Here are some of the must-know and most useful File Explorer search syntax and commands to improve the search results and filter out unnecessary results.
Searching in the File Explorer is trivial. You type what you want in the File Explorer search bar and it will show the results. Thanks to the enhanced mode, the File Explorer search is pretty fast too. For example, if I want to search for a movie file, I will type the movie name in the search bar. If what I typed is in the file name, File Explorer will find the file and shows it as a search result.
This is how a vast majority of us search in File Explorer. However, what if you don’t know the actual file name? What if you want to filter files by size or find large files? What if you want to find specific file types or files created on, before, or after a certain date? In those cases, you use the File Explorer Search Syntax.
Using the File Explorer search commands, you can narrow down the search results and filter out unnecessary results. In this quick and simple Windows 10 guide, let me share with you the most useful File Explorer search syntax commands that will improve that File Explorer search experience.
Below are some of the most useful file explore search commands, their syntax, and how to use them.
- Wildcard syntax to filter results
- Syntax to find specific file types
- Command to find video and music files
- Syntax to find image files
- Syntax to filter files by size
- Find files created on, after, or before a date
- File search syntax to filter folders only
- Use Boolean operators to mix & match commands
Go to the folder where you want to search and use the commands as shown. To search the entire hard disk, open the File Explorer, click on “This PC” on the sidebar and then search.
1. Wildcard syntax to filter results
When you don’t know the exact file name, you can use the wildcard syntax (*) to find and filter files in the File Explorer. The wildcard syntax forces File Explorer to ignore everything and show the results that only contain the search term. To use the wildcard syntax, you add “*” to either side or both sides of a search term. The search syntax will look something like this:
*<SearchTerm>
or
<SearchTerm>*
or
*<SearchTerm>*
For example, to find files with the word “copy” in their name, you should type “*copy*“. This will show all the files that have “copy” in their name either at the start, middle, or end.

If needed, you can chain multiple wildcards and search terms. A chained wildcard will look something like this: <SearchTerm>*<SearchTerm>*.
2. Syntax to find specific file types
You can use the wildcard syntax to find specific file types in the file explorer. The wildcard file type syntax is as follows:
*.<FileExtension>
For example, to find and folder JPEG files in a folder, you should type “*.jpeg” in the File Explorer search bar. When needed, you can include search terms for better results. For instance, to find a JPEG file with “day” in its name, you should type “*day*.jpeg“.

3. Command to find videos and music
To search for all video and music files regardless of their file type or extension, you can use the “kind” syntax in the File Explorer search.
To find all video files, use the below syntax.
kind:videos

For music files, use the below syntax.
kind:music
One thing to keep in mind while using the above syntax is that the File Explorer will only show files that it recognizes as a video or music file. If the File Explorer doesn’t know if a file is a music or video file, it will not appear in the search results.
4. Syntax to find images
To search for images or pictures regardless of their file type or extension, you can use the same “kind” syntax in the File Explorer search.
To find all images or pictures, use the below syntax.
kind:pics

5. Syntax to filter files by size
To find files of a specific size, you can use the “size” command in File Explorer. The best thing about the size command is that it comes with predefined flags. They are small (16KB to 1MB), medium (1MB to 128MB), large (128MB to 1GB), huge (1GB to 4GB), and gigantic (greater than 4GB). If that’s not enough, you can manually set the file size to search.
File Explorer search syntax to filter files by size:
size: small | medium | large | huge | gigantic
According to the above syntax, to find gigantic files, you need to type “size: gigantic” in the File Explorer search bar. As soon as you do that, File Explorer will show all the files that are over 4GB.
To set the size manually, you can use the greater than (>) or less than (<) symbols along with the actual file size you are targeting. For example, to find files bigger than 5GB, you would type “size: >5GB“. To find files less than 50MB, you would type “size: <50MB“.
Detailed article here -> how to filter files by their size in File Explorer.
6. Find files created on, after, or before a date
You can use the “date” command to find files created on, after, or before a certain date. Here is the syntax you should follow.
- Find files created today —
date:today - Find files created yesterday —
date:yesterday - To find files created this week —
date: this week - Find files created last week —
date:last week - Find files created last month —
date:past month
Apart from the predefined date flags, you also also specify a specific date. While using a specific date, use the below syntax.
date:DD/MM/YYYY
For example, to find files created on 18th March 2020, you have to type “date:18/03/2020” in the File Explorer search bar.
You can also search for files created after or before a certain date. To do that, you have to add the greater than (>) or less than (<) symbol at the start of the date. Here, the > and < symbols imply after and before a given date respectively. For instance, to find files created after 18th March 2020, you will type date:>18/03/2020.
7. File search syntax to filter folders only
While searching, you can use the “kind” command along with “folders” parameter to force the File Explorer to show folders only. Here is the syntax to search for folders in file explorer.
kind:folders
8. Use boolean operators to mix & match commands
File Explorer search syntax has multiple boolean operators to further narrow down the search results. They are — NOT, OR, (), and "".
Example usage:
- To find items that contain social, but not security —
social NOT security - Find files that contain social or security in their name —
social OR security - To find items that contain social and security in any order —
(social security) - To find items that contain the exact phrase social security —
"social security"
Important note: while using NOT and OR operators, it is important to capitalize them. If you don’t capitalize, File Explorer won’t recognize them as operators.
That is all. As you can see, the File Explorer has several search command that make your life a bit easier while searching for something.
If you think I missed any of your favorite File Explorer search command or if you need any help using the above syntax, command below and let me know.
Finding anything on your computer shouldn’t feel like digging for buried treasure. Windows File Explorer offers a built-in search bar, but sometimes it seems to miss more than it finds. Thankfully, you can use Windows File Explorer search syntax.
In this article, I will show you how to improve your file search experience on Windows by using advanced search syntax and more.
You can improve your file search experience on Windows by employing advanced search syntax options. These options enable you to tailor your search queries, resulting in more accurate and relevant results. These are some of the most helpful advanced search syntax choices in Windows File Explorer.
Searching by file extension
If you know what kind of file you are looking for, you can use the asterisk (*) wildcard character followed by the file extension to narrow down your search. For example, if you are looking for a PDF file that contains the word “report”, you can type in “report *.pdf” in the search bar. Alternatively, you can use the type: operator followed by the file extension to achieve the same result. For example, “report type:pdf”.

Searching by file type
The kind: syntax in Windows File Explorer allows you to search for files based on their type, such as documents, pictures, music, videos, etc. To use the kind: syntax, you need to type it in the search box of the file explorer, followed by a colon and the file type you want to find.
Examples:
kind:folder to find folders only.
kind:email to find email files (e.g., .eml, .msg).
kind:music to find music files (e.g., .mp3, .wav).
kind:picture to find image files (e.g., .jpg, .png).
kind:document to find document files (e.g., .docx, .pdf).
kind:video to find video files (e.g., .mp4, .mov).
How to use store: syntax in Windows File Explorer
While Windows File Explorer doesn’t have a built-in store: syntax for general searching, it does have a mechanism for searching within specific data stores or locations, primarily in the context of Windows Search.
To search within a specific app’s data or store, use store: followed by the app’s name or identifier.
Examples:
store:outlook to search within Outlook email content and attachments.
store:notes (if configured) to search within Lotus Notes data.
Other apps might have their own store names for searching, but this functionality isn’t always well-documented or user-friendly.
Applying filters
If you want to filter your search results by date, size, or other attributes, you can use various filters in your search query. These filters allow you to specify a range or a condition for your search criteria.
For example, if you are looking for a document modified in the last week, you can type “report datemodified:this week” in the search bar. If you are looking for a document that is larger than 1 MB, you can type in “report size:>1MB”. You can also use multiple filters together to further refine your search results.
Using boolean operators
If you want to combine multiple keywords or phrases in your search query, you can use boolean operators like AND, OR, and NOT. These operators allow you to specify whether you want to include or exclude certain terms from your search results.
For example, if you are looking for a document that contains both the words “report” and “summary”, you can type in “report AND summary” in the search bar.
If you want to find files that are either music or video files modified within the last week, use the parentheses and syntax “(kind:music OR kind:video) AND datemodified:lastweek”.

No Need to Remember Windows File Explorer Search Syntax
Windows search tools in File Explorer can help you use these search syntax. Here are some steps to use them:
Step 1. Open File Explorer from the taskbar or the Start menu, or press the Windows logo key + E.
Step 2. Click on the search box on the top right, the Search tab for Search Tools in the ribbon will be available
Step 3. Now you can click Kind, Size, Other properties, and Date modified to add advanced syntax in your file search.
If you want to search by file contents, you can click the Advanced options to enable it in Windows 10/11.
Limitations and Challenges with Windows File Explorer Search
While using advanced search syntax options can improve your file search experience on Windows, they still have some limitations and challenges. In that case, you may want to use Findstr commands or an alternative app for faster file search. Some of these limitations and challenges are:
Inconsistency: Windows may disregard or misinterpret some of your search terms, returning different results depending on how you type them.
Compatibility: Using advanced search syntax options may not work with all file types or apps. Some file formats or programs may use proprietary metadata or indexing methods that Windows does not recognize or support.
Performance: Depending on the intricacy of your search query and the amount of files involved, Windows may take longer to complete your request and use more system resources. Especially, when you click This PC to search your entire computer for a file.
Use AnyTXT for Quick File Search
If you are looking for a more powerful and efficient file search alternative for Windows, consider AnyTXT. It is a versatile and lightweight file search tool that can help you find any file on your hard drive in seconds. It supports various file formats, such as PDF, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, TXT, HTML, and more, and allows you to perform quick and accurate file searches with advanced search options.
Some of the key features of AnyTXT are:
– Fast indexing: AnyTXT can index your files in the background without affecting your system performance. It can scan your hard drive and create a searchable database of your files in minutes. You can also customize the indexing settings to include or exclude certain folders or file types from your index.
Quick search: AnyTXT can search your files in seconds using its powerful search engine. You can type in any keyword or phrase in the search bar and get instant results. You can also use advanced search options, such as boolean operators, filters, wildcards, and more, to refine your search results.
Customizable search options: AnyTXT can offer more customizable search options than Windows File Explorer because it uses its own search engine instead of following Windows’ default rules. You can use advanced search options, such as boolean operators, filters, wildcards, and more, to refine your search results according to your needs and preferences.
User-friendly interface: AnyTXT has a simple and intuitive user interface that makes it easy to use. You can access AnyTXT from the system tray or by pressing a hotkey. You can also preview your files in the search results window or open them with their default applications.
Conclusion
Mastering Windows File Explorer search syntax can help you improve your file search experience on Windows. However, it is slow and hard to use.
If you are looking for a more powerful and efficient file search alternative for Windows, you might want to consider AnyTXT. It is a versatile and lightweight file search tool that can help you find any file on your hard drive in seconds. It supports various file formats and allows you to perform quick and accurate file searches with advanced search options.
Cheat Sheet: Windows 11 AQS
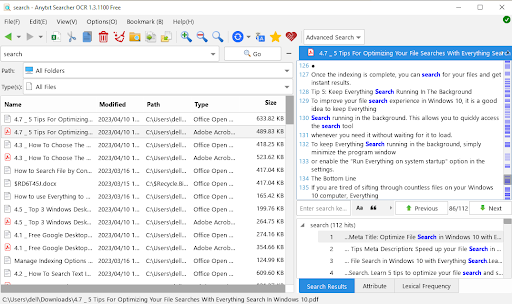
Syntax
| Type of Search | How it Works | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Search by keyword or phrase | report |
| File Name | Use filename: modifier |
filename:report.docx |
| File Type | Use kind: modifier followed by file kind |
kind:docs |
| Date Modified | Use datemodified: modifier with date |
datemodified:last week |
| Size | Use size: modifier with value and unit |
size:>10MB |
| Multiple Criteria | Combine terms with AND, OR, NOT | report AND finances NOT draft |
| Not Criteria | Exclude terms with NOT or — | report NOT draft or report -draft |
| Wildcards | Use * and ? for unknown characters | proj* or bud?et |
| Phrase | Exact phrase in quotes | "annual report" |
| Exclude Terms | Use — symbol to exclude | report -draft |
| Date Ranges | Use dates with before or after |
datemodified:after:01/01/2023 |
| Size Ranges | Use comparison operators for size | size:>1MB AND size:<10MB |
| Grouping | Use parentheses for complex criteria | (report OR review) AND quarterly |
| Property Search | Search by specific file properties | title:"Q1 Earnings" AND author:John |
| Scoped Location Search | Limit search to specific locations | foldername:MyDocuments |
| Boolean Operators | Use AND, OR, NOT to refine searches | project AND (timeline OR schedule) NOT old |
Common AQS Properties
| AQS Property | Function | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| author | Searches by the file’s author | author:"John Doe" |
| title | Searches by title of the document | title:"Annual Report" |
| subject | Searches documents by subject | subject:"Project Proposal" |
| folder | Limits search to a specific folder | folder:Documents |
| path | Searches by the path to a file | path:"C:\\Users\\John\\Reports" |
| tags | Searches by tags associated with the file | tags:"Reviewed" |
| participants | Searches emails by participants | participants:"Jane Doe" |
| from | Searches emails by the sender | from:"jane@example.com" |
| to | Searches emails by the recipient | to:"john@example.com" |
| cc | Searches emails by carbon copy recipient | cc:"manager@example.com" |
| bcc | Searches emails by blind carbon copy recipient | bcc:"HR@example.com" |
| hasattachment | Finds emails or files with attachments | hasattachment:true |
| isflagged | Finds items that are flagged | isflagged:true |
| isread | Finds emails that have been read | isread:false |
| importance | Searches by importance level of items | importance:high |
| album | Searches music files by album name | album:"Greatest Hits" |
| artist | Searches music files by artist | artist:"The Beatles" |
| genre | Searches by genre of music or video | genre:"Rock" |
Discover Metadata Properties
By right-clicking on a file and selecting Properties, then navigating to the Details tab, users can view a comprehensive list of all the metadata associated with that file. This metadata includes properties such as author, date created, tags, and many others which are searchable using AQS.
Created by Casey Anderson, 2024.
Website: http://caseyanderson.me
Here are some useful File Explorer search syntax and commands you need to know to improve your search results and filter out unnecessary results.

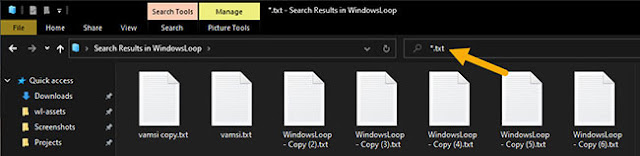
1. Syntax * to filter results
When you do not know the exact filename, you can use the * syntax to find and filter files in File Explorer. The * syntax forces File Explorer to ignore everything and show results that contain only the search term. To use this syntax, you add «*» to either side or both sides of the search term. The search syntax would look like this:
* <Search term>
Or
<Search term> *
Or:
* <Search term> *
For example, to find files with the word «copy» in the name, you need to enter * copy *. This will display all files with «copy» in the name at the beginning, middle or end.

If needed, you can string as many wildcard characters and search terms as follows:
<Search term> * <Search term> *
2. Syntax to find specific file types
You can use the * syntax to find specific file types in File Explorer. The syntax is as follows:
*. <File extension>
For example, to find and organize JPEG files in a folder you need to type «* .jpeg» into the File Explorer search bar. As needed, you can include search terms for better results. For example, to find a JPEG file named «day» you need to enter:
«*Day* .jpeg«
3. Video and music search commands
To search for all video and music files, regardless of their file type or extension, you can use the «kind» syntax in File Explorer search.
To find all video files, please use the syntax below.
kind: videos

For music files, please use the syntax below.
kind: music
One thing to note when using the above syntax is that File Explorer will only display files it recognizes as video files or music files. If File Explorer does not know whether the file is a music file or a video file, the file will not appear in the search results.
4. Image search syntax
To search for images regardless of their file type or extension, you can use the same kind of syntax in File Explorer search.
To find all images, please use the syntax below.
kind: pics

5. Syntax of file filtering by size
To find files of a specific size, you can use the command «size» in File Explorer. The best thing about the size command is that it comes with predefined flags. They come in small capacities (16KB to 1MB), medium (1MB to 128MB), large (128MB to 1GB), very large (1GB to 4GB) and huge (larger than 4GB). If that’s not enough, you can set the file size to search manually.
File Explorer’s search syntax to filter files by size:
size: small | medium | large | huge | gigantic
In the above syntax, to find large files, you need to enter size: gigantic in the File Explorer search bar. As soon as you do that, File Explorer will display all files over 4GB.
To manually set the size, you can use the larger (>) or smaller (<) symbols along with the actual file size you are targeting. For example, to find files larger than 5GB, you would type size:> 5GB. To find files less than 50MB, enter size: <50MB
6. Find files created on, after or before a day
You can use the «date» command to find files created on, after or before a certain date. Here is the syntax you should follow.
- Find the file created today — date: today
- Find the file created yesterday — date: yesterday
- Find the file created this week — date: this week
- Find the file created last week — date: last week
- Find the file created last month — date: past month
In addition to predefined date flags, you can also specify a specific date. While using a specific date, use the syntax below.
date: DD / MM / YYYY
For example, to find files created on March 18, 2020, you must enter date: 03/18/2020 in the File Explorer search bar.
You can also search for files created after or before a certain date. To do that, you must add a larger (>) or smaller (<) symbol at the beginning of the day. Here, the symbols> and <imply after and before a certain date, respectively.
For example, to find files created after March 18, 2020, you would type:
date:> March 18, 2020
7. Search syntax to filter only directories
While searching, you can use the «kind» command with the «folder» parameter to force File Explorer to display only folders. Here is the syntax to search for folders in File Explorer.
kind: folders
8. Use the boolean operator to mix and match commands
File Explorer’s search syntax has many boolean operators to further narrow the search results. They are NOT, OR, () and «».
Usage example:
- To find items that contain social, but not contain security — social NOT security
- To find files that contain social or security in the name — social OR security
- To find items that contain social and security in any order — (social security)
- To find items that contain the exact phrase social security — «social security»
Important Note:
While using the NOT and OR operators, it is important to capitalize them. If you don’t capitalize, File Explorer won’t recognize them as operators.
One of the most used features of Windows 11/10 is its Search. It lets you locate your files, folders instantly. Windows Search also refers to the Instant Search, which now has become an integral part of Windows, particularly in the latest versions of Windows.
Well, if you want to be more efficient in locating your files and e-mails in Windows 11,or Windows 10 using Windows Search, then Advanced Query Syntax (AQS) can help you do just that. You can get the desired results using AQS, allowing you to define and narrow your searches quickly.
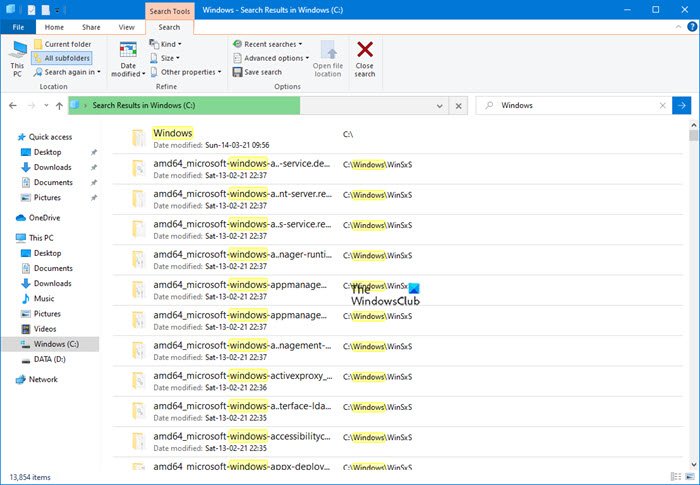
To make your searches specific, you can use a variety of keywords, or search parameters, which can restrict your query to specific locations, specific file types or properties within those types, or specific “file kinds”. At the top of the Windows Search Explorer, File kinds are displayed, which you can access by pressing the Windows Logo + F.
Use double Quotation marks to match a specific string literally, so that it does not get interpreted as a Keyword. The words will be matched exactly in the order they are entered in a search query between quotation marks.
An overview of syntax in the tables below can be used with Windows Search, including the properties that can be added to your search terms to narrow and refine your results.
Search Syntax
| Property | Example | Function |
| author:name | author:patrick | Finds items with patrick in the Author property. |
| author:(name) | author:(patrick hines) | Finds items with patrick hines in the Author property. |
| author:(name OR name) | author:(patrick OR bob) | Finds items with patrick or bob in the Author property. |
| author:name name | author:patrick bob | Finds items with patrick in the Author property and bob anywhere in the document. |
| from:name | from:patrick | Finds items with patrick in either fromName OR fromAddress, since “from” is a property name for both fromName and fromAddress. |
| before:date | before:10/9/2011 | Finds items whose PrimaryDate field contains a date before 10/9/2011. |
| after:date | after:10/9/2011 | Finds items whose PrimaryDate field contains a date after 10/9/2011. |
| has:attachment | report has:attachment | Finds items containing the word report that have attachments. Same as hasattachment:true |
| is:attachment | report is:attachment | Finds items that have attachments containing the word report. Same as isattachment:true |
Specifying Numbers and ranges
To specify a date range, enter the property followed by two dates. For instance, type from:Thomas sent:11/05/20..11/05/21. Windows Search identifies all Windows date formats and also recognizes the following values:
• Relative dates: Today, tomorrow, yesterday
• Multi-word relative dates: week, next month, last week, past month, or coming year. The values can also be entered contracted, as follows: thisweek, nextmonth, lastweek, pastmonth, comingyear.
• Days: Sunday, Monday … Saturday
• Months: January, February … December
| Syntax | Results |
| size:>50KB <70KB | Searches for files with a value in the Size between 50 KB and 70 KB, excluding the end values. |
| size:>=50KB <=70KB | Searches for files with a value in the Size property between 50 KB and 70 KB, including the end values. |
| Size: 50KB..70KB | Same as size:>=50KB <=70KB |
| date:>2/7/21<2/10/21 | Searches for a date in the Date property between the values 2/7/21 and 2/10/21, excluding the end dates. |
| date:>=2/7/21<=2/10/21 | Searches for a date in the Date property between the values 2/7/21 and 2/10/21, including the end dates. |
| date:2/7/21 .. 2/10/21 | Same as date:>=2/7/21<=2/10/21 |
Common file properties
The preceding table contains a list of words that can be used with any of the following file properties. For example, to find e-mail from “patrick” that was sent in 2021, your query would look like this: kind:email author:patrick after:12/31/2020.
| To restrict by file type | Use | Example |
| Communications | communications | kind:communications |
| Contacts | contacts person |
kind:person kind:contacts |
| kind:email | ||
| Instant Messenger conversations | im | kind:im |
| Meetings | meetings | kind:meetings |
| Tasks | tasks | kind:tasks |
| Notes | notes | kind:notes |
| Documents | docs | kind:docs |
| Music | music song |
kind:music kind:song |
| Pictures | pics pictures |
kind:pics kind:pictures |
| Videos | videos | kind:videos |
| Folders | folders | kind:folders |
| Folder name | foldername | foldername:mydocs |
| Programs | programs | kind:programs |
| Recorded TV | tv | kind:tv |
| Link | link | kind:link |
| Journal entry | journal | kind:journal |
To restrict by file store
You can use the store: indicator to narrow your search scope which will limit a query to either Microsoft Office Outlook or Outlook Express, in case if you have multiple accounts.
| Store | Use | Example |
| Files | file | store:file |
| Offline Files | csc | store:csc |
| Outlook | mapi | store:mapi |
| Outlook Express | outlookexpress | store:outlookexpress |
Properties for file type: All
| Property | Use | Example |
| Title | title, subject, about | title:manager |
| Status | status | status:active |
| Date | date | date:lastweek |
| Date modified | datemodified, modified | modified:lastweek |
| Importance | importance, priority | importance:high |
| Size | size | size:>50MB |
| Deleted | deleted,isdeleted | isdeleted:true |
| Is attachment | isattachment | isattachment:false |
| To | to, toname | to:johnsmith |
Properties for file type: Contact
| Property | Use | Example |
| Job title | jobtitle | jobtitle:manager |
| IM address | imaddress | imaddress:[email protected] |
| Assistant’s phone | assistantsphone | assistantsphone:555-1212 |
| Assistant name | assistantname | assistantname:roberto |
| Profession | profession | profession:accountant |
| Nickname | nickname | nickname:louis |
| Spouse | spouse | spouse:susana |
| Business city | businesscity | businesscity:redmond |
| Business postal code | businesspostalcode | businesspostalcode:98052 |
| Business home page | businesshomepage | businesshomepage:www.adventure-works.com |
| Callback phone number | callbacknumber | callbacknumber:882-8080 |
| Car phone | carphone | carphone:555-1212 |
| Children | children | children:anna |
| First name | firstname | firstname:maria |
| Last name | lastname | lastname |
| Home fax | homefax | homefax:555-1212 |
| Manager’s name | manager | manager:carlos |
| Pager | pager | pager:882-8080 |
| Business phone | businessphone | businessphone:555-1212 |
| Home phone | homephone | homephone:555-1212 |
| Mobile phone | mobilephone | mobilephone:882-8080 |
| Office | officelocation | officelocation:red/101 |
| Anniversary | anniversary | anniversary:yesterday |
| Birthday | birthday | birthday:tomorrow |
Properties for file type: Communications (e-mail, appointments)
| Property | Use | Example |
| From | from, organizer | from:simon |
| Received | received, sent | sent:yesterday |
| Subject | subject, title | subject:budget |
| Has attachment | hasattachment, hasattachments | hasattachment:true |
| Attachments | attachments, attachment | attachment:presentation.ppt |
| Bcc | bcc, bccname | bcc:michael |
| Bcc address | bccaddress, bcc | bccaddress:[email protected] |
| Cc address | ccaddress, cc | ccaddress:[email protected] |
| Follow-up flag | flagstatus flagstatus:followup |
flagstatus:unflagged flagstatus:completed |
| To address | toaddress, to | toaddress:[email protected] |
| Due date | duedate, due | due:10/15/2011 |
| Read | read, isread | isread:false |
| Is completed | iscompleted | iscompleted:true |
| Incomplete | incomplete | incomplete:true |
| Has flag | hasflag, isflagged | hasflag:false |
| Duration | duration | duration:>120 |
Properties for file type: Calendar
| Property | Use | Example |
| Recurring | isrecurring recurring |
isrecurring:true recurring:true |
| Organizer | organizer, by, from | organizer:jonas |
| Location | location | location:calgary |
Properties for file type: Documents
| Property | Use | Example |
| Comments | comments | comments:excellent |
| Last saved by | lastsavedby | lastsavedby:josh |
| Document manager | documentmanager | documentmanager:jonas |
| Revision number | revisionnumber | revisionnumber:4a |
| Date last printed | datelastprinted | datelastprinted:yesterday |
| Slide count | slides | slides:>20 |
Properties for file type: Music
| Property | Use | Example |
| Bit rate | bitrate | bitrate:>150kbps |
| Artist | artist, by | artist:U2 |
| Year | year | year:1910..1911 |
| Album | album | album:”greatest hits” |
| Genre | genre | genre:rock |
| Lyrics | lyrics | lyrics:”happy birthday to you” |
| Track | #, track | track:12 |
| Year | year | year:>1910<1911 |
Properties for file type: Picture
| Property | Use | Example |
| Camera make | cameramake | cameramake:nikon |
| Camera model | cameramodel | cameramodel:eclipse |
| Dimensions | dimensions | dimensions:8×10 |
| Orientation | orientation | orientation:landscape |
| Date taken | taken datetaken |
taken:last datetaken:6/12/2011 |
| Width | width | width:33 |
| Height | height | height:66 |
| Flash mode | flashmode | flashmode:no flash |
Properties for file type: Recorded TV
| Property | Use | Example |
| Broadcast date | broadcastdate | broadcastdate:2011 |
| Channel number | channel | channel:7 |
| Closed captioning | closedcaptioning | closedcaptioning:true |
| Date released | datereleased | datereleased:2011 |
| Episode name | episodename | episodename:zeppo |
Properties for file type: Video
| Property | Use | Example |
| Name | name subject |
name:vacation subject:hawaii |
| Ext | Ext filext |
ext:wma filext:wma |
Windows Search: Find files with Ratings
Here are some tips for searching files that have ratings!
Open Windows Search from the Start Menu. You can even access the search box from Windows Explorer.
In the search box enter:
Rating:>0 Star
This will find all files that have a rating of 1 to 5 stars. But let’s try some advanced parameters to really narrow the results.
Find files with a rating of 1 star
Rating:1 Star
Find files with a specific rating 2, 3, 4 or 5. In the example below, we are searching for 4-star ratings
Rating:4 Stars
Find files with a rating in a range. To find files rated from 2 to 4 we use
Rating:>1 stars <5 stars
Sourced from: Microsoft.
