This article aims to show you how to run your Windows-only games on Ubuntu. Out of the box, Linux is at a disadvantage because in general it is meant to be a robust system for the average user and does not pander to the gamers of the world. There are however ways of tailoring Linux to be a gaming machine. In general, getting the video system faster is the main thing. Some mods work better for some games, but not for others. some are even mutually exclusive, and you get to make a multi boot box so that you can be in the best environment for a particular game. Exactly how much effort you put into this project depends on how much of a gamer you are. consider it part of the game
Introduction
A common concern for of people thinking of switching to Ubuntu is the thought of having to leave behind all the Windows games they love. However it is possible to play many of these games under Ubuntu using a compatibility layer.
A compatibility layer acts much like an emulator providing an enviroment for Windows based programs to run, translating system calls and such. Generally you have two solutions; Wine and Cedega.
-
Wine is completely free and in the Ubuntu Repositories.
-
Cedega is a fork of Wine originally known as ‘WineX’ as it aimed to support DirectX to enable better support for Windows games. It is a proprietary product and requires a small monthly subscription (currently $5.00). However it is much more user-friendly and specificly designed with gaming in mind.
Windows games in action

Game howtos
Below is a list of links to that will explain how to run some of the more popular Windows games on Linux:
-
Diablo II — Forum guide by «dynacrylic» using Wine.
-
[WorldofWarcraft]

The continued (and usually justified) distaste for Windows 10 has given more momentum than ever to Linux as a desktop platform. Most Linux-based operating systems are free to use, have a consistent interface, and don’t break with every update—what’s not to like?
While Linux can run much of the same software that Windows can, including all major web browsers and many productivity tools, gaming has always been a rough point for the platform. Major games natively written for Linux are still few in number, but Windows compatibility layers like Wine and various emulators have been filling in the gaps.
Thankfully, Linux gaming has improved quite a bit in the past year. Steam Play allows you to play Windows games effortlessly through Steam, without fiddling with configuration files or installers yourself (most of the time, anyway). Meanwhile, tools like Lutris have made it easier than ever to play games through the Wine compatibility layer.
In this guide, we’ll show you the best ways to play Windows-only games on your favorite Linux distribution—whether it be Ubuntu, Debian, Arch, Fedora, or something else.
Steam Play/Proton
For years, the ‘Wine’ compatibility layer has made it possible to play Windows games on Linux. For the past three or so years, Valve has been working with Wine developers to improve game compatibility, and the result is Proton. Proton, also called ‘Steam Play,’ is a modified build of Wine developed by Valve—and it’s built right into Steam for Linux. That’s right, the dark days of installing Steam inside of Wine to play Windows-only Steam games are over.
Steam Play is an incredibly impressive compatibility layer, and it makes running Windows games in Linux easier than ever. It can translate Windows DirectX calls to Vulkan API calls, resulting in better compatibility and performance than ever before, and it works perfectly with external controllers and Steam Overlay.
To get started with Steam Play, install Steam for Linux if you haven’t already. This process varies a bit depending on what Linux distribution you’re running.
Keep up to date with the most important stories and the best deals, as picked by the PC Gamer team.
Installing Steam on Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Pop_OS, and most other Debian-based distros
Go to the Steam download page and click the big download button. You should get a .deb file. Double-click on the file, and a package manager will open asking you if you want to install the application. Once the process is complete, Steam should be available in your app launcher, and you can open it and log in.
Installing Steam on Elementary OS
While Elementary OS is based on Debian/Ubuntu, newer versions of Elementary don’t automatically have the application required to open .deb files. So first, you need to install ‘Eddy’ from the AppCenter. Once Eddy is installed, go to the Steam download page, click the big download button, and open the .deb file it gives you. After all that is done, Steam should be available in your app launcher. Try opening it and logging in.
Installing Steam on Fedora, Arch, and most other distros
If you’re using a distribution that isn’t based on Ubuntu/Debian, you’ll have to install Steam from the unofficial Flatpak. Flatpak is a way of packaging applications to work on a wide variety of Linux distributions.
First, some minor setup may be required depending on the exact distribution you’re using. The official Flatpak website has super easy instructions for getting everything set up.
Once that’s done (and you’ve rebooted your PC, if it said to in the instructions), we need to make sure the Flathub repository is set up. Run this command in the Terminal:
flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoThen install Steam with this command:
flatpak install flathub com.valvesoftware.SteamAfter that’s done, Steam should appear in your app launcher. Open it and log in.
Enabling Steam Play for all games
Valve currently tests games before officially certifying them for Steam Play. However, there is a setting in Steam that gives you the option of running non-certified games in Steam Play. While many titles work just fine, keep in mind that some games (especially newer ones, or some that use certain DRM methods) might have issues or won’t work at all. The worst that can happen is the game not running—you don’t have to worry about corrupting other games or breaking Steam.
To get started, click the Steam menu at the top-left of the main Steam window, and select ‘Settings’ from the dropdown. Then click ‘Steam Play’ on the left side, make sure the the box that says ‘Enable Steam Play for supported titles’ is checked, and check the box for ‘Enable Steam Play for all other titles.’
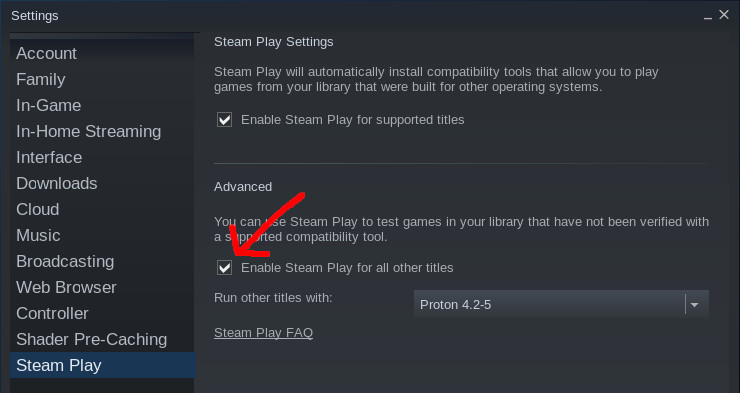
After that’s done, click OK. Steam might want to restart to apply your changes. With all that done, go to your Steam library, click the dropdown menu next to the search bar, and make sure ‘Games’ is selected. Now you can see all your Steam games—including those for Windows—and install them with just one click. The helpful «runs on this computer via Steam Play» message will let you know which games will be installed using the compatibility layer.
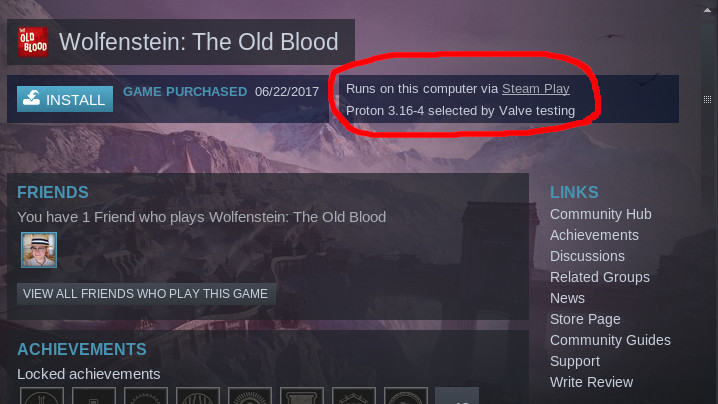
If you want to check if a certain game will run in Steam Play before you download it, check out ProtonDB. It’s a community-maintained database that can probably tell you if a certain game works or not, complete with helpful instructions and tips for getting troublesome games to run.
Steam Play is a fantastic piece of software, and it makes playing popular Windows games in Linux far easier than it ever was before… as long as the game is available in Steam. For games found on other storefronts and launchers, another tool might be able to help you out.
Lutris
Lutris describes itself as an «open source gaming platform for Linux.» It’s a front-end for programs like Wine, RetroArch, and DOSBox—you pick the game you want to play, and everything required to get it working is downloaded and set up for you. It supports games like League of Legends, Skyrim, Warframe, Overwatch, and more. It can even detect and add any Linux-native games you might already have installed and add them to the launcher.
Installing Lutris
Lutris has detailed installation instructions on its website, so we won’t re-invent the wheel here. On most distributions, it only takes a command or two to get everything installed.
How to use Lutris
To get started with Lutris, just open it from your app launcher, click the search button, type in a game, and click the ‘Search Lutris.net’ button. You’ll get a list of games you can install, and double-clicking on it will display the ways you can install it. For example, The Witcher 2 can be downloaded from GOG for Linux, GOG for Windows, Steam for Linux, and Steam for Windows.
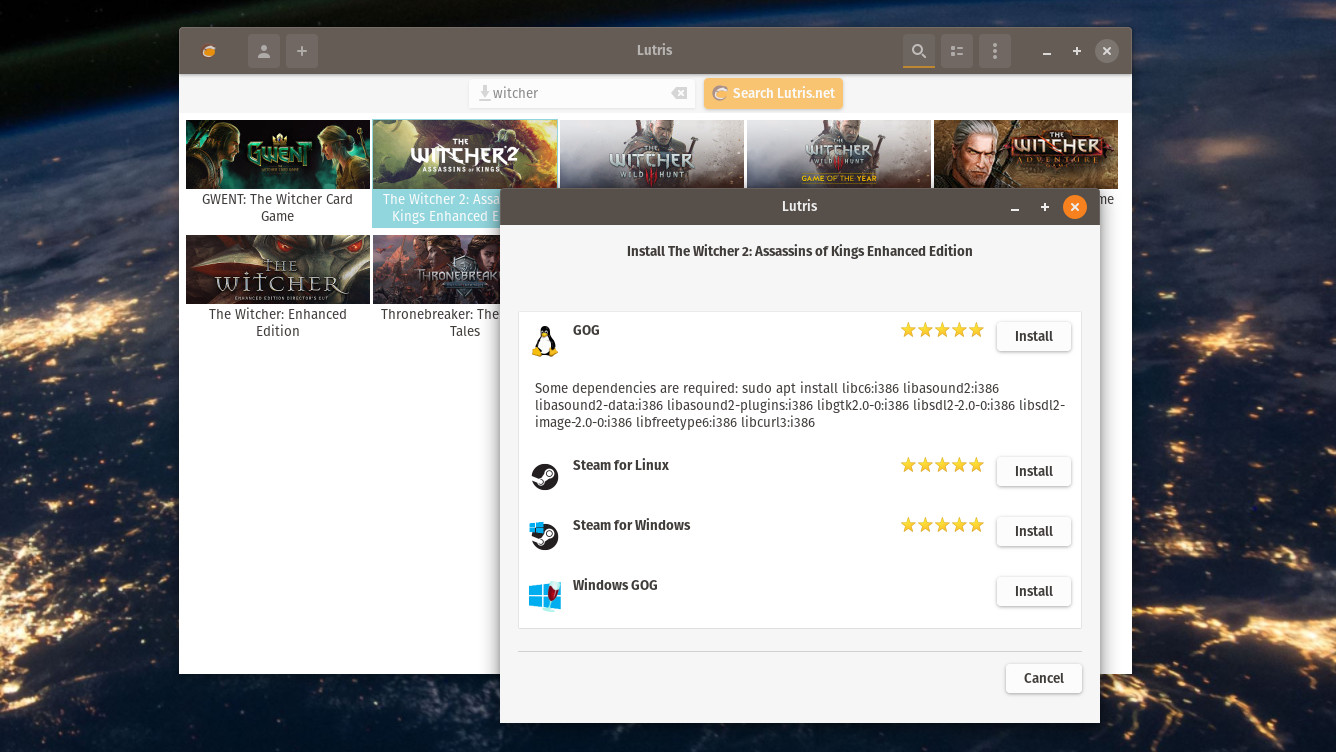
Also, Lutris supports more than just Windows games. It offers multiple «runners» for playing games from different platforms, including RetroArch (retro games), DOSBox (DOS games), MAME, ScumVM (LucasArts titles), Snes9x (SNES games), and ZDoom (DOOM-based titles).
If you’re feeling adventurous, you can install games manually using whichever runner you want. Lutis has no shortage of options and configuration settings.
Conclusion
Steam Play has made it easier than ever to run your entire Steam catalog on Linux, and Lutris is a significant improvement over the script-based game installers of old (anyone remember PlayOnLinux?). With these two tools, you can enjoy thousands of games that will likely never have an official Linux port.
Of course, there are still more ways to run Windows games on Linux. You can install VirtualBox and run a Windows virtual machine, though you’re likely to run into performance problems with newer games. If you’re feeling adventurous, you could try setting up a VM with support for GPU passthrough.
CrossOver by CodeWeavers is another popular way to run Windows software on Linux, and many of its developers helped Valve develop Steam Play. However, CrossOver is more oriented towards business use, so it doesn’t have as many supported games as Lutris.
Corbin is a tech journalist, software developer, and longtime PC Gamer freelance writer, currently based in North Carolina. He now focuses on the world of Android as a full-time writer at XDA-Developers. He plays a lot of Planet Coaster and Fallout and hosts a podcast all about forgotten stories from tech history.
This tutorial will help you to use Microsoft Windows programs and games on Ubuntu using Wine software. You will start by examples we provide (FOSS only) and getting familiar to installing, running, managing and removing programs. We also supply further references for you to learn more. Enjoy!

Subscribe to UbuntuBuzz Telegram Channel to get article updates.
About Wine
Wine (Wine Is Not Emulator) is a collection of software called ‘compatibility layer’ that allows Microsoft Windows programs and games to run on GNU/Linux operating system. To use Wine on GNU/Linux, one should double-click any EXE or MSI files (some configuration needed) and the program should run or the installer wizard should show as if it runs natively on Windows. Currently, many Windows applications both gratis and commercial ones, and also many games both 2D and 3D including the online ones, from the oldest to the newest (with various degrees of success), are successfully running on GNU/Linux thanks to Wine. There is no alternative to Wine to run Windows apps and games on GNU system. Wine is one of the world greatest compatibility layer projects in computing. Visit its website https://winehq.org.
Why do we need Wine?
In our opinion we will need Wine in several conditions:
1. To run needed, old applications that still do not have a FOSS replacement / continuation yet. This case is often found at companies and offices.
2. To test Free Software that released for Windows without having Windows itself.
3. To run games needed by you or people important to you.
4. To learn software development (engineering, debugging, reverse, API, etc.) both in general and in specific area for Windows.
5. To help with Wine development itself.
6. To help development of Windows-like operating system like ReactOS, and many other purposes.
In this tutorial, we will only give you examples of Free/Libre Open Source Software (also known as FOSS), such as LibreOffice, by their Microsoft Windows version. We don’t give example of proprietary software, both gratis and commercial kind, such as Photoshop.
Examples
We pick several applications and games in Windows format namely EXE and MSI as examples in this exercise. They are Free/Libre Open Source Software (FOSS). So please download them before practicing the rest of this tutorial.
1) Peazip https://peazip.github.io
2) Sumatra PDF https://sumatrapdfreader.org
3) LibreOffice https://www.libreoffice.org
4) Inkscape https://inkscape.org
5) Notepad++ https://notepad-plus-plus.org
Wine Versions
1) Wine32: for running i386-architecture version of Windows applications.
2) Wine64: for running amd64-architecture version of Windows applications.
Wine Front-Ends
A front-end is a user interface for another program that does not have user interface. Wine does not have user interface. So there are several Wine front-ends to help end-users add, install, run, remove, manage their Windows apps and games.
1) PlayOnLinux
2) Q4Wine
3) Bottles
Wine Installation
Refer to Installation Guide to add Wine software to your Ubuntu system.
Application Installation
Once you installed Wine properly, you can start installing applications.
1. Make sure you have the program file in .exe extension.
2. Right-click the file > Open with Wine.
If no Wine option exists, select Open With … instead and type wine in the text box and press Enter. (Note: this works with Dolphin file manager and does not work with Nautilus)
3. Wait for a while.
4. Windows application will run or its installer will show.
5. If it is an installer, simply click Next until Finish.
6. Run the application from start menu.
Game Installation
Similarly to normal applications, you can install games too, of course.
1. Make sure you have the program file in .exe extension.
2. Right-click the file and select Open With Wine.
(Note: this works with Dolphin file manager and does not work with Nautilus, see Terminal section below for solution)
3. The game will play or the installer will show.
4. If it is an installer, then click Next continuously until Finish.
5. Game is installed and can be played from start menu.

MSI Installation
Please note that in general Windows accepts two kinds of executable, namely .exe that has been explained above, and .msi that will be explained below. For clarification, MSI stands for MicroSoft Installer.
1. Make sure you have the program file in .msi format.
2. Right-click the file > Open With … > a dialog will show > type msiexec /i in the box > press Enter.
3. The program or game will show its installer.
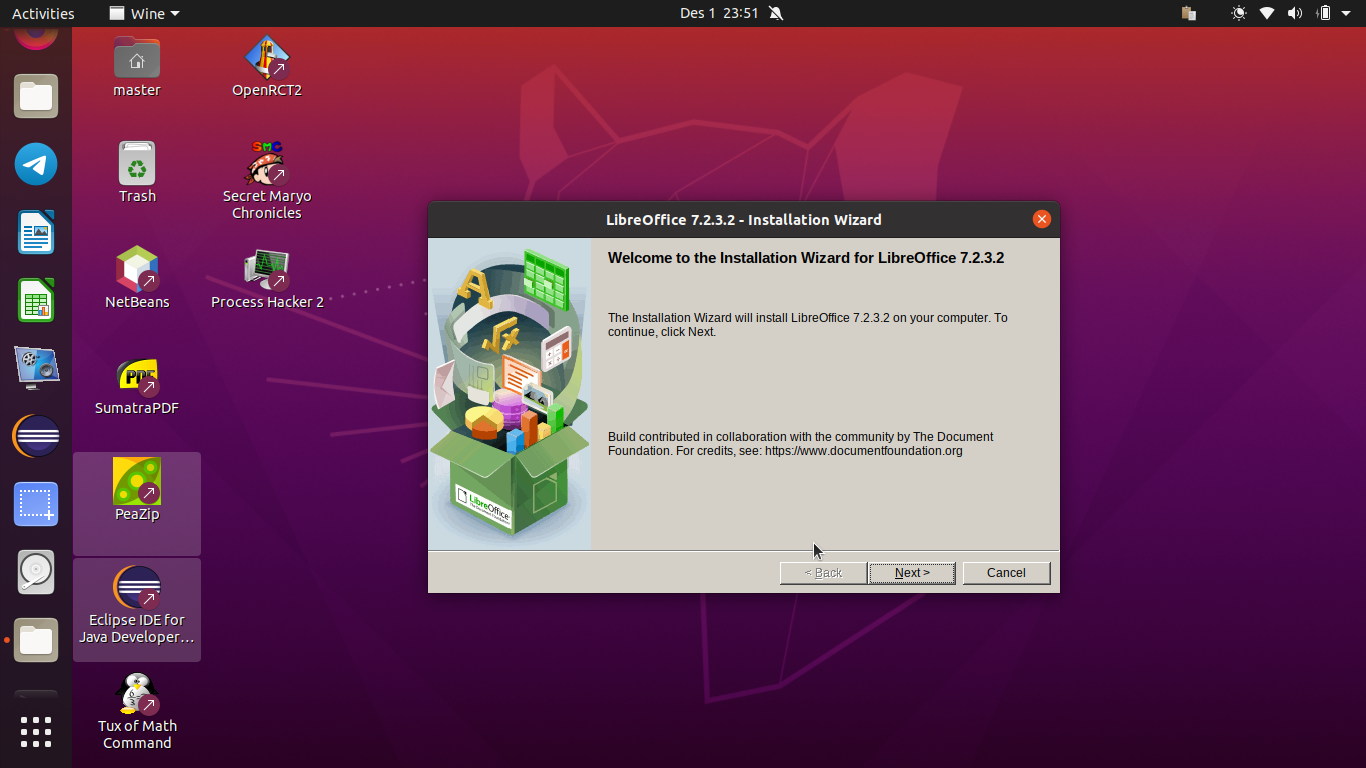
Running Applications using Terminal
If you cannot run Wine with methods explained above, you may use Ubuntu Files, that does not support calling command line. As a solution, we can also run the programs with wine command lines using Terminal. This will help you who use Ubuntu GNOME.
Running program files with .exe extension:
$ wine program-file.exe
Running program file with .msi extension:
$ msiexec /i program-file.msi
If you want to know more command lines, read Wine’s documentation:
$ man wine
References
This article is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0.
you can run windows programs in linux via wine. install it with sudo apt-get isntall wine1. 7 and install latest Nvidia or ATI driver,Then install your games.
- Can you play Windows games on Linux?
- How can I play Windows Steam games on Ubuntu?
- Can we play games on Ubuntu?
- Can you run Windows apps on Ubuntu?
- Why is Linux faster than Windows?
- Which Linux is best for gaming?
- Can you use Steam on Ubuntu?
- Can SteamOS run Windows games?
- Can we play Valorant on Ubuntu?
- Is Ubuntu good for programming?
- Is Linux Mint good for gaming?
- Is Linux good for gaming?
Can you play Windows games on Linux?
Play Windows Games With Proton/Steam Play
Thanks to a new tool from Valve called Proton, which leverages the WINE compatibility layer, many Windows-based games are completely playable on Linux through Steam Play. … Those games are cleared to run under Proton, and playing them should be as easy as clicking Install.
How can I play Windows Steam games on Ubuntu?
Play Windows-only games in Linux with Steam Play
- Step 1: Go to Account Settings. Run Steam client. On the top left, click on Steam and then on Settings.
- Step 3: Enable Steam Play beta. Now, you’ll see an option Steam Play in the left side panel. Click on it and check the boxes:
Can we play games on Ubuntu?
You can install Ubuntu along side Windows and boot into either one when you turn on your computer. … You can run Windows steam games on Linux through WINE. Though it will be a huge amount easier just running Linux Steam games on Ubuntu, it IS possible to run some of the windows games (though it may be slower).
Can you run Windows apps on Ubuntu?
Linux is a great operating system, but its software catalog can be lacking. If there’s a Windows game or other app you just can’t do without, you can use Wine to run it right on your Ubuntu desktop.
Why is Linux faster than Windows?
There are many reasons for Linux being generally faster than windows. Firstly, Linux is very lightweight while Windows is fatty. In windows, a lot of programs run in the background and they eat up the RAM. Secondly, in Linux, the file system is very much organized.
Which Linux is best for gaming?
7 Best Linux Distro for Gaming of 2020
- Ubuntu GamePack. The first Linux distro that’s perfect for us gamers is Ubuntu GamePack. …
- Fedora Games Spin. If it’s games that you’re after, this is the OS for you. …
- SparkyLinux – Gameover Edition. …
- Lakka OS. …
- Manjaro Gaming Edition.
Can you use Steam on Ubuntu?
The Steam installer is available in the Ubuntu Software Center. You can simply search for Steam in the software center and install it. … When you run it for the first time, it will download the necessary packages and install the Steam platform. Once this is finished, go to the application menu and look for Steam.
Can SteamOS run Windows games?
No, only Windows can play all Windows games. SteamOS is just another Linux distro. So it’s Linux using wine and maybe third-party related wine software. … I been successful installing old Windows games using wine and other third-party related wine software.
Can we play Valorant on Ubuntu?
This is the snap for valorant, «valorant is a FPS 5×5 game developed by Riot Games». It works on Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, and other major Linux distributions.
Is Ubuntu good for programming?
If you’re managing developers, Ubuntu is the best way to increase your team’s productivity and guarantee a smooth transition from development all the way to production. Ubuntu is the world’s most popular open source OS for both development and deployment, from the data centre to the cloud to the Internet of Things.
Is Linux Mint good for gaming?
Yes. It’ll run games really well. Just make sure you get the necessary downloads for Vulkan and Mesa if you intend on playing any games on Steam through DXVK.
Is Linux good for gaming?
Linux for Gaming
The short answer is yes; Linux is a good gaming PC. … First, Linux offers a vast selection of games that you can buy or download from Steam. From just a thousand games a few years ago, there are already at least 6,000 games available there.
Table of Contents
There are several ways to run Windows games on Linux using Wine, PlayOnLinux, Crossover, Steam Play, and Lutris. Let’s look at installing games using the last two apps.
In my opinion, Steam and Lutris offer the most modern and easy solutions for launching games. As an example, let’s play World of Tanks and World of Warships on Ubuntu 19.04.
Until recently, running Windows games in Linux was still a quest that overshadowed interest in the game due to the complicated and unsuccessful installation process.
With the advent of DXVK (a library based on Vulkan that allows you to broadcast 3D applications (games) Direct3D 10/11), and as a consequence, Steam Play (Proton) – the installation of many games in Linux has become almost as easy as in Windows.

#1 Install Windows games on Linux using Lutris
Lutris is a service with a game application that provides automated, customized scripts for installing games.
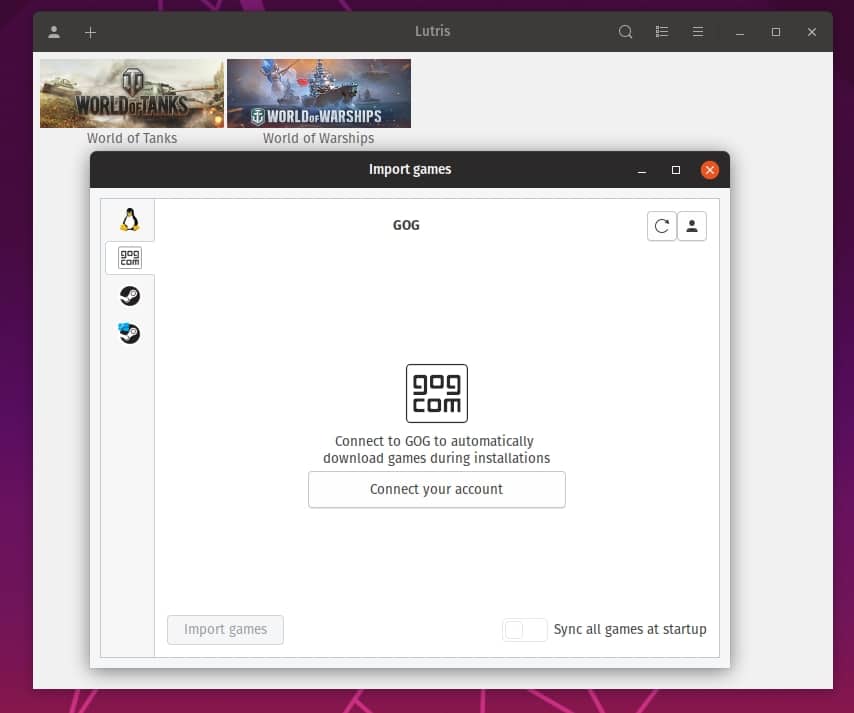
Integration with game stores such as GOG and Steam allows you to import an existing library of games, and community-supported installation scripts provide fully automated customization.
Step 1: Installing Lutris in Ubuntu-based distributions
For the correct operation of Lutris, the developers recommend pre-installing Wine (version of Staging). You can install Wine in Ubuntu according to the instructions of the official website: Installing WineHQ packages.
For Ubuntu distributions like this, add the Lutris repository:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:lutris-team/lutris
sudo apt update
sudo apt install lutris
For best performance, you need to install the latest version of the video driver and the Vulkan library.
Nvidia graphics card users need to add a repository with new drivers and then install the latest version of the drive conveniently:
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386 //поддержка 32 битной архитектуры (в том случае, если раньше ее не включили)
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:graphics-drivers/ppa
sudo apt update
You can select a driver using the built-in Utilities and Updates – Additional Drivers.
If the video card supports the Vulkan API, then install the necessary libraries (most likely they were already installed when installing the video driver. You can check if the video card supports Vulkan by following the link: Vulkan API):
sudo apt install libvulkan1 libvulkan1:i386
AMD/Intel graphics card users (Ubuntu 18.04 and above):
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:kisak/kisak-mesa
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt install libgl1-mesa-dri:i386
sudo apt install mesa-vulkan-drivers mesa-vulkan-drivers:i386
Step 2: Installing Games on Linux with Lutris
Go to the program’s official website in the Games section and select the game we need.
Having found the game, we select (if available) the version of the script with the server we need (for example, for World of Tanks, it will be the RU DXVK version). Click on Install. As an example, we will show the installation of the game World of Tanks in Ubuntu 19.04.
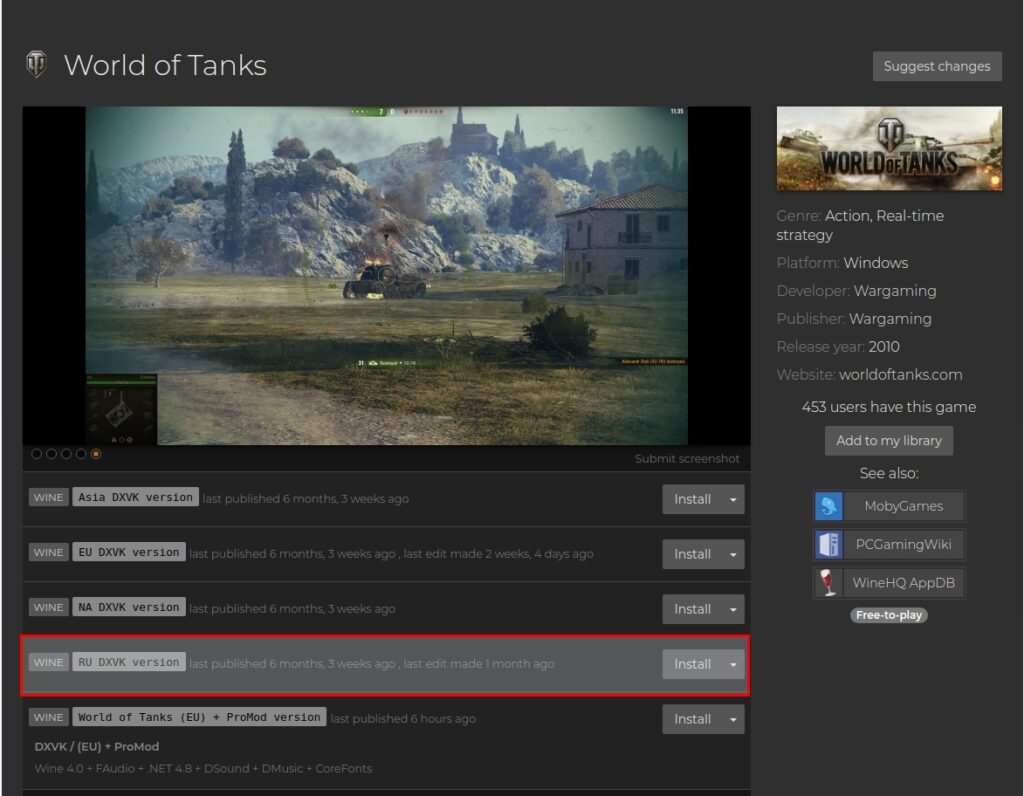
The link will open in the installed Lutris application. We will be prompted to install the game. Click on Install.
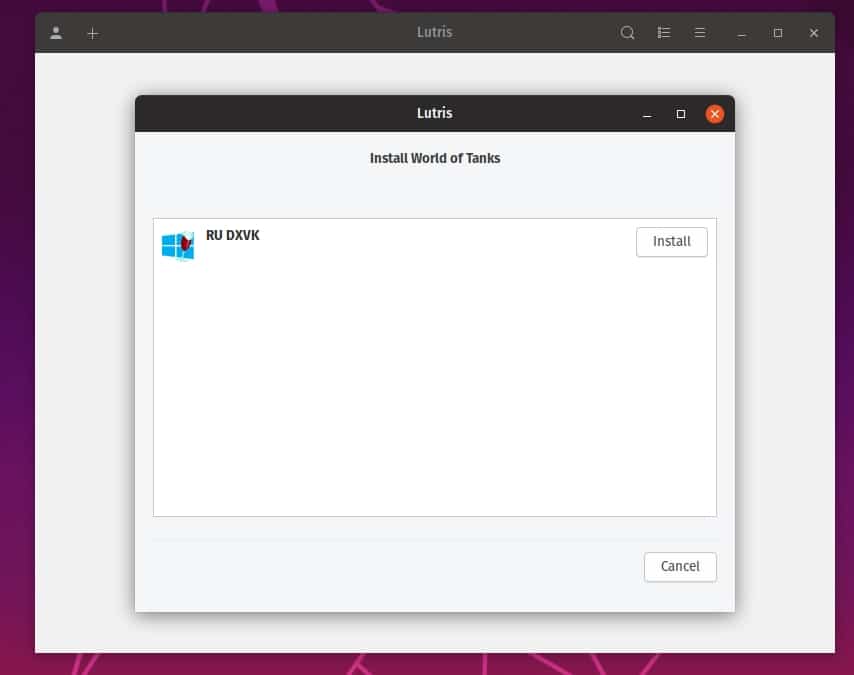
Then you can select the folder in which the game will be installed. We continue the installation. The version of Wine necessary for this game will be installed. We agree to all installations. When the online installer is complete, you will be prompted to create shortcuts and run the game.
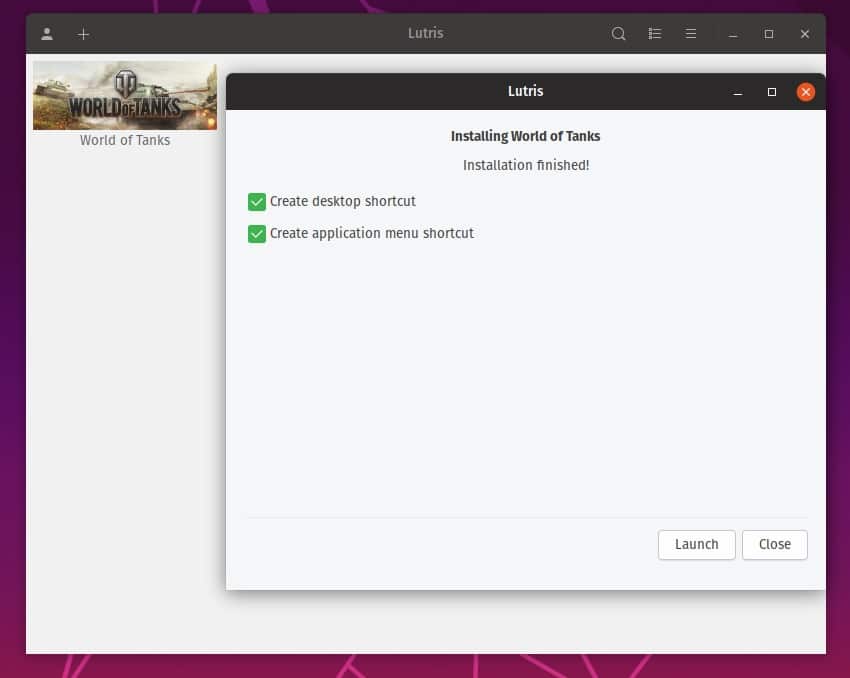
A full-screen window will then open in which the game will be installed. Do not be afraid. You can use the ALT+TAB keys to return to the working window.
You can launch the installed game both from the Lutris program and from the list of installed applications.
Similarly installed the game World of Warships in Ubuntu 19.04.
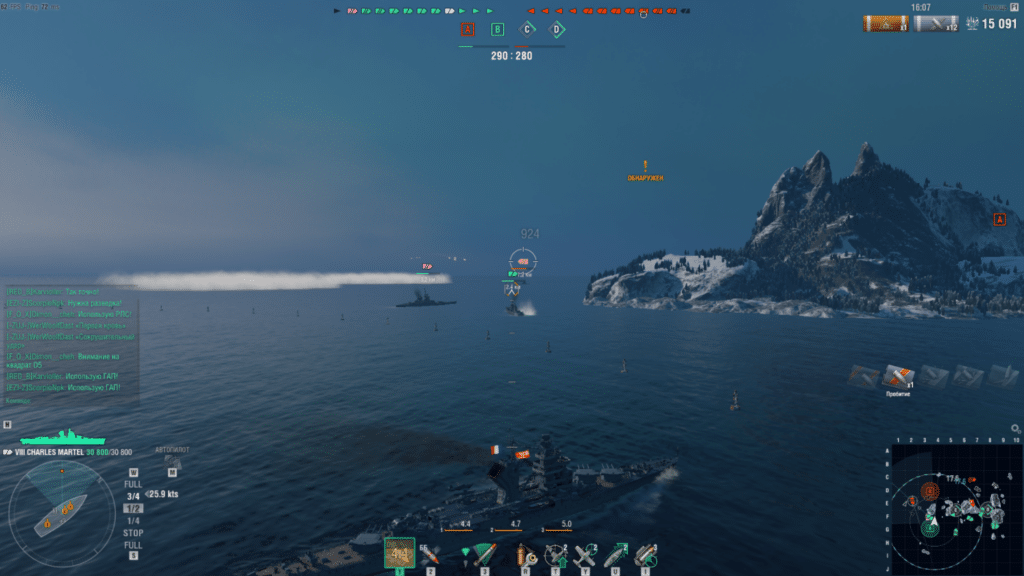
I encountered a problem in which the mouse cursor in the game did not allow you to make revolutions of about 180 degrees—previously installed the game in the KDE and Cinnamon environments (Linux Mint). If you display the cursor by pressing CTRL, you can capture other mouse turns. Solution: Switch the display of the game to windowed mode.
#2 Install Windows games on Linux using Steam (Proton)
For compatibility of games with GNU/Linux operating systems, Valve is developing the Proton (Steam Play) project, which in turn consists of various developments, such as Wine, DXVK, esync.
Information about the quality of support for Windows games on Steam Proton is available at ProtonDB.
To enable the Proton option, we need to open Steam – then Settings – Steam Play – and enable the available options.
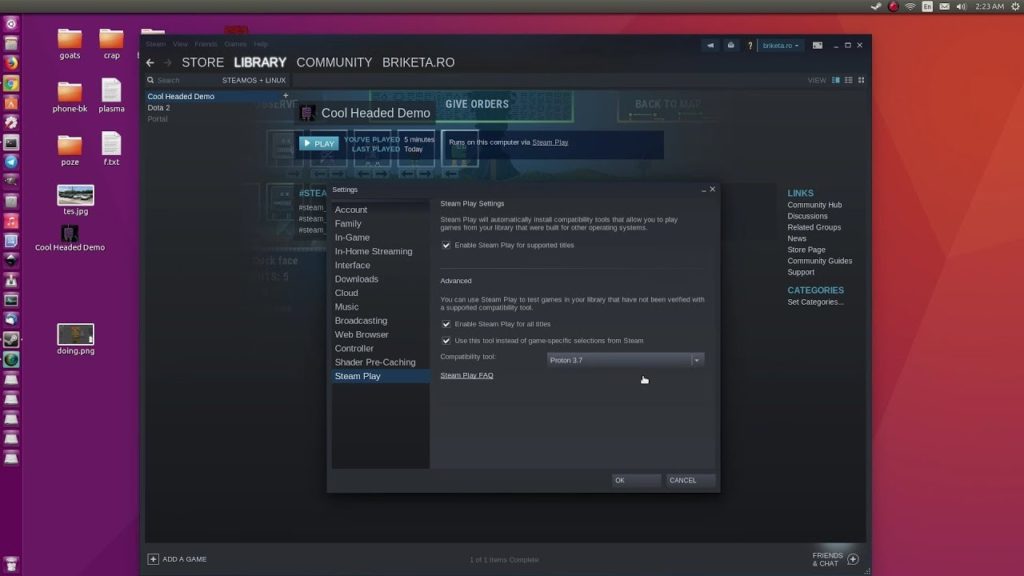
The steam version of Proton should be chosen as the most relevant, i.e., with a large number.
Further installation of games is no different from installation on a Windows system. Steam Play will automatically make the necessary settings to install the game.
Comparision: Nvidia Geforce 1060 Graphics Card Performance in Ubuntu 19.04 and Windows 10
The comparison was carried out on a laptop with an Nvidia Geforce 1060 graphics card (6 GB) and an Intel® Core™ i7 8750H processor. Windows 10 1903 operating systems (build 18362.10019), NVIDIA GeForce Game Ready 436.15 video driver version, and Ubuntu 19.04 with 430.40 (the most current in the PPA:graphics-drivers repository).
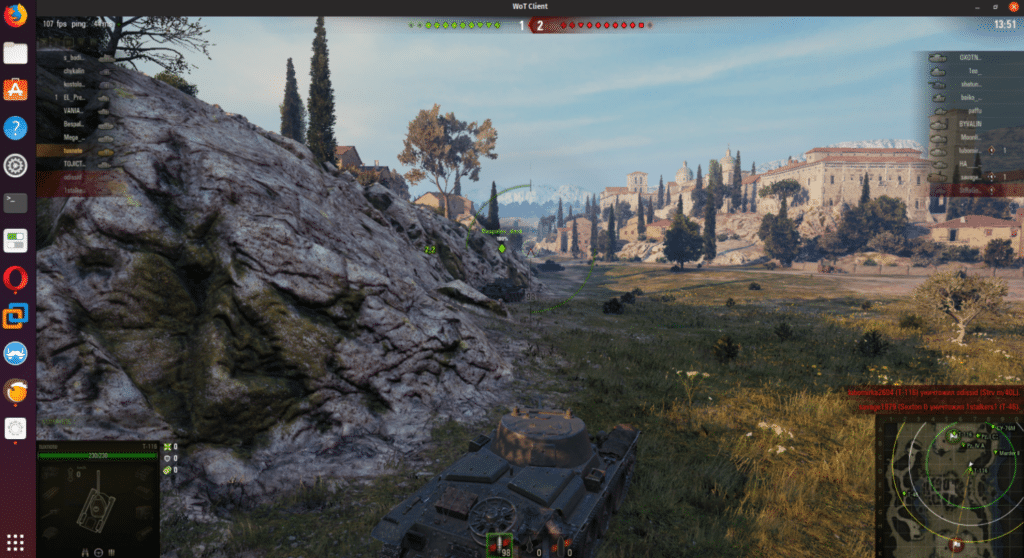
1. World of Tanks
Tank battles in World of Tanks in Windows 10 ranged from 115-130 fps to 150-165 fps, depending on the game scene.
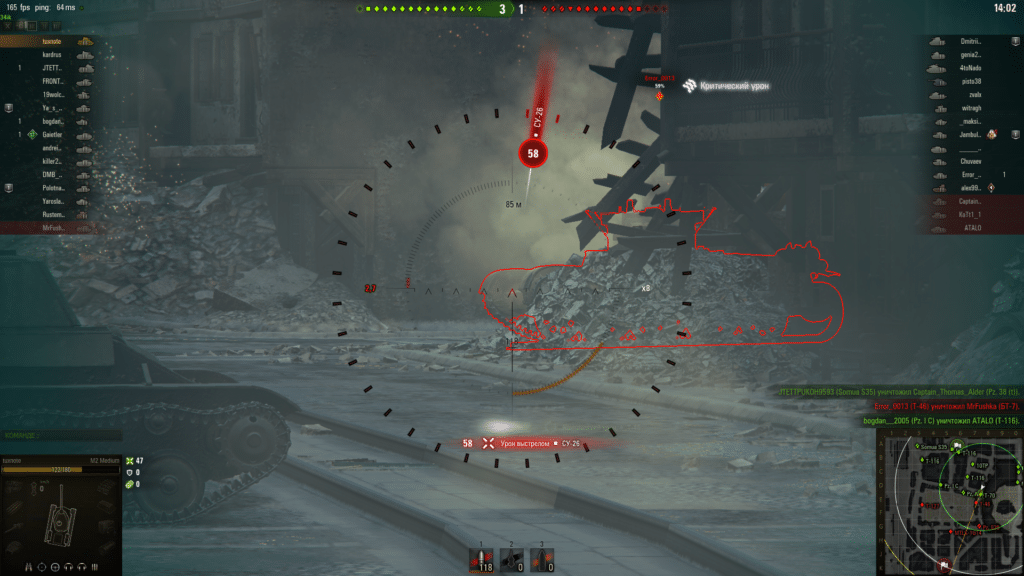
In Ubuntu 19.04 from 100 to 120 fps. Settings High, sd client.
2. World of Warships
In the Sea Battles of World of Warships in Windows 10, performance ranged from 65 to 75 fps.
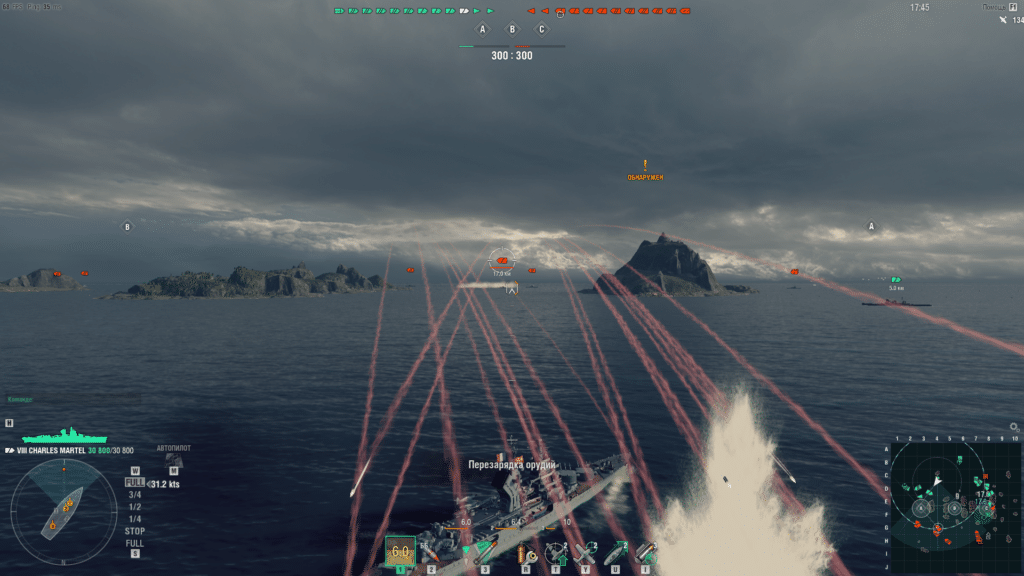
In Ubuntu 19.04, the game World of Warships showed performance from 60 to 70 fps but periodically saged strongly to 25 fps.

Both games in Ubuntu were installed using Lutris.
Here is the guide you can use: How to Install Wargaming Game Center on Linux
3. War Thunder
Also, with interest, I checked the performance of the video driver in the game War Thunder. In Windows 10, the game was installed using the native client, and in Ubuntu 19.04 using Steam (native version).
In naval battles in War Thunder in Windows 10, fps from 65 to 85 were displayed, in air battles, about 100 fps.
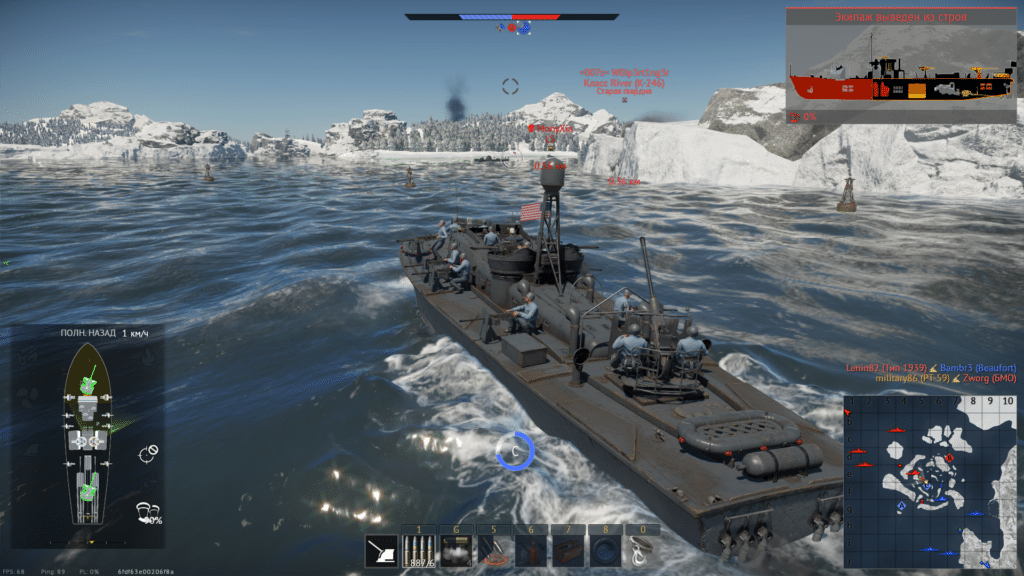
Ubuntu 19.04 ranged from 35-55 in naval battles and 75 fps in air battles.
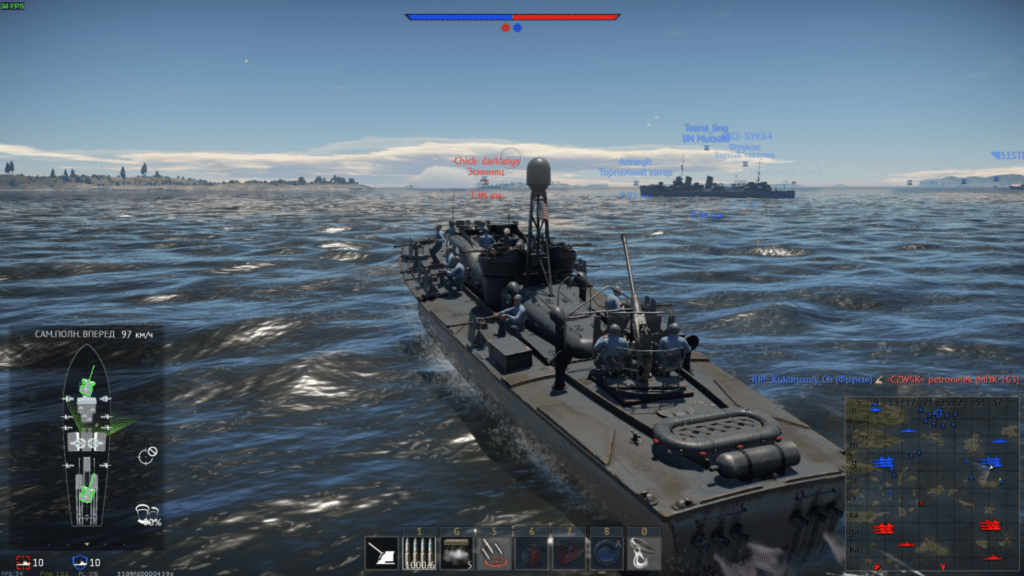
The version from Lutris using DXVK in Ubuntu 19.04 showed fps ranging from 50 to 75 in naval battles and 60 fps in air battles.
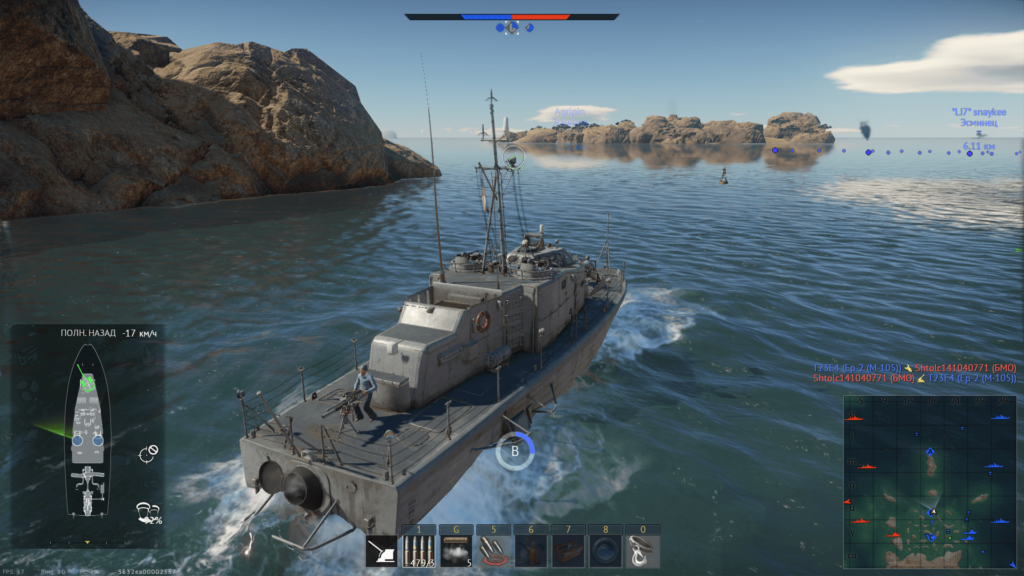
I know that the developers of War Thunder are testing the version using the Vulkan libraries. I have not tested it, but I am sure that the performance will be significantly higher than that of the native version that uses OpenGL.
4. Euro Truck Simulator 2
In the Euro Truck Simulator 2, Windows 10 was displayed from 85 to 120 fps.
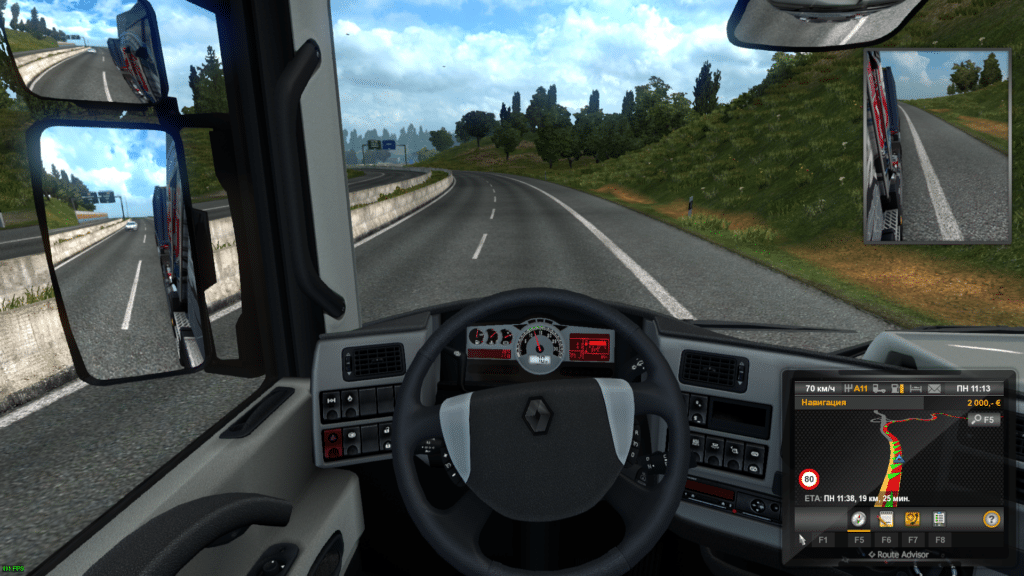
In Ubuntu 19.04, ETS 2 ranged from 55 fps (in rare cases) to 110 fps. In both cases, ultra settings were used.
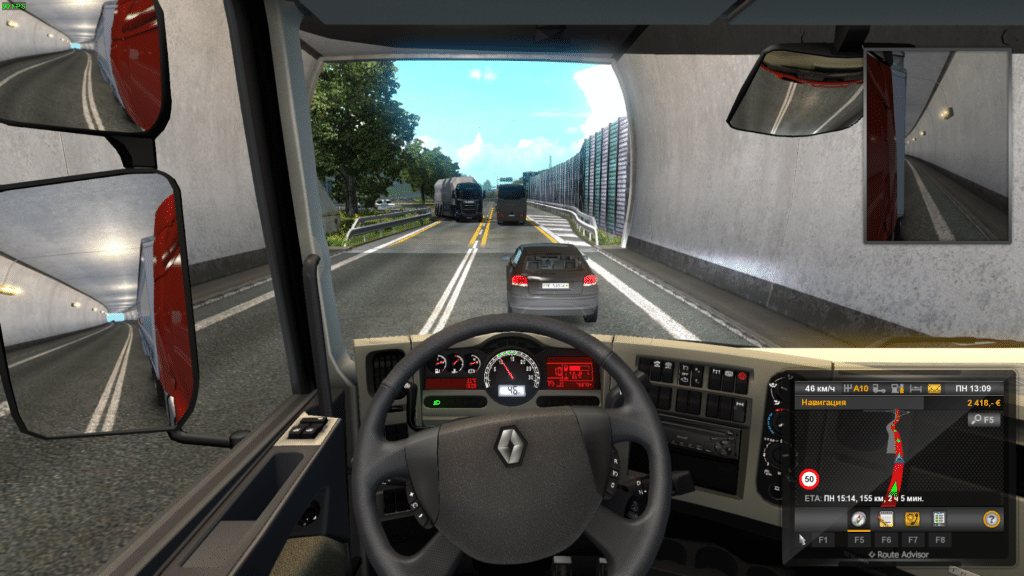
As you can see, the performance of games in Linux is inferior to Windows 10, but when using the DXVK and Vulkan libraries, the difference is much smaller than when using OpenGL. In any case, this is a breakthrough for Linux users: there are many more available games, and their installation has become as simple as possible.
In my opinion, it remains to solve the problem of the work of anti-cheats. Because of the problem with the outcome of some anti-cheats, many games are not yet available in Linux.
Conclusion:
I hope this guide on How to Run Windows Games on Linux was easy. If you face any issues, please comment down below. Here are some additional guides that you can use: How to Run Doom: Eternal on Linux and How to Run Forza Horizon 5 on Linux
