Last Updated :
16 May, 2024
While working on Windows devices, we used to work on Windows File Explorer for working with files. On File Explorer of Windows, the creation of new files as well as deleting old ones is one of the easiest processes. However, if your File Explorer is not responding, then the process to Delete Folder using CMD can be an alternative.
The Windows Command Prompt is the command line tool that executes different tasks with the help of Windows Commands. Using CMD in Windows, the File Creation for Windows can also be executed. If you are having trouble Deleting Files or Folders on Windows directly by right-clicking, then you can Delete files using CMD.
This article is going to discuss the commands required to Remove Files & Folders using the UsingCommand Prompt of Windows.
Table of Content
- Methods to Delete Files and Folders Using Command Prompt
- Method 1: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using DEL Command
- Method 2: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using RMDIR Command
- Delete a Folder and Subfolders in Command Prompt
Methods to Delete Files and Folders Using Command Prompt
To Erase Windows Files or Folders using CMD, the following guidelines should be used properly. Let us start with the DEL Command Execution.
Method 1: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using DEL Command
Note: DEL Command is used to delete a file. Here, we will take our sample file “hello.txt” located on the desktop, and try to delete it using the del command in CMD. Follow the steps given below to delete the file:
Step 1: Change the Path of the Directory in CMD and set it to the path of the file. Type the following command and press Enter.
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the file hello.txt with the following Windows Command.
del hello.txt

Method 2: Delete Files or Folders on CMD using RMDIR Command
Note: RMDIR Command is used to delete the entire folder or directory. Here, we will take our sample folder named “Tasks” placed on the desktop and try to delete it using RMDIR Command in CMD.
Step 1: Change the Directory’s Path in Command Prompt and set it to the path of the folder.
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the folder Tasks with the following command.
rmdir tasks

From the above discussion, this should become clear that the Deletion of Windows Files using CMD is a matter of a few seconds. You have to just move inside the Windows Directory using the Windows CD Command. And then, as per your choice execute any one of the Windows File Deletion Commands in CMD.
Delete a Folder and Subfolders in Command Prompt
Step 1: Open Command Prompt.
Step 2: Navigate to the directory where the folder you want to delete is located using the cd command.
Command: cd <FolderName>
Step 3: To delete a single folder, use the following command.
Command: rmdir <FolderName>
Step 4: To delete a folder and all its subfolders and files, just include “/s” in between the rmdir and <folderName>, use the following command.
Command: rmdir /s <FolderName>
Step 5: Press Enter to execute the command.
Also Read
- Useful CMD commands for daily use in Windows OS
- CMD Commands to Gather Information of a System
- How to Show all the previously connected WiFi Networks using CMD in Windows?
Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to use Command Prompt in Windows to delete files and folders efficiently when facing issues with File Explorer. We discussed two methods: using the DEL command to delete files and the RMDIR command to delete folders. Additionally, we provided a step-by-step guide on how to delete folders and subfolders using Command Prompt.
on August 5, 2015
Deleting files is one of the frequently done operation from Windows command prompt. This post explains how to use ‘del’ command from CMD for different use cases like deleting a single file, deleting files in bulk using wild cards etc. Before we start to look at the syntax, note that the command works only for files and can’t handle folders.
How to delete a file
Run del command with the name of the file to be deleted, you are done!
del filename
You do not see message after running the command if the file is deleted successfully. Error message is shown only when something goes wrong.
Delete files in bulk
Del command recognizes wildcard(*) and so can be used to delete files in bulk from CMD. Some examples below.
To delete all the files in current folder
del *
To delete all the files with ‘log’ extension
del *.log
Delete all files having the prefix ‘abc’
del abc*
Delete all files having ‘PIC’ somewhere in the file name.
del *PIC*
The above are the basic use cases of del command. Continue to read below for non trivial use cases.
Delete multiple files
‘Del’ command can accept multiple files as argument
del filename1 filename2 filename3 filename4....
Example:
D:\>dir /s /b 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf D:\>del 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf D:\> D:\>dir /s /b D:\>
Delete Read only files
We can’t delete a read-only file using simple‘del’ command. We get access denied error in this scenario.
c:\>attrib readonlyfile.txt A R C:\readonlyfile.txt c:\>del readonlyfile.txt c:\readonlyfile.txt Access is denied. c:\>
A read-only file can be deleted by adding /F flag.
del /F readonlyfile.txt
Alternatively, we can use the below command too
del /A:R readonlyfile.txt

Sometimes it’s just faster to do things with the command line.
In this quick tutorial we’ll go over how to open Command Prompt, some basic commands and flags, and how to delete files and folders in Command Prompt.
If you’re already familiar with basic DOS commands, feel free to skip ahead.
How to open Command Prompt
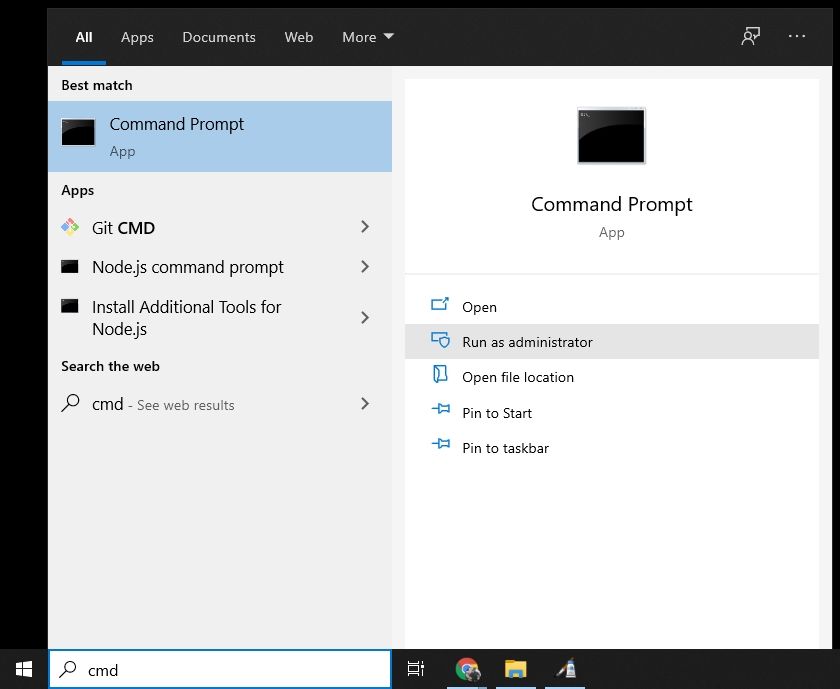
To open Command Prompt, press the Windows key, and type in «cmd».
Then, click on «Run as Administrator»:
After that, you’ll see a Command Prompt window with administrative privileges:
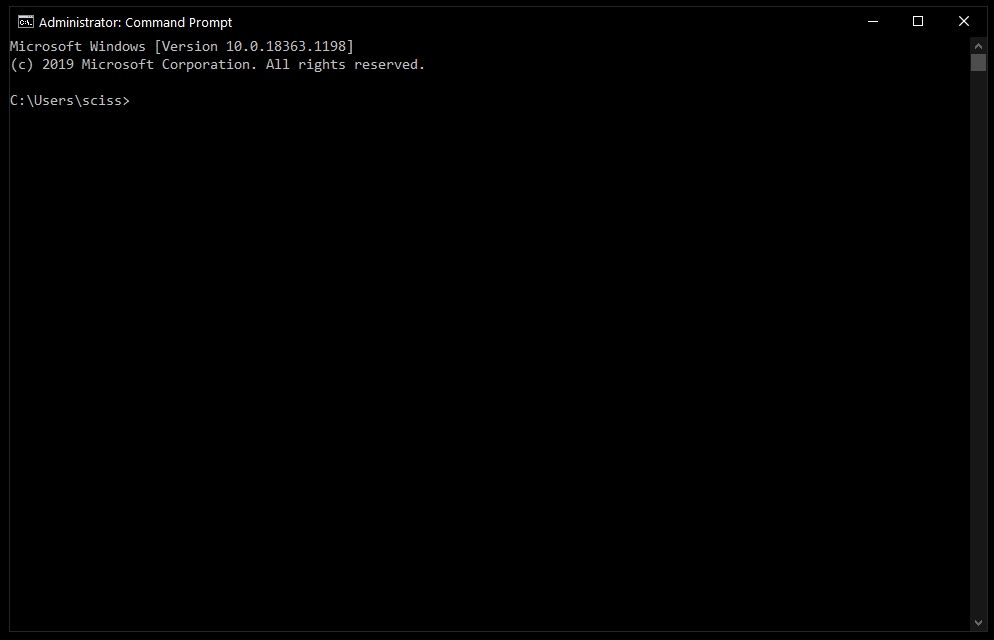
Screenshot of Command Prompt window
If you can’t open Command Prompt as an administrator, no worries. You can open a normal Command Prompt window by clicking «Open» instead of «Run as Administrator».
The only difference is that you may not be able to delete some protected files, which shouldn’t be a problem in most cases.
How to delete files with the del command
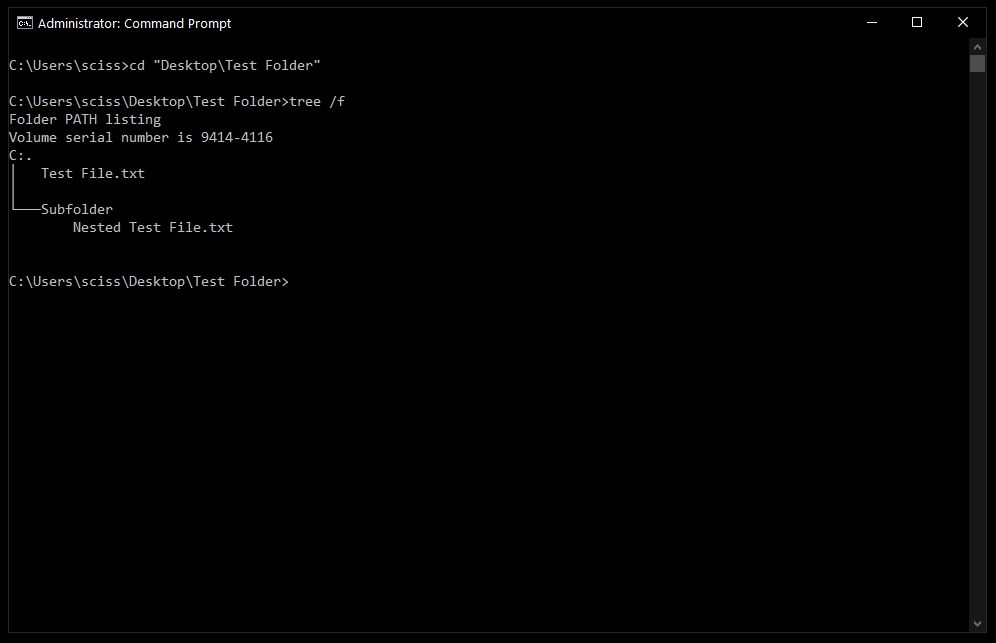
Now that Command Prompt is open, use cd to change directories to where your files are.
I’ve prepared a directory on the desktop called Test Folder. You can use the command tree /f to see a, well, tree, of all the nested files and folders:
To delete a file, use the following command: del "<filename>".
For example, to delete Test file.txt, just run del "Test File.txt".
There may be a prompt asking if you want to delete the file. If so, type «y» and hit enter.
Note: Any files deleted with the del command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
After that, you can run tree /f to confirm that your file was deleted:

Also, bonus tip – Command Prompt has basic autocompletion. So you could just type in del test, press the tab key, and Command Prompt will change it to del "Test File.txt".
How to force delete files with the del command
Sometimes files are marked as read only, and you’ll see the following error when you try to use the del command:
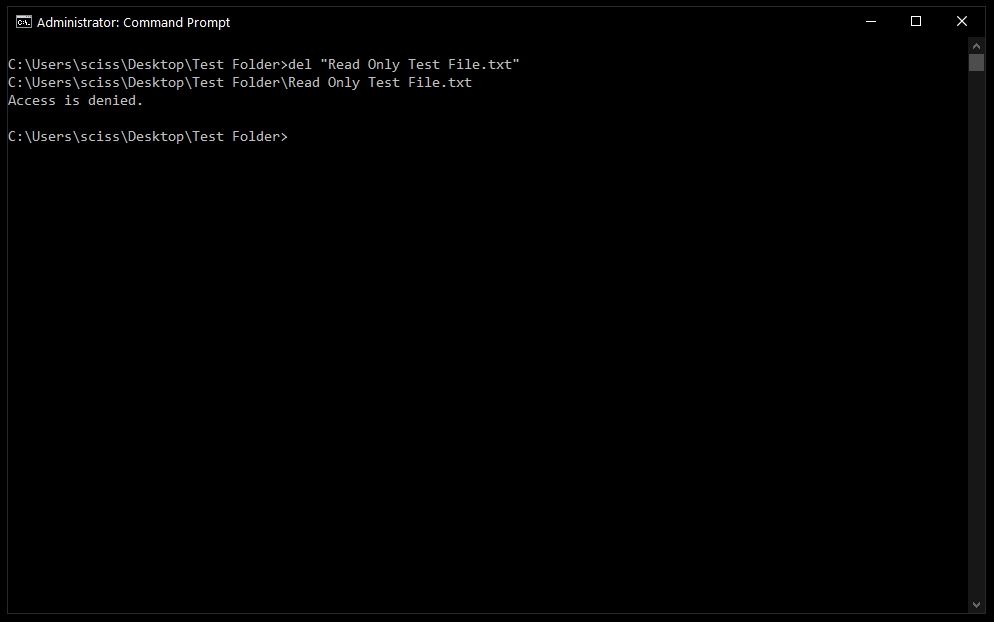
To get around this, use the /f flag to force delete the file. For example, del /f "Read Only Test File.txt":
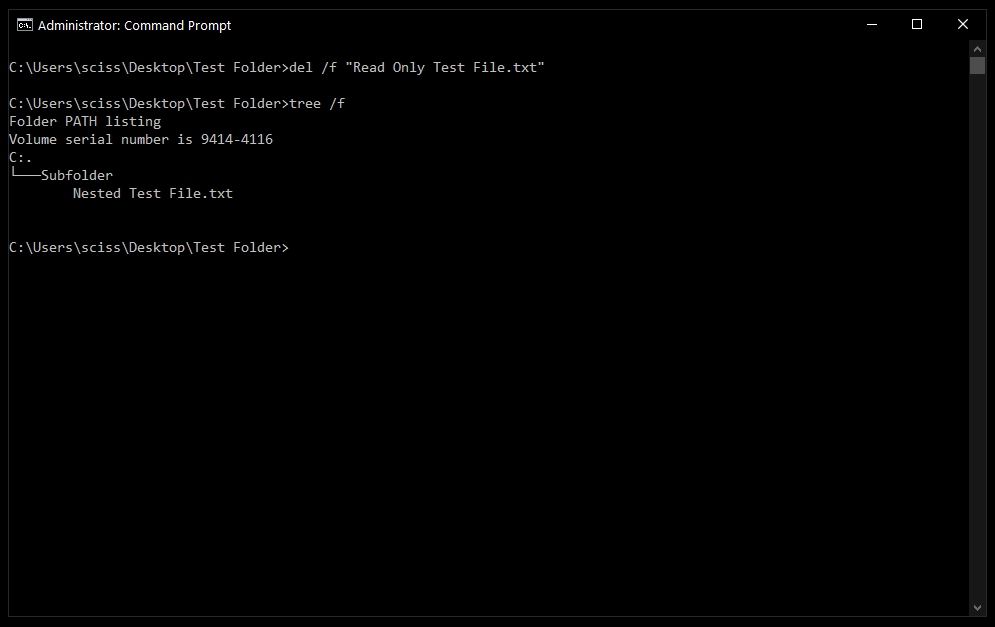
How to delete folders with the rmdir command
To delete directories/folders, you’ll need to use the rmdir or rd command. Both commands work the same way, but let’s stick with rmdir since it’s a bit more expressive.
Also, I’ll use the terms directory and folder interchangeably for the rest of the tutorial. «Folder» is a newer term that became popular with early desktop GUIs, but folder and directory basically mean the same thing.
To remove a directory, just use the command rmdir <directory name>.
Note: Any directories deleted with the rmdir command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
In this case I want to remove a directory named Subfolder, so I’ll use the command rmdir Subfolder:
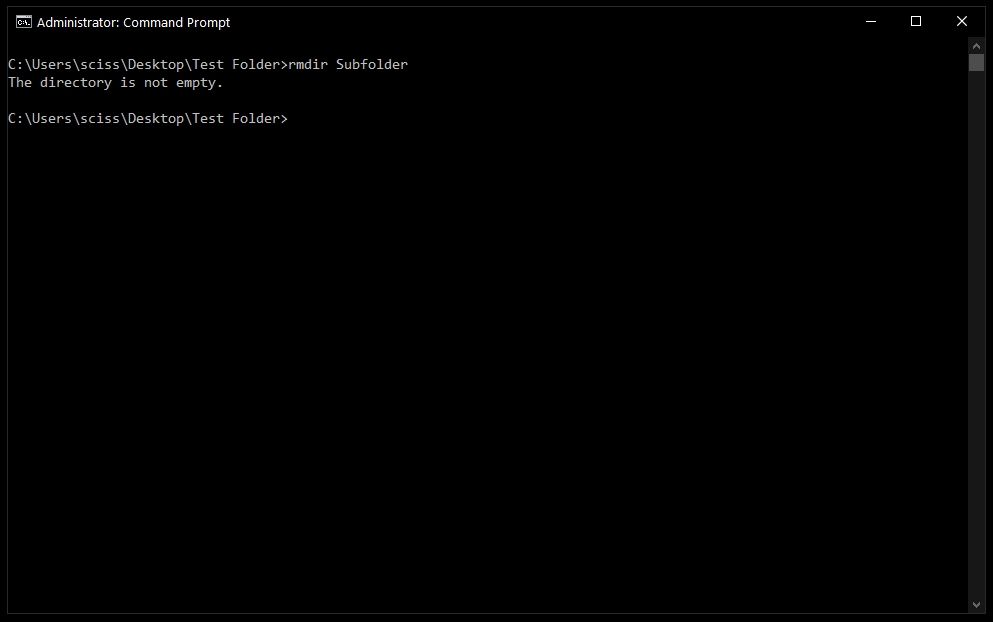
But, if you remember earlier, Subfolder has a file in it named Nested Test File.
You could cd into the Subfolder directory and remove the file, then come back with cd .. and run the rmdir Subfolder command again, but that would get tedious. And just imagine if there were a bunch of other nested files and directories!
Like with the del command, there’s a helpful flag we can use to make things much faster and easier.
How to use the /s flag with rmdir
To remove a directory, including all nested files and subdirectories, just use the /s flag:
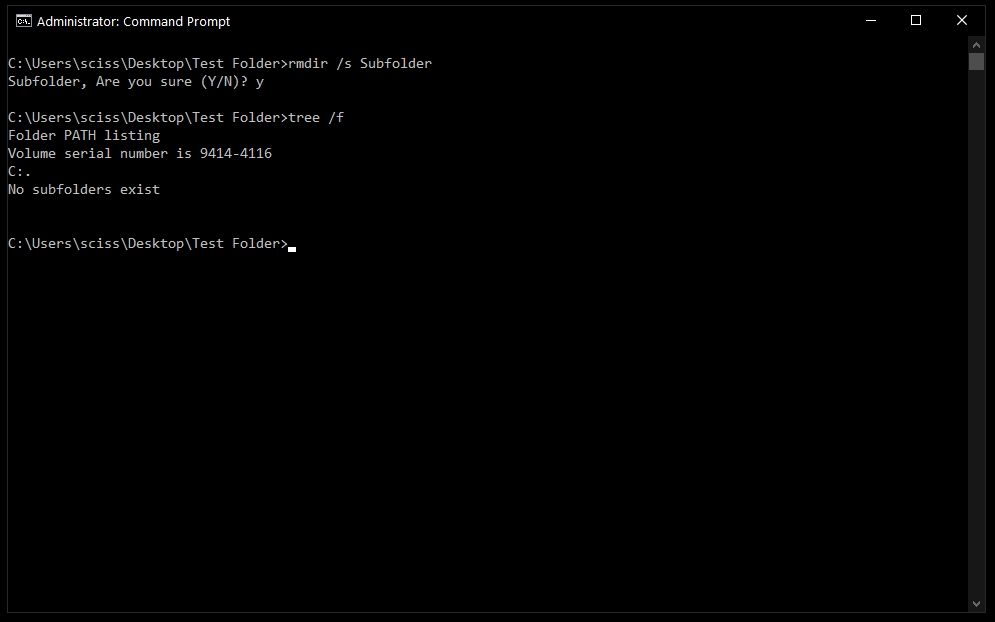
There will probably be a prompt asking if you want to remove that directory. If so, just type «y» and hit enter.
And that’s it! That should be everything you need to know to remove files and folders in the Windows Command Prompt.
All of these commands should work in PowerShell, which is basically Command Prompt version 2.0. Also, PowerShell has a bunch of cool aliases like ls and clear that should feel right at home if you’re familiar with the Mac/Linux command line.
Did these commands help you? Are there any other commands that you find useful? Either way, let me know over on Twitter.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Удалить файл или папку с диска или флешки – что, казалось бы, может быть проще? Да, это действительно просто, если только вы не работаете в среде восстановления, в которой Проводник недоступен. В таких случаях вам придется использовать командную строку – мощный инструмент управления Windows, о котором многие пользователи уже начали забывать. Консоль может вам понадобиться и в работающей системе, например, при удалении скрытых и недоступных только для чтения файлов, а также файлов, используемых процессом explorer.exe (после его завершения).
Для удаления файлов в классической командной строке Windows используются две команды – DEL и ERASE, которые функционально ничем не отличаются, имея одинаковый набор аргументов. Команда имеет следующий синтаксис:
del /key full path
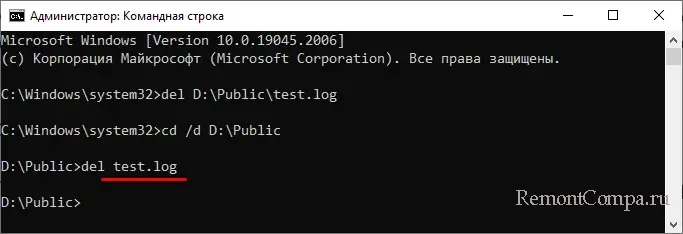
del или erase – это сама команда удаления, /key – это необязательный аргумент, а full path – полный путь к удаляемому файлу. Например, команда ниже удаляет файл test.log в папке Public на диске D:
del D:\Public\test.log
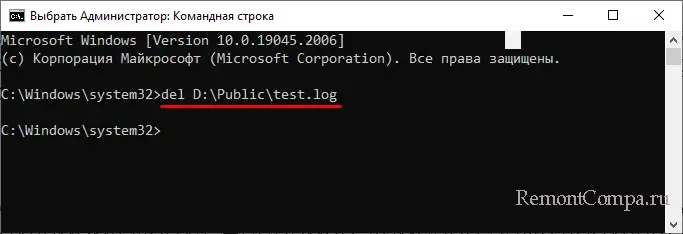
Кстати, указывать полный путь необязательно, если вы заранее перешли в папку с файлов. В этом случае указывается только команда удаления и сам файл:
del test.log
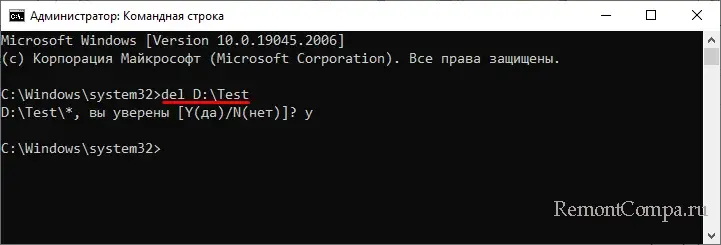
Файлы можно удалять не только по одному, но и все сразу, так, следующая команда удалит все файлы из папки Test:
del D:\Test
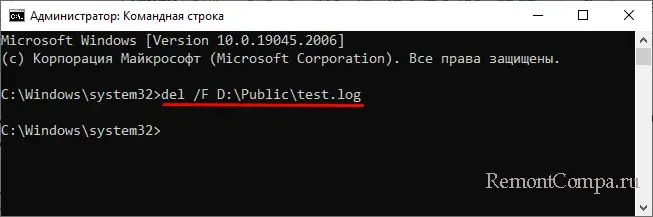
Будут пропущены лишь те файлы, которые имеют атрибуты «Только для чтения», «Скрытые», «Системные» и т. д. Для удаления таких файлов в команду добавляются специальные ключи, например, чтобы удалить файл с меткой «Только для чтения», в команду нужно добавить ключ /F, вот так:
del /F D:\Public\test.log
Помимо ключа /F, командой DEL поддерживает параметры /P, /S, /Q и /A. Рассмотрим их назначение чуть более подробно.
● /P – включает запрос на подтверждение удаления файла.
● /Q – отключает запрос на подтверждение удаления файла, обычно используется при удалении групп файлов.
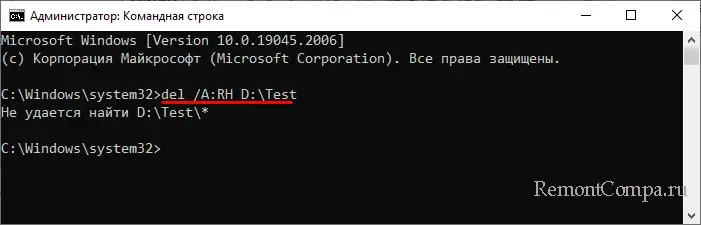
● /A – ключ используется, когда нужно удалить группу файлов с определенными атрибутами – del /A:RH D:\Test – в результате выполнения этой команды из папки Test будут удалены все файлы с атрибутами R (только для чтения) и Н (скрытые).
● /S – если нужно удалить файлы рекурсивно, то есть не только в указанной папке, но и во всех вложенных в нее папках, добавьте в команду ключ S, вот так:
del /S D:\Test.
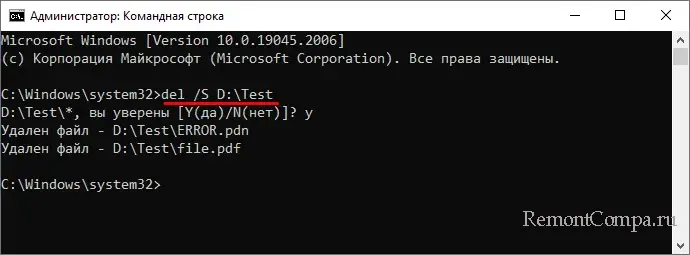
В принципе, этих знаний достаточно, чтобы удалить любой несистемный файл, но рассмотренная нами тема была бы не раскрыта без упоминания о другом консольном инструменте Windows – PowerShell. Помимо поддержки ею команд DEL и ERASE, PowerShell располагает собственным командлётом для удаления объектов файловой системы. Он называется Remove-Item и имеет следующий синтаксис:
Remove-Item -Path -key
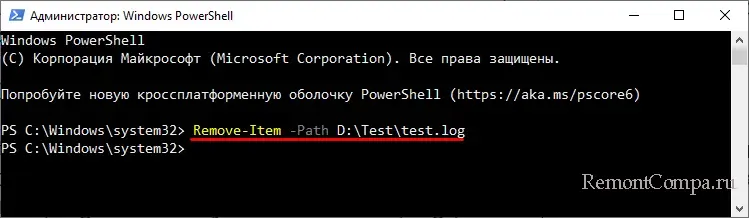
Командлёт очень похож на DEL, Path принимает значение пути к удаляемому объекту, а key – дополнительный параметр или несколько параметров. В отличие от DEL и ERASE, Remove-Item универсален и может использоваться для удаления как файлов, так и каталогов. Удалим файл test.log из папки Test:
Remove-Item -Path D:\Test\test.log
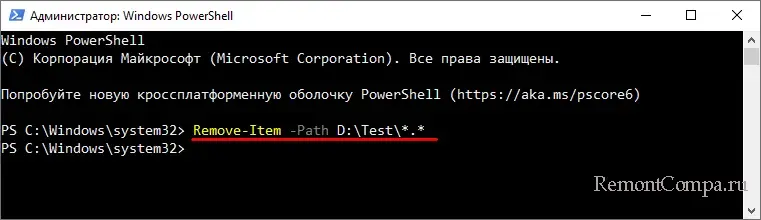
Использовать «-Path» необязательно, так как PowerShell и так понимает, что нужно делать. Папки удаляются аналогично, если нужно удалить только файлы, используется подстановочный знак, в данном случае точка перед расширением.
Remove-Item -Path D:\Test\*.*
Если путь содержит пробелы или кириллицу, его нужно взять в прямые двойные кавычки. Командлёт поддерживает около дюжины параметров, из которых вам наверняка пригодятся -Force и -Recurse.
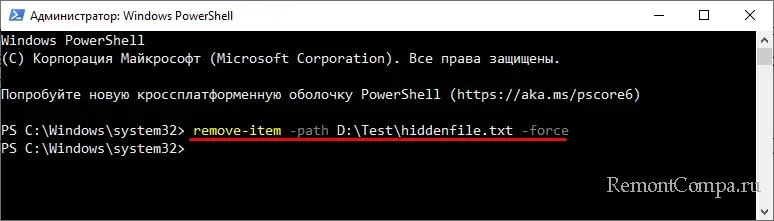
Параметр -Force используется для принудительного удаления файлов с атрибутами «Только чтения», «Скрытый», «Архивный» и «Системный».
remove-item -path D:\Test\hiddenfile.txt -force
Параметр -Recurse служит для удаления файлов в указанной папке и всех вложенных в нее каталогах. Поскольку параметр Remove-Item в связке с командлётом -Recurse работает корректно не во всех версиях PowerShell, вместо Remove-Item лучше использовать Get-ChildItem.
Get-ChildItem -Path «D:\Test» -File -Recurse | foreach { $_.Delete()}
Обращаем внимание, что эта команда удалит все файлы из папок в директории Test мимо Корзины, такова особенность ее работы. И на этом, пожалуй, достаточно. Более подробные сведения об использовании команд DEL, ERASE и Remove-Item можно получить в самой консоли, выполнив интересующую вас команду с ключом /? в классической командной строке и get-help название-командлёта в PowerShell.
Key Takeaways:
- You can use the “del” command to delete a single file, multiple files, files that contain a specific word, files with a specific extension, and all files in a folder at once.
- The Command Prompt can also help remove or delete stubborn files that you cannot delete from File Explorer.
- Deleting files using commands is also helpful when you want to delete a large number of files.
Generally, deleting a file in Windows is a simple process. All you have to do is select the file you want to delete and press the “Delete” key on your keyboard or right-click on the file and select the “Delete” option.
If you cannot delete a file using File Explorer, you can use the Command Prompt to delete files in Windows 10 and 11. The Command Prompt offers a quick and easy way to delete a single file, multiple files, files with a specific extension, or read-only files. The best thing is that this works even if the file is locked, in use, or blocked from deletion.
In this short tutorial, let me walk you through the process of deleting a file using cmd.
Table of contents:
- How to delete a file using CMD
- How to delete all files in a folder using CMD
- How to delete files with a specific extension using CMD
- How to delete read-only files using CMD
- Conclusion
Important note: Files deleted using cmd will skip the Recycle Bin. That means you cannot restore a deleted file from the Recycle Bin. So, be careful while using Command Prompt to delete files in Windows.
How to delete a file using CMD
To delete a single file, all you need to do is execute a single command with the file name.
- Select the “Start” icon on the taskbar.
- Search for “Command Prompt.”
- Click on the “Run as administrator” option.
- Use the “cd C:\path\to\folder” to navigate to the folder.
- Run the “del filename.ext” command to delete the file. Replace “filename.ext” with the actual file name and extension.
Steps with more details:
First, search for “cmd” in the start menu, right-click on Command Prompt and select “Run as administrator.” This action will open an elevated command prompt.
Note: The elevated Command Prompt is required to delete locked files, files belonging to other user accounts, etc.
Once the Command Prompt window opens, use the “cd” command to go to the folder where the files you want to delete are located. For instance, the files I want to delete are in a folder named “del” on my desktop. So, I use the following command.
Note: If the folder is located in another partition, like the D drive, execute the “DriveLetter:” command while replacing “DriveLetter” with the actual drive letter. For example, to change the directory to D drive, you have to execute the “D:” command. Once in the drive, you can use the “cd” command to navigate to the target directory.
cd c:\users\vamsi\desktop\del

Once you are in the folder, run the below command to delete a file. Don’t forget to replace <filename> with the actual file name along with its file extension. In my case, the file name is image-1.jpg.
del <filename>

If the file is locked in some way, use the below command to force delete the file.
del /f <filename>
On successfully deleting the file, you will not see any confirmation message. So, that’s a good thing. If there is a problem, the command prompt will show an error message.
How to delete all files in a folder using CMD
The Command Prompt offers a simple command to delete multiple files in a folder at once. Whether you need to delete specific files or all files in a folder, cmd provides the option to do so. I will show how to use the command to delete multiple files in both situations. Follow the one that best suits your needs.
Here’s the cmd to delete multiple files:
First of all, open Command Prompt as administrator from the Start menu.
Once the command window opens, use the “cd C:\folder\path” to go to the folder with the files you want to delete.
Next, to delete multiple specific files at once, execute the below command while replacing <filname1>, <filename2>, etc., with the actual file names along with the file extension. You can specify as many file names as you want.
del <filename1> <filename2>

You can use the “*” (wildcard) character to delete all the files in a folder. Here’s the command to remove all files in a directory.
del *
Since we are deleting all the files in a folder, the Command Prompt window will warn you. Simply type “Y” and press “Enter” to confirm file deletion.

You can also use the wildcard character to delete all files that start with a specific name in a folder. For that, use the below syntax. For instance, the below command will delete all the files in a folder that start with the name “image.”
del image*

Alternatively, you can also delete files that contain a specific word. The below command will delete all the files with the name that contains the “tFile” word.
del *word*

How to delete files with a specific extension using CMD
Sometimes, you might want to delete all the files with a specific extension. For instance, maybe you want to delete all the “.png” files in a folder. In that case, we can use the same wildcard character.
Here’s the command to delete files that have a specific file extension, then you can use below command. Don’t forget to replace “fileExtension” with the actual file extension, like png, jpg, zip, etc.
del *.fileExtension
For example, to delete all the PNG files in a folder, the command looks something like this.
del *.png

Use the below command to delete all files with a specific name and extension. Don’t forget to replace the file name and extension to match your needs.
del filename*.png

How to delete read-only files using CMD
Unlike regular files, read-only files are protected and difficult to delete by design. If you try to delete a read-only file using the normal commands shown above, you will receive the “Access is denied” error message.

First, open the command prompt from the Start menu and use the “cd C:\path\to\folder” command to go to the folder with the read-only file.
Once you are here, use one of the below commands to delete the read-only file. Replace <filename> with the actual filename and extension.
del /f <filename>
or
del /a:r <filename>

CMD to delete files in Windows – Conclusion
As you can see, commands to delete files in Windows are pretty simple and straightforward. With the commands and flags shown in this tutorial, you can delete individual files, read-only files, multiple files, or even all files in a folder. You can also use the Command Prompt to delete files that are locked, in use, or blocked from deletion. The steps shown above are handy when you need to delete a large number of files or when you cannot delete a file using the traditional File Explorer method.
I hope this simple and easy Windows how-to guide helped you.
If you are stuck or need help, send an email, and I will try to help as much as possible.
If you like this article, you might also want to know how to force delete locked files in Windows and how to delete a single URL from Chrome and Firefox’s auto-complete history.
