Using copy command, we can copy files from one directory to another directory. This command is similar to the Linux cp command, but it does not match with the full functionality of cp. Windows copy command can be used to copy files only, we can’t copy directories.
The syntax and usecases of copy command are explained below with examples.
Copy the contents of a file to another file
copy sourceFile destinationFile
Example: To copy a file from c:\data\file1.doc to D:\backup\file2.doc
copy c:\data\file1.doc D:\backup\file2.doc
If the destination file already exists you will be prompted for confirmation. To suppress this confirmation you can use /Y switch with copy command. This would be useful if you are executing copy command from a batch file.
c\> copy /Y c:\dir1\subdir1\file1.txt c:\dir2\subdir2\file2.txt
If the destination file exists, the above command will overwrite the same without asking the user for confirmation.
Copy file to another directory
When we specify a directory path as the destination, the files will be copied with the same name. We can assign a different name by specifying the new name in the destination path. Example is shown below.
To copy the file 1.doc loated at c:\data\documents to the directory c:\data\newdocs
c\> copy c:\data\documents\1.doc c:\data\newdocs\
Copy files with white space in name
If the file name has white space within it, we can wrap up the name in double quotes.
Example: To copy file, my resume.doc to another folder
copy "my resume.doc" D:\data\
Copy multiple files
We can’t specify multiple file names in copy command. However, we can use wildcards to identify a group of files and then copy all of them in a single command.
For example, to copy all excel files from current folder to another folder F:\backup
copy *.xls F:\backup\
To copy all files in current folder to another folder
copy * D:\dir1\dir2
Use of environment variables
We can use environment variables in the copy command to specify the path of the folders. Like USERPROFILE, SystemRoot, ProgramFiles, TEMP, WINDIR, APPDATA, HOMEPATH.
For example, to copy a file to a user’s documents folder
Copy D:\file.pdf %HOMEPATH%\Documents\
The above command copies the file to the My Documents folder of the current logged in user.
You may also want to read
- Xcopy command syntax and examples
- Robocopy command
To copy a directory and its contents in Windows Command Prompt, you can use the following command:
xcopy "C:\source_directory" "D:\destination_directory" /E /I
In this command, `C:\source_directory` is the path of the directory you want to copy, and `D:\destination_directory` is where you want to copy it to, with `/E` ensuring that all subdirectories are copied, including empty ones, and `/I` indicating that the destination is a directory.
Understanding Windows CMD Commands
What is CMD?
Command Prompt (CMD) is a command-line interpreter available in most Windows operating systems. It allows users to execute commands to interact with the system, automating tasks, and accessing advanced functionalities. Mastering CMD can significantly enhance your efficiency and control over Windows, especially for repetitive tasks.
Why Use CMD for Copying Directories?
Using CMD for copying directories has several advantages over graphical user interfaces (GUIs). CMD allows for:
- Speed: Copying directories through CMD is often faster than using Windows Explorer, particularly for large batches of files.
- Automation: It opens the possibility to automate files and directory management through scripts.
- Batch Processing: CMD enables you to execute multiple commands in a single go, making it ideal for advanced users.

Navigate Your Windows Cmd Home Directory Effortlessly
Basic Syntax of the Copy Command in CMD
Overview of the COPY Command
The basic structure of the CMD copy command is as follows:
`COPY [source] [destination]`
It is essential to understand the syntax of this command to utilize it effectively.
Difference Between COPY and XCOPY
While the COPY command can handle basic file copying tasks, it lacks the capability to copy entire directories with their subdirectories. For advanced copying tasks, including copying folders, XCOPY is the preferred command, as it provides additional options and functionality.

Windows Cmd Repair Commands: A Quick Guide
Using Windows CMD to Copy Directories
Basic Command to Copy a Directory
To copy a directory and its contents using CMD, you would typically use:
xcopy source_dir destination_dir
This command tells the system to copy everything from the source_dir to the destination_dir.
Code Example: Copying a Folder
An example command might look like this:
xcopy C:\SourceFolder C:\DestinationFolder /E /I
In this example:
- C:\SourceFolder is the path of the folder you want to copy.
- C:\DestinationFolder is where you want to place the copy.
- /E indicates that all subdirectories should be copied, including empty ones.
- /I tells the command to treat the destination as a directory if it does not exist.
Common Switches Used with XCOPY
When using XCOPY, various switches enhance functionality. Some of the most commonly used ones include:
- `/E`: Copies all subdirectories, including empty ones. This is crucial when you want an exact replicate of the folder structure.
- `/I`: If the destination does not exist, this switch assumes it is a directory, streamlining the process.
- `/Y`: Suppresses the prompt that asks for confirmation when overwriting existing files in the destination.
Using CMD to Copy a Folder with Attributes
In some cases, you may want to preserve file attributes (e.g., read-only status). You can achieve this with an additional switch:
xcopy source_dir destination_dir /E /I /K
Here, /K copies the attributes, ensuring that important file properties are retained after the copy.
Windows Cmd Clear: Refresh Your Command Line Effortlessly
Detailed Steps for Copying a Directory in Windows CMD
Opening the Command Prompt
Before you can use the `xcopy` command, you need to access the Command Prompt. Here’s how:
- Press Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type cmd and press Enter.
Step-by-Step Copy Process
Once you have CMD open, you can enter the `xcopy` command. For example, to copy a folder:
- Navigate to the folder you want to copy by typing `cd path_to_the_folder`.
- Enter the command with the necessary flags.
Verifying the Copy
After executing the copy command, it’s essential to verify that the files have been copied correctly. You can use the following CMD commands:
- `dir`: Lists files in the directory to check contents.
- `tree`: Displays a graphical representation of the directory structure, making it easy to see if the copying was successful.

Windows Cmd Repair: Quick Fixes You Need to Know
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Permission Denied Errors
One common issue when attempting to copy directories is encountering permission denied errors. This typically occurs due to insufficient permissions for the source or destination directories. To resolve this:
- Ensure you have administrative privileges.
- If necessary, run CMD as an administrator by right-clicking the CMD icon and selecting Run as administrator.
Directory Not Found Errors
If you receive a «Directory Not Found» error:
- Double-check the paths you entered in your command.
- Ensure there are no typos or missing directories in the specified paths.
Handling Large Directories
Copying large folders can be tricky due to timeouts or system limitations. To enhance performance, consider using the /J switch with your XCOPY command, which uses unbuffered I/O, like this:
xcopy source_dir destination_dir /J

Mastering Cmd Directory Navigation Made Simple
Advanced CMD Copying Techniques
Using Robocopy for Enhanced Functionality
For more advanced directory copying tasks, consider using Robocopy (Robust File Copy), which is included in Windows Vista and later. Its syntax is:
robocopy source_dir destination_dir
Robocopy is particularly useful for its resilience against interruptions and can handle more complex copying scenarios.
Example of Robocopy
To mirror a directory, you can use Robocopy as follows:
robocopy C:\SourceFolder C:\DestinationFolder /MIR
Here, /MIR mirrors the source directory, ensuring that the destination is an exact copy, including files and subfolders.
Automating Directory Copying with Batch Files
For users who frequently copy directories, creating a batch file can save time. A simple batch file might include commands like:
@echo off
xcopy C:\SourceFolder C:\DestinationFolder /E /I
This script can be saved with a `.bat` extension and executed whenever you need to perform the copy operation.

Mastering Windows Cmd Route: A Concise Guide
Conclusion
Recap of the CMD Copy Directory Process
In summary, mastering the use of Windows CMD to copy directories provides users with enhanced efficiency and control over file management tasks. From the basic `xcopy` command to advanced options like `Robocopy`, CMD offers powerful capabilities beyond what typical GUI tools can accomplish.
Additional Resources for Learning CMD
To continue enhancing your CMD skills, explore various online coding resources, tutorial sites, and forums dedicated to mastering command line operations.

Windows Cmd Grep: Your Essential Guide to Text Searching
Call to Action
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of how to use Windows CMD to copy directories, it’s time to practice! Try executing these commands in your own Windows environment, and consider subscribing to our updates for more CMD tips and tricks to improve your command-line skills.
Download Article
Download Article
Do you need to copy and paste files or folders without using the File Explorer? While navigating the file system with Windows Command Prompt (cmd) might seem daunting, it’s actually pretty easy once you get the hang of it. This wikiHow will teach you how to copy one or more files from one folder to another from the command line in Windows.
-
Find out your file’s location. You’ll need the file’s location—also known as a «directory»—in order to tell Command Prompt where to look for the file.
- You can find the file’s directory by going to the file’s location in File Explorer and then clicking the URL bar near the top of the File Explorer window.
- Most files will be somewhere in the following directory: [drive letter]:\Users\[username] (for example, «C:\Users\Kyle»). This is the directory in which almost every user-created file on your computer is located.
- A file on your desktop for the above example would be in the «C:\Users\Kyle\Desktop» directory, while a file in the Documents folder would be in the «C:\Users\Kyle\Documents» directory.
-
If you want to copy your file, you’ll need to know its name. Keep in mind that file names are case-sensitive in Command Prompt, so you’ll need to include the proper capitalization.
Advertisement
-
Open Start
. Click the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of the screen.[1]
-
Doing so will search your computer for the Command Prompt program.[2]
-
It’s at the top of the Start window. Doing so will open the Command Prompt program.[3]
- Keep in mind that if you’re on a shared computer (e.g., a school or public PC), you may not be able to access the Command Prompt.
Advertisement
-
Type in cd followed by a space, but don’t press ↵ Enter.[4]
-
Enter the directory in which the file that you want to copy is located.
-
Doing so will reset Command Prompt to look in the entered directory.
-
Type in copy followed by a space, but don’t press ↵ Enter yet.[5]
-
Type in your file’s name followed by a space, making sure to include the file’s extension (e.g., .txt) for a text file. Don’t press ↵ Enter after doing so.[6]
- If there are spaces in the file’s name, you need to put quotation marks around them. For example, a file named «Pickles are Good.txt» would be Pickles" "are" "Good.txt in Command Prompt.
-
Type in another directory (e.g., C:\Users\[you]\Desktop into which you want to copy the file.
- If you don’t do this, the file will be copied to your user directory (e.g., «C:\Users\[you]») by default.
-
Doing so will copy the file into your indicated directory. You can view the copied file by going to the directory in question in your computer’s File Explorer.
Advertisement
-
Type in cd followed by a space, then type in the folder’s directory and press ↵ Enter.[7]
- For example, if you want to copy all of the files inside of a folder called «Example» that’s on your desktop, you’d go to C:\Users\humpb\Desktop here.
-
Type in robocopy and then a space, but don’t press ↵ Enter yet.[8]
-
Enter a folder’s name. Type in the name of the folder that you want to copy, then add a space. Again, don’t press the ↵ Enter key just yet.
- As with file names, you’ll need to use quotes around any spaces in the folder name.
-
Type in a directory into which you want to copy the folder’s files.
- If there are lots of files in the folder, this can get messy if you copy them into an unorganized folder since the folder itself won’t be copied with the files.
-
Doing so will copy the contents of the folder into your destination folder.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
Which command should I use to copy files?
Copy «source path» «destination path». For example, you might copy «C:\Users\qclab\Desktop\Stuff.txt» «P:\IT\Confidential». The quotation marks are optional unless you have spaces in your folder or file names. To copy everything in a folder use *.* as the name and extension. For example, copy «C:\Users\qclab\Desktop\Stuff.txt» «P:\IT\Confidential».
-
Question
Is it possible to move a PDF file from one folder to another and not have it overwrite another file with the same name by having a different date?
You’ll have to rename the PDF file prior to moving it, as two files with the same name can’t reside in the same folder.
-
Question
How can I copy all files from sub directories with a similar name to a different directory?
After you do one, press the up key and then change the name, which shouldn’t take up much time.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
-
If you want to create a new destination folder for a set of copied files, enter the directory for the destination folder (including the destination folder itself) in conjunction with the «robocopy» command.[9]
-
You can copy all files in a directory by typing copy *[file type] (e.g., copy *.txt).
-
If you copy the Desktop folder’s contents into a new folder, that new folder will be renamed to «Desktop».
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
-
Copying files and folders within Command Prompt is potentially dangerous if you don’t know what you’re doing. Never copy or manipulate any files or folders that you don’t understand.
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Type «cd» followed by a space in command prompt, but don’t press «enter» yet.
2. Type the name of the directory your filed is located in.
3. Press «enter.»
4. Type «copy» followed by a space, but don’t press «enter.»
5. Type your file’s name followed by a space, but don’t press «enter.»
6. Type in the name of the directory you want to copy the file to.
7. Press «enter» to copy the file.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 2,435,851 times.
Is this article up to date?

In this tutorial, we will learn how to copy files and folders in the Windows Command prompt.
We are going to look at two cmd commands: Copy and Xcopy.
Note that the copy command has some limitations compared to the xcopy. For example, to copy directories or hidden files, you have to use the xcopy command.
Copy Command
On Windows, we can use the copy command to copy one or more files from one location to another:
copy C:\data\sales.doc C:\backupThe preceding command will copy sales.doc from C:\data\ to C:\backup.
Use the /y switch to overwrite duplicate files without confirmation:
copy /y C:\data\sales.doc C:\backupWe can also save a file to a different name. For example, the following command saves file1.txt as file2.txt in the same directory:
copy file1.txt file2.txtYou can also use wildcards to copy multiple files:
copy /y C:\data\* C:\backup
copy /y C:\data\*.doc C:\backupThe first command copies all files in the C:\data\ directory to C:\backup. The second command copies all files with a .doc extension to the C:\backup.

We can also combine several files into one:
copy file1+file2 file3
copy error* C:\backup\report.txtIn the first line, file1 and file2 are combined to make one file named file3. In the second line, all files whose names start with «error» are copied to the C:\backup, as a single file called report.txt.
You can get a list of all available options with the copy /? command.
Xcopy Command
The xcopy command offers more features. For example, with xcopy, we can copy directories and subdirectories, as well as hidden files.
Command Options
| /Y | Prompt before overwriting an existing file. |
| /H | Copy hidden files/system files. |
| /S | Copy directories and subdirectories. Empty directories are not included by default (use /e for that). |
| /E | Include empty directories. |
| /I | Create the destination folder if it does not exist. Use this option when you want to copy the parent folder itself. |
| /T | Copy directory tree without files. Empty directories are not included by default. Use /e option to include empty folders. |
| /P | Prompt for confirmation before creating each file. |
| /Q | Quiet mode. |
| /exclude | Specify a text file that contains a list of files to exclude. See the examples. |
| /Z | Resume mode. Use this option when copying files over a network. |
| /D:m-d-y | Copies files changed on or after the specified date. |
Examples of Using the Xcopy Command
Copy sales.doc from the current directory to C:\backup:
xcopy sales.doc C:\backupCopy C:\data\accounts (all files including subdirectories) to C:\backup:
xcopy /s /e /h /i /y C:\data\accounts C:\backup\accounts
In the following example (without /I switch), the contents of the folder are copied but not the folder itself:
xcopy /s /e /h /y C:\data\accounts C:\backup\Copy the directory structure of C:\OneDrive to the backup directory:
xcopy /s /e /t /y C:\OneDrive C:\backup\You can use wildcard characters to match patterns. The following command copies all files with a .jpg extension:
xcopy /s /h /y C:\data\*.jpg C:\backupUsing for loop to copy multiple files:
for %i in (sales.doc, products.doc) do xcopy /y %i C:\backupExcluding files with xcopy
With the /exclude, we can provide a text file that contains items we want to exclude.
xcopy /s /e /h /y /exclude:C:\Users\user1\files-to-exclude.txt C:\data\ C:\backup\The files-to-exclude.txt may look like the following:
.doc
sales*In this example, we exclude items with the .doc extension and files whose name starts with sales.
You can get a list of all available options with the xcopy /? command.
-
Home
-
Clone Disk
- CMD Copy File: How to Copy Files in Command Prompt Windows 10/11
By Ariel | Follow |
Last Updated
What command line can be used to copy files? How to copy files using CMD in Windows 10/11? A lot of users are confused about these questions. Now, this post of MiniTool explains the CMD copy file operation in detail.
When copying a large of files from one drive to another location, most people may choose File Explorer to copy files. Sometimes, however, various issues and errors may occur when copying large files such as “calculating the time required to copy the files”, “Windows delay write failure”, and so on. Under these situations, you may consider PowerShell and CMD copy files.
Compared with the traditional file copying ways, the copy file command line can help you copy and paste files with less time. Moreover, the Windows copy command enables you to leave the copying process alone automatically when unattended.
What Command Line Can Be Used to Copy Files
What command can be used to copy files? The answer depends on the way you want to copy file CMD. If you just want to copy a specific file in Command Prompt, then you can use the Copy command. If you want to copy the entire directory and its content, then the Xcopy command is a good choice.
Of course, different copy file command lines bring different results. For example, if you want to copy the encrypted files to the destination as decrypted files, then you need to add the “/d” to the end of the Windows copy command line. To know more about copy file CMD lines, you can refer to this article.
How to Copy Files Using CMD in Windows 10/11
How to move files using CMD? Here we summarize the most two common ways to copy file CMD. The first is to copy a specific file using the copy command, while the other is to copy the directory using the xcopy command. Let’s start trying.
Before the CMD Copy File
Before you start running the Windows copy command line, it’s necessary to know the directory/path and name of the file you want to copy. Also, you should write download the destination folder you want to copy to.
Step 1. Press the Win + E keys to open File Explorer.
Step 2. Find the location and name of the file, and note them down. For example, the file name is “pdr-ol-log.txt” and the location is “C:UsersAdministratorDownloads”.
Step 3. Note down the destination directory that you want to copy to.
# 1. Copy a Specific File via the Copy Command
Step 1. Type cmd in the Search box, and then right-click the Command Prompt window and select Run as administrator. Then click on Yes in the UAC window.
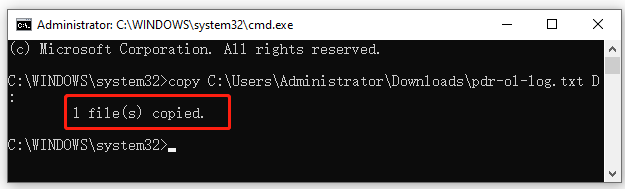
Step 2. In the elevated Command Prompt window, type the following command and hit Enter to copy the file “pdr-ol-log.txt” on the C drive to the D drive root. If it shows the “1 file(s) copied” message, it indicated that the file has been copied to the destination folder successfully.
copy C:UsersAdministratorDownloadspdr-ol-log.txt D:
Step 3. If you want to copy certain file extensions from one drive to another, you can run the “copy *.txt E:” command. You can replace the “.txt” with your file extensions such as “.png”, “.xls”, etc.
# 2. Copy the Whole Directory via the XCopy Command
If you want to copy all files under a directory to another directory quickly, you can use the XCopy command. Here’s how to do that:
Step 1. Open the elevated Command Prompt window as we explained above.
Step 2. Type the following command and hit Enter. Here you can replace the C:UsersAdministratorDownloads section with the directory you want to copy and replace the D:Ariel with your actual destination.
xcopy C:UsersAdministratorDownloads D:Ariel
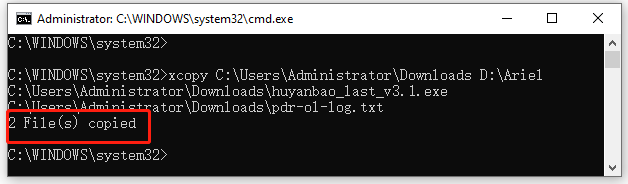
Now, all contexts under the directory should be copied into the destination path successfully.
Bonus Tip: Best Alternative to Copy Large Files Quickly
Although the CMD copy file is time-saving and convenient, it is relatively strange for many non-professionals to operate. If you have a large chunk of files that need to copy into an external drive, you can consider copying the partition to another drive. Compared with the command line copy method, it’s more efficient and simpler.
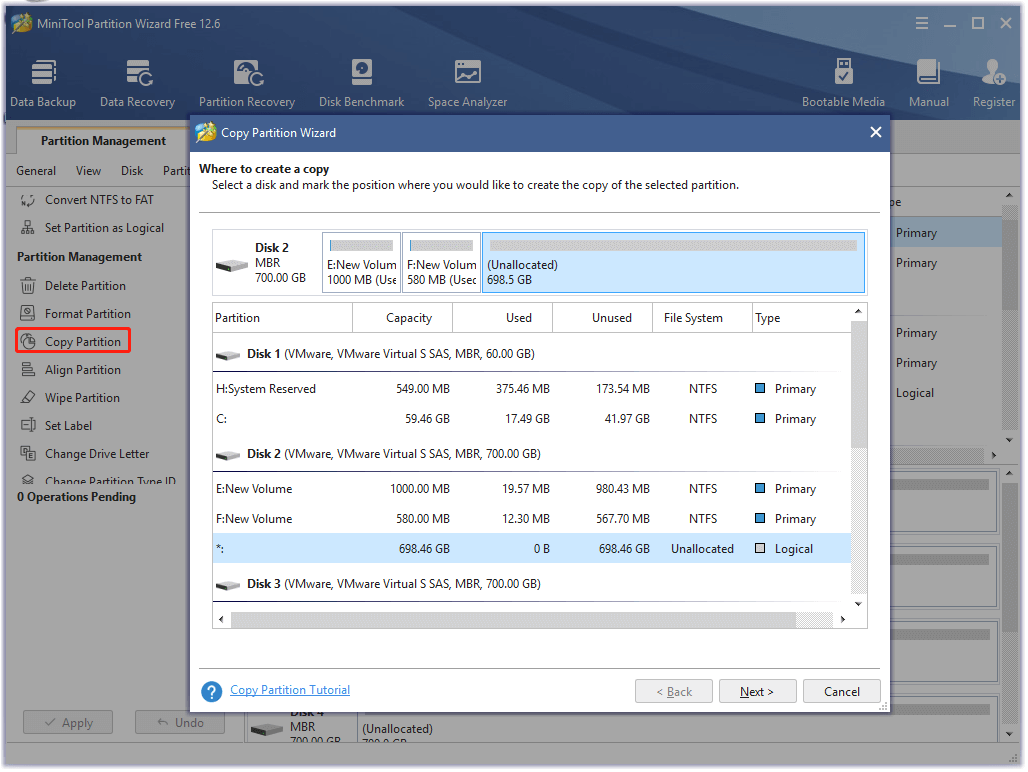
Here MiniTool Partition Wizard can help you copy the whole partition to another drive quickly with a few clicks. Besides, it can be used to copy disk, migrate OS to SSD/HD without reinstalling, convert MBR to GPT, etc.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Ariel has been working as a highly professional computer-relevant technology editor at MiniTool for many years. She has a strong passion for researching all knowledge related to the computer’s disk, partition, and Windows OS. Up till now, she has finished thousands of articles covering a broad range of topics and helped lots of users fix various problems. She focuses on the fields of disk management, OS backup, and PDF editing and provides her readers with insightful and informative content.


















