Last Updated :
07 Apr, 2025
We all know that one can easily create files using GUI options, but what if you can use a faster way to create files through the command-line interface? This is not a necessary but useful skill for anyone working with Windows. Whether you’re automating tasks, working on scripts, or preferring using the command prompt, knowing how to create a file in CMD can be incredibly useful.
This article will walk you through the steps to create a file using CMD, ensuring that you can efficiently manage your files directly from the command prompt.
Methods to Create A File on Windows using CMD
To start a new file on Windows using CMD, the following guidelines should be used. Let us start with the basic Echo Command.
Note: All of these methods should be executed in any certain directory. Otherwise, the operations will not completed. Use the CD Windows Command to enter into any certain Windows directory.
Method 1: Create Text File Using ECHO in Command Prompt
Step 1: Open CMD
- To create a file using CMD open CMD press Win + R key on your keyboard and type CMD to open CMD.
Step 2: Type ECHO Command
- Once the CMD opens execute the following command.
This method will directly save the file to the directory mentioned earlier. You have to put some text for it.
Command: echo. > Rapture.txt
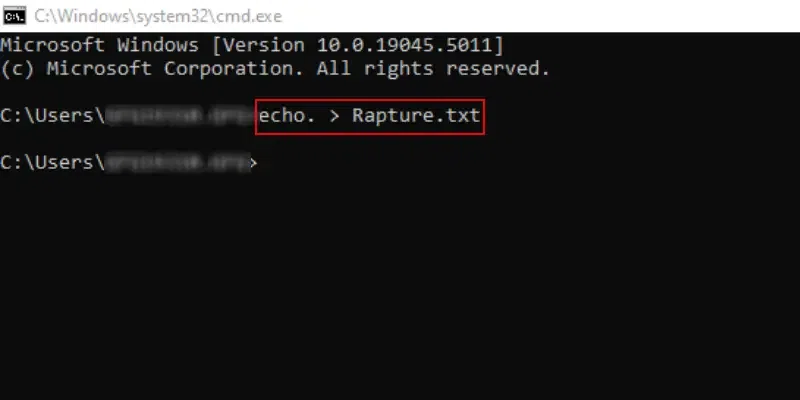
Congratulation! The New Text File on Windows is created using the Command Prompt with one simple command.
Method 2: COPY CON Command to Create a New File
Step 1: Use copy con in CMD
- You need to type «copy con» followed by the name of the file you wish to overwrite and once you’re done press the CTRL + Z to end the operation & the file will be directly saved to the directory.
Let’s understand this with the below-mentioned example where the file name = ‘Rapture’
Command: copy con Rapture.txt
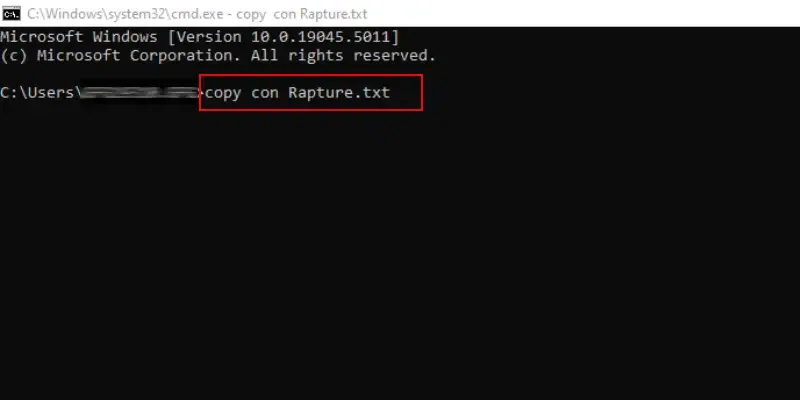
Hooray! We have successfully created a Text File on Command Prompt on Windows in a certain directory without opening it.
Method 3: Quick Guide to Create a File in CMD — NOTEPAD Command
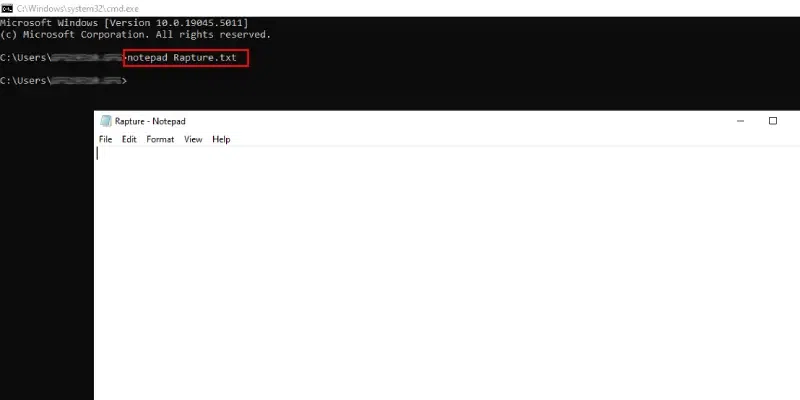
The following command can be used to open any Text File. Either, you can open the New File with any predefined name or any existing one in the certain directory. It will open the Notepad Windows Application, make changes there & press CTRL + S to save it.
Command: notepad Rapture.txt
Method 4: ‘fsutil’ Command to create a «specific» size file
The following command can be used to create a file in CMD for any specific size. Once you create the file, you do perform tasks accordingly.
For example: Let’s create a file of size 10 bytes with the filename as ‘Rapture’
Command: fsutil file createnew Rapture.txt 10
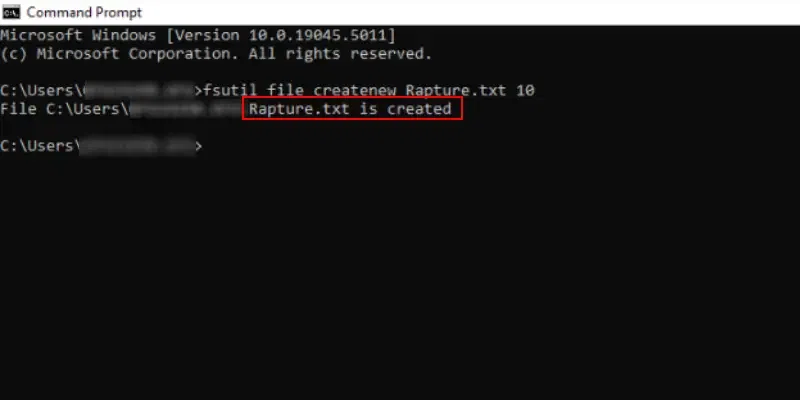
Method 5: «type nul» Command to create a new File
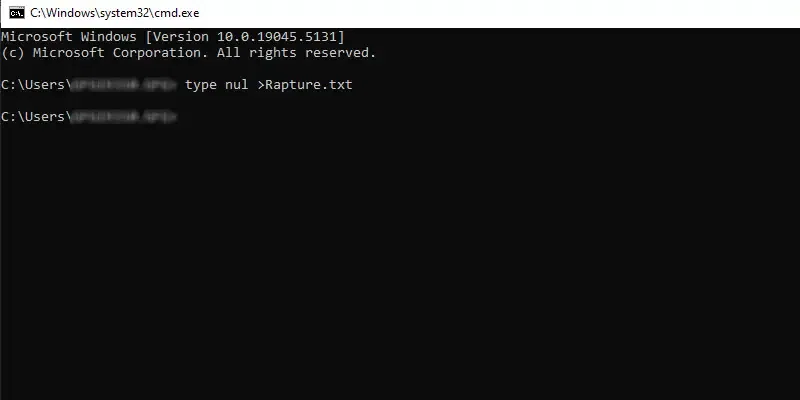
The type nul command in cmd can be used to create a new file wherein the «type nul» denotes to do nothing and starts with an empty file. Let’s understand this with an example below where the filename is ‘Rapture’.
Command: type nul >Rapture.txt
Conclusion
Mastering the ability to create a file in CMD is an essential part of becoming proficient with the command line in Windows. By using the right CMD command to create a file, you can streamline your workflow and perform tasks more efficiently. Whether you’re creating simple text files or working on more complex scripts, understanding how to make a file in CMD gives you greater control over your system.
Also Read
- Most Useful CMD Commands in Windows
- CMD Commands to Gather Information of a System
- How to Show all the previously connected WiFi Networks using CMD in Windows?
on January 3, 2009
We can create files from command line in two ways. The first way is to use fsutil command and the other way is to use echo command. If you want to write any specific data in the file then use echo command. If you are not bothered about the data in the file but just want to create a file of some specific size then you can use fsutil command.
To create file using echo
echo some-text > filename.txt
Example:
C:\>echo This is a sample text file > sample.txt C:\>type sample.txt This is a sample text file C:\>
To create file using fsutil
fsutil file createnew filename number_of_bytes
Example:
C:\data>fsutil file createnew sample2.txt 2000 File C:\data\sample2.txt is created C:\data>dir 01/23/2016 09:34 PM 2,000 sample2.txt C:\data>
Limitations
Fsutil can be used only by administrators. For non-admin users it throws up below error.
c:\>fsutil file /? The FSUTIL utility requires that you have administrative privileges. c:\>
Knowing how to conduct rudimentary file management at the Command Prompt comes in useful when you’re starting to code. Any file you make from the Command Prompt persists in multiple areas of Windows—this means that generating an index or document at the prompt fixes things so that you can access, utilize, and control that catalog or record in the Windows platform.
There are two ways to create files from the command line. The first method uses the fsutil command, and the second method uses the echo command.
Create File with Echo Command
|echo some-text > filename.txt
Create File with Fsutil Command
|fsutil file createnew filename number_of_bytes
Step-by-Step Process to Create Files via Command Line
STEP 1: Launch the command prompt.
The quickest way to implement this is to open the search bar by pressing Win + S, type cmd, and then select Command Prompt.
STEP 2: Choose the folder where you wish to save the file.
By default, the prompt will open under C:UsersYourName. Suppose the folder is elsewhere; type the cd path to the folder and hit Enter. Modify the way to the folder with the actual folder path.
STEP 3: Make a blank file.
Type |type nul > filename.txt
Modify filename.txt with a name according to your preference and hit Enter.
The “.txt” extension means that it’s a plain text file.
“.docx” (Word document), “.png” (empty photo), and “.rtf” (rich text document) are other popular file extensions.
All of these file formats may be viewed on any Windows system without the need for extra software.
Step 4: Make a file with certain text in it.
Replace testfile with the appropriate file name in copy con testfile.txt. Hit Enter.
Enter any text. This is a basic text editor, but it’s adequate for brief notes or coding. To move to the following line, use the Enter key.
Press Control + Z after you’re done editing the file.
Hit the Enter key. You should notice “1 file(s) copied,” meaning your file has been saved using the name you chose.
OR
|echo enter your text here > filename.txt.
STEP 5: Make a file of a specific size.
Avoid this step, if you don’t wish to deliver a document of a specific size. Utilize the accompanying order to produce a clear text document dependent on its byte size.
|fsutil file createnew filename.txt 1000
Replace filename with the name of your wish and 1000 with the exact number of bytes you want the document to be.
Other useful articles:
- Basic Windows CMD commands
- Cool CMD Commands Tips and Tricks
- Best CMD Commands for Hacking
- CMD Commands for Wireless Network Speed
- Useful Keyboard Shortcuts for CMD
- What Info about My Laptop Can I Check with CMD and How?
- Getting Started with CMD Windows
- TOP-12 Command-Line Interview Questions (Basic)
- Command-Line Interview Questions (Advanced)
- CMD Commands to Repair Windows
- CMD Commands to Speed Up Computer
- CMD Commands for MAC OS
- How Does the Command Line Work?
- MS-Dos Interview Questions in 2021
- Windows OS Versions and History
- Recent Windows Versions Compared
- Basic Windows Prompt Commands for Every Day
- Windows Command Line Cheat Sheet For Everyone
- Windows Command Line Restart
- Windows Command Line for Loop
- Windows Command — Change Directory
- Windows Command — Delete Directory
- Windows Command Line – Set Environment Variable
- How Do I Run Command Line
- Windows Command Line Create File
To create a new file using the Command Prompt (cmd), you can use the `echo` command followed by redirection to specify the file name.
Here’s the command:
echo This is a new file > newfile.txt
This command will create a file named `newfile.txt` containing the text «This is a new file».
What is CMD?
The Command Prompt (CMD) is a command-line interpreter available in Windows operating systems. It provides a direct method to interact with the system, facilitating a variety of tasks including network configuration, system management, and file manipulation. Understanding CMD is essential for anyone looking to gain more control over their computing environment. Its power lies in its simplicity and efficiency, making it a favored tool among both beginners and advanced users.

Cmd Count Files: Master File Counting in Cmd
Creating a File in CMD
Understanding File Creation in CMD
Creating a file in CMD involves using a set of commands that interact with the computer’s file system. These commands allow users to generate new files, edit existing files, and manage file contents. This is particularly useful for scripting, automation, or simply manipulating data without needing to navigate through graphical interfaces.
The Basic Command: `echo`
One of the simplest ways to create a new file in CMD is by using the `echo` command. This command outputs a line of text or a variable value to the console or redirects it into a new file.
Syntax:
echo [text] > [filename]
Example:
echo Hello, World! > example.txt
In this example, the command creates a text file named `example.txt` in the current directory, containing the text «Hello, World!». If the file already exists, this command will overwrite its contents. To append text to an existing file instead, you can use `>>`:
echo This will be appended. >> example.txt
The `copy con` Command
Another method of file creation involves the `copy con` command, which allows users to create a file interactively by typing directly into the console.
Syntax:
copy con [filename]
Example:
copy con example2.txt
When you execute this command, CMD will enter an input mode, allowing you to type the content you want. After typing, press `CTRL + Z` followed by `ENTER` to save the file.
This method is particularly useful for quickly creating small files without needing to open an editor. However, be mindful that if you exit the input mode incorrectly, you may lose your work.
Utilizing `fsutil`
The `fsutil` command is another powerful tool for file manipulation, especially for advanced users. It enables more intricate file management, including sparse file creation.
Syntax:
fsutil sparse setflag [filename]
Example:
fsutil sparse setflag examplefile.txt
Using `fsutil` requires administrative permissions, making it suitable for advanced operations. This command allows the creation of large files while only allocating disk space as data is written.
Creating Different File Types
Creating various types of files in CMD is straightforward, and the aforementioned commands can be adapted to suit different formats.
Text Files
You can easily create text files (.txt) or other text-based files using the `echo` or `copy con` commands.
Batch Files
Batch files (.bat) can be created in CMD to automate tasks. An example command that creates a simple batch file could be:
echo @echo off > myscript.bat
This command creates a file named `myscript.bat`, which when executed, will hide its own command prompt output.
Other Formats
Creating files in other formats, such as .csv for spreadsheets or .log for logging purposes, only requires a change in the filename extension.
For instance:
echo Name, Age, Occupation > data.csv
This command creates a CSV file that could be used for data storage in spreadsheet applications.
Effortless File Transfers: Cmd Move Files Made Easy
Practical Tips and Tricks
Quick File Creation Shortcuts
Creating files can often be expedited through shortcuts or advanced techniques. For instance, using `tab completion` can save time when specifying file names or paths if you are creating files in directories that contain spaces.
Creating Files in Specific Directories
To avoid cluttering your working directory, it’s a good idea to specify the path when creating files. This can be accomplished easily by including the full path in your command.
Example:
echo Hello > C:\Users\YourName\Documents\example.txt
This command creates the file directly in the designated Documents folder, keeping your workspace organized.
Checking for File Existence
Before creating files, it’s wise to check whether a file already exists, thus preventing unintentional overwrites. You can achieve this using the `IF EXIST` command.
Example:
IF EXIST example.txt echo File exists.
This line of CMD will only output text if the specified file is found in the current directory.

How to Create Directory Using Cmd in Simple Steps
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Permission Denied Errors
If you encounter permission denied errors when attempting to create a file, it’s often due to restrictions set on the directory or the file being accessed. Running CMD as an administrator can help to overcome this limitation.
Path Not Found Errors
Path issues commonly arise when the specified directory does not exist or is incorrectly entered. Ensure that the paths used are correct and note that CMD is sensitive to spelling and case.
How to Create Folder Through Cmd Efficiently
Conclusion
The versatility of CMD in file creation allows users to efficiently manage their data with just a few commands. From the straightforward `echo` and `copy con` to the specialized `fsutil`, there are various methods to cater to your needs. Mastering these commands not only enhances your productivity but also grants greater control over your files and system environment.

Mastering Cmd Formatting: A Quick Guide
Additional Resources
Recommended Tools and Software
Enhancing your CMD experience may also involve using third-party tools that provide GUI interfaces for command line operations, or scripting environments tailored for automation.
Further Reading and Tutorials
For users looking to expand their knowledge, many online resources offer extensive CMD tutorials and community forums for discussion and troubleshooting.
Community and Support
Engaging with communities, whether through online forums or local user groups, can be invaluable in accelerating your CMD learning journey and exchanging knowledge with others.
Wondering how to create a file using Command Prompt on Windows computers? This article will guide you on how you can easily do that.
We often find the need to create files and folders on our Windows computers to store various data types such as text, images, programs, and more.
While the Windows Graphical User Interface offers a user-friendly approach to do that, there are cases when using the Command Line Interface, specifically the Command Prompt, becomes essential.
Meanwhile, using the Command prompt to create a file on a Windows computer is equally uncomplicated. In the following sections, we will discuss how to create a file using Command Prompt on Windows PCs effortlessly.
Table Of Contents
- How to Create a File With Command Prompt on Windows?
- Method 1. Create an Empty File Using Command Prompt
- Method 2. Creating a File Containing Certain Text
- Method 3. Creating a file of a certain size
- Method 4. Creating Multiple Files
- Wrap Up
How to Create a File With Command Prompt on Windows?
If, for any specific reason, you aim to create a file via Command Prompt on Windows, there are several approaches at your disposal.
Before initiating the file creation process with the Command Prompt — even if you are using File Explorer — it is necessary to navigate or move to the directory where you intend to keep the file.
Say you intend to create a file in the Desktop directory/folder, you need to navigate to the Desktop folder on your computer. When using Command Prompt, it initially opens to the User directory level.
Hence, you can switch to the Desktop folder, a subfolder of the User directory, by using the cd (change directory) command. This can be done by following these steps:
1. Press Windows + R to open the Run Command Box.
2. Type cmd in the box and hit Enter.
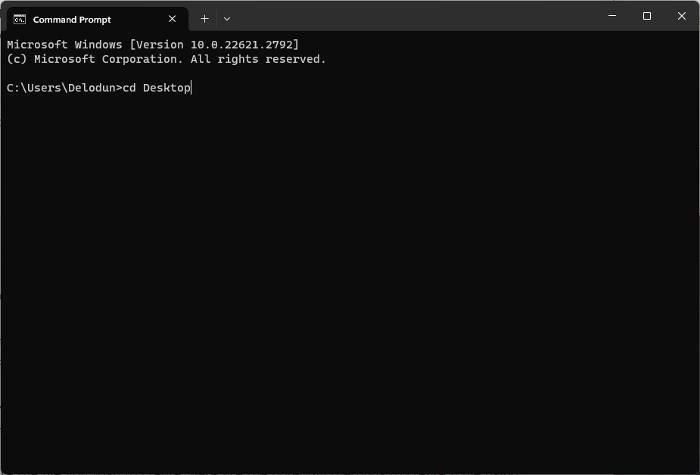
3. In the Command Prompt window, type cd Desktop and hit Enter to move to the Desktop folder. Immediately, you will have Desktop before the text cursor in the command prompt page showing that any command you will be running to create a file on the PC will be creating the file in the Desktop folder.
You can navigate to different folders using the command “cd folder name,” where the “folder name” part should be the name of the subfolder you wish to access and create a file in.
Additionally, to move to the directory where you want to save a new file, use the command “cd directory path.” For instance, you can type “cd C:\Users\Public\Pictures” to create a file in the CMD within the Pictures folder of the path used.
In a case when you want to create a new directory under your current directory level, you can do that by using the command below
mkdir directory_name
For example, to make a new folder/directory named MyFolder within the Desktop directory, enter the command mkdir MyFolder.
Subsequently, if you want to create a file using Command Prompt in this new folder, simply type cd new_directory_name. The command to be used in the case of our example above is cd MyFolder.
Note: You also can view the directories or folders within the current or opened directory level in the command prompt by executing the following command. Type dir in the command prompt and hit enter.
Having navigated to the directory you intend to store the file you wish to create, here are the potential methods to create a file using Command Prompt on Windows, according to your preferences:
Method 1. Create an Empty File Using Command Prompt
Command Prompt allows Windows users to effortlessly create an empty file of various types, such as png for images, docx for Word documents, txt for text files, and more. This command automatically produces the file in your present directory.
To create an empty file on your Windows PC using Command Prompt, input the following command and hit Enter:
type nul > filename.extension
Suppose I aim to create an empty Word document file named “EmptyDocs” at the Desktop directory level on my PC using Command Prompt. In that case, I would input the following command and press Enter:
type nul > EmptyDocs.docx
Therefore, the final part of the command – extension — will rely on the file format of the file you are creating.
Note: You can open the file created to confirm the method by entering filename.extension and pressing Enter.
CURRENT DIRECTORY LEVEL IMAGE
Method 2. Creating a File Containing Certain Text
Another capability of the Command Prompt on Windows for file creation involves creating a file with specific text. This method is tailored for creating text files and includes the ability to input text directly through the command prompt, unlike the first method mentioned above, which only permits the creation of an empty file.
There are two commands you can use for this method and here are they:
echo command
The echo command primarily showcases the text you input in the Command Prompt. However, it can also serve to generate a text file on Windows PCs, echoing the text entered with the command into the created file.
To use this command to create a text file with certain text, enter the following command and hit Enter:
echo the_text_to_input_in_the_file > filename.extension
For example, if you want to create a text file with the text “Thank you, Techworm”, simply enter the command below and hit Enter:
echo Thank you, Techworm > hello.txt
copy con command
Rather than using the echo command, an alternative method you can use is the copy con command. This also creates a text file with specific content on your PC. This process, however, follows a distinct sequence where you input the command first, run it, and then type the desired text into the file.
To employ the copy con command, initiate the text file creation and naming by entering the command below and pressing the Enter key:
copy con MyFile.txt
After that, type the text to be input in the file, press Ctrl + Z, then press Enter.
Your file will immediately be created in your current directory level.
Method 3. Creating a file of a certain size
You can easily create a file of a specific size using Command Prompt on Windows. This is a straightforward process and can be useful in various scenarios.
Just input the following command and press Enter:
fsutil file createnew filename.txt 1000
In the command, insert your desired file name in place of “filename,” while the digit at the end represents the file size in bytes.
Method 4. Creating Multiple Files
You can create multiple files in a folder at once by using the for loop command. This approach saves you the effort of manually creating numerous files with the same format one-by-one. This method can be used by entering the command below in your Command Prompt and pressing Enter:
for /l %a in (1 1 5) do type nul > "%a.txt"
This method uses the “type nul” command, as explained as the initial method in this article, enabling the creation of empty files in any format.
The (1 1 5) in the command instructs to create multiple files sequentially from 1 to 5 with an incremental step of 1. To generate a different number of files, such as 10, you would need to substitute the 5 with 10, adjusting accordingly for other quantities.
Also, the presence of .txt at the end of the command signifies the creation of text files. In a different scenario, such as wanting to create Word files, the command would need to be adjusted to::
for /l %a in (1 1 5) do type nul > "%a.docx"
The file created by this command will be saved in the directory where the command is executed.
In addition, you can assign a shared filename to multiple files rather than solely numbering them. You can do this by entering the following command and pressing Enter:
for /l %a in (1 1 5) do type nul > "filename %a.txt"
If you aim to name the files as TextFile-1, TextFile-2, and so on, the command to use would be:
for /l %a in (1 1 5) do type nul > "TextFile- %a.txt"
There you have it—five text files generated with just one command.
Wrap Up
The methods we covered above are some of the options for creating a file with Command Prompt on Windows. You can utilize any of the methods based on what you want to accomplish.
Additionally, you can delete files on your Windows PC using the Command Prompt as long as the file is under your current directory level. To do this, simply type Del filename.extension and press Enter.
Luqman
A tech junkie, and music fan.
I love writing Reviews, How-to, and explainer articles related to Android, iOS, and Windows. If I’m not on my laptop brainstorming ideas for content, you’ll most probably see me watching Tv shows or streaming videos on Youtube. Don’t forget to follow me on Twitter as @Luqqman14
