry.
We recommend NetStat, as you won’t have to download new software. Run the Command Prompt as administrator. Type the following command: netstat -ab and hit Enter. Wait for the results to load. Port names will be listed next to the local IP address. Just look for port 3306. You can press Ctrl + F and type 3306 in the word box to search for it. If the port is open, it will show in the results as LISTENING.
To check if port 3306 is open via CurrPorts, just sort by Local Port, then find port 3306. If the port is available, it will show in the list.
To use PortQry.exe to find port 3306, use the Command Prompt. Type -e [3306], then press Enter.
What are Predefined Services in PortQueryUI?
Predefined Services offers details on a small handful of services such as Domains and Trusts, Networking, Exchange Servers, etc. The option queries all required ports for the specified services and displays them in the UI.
For those who don’t know where Predefined Services resides, it is directly under the Help tab and in the UI. Both serve different needs.
The Help tab option immediately displays all predefined services without testing any ports, providing a quick reference to each port name, value, and protocol used for each listed service.
The UI option lets you specify what service you want to view and see port statuses.