Доброго времени суток, Уважаемый. Сейчас я постараюсь рассказать что такое Windows Hello для бизнеса и как это настроить.
Windows Hello — это система аутентификации в Windows 10, на основе PIN кода, биометрических данных или гравифеского пароля. Приставка для бизнеса значит, что все это будет работать в домене.
Почему пароль уже не очень хорошо? Потому что! Если серьезно, то можно почитать тут.
Что нам надо?
- Active Directory — Минимум 1 контроллер домена на базе Windows Server 2016. Уровень домена не ниже Windows Server 2012 R2.
- Public Key Infrastructure
- Azure Active Directory.
- Windows 10 в качестве клиента.
Настройка сертификатов контроллера домена
Клиенты должны доверять контроллерам домена; лучший способ это обеспечить — предоставить каждому контроллеру домена сертификат проверки подлинности Kerberos. Установка сертификата на контроллер домена позволяет центру распространения ключей (KDC) подтверждать свою подлинность другим членам домена.
Войдите в центр сертификации или на рабочие станции управления, используя учетные данные, эквивалентные администратору домена.
- Откройте консоль управления Центр сертификации.
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши элемент Шаблоны сертификатов и затем выберите Управление.
- В консоли «Шаблон сертификата» щелкните правой кнопкой мыши шаблон Проверка подлинности Kerberos в области сведений, а затем щелкните Скопировать шаблон.
- На вкладке Совместимость снимите флажок Показать последующие изменения. Выберите Windows Server 2012 или Windows Server 2012 R2 из списка Центр сертификации. Выберите Windows Server 2012 или Windows Server 2012 R2 из списка Получатель сертификата.
- На вкладке Общие в поле отображаемого имени шаблона введите Проверка подлинности контроллера домена (Kerberos). Измените срок действия и период обновления в соответствии с потребностями вашей организации. Примечание: если используются другие имена шаблонов, их необходимо помнить и заменить на эти имена в разных частях лаборатории.
- На вкладке Субъект нажмите кнопку Строится на основе данных Active Directory, если она еще не нажата. Выберите пункт Нет в списке Формат имени субъекта. Выберите DNS-имя в списке Включить эту информацию в альтернативное имя субъекта. Снимите все остальные флажки.
- На вкладке Шифрование выберите Поставщик хранилища ключей из списка Категория поставщика. Из списка Имя алгоритма выберите RSA. Введите 2048 в текстовое поле Минимальный размер ключей. Выберите SHA256 из списка Хэш запроса. Нажмите кнопку OK.
- Закройте консоль.
Замена существующего сертификата контроллера домена
Большое количество контроллеров домена может иметь существующий сертификат контроллера домена. Службы сертификатов Active Directory предоставляют шаблона сертификата по умолчанию от контроллеров домена — шаблон сертификата контроллера домена. Более поздние версии включают новый шаблон сертификата — шаблон сертификата проверки подлинности контроллера домена. Эти шаблоны сертификатов были предоставлены до обновления спецификации Kerberos, в которой указано, что центры распространения ключей (KDC), выполняющие проверку подлинности сертификатов, должны включать расширение KDC для проверки подлинности.
Шаблон сертификата проверки подлинности Kerberos — самый новый шаблон сертификата, предназначенный для контроллеров домена, и именно его следует развернуть на всех контроллерах домена (2008 или более поздней версии). Функция автоматической регистрации в Windows позволяет легко заменить эти сертификаты контроллеров домена. Можно использовать следующую конфигурацию для замены более старых сертификатов контроллеров домена новыми сертификатами с помощью шаблона сертификата проверки подлинности Kerberos.
Войдите в центр сертификации или на рабочие станции управления, используя учетные данные, эквивалентные администратору предприятия.
- Откройте консоль управления Центр сертификации.
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши элемент Шаблоны сертификатов и затем выберите Управление.
- В консоли «Шаблоны сертификатов» щелкните правой кнопкой мыши шаблон Проверки подлинности на контроллере домена (Kerberos) (или имя шаблона сертификата, созданного в предыдущем разделе) в области сведений и нажмите кнопку Свойства.
- Выберите вкладку Устаревшие шаблоны. Нажмите кнопку Добавить.
- Из диалогового окна Добавление устаревшего шаблона выберите шаблон сертификата Контроллер домена и нажмите кнопку ОК. Нажмите Добавить.
- Из диалогового окна Добавление устаревшего шаблона выберите шаблон сертификата Проверка подлинности контроллера домена и нажмите кнопку ОК.
- Из диалогового окна Добавление устаревшего шаблона выберите шаблон сертификата Проверка подлинности Kerberos и нажмите кнопку ОК.
- Добавьте другие шаблоны сертификатов предприятия, настроенные ранее для контроллеров домена, на вкладку Устаревшие шаблоны.
- Нажмите кнопку ОК и закройте консоль Шаблоны сертификатов.
Шаблон сертификата настроен для замены всех шаблонов сертификатов, перечисленных в списке устаревших шаблонов сертификатов.
Публикация шаблонов сертификатов в центр сертификации
Центр сертификации может выдавать только сертификаты, соответствующие шаблонам сертификатов, опубликованным в этот центр сертификации.
- Откройте консоль управления Центр сертификации.
- Разверните родительский узел в области навигации.
- В области навигации щелкните Шаблоны сертификатов.
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши узел Шаблоны сертификатов. Выберите пункт Создать и щелкните выдаваемый Шаблон сертификата.
- В окне Включение шаблонов сертификатов выберите шаблон Проверка подлинности контроллера домена (Kerberos), созданный в предыдущих шагах. Нажмите кнопку ОК для публикации выбранного шаблона сертификатов в центр сертификации.
- Если вы опубликовали шаблон сертификата проверки подлинности контроллера домена (Kerberos), следует отменить публикацию шаблонов сертификатов, включенных в список устаревших шаблонов.
- Чтобы отменить публикацию шаблона сертификата, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши шаблон сертификата, публикацию которого вы хотите отменить, в области сведений консоли «Центр сертификации», а затем выберите Удалить. Нажмите кнопку Да для подтверждения операции.
- Закройте консоль.
Настройка контроллеров домена для автоматической регистрации сертификатов
Контроллеры домена автоматически запрашивают сертификат на основе шаблона сертификата контроллера домена. Однако контроллер домена не знает о более новых шаблонах сертификатов или устаревших конфигурациях шаблонов сертификатов. Чтобы продолжить автоматическую регистрацию и обновление сертификатов контроллера домена, которые знают о более новых шаблонах сертификатов и устаревших конфигурациях шаблона сертификата, создайте и настройте объект групповой политики для автоматической регистрации сертификатов и свяжите объект групповой политики с OU контроллеров домена.
- Запустите Консоль управления групповыми политиками (gpmc.msc).
- В области навигации разверните домен и выберите узел Объект групповой политики.
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Объект групповой политики и выберите Создать.
- Введите Автоматическая регистрация сертификатов контроллера домена в поле имени и нажмите кнопку ОК.
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши объект групповой политики Автоматическая регистрация сертификатов контроллера домена и щелкните Изменить.
- В области навигации в узле Конфигурация компьютера разверните Политики.
- Разверните Параметры Windows, Параметры безопасности и выберите Политики открытого ключа.
- В области сведений щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Клиент служб сертификации: автоматическая регистрация и выберите Свойства.
- В окне Модель конфигурации выберите Включено.
- Установите флажок Обновлять сертификаты с истекшим сроком действия или в состоянии ожидания и удалять отозванные сертификаты.
- Установите флажок Обновлять сертификаты, использующие шаблоны сертификатов.
- Нажмите кнопку OK. Закройте Редактор управления групповыми политиками.
- В области навигации разверните домен и узел, имя которого соответствует имени вашего домена Active Directory. Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши подразделение Контроллеры домена и щелкните Связать существующий объект групповой политики…
- В диалоговом окне Выбор объекта групповой политики выберите Автоматическая регистрация сертификатов контроллера домена или имя объекта групповой политики регистрации сертификата контроллера домена, созданный ранее, и нажмите кнопку ОК.
Групповая политика «Включить Windows Hello для бизнеса»
Параметр групповой политики «Включить Windows Hello для бизнеса» необходим Windows для определения того, следует ли пользователю пытаться регистрироваться в Windows Hello для бизнеса. Пользователь будет пытаться регистрироваться только в случае, если этот параметр политики включен.
Создание объекта групповой политики Windows Hello для бизнеса
Объект групповой политики содержит параметры политики, необходимые для запуска подготовки Windows Hello для бизнеса, а также для обеспечения автоматического продления сертификатов проверки подлинности Windows Hello для бизнеса.
- Запустите Консоль управления групповыми политиками (gpmc.msc).
- В области навигации разверните домен и выберите узел Объект групповой политики.
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Объект групповой политики и выберите Создать.
- Введите Включить Windows Hello для бизнеса в поле имени и нажмите кнопку ОК.
- В области содержимого щелкните правой кнопкой мыши объект групповой политики Включить Windows Hello для бизнеса и выберите Изменить.
- В области навигации в узле Конфигурация пользователя разверните Политики.
- Разверните Административные шаблоны, Компонент Windows и выберите Windows Hello для бизнеса.
- В области содержимого дважды щелкните Использовать Windows Hello для бизнеса. Щелкните Включить и нажмите кнопку ОК.
- Закройте Редактор управления групповыми политиками.
Настройка безопасности в объекте групповой политики Windows Hello для бизнеса
Самый лучший способ развертывания объекта групповой политики Windows Hello для бизнеса— это использование фильтрации по группам безопасности. Благодаря этому можно легко управлять пользователями, которые должны получить Windows Hello для бизнеса, просто добавляя их в группу. Это позволяет развернуть Windows Hello для бизнеса в несколько этапов.
- Запустите Консоль управления групповыми политиками (gpmc.msc).
- В области навигации разверните домен и выберите узел Объект групповой политики.
- Дважды щелкните объект групповой политики Включить Windows Hello для бизнеса.
- В разделе Фильтрация ограничений безопасности области содержимого нажмите кнопку Добавить. Введите Пользователи Windows Hello для бизнеса или имя ранее созданной группы безопасности и нажмите кнопку ОК.
- Перейдите на вкладку Делегирование, выберите Прошедшие проверку и нажмите кнопку Дополнительно.
- В списке Группы или пользователи выберите Прошедшие проверку. В списке Разрешения для прошедших проверку пользователей снимите флажок Разрешить для разрешения Применить групповую политику. Нажмите кнопку OK.
Развертывание объекта групповой политики Windows Hello для бизнеса
При применении объекта групповой политики Windows Hello для бизнеса используется фильтрация по группам безопасности. Это позволяет привязать объект групповой политики к домену, что гарантирует, что объект групповой политики будет находиться в пределах области для всех пользователей. Тем не менее, фильтрация по группам безопасности гарантирует, что только пользователи, входящие в глобальную группу Пользователи Windows Hello для бизнеса, будут получать и применять объект групповой политики, что приводит к подготовке Windows Hello для бизнеса.
- Запустите Консоль управления групповыми политиками (gpmc.msc).
- В области навигации разверните домен, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши узел с именем вашего домена Active Directory и выберите Связать существующий объект групповой политики…
- В диалоговом окне Выбор объекта групповой политики выберите Включить Windows Hello для бизнеса или имя ранее созданного объекта групповой политики Windows Hello для бизнеса и нажмите кнопку ОК.
Azure Active Directory
Теперь важно обновить структуру синхронизации Active Directory с Azure Active Directory. Если этого не сделать, то при вводе PIN кода, пользователи будут видеть ошибку вида «функция (входа по PIN коду) временно недоступна».
Windows 10
Можно приступать к настроке PIN кода, отпечатка пальцев и т.д.
Время на прочтение8 мин
Количество просмотров26K
Делимся с вами обзорным материалом про службу Windows Hello, обеспечивающую двухфакторную проверку на Windows 10. Также вы узнаете, чем она будет полезна для крупных компаний, почему стоит выбирать PIN-код, а не пароль и как её настроить.

Windows Hello — что это и зачем?
В Windows 10 служба Windows Hello для бизнеса заменяет пароли на строгую двухфакторную проверку подлинности на компьютерах и мобильных устройствах. Она заключается в создании нового типа учетных данных пользователя в привязке к устройству, использовании биометрических данных или PIN-кода.
В первых версиях Windows 10 были службы Microsoft Passport и Windows Hello, которые обеспечивали многофакторную проверку подлинности. Чтобы упростить развертывание и расширить возможности поддержки, Microsoft объединила эти технологии в единое решение — Windows Hello. Если вы уже выполнили развертывание этих технологий, то вы не заметите никаких изменений в функционировании служб. Для тех, кому еще предстоит оценить работу Windows Hello, выполнить развертывание будет гораздо проще благодаря упрощенным политикам, документации и семантике.
Служба Hello призвана решать типичные проблемы пользователей, возникающие при работе с паролями:
- Пароли могут быть трудны для запоминания, и пользователи часто повторно используют пароли на нескольких сайтах.
- Взломы сервера могут раскрывать симметричные сетевые учетные данные.
- Пароли могут подлежать атакам с повторением пакетов.
- Пользователи могут непреднамеренно предоставить свой пароль вследствие фишинга.
Hello позволяет выполнить проверку подлинности учетной записи Microsoft, учетной записи Active Directory, учетной записи Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) и службы поставщика удостоверений или службы проверяющей стороны, которые поддерживают проверку подлинности Fast ID Online (FIDO) v2.0.
После начальной двухэтапной проверки при регистрации на вашем устройстве настраивается служба Hello, и вы сами устанавливаете жест, который может быть как биометрическим, например отпечатком пальца, так и PIN-кодом. Далее необходимо сделать жест для проверки своего удостоверения. После этого Windows использует Hello для проверки подлинности и предоставления им доступа к защищенным ресурсам и службам.
От имени администратора компании или общеобразовательной организации можно создать политики управления Hello для использования на устройствах под управлением Windows 10, которые подключаются к вашей организации.
Разница между Windows Hello и Windows Hello для бизнеса
Windows Hello предназначена для удобного и безопасного входа пользователя. Такое использование Hello обеспечивает отдельный уровень защиты, так как является уникальным для устройства, на котором настраивается, однако проверка подлинности на основе сертификатов при этом отсутствует.
Служба Windows Hello для бизнеса, которая настраивается групповой политикой или политикой MDM, использует проверку подлинности на основе ключа или сертификата.
В настоящее время в учетных записях Active Directory с использованием Windows Hello не поддерживается проверка подлинности на основе ключа или сертификата. Эта функция должна появиться в будущем выпуске.
Почему PIN-код, а не пароль?
Пароли представляют собой общие секреты, они вводятся на устройстве и передаются по сети на сервер. Перехваченные имя и пароль учетной записи могут быть использованы кем угодно. Например, учетные данные могут быть раскрыты при взломе сервера.
В Windows 10, в процессе подготовки, служба Hello создает пару криптографических ключей, привязанных к доверенному платформенному модулю (TPM), если устройство оснащено таким модулем, или в программной реализации. Доступ к этим ключам и получение подписи для проверки того, что пользователь владеет закрытым ключом, предоставляется только при вводе PIN-кода или биометрического жеста. Двухэтапная проверка, которая происходит при регистрации в службе Hello, формирует доверительные взаимоотношения между поставщиком удостоверений и пользователем, когда открытая часть пары «открытый/закрытый ключ» отправляется поставщику удостоверений и связывается с учетной записью пользователя. Когда пользователь выполняет жест на устройстве, поставщик удостоверений определяет по комбинации ключей Hello и жеста, что это проверенное удостоверение, и предоставляет маркер проверки подлинности, с помощью которого Windows 10 получает доступ к ресурсам и службам. Кроме того, в процессе регистрации генерируется претензия по удостоверению для каждого поставщика удостоверений, чтобы криптографически подтвердить, что ключи Hello привязаны к TPM. Если претензия по удостоверению во время регистрации не выставляется поставщику удостоверений, поставщик удостоверений должен предполагать, что ключ Hello создан программно.

Представьте, что кто-то подсматривает через ваше плечо при получении денежных средств из банкомата и видит вводимый вами PIN-код. Наличие этого PIN-кода не поможет им получить доступ к учетной записи, так как у них нет банковской карты. Аналогичным образом перехват PIN-кода для устройства не позволяет злоумышленнику получить доступ к учетной записи, так как PIN-код является локальным для конкретного устройства и не обеспечивает никакого типа проверки подлинности с любого другого устройства.
Hello как раз позволяет защищать удостоверения и учетные данные пользователей. Так как пароли не используются, фишинг и атаки методом подбора становятся бесполезными. Эта технология позволяет также предотвратить взломы серверов, так как учетные данные Hello являются асимметричной парой ключей, что предотвращает атаки с повторяющимися пакетами, так как эти ключи защищены доверенными платформенными модулями (TPM).
Также можно использовать устройства с Windows 10 Mobile в качестве удаленных учетных данных при входе на ПК под управлением Windows 10. В процессе входа в систему ПК под управлением Windows 10 он может подключаться и получать доступ к Hello на вашем устройстве под управлением Windows 10 Mobile по Bluetooth. Поскольку мы всегда носим с собой телефон, Hello позволяет гораздо проще реализовать двухфакторную проверку подлинности.
Функция входа через телефон в данный момент доступна только отдельным участникам программы принятия технологий (TAP).
Так как же PIN-код помогает защитить устройство лучше, чем пароль?
Преимущества PIN-кода в сравнении с паролем связаны не с его структурой (длиной и сложностью), а с принципом работы.
1. PIN-код привязан к устройству. Злоумышленник, получивший доступ к паролю, может войти в учетную запись с любого устройства, но в случае кражи PIN-кода вход в учетную запись будет невозможен без доступа к соответствующему устройству.
2. PIN-код хранится на устройстве локально. Пароль передается на сервер и может быть перехвачен в процессе передачи или украден с сервера. PIN-код задается на устройстве на локальном уровне, не передается и не хранится на сервере. При создании PIN-кода устанавливаются доверительные отношения с поставщиком удостоверений и создается пара асимметричных ключей, используемых для проверки подлинности. При вводе PIN-кода ключ проверки подлинности разблокируется и используется для подтверждения запроса, отправляемого на сервер для проверки подлинности.
3. PIN-код поддерживается оборудованием. PIN-код Hello поддерживается микросхемой доверенного платформенного модуля (TPM), представляющей собой надежный криптографический процессор для выполнения операций шифрования. Эта микросхема содержит несколько механизмов физической защиты для предотвращения взлома, и вредоносные программы не могут обойти функции безопасности TPM. TPM применяется во всех телефонах с Windows 10 Mobile и во многих современных ноутбуках.
Материал ключа пользователя создается и становится доступным в доверенном платформенном модуле (TPM) на устройстве пользователя, что защищает материал от перехвата и использования злоумышленниками. Поскольку технология Hello подразумевает использование пар асимметричных ключей, учетные данные пользователей не будут похищены в случае нарушения безопасности поставщика удостоверений или веб-сайтов, к которым пользователь осуществляет доступ.
TPM защищает от множества известных и потенциальных атак, в том числе атак методом подбора PIN-кода. После определенного количества попыток ввода неправильного PIN-кода устройство блокируется.
4. PIN-код может быть сложным. К PIN-коду Windows Hello для бизнеса применяется тот же набор политик управления ИТ, что и к паролю, в том числе сложность, длина, срок действия и история изменений. Несмотря на уверенность большинства пользователей в том, что PIN-код представляет собой простой код из 4 цифр, администраторы могут устанавливать для управляемых устройств политики, предполагающие уровень сложности PIN-кода, сопоставимый с паролем. Вы можете сделать обязательными или запретить специальные знаки, буквы в верхнем и нижнем регистрах, а также и цифры.
Раздел меню настроек в котором задаются параметры PIN-кода и биометрия:

Что произойдет в случае кражи ноутбука или телефона?
Для нарушения безопасности учетных данных Windows Hello, защищаемых TPM, злоумышленнику нужно осуществить доступ к физическому устройству, найти способ похитить биометрические данные пользователя или подобрать PIN-код. Все это нужно сделать раньше, чем функциональный механизм защиты от взлома TPM заблокирует устройство. Для ноутбуков, не имеющих TPM, можно настроить дополнительную защиту, активировав BitLocker и ограничив количество неудачных попыток входа в систему.
Настройка BitLocker без TPM
С помощью редактора локальных групповых политик (gpedit.msc) активируйте следующую политику:
Конфигурация компьютера → Административные шаблоны → Компоненты Windows → Шифрование диска BitLocker → Диски операционной системы → Требовать дополнительной проверки подлинности при запуске
В параметрах политики выберите Разрешить использование BitLocker без совместимого TPM, а затем нажмите кнопку ОК.

Перейдите в меню Панель управления → Система и безопасность → Шифрование диска BitLocker и выберите диск с операционной системой, который требуется защитить.
С помощью редактора локальных групповых политик (gpedit.msc) активируйте следующую политику: Конфигурация компьютера → Параметры Windows → Параметры безопасности → Политики учетных записей → Политика блокировки учетных записей → Пороговое значение блокировки.
Установите допустимое количество неудачных попыток входа в систему и нажмите ОК.

Как работает Windows Hello для бизнеса: основные положения
1. Учетные данные службы Hello основаны на сертификате или асимметричной паре ключей и привязаны к устройству, как и маркер, получаемый с помощью учетных данных.
2. Поставщик удостоверений (например, Active Directory, Azure AD или учетная запись Майкрософт) проверяет удостоверение пользователя и сопоставляет открытый ключ Hello с учетной записью пользователя на этапе регистрации.
3. Ключи могут генерироваться в аппаратном (TPM 1.2 или 2.0 для предприятий и TPM 2.0 для потребителей) или программном обеспечении на основании политики.
4. Проверка подлинности — это двухфакторная проверка с использованием сочетания ключа или сертификата, привязанного к устройству, и информации, известной пользователю PIN-код), или идентификационных данных пользователя (Windows Hello). Жест Hello не перемещается между устройствами и не предоставляется серверу. Он хранится локально на устройстве.
5. Закрытый ключ никогда не покидает устройство. Проверяющий подлинность сервер имеет открытый ключ, который был сопоставлен с учетной записью пользователя во время регистрации.
6. Ввод PIN-кода и биометрических жестов приводит к проверке удостоверения пользователя в Windows 10 и проверке подлинности с использованием ключей или сертификатов Hello.
7. Личные (учетная запись Майкрософт) или корпоративные учетные записи (Active Directory или Azure AD) использует один контейнер для ключей. Все ключи разделены по доменам поставщиков удостоверений в целях обеспечения конфиденциальности пользователя.
8. Закрытые ключи сертификатов могут быть защищены контейнером Hello и жестом Hello.
Сравнение проверки подлинности на основе ключа и сертификата
Для подтверждения личности служба Windows Hello для бизнеса может использовать ключи (аппаратный или программный) или сертификаты с ключами в аппаратном или программном обеспечении. Предприятия с инфраструктурой открытых ключей (PKI) для выпуска и управления сертификатами могут продолжать использовать PKI вместе со службой Hello. Предприятия, у которых нет PKI или которые хотят сократить объем работ, связанных с управлением сертификатами, могут использовать для службы Hello учетные данные на основе ключа.
Аппаратные ключи, которые создаются модулем TPM, обеспечивают наиболее высокий уровень гарантии. При изготовлении в модуль TPM помещается сертификат ключа подтверждения (EK). Этот сертификат EK создает корневое доверие для всех других ключей, которые генерируются в этом модуле TPM. Сертификация EK используется для генерации сертификата ключа удостоверения подлинности (AIK), выданного службой сертификации Microsoft. Этот сертификат AIK можно использовать как претензию по удостоверению, чтобы доказать поставщикам удостоверений, что ключи Hello генерировались одним и тем же TPM. Центр сертификации Майкрософт (CA) генерирует сертификат AIK для каждого устройства, пользователя и IDP, чтобы гарантировать защиту конфиденциальности.
Если поставщики удостоверений, например Active Directory или Azure AD, регистрируют сертификат в службе Hello, Windows 10 будет поддерживать тот же набор сценариев, что и смарт-карта. Если тип учетных данных представляет собой ключ, будет поддерживаться только доверие и операции на основе ключа.
Мы постарались написать для вас подробный и понятный туториал по работе со службой Windows Hello. Если у вас остались вопросы, задавайте в комментариях.
Last Updated on January 3, 2025 by Deepanshu Sharma

Biometrics technology, which uses biological features for user authentication, is gaining popularity and becoming an essential part of security technology. Methods such as facial recognition and fingerprint recognition are widely used in various industries including healthcare, banking, and hospitality to secure digital transactions and provide a seamless user experience. The global biometrics market is projected to reach $136.18 billion by 2031, with Asia and North America experiencing the highest adoption rates. The increasing use of biometrics can be attributed to factors such as the popularity of facial recognition, the convenience of voice biometrics, advancements in artificial intelligence, the need for multi-factor authentication due to terrorism and cybercrime, and the need for contactless methods of authentication during the COVID-19 pandemic. As technology continues to advance, barriers to adoption will decrease, leading to further growth and usage of biometrics.
How to Implement Biometric Authentication in Active Directory
Below are some of the easiest ways to get started with biometric authentication in Active Directory and Azure AD.
Use Windows Hello
Using Windows Hello is the most widely recommended method for implementing Biometric Authentication in Active Directory. It allows for fingerprint authentication across Windows devices and eliminates the need for users to remember pins or passwords. By requiring users to log in with facial recognition or a fingerprint scanner, the risk of unauthorized access is reduced. Windows Hello enrolls user credentials in Microsoft Passport, which allows for authentication into Microsoft accounts, Active Directory, and other services that support the Fast ID Online (FIDO) standard. This system can use mobile device cameras and fingerprint readers, as well as laptops with fingerprint readers.
Use Public Key Infrastructure
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) serves as the foundation for all strong authentication factors, including biometric authentication. Azure AD users can now access their accounts without passwords by using FIDO2 security keys, which can be generated by the Microsoft Authenticator app, or Windows Hello. These keys help verify the user and the device to the services within your Active Directory environment. Additionally, the combined registration portal in Microsoft Entra has been updated to enable users to create and manage FIDO2 security keys. FIDO2 security keys can also be used to authenticate across Azure AD-joined Windows 10 devices on the latest versions of Edge and Firefox browsers.
Prepare Devices Accordingly
During the setup process for a new Windows 10 device, the user is asked whether the device belongs to the organization or if it is a personal device. If it belongs to the organization, the user is prompted to select a preferred method of connecting to enterprise resources. They can choose between joining using Azure Active Directory or setting up a local account and manually joining a domain later. Once the user makes a successful selection, they are then asked to verify their identity. This can be done by receiving a phone call or a text message and entering a code. Sometimes, an authentication app is also used for this purpose. In certain cases, organizations may enable a Group Policy setting that allows for biometric authentication, such as fingerprint, iris, or facial recognition through Windows Hello. However, biometric authentication can only be used if the device is equipped with the necessary hardware.
Enable Microsoft Passport
Microsoft makes it easy to implement Microsoft Passport in the workplace using Group Policy. The integration of Microsoft Passport depends on the type of device being used, whether it’s domain-joined or a user-owned device. The ‘Use Biometrics’ setting in the Group Policy Object Editor allows the use of biometric devices, such as retina scanners and fingerprint readers, instead of a PIN. Biometric device use is enabled by default, but it can be disabled to only accept a PIN. If an organization chooses to allow biometric authentication, there are additional Group Policy settings specifically related to biometrics located in:
Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Biometrics.
Use The Expiration Setting
The ‘Expiration’ setting in Windows Server determines whether a user’s PIN will expire or not. If disabled or not configured, the PIN will never expire. Enabling this setting allows the administrator to specify the number of days after which the PIN will expire, with a minimum value of zero and a maximum of 730 days. The ‘History’ setting determines how many previous PINs are stored and prohibited for reuse. By default, Windows does not store PIN histories. Enabling this setting allows the administrator to specify the number of PINs to be stored, including the current PIN as one of the history items. The ‘Require Special Characters’ setting determines whether special characters can be used in a user’s PIN. By default, Windows does not allow special characters. Enabling this setting requires users to include at least one special character in their PIN.
How Lepide Helps
The Lepide Data Security Platform can provide an extra level of security to Active Directory by monitoring all authentication-related activities, and also covers a wide range of cloud platforms, including Azure AD. Lepide provides a centralized dashboard where administrators can easily view and manage all biometric events, configurations and policies. Lepide also has the ability to automatically rotate passwords on managed endpoints, bolstering the security of your authentication process. Lepide records all relevant events and provides real-time alerts for any suspicious or unauthorized access attempts. Additionally, Lepide simplifies privileged account management by enabling the definition of roles and assigning permissions to different users within the organization. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access and modify biometric configurations and PINs, further enhancing security and control.
If you’d like to see how the Lepide Data Security Platform can provide added security to your AD authentication process, schedule a demo with one of our engineers.
- Active Directory
Solution Overview
Windows Hello for Business is a solution that allows enterprise users to replace password-based sign-in with a more preferred strong authentication mechanism. Signing into Windows is simplified for the user as they can leverage fingerprints, iris, facial recognition or a pin code while the organization benefits from the increased security of a strong authentication process where a password is no part of the equation.
The easiest way for an organization to adopt Windows Hello for Business is to deploy the necessary client policies after hybrid-joining or natively joining Azure Active Directory from their Windows 10/11 endpoints. Without Azure Active Directory, deploying Windows Hello for Business in an on-premises only environment requires quite a bit of additional infrastructure and setup such as an enterprise PKI, an Active Directory Federated Services (ADFS) deployment, etc. If a Windows device is hybrid-joined or pure Azure Active Directory joined, deploying the Windows Hello for Business policy settings are all that’s required from the enterprise IT infrastructure perspective to get started.
After Windows Hello for Business is setup for the enterprise clients and users have registered their credentials on devices, they can begin using the new strong authentication methods for logging into Windows.
If users are only accessing cloud-based resources such as OneDrive, SharePoint Online, Teams, etc., you should be all set with no additional setup required. However, if your users will continue to access any on-premises, Active Directory-backed resources such as file shares, print shares, etc., your environment will need a bit more setup. This is where the cloud Kerberos authentication comes into play.
Without additional configuration of the on-premises Active Directory environment, a user who has logged into Windows with Windows Hello for Business credentials and attempts to access an AD-protected resource will be greeted with the following prompt for re-authentication:

This prompt is because the user does not have a ticket-granting-ticket (TGT) from Kerberos for on-premises authentication. When the client attempts to obtain a TGT from a domain controller, they are prompted for authentication. This process can be automated/hidden from the user by deploying one of the following solutions:
- Cloud Kerberos trust deployment – the recommended deployment model when compared to the key trust model. It is also the preferred deployment model if you do not need to support certificate authentication scenarios. No additional on-premises infrastructure is required.
- Key trust deployment – An enterprise PKI is required as trust anchor for authentication. Domain controllers require a certificate for Windows clients to trust them.
- Certificate trust deployment – An enterprise public key infrastructure (PKI) is required as trust anchor for authentication. Domain controllers require a certificate for Windows clients to trust them. The enterprise PKI and a certificate registration authority (CRA) are required to issue authentication certificates to users. Hybrid certificate trust deployment uses AD FS as a CRA.
This article will focus on deploying the recommended Cloud Kerberos trust model. In this model, Azure AD Kerberos is leveraged to grant requested TGT’s for clients accessing on-premises AD protected resources. With the security exchange happening between the client and the device trusted Azure AD directory, no user prompts for authentication arise and the client obtains the necessary TGT to authenticate to the on-premises Active Directory backed resource.
After enabling Azure AD Kerberos in a Windows Server Active Directory domain, you will see an AzureADKerberos computer object when browsing the domain controllers container in Active Directory Users and Computers tool.

This computer object is required for Azure AD to generate the TGT’s mentioned previously, and functions like a Read Only Domain Controller (RODC). Now, let’s dive into the deployment!
Deployment Prerequisites
- Azure AD Multifactor Authentication
- Windows 10 21H2 or later
- Windows 11 or later
- Windows Server 2016 or later domain controllers
- Microsoft Intune or another modern device management platform for deploying the Cloud Kerberos trust policy settings
Important note: users that are directly or indirectly nested in any privileged groups in Active Directory will not be able to use Cloud Kerberos authentication. You should not be using privileged user accounts to log into Windows endpoints as a best practice.
Deploy Azure AD Kerberos
- Download and install the Azure AD Kerberos PowerShell module. You can do this by opening a Windows PowerShell prompt, running as an administrator:, and running the following:
- First, ensure TLS 1.2 for PowerShell gallery access: [Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
- Install the Azure AD Kerberos PowerShell Module: Install-Module -Name AzureADHybridAuthenticationManagement -AllowClobber
- Create a Kerberos Server object by running the following script from Microsoft and providing credentials when prompted:
# Specify the on-premises Active Directory domain. A new Azure AD
# Kerberos Server object will be created in this Active Directory domain.
$domain = $env:USERDNSDOMAIN
# Enter an Azure Active Directory global administrator username and password.
$cloudCred = Get-Credential -Message 'An Active Directory user who is a member of the Global Administrators group for Azure AD.'
# Enter a domain administrator username and password.
$domainCred = Get-Credential -Message 'An Active Directory user who is a member of the Domain Admins group.'
# Create the new Azure AD Kerberos Server object in Active Directory
# and then publish it to Azure Active Directory.
Set-AzureADKerberosServer -Domain $domain -CloudCredential $cloudCred -DomainCredential $domainCred
3. Verify the successful creation of the Azure AD Kerberos Server by running the following command: Get-AzureADKerberosServer -Domain $domain -CloudCredential $cloudCred -DomainCredential $domainCred 
In this guide, I’m going to assume you’ve already deployed Windows Hello for Business via either the tenant-wide settings or via individual policies deployed to clients. If you haven’t done either, this is the time to configure it. Since this is impactful for the user, it’s highly advisable to prepare users for the registration process and how Windows Hello for Business will operate. I highly advise against simply flipping the solution on in production without planning the end user rollout.
Deploy Cloud Kerberos Trust Settings to Clients
You will now need to deploy additional Cloud Kerberos trust policy settings to clients via modern device management policy deployment and OMA-URI settings. Here are the instructions for the process via Microsoft Intune:
- Create a new Windows device-based profile. For profile type, select Templates and then select the Custom template.

- Provide the profile with a name and description, then click Next.
- On the configuration settings page, add a new configuration with the following values:
- Name: Windows Hello for Business Cloud Kerberos Trust
- Description: Enable Windows Hello for Business cloud Kerberos trust for sign-in and on-premises SSO
- OMA-URI: ./Device/Vendor/MSFT/PassportForWork/<TENANT ID>/Policies/UseCloudTrustForOnPremAuth <TENANT ID> should be replaced with your Azure AD Tenant ID.
- Data Type: Boolean
- Value: True

- Click Save, then Next to continue.
- Target the Windows devices that have been enabled for Windows Hello for Business for the new policy and complete the new policy wizard.
After devices receive the updated Windows Hello for Business Cloud Kerberos trust settings, users will no longer be prompted for authentication when accessing on-prem AD protected resources while signed in with Windows Hello for Business credentials!
Are you finding the content on my site particularly helpful? Please consider donating to help me offset the costs of maintaining this site. Your support is greatly appreciated!
Solution ID : SO071021150354
Last Modified : 10/21/2023
Solution
This document describes the installation and configuration steps for enabling certificate issuance through the DigiCert Autoenrollment server for Windows Hello® for Business.
- Introduction
- About Windows Hello for Business
- How DigiCert Contributes in Windows Hello for Business
- Windows Hello for Business Authentication Process
- Windows Hello for Business Certificate Issuance Process
- Pre-requisites
- Supported Deployment Model and Trust Type
- Required Windows Hello for Business Setup
- Required Autoenrollment Server Setup
- Setting Up Windows Hello for Business with Autoenrollment Server
- Creating Certificate Profiles
- Downloading and Importing Autoenrollment Configuration File
- Assigning Group/User Access for Each Template
- Issuing Domain Controller Certificates
- Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services
- Adding User Principal Name to Service Account
- Provisioning
- Windows Hello for Business Authentication Certificate Lifecycle
- Renewal
- Expiration
- Revocation
- Reset
- Troubleshooting
Introduction
About Windows Hello for Business
Windows Hello® for Business, a feature by Microsoft® starting from Windows 10, introduced password replacement with strong two-factor authentication, consisting of a new type of user credential bound to a device and accessed using a biometric or PIN. DigiCert now has an offering to issue certificates from the DigiCert PKI Platform hosted Certificate Authorities for this new user credential.
For a detailed overview of Windows Hello for Business, please refer to the official Microsoft documentation: Windows Hello for Business Overview.
How DigiCert Contributes in Windows Hello for Business
Windows Hello for Business depends on multiple technology stacks, but Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is one of its many foundations. DigiCert PKI Platform can provide all certificates which are required to enable Windows Hello for Business through our Certificate Authority, and automatically provision them via our Autoenrollment Server.
Following table shows the type of certificates required by Windows Hello for Business.
| Certificate Type | Required By | Description |
| Domain Controller |
Domain Controllers (DC) |
Certificate to install in DC to assure that the server is trusted. |
| Windows Hello for Business Authentication | End Users | Certificate used by end users to authenticate to Active Directory or Azure. This is used in the background after successful PIN or biometrics authentication. |
| Enrollment Agent | Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) | Certificate used by AD FS to sign Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate request sent from end users. |
| SSL/TLS Server | Active Directory Federation Services | Certificate to install in AD FS to assure that the service is trusted.
Installation for this type of certificate is not covered in this document, but you can issue private server certificate using Generic Server template. Refer to “DigiCert® Autoenrollment Server Deployment Guide” for details. For public server certificate, please contact our sales representative. |
Note: Above table only covers certificates required by Hybrid Azure AD joined Certificate Trust Deployment model which DigiCert supports currently. See below, “Supported Deployment Model and Trust Type” for more details.
Below sections describe how they are used and issued in more details.
Windows Hello for Business Authentication Process
Windows Hello for Business enables users to use PIN or biometrics to authenticate. But PIN or biometrics are only used to access the private key stored in the device. They act as a key to open a box which stores the master key. The authentication with Active Directory and Azure solely relies on authentication request signed by this private key.
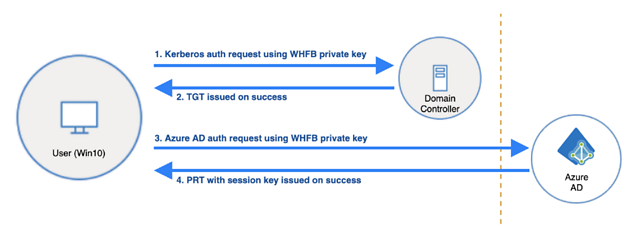
The above diagram shows the authentication process using Windows Hello for Business. After user has retrieved the Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) and Primary Refresh Token (PRT), he/she can access any on-premise service with Kerberos Authentication using TGT and any Azure service using PRT. For more information about PRT and TGT, check the following links.
-
Ticket-Granting Tickets
-
Primary Refresh Token (PRT) and Azure AD
Additionally, when user authenticates with the Domain Controller, it is required that the server has the correct DC certificate. This is because the user also check if the Domain Controller can be trusted.
For more details about the authentication sequence, check the following link.
-
How Windows Hello for Business works — Authentication: Hybrid Azure AD join authentication using a Certificate
Windows Hello for Business Certificate Issuance Process
Following diagram shows how the Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate is issued to the end user using DigiCert Certificate Authority using Autoenrollment Server.
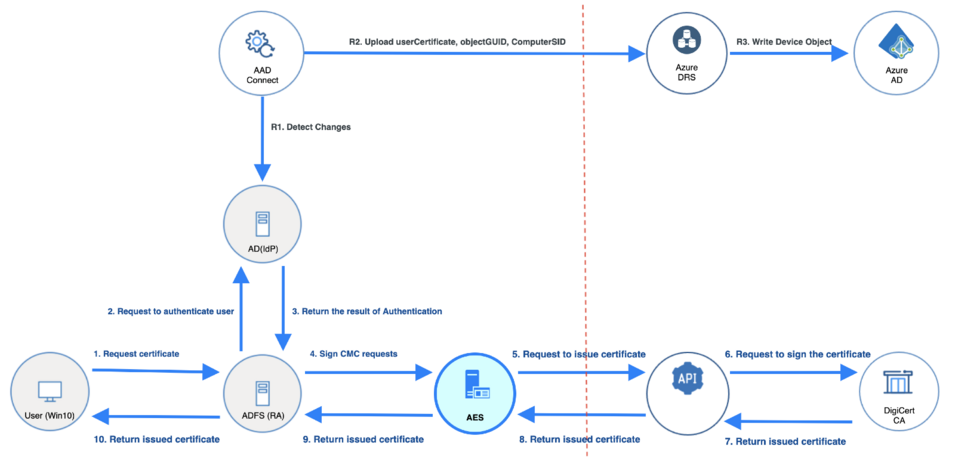
You can see from the diagram that user requests certificate through AD FS. AD FS authenticates the user and also signs the CSR (Certificate Signing Request) sent by user. This is called “Enroll on Behalf of”, since AD FS enrolls for the certificate on behalf of the user. This process requires that AD FS has its own Enrollment Agent certificate, which is automatically issued to AD FS during this process if AD FS does not have an Enrollment Agent certificate.
The request is sent to Autoenrollment Server using CMC (Certificate Management over CMS), where Autoenrollment Server checks the signature of the request. If the signature is valid, Autoenrollment Server will call the DigiCert API to issue certificate. The issued certificate will be returned to AD FS, and AD FS will return it to the user.
The issuance process explained in this section is also part of a process called “Provisioning“ in Windows Hello for Business terms, where initial certificate issuance occurs after user has successfully authenticated to both Active Directory and Azure AD using credentials or MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication).
For more details about the certificate issuance sequence, check the following link.
-
How Windows Hello for Business works — Provisioning: Hybrid Azure AD joined provisioning in a synchronous Certificate Trust deployment in a Federated environment
Pre-requisites
Supported Deployment Model and Trust Type
When enabling Windows Hello for Business for your organization, you will need to decide which deployment model and trust type suit your organization. There are five different deployment model and trust type combinations:
-
Cloud Only Deployment
-
Hybrid Azure AD joined Certificate Trust Deployment
-
Hybrid Azure AD joined Key Trust Deployment
-
On-premises Certificate Trust Deployment
-
On-premises Key Trust Deployment
Check the official Microsoft documents, Planning a Windows Hello for Business Deployment and Windows Hello for Business Deployment Prerequisite Overview for full details about which model you should and can use.
You do not need to consider about Windows Server Certificate Authority stated in the Microsoft Prerequisite document, since it will be covered by DigiCert.
Currently, DigiCert supports the Hybrid Azure AD joined Certificate Trust Deployment model but planning to support additional certificate-based trust models. DigiCert will not support any of the two Key Trust Deployment models.
Required Windows Hello for Business Setup
Following shows the steps required to set up a Windows Hello for Business solution for Hybrid Azure AD joined Certificate Trust Deployment. They are steps outlined in the official Microsoft deployment guides. The links for each step will take you to the official Microsoft documents.
- Hybrid Certificate Trust Deployment Overview
- Prerequisites
- New Installation Baseline — skip “Public Key Infrastructure” section
- Device Registration
- Configure Windows Hello for Business settings
- Active Directory
- Public Key Infrastructure — replaced by this document
- Active Directory Federation Services — “Configure the Registration Authority” section replaced by this document
- Group Policy
- Sign-in and Provision
You will need to complete all steps to 5-a. “Active Directory”, but in 3. “New Installation Baseline“, skip “Public Key Infrastructure” section. Also you can skip 5-b. “Public Key Infrastructure” and 5-c. “Active Directory Federation Services“, and finish 5-d. “Group Policy” first. This document replaces those sections, substituting Windows Server Certificate Authority with a DigiCert Certificate Authority.
When all the steps covered in this document are completed, you can move on to 6. “Sign-in and Provision”. If all the configurations are properly in place, provisioning should happen when user logs on to their Windows machine.
Required Autoenrollment Server Setup
To enable Windows Hello for Business certificates to be issued from a DigiCert Certificate Authority, the DigiCert Autoenrollment Server is required to be installed and configured in your enterprise Windows domain. Follow the directions in “DigiCert® Autoenrollment Server Deployment Guide” which can be downloaded from DigiCert PKI Platform & Autoenrollment Server Deployment Guides to install and configure.
All steps from the document need to be completed, and it is recommended to first check if certificates can be issued using a Non-Windows Hello for Business Certificate Profile. The issuance process for Windows Hello for Business is complicated, and it will be easier to troubleshoot by ensuring that your Autoenrollment Server can issue certificates properly before configuring for the Windows Hello for Business solution.
The Windows Hello for Business solution can be provisioned where:
- DigiCert Autoenrollment Server is setup on Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019 or Windows Server 2022.
- ADFS is setup on Windows Server 2019 or Windows Server 2022.
Setting Up Windows Hello for Business with Autoenrollment Server
Creating Certificate Profiles
You will need to create three different certificate profiles from each certificate templates described below to enable Windows Hello for Business for your organization.
| Certificate Template Name | Description |
Enrollment Methods |
| Domain Controller for Windows Hello for Business | This profile issues certificates to Domain Controllers in your Active Directory domain. This certificate is used when users using Windows Hello for Business credentials try to authenticate to your Active Directory domain. | CSR
Microsoft® Autoenrollment |
| Microsoft® Enrollment Agent | Enables organization to issue Microsoft® Enrollment Agent certificates which allows certificate enrollment on behalf of another entity in your Active Directory domains. | Microsoft® Autoenrollment |
| Windows Hello for Business Authentication | Enables organization to issue Windows Hello for Business certificates to users in your Active Directory domains. | Microsoft® Autoenrollment |
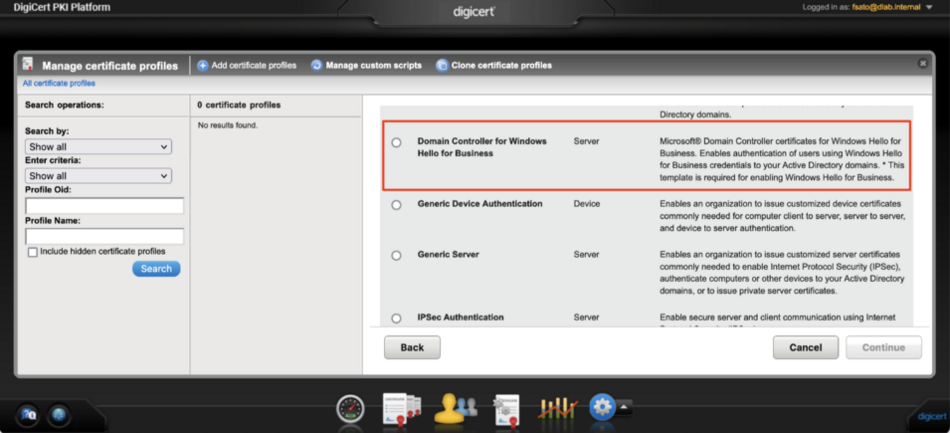
Screenshot shows the profile for “Domain Controller for Windows Hello for Business”
The “DigiCert® Autoenrollment Server Deployment Guide” (downloadable from DigiCert PKI Platform & Autoenrollment Server Deployment Guides) section “Creating Autoenrollment Certificate Profile” will guide you through on how to create certificate profiles for Autoenrollment Server. When selecting certificate template, make sure to select from one of the three templates described above.
After you create the profiles, make sure to note the Certificate Profile OID for two profiles created from following templates.
- Microsoft® Enrollment Agent
- Windows Hello for Business Authentication
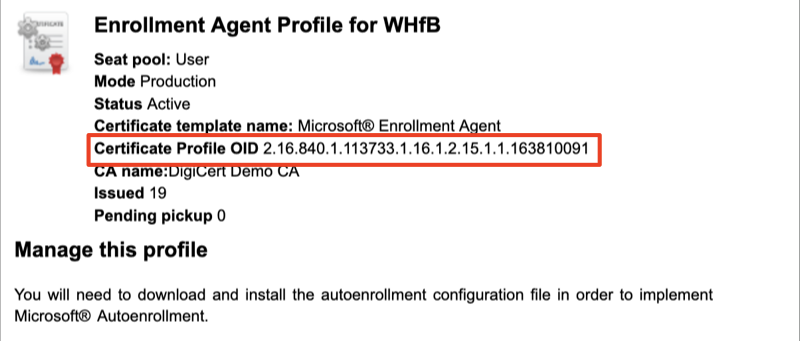
This information will be required later in section “Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services”.
NOTE: When creating Microsoft® Enrollment Agent template, make sure to select Yes for Allow duplicate certificates.
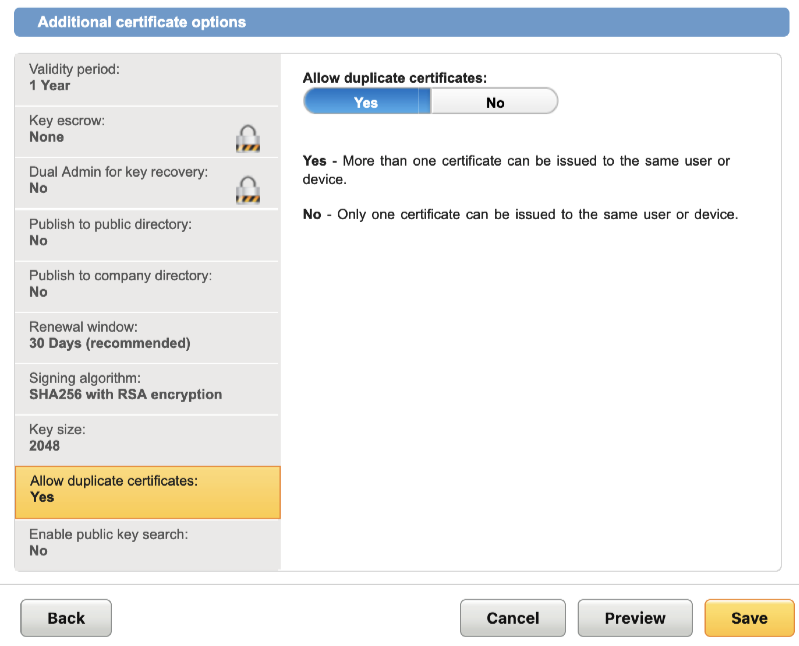
This is required since Active Directory Federation Service will try to issue certificate from this profile every 12 hours for status check. If duplicate certificate is not allowed, status check will fail.
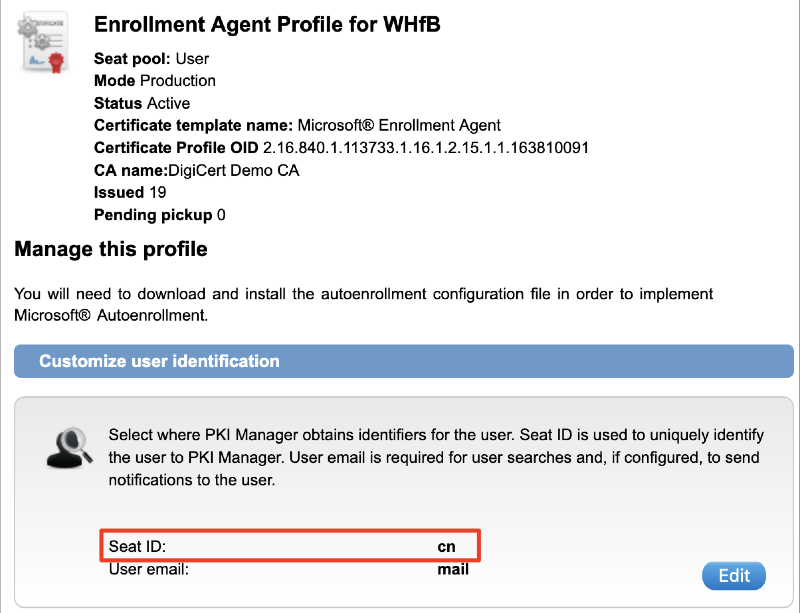
NOTE: Microsoft® Enrollment Agent template Seat ID will be mapped to ‘cn’ (Common Name) by default. This should not be changed to mail when the AD FS is run by Service Accounts, since Service Accounts does not have email address.
Downloading and Importing Autoenrollment Configuration File
After you have successfully created the required three certificate profiles, you will need to download and import the Autoenrollment configuration file.
To do so, refer to the “DigiCert® Autoenrollment Server Deployment Guide” (downloadable from DigiCert PKI Platform & Autoenrollment Server Deployment Guides) section “Importing the Autoenrollment Configuration File”.
NOTE: If you have selected CSR as Enrollment Method for Domain Controller for Windows Hello for Business template, then while downloading the AutoEnrollment configuration file from DigiCert PKI Platform ensure to Un-Check AES based profile for Domain Controller for Windows Hello for Business template.
Assigning Group/User Access for Each Template
After you have imported the Autoenrollment configuration file into the Autoenrollment Server, you will need to assign access permissions to the imported templates. The required permission for each template is described below. Refer to the “DigiCert® Autoenrollment Server Deployment Guide” (downloadable from DigiCert PKI Platform & Autoenrollment Server Deployment Guides) section “About the Preparation of Certificate Templates” and “About the Assignment of Group/User Access to Templates“ for more details on how to configure them.
Certificate Template Name
Required Access Permission
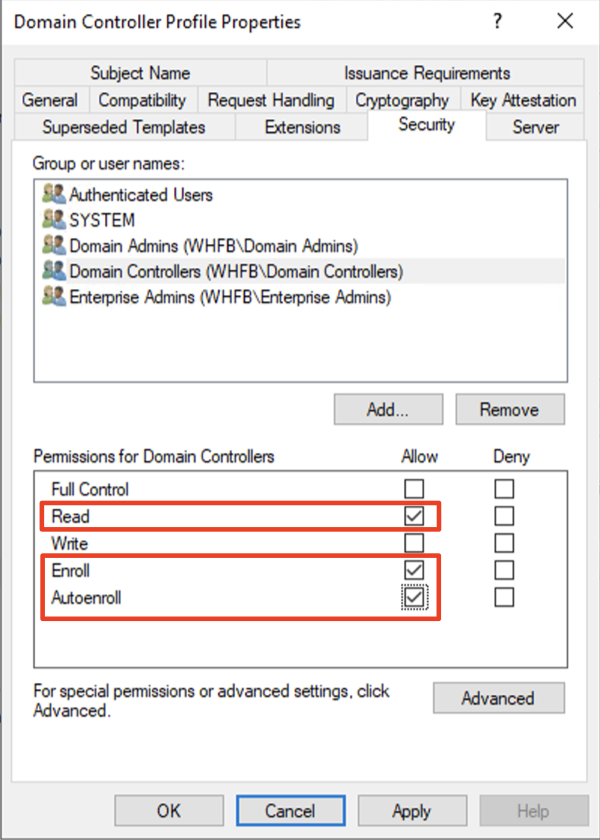
Domain Controller for Windows Hello for Business
NOTE: Skip if you have selected CSR as Enrollment Method for Domain Controller for Windows Hello for Business template.
Group which has all the Domain Controllers in your domain.
By default, Domain Controllers group should include all the domain controllers.
Check Read, Enroll, and Autoenroll.
Microsoft® Enrollment Agent
Group which includes the account user for AD FS, or specify the account directly.
If the account is a Service Account, following operation is required to show the Service Account objects:
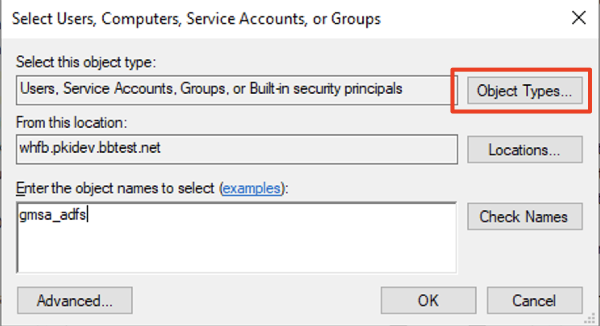
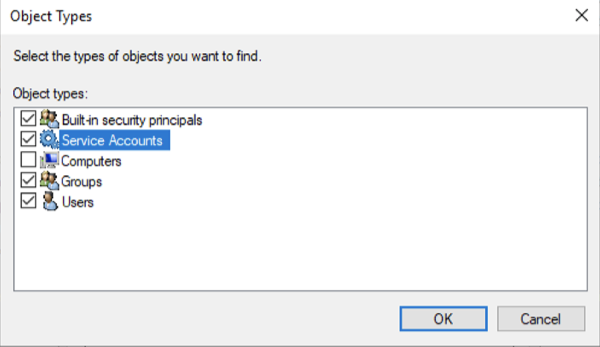
- After clicking Add click Object Types
- Check Service Accounts
Check Read, and Enroll. Autoenroll is not required. Certificate from this template will be issued to AD FS account user automatically as part of Windows Hello for Business flow.
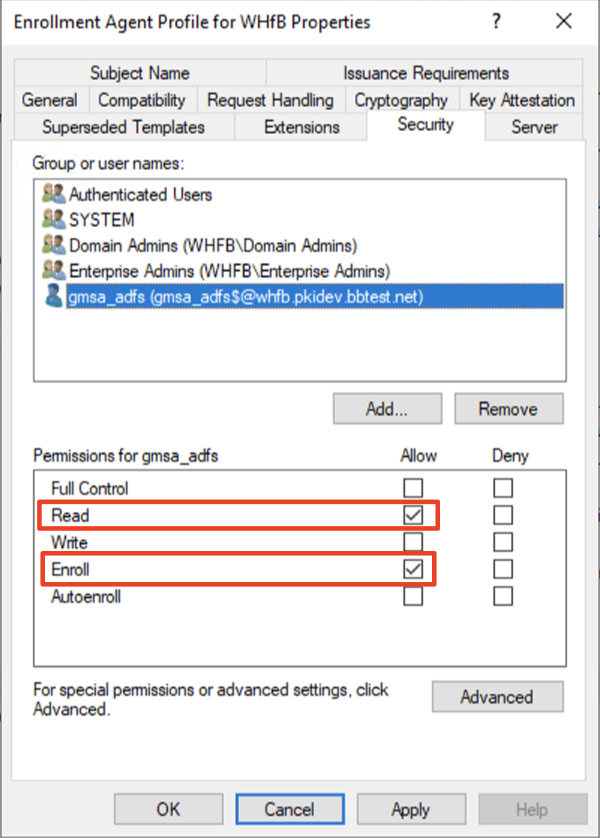
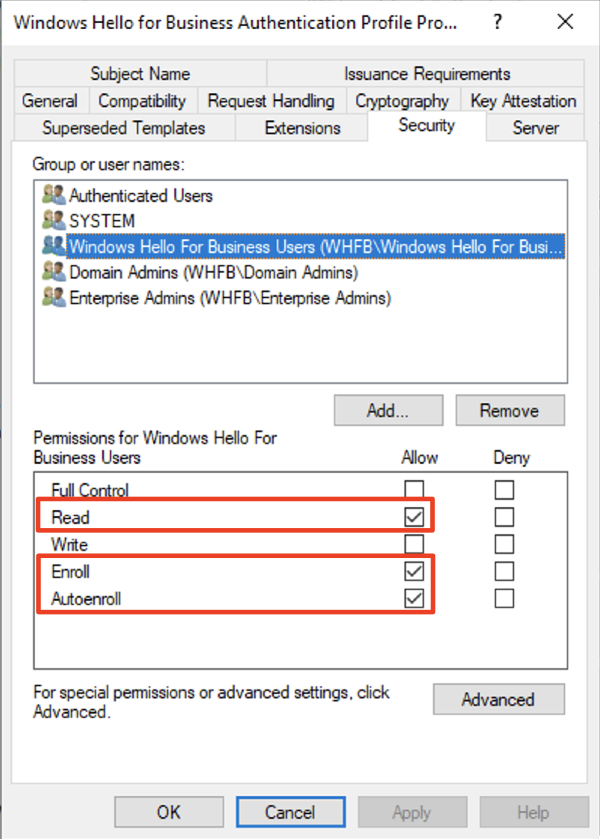
Windows Hello for Business Authentication
This should be Windows Hello for Business Users group that was created during 5-a. “Active Directory” from the official Microsoft documentation. The name does not have to exactly match, but needs to be group of users that you are trying to assign Windows Hello authentication to.
Check Read, Enroll, and Autoenroll.
Issuing Domain Controller Certificates
There are different ways to issue Domain Controller certificates depending on the Enrollment Method chosen during the profile creation. Proceed to the appropriate section depending on the Enrollment method you have selected.
Issuing Domain Controller Certificates with CSR:
If you selected CSR as Enrollment Method, follow the steps in this section. These steps are completed on the Domain Computer where you are planning to issue the certificate to. The user who performs these steps must have administrator rights for the computer.
1. Create a text file named dccert.inf with following contents:
[NewRequest]
RequestType = PKCS10
ProviderName = «Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider»
Subject = «CN=<machine name>»
MachineKeySet = True
HashAlgorithm = SHA256
KeyAlgorithm = RSA
KeyLength = 2048
Exportable = <True|False>
SMIME = False
UseExistingKeySet = False
KeyUsage = 0xA0
Make sure to edit Subject and Exportable property appropriately. Save it to a temporary location.
2. From a command prompt, run the following command to generate the CSR in .pem format. The command outputs the CSR to the file dccert.req. You can run this utility from any location. However, unless you run it from the location where you saved the dccert.inf file, you must specify the path to this file.
certreq -new dccert.inf dccert.req
This command writes the dccert.req file to the directory where you ran the command. Specify the full path to a different location.
3. Copy the dccert.req file to the computer that has access to the DigiCert PKI Platform 8 Certificate Service. How to issue the certificate varies depending on which Authentication Method you chose for Domain Controller for Windows Hello for Business profile. Here, we will go through the steps using commonly used Manual approval method.
- Access certificate service link with browser. This link should have appeared in the PKI Manager after creating the profile
- Input required enrollment information. Following is required:
- Common name: Machine name of the Domain Controller
- DNS Name: Fully qualified domain name of the Domain Controller
- CSR: Content of dccert.req generated on the previous step
4. In PKI Manager, go to Manage users, and approve the request.
5. The certificate will be sent to the requestor. Copy the certificate from ——BEGIN CERTIFICATE—— to ——END CERTIFICATE—— and paste it into a file named dccert.pem in the Domain Controller.
6. Install the new certificate on the Domain Controller machine:
certreq -accept -machine dccert.pem
When successful, it should show the installed certificate as an output. Following shows an example:
> certreq -accept -machine dccert.pem
Installed Certificate:
Serial Number: 6081c45c965e3877715d420a91d5af
Subject: OU=MULTI-ALLOWED, OU=DOMAIN-CONTROLLER, CN=w19-whfb-220 (DNS Name=w19-whfb-220.whfb.pkidev.bbtest.net)
NotBefore: 1/13/2023 4:00 PM
NotAfter: 1/14/2024 3:59 PM
Thumbprint: 7297b227bb692e2329204417ae236a26decca7ff
Issuing Domain Controller Certificates with Microsoft® Autoenrollment
If you selected Microsoft® Autoenrollmentas Enrollment Method, follow the steps in this section.
After you have assigned access permissions to the Domain Controller template for the Domain Controllers, Domain Controller certificate will be issued automatically to the Domain Controllers. The timing depends on how the operating system handles them. To make sure that the certificate has been issued properly to the Domain Controllers, follow the direction below.
Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services
After certificate templates are imported and access permission is set, you will need to configure the Registration Authority templates to use for Windows Hello for Business with AD FS. This section covers the first part of “Active Directory Federation Services“ from the Microsoft official documentation, but provides little more information about what to specify for Windows Hello for Business Enrollment Agent and Windows Hello for Business Authentication template names when using DigiCert Autoenrollment Server.
To configure the Registration Authority:
- Sign-in the AD FS server with Domain Admin equivalent credentials.
- Open a Windows PowerShell prompt.
- Enter the following command:
Set-AdfsCertificateAuthority -EnrollmentAgent -EnrollmentAgentCertificateTemplate <Windows Hello for Business Enrollment Agent OID> -WindowsHelloCertificateTemplate <Windows Hello for Business Authentication OID> -WindowsHelloCertificateProxyEnabled $true
For <Windows Hello for Business Enrollment Agent OID>, enter the OID for profile created using Microsoft® Enrollment Agent certificate template. For <Windows Hello for Business Authentication OID>, enter the OID for profile created using Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate template. For example, it will look something like the following:
Set-AdfsCertificateAuthority -EnrollmentAgent -EnrollmentAgentCertificateTemplate 2.16.840.1.113733.1.16.1.2.15.1.1.163810091 -WindowsHelloCertificateTemplate 2.16.840.1.113733.1.16.1.2.4.2.1.163810095 -WindowsHelloCertificateProxyEnabled $true
After above configuration is completed, continue from “Group Memberships for the AD FS Service Account” in “Active Directory Federation Services“ from the Microsoft official documentation. Additionally, make sure that ‘ugs’ scope is configured correctly as mentioned in the Note section of the document. This is extremely important since provisioning will not start without this ‘ugs’ scope properly configured.
Adding User Principal Name to Service Account
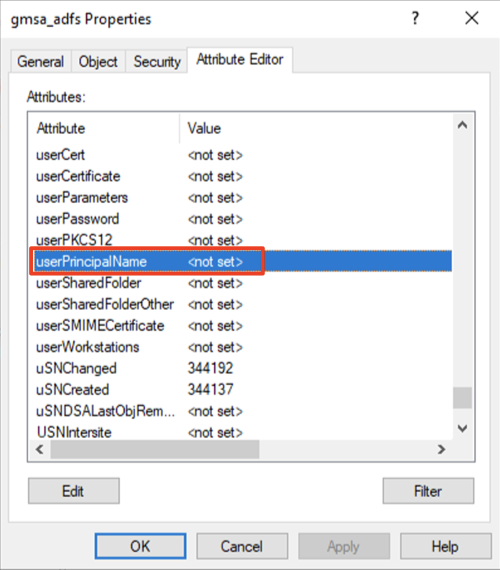
This section will guide you on how to add User Principal Name (UPN) to Service Account. You will need to follow the direction here if your AD FS is configured to run using a Service Account. You can check whether AD FS is using Service Account by using the Services Tool (open Start Menu and type services). If Log On As for Active Directory Federation Services ends with ‘$’ (dollar sign), this indicates that your AD FS is running using a Service Account.
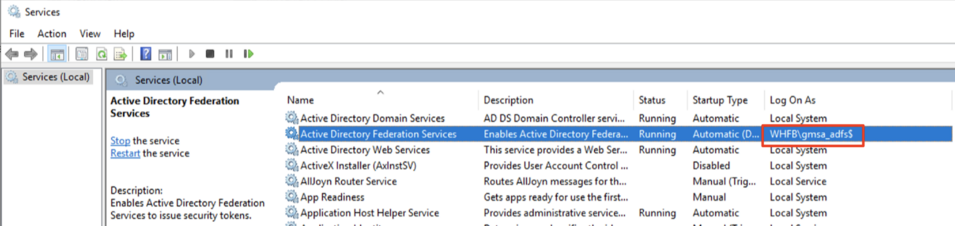
UPN is required to identify the end entity of the issued certificate, but since Service Account does not have UPN by default, it is required that this information is filled out before issuing Enrollment Agent certificate to the Service Account.
To add UPN to Service Account:
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers from Windows Administrative Tools.
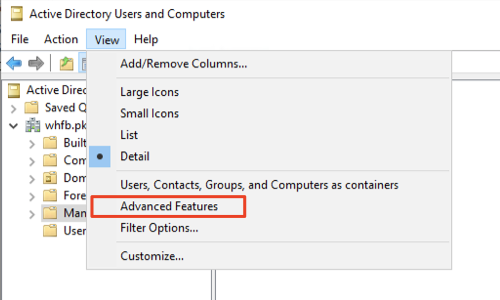
- Click View menu and enable Advanced Features by selecting the option. This will enable editing the attribute of the Service Account.
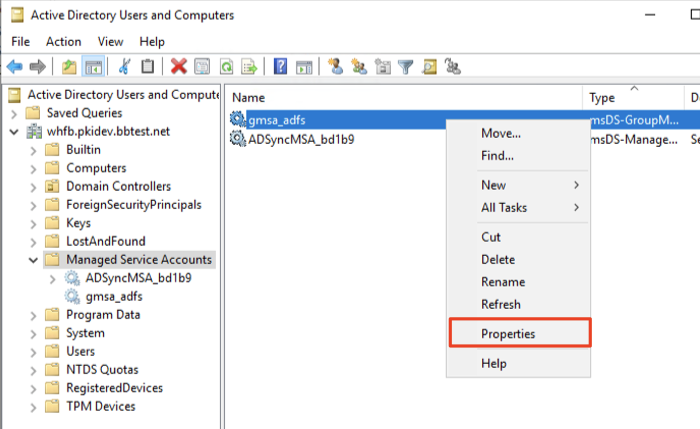
- In the tree window at the left, collapse the domain in which the Service Account exists, and select Managed Service Accounts. Right-click the Service Account configured for AD FS and select Properties.
- In the Properties dialog, select the Attribute Editor tab, scroll down and select userPrincipalName. Click Edit.
- In the String Attribute Editor dialog, enter userPrincipalName of the Service Account. UPN will need to be in the format, <cn of the Service Account>$@<domain name>. For this example, the cn (or the shown name) of the Service Account is “gmsa_adfs”, and domain is “whfb.pkidev.bbtest.net”. Resulting UPN for this example will be “gmsa_adfs$@whfb.pkidev.bbest.net”.
- Click “OK” twice to apply the change and close the dialogs.
Provisioning
After all configurations have been set and user logs on to their device, user should be prompted to provision Windows Hello for Business. Refer to “Sign-in and Provision” from the Microsoft official documentation for details.
Windows Hello for Business Authentication Certificate Lifecycle
Renewal
Renewal of the certificate will occur in the background automatically when the certificate nears the expiration period. But for the certificate to renew, it requires that user to be logged in to the machine. If the user misses the renewal period for some reason, certificate will reach expiration.
During Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate renewal, only the certificate information is updated (such as validity notBefore and notAfter) and asymmetric keys are not regenerated.
Expiration
When the automatic renewal does not occur during the renewal period for some reason, certificate will expire. But users should be able to log on to their machine using the Windows Hello credential for the first time after certificate reaches the expiration. After successful login, the operating system will try to re-issue the certificate in the background. If the user logs out of the machine before this takes place, user will not be able to login using their Windows Hello credential, with screen like below.
User will need to login using Active Directory credential if this happens, but Windows Hello credential should be re-issued after sometime automatically after successful login.
During re-issuance, only the certificate information is updated (such as validity notBefore and notAfter) and asymmetric keys are not regenerated.
Revocation
When Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate is revoked, user will not be able to login using their Windows Hello credential, with screen like below.
The timing that OS identifies that the certificate is revoked depends on the update time of CRL or OCSP, so it may not be reflected immediately after the certificate is revoked.
User will need to reset Windows Hello credential by such method as using “I forgot my PIN” in the login screen. See below “Reset” for more details.
Reset
When user resets their Windows Hello credential such as using “I forgot my PIN” in the login screen, user will be re-provisioned and certificate will be issued again. Asymmetric keys will be regenerated and new certificate will be issued.