Last Updated :
20 Oct, 2020
The move is an internal command found in the Windows Command Interpreter (cmd) that is used to move files and folders/directories. The command is robust than a regular move operation, as it allows for pattern matching via the inclusion of Wildcards in the source path.
The command is a very generic one and is available (in one form or the other) in almost every single operating system out there (under different aliases). In this article, we will learn about the move command and would learn various uses/applications of it.
Description of the Command :
MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [drive:][path]dirname1 dirname2
- [drive:][path]filename1 –
Specifies the location and name of the file or files you want to move. - destination –
Specifies the new location of the file. The destination can consist of a drive letter and colon, a directory name, or a combination. If you are moving only one file, you can also include a filename if you want to rename the file when you move it. - [drive:][path]dirname1 –
Specifies the directory you want to rename. - dirname2 –
Specifies the new name of the directory. - /Y –
Suppresses prompting to confirm you want to overwrite an existing destination file. - /Y –
Causes prompting to confirm you want to overwrite an existing destination file.
The switch /Y may be present in the COPYCMD environment variable. This may be overridden with /-Y on the command line. The default is to prompt on overwrites unless the MOVE command is being executed from within a batch script. The above output can be obtained by executing the command move /? in cmd.
The above text is a little cryptic at first, but the command is really basic and follows the minimal blueprint.
Syntax :
MOVE [options] (Source) (Target)
Key :
- [option] –
An optional flag denoted by /Y or /-Y, that is used to suppress the confirmation prompt on overwritten files. The default is to prompt on overwrites unless the MOVE command is being executed from within a batch script. - (Source) –
A path of the file/files that would be used to move them. This path can contain wildcards ( * ? ) in the path. If more then files are made to move, then wildcards are used. - (Target) –
A path for the new location of the file.
Using the Command :
Throughout this section, we would take the following directory as example for demonstrating the usage of move command.

Moving a File from One Folder to Another :
move source_path destination_path
- source_path –
It is the path of the file which we are willing to move, and the destination_path is the location to which we want the file to be moved.
Example :
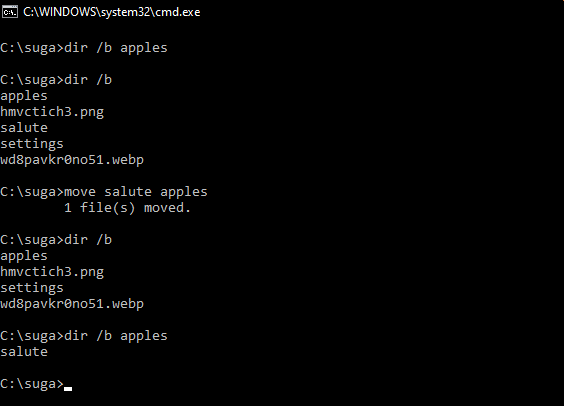
- The Dir /b command is used to list all the files and folders inside a directory.
- In the above example, we have moved an extension-less file named salute from C:\suga to C:\suga\apples directory.
Moving Multiple Files from One Path to Another :
move source_path destination_path
- source_path –
It is a path containing wildcards that will allow more than one file to be taken as a source. The destination_path is now a path to a directory where the moved files would reside (should not contain wildcards).
Example :

- In the above example we have moved all the files inside C:\suga folder which matches the pattern *.* to C:\suga\Apples directory.
- It should be noted that wildcard in source_path should match with the file(s) otherwise it would result in source_path being null, and a subsequent error.
Moving Directory from One Path to Another :
move source_dir_path Destination_dir_path
- source_dir_path –
It is the path to the directory to which we are moving, and destination_dir_path is the new location where it would be moved to.
Example :

- In the above example, we have moved the C:\suga\apples directory to C:\Users\Public directory.
- Multiple Directories can be moved using the method described in Moving multiple files from one path to another (with little modification to make is eligible for directories).
Moving a File to Another Folder with a Same Name File already existing :
There are two ways to tackle this situation –
- Abort the move process.
- Continue the move process, by overwriting the existing file with the newer one.
By default, the move command upon encountering any name collisions would prompt the user, asking whether he wants to rewrite the existing file with the new one, or stop the move process (via a Y/N prompt). To abort the move process, the user can simply enter N in the prompt input, stating that the file should not be overwritten. The prompt seeking for user input (for overwrite of files) appears as follows –
Overwrite {full_file_path}? (Yes/No/All):
When the users enter N in the prompt the output appears as follows –
Overwrite {full_file_path}? (Yes/No/All): N
0 file(s) moved.
When the user enters Y in the prompt the output appears as follows –
Overwrite {full_file_path}? (Yes/No/All): Y
1 file(s) moved.
To continue the move process by overwriting existing files (on all name collisions), a /Y switch needs to be added to the command as follows –
move /Y source_path destination_path
The `move` command in CMD is used to move files or directories from one location to another within the file system.
move C:\Users\YourUsername\Documents\example.txt D:\Backup\
Understanding the CMD Move Command
What is the Move Command?
The move cmd command is a powerful tool within the Windows Command Prompt that facilitates file and directory management. Its primary purpose is to transfer files or folders from one location to another on the file system. This command streamlines file organization and enhances efficiency, particularly for users who prefer keyboard shortcuts over graphical interfaces.
Syntax of the Move Command
The basic syntax of the move cmd command is as follows:
move [source] [destination]
- source: This is the path to the file or directory you wish to move. It can be an absolute path (full path) or a relative path (relative to the current directory).
- destination: This specifies the new location where the file or directory will be moved. Again, it can be an absolute or relative path.
Having a clear understanding of this syntax is essential for effectively using the move cmd command.

Mastering Remote Cmd Line: A Quick Guide
How to Move a File in CMD
Moving a Single File
To move a single file, open Command Prompt and execute the following command:
move C:\Users\YourName\Documents\file.txt D:\Backup\
In this example, the command transfers the file `file.txt` from the `Documents` folder to `D:\Backup`. This intuitive process not only simplifies file management but also saves time, especially for users who often deal with multiple files.
Moving Multiple Files
Using Wildcards
Wildcards are invaluable for moving multiple files at once. The asterisk (*) wildcard allows you to specify groups of files. For example, if you want to move all text files from your documents to a specific folder, the command would look like this:
move C:\Users\YourName\Documents\*.txt D:\TextFiles\
This command moves every `.txt` file within the `Documents` directory to the `TextFiles` folder on the D: drive. Utilizing wildcards enhances efficiency, particularly when managing large collections of files.
Moving Files to a Different Drive
It’s common to move files between different drives. To accomplish this, specify the full path of the source and the target drive in your command. For instance:
move C:\Users\YourName\Documents\file.txt E:\
This command moves `file.txt` from the C: drive to the E: drive. Keep in mind that moving files across drives may sometimes lead to unexpected errors, especially related to file access permissions. When encountering issues, it’s advisable to check user permissions.
Clone Cmd: A Quick Guide to Cmd Cloning Techniques
Additional Features of the Move Command
Renaming Files During Move
An intriguing feature of the move cmd command is its capability to rename files as they are moved. This function can be particularly useful when reorganizing your files. For example, if you want to move and rename a file simultaneously, you can use the following syntax:
move C:\Users\YourName\Documents\file.txt D:\Backup\new_filename.txt
Here, `file.txt` is moved to the `D:\Backup\` folder, but it is renamed to `new_filename.txt` in the process. This feature can help streamline file management by reducing the need for subsequent renaming.
Overwriting Existing Files
When you move a file to a destination where a file with the same name already exists, CMD will prompt you for confirmation before overwriting. However, if you want to overwrite the existing file without the prompt, you can use the `/Y` option:
move /Y C:\Users\YourName\Documents\file.txt D:\Backup\
Using `/Y` instructs CMD to overwrite the target file automatically if it exists. Be cautious with this feature, as unintentional data loss could occur if you’re not careful about which files you overwrite.

Mastering Psexec Remote Cmd for Seamless Command Execution
Common Errors with the Move Command
Insufficient Permissions
One of the most common obstacles faced while executing move commands is permission-related issues. If you encounter errors stating that access is denied, it’s often due to insufficient user permissions. Solutions include:
- Run CMD as an administrator: Right-click on the Command Prompt icon and select «Run as administrator.»
- Check file/folder permissions: Ensure you have the necessary permissions to move the files in question.
Specifying Invalid Path
Another frequent error arises from typing incorrect paths. It’s crucial to ensure that both the source and destination paths are correct. Always double-check for typos, and remember that paths are case-sensitive. Using quotation marks around paths containing spaces can also help avoid this issue:
move "C:\Users\Your Name\Documents\file.txt" "D:\Backup\"

Unlocking Common Cmd Commands for Quick Mastery
Practical Examples of Moving Files in CMD
Organizing Your Files
Moving files can help keep your directories organized, which is particularly valuable for users who manage extensive amounts of data. For example, suppose you have scattered project files in various folders. You can create a specific project folder and use CMD to move all related files there:
move C:\Users\YourName\Projects\Project1\* D:\Projects\Final\
This command swiftly consolidates your Project 1 files into a dedicated Final folder.
Backing Up Important Files
The move cmd command can effectively create backups of vital files. You can transfer files from your main working directory to a backup location, ensuring that essential documents are not only safe but also organized. An example command for this might be:
move C:\Users\YourName\Documents\ImportantFile.docx D:\Backup\ImportantBackup\
This action initiates a safe transfer of `ImportantFile.docx` to the designated backup area, providing peace of mind in the event of data loss.

Mastering Vs Code Cmd: Quick Commands for Ultimate Efficiency
Conclusion
The move cmd command serves as an essential utility in the Windows Command Prompt, providing users with a reliable method to manage their files efficiently. Mastering this command opens up new possibilities for seamless file organization and management. By practicing and exploring other CMD commands, users can enhance their productivity and system management skills. Stay engaged with more CMD tips and tricks to continue elevating your technical proficiency!
This tutorial explains how to move files or directories to another location on a Windows system.
Move files to another directory
move filename destinationFolder
Example: to move file ‘data.docx’ to the folder ‘d:\backup\folder’
move data.docx d:\backup\folder\
You can also rename the file while moving it to the new location
move data.docx d:\backup\folder\newData.docx
We can’t move multiple files with single command. i.e the below command would not work.
move file1 file2 D:\folder1\folder2
This would give the error The syntax of the command is incorrect.
However we can use wildcards to move files in bulk. For example, if you want to move all text files from current folder to a new location you can use the below command.
move *.txt destinationDirectory
To move all files starting with letter ‘A’, you can use below command.
move A* destinationDirectory
Move directories
Syntax:
move directory newDirectoryPath
Example: To move the directory ‘data’ to ‘D:\data\folder1\’
move data D:\data\folder1
1. Can we move multiple directories using wild cards like the way we do it with files?
No, wild cards does not work for directories. You get the below error
C:\>move tmp* Documents\folder1\ The filename, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrect.
2. How to specify the directories/files which have white spaces in the names?
You need to enclose the name of the file/directory in double quotes.
Example: move "file with spaces" "D:\directory with spaces"
Errors
If you do not have write privileges on source file/directory or on the destination folder, you would get error as below.
C:\Users\user1>move mydata.pdf c:\users\user2
Access is denied.
0 file(s) moved.
In the Windows Command Prompt, we use the move command to move files from one directory to another (cut and paste).
The syntax of the move command is as follows:
move <Source> <Target>We can also use the move command to move folders from one location to another.
Command Options
| /Y | Do not ask for confirmation if a duplicate file is found at the destination. The destination file will be overwritten. |
| /-Y | Ask before overwriting destination files. |
Examples
Move sales.doc in the current directory to C:\backup directory:
move sales.doc C:\backupMove C:\data\sales.doc to C:\backup directory. The file will be overwritten if it already exists in the destination folder:
move /y C:\data\sales.doc C:\backupMove C:\data\finance to C:\backup folder:
move C:\data\finance C:\backupMove all files in a directory
You can use wildcards with the move command. For example, the following command moves all files in the C:\data to C:\backup.
move /y C:\data\* C:\backupThe following command moves all files with a .doc extension to the backup folder:
move /y C:\data\*.doc C:\backupIn the following example, all files whose names start with screenshot are moved to the C:\backup directory.
move /y C:\data\screenshot* C:\backup
Move two or more files
To move two or more files without using wildcards, you have to use a for loop, as shown in the following example:
for %i in (sales.doc, products.doc) do move /y %i C:\backupIf you want to run the for command in a batch file, you would use two % (%%) with the variable.
for %%i in (sales.doc, products.doc) do move /y %%i C:\backupThe move command deletes the source file after it is copied to the destination. If you want to keep the original file, use the copy or xcopy.
- Описание команды move
- Формат командной строки move
- Параметры командной строки move
- Примеры использования move
Описание команды move
С помощью команды move можно переместить один или несколько файлов из одного каталога в другой. Также можно произвести переименование файлов и папок.
Перемещение зашифрованных файлов на том, который не поддерживает результаты шифрованной файловой системы (EFS), приведет к ошибке. Сначала необходимо расшифровать файлы или переместить их на том, который поддерживает EFS.
Ключ /Y может присутствовать в значении переменной среды окружения COPYCMD.
Оно может перекрываться ключом /-Y в командной строке. По умолчанию используется предупреждение о перезаписи, если только команда MOVE не выполняется как часть пакетного файла.
При перемещении папки в несуществующий каталог, каталог не будет создан автоматически и команда завершится ошибкой.
Пример:
move C:\dirtest\test.docx z:\1\test2.docx
Системе не удается найти указанный путь.
Перемещено файлов: 0.
Команда move не позволяет перемещать папки на другие логические диски.
Команду move нельзя использовать для работы с файлами, имеющими атрибуты «скрытый » и «системный», команда завершится ошибкой.
Пример:
move C:\dirtest\test.docx C:\dirtest\test3.docx
Не удается найти указанный файл.
Формат командной строки move
move [{/y|-y}] [<source>] [<target>]Параметры командной строки move
| /y | Перезаписывать существующие файлы назначения без предупреждения. |
| -y | Предупреждать при перезаписи существующего файла назначения. |
| <source> | Указывает путь и имя перемещаемых файлов. Чтобы переместить или переименовать каталог, источником должен быть текущий путь к каталогу и его имя. |
| <target> | Указывает путь и имя для перемещения файлов. Чтобы переместить или переименовать каталог, целевым объектом должен быть путь к каталогу и его имя. |
| /? | Отображение справки в командной строке. |
Примеры использования move
| move testdir testdir_2 | Переименовывает папку с именем testdir в testdir_2 в текущем каталоге. |
| move C:\testdir_2 c:\dirtest | Переименование с указанием абсолютных путей каталога. |
| move C:\dirtest\test.docx z:\ | Переместит файл test.docx из папки C:\dirtest на диск Z: |
| move C:\dirtest\test.docx z:\dirtest\test3.docx | Переместит файл test.docx из каталога dirtest диска C: в каталог dirtest диска Z: под именем test3.docx |
| move C:\dirtest\*.* Z:\dirtest\ | Переместит все файлы из каталога dirtest диска C: в каталог dirtest диска Z: |
| move C:\dirtest\*.* Z:\dirtest\ | Попытка переместить существующие файлы в каталоге dirtest диска Z: из каталога dirtest диска C:, команда завершится ошибкой. |
| move /y C:\dirtest\*.* Z:\dirtest\ | Ключ /y позволит переместить существующие файлы в каталоге dirtest диска Z: из каталога dirtest диска C: |
