Оснастка Active Directory Users and Computers (или ADUC) – это одна из наиболее часто используемых консолей управления объектами в домене Active Directory. Вы можете установить mmc оснастку ADUC как на Windows Server, так и на десктопные Windows 10 и 11. Консоль ADUC входит в состав набора компоненту администрирования Microsoft Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT). В этой статье мы покажем, как установить и использовать консоль управление Active Directory Users and Computers в Windows.
Содержание:
- Установка оснастки RSAT Active Directory в Windows 10 и 11
- Как пользоваться консолью Active Directory?
- Подключение консоли ADUC к домену из рабочей группы
Установка оснастки RSAT Active Directory в Windows 10 и 11
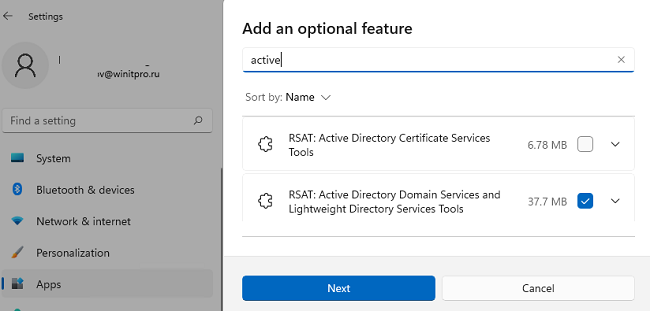
В современных версиях Windows 10 (начиная с билда 1809) и в Windows 11 инструменты администрирования RSAT устанавливаются онлайн в виде Features on Demand. Чтобы установить инструменты администрирования RSAT Active Directory в Windows 10/11, перейдите в Settings -> Apps -> Optional Features -> Add an optional feature (View features).
Наберите в поисковой строке Active Directory и выберите для установки компонент RSAT: Active Directory Domain Services and Lightweight Directory Services Tool.
Нажмите Next-> Install для начала установки.
Windows подключится к серверам Microsoft, скачает и установит набор инструментов для управления Active Directory (включает в себя графические консоли Active Directory, утилиты командной строки и модуль Active Directory PowerShell).
Либо вы можете установить набор компонентов администрирования AD с помощью PowerShell:
Add-WindowsCapability –online –Name Rsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
В изолированных сетях, в которых нет доступа в интернет, вы можете установить инструменты RSAT Active Directory с помощью ISO образа Windows 10 Features on Demand (образ FoD можно скачать из кабинета лицензирования Microsoft).
Для установки инструментов Active Directory, из сетевого каталога с содержимым образа FoD выполните команду:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0 -LimitAccess -Source \\fs01\Distr\Windows10-FOD\
В предыдущих билдах Windows 10, а также в Windows 8.1, установить RSAT можно с помощью MSU обновления. Скачать RSAT можно здесь:
- RSAT для Windows 10 1803/1709 — https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=45520
- RSAT для Windows 8.1 — https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=39296
Скачайте версию файла RSAT в зависимости от разрядности вашей операционной системы и установите его. Дважды щелкните по файлу для начала установки:
Или установите MSU файл RSAT из командной строки в «тихом» режиме:
wusa.exe c:\Install\WindowsTH-RSAT_TP5_Update-x64.msu /quiet /norestart
После окончания установки RSAT нужно перезагрузить компьютер.
Осталось активировать необходимый функционал RSAT. Для этого:
- Щелкните ПКМ по кнопке Start и выберите Control Panel (Панель управления)
- Выберите Programs and Features (Программы и компоненты)
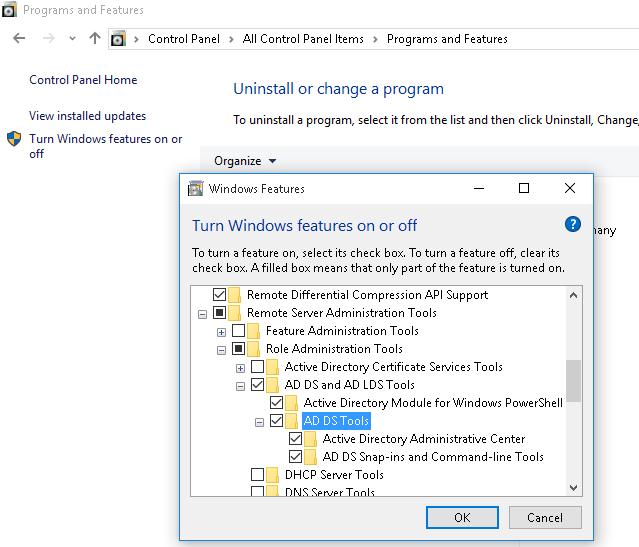
- В левой панели нажмите кнопку Turn Windows features on or off
- В дереве компонентов разверните Remote Server Administration Tools-> Role Administration Tools -> AD DS and AD LDS Tools
- Отметьте раздел AD DS Tools и нажмите OK.
Установка оснастки ADUC также может быть выполнена из командой строки. Последовательно выполните 3 команды:
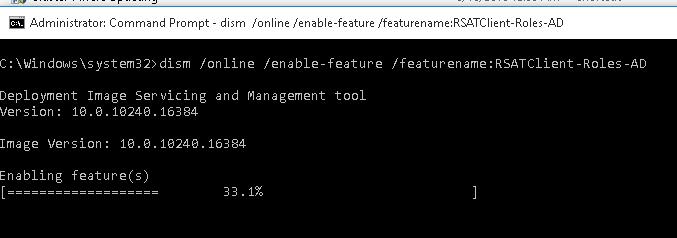
dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:RSATClient-Roles-AD
dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:RSATClient-Roles-AD-DS
dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:RSATClient-Roles-AD-DS-SnapIns
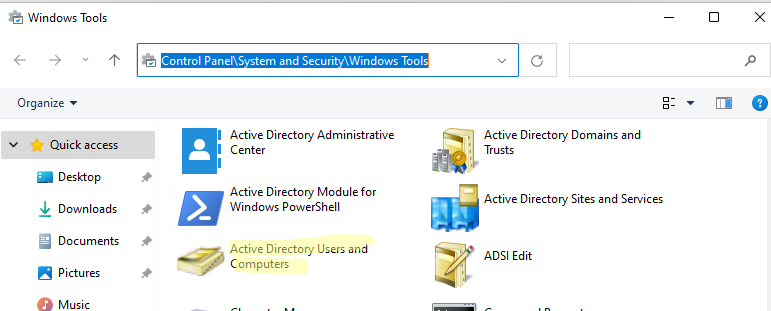
После установки оснасток управления, в разделе Administrative Tools панели управления (Control Panel\System and Security\Windows Tools) появится ссылка на консоль Active Directory Users and Computers.
Как пользоваться консолью Active Directory?
Чтобы запустить консоль ADUC, щелкните по ярлыку в панели управления или выполните команду:
dsa.msc
Все аутентифицированные пользователи домена могут использовать консоль ADUC для просмотра объектов Active Directory.
Если ваш компьютер состоит в домене Active Directory, то консоль ADUC подключится к контролеру домена, на основании текущего Logon сервера. Имя контроллера домена, с которого вы получаете информации указано в верху.
Вы можете подключиться к другому контроллеру домена AD или другому домену, щелкнув по корню консоли и выбрав пункт в контекстном меню.
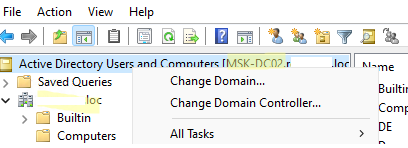
В консоли Active Directory отображается древовидная структура организационных юнитов (Organizational Unit, OU) вашего домена (и отдельный раздел с сохраненными запросами/ Saved Queries AD).
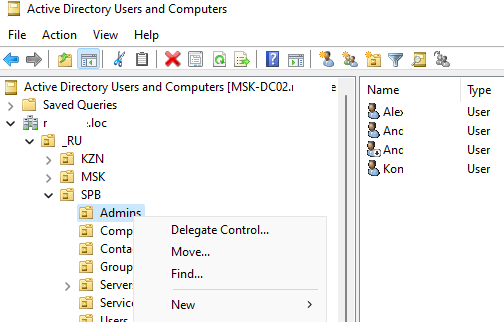
Администратор домена может создавать контейнеры (OU) в соответствии с физической или логической структуры предприятиями. С помощью контекстного меню можно создать новые объекты в AD (пользователей, группы, компьютеры, OU, контакты), переименовать, переместить или удалить объекты. В зависимости от типа объекта, который вы выбрали пункты контекстного меню могут отличаться.
Например, у пользователя есть опции на сброс пароля в AD или блокировку/разблокировку учетной записи.
Вы можете использовать контекстное меню Search для поиска объектов в AD.
Администратор может делегировать права на создание/редактирование/удаление объектов в Active Directory другим пользователям или группам.
С помощью меню View -> Add/Remove columns можно добавить атрибуты объектов, которые вы хотите отображать в консоли ADUC.
В консоли ADUC можно посмотреть или изменить свойства объектов домена. Например, можно открыть свойства пользователя и изменить его настройки. Часть свойств пользователя находится на соответствующих вкладках, а полный список атрибутов пользователя доступен на вкладке редактора атрибутов AD (Attribute Editor).
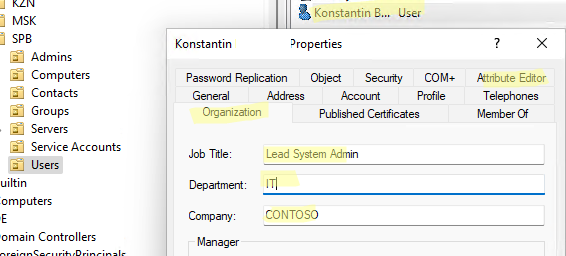
Можно добавить отдельную вкладку с фотографией пользователя AD.
Чтобы показывать системные контейнеры и свойства объектов в оснастке AD (по умолчанию скрыты), включите опцию View -> Advanced features.
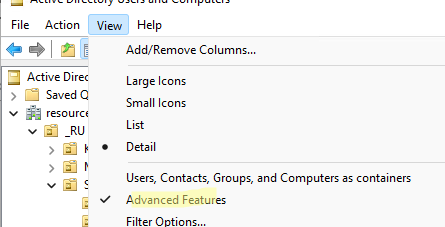
После этого у всех объектов появится ряд системных вкладок. Например, на вкладке Object можно получить каноническое имя объекта, дату создания учетной записи и включить опцию защиты от удаления (protect object from accidental deletion).
Подключение консоли ADUC к домену из рабочей группы
Если вы хотите подключится консолью ADUC к контроллеру домена с компьютера, который не включен в домен (состоит в рабочей группе), воспользуйтесь таким методом:
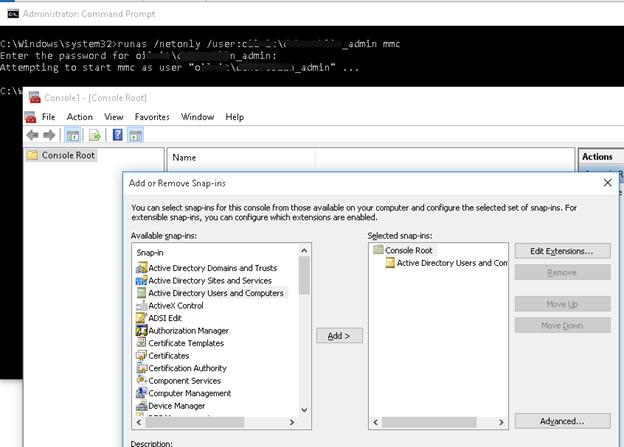
- Запустите командную строку и выполните команду запуска оснастки от имени другого пользователя:
runas /netonly /user:winitpro\aaivanov mmc - В пустой консоли MMC выберите File->Add/Remove Snap-In
- Перенесите оснастку Active Directory Users and Computers в правую панель и нажмите Add;
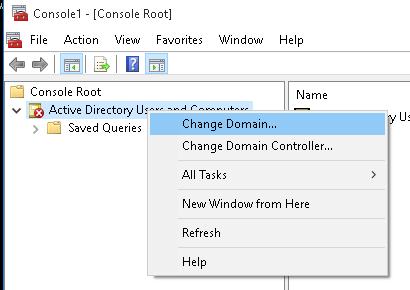
- Чтобы подключится к домену, щелкните по корню консоли и выберите Change domain. Укажите имя домена.
В результате консоль ADUC подключится к контроллеру домена, получит и отобразит структуру контейнеров (OU) данного домена Active Directory.
We’ve compiled a MASSIVE List of the Best (and Free) Active Directory Tools (Update for 2025) for Windows admins that will help with any of your Auditing, Reporting, and Management needs. We’ve gone through this list and will update it as more tools become available or become obsolete, as not every software manufacturer updates their tools for the latest version of Active Directory (2003, 2012 & 2016).
Here is our list of the Top-10 Active Directory Tools:
- ManageEngine ADManager Plus – EDITOR’S CHOICE A package of AD management tools with functions that can interface with Microsoft 360 as well as your Azure, AWS, and on-premises AD implementations. Available for installation on Windows Server or as Azure and AWS services. Start a 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine ADAudit Plus – FREE TRIAL A package that provides analysis of AD implementations and can also be used to track user activity. Available for Windows Server or as a service in Azure and AWS. Start a 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus A package that provides single sign-on, multi-factor authentication, and self-service password management. Available for Windows Server or as services on Azure and AWS.
- ManageEngine AD360 This service monitors system activities in terms of user actions and file and device access events. Offered for Windows Server or as a service in Azure and AWS.
- MaxPowerSoft Active Directory Reports Lite Available in free and paid versions, this tool helps you manage user accounts and device permissions in multiple AD implementations. Runs on Windows.
- SolarWinds Permissions Analyzer for Active Directory This excellent tool will give you insights into both the user account structure and the device permissions that are currently laid out in your AD implementations. Runs on Windows Server.
- SolarWinds Admin Bundle This free user account management tool lets you upload accounts in bulk into AD and helps you spot inactive users, together with network management tools. Runs on Windows Server.
- AD Tidy An Active Directory user management tool that spots inactive and abandoned accounts and has a free version. Runs on Windows.
- SpecOps Gpupdate A package of remote endpoint management tools that includes Active Directory interfacing to support its operations. Runs on Windows.
- Specops Command This is a user and device management package that uses AD data in its processes. Runs on Windows.
Many of the tools below have very basic and limited functionality, as some, if not all, Are Completely FREE!
Yes, you won’t need to buy a majority of the software below unless you want some premium features that some of them require payment for, but they work nonetheless without Upgrading.
The Top Active Directory Tools of 2025
Our methodology for selecting Active Directory Tools and software
We reviewed various Active Directory tools and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- An autodiscovery system to log all network devices
- A facility to analyze network performance over time
- Graphical interpretation of data, such as charts and graphs
- A free trial period, a demo, or a money-back guarantee for no-risk assessment
- A good price that reflects value for money when compared to the functions offered
With these selection criteria in mind, we looked for useful systems that will save you time and enable you to tighten system security by tightening access rights.
1. ManageEngine ADManager Plus – FREE TRIAL
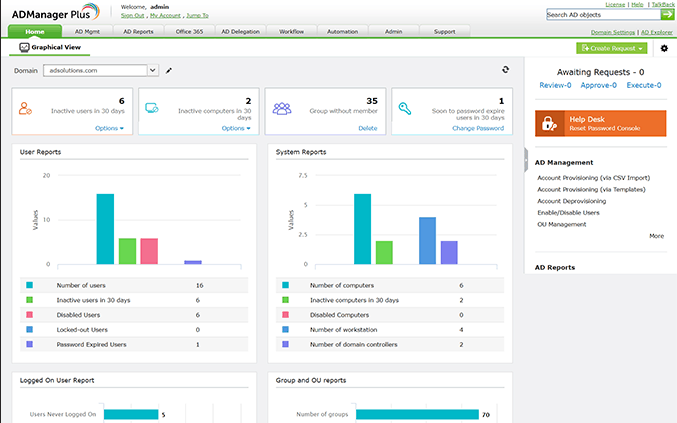
ADManager Plus gives you the ability to manage AD Objects, users, Groups, and much more from a Centralized GUI, along with options for generating extensive reports of Active Directory.
Key Features:
- Abandoned account detection
- Bulk upload
- Mass updates
Unique Feature
Uses a role-based security model to manage AD users. Also, makes it easy to audit the defined security permissions.
Why do we recommend it?
A 100% web-based solution through which you can create or modify users on AD. It also comes with reporting and workflow management capabilities.
Features include not only Active Directory user management but Real Last Logon Time Reports, Bulk User management, and Group & Computer Management capabilities.
Who is it recommended for?
It works well for network and AD administrators who want to stay on top of their AD performance. Also, a good choice for businesses that use Office 365, Exchange, Skype for Business, and Google Workspace Management.
Pros:
- Detailed reporting, can generate compliance reports for all major standards (PCI, HIPAA, etc)
- Supports multiple domains
- Supports delegation for NOC or helpdesk teams
- Allows you to visually view share permissions and the details of security groups
Cons:
- Has a steeper learning curve than similar tools
You can download a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR’S CHOICE
ManageEngine ADManager Plus is our top pick for a software package for AD management because this system provides a range of services that center around an alternative console for managing Active Directory domain controllers. Once you have this tool installed, you won’t need to wade your way through the clunky native screens of Active Directory. The ManageEngine system is much better presented than AD’s own administration interface and it is much easier to use. The ManageEngine console interacts live with Active Directory. The tool provides bulk actions such as uploading or updating of user accounts or device records. The system also provides administration automation that includes approval workflows. The system also provides a backup and recovery service to protect records from damage, destruction, or tampering. The ADManager Plus system will manage Active Directory for your on-premises systems, for Microsoft 365, for Entra ID (Azure AD), and for Google Workspace.
Download: Access a 30-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.manageengine.com/products/ad-manager/download.html
OS: Windows Server, AWS, and Azure
2. ManageEngine ADAudit Plus – FREE TRIAL
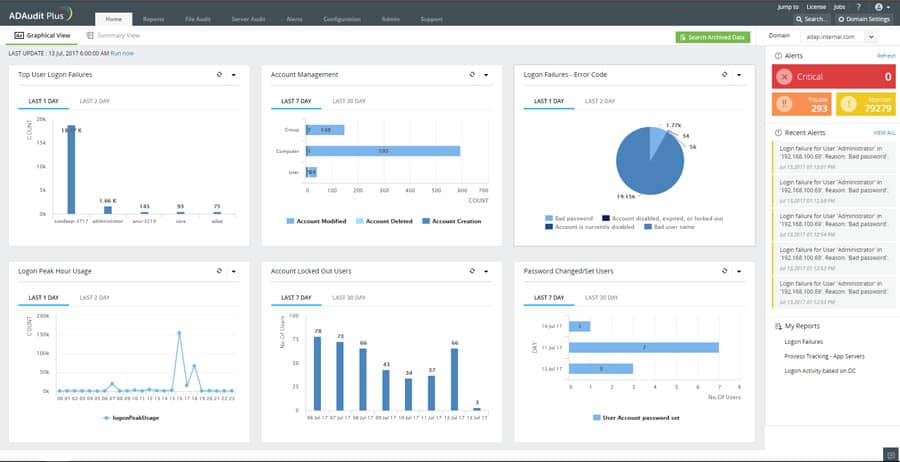
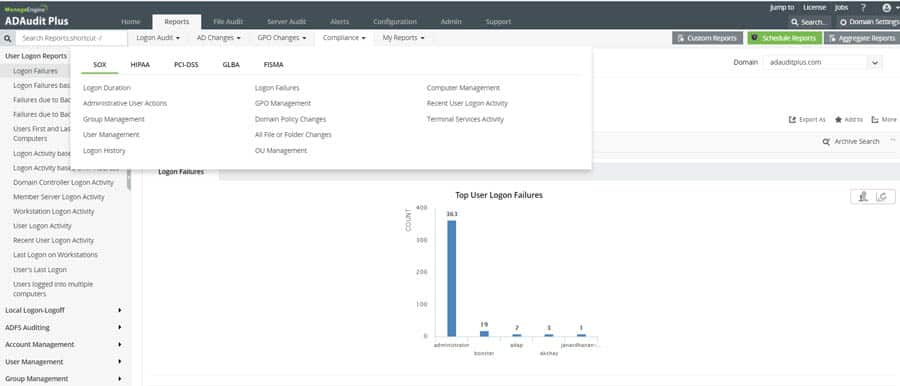
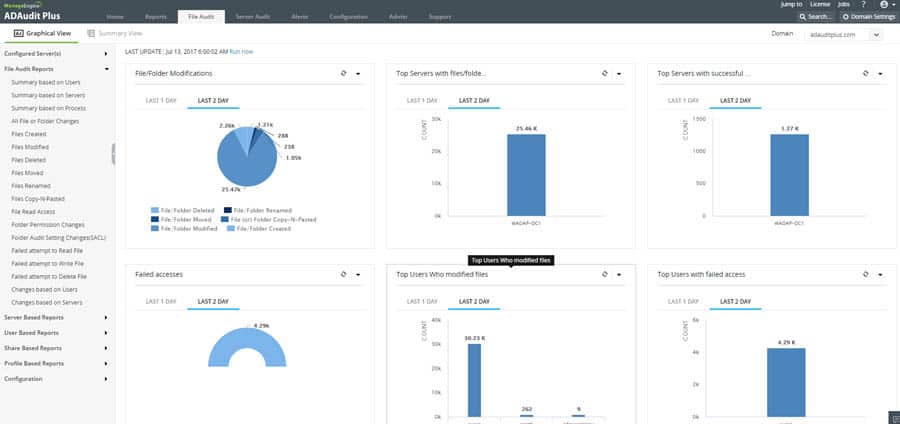
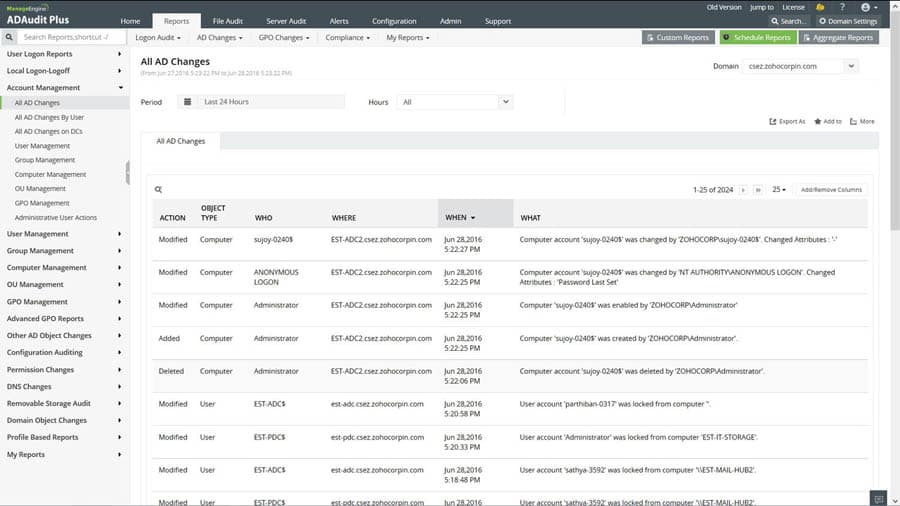
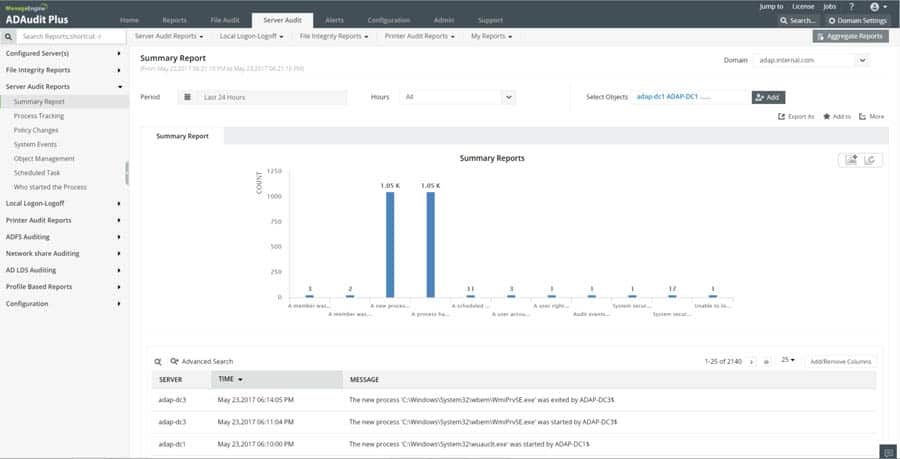
ADAudit Plus offers Real-time monitoring, user and entity behavior analytics, and change audit reports that help you keep your AD and IT infrastructure secure and compliant.
- Track all changes to Windows AD objects including users, groups, computers, GPOs, and OUs.
- Achieve hybrid AD monitoring with a single, correlated view of all the activities happening across both on-premises AD and Azure AD.
- Monitor every user’s logon and logoff activity, including every successful and failed logon attempt across network workstations.
- Audit Windows file servers, failover clusters, NetApp, and EMC storage to document changes to files and folders.
- Monitor system configurations, program files, and folder changes to ensure file integrity.
- Track changes across Windows servers, printers, and USB devices with a summary of events.
- Leverage advanced statistical analysis and machine learning techniques to detect anomalous behavior and defend against cyber attacks.
Key Features:
- File integrity management
- Sensitive data protection
- Detects AD tampering
Unique Feature
A one-stop IT auditing solution that secures your Windows Server and ensures compliance with leading standards.
Why do we recommend it?
It goes beyond just AD and also monitors your file servers, Windows servers, workstations, Azure AD, and more. It also comes with many advanced features like real-time change notification, Windows logon monitoring, account lockout analysis, and more.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for growing organizations, where the administrator has to delegate roles to employees across different departments.
Pros:
- Focused heavily on compliance requirements, making it a good option for maintaining industry compliance
- Preconfigured compliance reports allow you to see where you stand in just a few clicks
- Features insider threat detection – can detect snooping staff members or blatant malicious actors who have infiltrated the LAN
- Supports automation and scripting
- Great user interface
Cons:
- Better suited for larger environments
Register and download the 30-day free trial.
ManageEngine ADAudit Plus
Start a 30-day FREE Trial
3. ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus
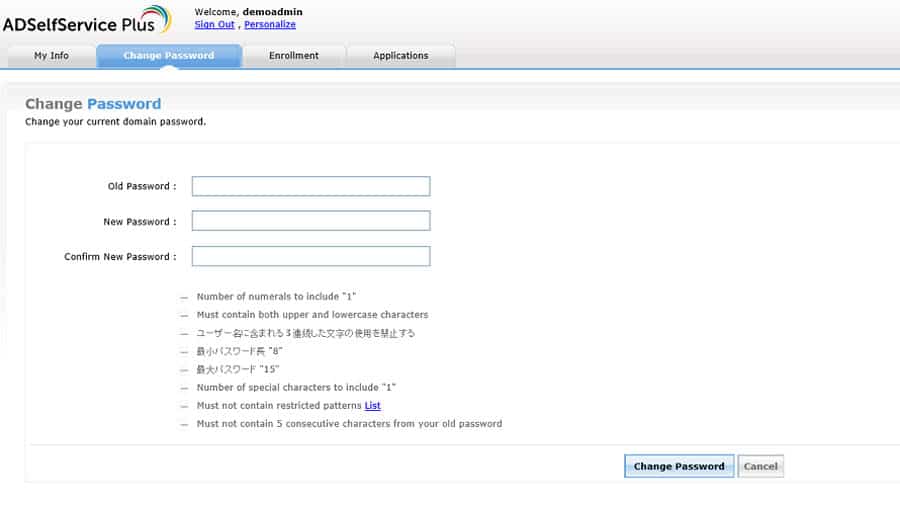
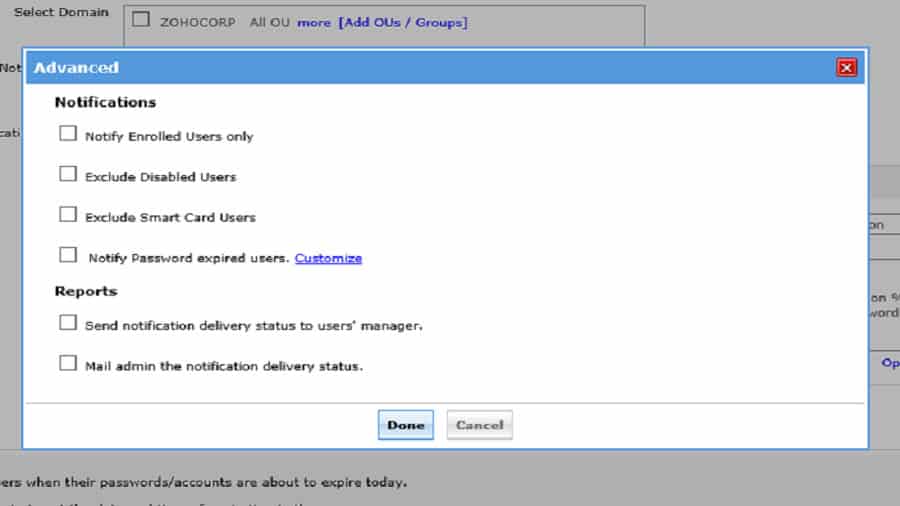
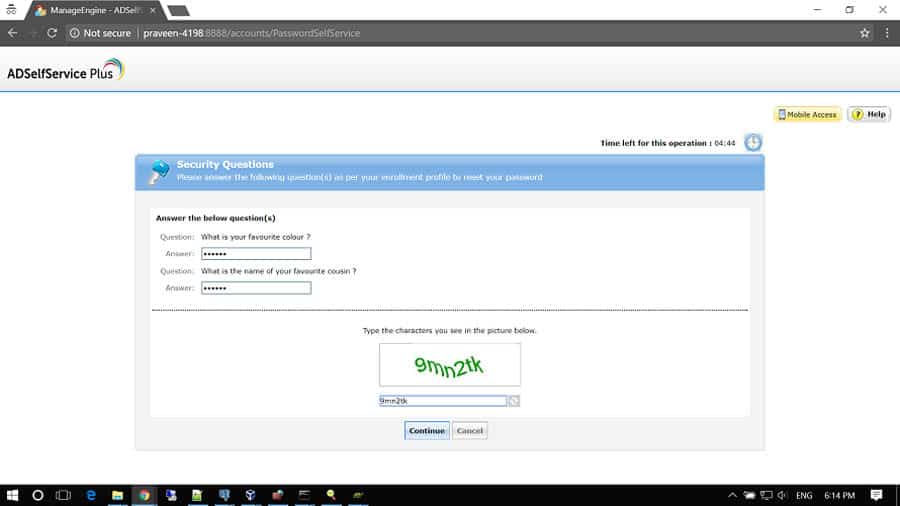
ADSelfService Plus offers password self-service reset/unlock, password expiration reminders, a self-service directory updater, a multiplatform password synchronizer, and single sign-on for cloud applications.
Key Features:
- User portal
- Reduces technician workload
- Mobile apps
Why do we recommend it?
This tool allows users to perform password resets and other self-service actions from any time and anywhere, relieving IT admins to focus on the more important tasks. It also comes with mobile apps for Android and iOS.
Use the ADSelfServicePlus Android and iPhone mobile apps to facilitate self-service for end users anywhere at any time.
ADSelfService Plus supports the IT help desk by reducing password reset tickets and spares end users the frustration caused by computer downtime.
Who is it recommended for?
Works well for organizations that want to balance security with convenience while enhancing the efficiency of the IT department.
Pros:
- Empowers users to change their own passwords – eliminating extra tickets
- Offers a variety of password policy enforcement options
- Supports multi-factor authentication
- Syncs passwords in real-time across the cloud and on-premises AD
Cons:
- Best suited for small to medium-sized helpdesk teams
4. ManageEngine AD360
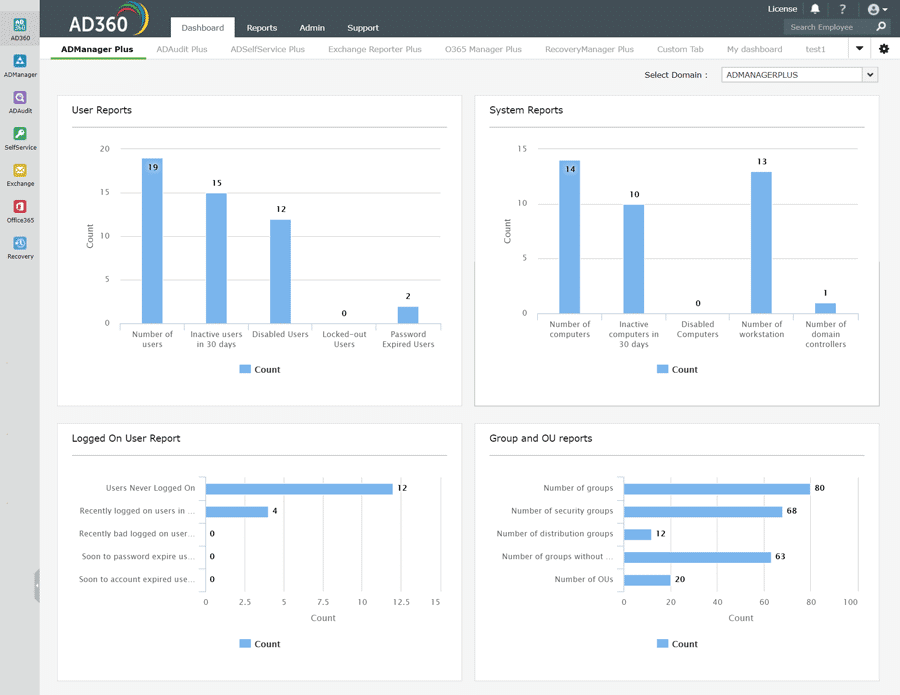
AD360 is an integrated solution for Identity and Access Management (IAM) needs in a Windows environment.
Key Features:
- Package of four tools
- Self-service
- Exchange Server reporting
Why do we recommend it?
An integrated solution that comes with many capabilities like identity and access management, account lockout management, Exchange auditing, and more. It eliminates the need to have multiple tools and manage them.
This web-based software portfolio unifies all the functionalities needed for an enterprise: from user provisioning, and self-service to risk governance, and offers it with a simple, easy-to-use interface.
AD360 is the right solution for bridging the gap between technology and complex business needs.
AD360 automates all the routine Identity and Access Management tasks like provisioning/de-provisioning bulk user accounts and other AD objects, secure management of account passwords, modifying multiple attributes of user accounts, and managing user mailboxes and their email traffic.
Who is it recommended for?
A good choice for IT administrators of large Windows environments.
Pros:
- Dramatically improves the usability of Active Directory, making routine tasks easier to perform and automate
- Can monitor changes across both local and cloud-based AD environments
- Supports SSO and MFA, great for securing your access management with multiple layers of authentication
- Extensive 60-day trial period
Cons:
- Only runs on Windows Server in an Active Directory environment
5. MaxPowerSoft Active Directory Reports Lite
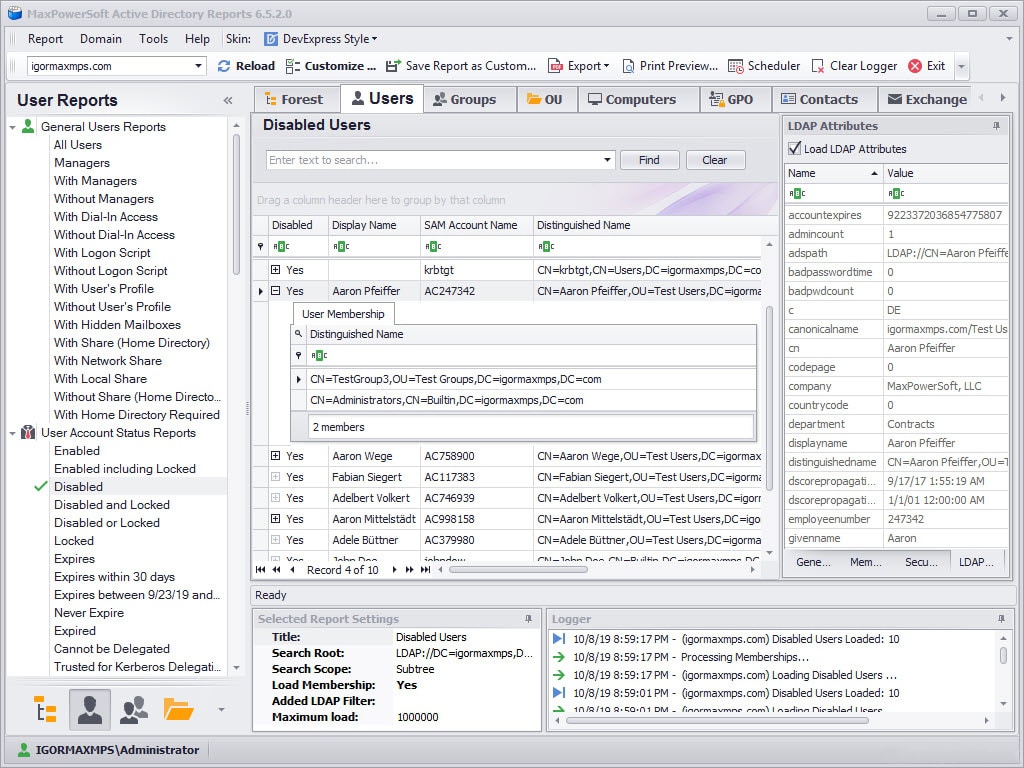
MaxPowerSoft’s Free offering allows you to load up to 200 objects from Active Directory, along with User Reports, Group and OU Reports, Computer Reports and GPO reports from within their program.
Key Features:
- Free tool
- Bulk upload
- Permissions assessment
Why do we recommend it?
Makes it easy to create custom reports for specific needs. You can load up to 200 objects from AD to generate the reports you want.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network administrators who want to create AD reports for auditing and compliance.
Pros:
- Available as both a free and paid tool
- Includes bulk management features
- Supports up to 200 different objects at once
- Great for sorting GPOs at scale
Cons:
- Can take time to fully explore all features and tools
6. SolarWinds Permissions Analyzer for Active Directory
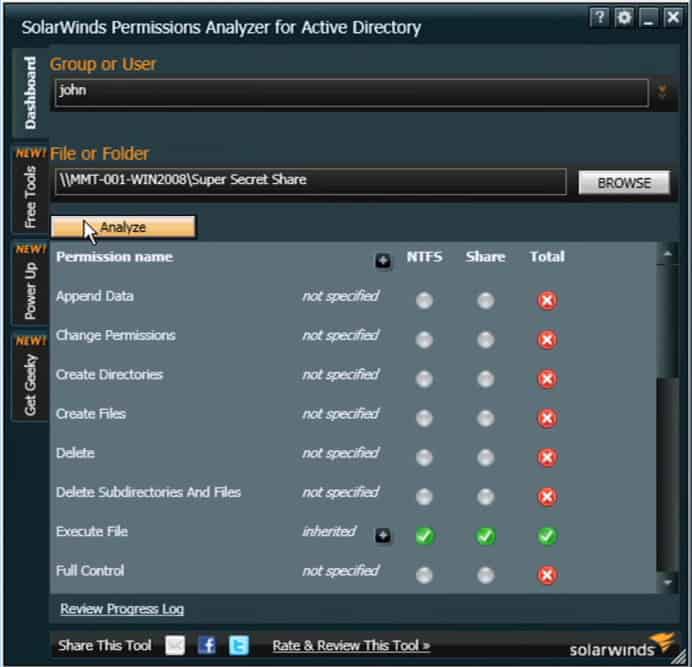
SolarWinds offers a Truly Free Active Directory Users and Computers permissions analyzer, allowing you to browse and identify with groups and users have which permissions. Also, you can see the breakdown of inherited permissions of each user by their group membership.
Key Features:
- Free to use
- On-premises
- Inheritance management
- Group membership analysis
- Permissions browser
Unique Feature
A free tool for analyzing assigned and inherited permissions for files and folders in a Windows environment.
Why do we recommend it?
Highly usable, as you can quickly query the permissions on any file or folder without having to log into the server. Also, installation is super simple.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network engineers, administrators, and security specialists who want to understand the access mapping between users and resources in the AD domain.
Pros:
- Provides a simple yet powerful way to gain insight into your access controls and account security
- Offers a great visual way to see inherited permissions and permission groups
- Supports continuous permission monitoring
- Great for audits, detecting inside threats, and ATO attack prevention
- Is completely free
Cons:
- Ideal for larger more complex environments
7. SolarWinds Admin Bundle
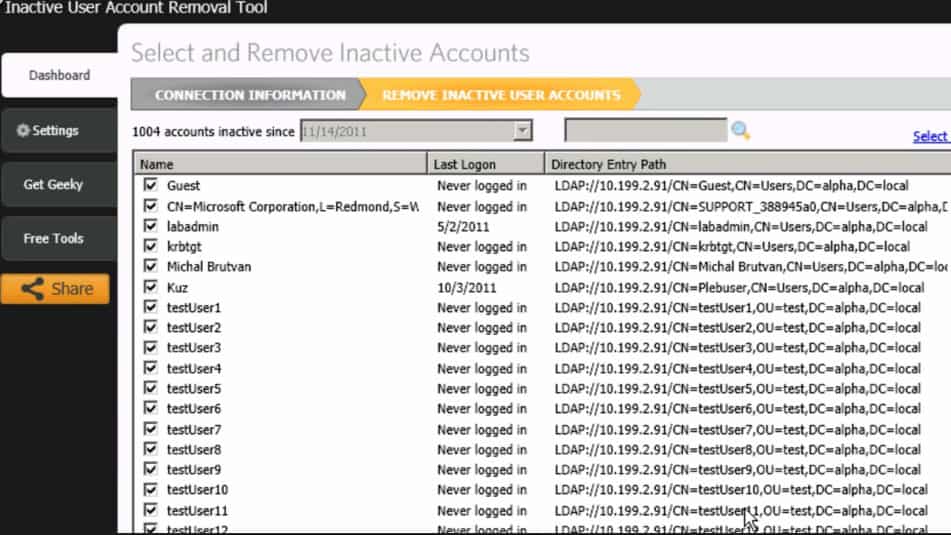
The Admin Bundle for Active Directory from SolarWinds Consists of 3 separate software utilities that will assist in the daily, weekly, and monthly Administrative Tasks of AD. This includes the following utilities:
- Inactive User Account Removal Tool
- Import User in Bulk
- Inactive Computer Removal Utility
Each utility has its own function which allows you to quickly Remove Inactive Active Directory USER Accounts and Computer accounts. They each have a friendly and easy-to-use Graphical Interface and come in very handy without having to log into your Domain Controller.
Key Features:
- Free package
- On-premises
- Spots abandoned accounts
- Bulk upload
Unique Feature
A free tool that comes bundled with many features to keep your AD tidy and manageable.
Why do we recommend it?
Simplifies AD management, as you can easily add or remove computers and users from the AD in bulk or individually. You can also add filters to identify and remove specific users.
Who is it recommended for?
A good choice for AD administrators who want comprehensive control and visibility into the working of their AD domains.
Pros:
- A small suite of tools that add additional features to the default access control in AD
- Helps speed up routine access management tasks when on/offboarding users
- Is completely free – great for smaller environments
- Great for bulk AD tasks
- Completely free
Cons:
- Larger networks may require more features
8. AD Tidy

AD Tidy helps you search and find Inactive Users from ADUC as well as Dormant and Inactive Computer Accounts as well to minimize any possible security issues.
Key Features:
- Abandoned account detection
- Removes accounts for retired devices
- Bulk actions
Why do we recommend it?
A free utility that enables administrators to look up a user or computer easily. It also enables the viewing of converted schema attributes that are not readable natively.
Who is it recommended for?
It is perfect for the IT administrators of small and medium businesses who want to look up objects in their AD.
Pros:
- Includes a free version of the tool
- Can identify and group abandoned AD objects
- Simple interface
Cons:
- Focuses mostly on clearing up old AD objects
9. SpecOps Gpupdate
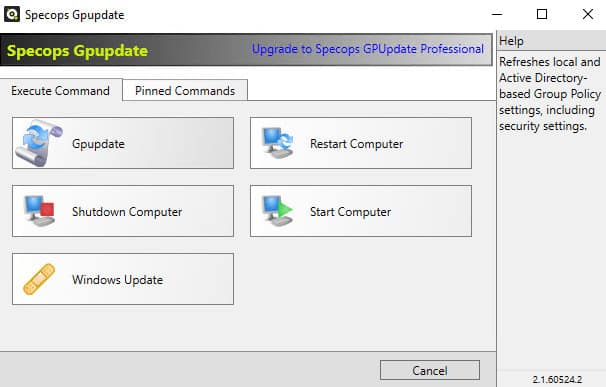
SpecOps GPUPDATE software gives you the power to remotely administer a Single Computer or Multiple Computer accounts from Active Directory. Options include Refresh Group Policy Remotely, using WSUS to confirm Updates Remotely, Remotely Wake-Up Computer using WOL (Wake-On Lan) features, and Remotely Shutdown/Restart PC.
Key Features:
- Remote administration
- Includes WSUS
- Group policy management
Why do we recommend it?
A free tool that integrates with AD users and computers. It also allows the administrator to do tasks remotely using Group Policy.
Who is it recommended for?
An optimal solution for network administrators who want to remotely administer or perform tasks on computers.
Pros:
- Simple and easy-to-use interface
- Includes remote admin tools
- Can manage group policy
- Includes WSUS management
Cons:
- Better suited for smaller AD environments
10. Specops Command
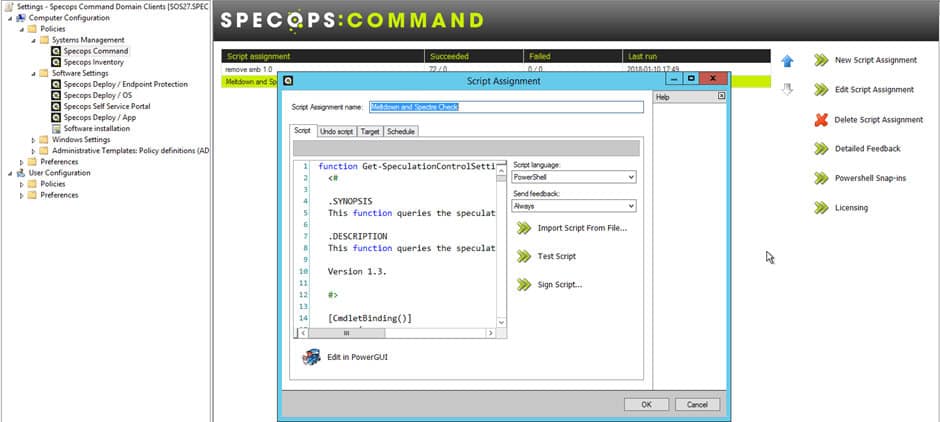
SpecOps Command utility allows you to administrate Computers and Users within your network and run VBScripts or PowerShell scripts using Group Policy quickly and ensure all feedback is received at the utility.
Key Features:
- Update script management
- Edit and launch scripts
- AD management library
Why do we recommend it?
This tool combines Windows PowerShell and Group Policy to help manage computers and users on your network. It also simplifies app installation in your Azure AD environment.
Features include Scheduling scripts to run at certain times and how often to run as well as web-based Reporting of feedback from scripts that have run.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is well-suited for AD administrators who require security and flexibility.
Pros:
- Powerful script management tools
- Features a robust management library
- Ideal for larger AD environments
- Simple and easy-to-use interface
Cons:
- Better suited for environments that heavily rely on scripts
11. AD PHOTO EDIT
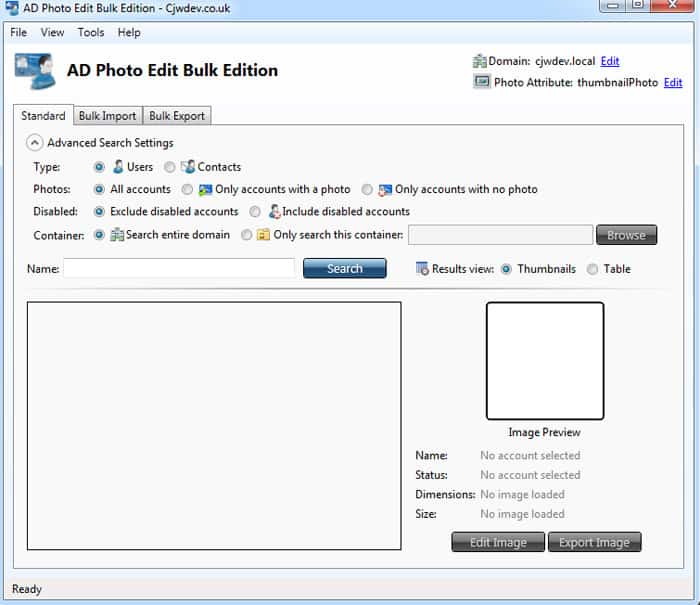
AD Photo Edit allows you to import and Upload images to an AD attribute that Outlook 2010 Displays, as well as Lync and Sharepoint.
Why do we recommend it?
A user-friendly application with which you can easily upload, edit, and export user and contact photos in AD.
Who is it recommended for?
It is for AD/network administrators of small and medium organizations.
The free version allows you to view existing images for Users and Contacts in the active directory, Export Images, Remove Existing Images, Upload New images, Rotate/Resize/Adjust the Quality of Images, and much more.
12. AD Info
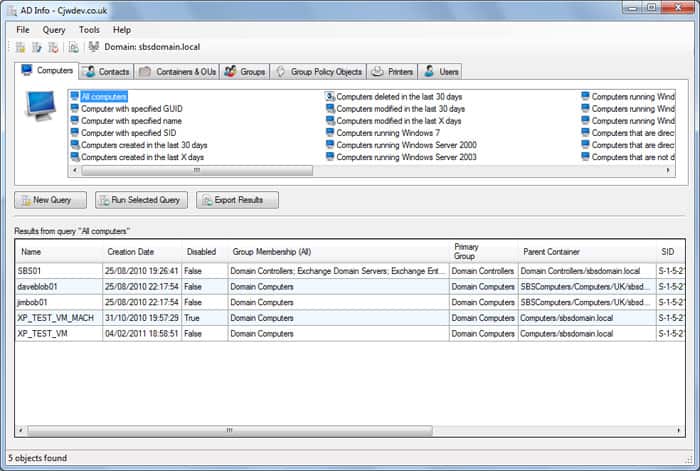
AD Info tool comes with 190 different pre-built reports that allow you to query a large number of attributes including Users, Computers, Contacts, Organization Units, GPO’s, Printers and more! One of the benefits of this is you can run this program without Domain Admin privileges.
Why do we recommend it?
This tool is modern and user-friendly. You can also use its 150 built-in queries to generate the reports you need.
Who is it recommended for?
This free tool can come in handy for AD administrators, project managers, IT department heads, and anyone else who needs AD-related reports.
Export your query results to CSV and query any domain you have access to.
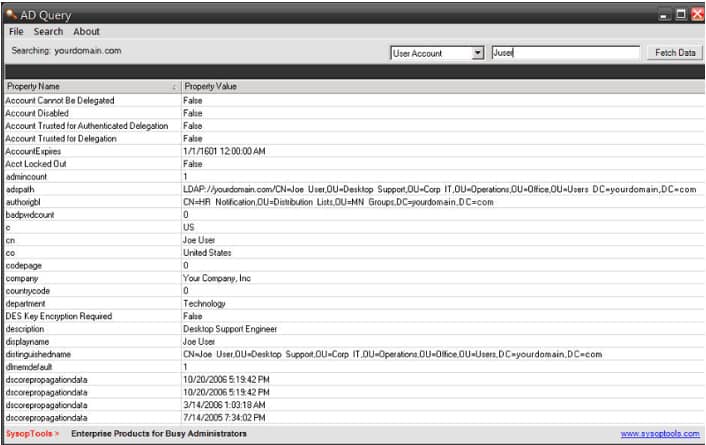
Ad Query is a Free executable tool (no installation required) that can be used to easily and quickly search Active Directory for information regarding a User or Computer for specific information.
Why do we recommend it?
It comes with a convenient user interface, using which you can query the AD to get any desired data.
Who is it recommended for?
Works well for IT, network, and AD administrators who want to get AD-related information.
You can search ALL data from Schema, LDAP, and Exchange mail-enabled objects within your AD.
14. Recovery Manager for Active Directory
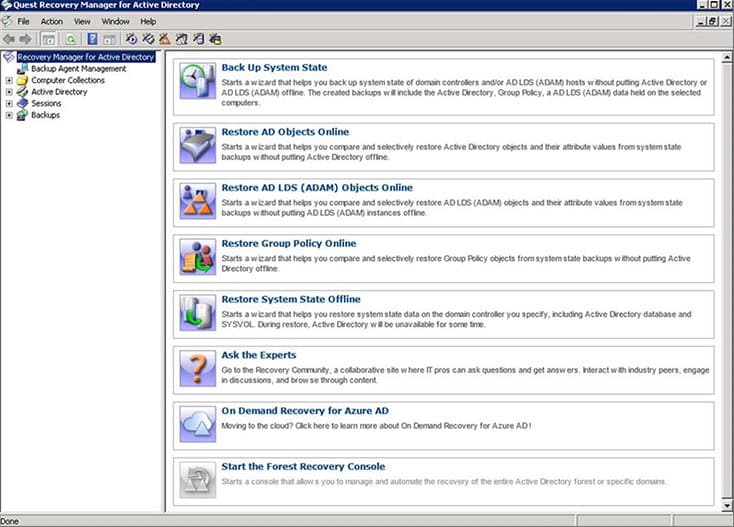
Recovery Manager for AD from Quest gives you the ability to recover any objects from AD without having to restart the Domain Controller.
Why do we recommend it?
Helps to get AD back on track quickly. As a result, it reduces downtime and users can start working without having to restart the domain controllers.
Who is it recommended for?
A good choice for IT administrators who want to reduce the negative impact on end users.
This includes restoring objects from Users, Attributes, OUs, Computers, Subnets, Group Policy Objects, and more.
15. SysAdmin Anywhere
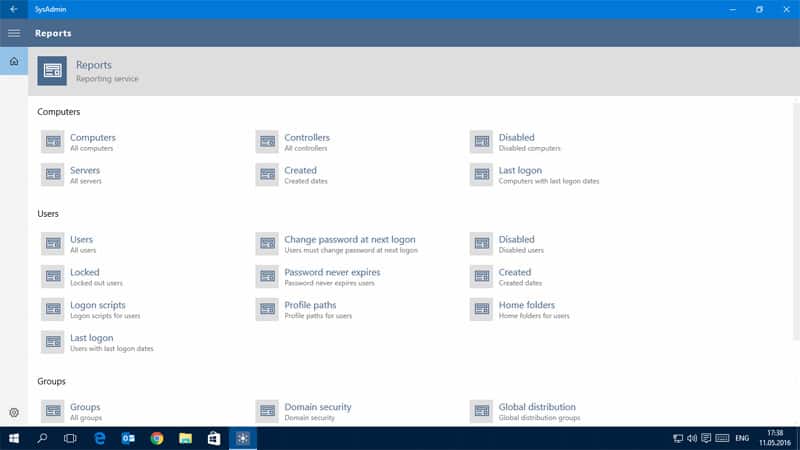
SysadminAnywhere is a great Active Directory Tool for Windows 10 that has a long list of features for AD Administration and Management.
Why do we recommend it?
Helps administer multidomain AD-based networks. Using this tool, you can manage domains, servers, computers, groups, users, and more.
Who is it recommended for?
A good choice for IT admins who want to remotely administer and manage devices. Also, helps to generate inventory.
Some features include Resetting Users password, Add/Edit/Delete Objects in AD, Add Photos, Restart/Shutdown Computers remotely in AD, Check for Updates, and Monitoring Hardware and Computers (CPU, Drive, Memory, HTTP, ping, Services, Events).
16. BeyondTrust PowerBroker Auditor
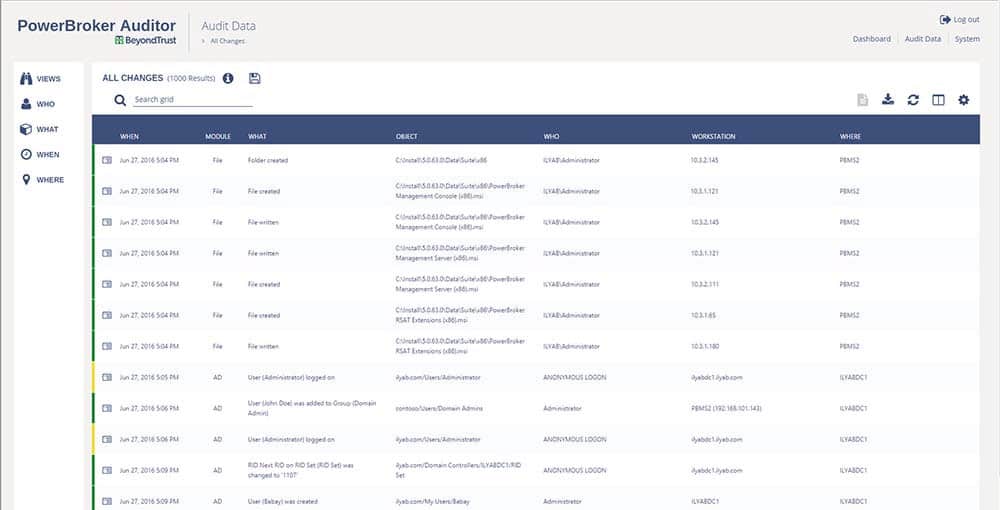
PowerBroker is an all-encompassing tool for Active Directory that allows admins and organizations to keep their AD locked down tight and have a firm grasp of what’s going on inside their AD environment in order to meet PCI, SOX, and HIPAA compliance.
Why do we recommend it?
A helpful tool to pinpoint changes in AD. Using this information, you can identify security risks and compliance,
Who is it recommended for?
A good choice for security specialists to understand compliance rates and improve operational efficiency.
This is done through audits and alerting of AD configuration and changes in real-time so you know exactly what is changing how it affects your compliance and whether you at risk or not.
17. Managed Service Accounts GUI
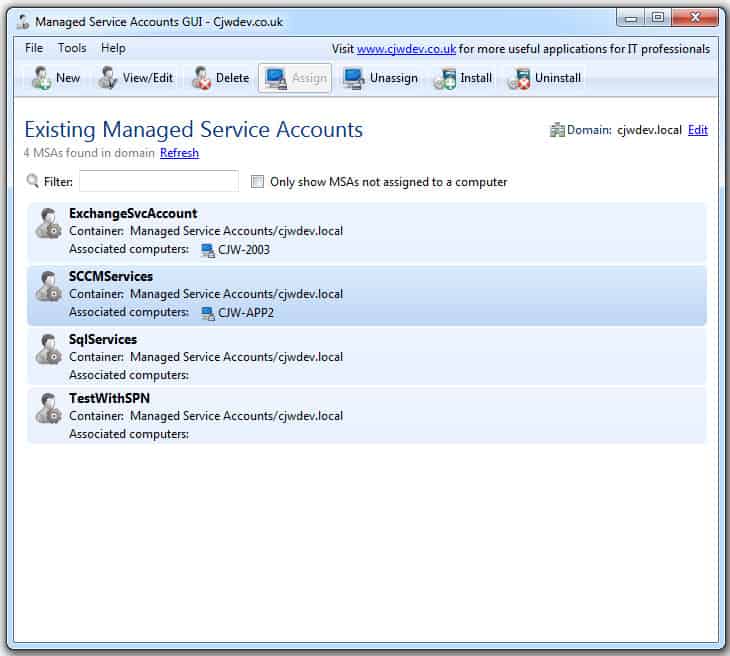
This little utility helps you configure Managed Service Accounts using an easy GUI interface and without the need of Powershell or any PS commands.
Why do we recommend it?
This tool allows you to create, configure, and install Managed Service Accounts. No prior PowerShell knowledge is needed to use it.
Who is it recommended for?
A perfect choice for AD admins, as its GUI makes it easy to configure managed service accounts.
This utility cuts out the need to run 3 separate commands via Powershell and helps you create/delete new and Old Managed Service accounts with the click of a button.
18. Microsoft Active Directory Topology Diagrammer
This topology mapper/diagram tool reads AD configurations and automatically Creates a Visio file of your AD topology using LDAP and maps out your entire Active Directory and Exchange Server Topology automatically within an easy-to-read Visio Diagram.
Why do we recommend it?
With this tool, you can easily read an AD configuration and even generate a Visio diagram of your AD and Exchange Server topology.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for IT admins managing a Windows environment.
ManageEngine offers several Great utilities for managing Active Directory – including the following tools that can be found at the URL below: AD Query Tool, CSV Generator (generate a CSV file from any AD Attributes), Last Logon Reporter, Active Directory Replication Manager and Many more! Check out their Full list of tools at the link below.
Why do we recommend it?
A comprehensive suite of tools for managing identities, user provisioning and de-provisioning, auditing, and more.
Who is it recommended for?
Works well for AD admins, as it eases the management of AD objects while generating relevant reports.
20. Group Manager
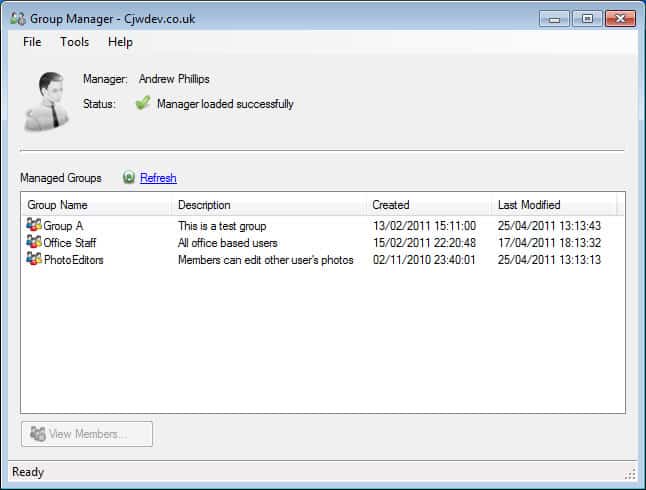
This tool allows a user that is assigned as a Manager of a group to manage members and settings of that given group including adding and removing other users and exporting group members to a CSV file.
Why do we recommend it?
Makes it easy to manage group membership for AD groups and helps managers add or remove users.
Who is it recommended for?
A good choice for the manager of a group who is responsible for managing the roles in an organization. Also, works well for end users who wish to edit group membership for security or distribution groups.
You additional configuration is required, the utility will automatically detect which groups you are a Manager of and allow you to make changes as necessary.
21. Softerra LDAP Browser
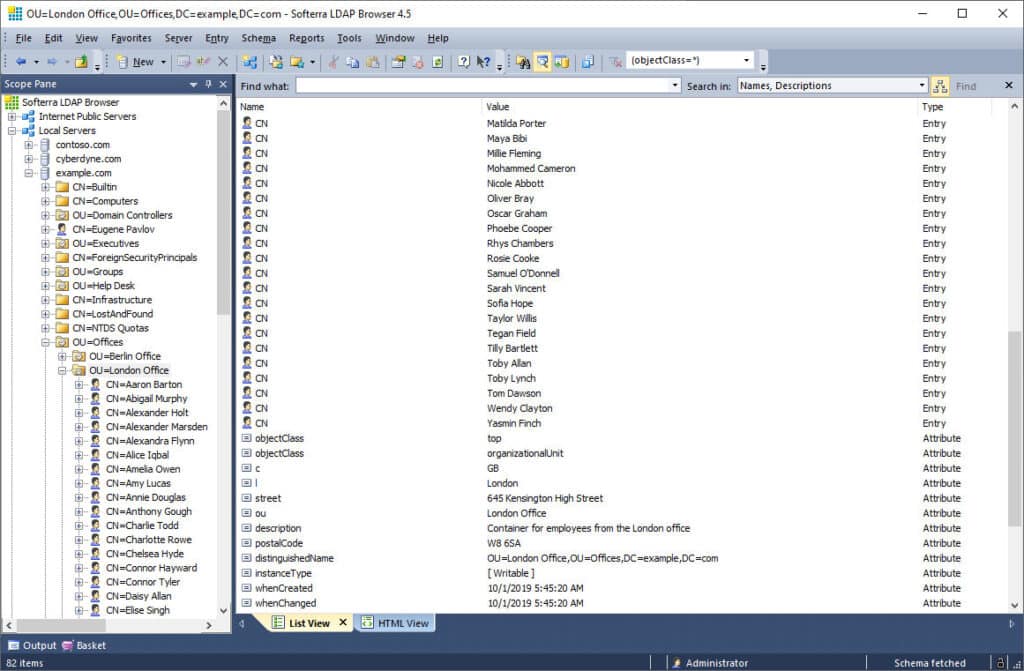
This LDAP Browser is a lightweight tool that supports Read-Only of your LDAP infrastructure and allows you to View, Browse, Search and Export information from LDAP.
Why do we recommend it?
This tool comes with a wide range of features for browsing, viewing, and analyzing LDAP directories, and their infrastructure and objects.
Who is it recommended for?
Softerra LDAP Browser is a good choice for AD admins.
22. IT Environment Health Scanner
This Health Scanner from Microsoft is specifically targeted towards Admins and Engineers who want to get an Overview of their current Active Directory Health by scanning it for Problems and inconsistencies.
Why do we recommend it?
This diagnostic tool assesses the overall health of the network infrastructure.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network administrators of small or medium-sized companies, typically up to 20 servers and 500 client computers.
This tool is great for scanning your network infrastructure and pinpointing issues that could cause your AD from functioning correctly. You must be a member of the Domain Admins group to run this utility.
23. NetWrix Restore Deleted AD Users, Groups, Etc
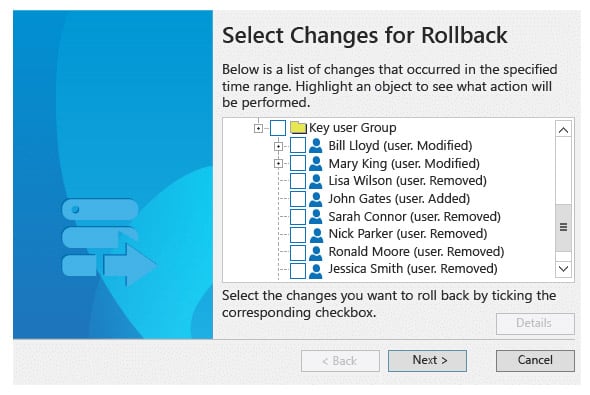
Netwrix Restore tool helps you recover and restore deleted Active Directory objects with 3 Steps – Identify the Day/Time that you want to Restore back to – Select the Recovery/Rollback Source (either AD Tombstone or Netwrix Snapshot) – and Lastly choose the Changes you want to Revert back.
Why do we recommend it?
This tool protects your organization from security breaches and makes it easy to revert entire AD objects without any downtime.
Who is it recommended for?
A good choice for AD admins to maintain the security of the AD, without impacting employee productivity.
You have the ability to restore AD Deleted objects and if necessary, revert back to previous time periods if you made the wrong changes.
24. ADRestore.NET
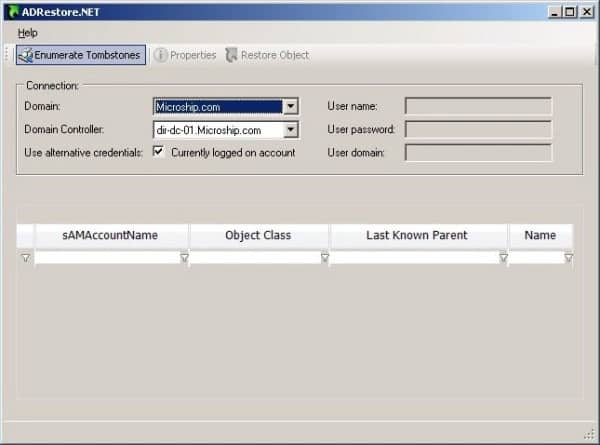
AdRestore.NET is a GUI version of the ADRestore command line utility. AdRestore enumerates all Tombstoned objects in your Domain and gives you the option to restore them individually as needed per your selections.
Why do we recommend it?
Offers a GUI to locate and restart soft-deleted AD objects.
Who is it recommended for?
Works well for AD admins who want to restore accidentally-deleted AD objects.
This was all done through the command-line, until recently Guy Teverovsky created a GUI version of the program for those not comfortable or familiar with the command-line version. For more information and to download AdRestore.NET, please visit the official site. For more information on GUI Edition, click here.
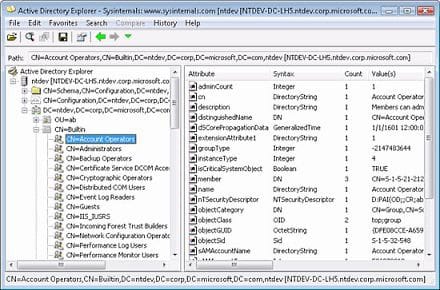
AD Explorer is an Advanced Viewer for searching, editing, and viewing Active Directory objects and properties quickly and easily without having to drill down into each object individually. You can even create snapshots of AD to view offline if you would like to work off a snapshot rather than AD live.
Why do we recommend it?
Makes it easy to navigate an AD database, including defining favorites, viewing object properties, and executing sophisticated searches.
Who is it recommended for?
Well-suited for AD admins and network administrators working in a Windows environment.
26. ADMX Migrator
ADMX Migrator is an easy-to-use GUI that comes in the form of a MMC Snap-in for converting your existing GPO ADM templates to the new ADMX file format.
Why do we recommend it?
Provides support to convert ADM files to the ADMX format. It also provides multilanguage support and version control capabilities.
Who is it recommended for?
A useful tool for network admins who want to use the ADMX format of Microsoft Windows Vista Service Pack 1.
27. BeyondTrust Privilege Explorer
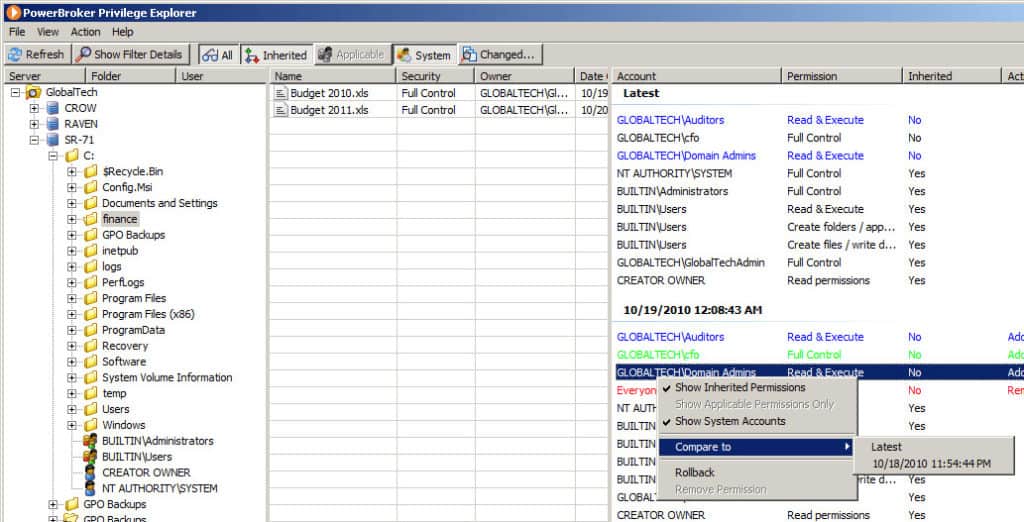
Privilege Explorer is a utility that automates the process of Active Directory file permissions by analyzing and reporting on permissions levels. This program brings automation to permission analysis and reporting to one central location and assists with compliance and intrusion detection, as well as verifying that all permissions are tight and minimizing excessive permissions for unauthorized users.
Why do we recommend it?
This tool unifies multiple capabilities like centralized management, reporting, analytics, and more.
Who is it recommended for?
This is a helpful tool for admins who have to provide the necessary insights to decision-makers to help them make informed decisions.
28. Netwrix Account Lockout Examiner
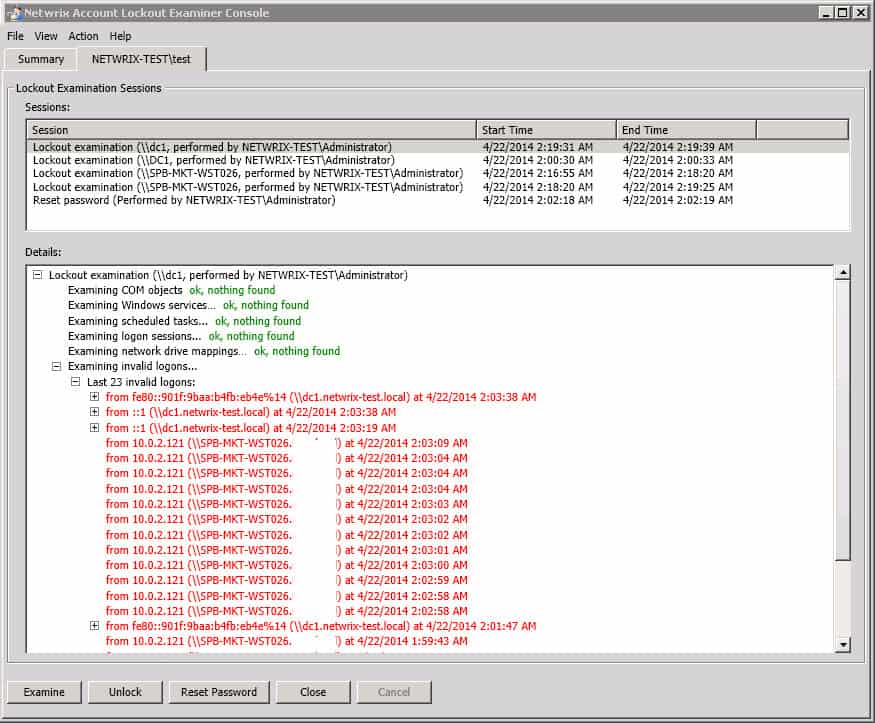
Netwrix Account Lockout Examiner does just what it says in the name – It is a Freeware utility that alerts IT personnel when an account has been locked out of Active Directory and allows you to unlock the account from within the GUI of the tool or your mobile device quickly.
Why do we recommend it?
A client-server application that performs tasks like monitoring security event logs on specific domain controllers.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network administrators who want to detect account lockouts in real-time.
29. NetWrix Inactive or Stale Users Finder
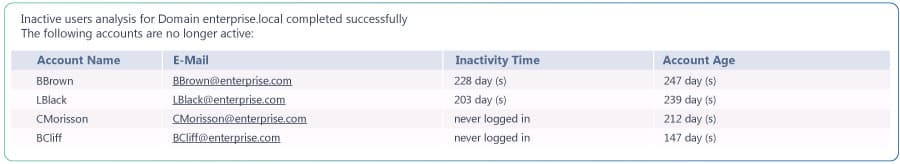
This tool also does exactly what it says – automates the process of finding and locking down Stale or Inactive accounts in ADUC and helps you mitigate any risk of those accounts becoming compromised and being used for malicious activities.
Why do we recommend it?
This is a free tool that supports AD user account management. It ensures that inactive accounts are not taken over by malicious actors.
Who is it recommended for?
Works well for security professionals and network admins who want to maintain the security of your network.
30. ADREPLSTATUS
Active Directory Replication Status utility is a tool that helps you analyze the Replication of Domain Controllers in your network to ensure that replication is actually replicating. This tool helps you pinpoint which domain controller has errors and which ones are not replicating correctly.
Why do we recommend it?
A small and handy tool that provides information about objects in an AD forest. Note that you can use this tool only to read information.
Who is it recommended for?
Helps AD admins to address replication issues.
31. AD Permissions Reporter
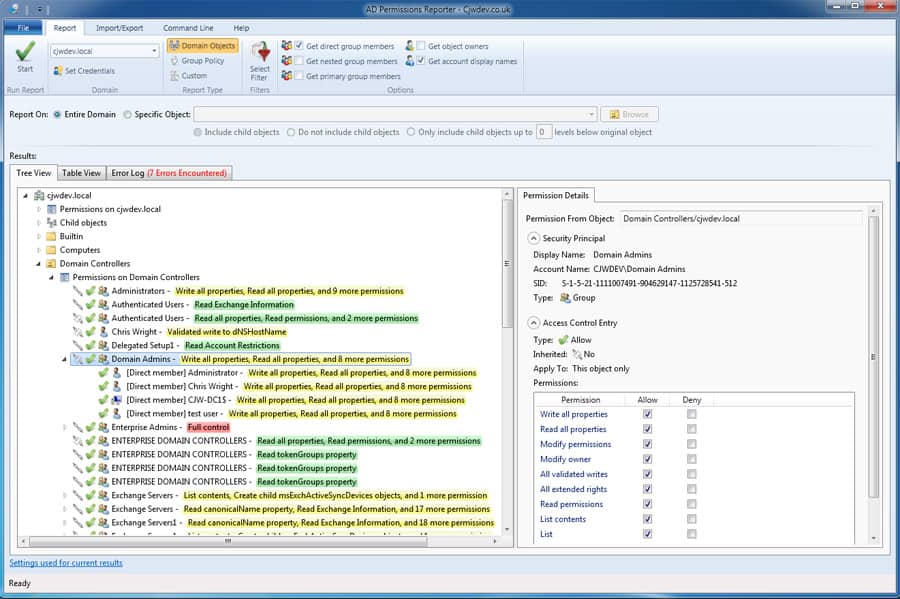
AD Permissions Reporter is used for extracting all permissions from within your domain for every object. You can additionally filter down certain objects or permissions you would like to analyze to get an understanding of their permission levels.
Why do we recommend it?
A convenient tool for reporting the permissions assigned to objects in the AD forest. It also has more than 30 predefined reports for assigning delegation rights.
Who is it recommended for?
Works well for AD admins who want to better manage the security permissions on AD objects.
32. Bulk Password Control
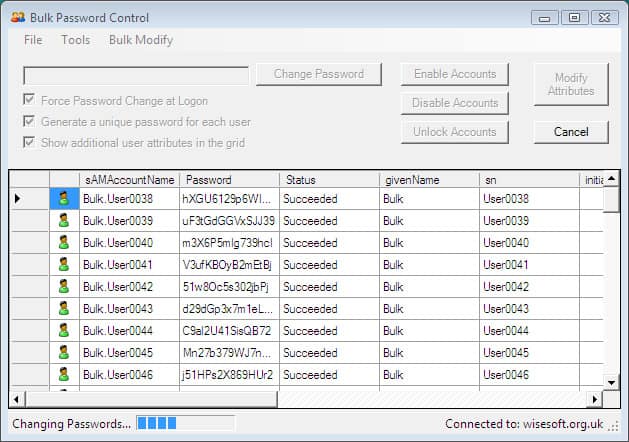
As the name of the software implies, this utility allows you to change passwords on Multiple/Bulk accounts at the same time using their Password generator feature. You can also use the same password for every account if needed as well. Additional features of this utility include enabling and disabling active directory accounts in bulk, as well as Unlocking them in bulk.
Why do we recommend it?
A handy utility for changing passwords in bulk. It also comes with query features to easily find the passwords you want to update.
Who is it recommended for?
A good tool for security professionals and network admins of small organizations.
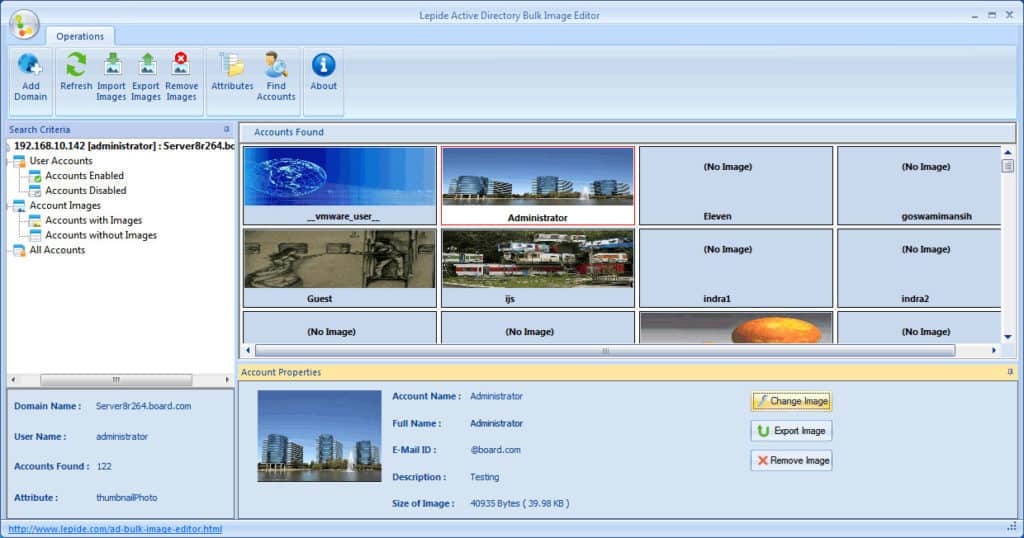
Bulk Image Editor gives you the flexibility of uploading and managing images for Active Directory “thumbnailPhoto” and “jpegPhoto” attributes on the fly – and FREE!
Why do we recommend it?
A free tool that makes it easy to upload images to AD in bulk. Also, it’s a small program that consumes little resources.
Who is it recommended for?
A useful tool for AD admins, especially in organizations that are setting up or migrating to AD.
You can also display images from all accounts, export existing images, and upload images in bulk using the SAM or common name of accounts as well.
34. Lepide Last Login Report

Extracting Last Login information for Active Directory Users is Easier than ever with Lepide’s Last Login Report tool – you can easily display information about users and their last Login time in bulk and export if necessary to CSV or HTML format for further processing.
Why do we recommend it?
Provides detailed information about all AD activities and generates reports accordingly. It also comes with predefined templates.
Who is it recommended for?
A handy option for AD users to generate detailed reports.
You can also search individual login times and dates by searching any column for specific information.
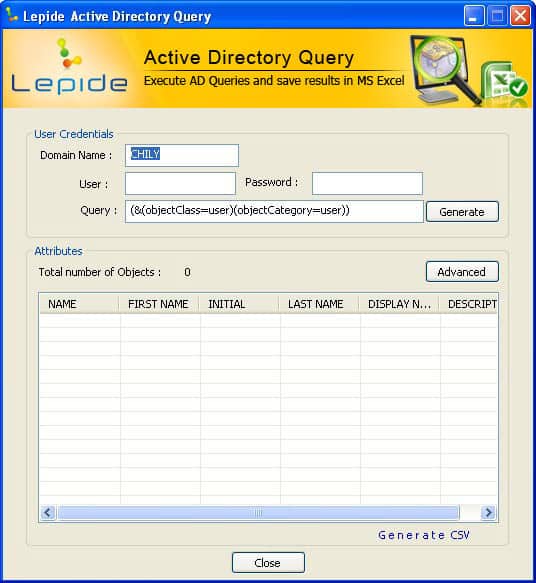
Easily query Active Directory to get detailed information about users and objects with Active Directory through this easy, GUI based utility. You can further export data to a CSV file and get individual reports as necessary.
Why do we recommend it?
Makes it easy to monitor and audit all that’s happening on your AD platform. It can also generate alerts.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for AD admins as it helps them to find vulnerabilities and fix them right away.
36. Specops Password Auditor
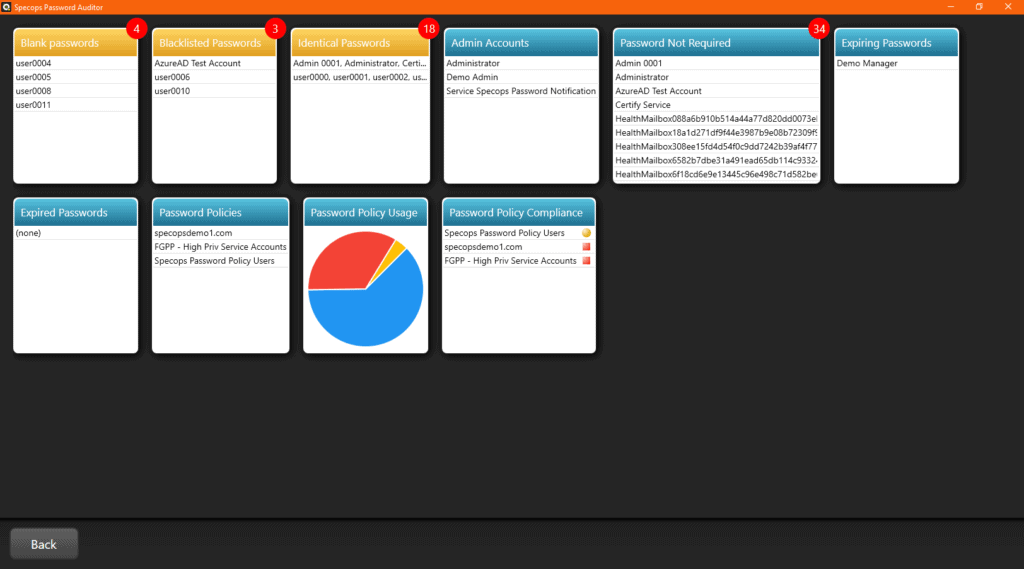
Specops Password Auditor is a free tool that scans Active Directory to detect password and privileged account security vulnerabilities. These insights can be used to reduce attack surface or maintain compliance.
Why do we recommend it?
A free tool that checks AD for password vulnerabilities and provides contextual information about them.
Who is it recommended for?
Well-suited for AD admins who work in large organizations. Specifically, it is suited for organizations that have to meet strict compliance requirements.
The tool scans Active Directory to identify accounts that are utilizing leaked passwords against a list of close to billion previously leaked passwords, in addition to gauging password policy strength against brute force attacks and compliance requirements such as NIST and PCI.The tool can also pin-point stale or inactive admin accounts in addition to the following:
- Accounts with identical passwords
- Accounts that don’t require passwords
- Accounts that don’t have password complexity requirements
- Accounts with expired passwords
- Accounts that have password expiration approaching
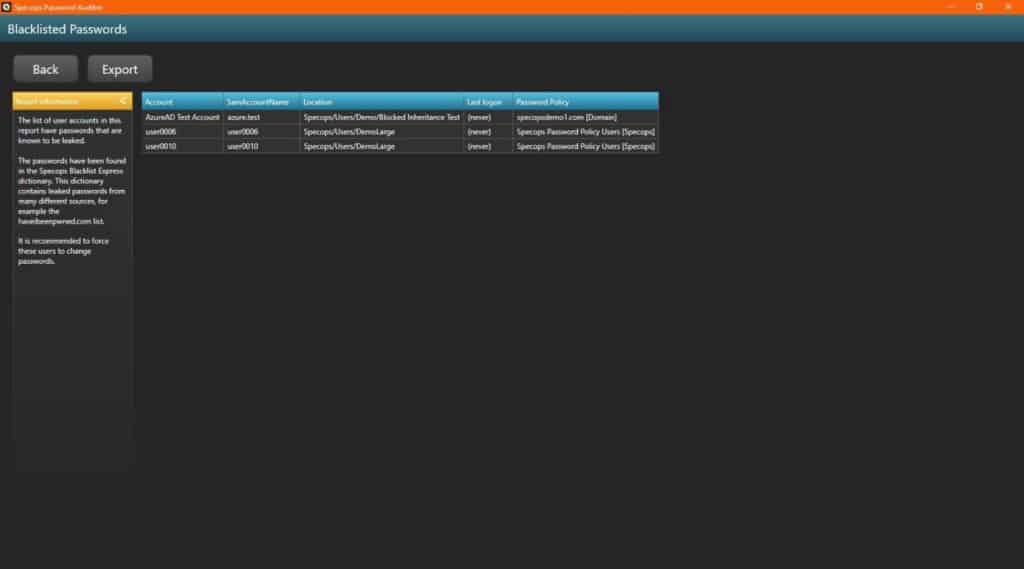
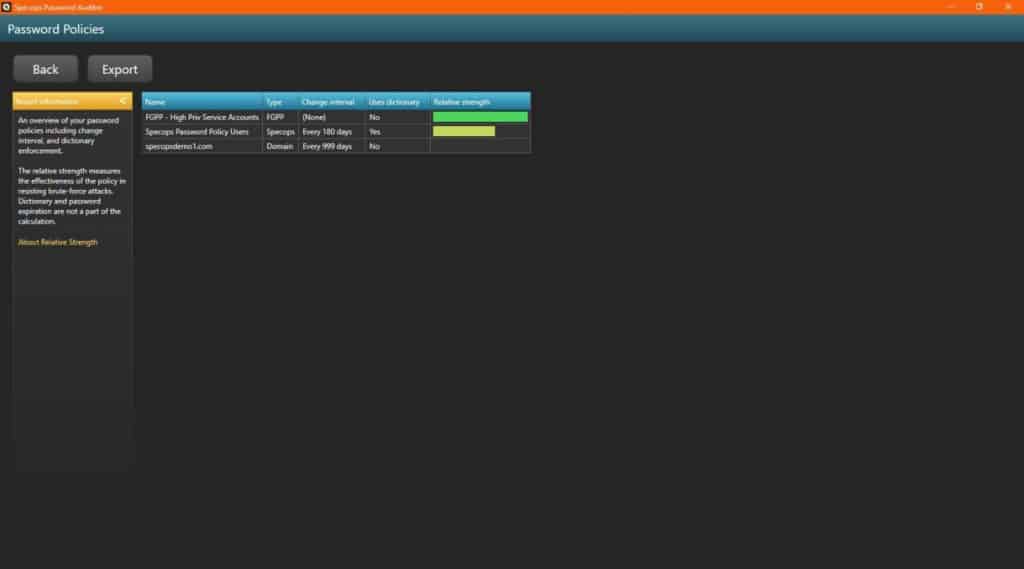
The collected information will be used to display multiple interactive reports depicting the aforementioned vulnerabilities. The reports are exportable to csv files and some useful display features include:
- Sliding timeline to track days since last login for stale admin accounts
- Sliding timeline to track days until password expiration
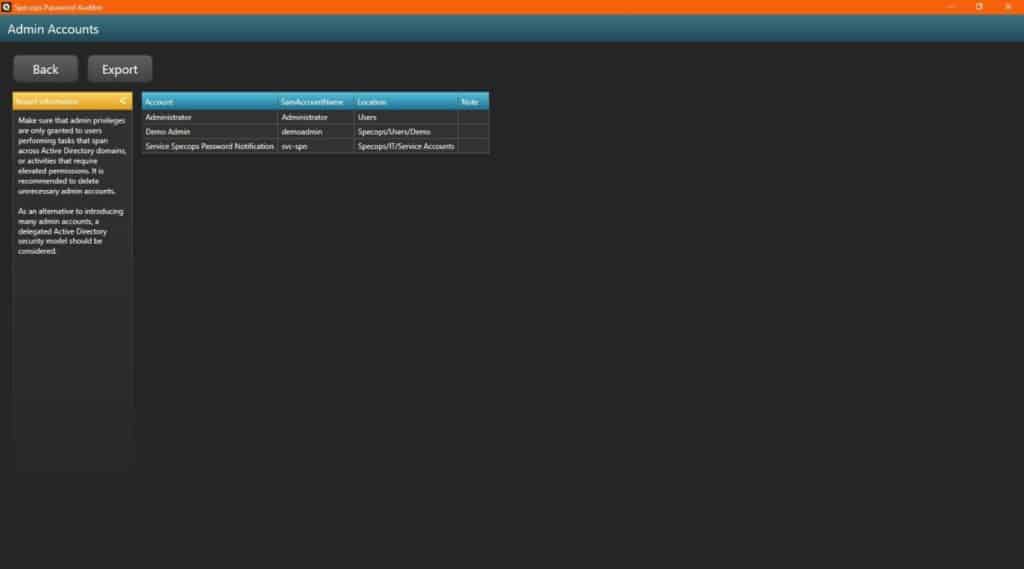
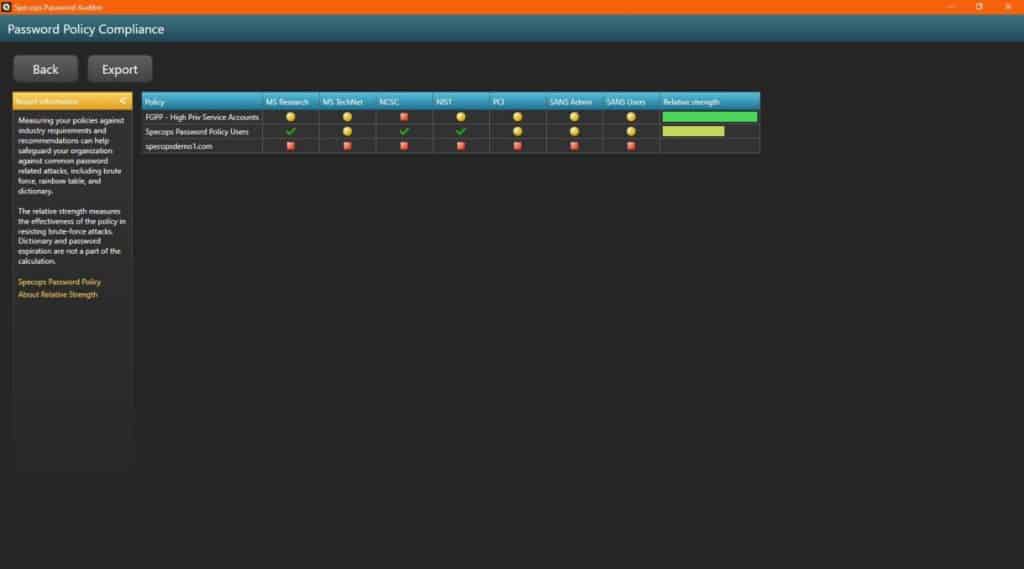
Specops Password Auditor will only read information from Active Directory, it will not make any changes. It will compare password hashes against password hashes in the blacklist and read the Default Domain Password Policy and any Fine-Grained Password Policies if it’s run by a user with administrative privileges in Active Directory.
It will read the Default Domain Password Policy and any Fine-Grained Password Policies if it’s run by a user with administrative privileges in Active Directory.
37. AD FastReporter
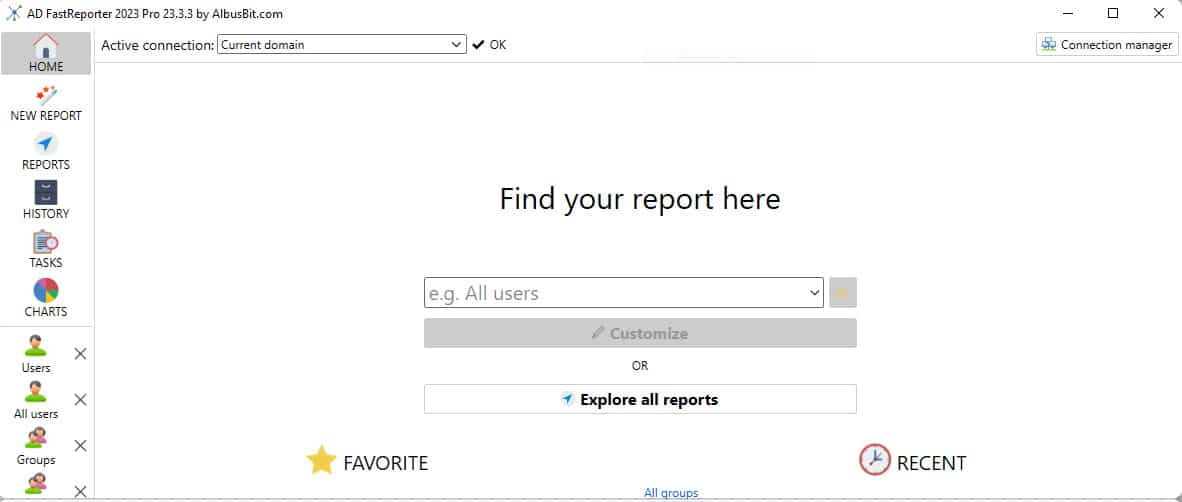
AD FastReporter by Albusbit is a tool that assists you with Generating reports on your AD infrastructure.
You have the option to choose from several report categories including the following:
- Users
- Computers
- Groups
- Exchange
- Contacts
- Printers
- Group Policy Objects
- Organizational Units (OU)
They have pre-built reports that allow you to quickly run a report without much effort and output the information that your looking for fairly quickly. Ad FastReporter utilizes a built-in Local database so there is no overhead or stress on your AD infrastructure when running reports and storing them.
Features that Ad FastReporter includes are as follows:
- Compile and Export AD Reports
- Email Reports directly from within the Program
- Custom Reports using Filters and Granular Options (Pro Version only)
- Compatible with Windows XP Sp3 to 2003 Server
- Over 200 Pre-Built Reports
Why do we recommend it?
Helps ensure all AD reporting modules are working fine. This includes generation, storing, and scheduling modules.
Who is it recommended for?
A good tool for AD admins who are responsible for generating timely reports.
They also give you the option to export reports to CSV, XLSX, and HTML and send reports via Email as well!
This Program has a FREE Version and a Paid version that allows for added Features and Automation (Windows Task Schedular, etc)
38. AD Photo Editor
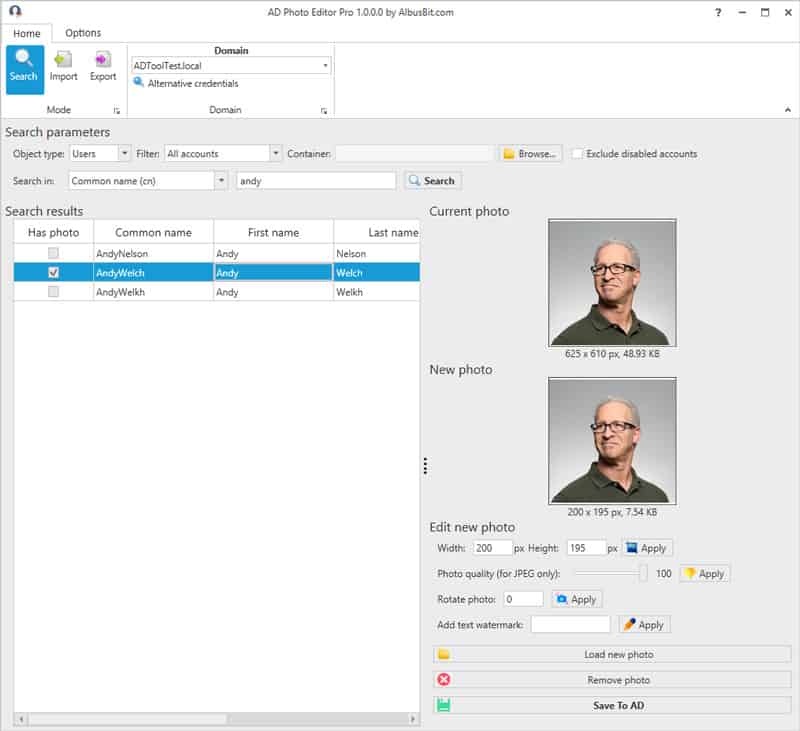
AD Photo Editor from Albusbit.com allows you import/upload custom images for Active Directory User and Contacts as either thumbnailPhoto or jpegPhoto attribute.
These Photos can then be used within the following programs that integrate with AD:
- Outlook Emails
- Outlook Contacts
- Global Address List Photos (GAL)
- Sharepoint
- Lync
- Skype for Business
- and other other 3rd Party App
Why do we recommend it?
Makes it easy to upload user information including photos. Integrates well with many third-party applications.
Who is it recommended for?
A user-friendly application for AD admins to better manage their AD users.
There are 2 Versions of this software – a FREE Version and a Paid version. The Free Version allows you to Find Accounts and Upload/Edit Photos within AD and the Pro Version allows you to Bulk Import/Export Photos to and from Active Directory!
You can Find/Import photos into Active using:
- common name (cn),
- username (sAMAccountName),
- ambiguous name resolution (anr),
- email address (mail),
- employee ID (employeeID),
- or add additional custom attributes
On top of all those benefits, you can also adjust and modify images at upload, including Changing Dimensions, Rotate AD Images, Change Quality (compression) of Images and Add Watermarks to AD images as well.
This program really does have quite a few features that should Cost something, but in all reality is FREE! We definitely like the value in this AD tool!
39. AD Administrator from AlbusBit
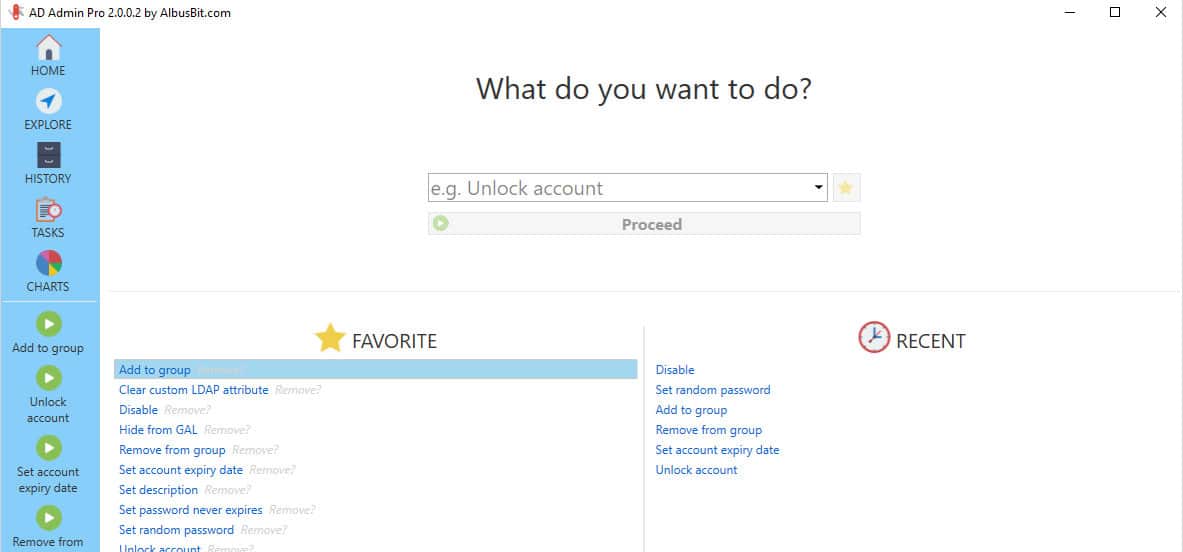
AD Administrator tools from AlbusBit were built with the sole purpose of quickly managing AD Users/Computers for a single interface.
This tool has the following features for Managing Active Directory:
- Manage, Search, View and Edit AD Accounts/Users and Computers
- 16 Built-In Functions for that can be Run against AD, including:
- Disable
- Delete
- Enable
- Move to OU
- Set description
- Set expiry date
- Add to group
- Remove from group
- Remove from all groups
- Hide from GAL
- Set random password
- Set password never expire
- Delete home drive
- Run external script
- Clear custom LDAP attribute
- Disable OWA
- Find Inactive Users/Computer Accts that are Dormant
- Manage Multiple Active Directory Domains from Single Interface
- Export Reports to Excel, CSV and HTML
Why do we recommend it?
Provides a single interface for managing user and computer accounts across your entire AD domain. It’s also a lightweight and affordable desktop app.
Who is it recommended for?
Works well for AD admins of small organizations.
This is a great all-in-one tool for managing AD Users and Accounts from a centralized location and gives you the ability to manage multi-domain environments as well!
40. Sysmalogic AD Reporter Builder
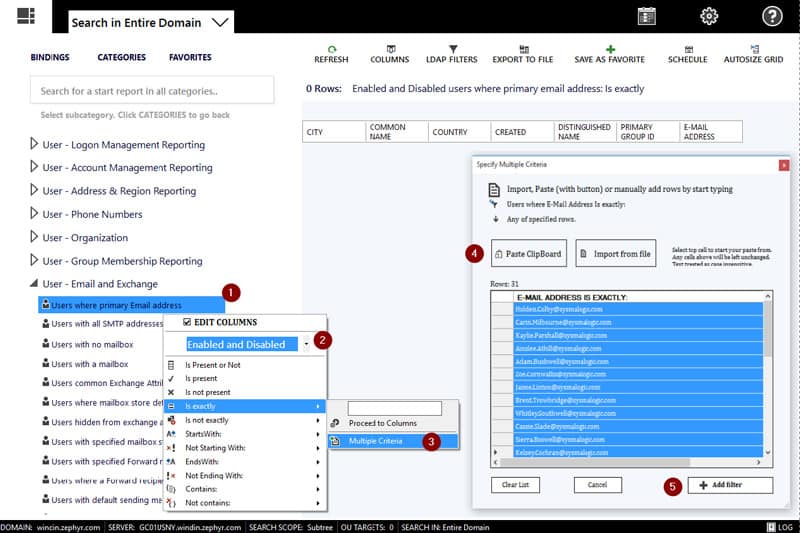
We reviewed Symalogic AD Report builder here and wanted to add this software to this post as well, as they have a FREE Version that gives you some great features to use without having to upgrade to the full version.
To see a Full list of their Features, have a look at the link below – We’ll highlight the features of their Free Versions here:
- Full result view (no row limit)
- No expiration date
- Multi-domain use
- All Built-in reports
- Add or remove columns
- Non-replicated reports
- Set any search target
- Grid text filters/column
- Export report to CSV
Why do we recommend it?
A simple tool to search through AD objects and generate tabular reports as needed. It can also be used across domains.
Who is it recommended for?
A handy tool for AD admins who want to generate reports across multiple domains.
This tool helps you audit Active Directory for Compliance as well as gives you insights and reports into your AD infrastructure, Computers/Users and OU’s!
Grab a Free Download from their site to get started!
In this guide, I’ll show you how to install the RSAT tools on Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server. I’ll also show you how to install RSAT using PowerShell.
To remotely manage Active Directory, DNS, DHCP, and other Windows features you will need the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) installed.
- Install RSAT Tools on Windows 10
- Install RSAT Tools on Windows 11
- Install RSAT Tools on Windows Server
- How to Install RSAT using PowerShell
Note: Starting with Windows 10 October 2018 Update, the RSAT tools no longer need to be downloaded. They are now included with the Windows build and just need to be installed. RSAT tools are only supported on Windows Pro and Enterprise versions of Windows 10 and 11.
1. Open Apps & features and click on “Optional features”

2. Click on Add a feature.
3. Type rsat and then select the RSAT tools you want to install.
In this example, I’ll install the Active Directory, DHCP, and DNS tools.

4. Click install to start the installation.
When the installation is complete the status will say installed.

You can now navigate to the start -> Windows Administrative Tools to open one of the RSAT tools.

Install RSAT on Windows 11
On Windows 11 go to settings and then Apps.
Click on Optional Features.

Click on the View Features button.

Type in rsat and select the tools you want to install.
In this example, I’ll select the Active Directory Domain Services tool.

Click “Next”.
Click “Install”.
When the installation is complete, you can access the tools by going to all apps -> Windows Tools.

Install RSAT on Windows Server
These steps work for Server 2016, 2019, and 2022.
1. Open the Server Manager and click on Add roles and features

Click Next.
Select “Role-based or featured-based installation” and click next
Select your server and click next.
For server roles click Next. (We are not adding any server roles).
For features scroll down to Remote Server Administration Tools).
Select the tools you want to install and click next.

Confirm the selections and click install.
When the installation is complete the tool can be accessed from start -> Windows Administration Tools

Using PowerShell to Install RSAT
You can install individual RSAT tools or all of them using Powershell.
Example 1.Install all RSAT tools run the below command.
Get-WindowsCapability -Name RSAT* -Online | Add-WindowsCapability –Online

Example 2. Install Specific RSAT Tool using PowerShell
To install individual tools you will use the Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name command followed by the PowerShell tool name.
In this example, I’ll install the Active Directory Domain Servers tools using the command below.
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Use the names below to install other RSAT tools via PowerShell.
Active Directory Domain Servers and Lightweight Directory Services Tools: Rsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
BitLock Drive Encryption Administration Tools: Rsat.BitLocker.Recovery.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Active Directory Certificate Services:
Rsat.CertificateServices.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
DHCP Server Tools:
Rsat.DHCP.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
DNS Server Tools:
Rsat.Dns.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Failover Clustering Tools:
Rsat.FailoverCluster.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
File Services Tools:
Rsat.FileServices.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Group Policy Management Tools:
Rsat.GroupPolicy.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
IP Address Management (IPAM) Client:
Rsat.IPAM.Client.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Data Center Bridging LLDP Tools:
Rsat.LLDP.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Network Controller Management Tools:
Rsat.NetworkController.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Network Load Balancing Tools:
Rsat.NetworkLoadBalancing.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Remote Access Management Tools:
Rsat.RemoteAccess.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Remote Desktop Services Tools:
Rsat.RemoteDesktop.Services.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Server Manager:
Rsat.ServerManager.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Shielded VM Tools:
Rsat.Shielded.VM.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Storage Migration Service Management Tools:
Rsat.StorageMigrationService.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Storage Replica Module for Windows PowerShell:
Rsat.StorageReplica.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
System Insights Module for Windows PowerShell:
Rsat.SystemInsights.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Volume Activation Tools:
Rsat.VolumeActivation.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Windows Server Update Services Tools:
Rsat.WSUS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
You can use PowerShell to view which RSAT tools are installed with the following command.
Get-WindowsCapability -Name RSAT* -Online | Select-Object -Property DisplayName, State
Simplify Active Directory Management with AD Pro Toolkit
Managing Active Directory with the RSAT tools has its limitations, such as bulk editing and no reporting. Fortunately, the AD Pro Toolkit simplifies bulk management and reporting with its comprehensive set of Active Directory Tools. The toolkit also includes a built in scheduler to automate tasks and reporting.
AD Pro Toolkit Key Features:
- Bulk import users
- Bulk update users
- Cleanup inactive user and computer accounts
- User management tools
- Quickly unlock and reset user passwords
- Manage user group membership
- Onboard and offboard users
- 200+ built-in Active Directory reports

In addition to the management tools, the toolkit includes over 200 built in Active Directory Reports. Create security reports, compliance reports, customize reports and send email reports.
Try the AD Pro Toolkit for 14 days and experience the All-in-One Toolkit that makes managing Active Directory fast, easy and efficient. Download AD Pro Toolkit now and try it for yourself. Easy to Install and get started in minutes
I hope you found this article helpful. If you have questions leave a comment below.
To start configuring Active Directory from a Windows machine, you’ll need RSAT tools, which include Server Manager and other vital consoles like PowerShell. From the “Server Manager,” you’ll be able to monitor your server and add new key roles and features like AD DS and DNS— tools necessary to start with Active Directory.
In this Active Directory tutorial, you’ll learn how to set up Active Directory from scratch. We’ll provide you with step-by-step guidance into installing RSAT to log and manage AD, and we’ll also go through the process of installing Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) to set up an Active Directory Forest and Domain Controller. Finally, we’ll configure the DNS server zones and wrap up with additional key settings.
Table of Contents
- Installing RSAT Tools
- Installing and running the AD DS On the Windows Server 2019
- Creating an Active Directory Forest and Domain
- Configure the Active Directory DNS server zones
- Additional Active Directory Setup
1. Setup Active Directory with RSAT
To set up Active Directory, you’ll need to have Microsoft Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) running on a Windows machine. RSAT allows IT admins to remotely manage the roles and features in Windows Server 2012 and 2016. RSAT includes the Server Manager, Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-ins, PowerShell cmdlets, consoles, and additional command-line tools to administer Windows Server’s roles and features.
- RSAT is compatible with Windows servers running Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, or Windows Vista.
- You can install RSAT 10 only in the full edition of Windows Professional, Windows Enterprise, or Windows Education versions.
- You cannot install RSAT in Windows Home, Standard edition, or on computers running Windows RT 8.1
How to install RSAT?
If you have the Windows 10 Oct 2018 update (1809) or later, RSAT is already included as a set of Features on Demand.
- Go to Settings > Click on “Apps” > Apps & Features > Manage Optional Features > Add Feature.
- Scroll down, find, and select RSAT: Active Directory Domain Services and Lightweight Directory Tools. Click on Install.
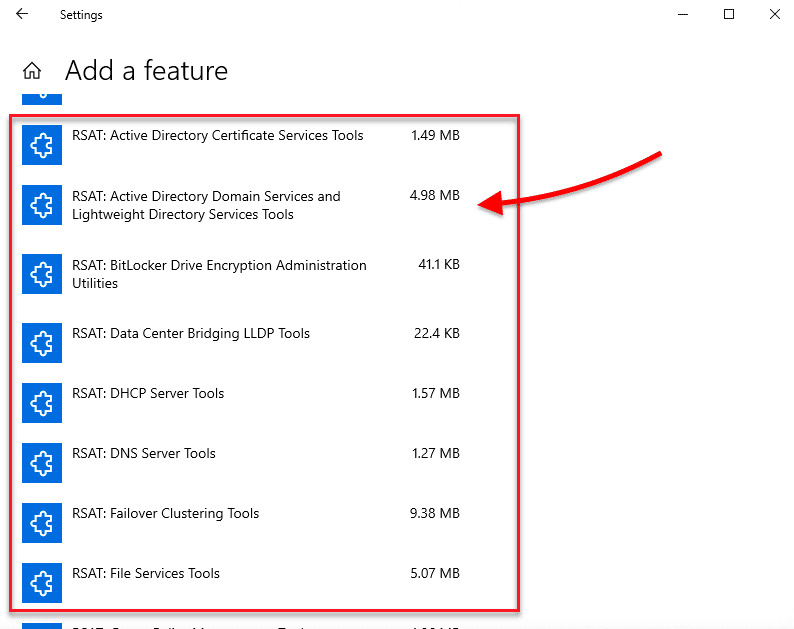
Prior to the October 10 update (1809) – Windows 8 or Windows 10 (1803)
- Download RSAT for Windows 10 from Microsoft’s official site.
- Double-click on the installer (.msu) and click on “Install”. Go on and accept the license terms and wait for the installation to finish.
- Go to Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features > Turn Windows features on or off.
- Scroll down, find, and expand the “Remote Server Administration Tools”.
- Click on Role Administration Tools. Ensure that “AD DS and AD LDS Tools” are selected. Click on “AD DS and AD LDS Tools” to verify that Active Directory Module for Windows PowerShell and AD DS Tools are checked.
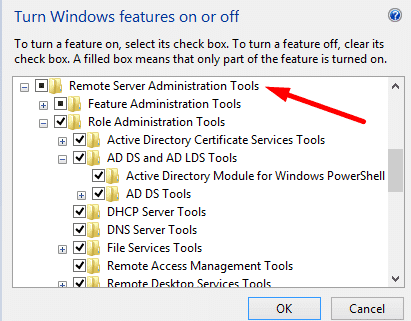
2. Installing and running the AD DS On the Windows Server 2019
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) provide the core Active Directory functions that manage users and computers. The server running the AD DS role is considered the Domain Controller (DC). This server authenticates and authorizes all users and computers within a Windows domain. It also assigns and enforces security policies and pushes software installs and updates.
To set up Active Directory DS on a Windows Server 2019, you’ll need the following:
- The administrative privileges on the server.
- Server with a static IP address.
- Knowing the organizational naming standards.
How to install the AD DS role
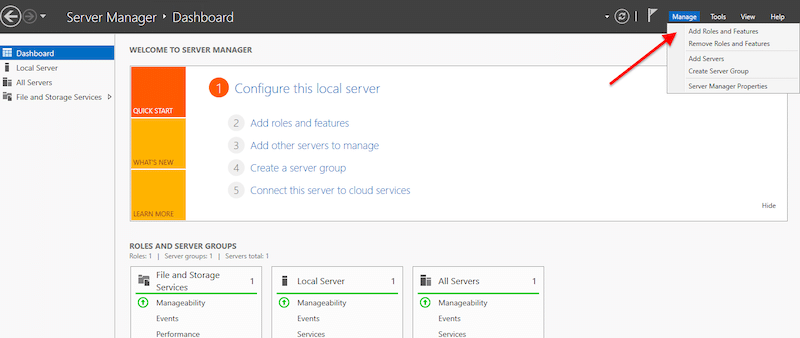
- Open Server Manager > Manage > Add Roles and Features.
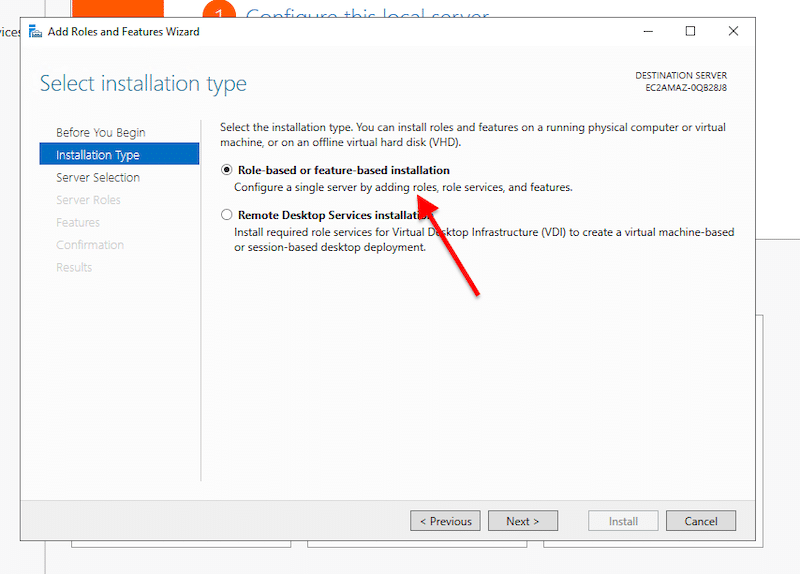
- On Installation Type, choose the “Role-based or feature-based installation” and click on Next.
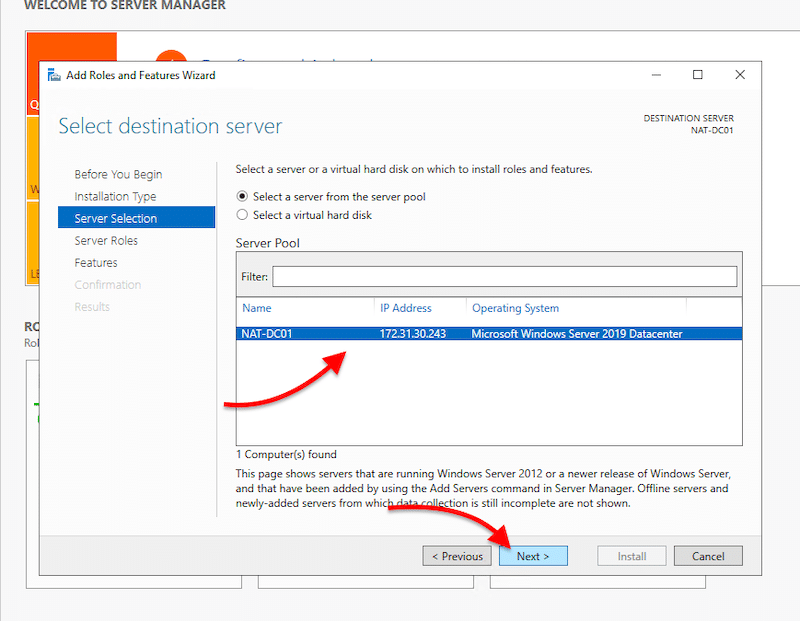
- On Server Selection, you’ll need to select your local server (or any remote server) where you wish to install the AD DS role. This option shows our local server, NAT-DC01, with an IP and the OS version.
- Go ahead and select your server and click on Next.
- On Server Roles, find and select “Active Directory Domain Services”. Once you choose that option, a new pop-up window will appear. This window shows the features required for AD DS that you will need to include. Go ahead and click on “Include management tools” and click on “Add Features”.
- If your AD Server also has the DNS server role, you’ll need to select it here. Scroll down to “DNS Server” and include the required features. For your server to be a DNS server, you’ll need to have a static IP address.
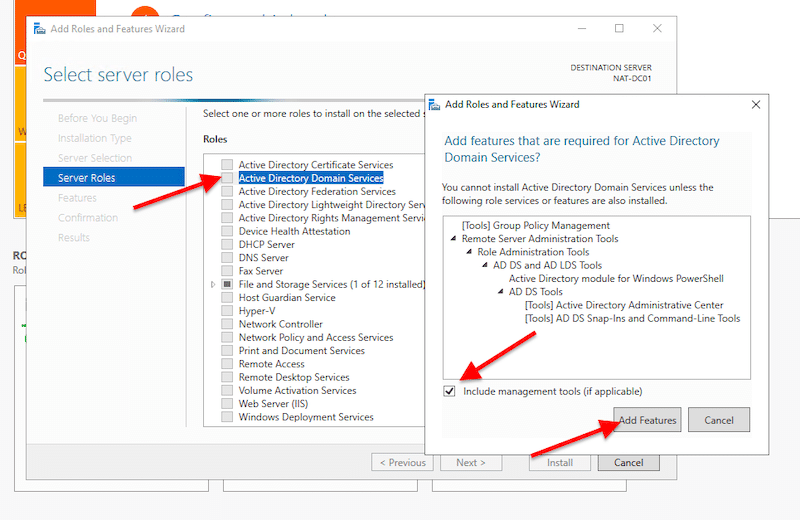
- On Features, AD DS, and DNS Server, click on “Next”.
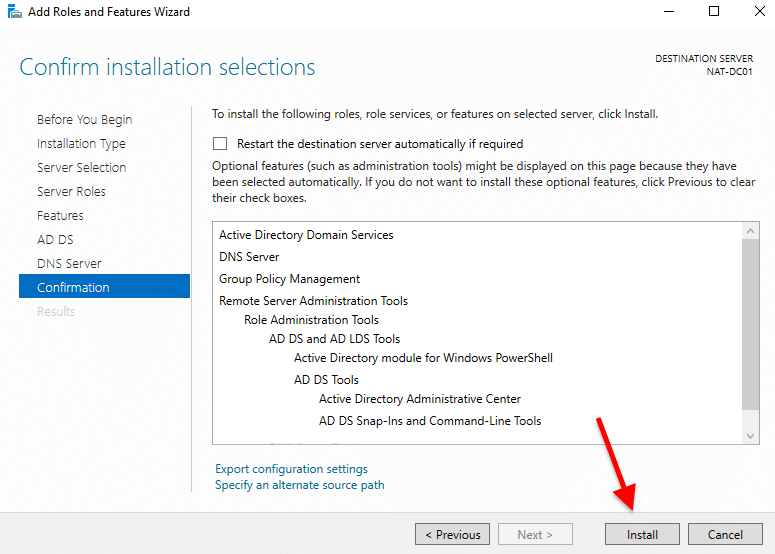
- On Confirmation, verify your configuration and click on “Install”.
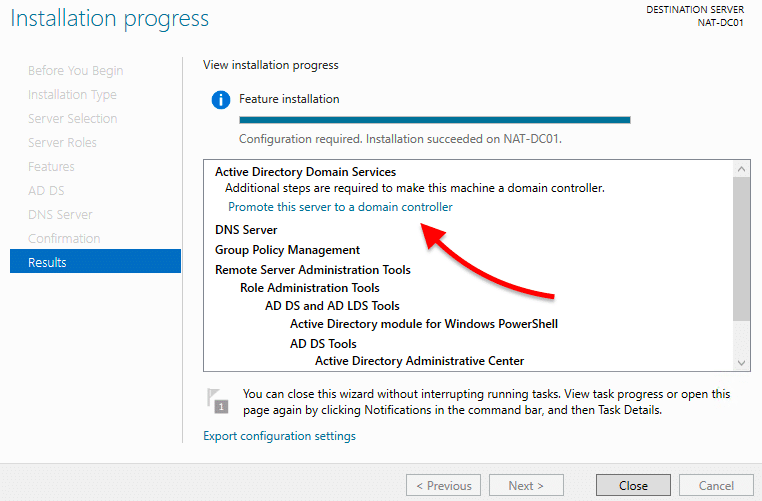
- Wait for your installation to finish. Don’t close the “Results” step on the Installation wizard yet.
3. Creating an Active Directory Forest and Domain
Once the installation is booming, and before closing the Installation wizard, go ahead and select “Promote this server to a domain controller”.
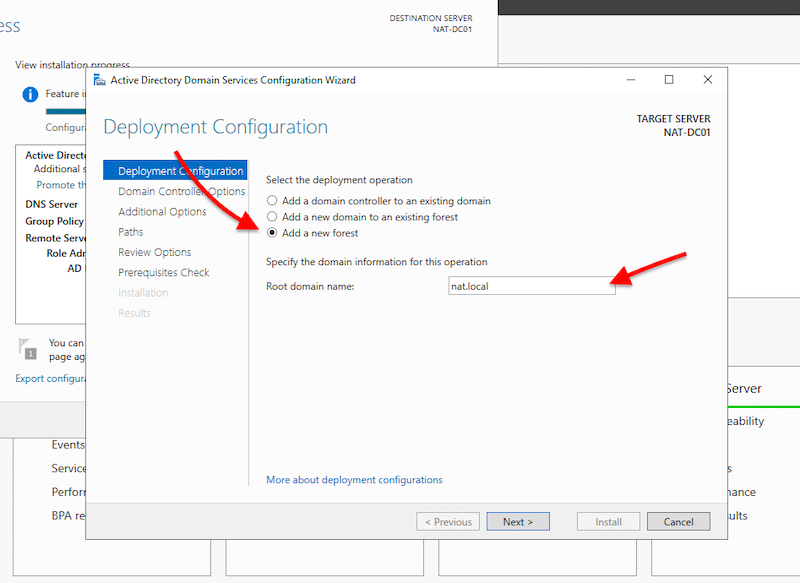
- A new Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard will open. This contains three options for deployment: “Add a domain controller to an existing domain”, “Add a new domain to an existing forest”, or “add a new forest”. Since we are starting from scratch, we are going to create a brand new forest.
Note: Before creating your first Domain Controller, you’ll need a forest, and before a forest, you’ll need a valid root domain. All Active Directory clients use the DNS protocol to find domain controllers, and all domain controllers also use DNS to communicate. An example of an AD root domain name can be something like “nat. local” or “nat-internal.company.com,” where “nat-internal” is the internal AD domain name, and “company.com” is the external resources name.
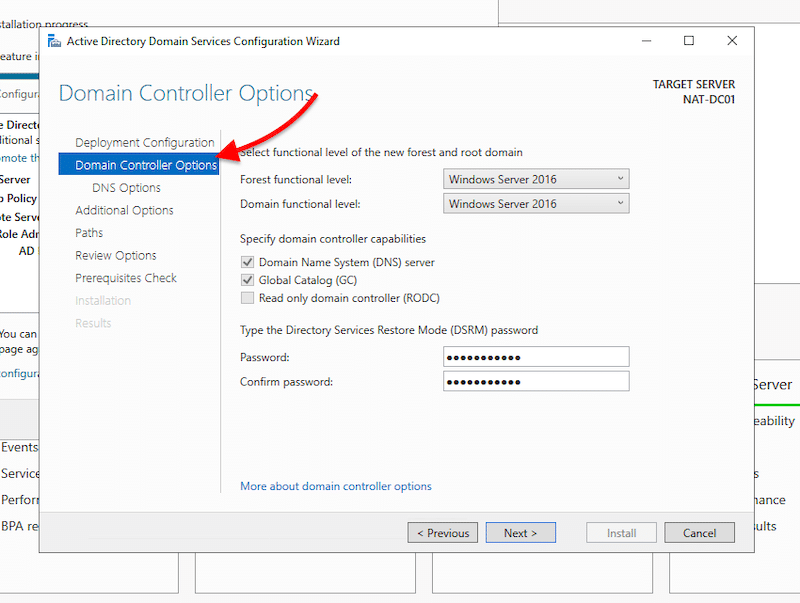
- In the next screen: “Domain Controller Options”, you’ll be able to select the functional level of the new forest and root domain.
Note: The functional levels are the controls that specify the AD DS features used in the domain or forest. As of Nov 2020, the latest available levels are those of Windows Server 2016.
- Specify the domain controller capabilities. Since this is the first AD domain controller, check the DNS server and Global Catalog boxes.
- Give the Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) a password. And click on “Next”.
- Skip DNS Options. No need for DNS Delegation now.
- In Additional Options, you’ll see the NetBIOS domain name taken from the root domain. But you are also free to change it.
- In Paths, you’ll be able to specify the location of the AD DS database, log files, and SYSVOL folders.
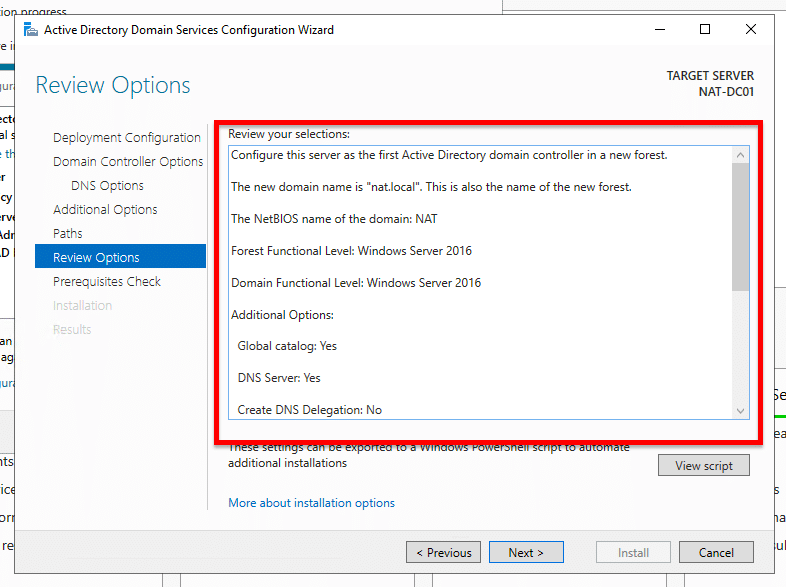
- In review options, you’ll be able to check your configuration and go back if you want to make any changes before installation.
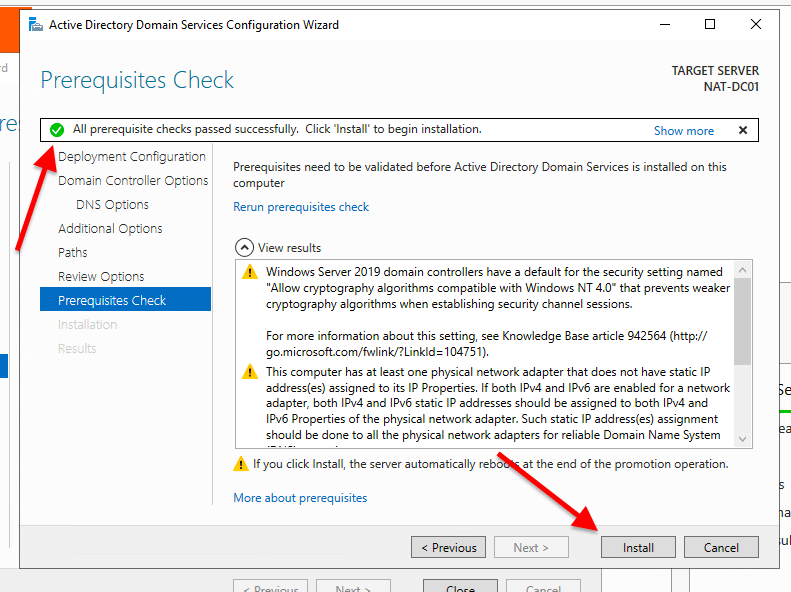
- The Prerequisites Check will show you a checklist with warnings or critical alarms. If the check passes, it will show a green light, and you’ll be able to install AD DS with the new domain controller and forest. You can take care of these warnings later on.
- Click Install. The server will install and restart automatically.
Note: If you got a similar message as mine (this server has one physical network adapter that does not have a static IP address), it is because you didn’t configure the static IP. To do this, go to Control Panel >Network & Internet > Network Connections > Select Ethernet adapter > right-click and go to Properties. In Ethernet Properties, select IPv4 and click on Properties.
- Select “Use the following IP address”. Then, according to your IP addressing scheme, give your server the IP address, subnet, and default gateway information, along with DNS information (your IP).
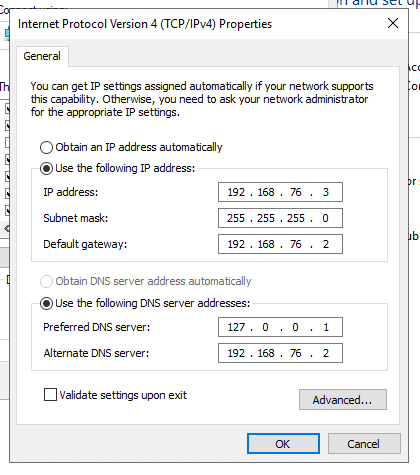
As you might notice, the server is using 127.0.0.1 (loopback IP address) because the server itself is acting as a DNS server. Therefore, you’ll need to change “Preferred DNS Server” to the static IP address of your server (192.168.76.3, for example).
Verify your configuration
- Access the AD DS management console. Go to “Server Manager” and click on “Tools”.
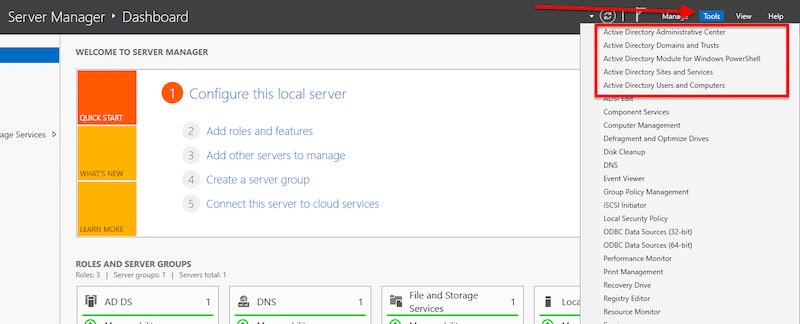
- Open “Active Directory Users and Computers” to ensure the naming and functional levels of your new DC are correct. Next, explore your domain controller (nat. local in our case) by right-clicking on it and opening “Properties”.
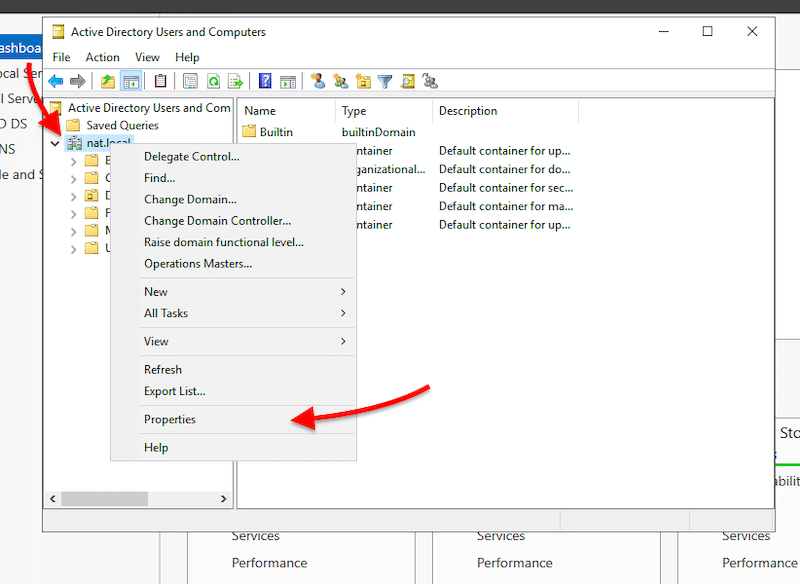
- On properties, verify your DC name and functional level.
4. Configure the Active Directory DNS server zones
You already installed AD DS, the DNS role, and created a new forest and DC. Now you’ll only need to configure the DNS zones.
A DNS zone is formed by resource records (IP blocks and naes) used to resolve DNS queries. The most common zone type in Active Directory is the Active Directory-integrated DNS zone. To learn more about Active Directory and zones, check this great guide to terminology, definitions, and fundamentals.
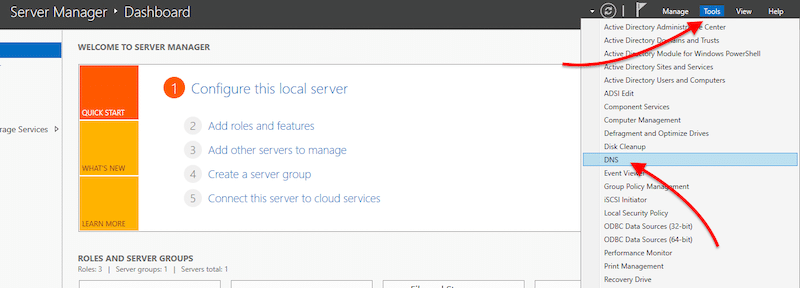
- Open “Server Manager” > Go to “Tools” > Click on “DNS”.
- Within DNS, expand your server and open “Forward Lookup Zones”. You’ll notice two AD integrated primary DNS zones. The “nat. local” is the root domain name we assigned in the previous AD DS configuration process. The _msdcs zone is a separate zone stored in the application partition. This zone is replicated to every DC that is a DNS server.
- As you notice, the Forward lookup zones are already there, but now, you’ll need to create a reverse lookup zone.
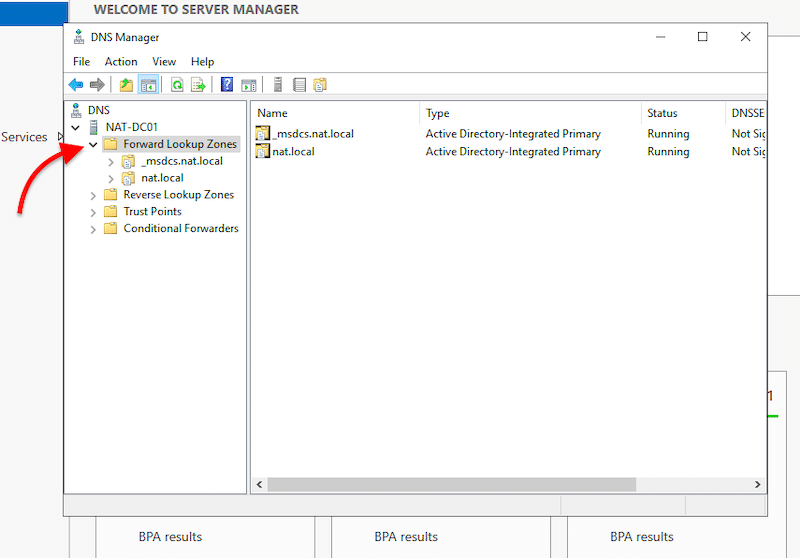
Note: Forward Lookup Zones vs Reverse Lookup Zones? Forward lookup zones resolve names to IP addresses, while reverse lookup zones resolve IP addresses to names.
- Now, let’s configure the reverse lookup zone. First, Right-click on “Reverse Lookup Zone” and click “New Zone…”
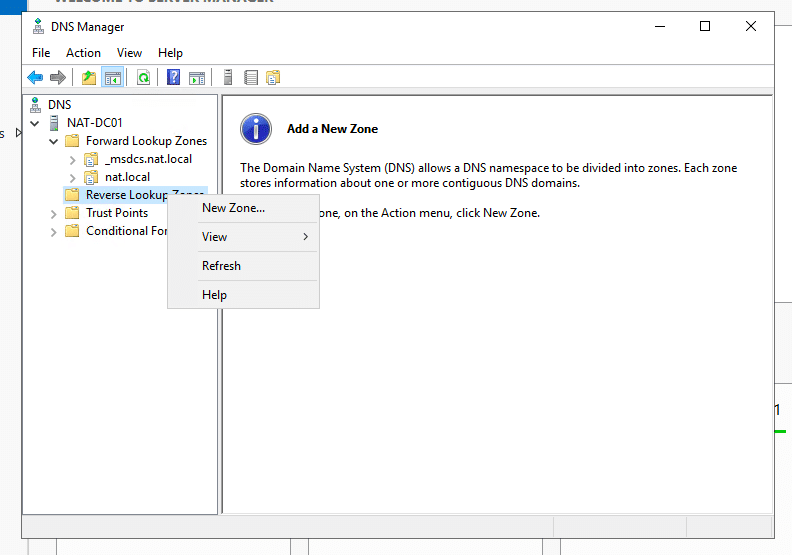
- In the New Zone Wizard, leave the zone type as “primary zone” and check the “Store the zone in Active Directory” box. Then, click “Next”.
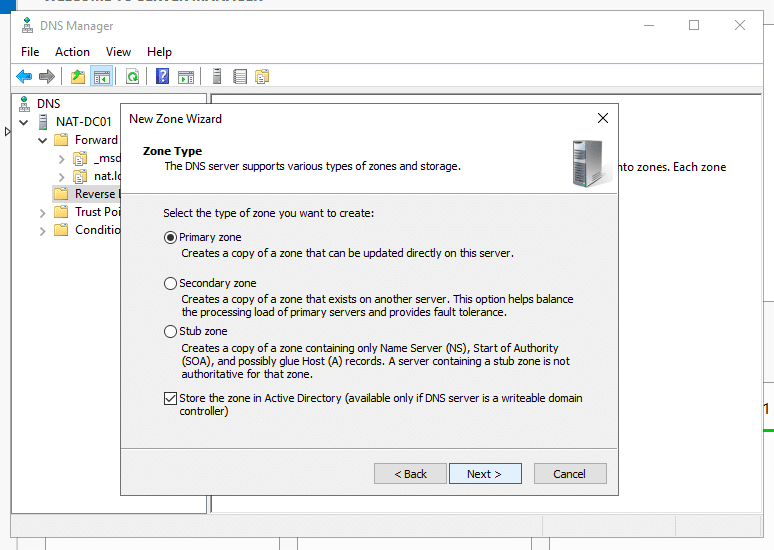
- In “AD Zone Replication Scope,” how do you want DNS data to be replicated? select, “To all DNS Servers running on domain controllers in this domain: (your domain name)”.
- On the next screen, select “IPv4 reverse lookup zone” and click “Next”.
- Specify the Network ID of the reverse zone to help identify the reverse lookup zone. These first three octets are the network ID of your server.
- If you don’t know your server IPv4 address, use the “cmd” utility and the “ipconfig” command.
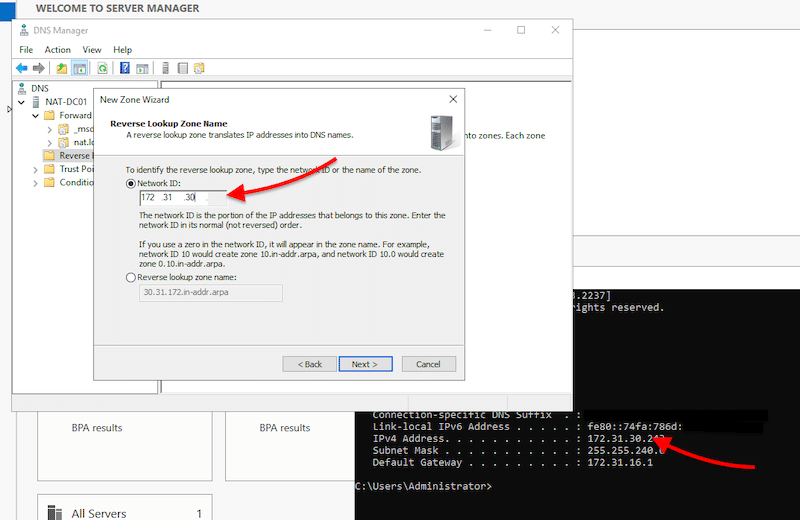
- Click on “Next” > “Next” > and “Finish”.
- Check your new reverse lookup zone. Inside, you should see two DNS resource records, SOA and NS.
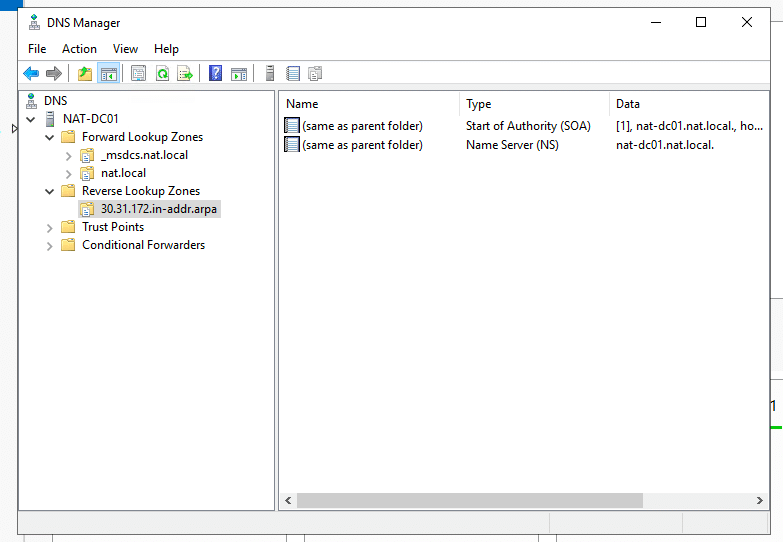
- Update your A record. The A record, also known as the host record or DNS host, is in your domain’s DNS zone file. It makes the connection between domains and matching IP addresses. In other words, the A record contains the hostnames with their associated IPv4 addresses.
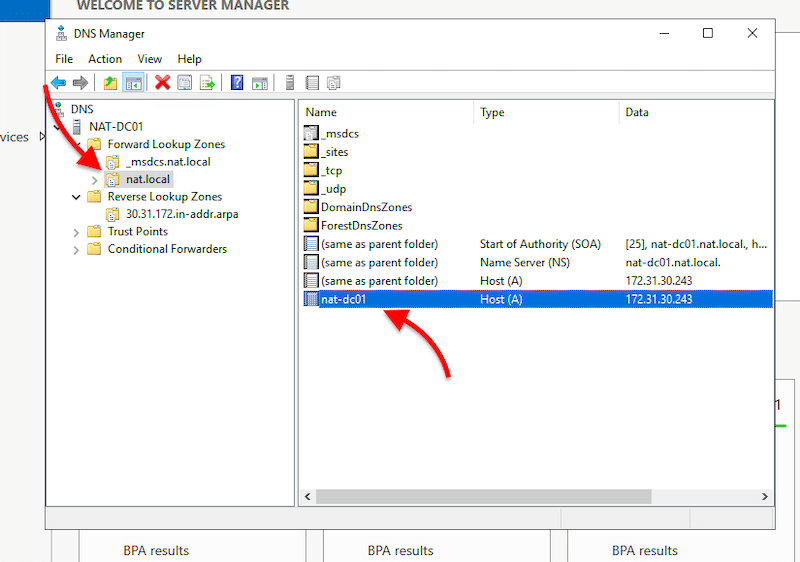
- To enable the reverse lookups, you’ll need to allow the Pointer (PTR) Record. The PTR record creates a pointer that maps the IPv4 address to a hostname.
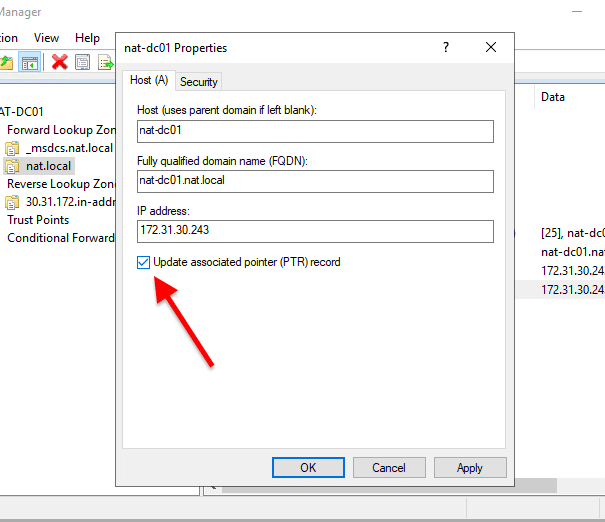
- Right-click on the Host A record and click on “Properties”. A new “Properties” window will appear. First, check the box, “Update associated pointer (PTR) record”. Then, click on Apply > Ok.
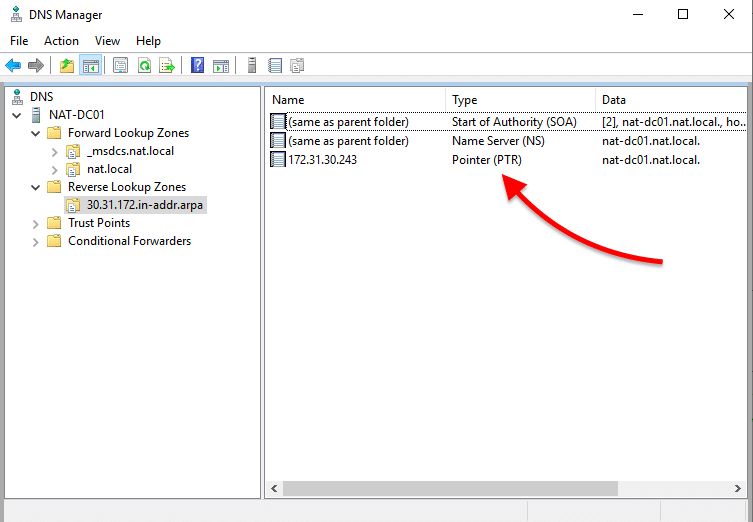
- Verify your reverse lookup zone. If you don’t see the PTR record in the reverse lookup zone, you’ll need to refresh. Right-click on the blank space and click on “refresh”. The new PTR record should appear.
Rename your AD Domain Server
Optional: If you want to configure a new DNS server, you’ll need to rename your current Domain server and create new zones.
- Open DNS Manager, open your server, and expand “Forward Lookup Zones”. Now, you’ll need to create two more zones, so go ahead and right-click on “Forward Lookup Zones” and click on “New Zone”.
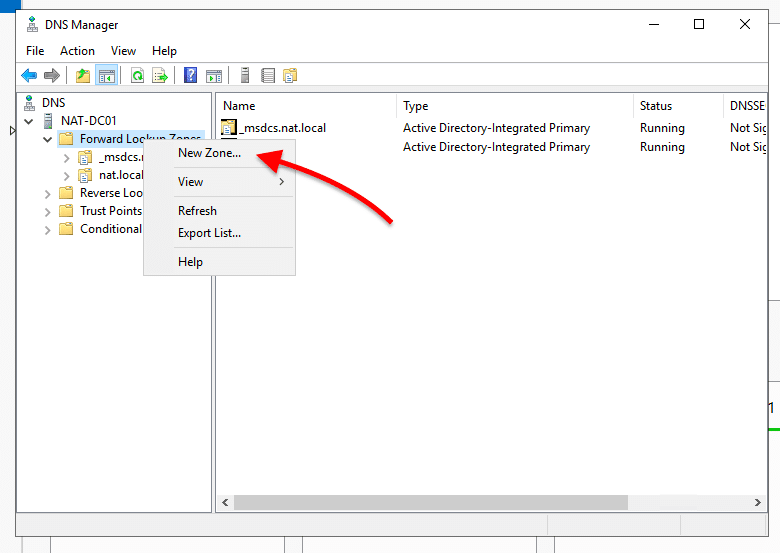
- This will open the “New Zone Wizard”.
-
- In Zone Type, select “Primary Zone” and check on the box “Store the zone in Active Directory”.
- In AD Zone Replication Scope. Select how you want DNS data to be replicated.
- Give your DNS a zone name (netadmintools.com, for instance).
- Leave Dynamic updates by default, and click on next.
- Do the same for the second zone name, but change the naming and replication scope. For the name use an underscore sign (_) + msdcs (for example, _msdcs.netadmintools.com), and for the replication, use the option: “to all DNS servers running on domain controllers in this forest: … ”
- You’ll end up with two new DNS zones.
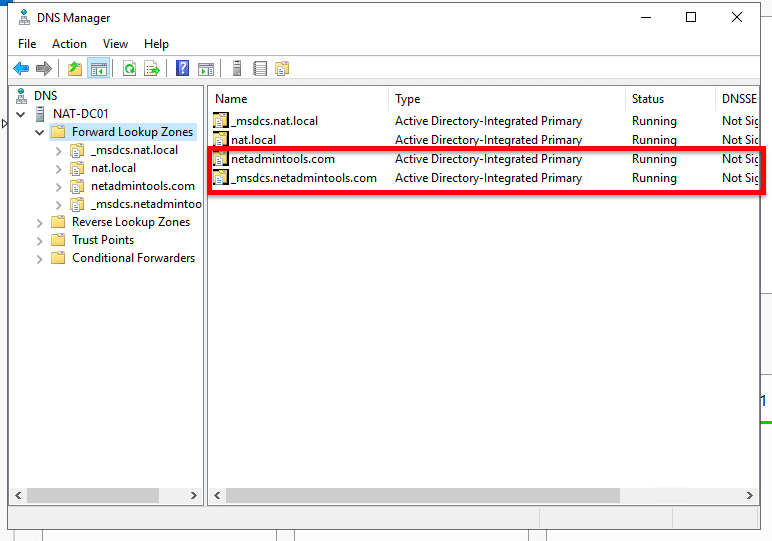
- These two zones are doing nothing now, as each DC in the forest is still using the old zones.
- You’ll need to rename the Active Directory domain name. You can use the PowerShell command-line utility “Rendom /list” to list the naming context in the forest in XML format.
- Open the XML file and replace the DNS name for each Domain Controller in the forest. Then proceed to upload the XML file to the forest partition using “Rendom /upload”. To make the DC change, issue a “Rendom /prepare” and “Rendom /execute” and restart the server.
5. Additional Active Directory Setup
Below are two critical additional Active Directory setups.
Adding a new Domain Controller to an Existing Root Domain
- Make sure both domains have connectivity.
- Create a new domain. Go to Add Roles and Features, select role-based or feature-based installation, and select the local server. On server roles, pick the Active Directory Domain Services.
- Before closing installation, choose “promote this server to a domain controller”. In the next screen: “Deployment configuration,” select “Add a domain controller to an existing domain”. Select your domain through name or credentials.
- On additional options, select “Replicate from” and “your root domain controller”. Then, go ahead and install it.
- Change the DNS server of the new domain controller to the core DNS server.
Create a new Active Directory Users, Computers, or Groups
- Go to Server Manager > Local Server > Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Right-click on your domain name (or within any OU) > “New” > Users, Computer, or Group.
- If you are creating a new user, you’ll need to add the first and last name, the login name, and the password. If you make a new Group, give it a new name.
- To add the new user or computer to the new group, right-click on the new user, “Add to a group” > Go ahead and find and select the group.
Managing multiple AD instances
Active Directory provides the access rights management system in Windows Server for on-premises resource access but it is also built into many other systems. If you use Microsoft 365 on the cloud, you have another implementation to deal with that you can’t manage from the interface that is built into Windows Server. There are other tools that use Active Directory for user account management, such as Google Workspaces and there are AD implementations available on Azure and AWS.
Although all of these different flavors of AD are functionally the same, they are technically separate because of the different infrastructure that supports each service, you can’t merge their administration through the native consoles offered by each package. Instead, you need to set up your user accounts in one system and export it to the others – this is known as replication. With this technique, you can create a consistent list of user accounts across all of the applications and platforms that your business users need to get into to and construct a single sign-on environment.
ManageEngine AD360 – FREE TRIAL
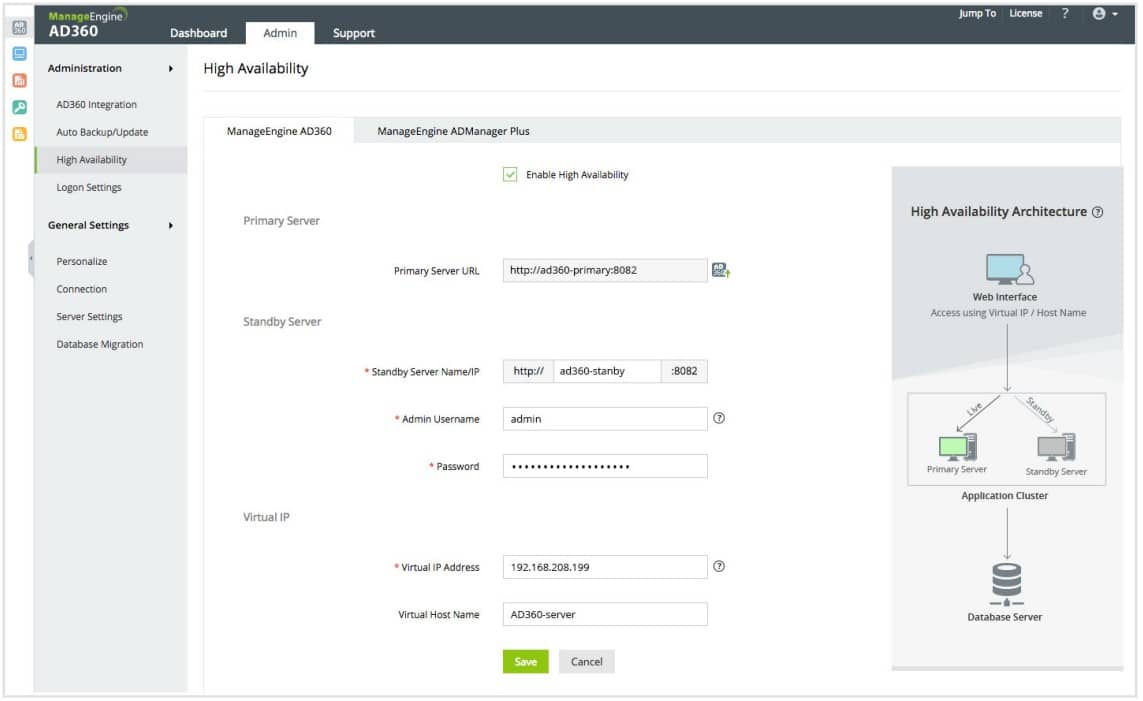
The easiest way to coordinate all of your Active Directory services is through a coordinating third-party tool, such as ManageEngine AD360. The AD360 system is a bundle of AD services and it provides a console that substitutes for the interface of Active Directory. With this system, you manage your standard Active Directory instance through AD360 and that tool ripples those values through to all of your AD instances automatically behind the scenes. The best way to understand the time-saving benefits of such as system is to access the 30-day free trial of AD360.
Features of ManageEngine AD360
ManageEngine AD360 is an integrated Active Directory (AD) management and reporting solution that helps IT administrators simplify their day-to-day tasks. It provides a comprehensive set of features to help manage, monitor, and report on the health and performance of your AD environment. Here are some of its features:
- Keeps Track of Exchange Traffic: With ManageEngine AD360, users can keep track of all aspects of Exchange traffic, including mailbox size, email traffic, OWA consumption, etc. It also allows users to export reports in different formats like PDF, HTML, CSV, and XLS.
- AD Audit and Compliance: Runs AD audits and checks whether significant changes to AD objects comply with IT regulatory compliance standards like SOX, HIPAA, PCI, etc.
- Automated Workflow: ManageEngine AD360 provides automated workflows for automating mundane tasks like creating users or resetting passwords. Further, it helps IT administrators easily create reports on user activity, monitor security events, enforce password policies, and more.
- Single sign-on Management: With AD360, you may implement a single sign-on environment and use the tool’s multi-factor authentication management features. Further, you have access to change the design of the control console. This enables you to grant Help Desk personnel and junior staff partial views so they may fulfill assigned duties without having full access to your user rights.
- Monitor Active Directory’s on-premises and cloud-based implementations: Microsoft Office and Microsoft Exchange Server email systems are all within the authority of AD360’s Active Directory coverage. With the help of remote domain controllers, it can also monitor access to cloud-based services. Further, you may add, remove, change, and suspend access rights with AD360.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine AD360 offers an all-in-one solution for Active Directory management, addressing the challenges that IT administrators often face when dealing with fragmented AD environments. The ability to centrally manage both on-premises and cloud-based implementations means that organizations can maintain a consistent and secure AD environment regardless of where their resources are located. Its comprehensive reporting and auditing capabilities help organizations maintain compliance and understand their AD environment’s health and performance.
Who is it recommended for?
ManageEngine AD360 is ideal for IT administrators and organizations that use multiple AD services, both on-premises and in the cloud. It’s especially beneficial for larger organizations with complex AD environments that need to maintain consistency, security, and compliance across all their AD instances.
Pros:
- With ManageEngine AD360, you can easily set up automated reports for user accounts, computers, groups, GPOs, OUs, and more.
- You can access real-time insights into the health of your network with its advanced monitoring capabilities.
- ManageEngine AD360 offers powerful tools to help you troubleshoot problems quickly and efficiently.
- Helps streamline the Active Directory environment.
- It is a comprehensive Active Directory management solution that helps IT administrators manage and secure their Windows-based networks.
Cons:
- Lacks support for software
- ManageEngine AD360 only works in an Active Directory configuration on Windows Server
ManageEngine AD360
Start a FREE Trial

Microsoft uses Active Directory (AD) extensively, both in its operating system and in its applications. If you are a systems administrator, you are probably already well-versed in the tool. If you are new to using Active Directory for your user permissions system, there are lots of tips and tricks for you to pick up.
Not many people realize that they don’t have to rely on the management utilities of the Active Directory application. There are a lot of useful assistants that you can install to improve your AD management.
Active Directory’s standard facilities don’t provide automation or data tracking. These additional tools are available from third-party software houses, and many of them are free.
Here is our list of the best Active Directory tools:
- ManageEngine ADManager Plus (FREE TRIAL) Groups together the administration of multiple AD instances in one console and automates tasks, such as inactive account detection. Runs on Windows Server. Start a 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine ADAudit Plus (FREE TRIAL) Groups together the administration of multiple AD instances in one console and automates tasks, such as inactive account detection. Runs on Windows Server. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Paessler Active Directory Monitoring with PRTG (FREE TRIAL) Monitors the automated administration activities of the Active Directory environment, such as replication events. Start a 30-day free trial.
- SolarWinds Access Rights Manager This access rights advisor scans through Active Directory and identifies poorly planned user groups and device permissions. Runs on Windows Server.
- SolarWinds Admin Bundle for Active Directory Bulk import user accounts, discover inactive user accounts, and delete them. Runs on Windows Server.
- AD Tidy Provides an easy-to-use front-end for Active Directory and includes task automation, such as account cleanup. Installs on Windows and Windows Server.
- AD Permissions Reporter A useful tool for documenting AD permissions and assessing object structures with free and paid versions. Runs on Windows and Windows Server.
- Specops Password Auditor A nice free tool that provides an attractively presented summary of account statuses and security issues. Runs on Windows Server.
- Recovery Manager for Active Directory Protects AD instances from accidental or malicious damage or loss through automated backup and recovery processes. Available for Windows Server.
- Netwrix Auditor A comprehensive system security monitor that scans for vulnerabilities, including AD object structure assessments. Runs on Windows Server.
- Microsoft Active Directory Explorer A free tool that provides an alternative front-end to Active Directory with search facilities. Runs on Windows and Windows Server.
- Netwrix Inactive User Tracker A free utility that scans an active Directory database for abandoned accounts. Runs on Windows Server.
You can read about these tools in the following sections.
Our methodology for selecting the best AD tools
We’ve broken down our analysis for you based on these key criteria:
- User interface and ease of navigation
- Scope of monitoring and management features
- Compatibility with various operating systems and platforms
- Security features and compliance with industry standards
- Support and resources available for troubleshooting and learning
1. ManageEngine ADManager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
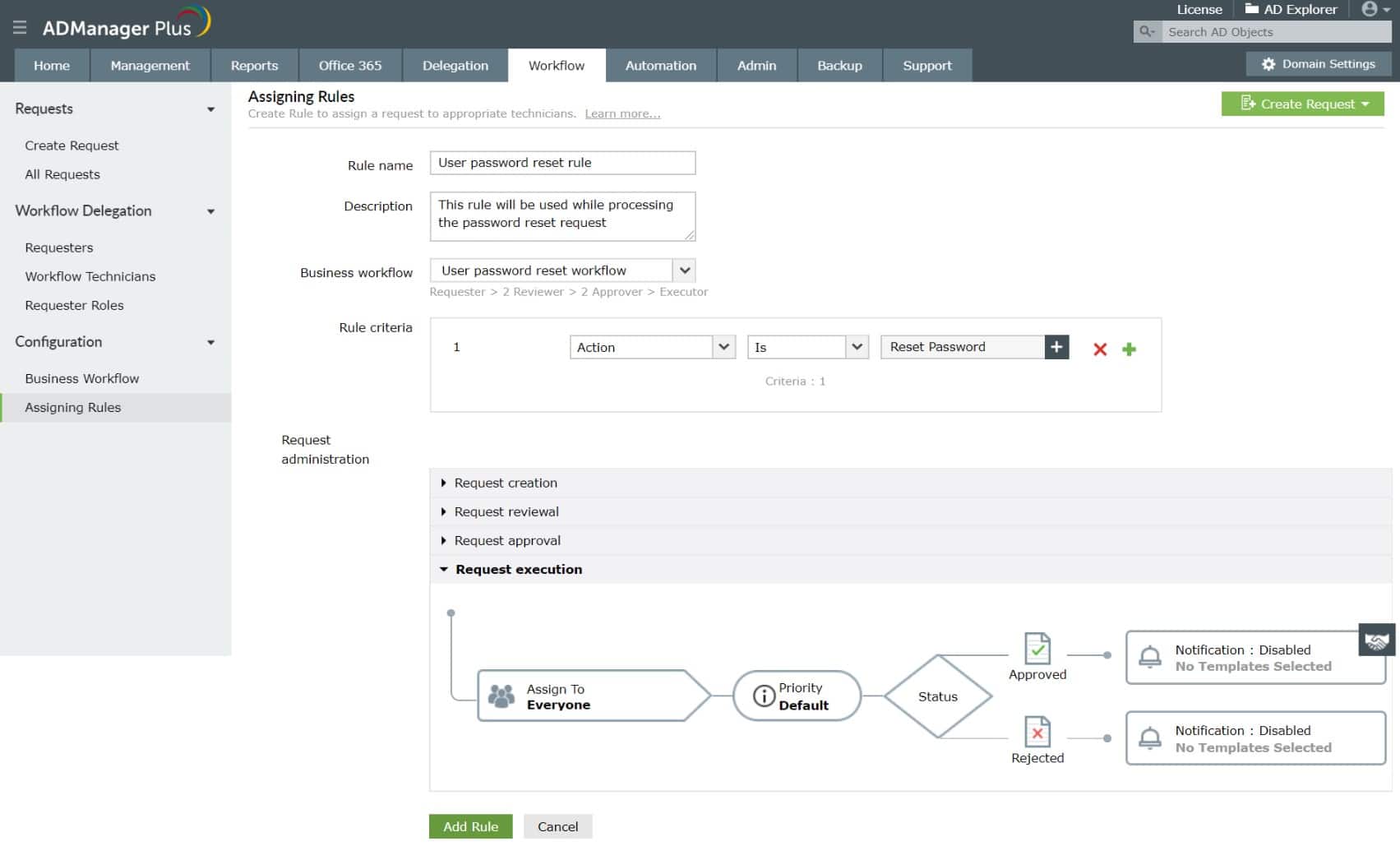
ManageEngine ADManager Plus gives you a front-end to all of your AD domain controllers. The interface acts as a central control console and unifies all of your domain and global administration tasks. This interface is a lot more user-friendly than the standard AD front-end and it has more features and controls. You can manage Office 365, Exchange, G-Suite, and Skype domains through the interface.
Key Features:
- Unified AD domain control
- Mobile access support
- Automates standard AD tasks
- Compliance reporting included
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine ADManager Plus simplifies domain and global administration tasks. It unifies all AD domain controllers, making it easy to manage Office 365, Exchange, G-Suite, and Skype domains. With automation for user and group management, bulk operations, and robust reporting, it’s an invaluable resource for IT administrators, helping maintain compliance with standards like SOX and HIPAA.
This tool is web-based, so you can access it from anywhere. ManageEngine even provides an app that allows you to access the console from your mobile device.
A number of standard Active Directory user, group, and object management tasks can be automated through ADManager Plus and it also enables you to create, adapt, or remove objects in bulk. Facilities in the tool enable you to identify defunct object records and inactive user accounts.
The reporting module of ADManager Plus includes pre-written formats that include compliance reporting standards for SOX and HIPAA among others. Reports can be scheduled to run automatically. The interface can be adapted to Help Desk teams and limited control versions of the dashboard allow you to grant access to the console to support team members safely.
Who is it recommended for?
ManageEngine ADManager Plus is recommended for IT administrators and teams looking to streamline Active Directory management. After testing and using the tool, we found it suitable for small, medium, and large enterprises. The Free edition is ideal for single-domain management, while the Standard edition offers broader functionality. For organizations seeking advanced features and Help Desk modules to improve productivity and compliance, the Professional edition is a great choice.
Pros:
- Centralized control for AD tasks
- Supports mobile access
- Streamlines user and group management
- Compliance-focused reporting tools
Cons:
- Can be overwhelming for new users
There are three editions of ADManager Plus; Free, Standard, and Professional. The Free edition only allows you to manage one domain. The standard version has a wider scope and the Professional edition includes the Help Desk modules. The download for the Free and Professional version is the same. You get a 30-day free trial of the full version and if you choose not to buy at the end of the trial, the package switches to the Free version.
ManageEngine ADManager Plus
Download 30-day FREE Trial
2. ManageEngine ADAudit Plus (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine ADAudit Plus gives deeper reporting and system checking facilities than ADManager Plus. The tool is web-based, so it can be accessed from any computer and also from mobile devices.
Key Features:
- Extensive AD auditing
- Compliance-focused reporting
- Intruder activity tracking
- User connection monitoring
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine ADAudit Plus excels in tracking user connections and identifying suspicious activities, making it a valuable tool for detecting compromised accounts and security threats. The auditing and reporting features align with various industry data security standards, ensuring compliance with SOX, PCI-DSS, FISMA, HIPAA, and GLBA. The Professional edition offers comprehensive Active Directory auditing, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
One of the main duties of ADAudit Plus is to track user connections and log them. Two intruder activities that this service could highlight include the signs of a compromised account, such as logins from far-apart locations, and repeated failed login attempts.
The auditing and reporting feature of the tool is designed in accordance with a range of industry data security standards including SOX, PCI-DSS, FISMA, HIPAA, and GLBA. You get extensive Active Directory auditing functions with the Standard edition of ADAudit Plus.
Who is it recommended for?
ManageEngine ADAudit Plus is recommended for organizations seeking in-depth Active Directory auditing and robust security monitoring. After our own evaluation of the tool, we believe it’s suitable for businesses, regardless of their size. The Free edition is perfect for monitoring up to 25 workstations, while the Standard edition provides extensive Active Directory auditing.
Pros:
- Detailed auditing features
- Strong focus on compliance
- Monitors user activity effectively
Cons:
- Complexity may deter smaller teams
The Professional edition also includes auditing of Active Directory records. There is also a Free edition, which is restricted to monitoring 25 workstations. You can get a 30-day free trial of the Professional edition. When the trial period expires, the system will switch to the Free edition if you don’t want to pay for the Standard or the Professional Edition.
ManageEngine ADAudit Plus
Download 30-day FREE Trial
3. Paessler Active Directory Monitoring with PRTG (FREE TRIAL)
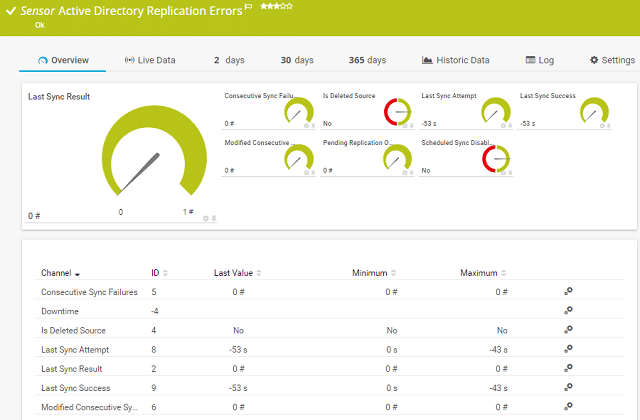
Paessler’s PRTG is a network, server, and application monitoring tool. The system is composed of ‘sensors’. Each sensor is a monitoring utility and PRTG includes sensors that work with Active Directory.
Key Features:
- Multi-domain replication checks
- Permission group management
- Active Directory sensors
- Scalable sensor-based model
Why do we recommend it?
PRTG excels in scrutinizing replication and distribution functions, ensuring seamless coordination and separation within AD domains and forests. PRTG’s ability to monitor user connections, manage permission groups, and represent inheritance of permissions makes it a valuable asset for maintaining a secure and well-organized Active Directory environment.
The Active Directory coordination and monitoring capabilities of PRTG extend to a scrutiny of the replication and distribution functions of complex AD implementations for large organizations. If you deploy a series of AD domain controllers and if you have a forest of domains, the tool can check that replication between servers does not produce errors. It can help you ensure coordination where needed and separation where required.
PRTG notes which users are connected to the system and which are not. It is able to manage permission groups and represent the inheritance of permission between groups. The Active Directory monitoring functions of PRTG requires the activation of four sensors – two of which would need to be customized. Paessler gives all customers the full version of the package.
Who is it recommended for?
Paessler’s PRTG is recommended for organizations of all sizes, particularly those with complex AD implementations and large-scale Active Directory environments. After our thorough evaluation, we believe that PRTG is suitable for businesses looking to monitor and manage their AD effectively. The tool’s pricing flexibility, which includes a free version for smaller deployments, makes it accessible to a wide range of organizations. Whether you have a small AD infrastructure or a complex network of domain controllers, PRTG’s monitoring capabilities can help ensure the smooth operation of your Active Directory.
Pros:
- Effective in large, complex environments
- Customizable sensor options
- Monitors user connectivity and permissions
Cons:
- May be too intricate for small setups
The price bands for the tool are dictated by the number of sensors that get activated. You can use PRTG for free if you only activate up to 100 sensors. You can get a 30-day free trial of PRTG with unlimited sensors. The software installs on Windows Server.
Paessler Active Directory Monitoring with PRTG
Start a 30-day FREE Trial
4. SolarWinds Access Rights Manager

The Access Rights Manager is part of the large SolarWinds stable of IT infrastructure management tools. SolarWinds is very competent at producing network and server monitoring systems and the Permissions Analyzer meets that high standard. This tool can be installed on all versions of Windows Server.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive user group visualizations
- Automated user account management
- Compliance and security analysis
- Efficient permission tracking
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Access Rights Manager excels in providing robust Active Directory management. As part of the SolarWinds suite, it stands out for its capabilities in simplifying user group management and permission visualization. This tool is incredibly user-friendly and offers features for Active Directory, Microsoft Exchange, Windows File Share, and SharePoint management. It facilitates user account creation through automated workflows and forms and even includes a self-service portal for password management.
The tool has some great visualizations of user groups and inherited permissions. This is a factor that is often difficult to keep track of, so the attractive layout of the Access Right Manager dashboard is a great help. The tool will help you to manage:
- Active Directory
- Microsoft Exchange
- Windows File Share
- SharePoint
You will be able to automate user account creation steps through forms and workflows and also keep track of the group profiles that you operate on your system. The provisioning utilities of the tool include a self-service portal to enable users to manage their own passwords and request different access levels.
Analysis functions help you confirm data security standards compliance and meet service level agreements. The tool includes logging features that enable you to track user activity and identify the efficiency of your permissions system.
SolarWinds offers a 30-day free trial of the Access Rights Manager. However, if you want to get an access manager without ever paying for it, you should check out the SolarWinds Permissions Analyzer for Active Directory. This is a “lite” version of the Access Rights Manager that is free to use.
The straightforward layout of the interface helps you keep track of user groups and permission inheritance. These concepts are relatively simple to understand, but can quickly become unmanageable if you don’t have a tool that can properly express the relationship between users, groups, and parent groups.
As the name of the tool suggests, there are also analytical facilities in the utility. You can get filtered data out of the tool to see which permissions have been allocated to which groups. You don’t get the comprehensive standards auditing, snazzy graphics, or security features of the Access Rights Manager with the Permissions Analyzer, but you do get a useful, easy-to-use AD management utility.
Who is it recommended for?
SolarWinds Access Rights Manager is recommended for IT administrators and organizations looking for efficient Active Directory management and permissions analysis. Small to large enterprises can benefit from its straightforward interface and automation capabilities, which streamline user group and permission tracking. Whether you need to manage Active Directory, Microsoft Exchange, Windows File Share, or SharePoint, this tool offers comprehensive solutions. SolarWinds Access Rights Manager caters to those who value user-friendliness and efficiency in Active Directory management, making it a strong recommendation for IT professionals and organizations of all sizes.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface for complex tasks
- Automates user account management efficiently
- Ensures compliance with data security standards
- Detailed logging for user activity monitoring
Cons:
- Can be complex for smaller organizations
5. SolarWinds Admin Bundle for Active Directory
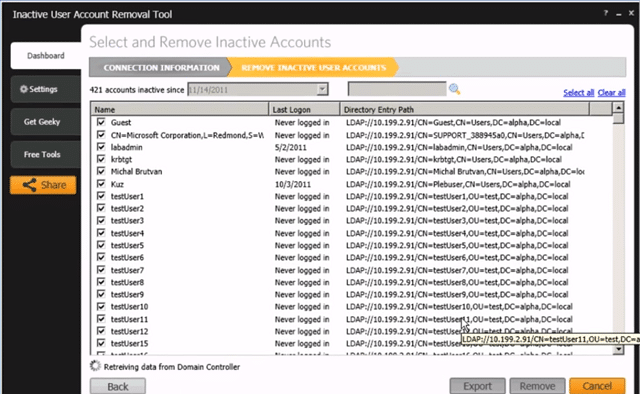
SolarWinds gives you another free option for monitoring AD with the Admin Bundle for Active Directory. This tool runs on all versions of Windows Server.
Key Features:
- Bulk user account management
- Activity monitoring for accounts
- Simplifies AD cleanup
- Free and efficient
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend the SolarWinds Admin Bundle for Active Directory as a valuable set of free tools for Active Directory monitoring. The User Import Tool simplifies the process of creating user accounts in bulk by importing data from CSV files. Although not as feature-rich as the Access Rights Manager, this free bundle offers essential functions for Active Directory management.
The pack includes three tools:
- Inactive User Account Removal
- Inactive Computer Account Removal Tool
- User Import Tool
With these three utilities, you can create user accounts in bulk by importing them into Active Directory in a CSV file. The two activity monitors will show you which user accounts have not had any activity on them and which devices have not been accessed for a while. This will enable you to identify accounts that should have been deleted and facilities that have probably been retired.
These three tools are not as impressive as the Access Rights Manager. However, it is free and it will help you eliminate dead accounts and defunct records in your AD implementation.
Who is it recommended for?
The SolarWinds Admin Bundle for Active Directory is recommended for IT professionals and organizations seeking free tools for Active Directory maintenance. Small to large enterprises will find value in the included utilities, which help identify and remove inactive user and computer accounts, as well as streamline user account creation. If your goal is to ensure a clean and efficient Active Directory implementation without the expense, this bundle is an excellent choice. It simplifies account and device management, making it suitable for IT teams looking for cost-effective solutions for Active Directory maintenance.
Pros:
- Efficient bulk account management
- Identifies inactive accounts easily
- Free and straightforward to use
Cons:
- Less comprehensive than paid tools
6. AD Tidy

Cjwdev produces a few Active Directory tools that any systems administrator would find useful. The developer is a former sysadmin who started developing tools for himself and then decided to share them with the world. AD Tidy enables you to check on the status of user accounts and objects listed in your domain controller, and accounts that show no activity can be removed.
Key Features:
- Efficient account status checks
- Flexible account management tools
- Exportable search results
- Free and paid versions available
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend AD Tidy for its user-friendly interface and efficient management of Active Directory user accounts and objects. As part of our testing and review, we found that AD Tidy provides valuable capabilities, including checking the status of user accounts, disabling, moving, and removing members from groups, and even resetting passwords to random characters. This tool offers a more intuitive interface compared to the native Active Directory front-end and allows easy export of search results to XLS or CSV files. It also offers the convenience of saving and re-executing searches and supports seamless navigation between domains and organizational units, making it an essential tool for systems administrators.
The tool’s interface has the ability to disable, move, and remove members from groups. It is also possible to reset the passwords of accounts to strings of random characters. This small utility offers a better interface to your domain controllers than the native Active Directory front-end. Search results from the tool can be exported to XLS or CSV files. Searches can be saved in order to be re-executed with ease.
You can switch between domains and even hop between organizational units, as well as display the records from the domain controllers to search timestamps in order to identify inactivity. Two utilities built into the tool give you extra checks on the continued existence of an object. These are a DNS lookup and a Ping test.
Who is it recommended for?
AD Tidy is recommended for systems administrators and IT professionals who work with Active Directory, regardless of the organization’s size. After personally evaluating this tool, we believe it is a valuable addition to any admin’s toolkit, simplifying user account management and object cleanup in the domain controller. The availability of both free and paid versions ensures accessibility to a wide range of users, and its compatibility with various Windows versions makes it a versatile solution for AD maintenance and optimization. Whether you need to identify inactive accounts, manage group memberships, or streamline your AD tasks, AD Tidy offers practical features for efficient administration.
Pros:
- Simplifies AD management and cleanup
- Search results are exportable
- User-friendly interface
Cons:
- Automation features limited to paid version
The tool is available in free and paid versions. The free version has all of the features of the paid edition except for the ability to reverse actions and the availability of automation rules, which create automatic clean up actions. Both editions run on any Windows version above XP.
7. AD Permissions Reporter
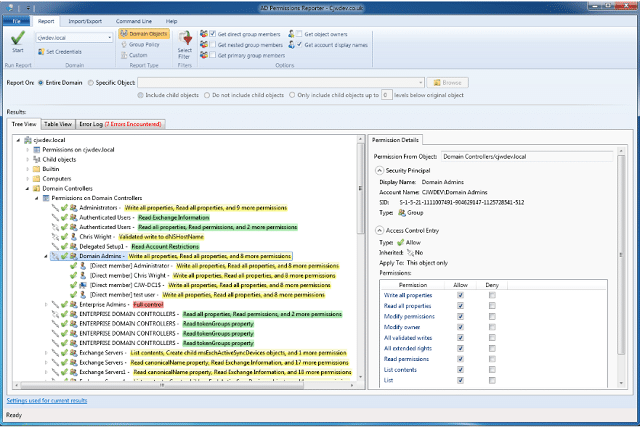
Cjwdev has a modular approach to Active Directory management. There are actually several tools for AD available form this developer. Others include AD Info, which is a query tool for Active Directory domain controllers.
Key Features:
- Detailed permissions reporting
- Free and paid options
- Exportable reports
- Integrates with other AD tools
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend AD Permissions Reporter for its valuable role in Active Directory management. During our own testing and usage of this tool, we found it to be a great asset for querying and listing permissions on objects within an Active Directory domain. Its modular approach, along with various other tools from Cjwdev, caters to the specific needs of administrators. In the case of AD Permissions Reporter, it streamlines the often complex task of understanding and managing permissions on documents and objects in the Active Directory.
There is also a utility, called AD Photo Edit, which inserts images into AD records, so you can associate a picture of a user with each account. The Group Manager helps you manage the allocation of members to groups in Active Directory. AD Account Reset Tool enables users or administrators to reset passwords.
The AD Permissions Reporter is a great little tool for querying the permissions available on objects in your Active Directory domain. Specifically, this reporter will list the permissions granted on documents within your system.
Who is it recommended for?
AD Permissions Reporter is ideal for systems administrators and IT professionals who work with Active Directory and need to gain insights into permissions granted on objects. After our firsthand experience with this tool, we believe it is suitable for organizations of all sizes. The availability of both free and paid versions ensures accessibility for a wide range of users. Whether you require efficient reporting of document permissions or integration into scripts for automated searches, AD Permissions Reporter offers practical features that enhance the management of Active Directory permissions.
Pros:
- In-depth permissions analysis
- Export capabilities enhance utility
- Complements other AD management tools
Cons:
- More specialized than comprehensive tools
The tool is available in free and paid versions. You can export search results to CSV and HTML format in the free version and ADPR and XLS formats are also available in the paid version. The paid version is available in a command line version to enable searches of the object permissions to be integrated into scripts.
8. Specops Password Auditor
Specops specializes in password verification and fortification tools. The company’s Password Auditor is a free tool that runs on Windows Server 2008 and higher.
Key Features:
- Password policy analysis
- Identifies weak passwords
- Standards compliance aid
- Free for Windows Server
Why do we recommend it?
We can recommend Specops Password Auditor based on our extensive testing and its specialized approach to password verification and strengthening. This robust tool operates seamlessly within Windows Server environments, allowing organizations to significantly enhance their password security. It facilitates the creation and enforcement of stringent password policies, improving overall network safety. By scanning Active Directory entries, it identifies weak passwords and inactive user accounts, presenting the results in detailed, actionable reports. Specops Password Auditor doesn’t include remediation scripts, but its efficiency, combined with our testing, underscores its significance in bolstering system security.
This utility strengthens security by helping you to design a password policy, which includes requirements to renew passwords and the enforcement of password compositions that are harder to guess or crack. The utility operates on Active Directory entries.
The tool will search through your domain controllers, identifying accounts with weak passwords. The tool will also identify inactive user accounts. The results of this scan are a series of reports, which will identify accounts that represent security weaknesses. These system checks and reports also enable you to prove standards compliance for NIST, PCI, Microsoft, and SANS.
Specops Password Auditor doesn’t include remediation scripts, so you will have to address stale accounts and weak password issues with some other tool, or manually. However, this tool is quick and easy to follow so it will prove an essential utility for your system security.
Who is it recommended for?
Our comprehensive testing affirms that Specops Password Auditor is ideal for IT professionals and organizations committed to optimizing password security in Windows Server environments. While it lacks remediation scripts, this tool offers a quick, user-friendly solution for identifying and rectifying security weaknesses associated with passwords and user accounts. Small to large enterprises will find its features invaluable, making it a highly recommended asset for fortifying system security while adhering to industry standards.
Pros:
- Enhances password security
- Free and easy to use
- Helps in achieving compliance
Cons:
- No remediation features included
9. Recovery Manager for Active Directory

Recovery Manager for Active Directory is a comprehensive backup system to protect your authentication system. This tool will run on Windows Server versions from 2008 and Windows Vista and later. There is also an app so that you can contact the manager’s console from a mobile device.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive AD backup
- Supports Azure AD
- Mobile app access
- Cloud backup capabilities
Why do we recommend it?
Recovery Manager for Active Directory is designed to safeguard your authentication system, ensuring the resilience and security of your Active Directory. It runs seamlessly on various Windows Server versions, including 2008 and later, offering flexibility in deployment. The tool provides the critical ability to back up and restore Active Directory databases, with backup locations including network-accessible destinations and even the Cloud. Notably, it supports Azure Active Directory backup, enabling organizations to choose between on-premises and Cloud-based solutions. With scheduled backup transfers during off-peak hours, this tool enhances disaster recovery preparedness.
The recovery manager will back up your Active Directory databases and restore them. The location of the backup can be anywhere that is contactable over the network, including on the Cloud. You can also backup Azure Active Directory. So, you can have either or both your AD server and your backup server on premises or in the Cloud. Backup transfers can be scheduled for quiet hours.
Who is it recommended for?
Our hands-on assessment confirms that Recovery Manager for Active Directory is an invaluable solution for IT professionals and organizations seeking to fortify their authentication systems and prepare for data recovery scenarios. While it comes at a cost, the tool offers a 30-day free trial for exploration. The availability of a global implementation version makes it suitable for organizations of all sizes and geographical scopes. With a range of AD-related products from the same software house, including Enterprise Reporter for Active Directory, Change Auditor for Active Directory, Active Roles, Active Administrator for Active Directory Health, and GPOADmin, Recovery Manager offers a comprehensive suite for Active Directory management and security.
Pros:
- Reliable AD backup and restore
- Cloud and Azure AD support
- Accessible through a mobile app
Cons:
- More suitable for larger organizations
This is a paid tool, but you can get a 30-day free trial. There is also a version of Recovery Manager for Active Directory that specializes in global implementations. The software house that produces the Recovery Manager for Active Directory has a large range of AD-related products. These include Enterprise Reporter for Active Directory, Change Auditor for Active Directory, Active Roles, Active Administrator for Active Directory Health, and GPOADmin.
10. Netwrix Auditor
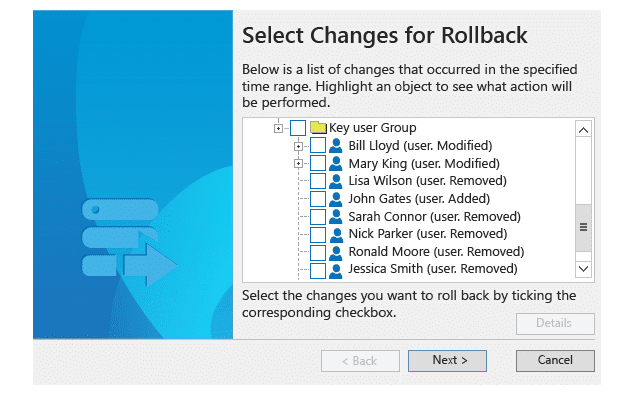
Netwrix Auditor is not specifically tailored to Active Directory. However, it does include functions that manage Active Directory entries. The tool is a system-wide auditing utility that will help you protect your network and servers from intrusion and accidental damage.
Key Features:
- System-wide auditing
- AD and Azure AD support
- Compliance-focused
- Active Directory backup
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend Netwrix Auditor as an essential addition to your network and server protection toolkit. While it isn’t exclusive to Active Directory, this comprehensive auditing utility provides critical functions for managing Active Directory entries. It offers an extensive range of audit and monitoring capabilities, essential for safeguarding against intrusion and unintentional damage. This comprehensive tool ensures the security of your Active Directory implementations, Azure AD, Microsoft Exchange Server, Windows 365, and Windows File Server systems. It logs user activities and access to the authentication database, offering comprehensive insights and control over your Active Directory data.
The organization of Netwrix Auditor is designed to serve the needs of administrators who are adhering to HIPAA, GDPR, SOX, PCI DSS, NIST, FERPA, GLBA, FISMA, CJIS, NERC CIP, and ISO/IEC 27001 data protection standards.
The tool will protect your Active Directory implementations, including Azure AD, Microsoft Exchange Server, Windows 365, and the Windows File Server system. The tool will log activities relating to user activities using the AD records in your domain controllers and it will also log all access to the authentication database. You can back up Active Directory data through the tool, controlling any changes that occur and restoring records individually or en masse if your AD system gets damaged or compromised by intruders.
Who is it recommended for?
Our in-depth assessment reveals that Netwrix Auditor is an indispensable asset for administrators and organizations that prioritize robust network and server security and compliance with data protection standards. It serves as a vital component for Active Directory management, as well as data protection, logging, and backup. It is compatible with all Windows Server versions and available as a virtual appliance for Hyper-V and VMWare environments, ensuring broad accessibility for various IT environments. Whether you are maintaining large or small-scale infrastructures, this tool offers valuable auditing and protection capabilities, reinforcing your overall security posture.
Pros:
- Wide range of auditing capabilities
- Strong focus on compliance
- Supports multiple AD environments
Cons:
- Complexity may be daunting for some
This is a paid tool, but you can check it out on a 20-day free trial. The software installs on all versions of Windows Server and it is also available as a virtual appliance to run over Hyper-V and VMWare.
11. Active Directory Explorer
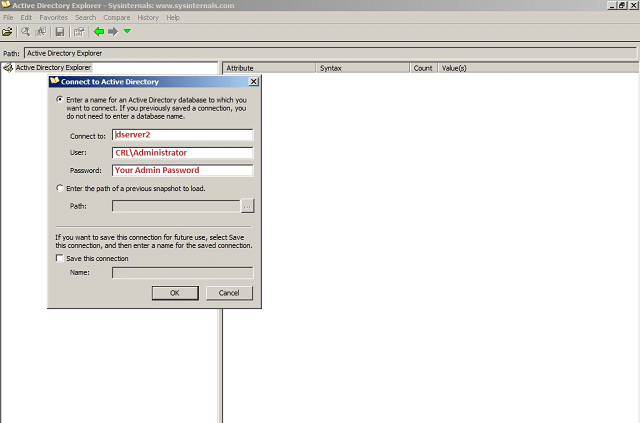
Active Directory Explorer is a front-end to Active Directory domain controllers that has the look and feel of the standard Windows File Explorer utility. This is a free tool that can be downloaded directly from the Microsoft website.
Key Features:
- Familiar Windows interface
- Basic AD management functions
- Free and easy to use
- Quick search and edit options
Why do we recommend it?
What sets Active Directory Explorer apart is its user-friendly interface, mirroring the familiar Windows File Explorer utility, which significantly eases the navigation and administration of Active Directory structures. While offering basic functions, it excels in providing an uncomplicated way to search, delete, and edit specific entries within your Active Directory. A notable advantage is that Active Directory Explorer is freely available, directly from the Microsoft website. Although it doesn’t boast advanced features or automation capabilities, it serves as a swift and accessible tool for fundamental Active Directory management tasks.
The left panel in the tool shows a tree structure view of your domain permissions. The right panel shows details of the item selected in the left panel. The interface enables you to search for a specific entry, and then delete it, or edit it. The Explorer is a quick tool that gives you all of the basic functions that you need in order to manage Active Directory. However, it doesn’t have many features. For example, there is no automation in the tool either for account provisioning or for security tracking.
Who is it recommended for?
Active Directory Explorer is recommended for system administrators and IT professionals who require a straightforward and convenient solution for managing Active Directory domain controllers. It proves especially useful when you need to quickly access, inspect, and make essential modifications within your Active Directory structure. This tool is particularly suitable for those who prefer a simplified, Windows File Explorer-like interface for their Active Directory tasks. However, if you demand advanced automation features for account provisioning or in-depth security tracking, you may need to consider supplementary tools. As a free utility, Active Directory Explorer is a budget-friendly choice for organizations of all sizes looking to streamline their Active Directory management processes.
Pros:
- User-friendly, familiar interface
- Ideal for basic AD tasks
- Free and readily accessible
Cons:
- Lacks advanced management features
12. Netwrix Inactive User Tracker
Netwrix produces a number of free system security tools and the Inactive User Tracker is a handy utility for tidying up Active Directory.
Key Features:
- Identifies inactive accounts
- Security risk reduction
- Compliance documentation aid
- Free tool
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend Netwrix Inactive User Tracker for its efficiency in addressing a critical security aspect of Active Directory. This free utility excels in swiftly identifying and listing inactive user accounts within your domain controllers by examining their last login dates. Recognizing the importance of mitigating security risks associated with stale accounts, the tool assists in enhancing your overall security posture. Moreover, it generates detailed reports that serve as valuable documentation for maintaining security standards compliance, aiding in comprehensive security management.
This quick tool searches through your domain controllers and checks on the last login dates for each listed account. This catches stale accounts. Inactive accounts are great opportunities for hackers, so they represent a security weakness.
The report that comes out of a run of this tool lists inactive accounts with their last active dates. Those reports also form useful documentation for your security standards compliance file.
This tool is a cut-down version of the Netwrix Auditor. It doesn’t have the automation features of the paid tool. However, if you are prepared to put in the work to remove accounts manually, you will save a lot of money by going for this free option.
Who is it recommended for?
Netwrix Inactive User Tracker is highly recommended for system administrators and security professionals who are focused on maintaining the security and integrity of their Active Directory environments. It proves particularly beneficial for organizations seeking a cost-effective solution to identify and address inactive user accounts, which are often targeted by malicious actors. While it lacks the automation features of the paid Netwrix Auditor, this free tool is an excellent choice for those willing to manage account removal manually, providing significant cost savings and robust security enhancement.
Pros:
- Simplifies tracking of inactive accounts
- Enhances AD security
- Free and easy to use
Cons:
- Limited to account activity tracking
Active Directory Management
This guide has given you a lot of options for monitoring and managing your Active Directory implementations. The range of tools listed here includes very simple interfaces, such as the Microsoft Active Directory Explorer through to very sophisticated tools such as the SolarWinds Access Rights Manager.
Your favorite from this list will probably depend on the size of your network, the size of your administration team, and the amount of money that you have available for new tools. The presence of free tools on this list should help you if you have no budget at all for tools. However, keep in mind that the paid tools are charged for and still attract plenty of customers, so they represent a value of money that appeals to systems administrators all over the world. If you are curious about what exactly makes these tools worth paying for, you can at least check them out by accessing the free trials that their creators offer.
Do you use any Active Directory management tools? Have you tried any of the tools on this list? Leave a message in the Comments section below and share your experience with the community.