As you use Windows, there are times you will need to execute commands in the Command Prompt (CMD) to perform certain tasks. There are commands that will only work when they are executed in the right directory. This short guide will show you how to change the directory or drive in CMD on Windows 11.
The commands to change directory or drive can also be used in the Windows Terminal (a new command-line tools and shells similar to CMD) in Windows 11.
Change directory or drive in Command Prompt
In Command Prompt, you can use the CD command to change the current directory to any other directory you want. This is provided if you have access to the directory and if the directory you want to change to does exist.
For example, the command below will change the current directory to “C:\test” in CMD.
cd C:\test
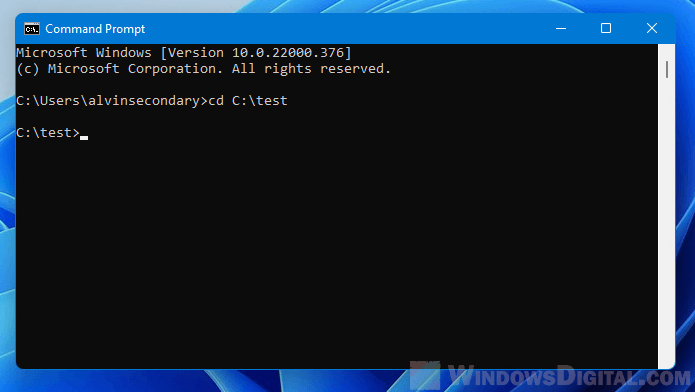
If the directory or path name contains spaces, it’s recommended to use quotes around the directory. For example, the command below will change the directory to “C:\New folder” in CMD.
cd "C:\New Folder"
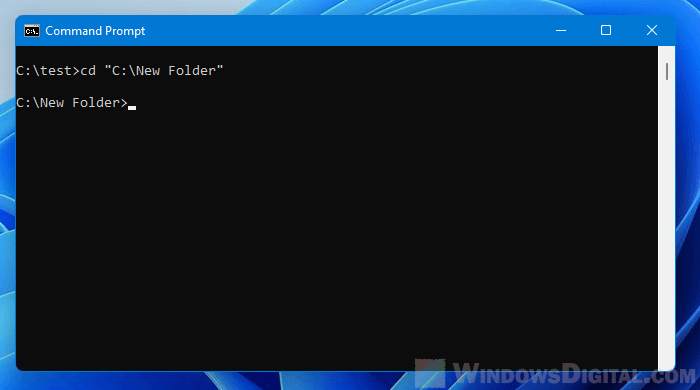
To change the current directory to a different drive in CMD, simply enter the drive letter. For example, the command below will change to D: drive.
d:
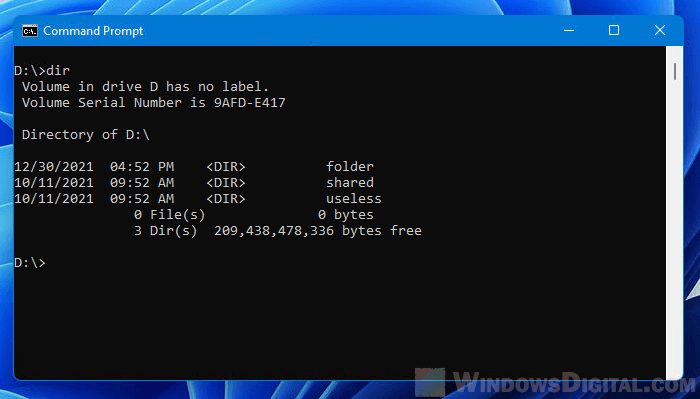
Tip: To view a list of all folders (sub-directories) in the current directory in CMD, enter “dir” in Command Prompt.
dir
Can’t change directory in CMD
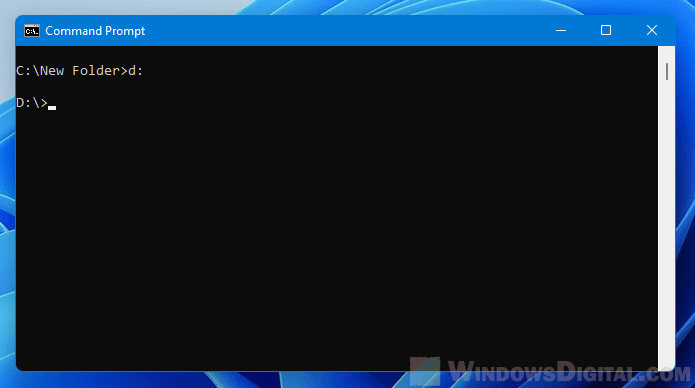
If the CD command does not work to change directory or drive in CMD, it is because CD is usually used for changing directory in the same drive. If you want to change the directory to a different drive, for example, from C: to D: drive, just type D: in the command prompt.
D:

After changing the drive, you can then continue using the CD command to change the directory in that drive in CMD.
Alternatively, you can force use CD with a switch “/d” to tell the command prompt you are switching to another drive using the CD command. For example, the command below will change from any directory or drive to “D:\folder\sample” using CD command.
cd /d d:\folder\sample
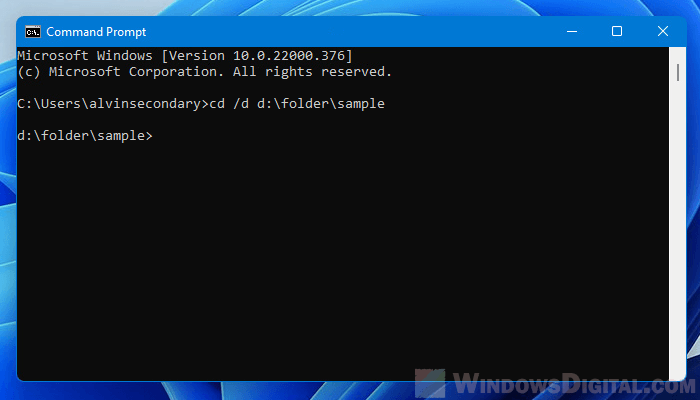
The system cannot find the path specified error in CMD
Note that if the directory you are changing to does not exist, command prompt will return an error that says “The system cannot find the path specified“. Check the path name and try again.
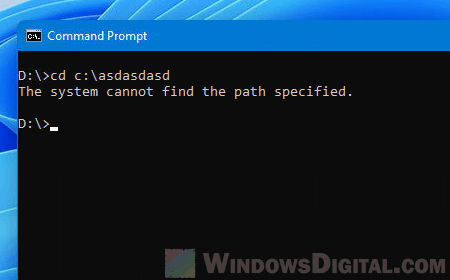
Unable to change directory in CMD because “Access is denied”
If you receive the “Access is denied” error when you try to CD to a directory, it means that you do not have the privileges required to access the folder or directory. If you are an administrator in the system and you do own the folder, take ownership of the folder and try again. Read: How to Take Ownership of a File, Folder or Drive in Windows 11.
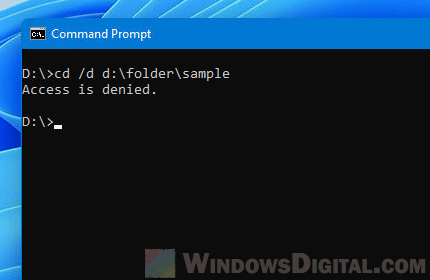
Change default directory in CMD on Windows 11
By default, if you open Command Prompt from the Start menu or Run window, it will usually open in your Windows profile directory which is something like C:\users\alvin. Or, if you run CMD as administrator, it will always start in C:\Windows\system32.
There is no setting that allows you to change the default directory if you start CMD from Start or Run. However, there is a workaround to force CMD to start in any directory you want it to. You can create a shortcut pointing to cmd.exe and configure the Start in field to any directory you want the command prompt to start in. Here’s how to do it.
First, right-click anywhere on the desktop and select New > Shortcut to create a shortcut.
In the Create Shortcut wizard, enter the path to cmd.exe, in most cases, it should be in “C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exe“. Change the C: drive if your Windows is installed on a different drive. Click Next to continue. Give your shortcut any name you like and click Finish to complete the wizard.
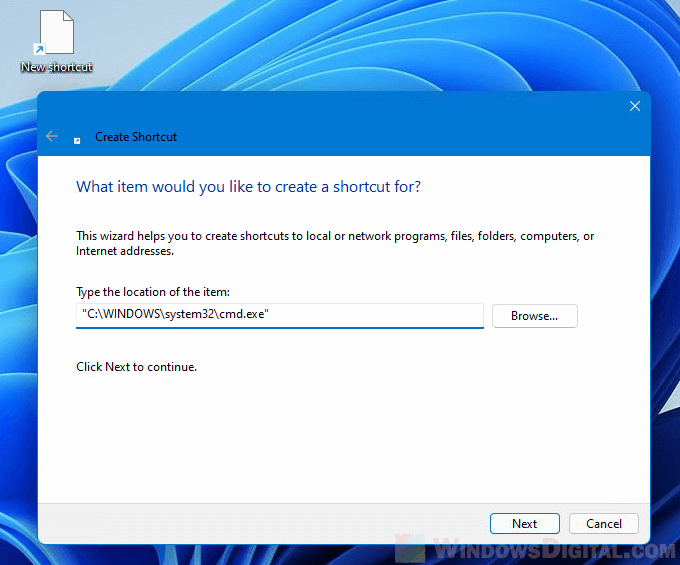
Next, right-click the newly created shortcut and select Properties. Then, go to the Shortcut tab. In the Start in field, enter the default directory where you want CMD to start in when you open this shortcut. Click OK to save the changes.
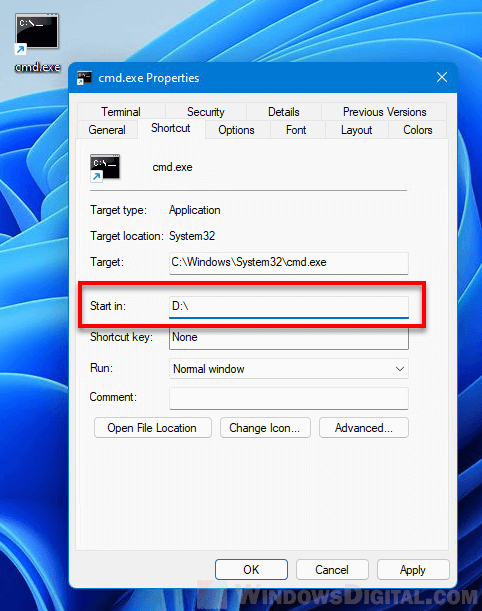
Whenever you open CMD through this shortcut, Command Prompt will automatically start in the directory you’ve entered in the “Start in” field earlier.

In the Windows command prompt (CMD), we use the cd command to change from one directory to another. However, it only changes the path inside the current drive by default.
If you want to change to a different drive in CMD, you need to use the /d switch.
cd /d D:For example, I am working on the command prompt, inside the C:\Users\user1 folder. Now I want to move into a folder called data which is in the D: drive.

In the above screenshot, you can see that the command didn’t work. The solution is to use the /d switch.

Alternatively, simply enter the drive letter followed by a colon, as follows:
D:However, this method only changes to the root of the drive. If you want to go to a folder, you have to use the CD command.
To change the current drive in Windows Command Prompt, simply type the drive letter followed by a colon and press Enter.
D:
Understanding CMD Commands
What is CMD?
CMD, or Command Prompt, is a command-line interpreter in Windows operating systems that allows users to execute commands for various tasks, such as file manipulation, system configuration, network management, and program execution. It serves as a powerful tool for users seeking to perform advanced processes without relying on the graphical user interface (GUI).
Basic Structure of CMD Commands
Understanding the basic structure of CMD commands is crucial for efficient usage. Commands typically consist of the command itself, options (if any), and parameters. The syntax is sensitive to spacing and formatting, making it essential to adhere strictly to the rules. For instance, if you forget a space or misplace a directory path, you may encounter errors when trying to run your commands.

Windows Change Drive Cmd: A Simple Guide
How to Change Drive in CMD
Switching Between Drives
One of the primary functions in CMD is the ability to switch between different drives. This feature is especially useful in systems with multiple drives or partitions, allowing you to easily navigate your file structure.
To switch to a different drive, simply type the drive letter followed by a colon and then hit Enter. For example, if you wish to switch from drive C: to drive D:, you would enter:
D:
This command will take you directly to the root of drive D:, allowing you to continue executing further commands.
Displaying Current Drive
Knowing which drive you are currently in is just as important as being able to switch drives. You can easily check your current drive and directory by executing the following command:
cd
This command will display the current working directory, which includes the drive letter and path.

Navigate Your Windows Cmd Home Directory Effortlessly
CMD Change Directory: The Essentials
What is Changing Directory?
Changing directories is essential for managing files effectively within CMD. When you change directories, you’re navigating to a different folder on your current drive, enabling you to access files and execute commands in that directory.
How to Change Directory in CMD
Using the `cd` Command
To change to a specific directory within the current drive, you’ll use the `cd` command (short for «change directory»). This command requires the path of the folder you wish to access.
Basic Syntax:
cd [directory_path]
Example Usage: If you want to change to a folder named ‘Documents’ located at the root of the current drive, you would write:
cd \Documents
This command effectively navigates you into the Documents folder.
Going Back One Directory Level
If you need to move back one level in the directory structure, use the following command:
cd ..
This command will take you up to the parent directory, allowing you to navigate back through your folder hierarchy. Understanding this concept is particularly useful when you’re nested deeply within a directory.
Changing Directory with Full Path
When dealing with more complex file structures, you may need to specify the full path to change directories. This approach is useful if the directory is on the same drive or even on a different one.
For example, to navigate directly to a folder named ‘Projects’ located in ‘D:\MyFiles’, you would execute:
cd D:\MyFiles\Projects
Here, each part of the command is significant; it specifies exactly where in the file system you want to navigate.

Mastering Windows Cmd Copy Directory in No Time
CMD Change Drives: Advanced Techniques
Combining Drive and Directory Change
CMD allows you to change both the drive and the directory in one command, making navigation even quicker. The `/d` switch enables you to switch to a different drive while also specifying a directory.
Example Command:
cd /d D:\NewFolder
In this case, the command not only switches to the D: drive but also navigates directly into the ‘NewFolder’ directory. Using this technique can save time, especially when working on extensive projects.
Utilizing Environment Variables
Environment variables are a powerful way to create flexible commands in CMD. These variables can dynamically point to specific directories or settings, adapting to different user profiles or configurations.
For instance, if you want to navigate to your Documents folder, you can use the following command:
cd %USERPROFILE%\Documents
This command automatically directs you to the Documents folder of the currently logged-in user, regardless of the specific username or system setup. This versatility is invaluable for scripting and automation.
Windows Cmd Clear: Refresh Your Command Line Effortlessly
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Error Messages
As you work with CMD, you may encounter various error messages when changing drives or directories. Common errors include «The system cannot find the path specified» or «Access is denied.»
Understand that paths must be exact, and any discrepancies will result in these errors. Double-check the spelling and directory structure if you face such issues.
Permissions Issues
Sometimes, you may encounter permissions issues, especially when attempting to navigate to system directories or other users’ files. When running into such errors, consider:
- Running CMD as Administrator: Right-click on Command Prompt and select «Run as administrator.»
- File Permissions: Ensure you have the necessary permissions to access the directory in question.

Windows Cmd Grep: Your Essential Guide to Text Searching
Conclusion
Mastering how to change drives and directories via CMD is essential for efficient file management in Windows. With the commands and techniques discussed in this guide, you will be able to navigate your file system more effectively, enhancing your overall productivity. Practice these commands regularly to build your confidence and improve your skills. Consider joining our community for more tips and further insights into CMD usage.

Mastering Windows Cmd Attrib: A Quick Guide
Additional Resources
For further reading and hands-on practices, explore tutorials and video resources aimed at CMD proficiency. Understanding these basic commands can pave the way to more advanced command-line skills in the future.
Geeks and experts love the Command Prompt because of the advanced commands it can run. Fortunately, Command Prompt is not built only on advanced commands, but also on simple ones, designed to perform basic operations. In this article, we show you how to change the directory in CMD, change the drive, see the contents of a directory, how to rename, copy, and delete files and folders, and also how to launch an application from the Command Prompt. We’ll also cover how to get help in CMD. Let’s get started:
NOTE: The information shared in this tutorial applies to Windows 11, Windows 10, and even older Microsoft operating systems such as Windows 7.
1. How to change the directory in CMD (CD in Command Prompt)
The first command from the list is CD (Change Directory). This command enables you to change the current directory or, in other words, to navigate to another folder from your PC.
How to go to the root of the drive, in CMD (CD\)
The first iteration of the CD command you should know is CD\. It takes you to the top of the directory tree. To see how it works, after you open the Command Prompt, type:
cd\
… and press Enter on your keyboard. You should see how the CD\ command takes you to the top of the directory tree. In this case, to the C: drive.
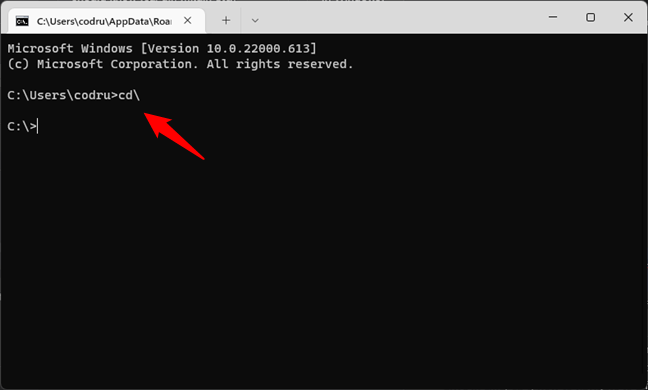
Running the CD\ command to change the directory to root
The Command Prompt is not case sensitive, meaning that you can type commands using capital letters, lowercase, or any combination of them. The commands CD, cd, or Cd, all work the same way.
NOTE: Did you notice in the screenshot above that Command Prompt looks slightly different than what you’re used to? That’s because we’re using it inside the Windows Terminal. For more information, read: What is the Windows Terminal?
How to navigate to a specific folder in CMD (CD path)
Going back to the CD command, now you are working on the root of the C: drive. If you need to go to a specific folder from this drive, run the command CD Folder. The subfolders must be separated by a backslash character: \. For instance, when you need to access the System32 folder located in C:\Windows, type:
cd windows\system32\
… as shown below, and then press Enter on your keyboard.
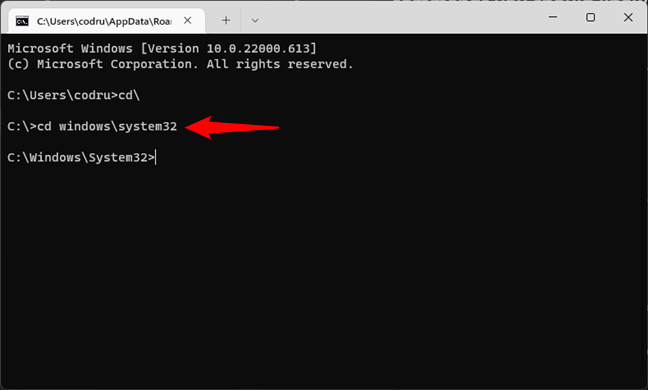
How to navigate to a folder in CMD
How to change the parent directory in CMD (CD..)
When you need to go one folder up, use the cd.. command. Let’s assume that you’re inside the system32 folder and want to go back to the Windows folder. Type
cd..
… and press Enter on your keyboard.
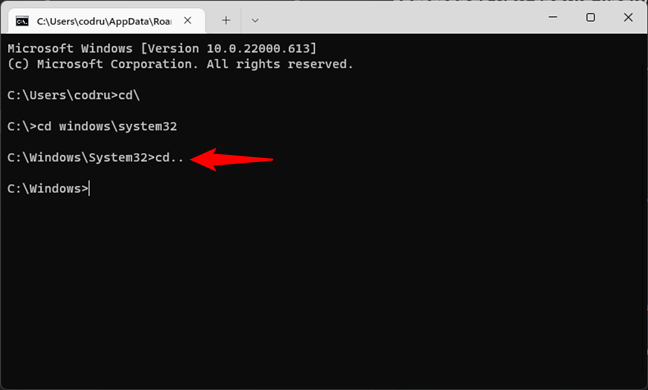
Running the CD.. command to go up one level in the directory tree
The effect is that your current directory changes to C:\Windows.
How to change directory in CMD to desktop (or other user folders)
What about changing the directory in CMD to a personal folder, like your Desktop or Documents? It’s done the same way, using the CD command, but you need to know the locations of your personal folders. In both Windows 10 and Windows 11, all user folders are found in:
C:\Users\[username]\
For example, to change the directory in CMD to your Desktop, the command you’ll have to run is this:
cd C:\Users\[your_user_name]\Desktop
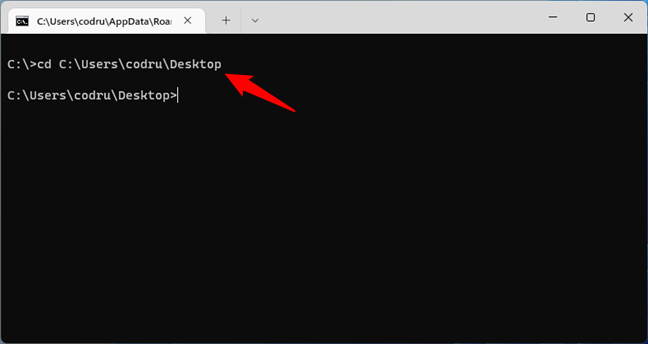
Change path to the Desktop folder in CMD
Similarly, if you want to navigate to another user folder in CMD, run the same command but replace Desktop with the directory you need to get to. For example, if you want to change the path to your Documents folder, run:
C:\Users\[your_user_name]\Documents
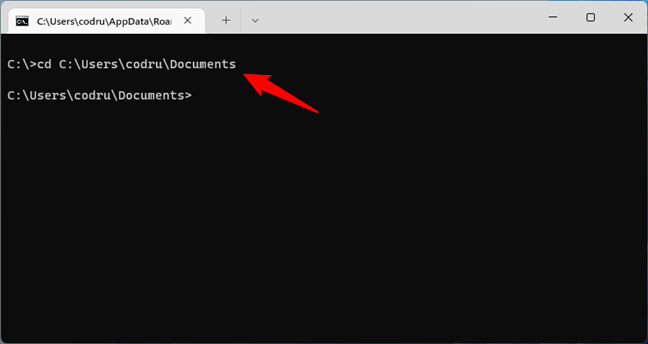
Change directory to a user’s Documents folder in CMD
TIP: Alternatively, instead of entering the name of your user folder manually, you can replace the path to a directory in CMD with the %userprofile% environment variable. Here’s an example of how to change the directory in CMD to Desktop:
cd /d %userprofile%\Desktop
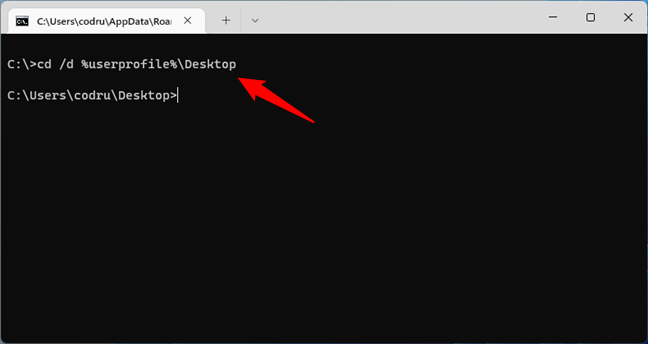
How to change directory in CMD to desktop
2. How to change the drive in CMD (Command Prompt)
To access another drive, type the drive’s letter, followed by :. For instance, if you wanted to change the drive from C: to D:, you should type:
d:
… and then press Enter on your keyboard.
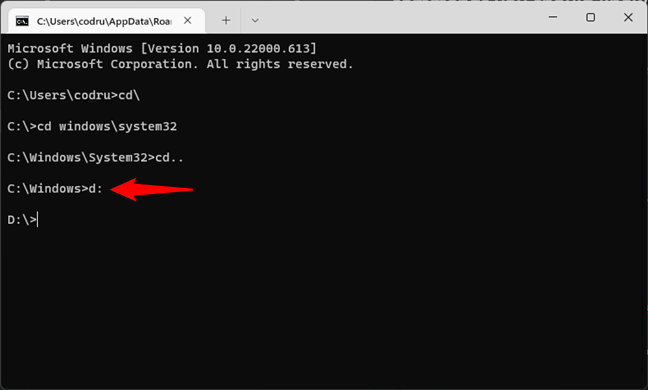
How to change the drive in Command Prompt
To change the drive and the directory at the same time, use the cd command, followed by the /d switch. The /d parameter is used to change the current drive to a specific folder from another disk volume.
For instance, if you are now on the D: drive and you want to go back to the Windows folder from the C: drive, you should type:
cd /d C:\Windows
… and press Enter on your keyboard, like in the following screenshot.
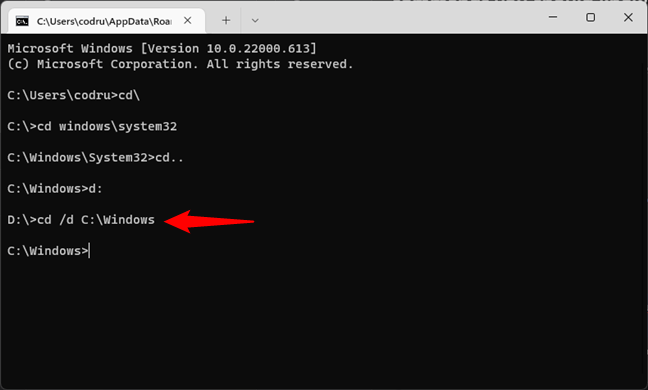
Changing the drive and directory in Command Prompt
NOTE: By typing only the drive letter you automatically move to your most recent location on that drive. For instance, if you are on the D: drive and type cd C:\Windows nothing seems to happen. However, if you type C: afterward, then the working folder changes to C:\Windows.
3. How to view the contents of a directory in Command Prompt (DIR in CMD)
You can view the contents of a folder by using a command called DIR. To test it, we have created a folder named Digital_Citizen on the D: drive, with several files and subfolders. You can see them all in the screenshot below.
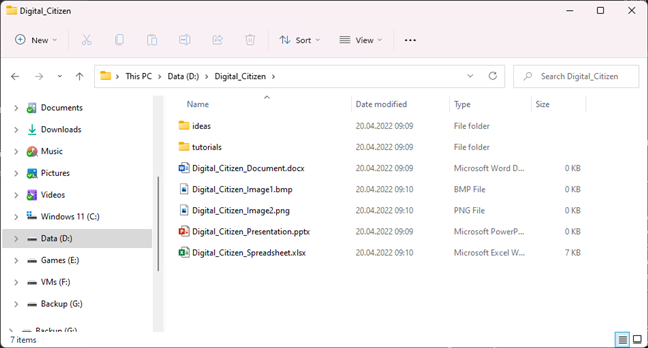
The contents of a folder found in the root of the D drive
The last time, our working folder was C:\Windows. To navigate to the folder mentioned above, we have to use the command cd /d D:\Digital_Citizen. To view the contents of the folder, type:
DIR
… and press Enter. This displays a list of the files and folders contained in it, together with some details about each of them (the size and the date and time when they were last modified).
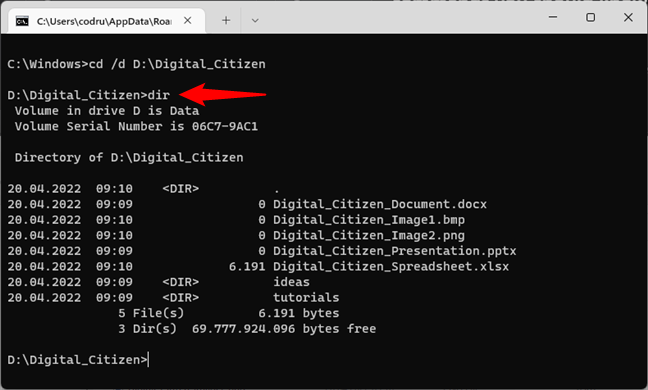
Using the DIR command to see the contents of a directory
4. How to create a new directory with Command Prompt (MD in CMD)
You can make a new folder using the MKDIR (Make Directory) or the MD command. The syntax of these commands is
MKDIR Folder
or
MD Folder
Let’s say we need to create a new folder called Digital_Citizen_Life that is going to be placed in the D:\Digital_Citizen folder. To do that, we need to type:
mkdir Digital_Citizen_Life
… and then press Enter, as shown below.
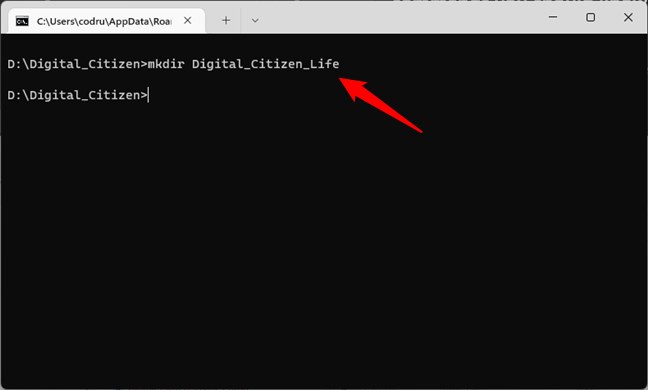
The MKDIR command in Command Prompt
TIP: If you want to create a folder that contains spaces in its name, make sure to wrap its name between quotes or apostrophes. For example, if you want to create a folder called Digital Citizen, run the MD command like this:
md “Digital Citizen”
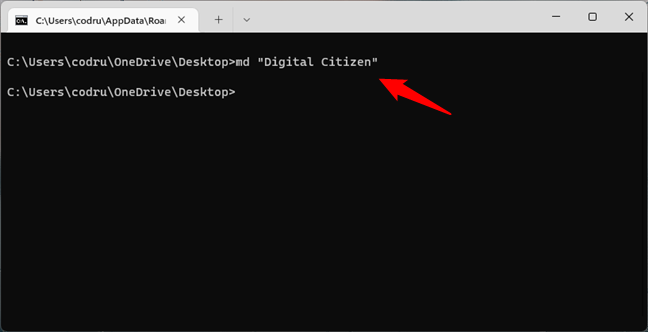
How to create a directory in CMD with spaces in its name
To test if it worked, use the DIR command again. The newly created folder appears in the list.
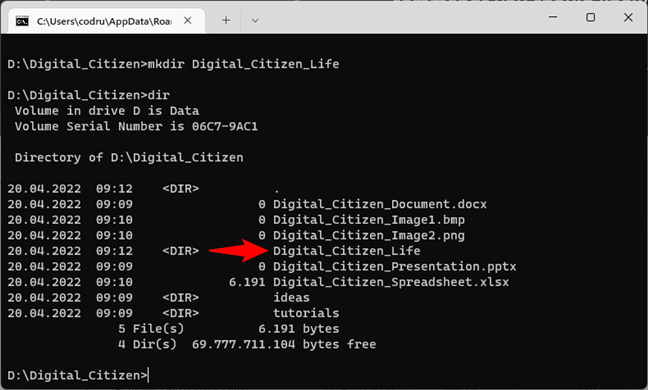
Using DIR to see the contents of the directory in Command Prompt
IMPORTANT: Do not forget that all these commands depend on your current location in the Command Prompt. For instance, if you are on the C: drive and type MKDIR test, the new folder is created in the root of the C: drive.
Another way to create a folder without having to go to the desired location for it is to type the complete path of the new folder. For example, if you are working on the D: drive and you want to create a new folder in C:, called other_stuff, type:
mkdir c:\other_stuff
… and then press Enter.
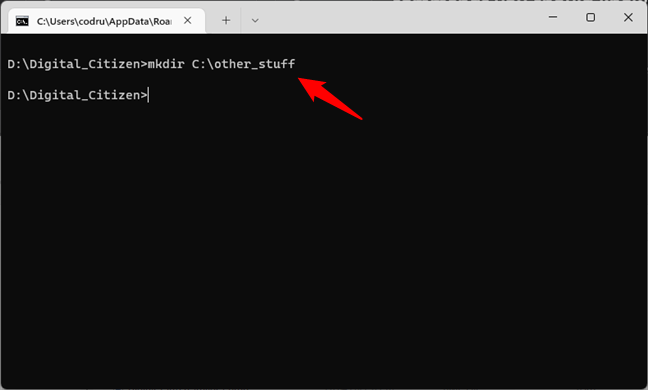
Using MKDIR to create a new directory, with a full path
When you need to create a folder with subfolders at the same time, you can use this command:
MKDIR Folder\Subfolder
.
For instance, if we type:
mkdir Digital_Citizen_Tests\Beta\Test1
… three folders are created: Digital_Citizen_Tests, Beta, and Test1, in a tree-like structure.
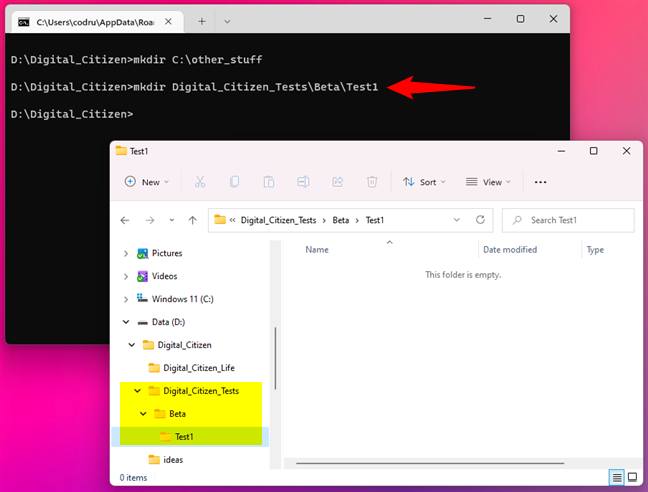
Creating a folder with subfolders using MKDIR in Command Prompt
5. How to rename files and folders with Command Prompt (REN in CMD)
To rename files and folders, you need to use the REN (Rename) command. To rename folders, type:
ren Folder NewFolderName
For example, if we wanted to rename the Digital_Citizen_Tests folder to Digital_Citizen_Final_Tests, we should run:
ren Digital_Citizen_Tests Digital_Citizen_Final_Tests
… and press Enter.
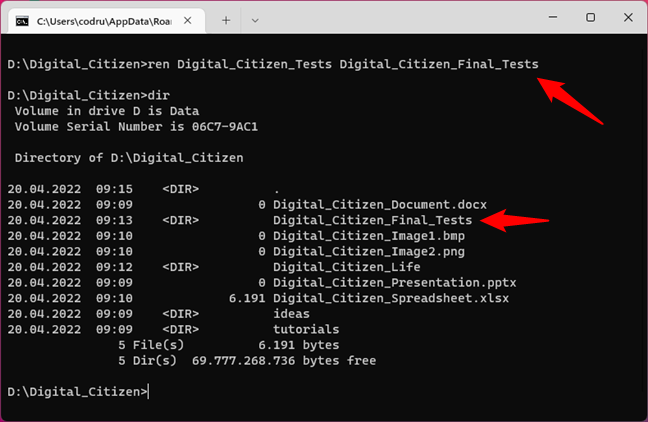
Renaming folders with the REN command in Command Prompt
To rename a file, use the same command, like this:
ren filename.extension newname.extension
For instance, to rename the Digital_Citizen_Picture1.bmp file to Image0.bmp, we have to run the command:
ren Digital_Citizen_Image1.bmp Image0.bmp
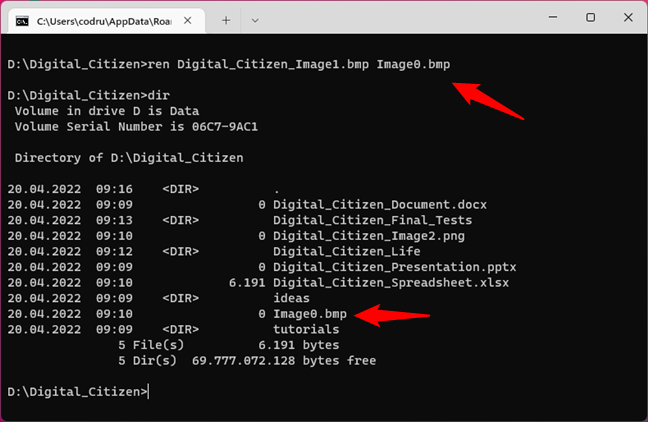
Renaming files with the REN command in Command Prompt
6. How to copy files in CMD (COPY in Command Prompt)
The COPY command allows you to copy files from one location to another. To use this command, type:
copy location\filename.extension newlocation\newname.extension
For example, let’s use this command to copy the Image0.bmp file from the Digital_Citizen folder located on the D: drive to the D:\Digital_Citizen\Digital_Citizen_Tests\ folder. To make things more interesting, we want the file to be named Testing_Picture1.gif. To do all that, we must type the command:
copy D:\Digital_Citizen\image0.bmp D:\Digital_Citizen\Digital_Citizen_Tests\testing_picture1.gif
… followed by Enter. You should also receive a confirmation of the operation, as you can see below.
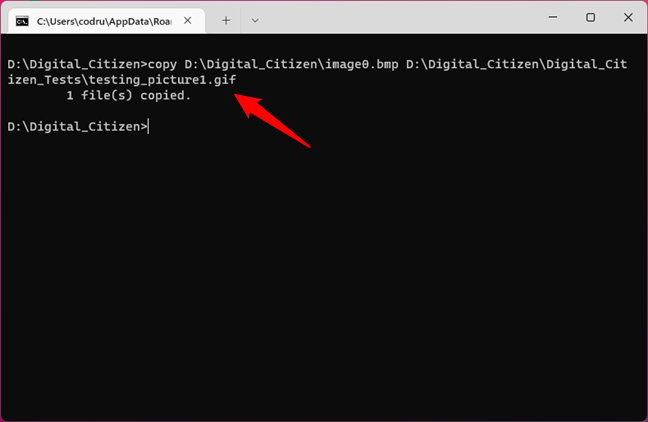
Using COPY to copy files with Command Prompt
If you are copying within the same directory, you do not have to include the path in the command. As an example, let’s copy Digital_Citizen_Notes.txt from D:\Digital_Citizen in the same folder, only with a different extension: let’s say Digital_Citizen_Notes.docx. To do that, we have to run the command:
copy Digital_Citizen_Notes.txt Digital_Citizen_Notes.docx
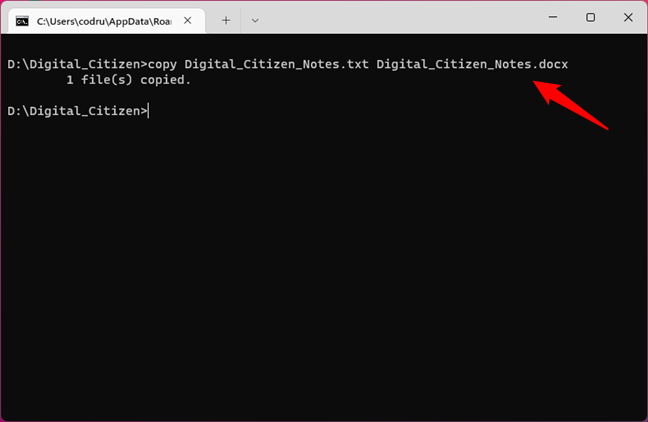
Using the COPY command to copy files in the same directory
7. How to copy folders in CMD, including their contents (XCOPY in CMD)
To copy a folder and its content from one location to another, use the XCOPY command:
XCOPY /s /i
Let’s assume that we need to copy a folder from D:\Digital_Citizen to C:\Backup_Digital_Citizen. To do that, we have to run the command:
xcopy /s /i d:\Digital_Citizen c:\Backup_Digital_Citizen
The /s parameter ensures that all the directories and subdirectories are going to be copied, except the ones that are empty. The /i parameter creates a new directory if the destination folder does not exist and copies all the files in it.
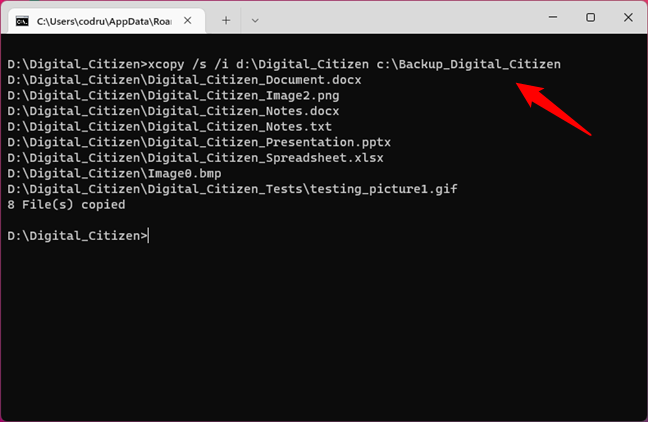
Using XCOPY to copy folders and their contents in Command Prompt
8. How to delete files with Command Prompt (DEL in CMD)
The DEL (Delete) is used to delete files from the folders you have created. To delete all the files from a folder, you can run the command
del folder
For instance, let’s say we want to delete all the files from the Digital_Citizen_Tests folder found in the D:\Digital_Citizen directory. For that, you first open the Digital_Citizen folder in Command Prompt and then you run this command:
del Digital_Citizen_Tests
You must confirm the delete process by typing the letter y for Yes, and then pressing Enter.
NOTE: To also delete hidden files from the folder, you must add the /h parameter. Also, note that the DEL command does not work for deleting folders — for that, you have to use the RD command, covered in the next section of this tutorial.
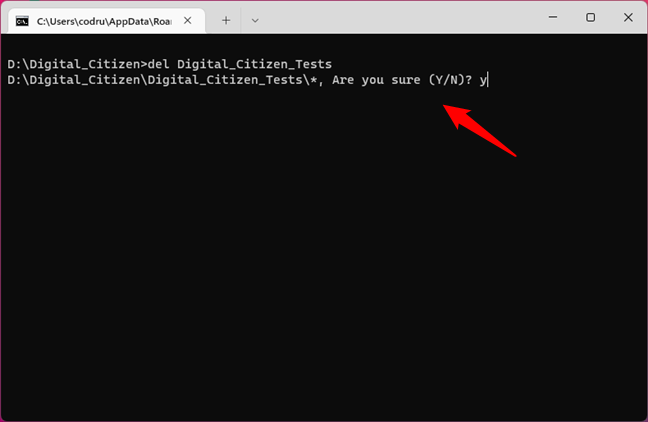
Using the DEL command to delete all the files in a directory in Command Prompt
If you need to delete a single file, use the DEL command followed by that file’s name. For instance, to delete the file Digital_Citizen_Notes.txt from D:\Digital_Citizen, we should run the command:
del Digital_Citizen_Notes.txt
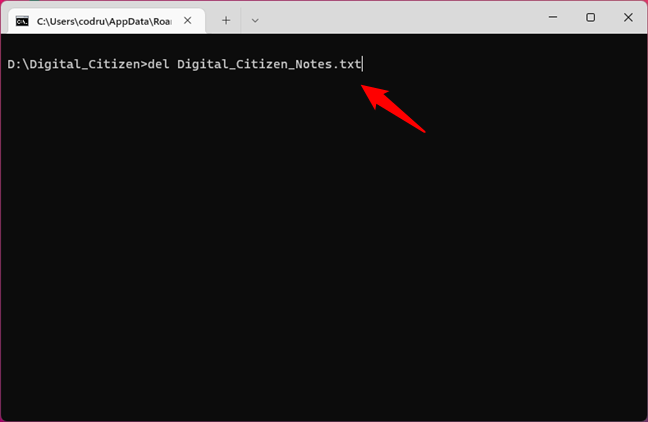
Using the DEL command to delete a single file in Command Prompt
Here is a list of useful DEL combinations that are worth mentioning:
DEL *.DOCX
… deletes all the files in the current folder that have the DOCX extension (you can use any file extension necessary, DOCX is just an example).
DEL Test*.*
… deletes all the files in the working folder whose names begin with Test.
DEL *.*
… deletes ALL the files in the current folder.
9. How to delete a folder from CMD (RD in Command Prompt)
The DEL command cannot be used to delete folders. Therefore we must use another command to remove any empty folder, which is RD:
RD [Folder]
We have previously deleted all the files from the Digital_Citizen_Tests folder. It is now time to delete the directory too, by typing:
RD Digital_Citizen_Tests
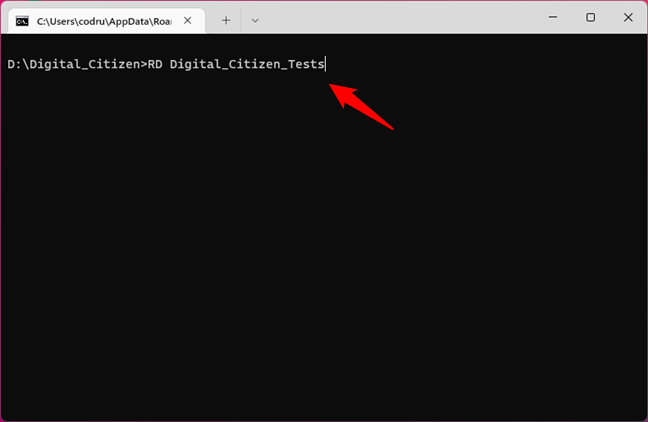
Using the RD command to delete folders in Command Prompt
10. How to launch an app from CMD (Command Prompt)
To run a program from the Command Prompt, you can navigate to the folder that contains the executable and type the program’s name. For example, if you want to launch Control Panel using Command Prompt, go to C:\Windows\System32, where its executable is: control.exe. Let’s see how this operation is done if you were in your user directory. First of all, change the working directory to the application’s folder by typing:
cd /d c:\windows\System32\
Then, type the name of the app’s executable file:
control.exe
… and press Enter.
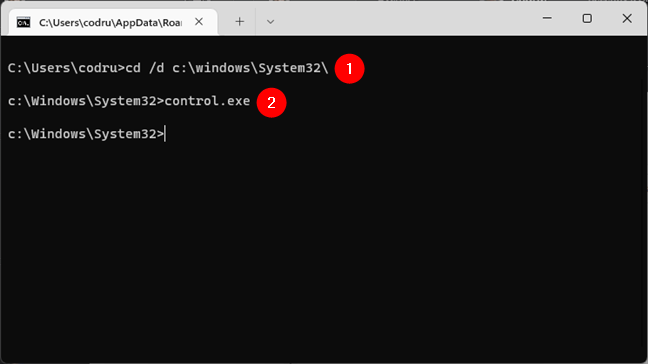
Launching an app from Command Prompt
Alternatively, you can also run an app from CMD directly, no matter what folder you’re currently browsing, by specifying the app’s executable file and its full path in Command Prompt. Opening Control Panel from the previous example would look like this, regardless of your current directory in CMD:
C:\Windows\System32\control.exe
11. How to get help in the Command Prompt (HELP in CMD)
To access help in the Command Prompt, you can use the HELP command:
help
… and then press Enter. This displays a list of all the available commands, as you can see below.
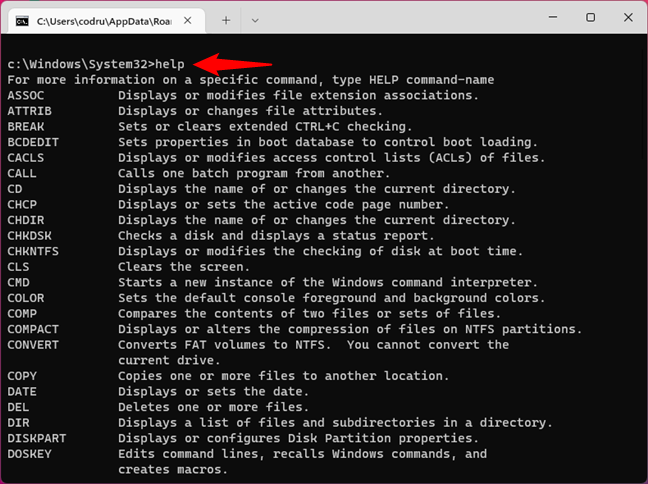
The HELP command from Command Prompt
If a particular command interests you, type help followed by the name of that command. Another way to do the same thing is to type the command’s name followed by the /? parameter. To test it, use
help cd
or
cd/?
… to display information about the cd command. In the picture below you can see the result:
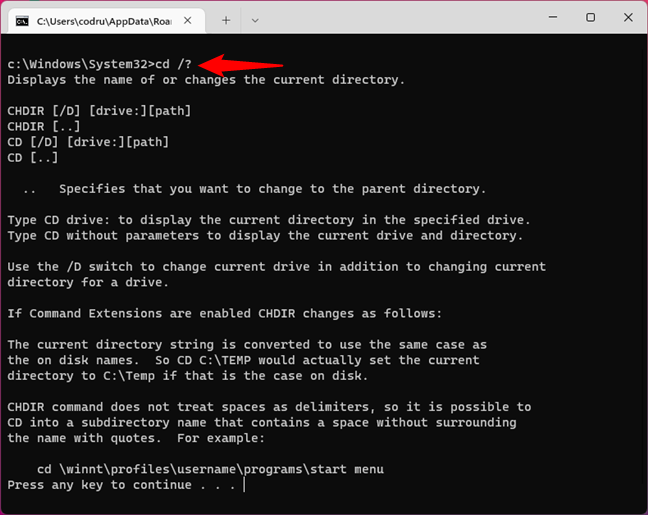
Using the HELP command or the /? parameter to find help in Command Prompt
NOTE: This tutorial covers only a couple of commands for Command Prompt. If you want to delve deeper, you can also read:
- View system information and manage processes from CMD or PowerShell
- Command Prompt (CMD) — 8 network commands you should know
Do you use Command Prompt in Windows 10 or Windows 11?
The Command Prompt is a powerful tool for Windows computer users who are willing to get their hands dirty and learn new things. We hope that this article was useful in helping you learn the basics of running commands in the Command Prompt. If you have any questions about it, do not hesitate to leave us a comment below.
In this article, let’s learn how to navigate through directories in Command Prompt — The Command Prompt (CMD) in Windows is a powerful tool for executing commands, managing files, and navigating your system. One of the most common tasks you’ll perform in CMD is changing directories, which allows you to move between folders to access and manage files. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, knowing how to change directories in Command Prompt is essential for effective system navigation.
This guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of changing directories in Windows 11 and Windows 10 using basic commands like cd (change directory) and dir (list contents), along with helpful tips to make your file management easier. Whether you’re navigating through your system’s folders, opening a project folder, or accessing a specific directory for troubleshooting, changing directories is a fundamental task in CMD.

Understanding Directories in Windows
When working with Windows, you’ve likely encountered the term «directory.» But what exactly is a directory in Windows? In this article, we’ll delve into the world of directories, exploring their definition, types, and importance in the Windows operating system.
What is a Directory in Windows?
A directory, also known as a folder, is a container used to store and organize files and subdirectories on a computer. It’s a way to categorize and structure your files, making it easier to locate and access them. Think of a directory as a physical file folder, where you can store related documents, images, or other files.
Types of Directories in Windows
- Root Directory: The root directory, denoted by a backslash (), is the topmost directory on a hard drive or storage device. It contains all other directories and files.
- Subdirectories: Subdirectories are directories within directories. They help further organize files and can be nested multiple levels deep.
- System Directories: System directories, such as Windows, System32, and Program Files, are created by the operating system and contain essential files and programs.
- User Directories: User directories, such as Documents, Pictures, Music, and Videos, are created by the operating system for each user account. They serve as default locations for storing personal files.
- Program Directories: Program directories, such as Program Files (x86) and Program Files, contain installed applications and their associated files.
- Temporary Directories: Temporary directories, such as Temp and %temp%, store temporary files created by applications and the operating system.
- System Volume Information: The System Volume Information directory contains system files, such as restore points and indexing data.
- Recycle Bin: The Recycle Bin is a special directory that stores deleted files until they are permanently erased or restored.
- Hidden Directories: Hidden directories, such as AppData and Local Settings, contain configuration files and data used by applications and the operating system. They are hidden by default to prevent accidental modification or deletion.
- Network Directories: Network directories, such as shared folders and network drives, provide access to files and resources on other computers or devices over a network.
- Virtual Directories: Virtual directories, such as those created by subst or mklink commands, are symbolic links that map a directory to a different location on the same or another drive.
- Mount Points: Mount points are directories that serve as entry points for mounted volumes, such as USB drives or network shares.
- Reparse Points: Reparse points are directories that contain reparse data, which allows the operating system to redirect file system requests to a different location.
- Junction Points: Junction points are directories that link to another directory on the same volume, allowing multiple paths to access the same files.
- Symbolic Links: Symbolic links are directories that link to a file or directory on the same or another volume, allowing multiple paths to access the same file or directory.
How to Change Directories in CMD at Different Levels (With Examples)
Before moving ahead with Changing Directories to Windows Folders, we have to understand Directory Changing to Different Levels. Let us discuss all the methods for Changing Directories in CMD at different levels in Windows 10 or 11.
1. Root Level Directory
Open Command Prompt to change to a directory in the root directory (such as»C:\» on Windows), you can use the `cd` command followed by the directory name.
Example:
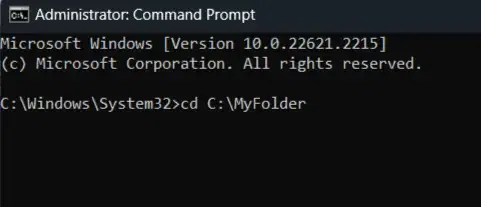
2. Parent Level Directory
Open Command Prompt to move to a directory within the parent directory (like going from «Documents» to «Users»), simply use the `cd` command followed by `..` to go up one level, and then the name of the parent directory.
Example:
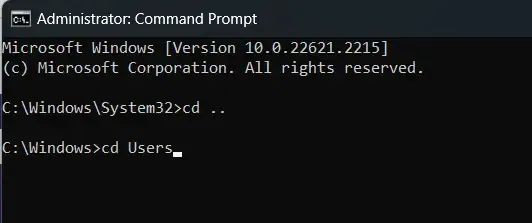
3. Subdirectories Level Directory
Open CMD or Command Prompt to enter a subdirectory within your current directory (such as going from «Documents» to «Photos»), use the `cd` command followed by the name of the subdirectory.
Example:
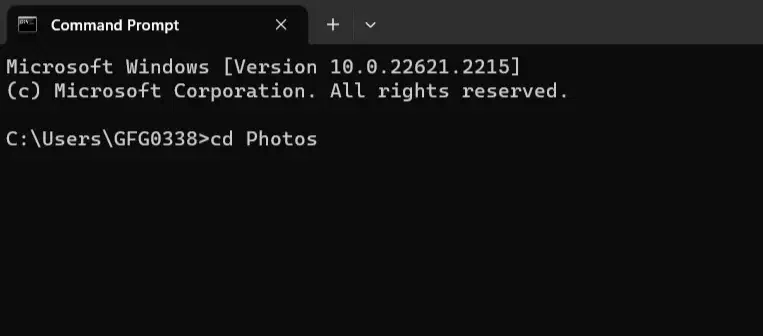
4. Nested Subdirectories Level
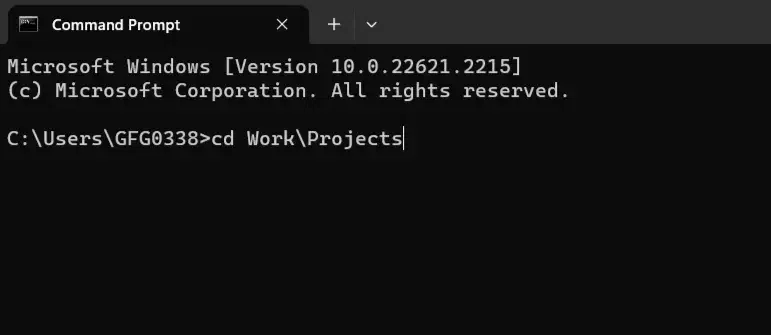
Open CMD to navigate to a deeply nested subdirectory (like going from «Documents» to «Work > Projects»), use the `cd` command with each subdirectory name, separated by a backslash (\).
Example:
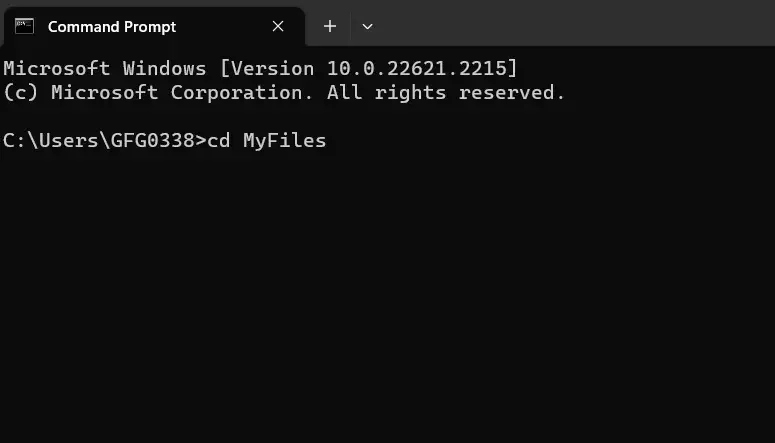
5. Leaf Level Directory
Open Command Prompt in Windows 10 or 11 to enter a directory that doesn’t contain any subdirectories (like going to a folder with just files), use the `cd` command followed by the leaf directory’s name.
Example:
Note: Remember, you can always type `cd ..` to go up one level and explore different directories easily.
Changing Directories in Command Prompt to Different Folders
Now, after discussing Directory Change in Different Levels, we will discuss all the possible methods that are required to Change Directories to Folders in the Windows Command Line Tool.
Method 1: Using Drag and Drop
For those who prefer a graphical approach, changing directories using drag and drop is simple. You can open File Explorer, locate the desired directory, and drag it to the Command Prompt window. This action automatically populates the Command Line with the directory path.

Method 2: Using Commands
Changing directories using commands may seem tricky at first, but it’s essential to get the hang of it in Command Prompt. Here are some easy methods to do it:
1. Absolute Paths
This is like using a full address to find a place. In Command Prompt, you can use the full path to a folder to get there directly. This will take you straight to your «Documents» folder. For instance:
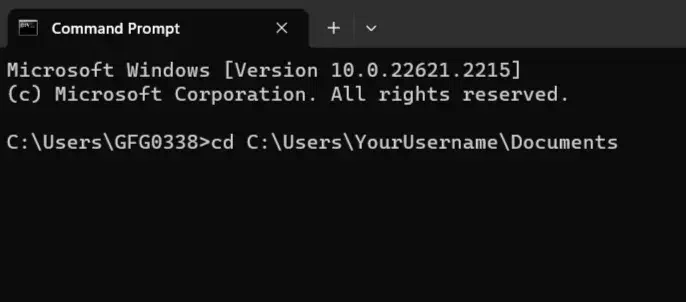
2. Relative Paths
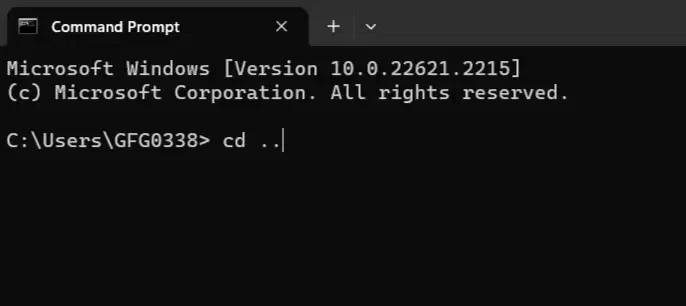
Think of this as giving directions from where you are. You can use `..` to move up one level and the folder name to go into a subfolder. This will take you up one level from where you are right now. For example:
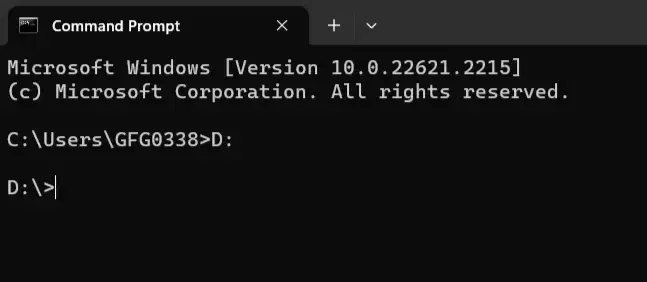
3. Drive Letters
Imagine switching between different drives as changing streets. To switch to a different drive, just type its letter and a colon. This will take you to the D: drive. For example:
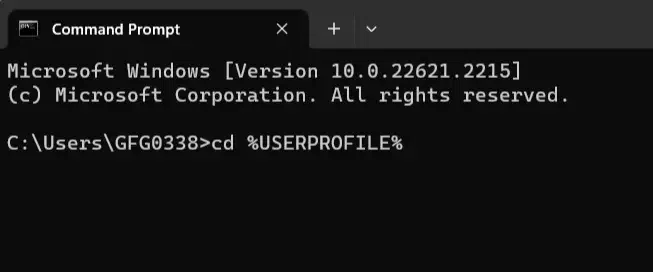
4. Environment Variables
These are like shortcuts to important places. You can use names like `%USERPROFILE%` to go to common folders without typing the whole path. This will take you to your user profile folder. For example:
5. Tab Auto-Completion
Think of this as your Command Prompt assistant. When you start typing a folder name and press Tab, Command Prompt will try to finish it for you. If there’s more than one option, it will show you a list.
6. Previous Directory (`cd ..`)
This is like having a «go back» button. If you want to return to the folder you were in before, just type `cd ..`. It’s like a quick way to backtrack.
7. Using Wildcards
Wildcards are like search filters. You can use `*` to find folders based on patterns. This will take you to a folder with a name starting with «sep». For example:
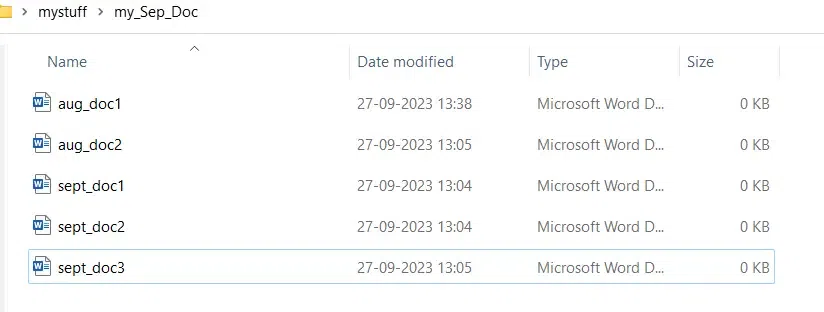
cd C:\Users\GFG0338\Desktop\mystuff\my_Sep_Doc>dir sep*.*
8. Using the «dir» command
It lists all Windows Files and Directories (folders) in the current directories. This helps the users to quickly see what Files and Directories are present in a particular location
For example, if you want to list the content of » C:\Users\GFG0338\Desktop\mystuff\my_Doc «, you would type the following:
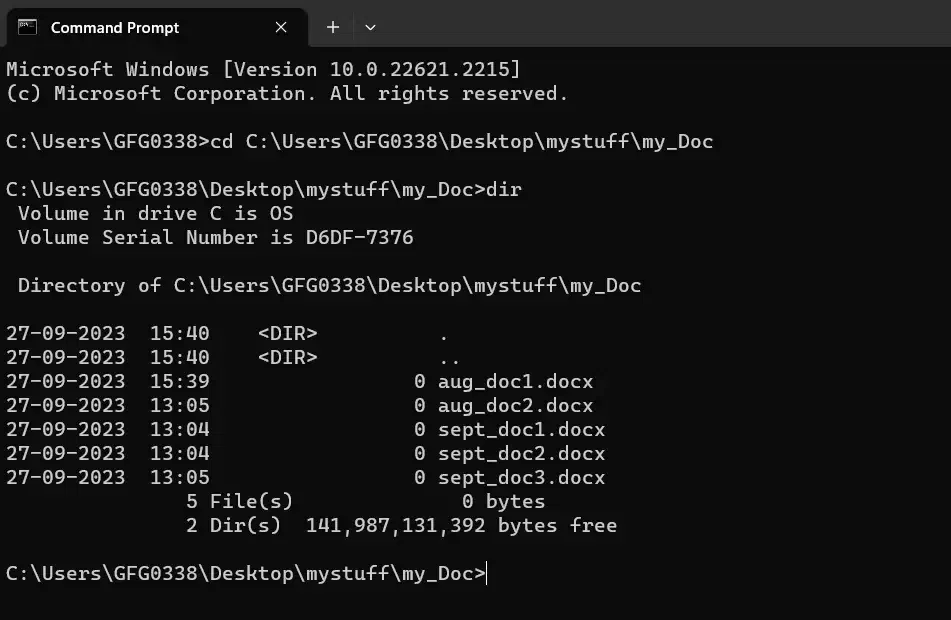
This will give you a list of Files and Directories in that folder along with respective attributes.
How to Navigate to a Folder in Command Prompt
When you want to navigate to a different folder in the Command Prompt, it’s like giving your computer directions. Here’s how to do it in simple steps:
- Open Command Prompt: First, you need to open Command Prompt in Windows 10 or 11. You can do this by pressing the Windows key, typing «Command Prompt,» and hitting Enter.
- Understand Your Starting Point: Before you start, it’s good to know where you are. Command Prompt opens in a default location, usually your user folder.
- Type ‘cd’ and Space: To tell Command Prompt you want to change the folder, type `cd` (which stands for «change directory») followed by a space.
- Enter the Folder Name: Now, type the name of the folder you want to go to. If your folder name has spaces, put it in double-quotes. For example, if you want to go to a folder named «My Stuff,» you’d type: cd «My Stuff»
- Hit Enter: Press the Enter key on your keyboard. This tells Command Prompt to follow your directions and take you to the folder.
- Check Your Location: To make sure you’re in the right place, you can type `cd` without any folder name and press Enter. Command Prompt will show you the full path of where you are.
Note: Remember, you can always use the `cd ..` command to go up one level if you ever want to backtrack.
Tips for Navigating Directories in Command Prompt
Below we have highlighted a few tips and tricks to make directory navigation in the Command Prompt much easier, let’s check them out:
1. The dir Command
The dir command is being used in CMD to list down all the files and directories in the current folder, here’s a quick example for this:
Example:
dir
2. The cd .. Command
The cd .. command helps in navigating back to the previous directory instantly, here’s a quick example for this:
Example:
cd ..
3. Drag & Drop
You can also choose to simply drag a folder from File Explorer into the Command Prompt. This woll automatically insert the entire path of that directory into CMD.
Tips and Tricks while Changing Directory
There could be five possible reasons if you’re unable to change directory in CMD (command prompt). Let’s identify them in segregated format:
1. Incorrect Syntax
If you are not using the correct command, it might led to throw Syntax error. For example,
cd C:\Path\To\Directory (no quotes unless the path contains spaces)2. Permission Issues
Since, normal users have the limited access so there are high chances that you might not beable to access to certain directories. So, it’s recommended to run CMD as an administrator.
3. Non-Existent Directory
Sometimes, we do try to access to a certain directory that might not exist. So, it’s better to verify the path using dir to list down all the available directories.
4. Special Characters or Spaces
If the path contains spaces or special characters, enclose the path in double quotes, For example,
cd "C:\My Folder"5. Drive Mismatch
If you’re trying to change to a directory on a different drive, make sure to switch drives first by typing the drive letter. For example D: before using cd.
D: cd
Best Practices for Directory Management
To ensure efficient directory management, follow these best practices:
- Use Clear and Concise Names: Use descriptive names for directories and files to facilitate easy identification.
- Avoid Deep Nesting: Limit the number of subdirectories within directories to prevent confusion and disorganization.
- Regularly Clean Up Directories: Periodically review and remove unnecessary files and directories to maintain a clutter-free file system.
Conclusion
Changing directories in Command Prompt is an important skill that simplifies file system navigation and task management. Whether you’re working with relative paths, absolute paths, or switching between drives, mastering these commands ensures a smoother and more efficient CMD experience.
Also Read
- Most Useful CMD Commands in Windows
- 10 Ways to Open the Command Prompt in Windows 10
- How to Change Colours in Command Prompt in Windows?
