Last Updated :
06 Mar, 2025
Struggling to find or organize files buried in folders on your Windows PC? While File Explorer offers a visual way to browse, the Command Prompt (CMD) provides a faster, more powerful method to list, sort, and manage files, especially when dealing with large directories or automating tasks.
In this quick guide on how to list all files in a directory using CMD in Windows, you will explore how to use simple CMD commands like dir to instantly display every file and subfolder in any directory. We’ll break down the syntax, explain how to filter results (by name, date, or type), and share tricks to export lists for backups.
Prerequisites to Access Directory in Win
- Windows PC (11, 10, 8 or 7)
- Administrator Rights
- Familiar with Command Prompt actions (or knowing how to open it, i.e. Win + R & type CMD)
What Command Can Be Used to List Files
The «dir» command is fundamental in the Windows Command Prompt, which is used to list the contents of a directory. Here’s a bit more detail on how it works.
1. Basic Usage
- When you type dir and press Enter in the Command Prompt, it lists all the files and directories in the current directory.
- By default, it displays the file name, size, and modification date and time.
2. Options
- /A: This option displays files with specified attributes. For example, /A: H displays hidden files.
- /B: Uses a bare format with no heading information or summary. It simply lists the names of files and directories.
- /O: Specifies the order in which files are sorted. For instance, /O: N sorts files by name.
- /S: Displays files in the specified directory and all subdirectories.
- /P: Pauses after each screenful of information.
- /W: Uses wide list format, displaying as many as five file names in each row.
3. Example Usage
- dir /A: Lists all files including hidden files in the current directory.
- dir /B: Displays a bare list of files and directories without any additional information.
- dir /O:N: Sorts files by name.
- dir /S: Lists files in the specified directory and all subdirectories.
How to List All Files in a Directory
Now, we will be discussing 4 basic steps to list all files in a directory using the Command Prompt. Let’s check them out:
Step 1: Open Command Prompt
- First things first, let’s open the Command Prompt. You can do this by searching for «Command Prompt» in the Start menu or by pressing the Win + R keys, typing «cmd» in the «Run» dialog, and hitting Enter.
Step 2: Navigate to the Directory
- Once you have the Command Prompt open, you need to navigate to the directory whose files you want to list. To do this, use the cd command followed by the path of the directory. For example, if you want to list files in a directory named «Documents» located in your user folder, you would type:
cd Documents
Press Enter after typing the command to change the directory.
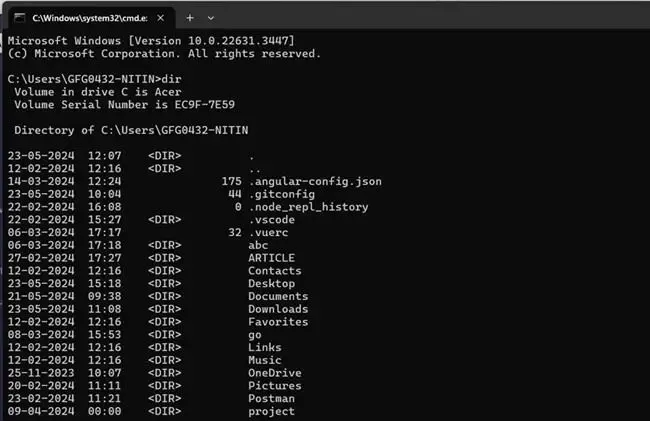
Step 3: List Files
- Now that you’re in the desired directory, it’s time to list all the files it contains. To do this, simply type the «dir» command and press Enter. This command displays a list of files and directories in the current directory.
Step 4: Additional Options (Optional)
- If you want to customize the way files are listed, you can use various options with the dir command. Here are some common options:
/A: Displays files with specified attributes.
/B: Uses bare format (no heading information or summary).
/O: Specifies the order in which files are sorted.
/S: Displays files in specified directory and all subdirectories.
For example, if you want to list all files including hidden files in bare format, you would type:
dir /A /B
Use Cases for Listing Files in CMD
- IT Audits: Export a list of all
.exefiles in a directory for compliance checks. - Scripting Backups: Automate file logging with a batch script.
- Troubleshooting: Identify missing or corrupted files in large folders.
CMD vs PowerShell: Which One to Use
| Task | CMD Command | PowerShell Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| List files | dir |
Get-ChildItem |
| Filter by date | dir /od |
Get-ChildItem | Sort LastWriteTime |
| Export to text file | dir > output.txt |
Get-ChildItem > output.txt |
Conclusion
Mastering the dir command in CMD lets you efficiently manage files, automate tasks and troubleshoot Windows system within a few steps. By following the outline steps, you can use the Command Prompt to organize your workspace or troubleshooting, without replying on graphical interfaces. Whether you’re an IT expert, a developer (for scripting batch jobs) or a casual user organizing personal documents, the ability to list files in a directory using CMD is a must-know job that everyone should know.
Also Read
- CMD | Dir command
- How to Delete a File or Folder Using CMD?
- Search Files Faster on Windows 10 using Command Prompt
To list files in a directory using the Windows Command Prompt, you can use the `dir` command. Here’s how:
dir
Understanding CMD Commands
What is CMD?
The Command Prompt, commonly known as CMD, is a command line interpreter included with Windows operating systems. This lightweight interface allows users to interact with their system through text commands, providing a powerful means of automation and troubleshooting.
Using CMD can drastically enhance your ability to perform system-level tasks swiftly and efficiently.
Benefits of Using CMD
Using CMD comes with numerous benefits:
- Speed and Efficiency: CMD provides a quicker way to execute commands compared to navigating a traditional graphical user interface (GUI).
- Advanced Functionalities: Advanced users can manipulate system settings and files in ways not possible or more cumbersome through a GUI.
- Automation: CMD enables scripting and batch processing, allowing complex tasks to be accomplished effortlessly.

List Disk Cmd Windows: Quick Guide to Disks Management
Navigating Directories in CMD
Opening Command Prompt
There are various ways to access CMD on your Windows system:
- Type «cmd» in the search bar and hit Enter.
- Use the Windows + R shortcut to open the Run dialog, type «cmd,» and click OK.
Basic Navigation Commands
To navigate through directories in CMD, you’ll primarily use the `cd` command:
cd (Change Directory)
This command allows you to move between directories.
Example:
cd C:\Users
By executing this command, you move into the Users directory on the C drive.
dir (Display Directory)
The `dir` command lists the contents of the current directory, showing files and subdirectories.
Example:
dir
Executing this command in a CMD window will display all files and folders present in your current working directory.

Customize Cmd Windows 11: Tips for a Personalized Experience
Listing Files in CMD
Using the dir Command
Basic Usage
The simplest way to see what’s in your directory is to issue the `dir` command without any parameters.
Example:
dir
This command will give you a list of all files and folders complete with details such as size and creation date.
Listing Files in a Specific Directory
You can also specify a particular directory from which you want to list files.
Example:
dir C:\Documents
This retrieves a list of files located in the Documents folder on the C drive.
Filtering Output with dir
Using Wildcards
You can narrow down your search with wildcards, which help to match patterns.
- The `*` wildcard represents any characters.
- The `?` wildcard represents a single character.
Example to list all text files:
dir *.txt
In this instance, only files with the ‘.txt’ extension will be displayed.
Sorting and Formatting Options
Manipulating the output of your `dir` command can be done with various options:
-
Using `/O` for Ordering: You can sort the output by certain criteria such as name, size, or date.
Example:
dir /O:NThis command lists all files in ascending order by name.
-
Using `/P` for Pagination: If your directory contains many files, you can paginate the output using this option.
Example:
dir /PThis will display files one page at a time, allowing easier viewing.
Detailed File Information
You can get more details about the listed files by using specific switches:
Using the /Q and /T Switches
The `/Q` switch reveals the owner of each file in the directory, while the `/T` options allow you to filter by specific time attributes (creation, modification, etc.).
Example to list file owners:
dir /Q
Example for listing files with creation time:
dir /T:C
This outputs the detailed file list, including creation times for each file.

Set Path Cmd Windows: A Quick Guide to Path Management
Advanced Directory Listing Techniques
Recursive Listing
If you want to delve deeper into subdirectories, the `/S` switch allows you to search recursively through a directory tree.
Example:
dir /S
Executing this command will show you all files and folders within the current directory and all of its subdirectories.
Output Redirection
Another advanced technique is saving the output of your `dir` command to a text file. This is especially useful for documentation or if you want to share the list with others.
Example:
dir > filelist.txt
This command creates a text file named filelist.txt in the current directory containing the results of your listing.
Using PowerShell for Advanced Listings
For users looking for more powerful tools, PowerShell is often recommended. It provides more versatile commands for file handling.
Example command to list files:
Get-ChildItem
PowerShell also allows you to incorporate more complex scripts and perform tasks beyond traditional CMD capabilities.

Mastering Diskpart Cmd Windows 10: Your Quick Guide
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Common Errors in CMD
While using CMD, you may encounter some typical issues:
Invalid Path Errors
If you receive an error indicating an invalid path, ensure you have typed the directory correctly and that it exists on your machine.
Permission Denied
Often, you may run into permissions issues when trying to list files in restricted directories. Running CMD as an administrator can resolve these issues.
Tips for Effective CMD Usage
To enhance your CMD experience, consider these tips:
- Shortcuts for Frequent Commands: Familiarize yourself with keyboard shortcuts to save time performing repetitive tasks.
- Utilizing Command History: Use the up arrow key to cycle through previously entered commands, allowing you to execute them again without retyping.
Make File in Windows Cmd: A Quick Guide
Conclusion
Mastering the CMD interface, specifically how to list files in CMD on Windows, can significantly boost your productivity. By learning the various commands and techniques outlined in this guide, you will be equipped to navigate your file system efficiently.
Practice these commands to enhance your CMD skills and streamline your workflows further! Ready to take your CMD skills to the next level? Join our course for more insights!

Add User Cmd Windows 10: Your Quick Start Guide
Additional Resources
For further exploration of CMD functionalities, consider visiting Microsoft’s official documentation or engaging in forums dedicated to CMD and scripting. Suggested follow-up topics might include batch scripting, advanced PowerShell commands, and automation with CMD.
- Use the “DIR” command to list files and folders in the current directory, or “DIR /S” to list files and folders recursively, in subdirectories as well.
- To search for specific file types use the asterisk followed by the file extension type, in this syntax: DIR *.jpg
- Use attribute switches to filter the type of files and folders to list.
It can be tricky to keep tabs on all files and folders on a Windows computer, especially if there are too many. There can be many folders and subfolders inside a partition, and many different types of file extensions. It can be difficult to view all the files and folders, or even search for specific ones using File Explorer.
Using the Command Prompt, you can view and list all sorts of files and folders inside a directory, and even its subdirectories using recursive switches. Not only that, but you can also list all items with a specific file type, or exclude them. Moreover, you can also view hidden items as well directly from the Command Prompt.
In this article, we give you a bunch of different examples to list files and folders inside the Command Prompt using the DIR cmdlet.
Command to List Files and Folders in Command Prompt
The DIR command is used to list files and folders inside a directory in Command Prompt. This command can be used with a number of switches and attributes to filter the items to display, their order or displaying, to include and exclude, and so on.
However, the only switches we will be interested in are /a and /s.
Using the DIR command alone will display all the files and folders inside that particular directory. It will not show any hidden items, and it will now show any items inside the subdirectories. However, if you use DIR /a, it will show the hidden items as well.
To perform a recursive search, we must use the /s switch.
The table below summarises the commands to use to list files and folders and these switches:
| Command | Description |
| DIR | Display items inside the current directory |
| DIR /a | Display all items inside the current directory, including hidden ones. |
| DIR /s | List items inside the current directory as well as all subdirectories |
With that known, there is a list of attributes that you can use with the DIR /a cmdlet to filter the type of information you want to list. Here is a list of the attributes you can use with /a.
| Attribute Alphabet | Description | Syntax Example |
| d | Shows directories only | DIR /ad |
| h | Show hidden items only | DIR /ah |
| s | Show system files only | DIR /as |
| l | Show reparse points only | DIR /al |
| r | Show read-only files | DIR /ar |
| a | Show files that can be archived | DIR /aa |
| i | Show files whose content is not indexed | DIR /ai |
| – (hyphen) | Used before an attribute to exclude it from the list | DIR /a-s (hide system files) |
| : (colon) | To combine multiple attributes | DIR /a:h-s (Show hidden items but hide system files) |
Example Commands to List Files and Folders in Command Prompt
Let us now continue to see more extensive examples with images to better understand how you can list files and folders using the DIR cmdlet.
-
To list all files and folders in the current directory:
DIRList files and folders in the current directory using Command Prompt -
To list all files and folders in the current directory and subdirectories:
DIR /SList recursive files and folders in Command Prompt -
To list only folders in the current directory:
DIR /ADList only folders in the current directory in Command Prompt -
To list only folders in the current directory and subdirectories:
DIR /AD /SList only folders in the current directory and subdirectories in Command Prompt -
To list all files in the current directory and exclude all folders:
DIR /A-DList all files and exclude folders in the current directory in Command Prompt -
To list all hidden system files in the current directory:
DIR /ASHList all hidden system files in current directory in Command Prompt -
To list all system files and exclude read-only files in the current directory and subdirectories:
DIR /A:S-A /SList all system files and exclude read-only files in the current directory and subdirectories using Command Prompt -
To list all specific file type files in the current directory and subdirectories:
Note: You can change the file type extension to list the files you are looking for.
DIR *.txtList all files with a specific file type using Command Prompt -
To list multiple file types in the current directory and subdirectories:
DIR *.txt *.doc *.docx /SList multiple file types in the current directory and subdirectories from Command Prompt
There can be many different examples and syntaxes to list files and folders inside the Command Prompt. However, we hope that the examples above are sufficient so that you can combine and modify them as per your requirements.
Closing Words
The Windows command line offers much more control over the fetched data than its GUI. Using the Command Prompt, you can list different files and folders inside the current directory as well as its subdirectories. You can also filter out the type of files and folders to include, or exclude from the list.
-
Home
-
Partition Magic
- CMD List Files: How to List Files in Command Prompt Windows 10/11
By Ariel | Follow |
Last Updated
What command can be used to list files in a directory? How to list files in Command Prompt Windows 10/11? A great many people are confused about these questions. In this post, MiniTool explains the Command Prompt list files topic in detail and introduces an alternative to CMD list files.
CMD (Command Prompt) is a powerful Windows built-in tool that can be used to do many works such as CMD copy files, CMD list drives, CMD WiFi password, and more. However, a lot of users don’t how to list files in Command Prompt. Here’s a true example from the StackOverflow forum:
I tried searching for a command that could list all the files in a directory as well as subfolders using a command prompt command. I have read the help for the «dir» command but couldn’t find what I was looking for. Please help me with what command could get this.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/15214486/command-to-list-all-files-in-a-folder-as-well-as-sub-folders-in-windows
Although there are already many discussions and posts about the Command Prompt list files, most of them lack clear steps and screenshots, which makes people difficult to understand the “CMD list files” operation. Thus, we want to write a complete guide to explain it. Let’s keep reading.
What Command Can Be Used to List Files
To list directory CMD smoothly, you need to know what command can be used to list files in a directory Windows first. The answer is to use the DIR command. This command can be used to show all files and subfolders in the current directory. In addition, it displays the file name, size, and last modification date of each file like File Explorer.
The DIR command is available in CMD for almost all Windows systems, including Windows 11/10/8/7/Vista/XP. Here are the most commonly used command lines about the CMD list directory/files:
- D: List all directories in the current path
- R: Show read-only files
- H: Show hidden files
- A: Archive files
- S: List system files
- I: Not content indexed files
- L: Reparse points
- -: Add a minus in front of any of the file attribute to let the DIR command not show that kind of file.
How to List Files in Command Prompt Windows 10/11
How to list files in CMD Windows 10/11? The answer depends on what files you want to list. Here we summarize several common examples of the Windows Command Prompt list files.
Step 1. First of all, you need to navigate to the directory in which you want to list files in File Explorer.
Step 2. Click on the address bar and type cmd in the file path and hit Enter, which will open the Command Prompt window.
Tips:
Also, you can locate the directory first in File Explorer, and then press the Win + R keys to open the Run box, type cmd in it, and hit Enter to open the Command Prompt window.
Step 3. In the pop-up window, you can list file CMD according to your needs. For example:
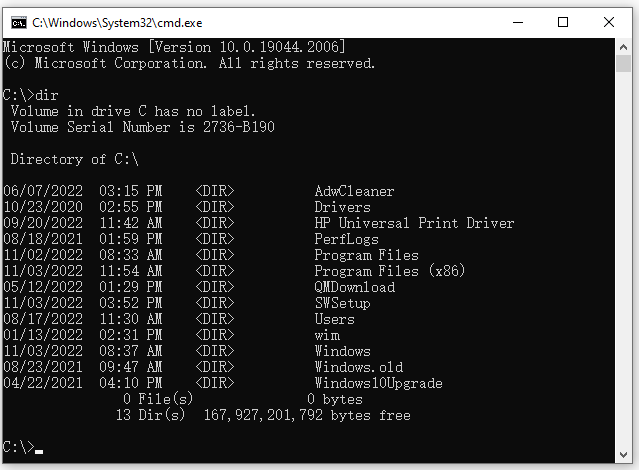
Example 1. CMD List all directories and folders under the current path.
dir
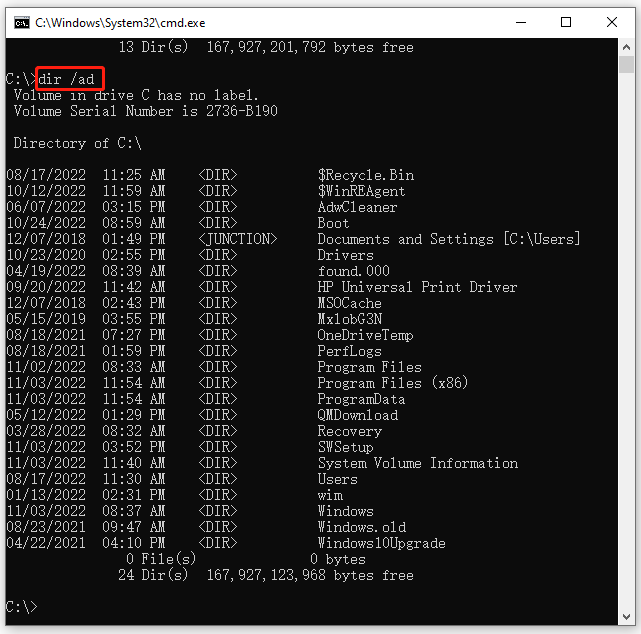
Example 2. CMD List folders of the current directory only.
dir /ad
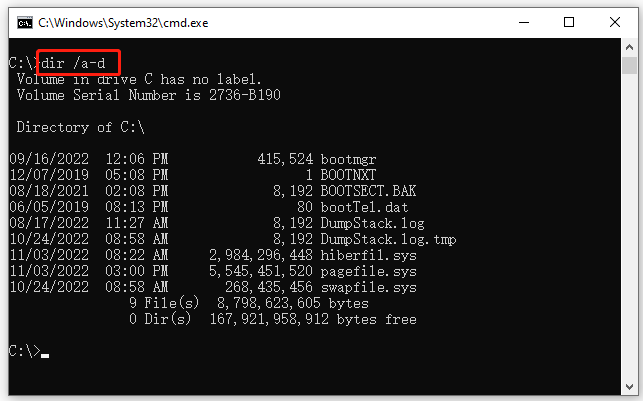
Example 3. CMD list files only under the directory.
dir /a-d
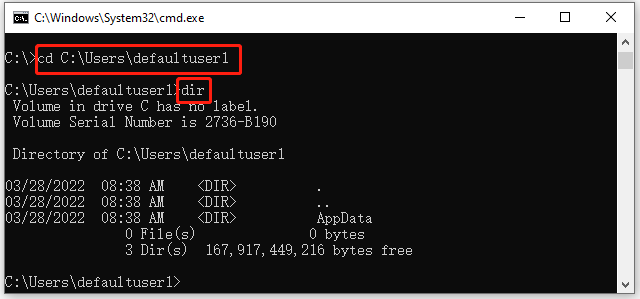
Example 4. CMD list files and folders under a specific directory (e.g. C:Usersdefaultuser1)
cd C:Usersdefaultuser1
dir
Example 5. CMD list all system files under the directory.
dir /s
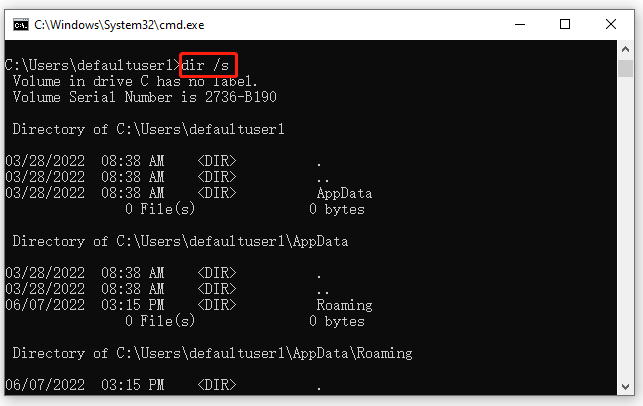
Example 6. CMD list all read-only non-achieve files.
dir /a:r-a
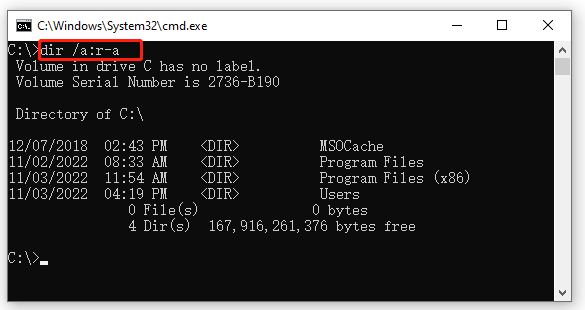
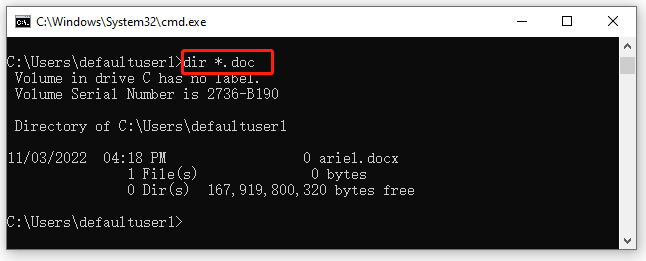
Example 7. CMD list all files with the file extension .doc.
Tips:
You can replace the doc with other file extensions such as exe, png, xml, etc.
dir *.doc
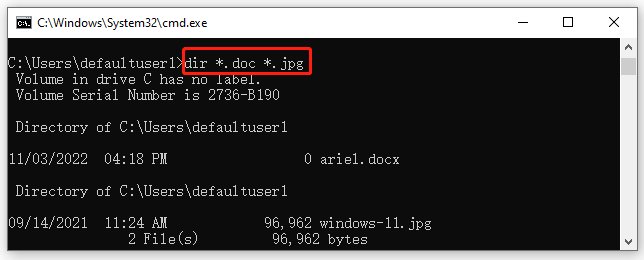
Example 8. CMD list all files with the file extension .doc and .jpg.
dir *.doc *.jpg
Of course, there are many other dir commands to list file CMD on Windows 10/11 and we can’t explain all in this post. If you want to know more information about Windows CMD list files, you can search for corresponding commands online on Google.
Better Alternative to Command Prompt List Files
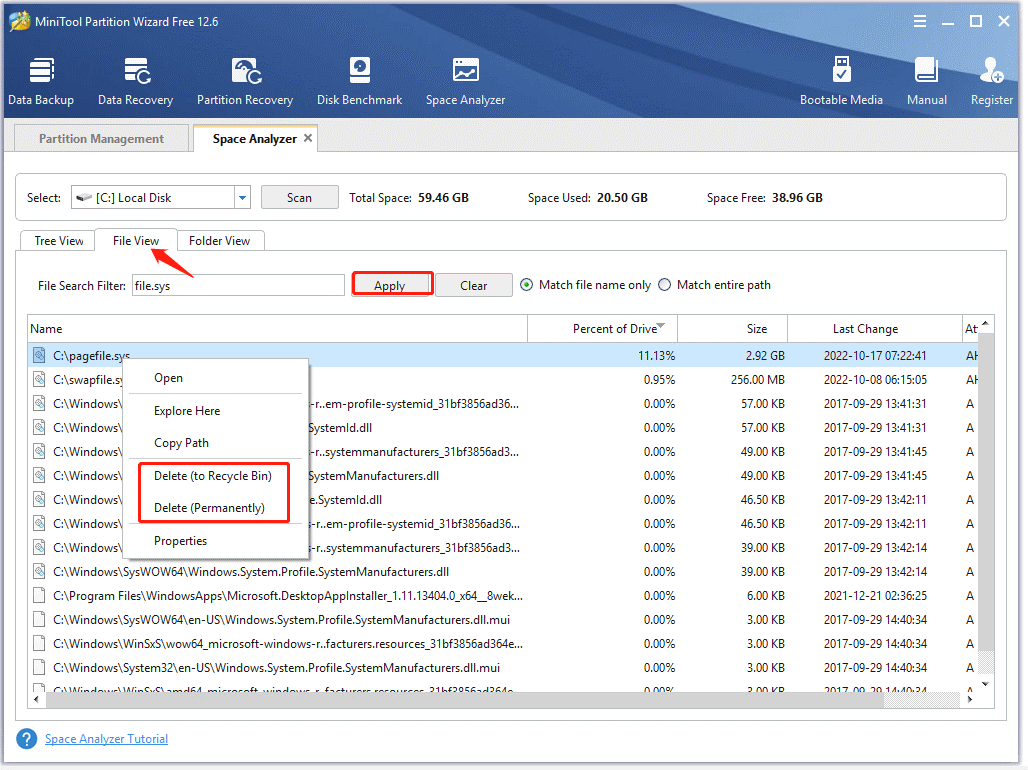
Although you can list files in a directory CMD, many professional commands might be unfamiliar to you. How to list all files/folders under a directory more easily? MiniTool Partition Wizard is a better alternative to Windows Command Prompt list files.
Its Space Analyzer feature can show all files/folders under a specific path in the file name, size, last change, extension, percentage of drive, etc. In addition, it tells you what files are taking up your disk space and helps you free up disk space.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Ariel has been working as a highly professional computer-relevant technology editor at MiniTool for many years. She has a strong passion for researching all knowledge related to the computer’s disk, partition, and Windows OS. Up till now, she has finished thousands of articles covering a broad range of topics and helped lots of users fix various problems. She focuses on the fields of disk management, OS backup, and PDF editing and provides her readers with insightful and informative content.
Whenever you want to search and make a list of all files on a specific folder, you used the windows explorer interface to do that. But today in this article we will show other easy ways to that. We will list files using the cmd tool. Command-line provides a simple way to list all the files of a certain type– for example, all your PDF files using the “dir” command. This command will be old news to many but it remains one of the most useful for average PC users. At the end of the post, you will have all switches in order t play with them based on your needs,
How to List all the files in a folder using CMD
- Searching on windows the “cmd” name an open as administrator
- Navigate to your path where you need to list the file by type cd and the path:
cd c:\Test\
- Click Enter
- Execute the following command
dir
Enter “dir” to list the files and folders contained in the folder.
How to List all the files in a folder and subfolder using CMD
If you want to list the files in all the subfolders as well as the main folder, enter:
dir /s
The lists can be quite long and we will create a file containing the list in order to be very easy. You can rename multiple files at once using CMD.
How to list specific file using wildcards
The dir command can also be used to search for specific files and directories by using wildcards. For example, to list files or directories that begin with the letter “B” you could type:
dir b*
To list only the items starting with the B letter.
How to Display Based on File Attributes
You can add “/A” followed by a letter code after the DIR command to display files with a specific attribute. These letter codes include:
- D: Displays all directories in the current path
- R: Displays read-only files
- H: Displays hidden files
- A: Files that are ready for archiving
- S: System files
- I: Not content indexed files
- L: Reparse points
How to create a text file listing of the files
- Open the command line in the folder of interest. Example:
cd c:\Test\
- Execute the following command:
dir > listoffiles.txt
- The command will create a list with the files and folders contained in the folder.
- If you want to list the files in all the subfolders as well as the main folder, enter the following command
dir /s >listmyfiles.txt
The file “listoffiles.txt” will be created automatically in the working folder.
Give the full pathname to create the file elsewhere. For example:
dir >D:\listmyfiles.txt
Could be used to place the list on an external drive D:
How to create a text file listing only certain types of files
You may want a list of certain types of files such as pdf files. The dir command allows the use of the wildcard symbol *, which adds very useful functionality. Here are some examples.
How to create a list of all the PDF files in a folder and its subfolders:
The command is:
dir /s *.pdf >listpdf.txt
The command will create a list of PDF files only.
A simpler format:
The commands as written will make lists that include information about files such as size and date of creation. A simpler list containing only file names (with full path) can be obtained with the switch “/b”. An example would be:
dir /s/b *.pdf >listpdf.txt
You can also change extension of multiply files using the command line.
How to display only files without folder names
Adding /a-d to the command removes the names of the directories, so all we have are the file names.
dir /a-d /b >..\listmyfiles.txt
How to Display Results in Columns
You can use the /D switch to display results in two columns instead of one. When you display results this way, the Command Prompt does not show extra file information (file size and so on)—just the names of the files and directories.
dir /D
How to Display Results in Lowercase
The /L switch displays all names of files and folders as lowercase.
dir /L
Display Results Sorted by Time
Using the /T switch along with a letter code lets you sort results by the different time stamps associated with files and folders. These letter codes include:
- A:The time the item was last accessed.
- C:The time the item was created.
- W:The time the item was last written to. This is the default option used.
So, for example, to sort results by the time items were created, you could use the following command:
dir /TC
All Switches Key
Below are all switches where you can use to create a complex list:
Syntax DIR [pathname(s)] [display_format] [file_attributes] [sorted] [time] [options]
Key
- [pathname] The drive, folder, and/or files to display, this can include wildcards:
- * – Match any characters
- ? – Match any ONE character
- [display_format]
- /P Pause after each screen of data.
- /W Wide List format, sorted horizontally.
- /D Wide List format, sorted by vertical column.
- [file_attributes] /A[:]attribute
- /A:D Folder /A:-D NOT Folder
- /A:R Read-only /A:-R NOT Read-only
- /A:H Hidden /A:-H NOT Hidden
- /A:A Archive /A:-A NOT Archive
- /A:S System file /A:-S NOT System file
- /A:I Not content indexed Files /A:-I NOT content indexed
- /A:L Reparse Point /A:-L NOT Reparse Point (symbolic link)
- /A:X No scrub file /A:-X Scrub file (Windows 8+)
- /A:V Integrity /A:-V NOT Integrity (Windows 8+)
- /A Show all files
Several attributes can be combined e.g. /A:HD-R
- [sorted] Sorted by /O[:]sortorder
- /O:N Name /O:-N Name
- /O:S file Size /O:-S file Size
- /O:E file Extension /O:-E file Extension
- /O:D Date & time /O:-D Date & time
- /O:G Group folders first /O:-G Group folders last
several attributes can be combined e.g. /O:GEN
- [time] /T: the time field to display & use for sorting
- /T:C Creation
- /T:A Last Access
- /T:W Last Written (default)
- [options]
- /S include all subfolders.
- /R Display alternate data streams.
- /B Bare format (no heading, file sizes, or summary).
- /L use Lowercase.
- /Q Display the owner of the file.
- /N long list format where filenames are on the far right.
- /X As for
- /N but with the short filenames included.
- /C Include thousand separator in file sizes.
- /-C Don’t include a thousand separators in file sizes.
- /4 Display four-digit years. In most recent builds of Windows, this switch has no effect.
The number of digits shown is determined by the ShortDate format set in the Control Panel.
Conclusion:
This is all about the methods of how to list files in cmd. Not only but also playing with to get a certain result like export them on a text file or listing only certain types of files.









