Table of contents
- What Is the Windows Event Viewer?
- Most Common Windows Reboot and Shutdown Event IDs
- How to See PC Startup and Shutdown Logs in Windows 10/11?
- Method 1: View the shutdown and restart log from the Event Viewer
- Method 2: View the shutdown and restart log using the Command Prompt
- Windows Restart/Shutdown Logs: Explained
- FAQ
Are you wondering what happens when your computer shuts down and after it restarts? Many things happen within that period, and thankfully, Windows helps track the entire process and keeps a record in the system log.With the built-in Windows Event Viewer, you can monitor the activities that occur on your computer before, during, and after it shuts down or restarts. In this article, we’ll teach you how to do that, but first, what is the Event Viewer?
What Is the Windows Event Viewer?
The Event Viewer
records application and system messages on a Windows 10 PC and logs every action taken while working on the computer. That said, if many users operate a computer, you can use the Event Viewer to monitor each user’s activities while the device is running. Also, it helps users discover errors, such as blue screens of death (BSODs) , information messages, and warnings on their PCs. What’s more, you can’t alter, stop, or disable the activities of the Event Viewer altogether because it’s a core Windows service. In many cases, you can start troubleshooting any issue on a Windows computer from the Event Viewer. However, as a rule of thumb, you don’t need to panic even if there are alarming messages or warnings in the system log. Unfortunately, some fraudsters take advantage of messages in the Event Viewer to scare and defraud people. They can manipulate it to display error messages and warnings even if your computer is working correctly. Without much ado, let’s show you how to track what happens when your computer shuts down or starts using the Windows Event Viewer or the Command Prompt.
Most Common Windows Reboot and Shutdown Event IDs
There are many identified events related to shutting down and restarting a PC. However, we will show you the most common four in this article, and they include the following:
- Event ID 41: This Event Viewer restart event ID shows that your Windows computer didn’t shut down completely and restarted .
- Event ID 1074: When a certain app forces your laptop or PC to shut down or restart, you’ll see this shutdown/ restart event ID reflected in the Windows restart log . It will also show you if the PC was shut down (or restarted) using the Ctrl + Alt + Del combo or directly from the Start menu .
- Event ID 6006: This one is the Event Viewer shutdown event ID that shows that your PC shut down properly .
- Event ID 6008: You will see this event in your Windows shutdown log if your PC shut down unexpectedly.
How to See PC Startup and Shutdown Logs in Windows 10/11?
Using the Windows Event Viewer, you can quickly determine the shutdown or reboot event IDs on your computer after shutting down or restarting. You can also access some of the events using the Command Prompt, as we will show you below.
Generally, there are two methods to check the reboot or shutdown event ID s on your computer. The steps for both methods to view the Windows shutdown log (or the restart one) on Windows 10 and 11 are absolutely the same.
Method 1: View the shutdown and restart log from the Event Viewer
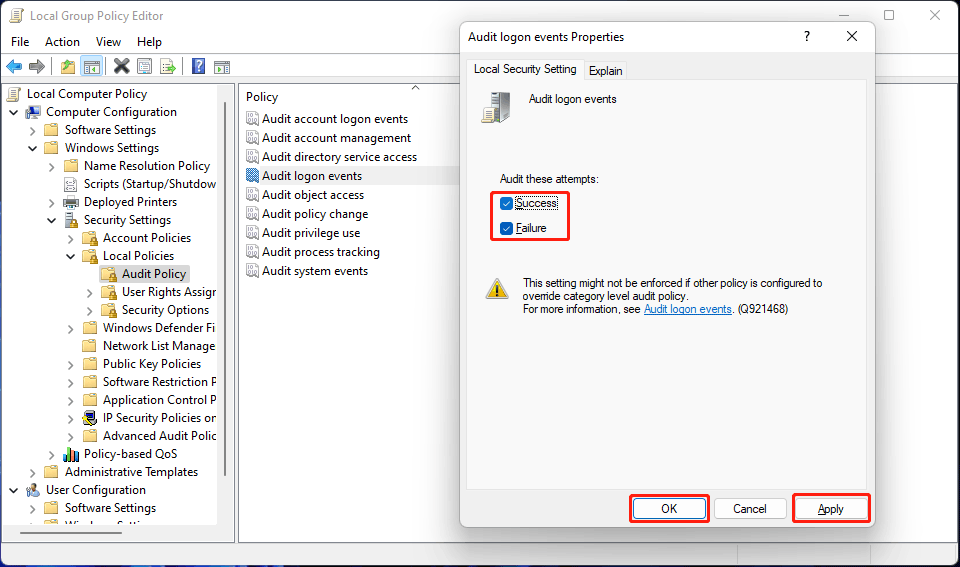
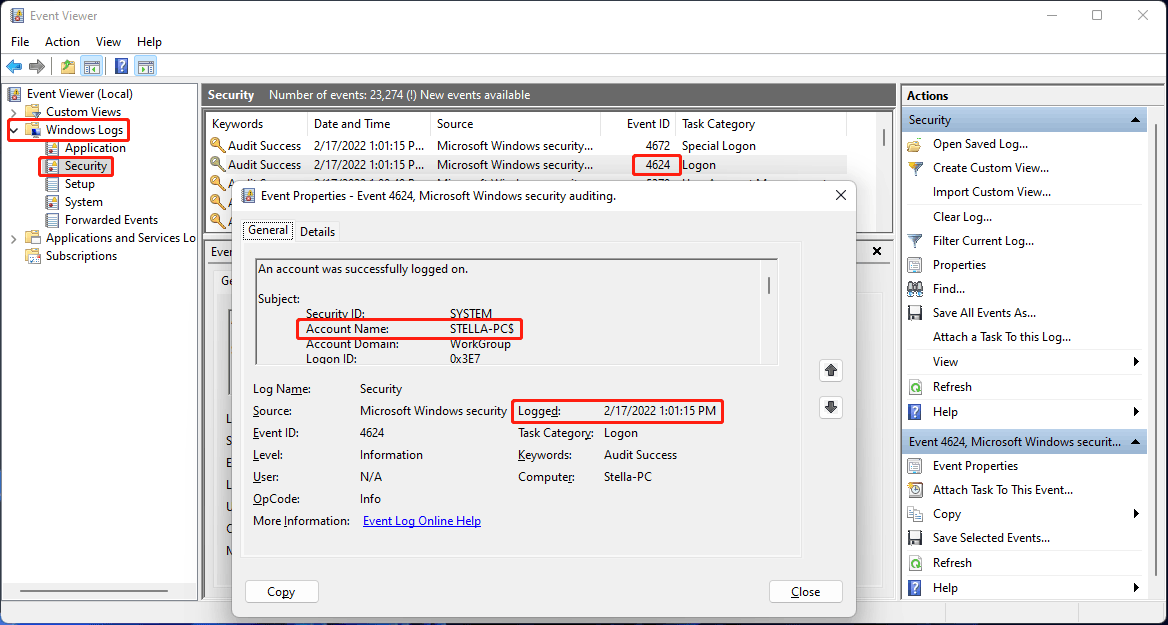
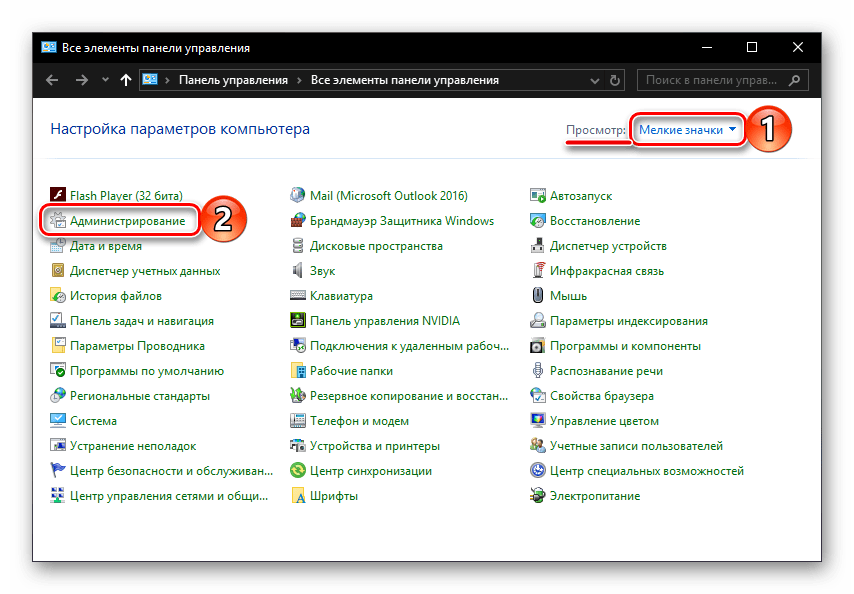
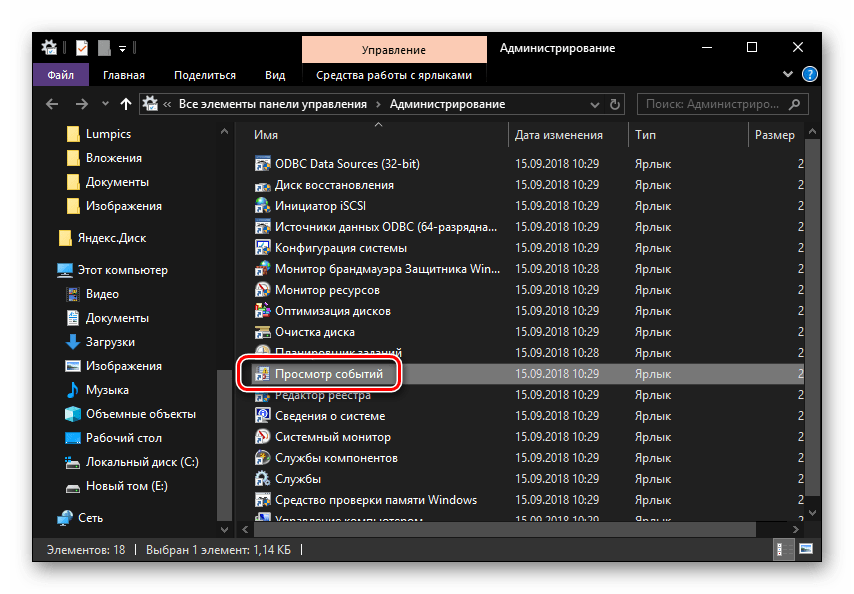
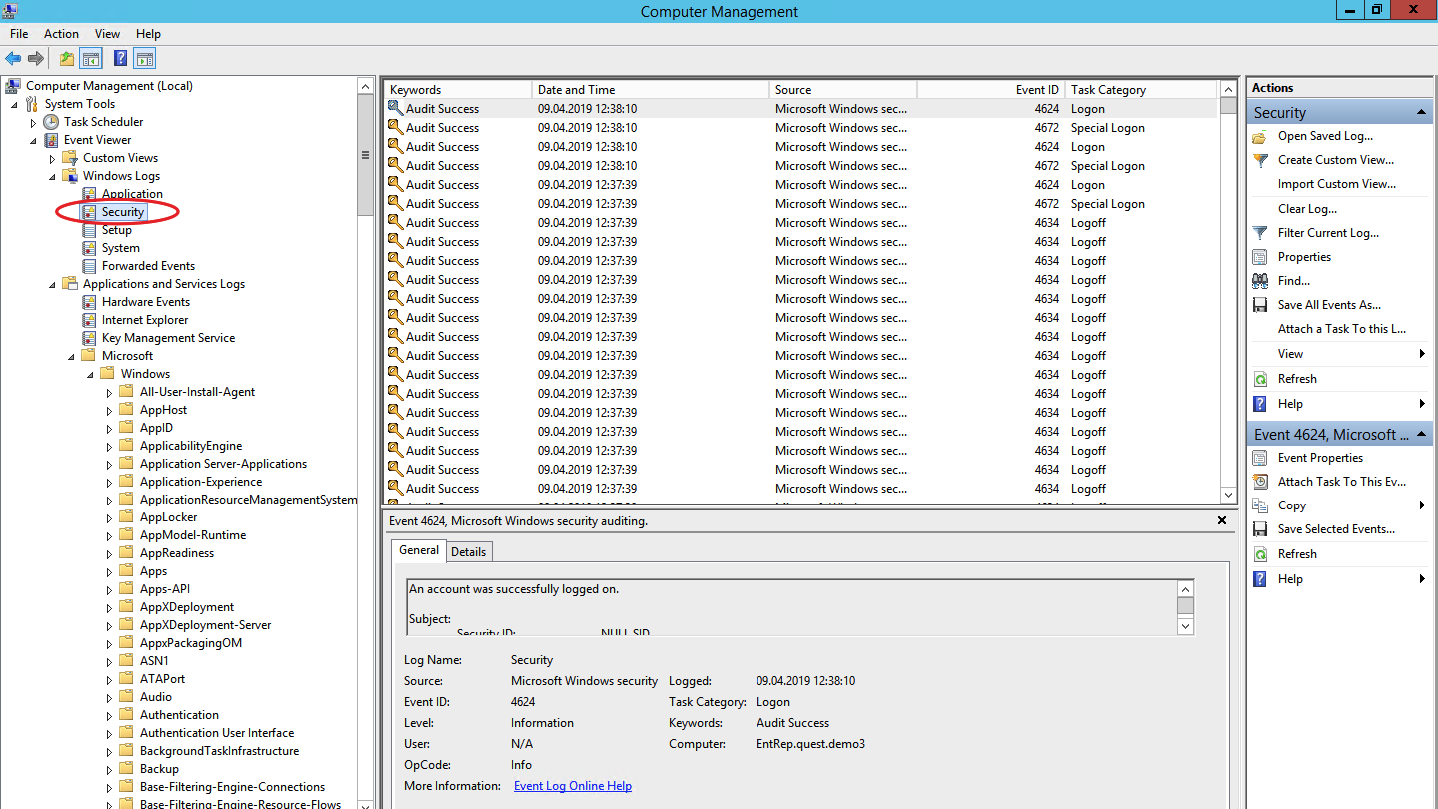
Follow the steps below to view shutdown and restart activities using Event Viewer:
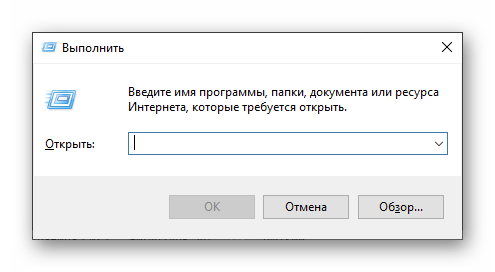
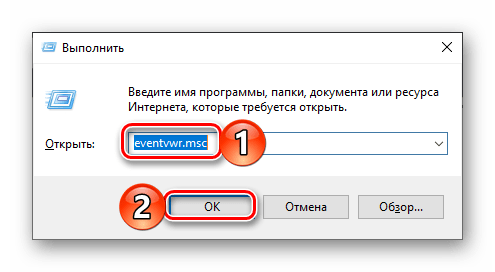
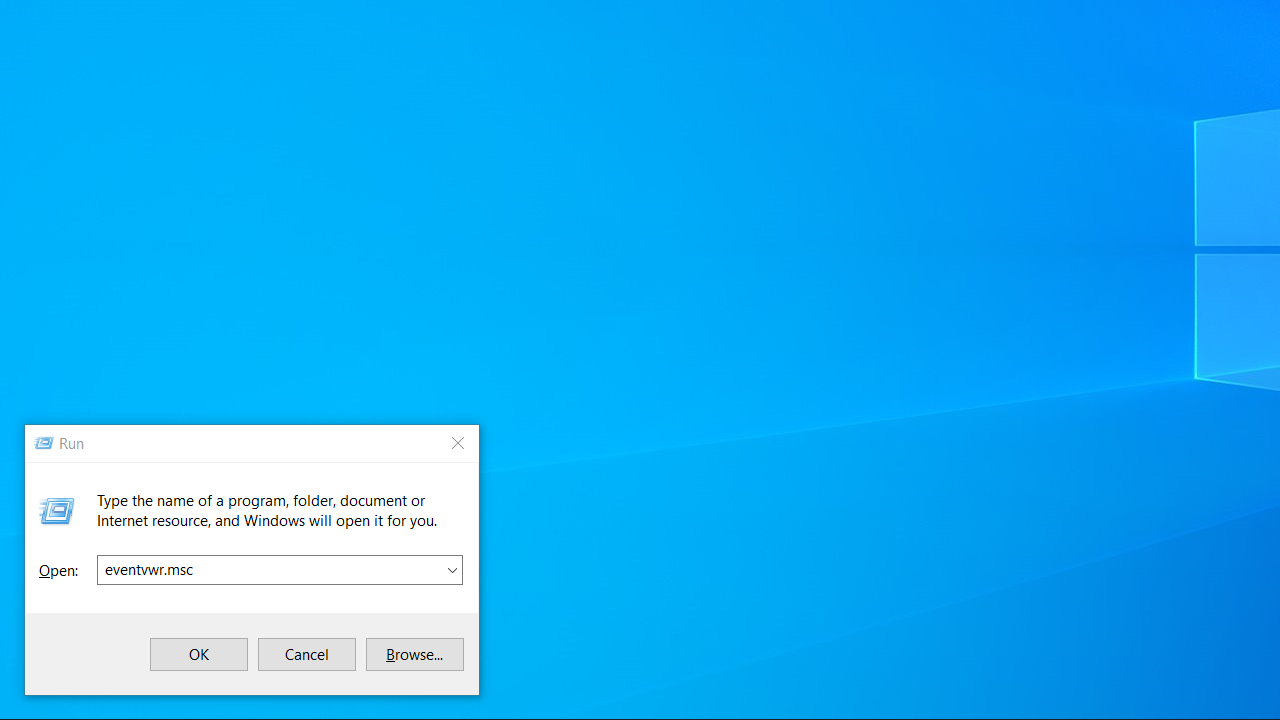
- Press the
Windows logo + Rkeys to invoke the Run dialog. - Type
eventvwr.mscand hitEnter.
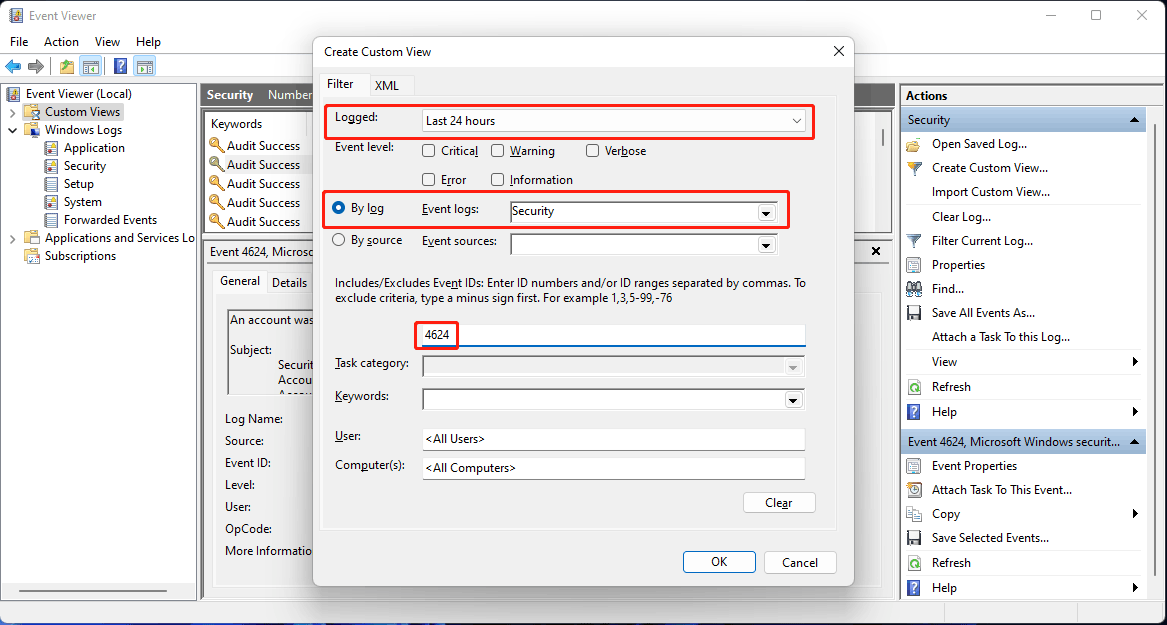
- The Event Viewer window will open. After that, navigate to Windows Logs > System on the left pane.
- Click on Filter Current Log on the right.
- Type
41,1074,6006,6008into the textbox under Includes/Excludes Event IDs , and then click OK to filter the event log to the desired shutdown/ reboot event ID s.
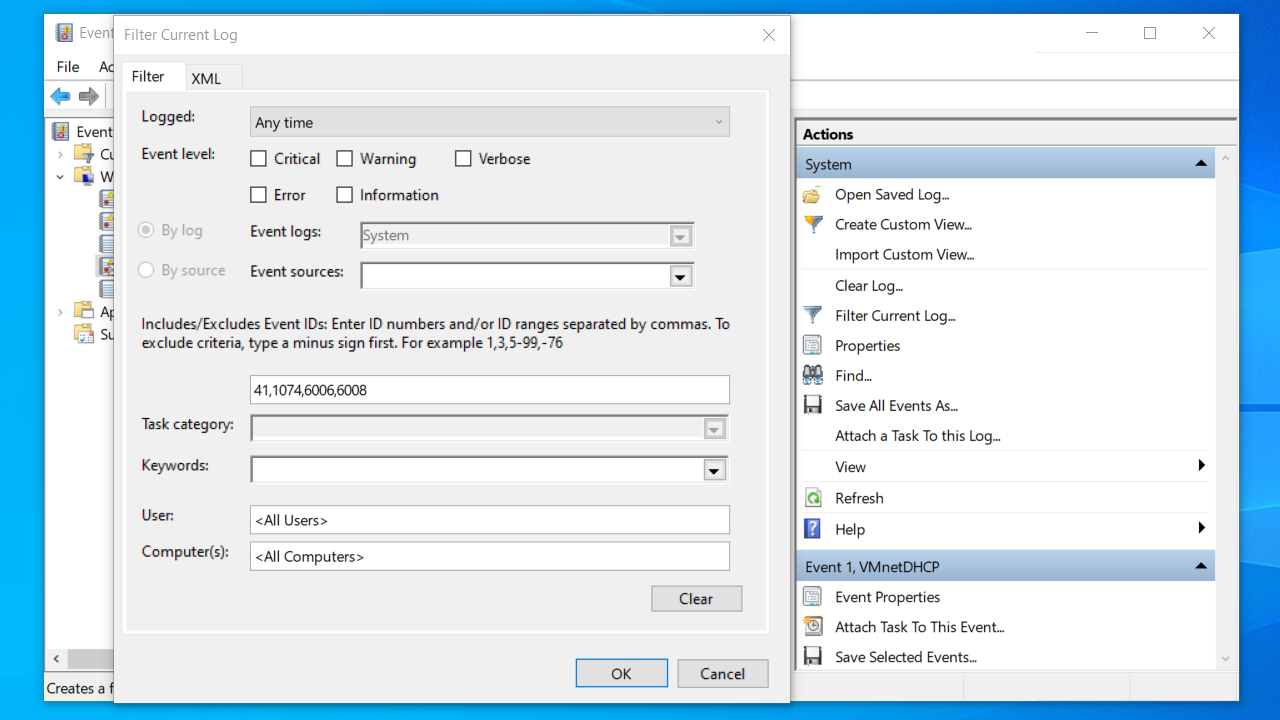
After completing all the steps, the Event Viewer will only display the Windows shutdown log .
Important!
From the Windows 10 Fall Creators Update ( also known as version 1709 ), the OS can automatically reopen apps that were running before your computer shut down or restarted.
This information is handy for Windows users who upgraded their OS to the recent release.
You can avoid this Windows update issue by doing the following:
- Adding a unique Shut Down context menu to the desktop to restore the classic behavior.
- Seeing the last shutdown time using the Command Prompt .
Also read:A Problem Has Been Detected and Windows Has Been Shut Down
PRO TIP
We always advise people to use our recognized software tool to get rid of all sorts of computer problems. Auslogics BoostSpeed can remove all harmful files in the registry, tweak system settings to boost your computer’s speed and performance, and modify internet connection settings to ensure seamless browsing, quicker downloads, and better audio/video call quality.
Method 2: View the shutdown and restart log using the Command Prompt
If the first method is not convenient for you, you can use the Command Prompt to check the Windows restart log (or the shutdown one if that’s your case) by following the steps below:
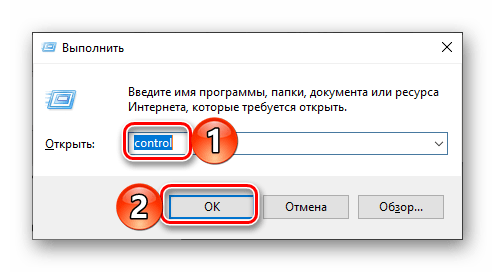
- Press the
Windows logo + Rkeys to open the run dialog, and then typecmd. That’s how you open the Command Prompt.
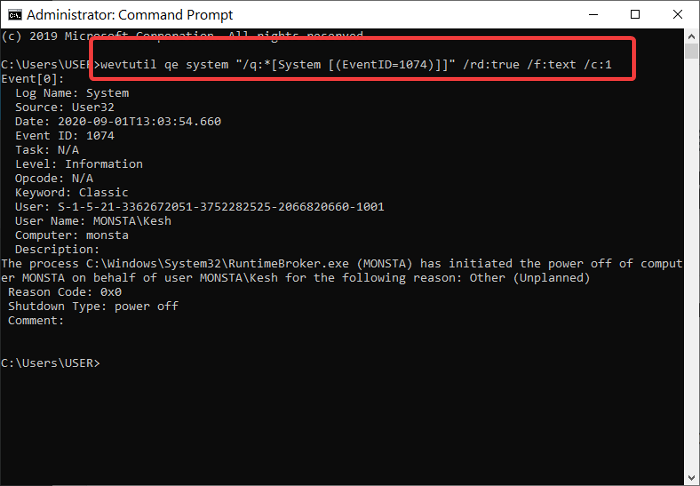
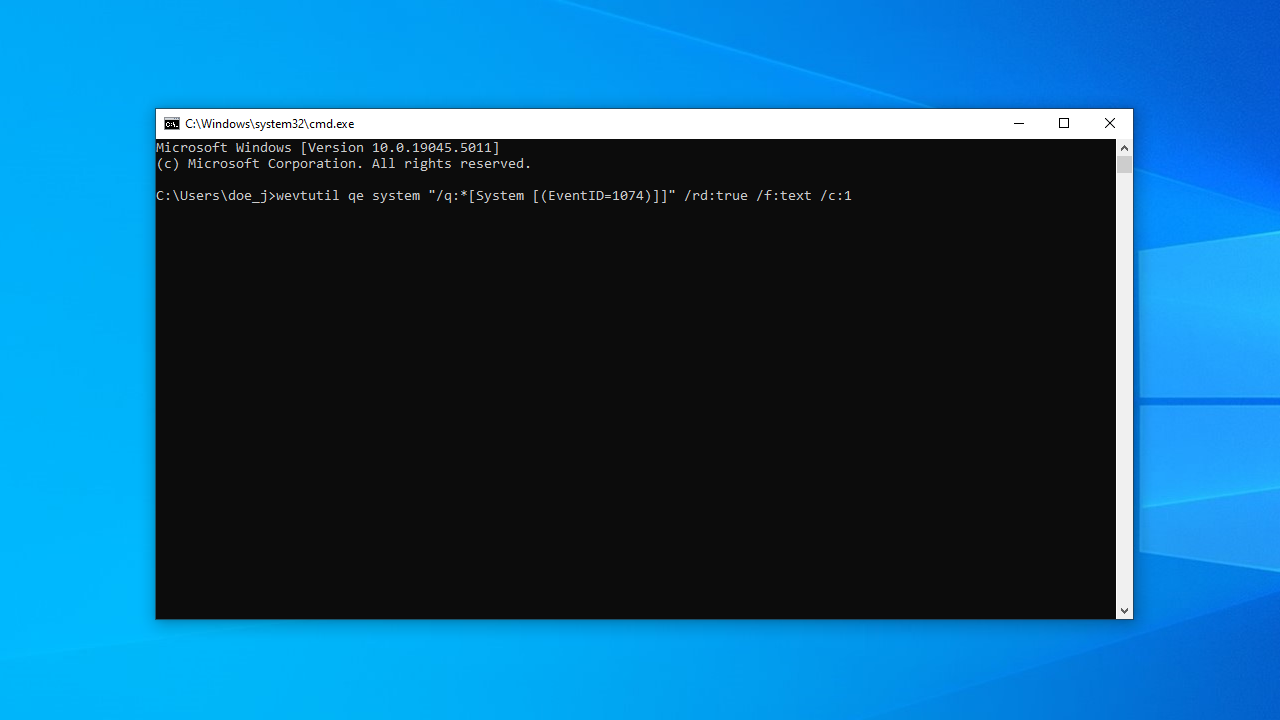
- Now, you can simply copy and paste (or type it yourself if you’re feeling like it) the code you see below into the Command Prompt window and press
Enter:
wevtutil qe system "/q:*[System [(EventID=1074)]]" /rd:true /f:text /c:1
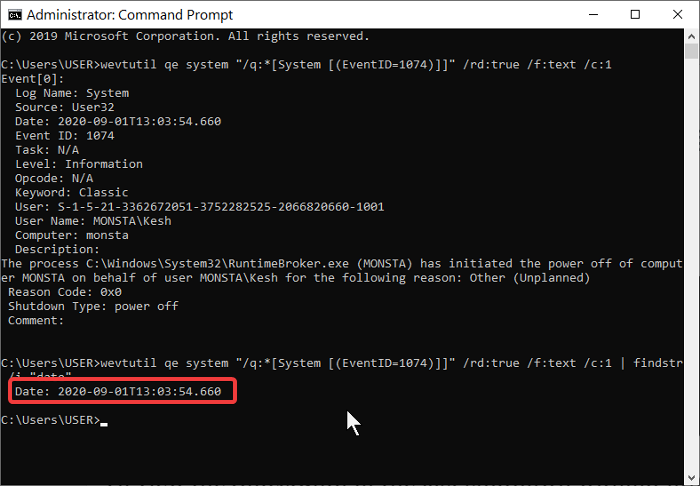
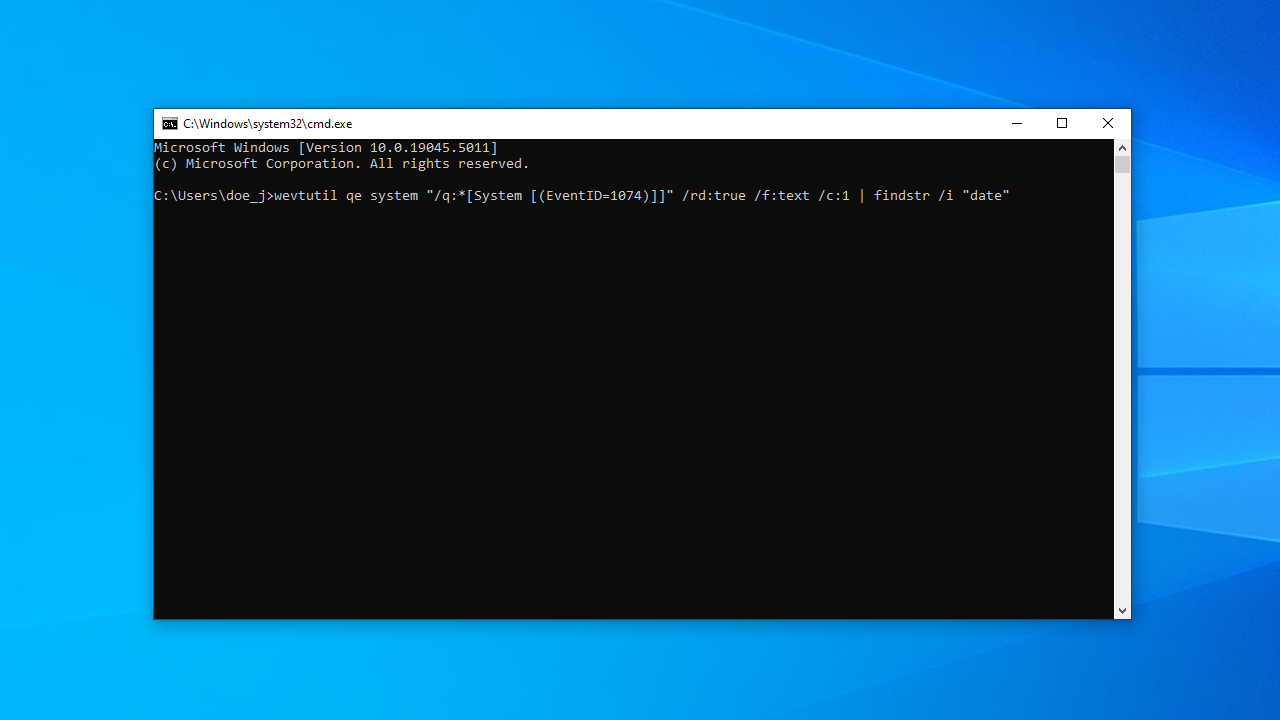
- If you don’t need the complete Windows restart log with the reboot/ shutdown event ID and other information and want to view only the date and time of the last shutdown, you can use the code below:
wevtutil qe system "/q:*[System [(EventID=1074)]]" /rd:true /f:text /c:1 | findstr /i "date"
That’s all! You can use the Command Prompt to view the Windows shutdown and startup log on Windows 10 and 11. However, I recommend using the Event Viewer, mainly because it’s simple and straightforward. Moreover, you don’t have to copy-paste codes, which fraudsters can take advantage of to hack into your computer.
Are you unable to view the restart and shutdown log on your Windows 10 /11 PC?
If you have computer issues like junk or corrupted files or registry keys, it may be challenging to get to see the Windows restart log (or the shutdown one) and view restart and shutdown events on your PC.
Windows Restart/Shutdown Logs: Explained
If you still can’t get to see the Windows shutdown log to view startup and shutdown events on your computer using the methods we have shared, please provide us with more details.
We’d also love it if you left a comment and shared our post on your social media. For more tips about Windows-related issues, visit our blog.
FAQ
It could be due to junk files, corrupted system files, or problematic registry keys. In such a case, I suggest that you run Auslogics BoostSpeed, which can help clear out these problems and allow you to view the logs properly.
That’s pretty straightforward. Follow these steps:
- Right-click anywhere on your desktop and select New > Shortcut .
- For a shutdown shortcut, type
shutdown /s /f /t 0in the location box. - For a restart shortcut, type
shutdown /r /f /t 0. - Click Next, name your shortcut (e.g., “Shutdown” or “Restart”), and click Finish.
If your computer is stuck in a restart loop , try booting into Safe Mode:
- Restart your computer and press the
F8key (orShift + F8) before the Windows logo appears to enter the Advanced Boot Options. - Select Safe Mode and press
Enter. - Once in Safe Mode, use the System Restore feature or uninstall recently installed updates or drivers that you suspect might be causing the issue.
If you’re still stuck, you might need to use a bootable USB to repair your Windows installation.
To turn off Fast Startup :
- Open Control Panel and navigate to Hardware and Sound > Power Options .
- Click on Choose what the power buttons do on the left.
- Click on Change settings that are currently unavailable .
- Under Shutdown settings , uncheck the box next to Turn on fast startup (recommended) .
- Click Save changes.
Follow these steps:
- Press the
Windows logo + Rkeys, typecmd, and hitEnterto open the Command Prompt. - Copy and paste the following command and press
Enter:
wevtutil qe system "/q:*[System [(EventID=1074)]]" /rd:true /f:text /c:1 | findstr /i "dat e"