What is an environment variable in Windows? An environment variable is a dynamic “object” containing an editable value which may be used by one or more software programs in Windows.
In this note i am showing how to list environment variables and display their values from the Windows command-line prompt and from the PowerShell.
Cool Tip: Add a directory to Windows %PATH% environment variable! Read More →
The environment variables in Windows can be printed using the Windows command-line prompt (CMD) or using the PowerShell.
Windows Command-Line Prompt (CMD)
List all Windows environment variables and their values:
C:\> set
“Echo” the contents of a particular environment variable:
C:\> echo %ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE%
Windows PowerShell
Print all Windows environment variables (names and values):
PS C:\> gci env:* | sort-object name
Show the contents of a particular environment variable:
PS C:\> echo $env:ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE
Cool Tip: Set environment variables in Windows! Read More →
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
You can view environment variables in the Command Prompt by using the `set` command, which lists all environment variables in the current session. Here’s how to do it:
set
What Are Environment Variables?
Environment variables are dynamic values that the operating system uses to determine how to behave in different circumstances. They serve as a list of key-value pairs that can be used by various applications and scripts running on your computer.
There are two main types of environment variables:
-
User Variables: These are specific to the user account currently logged into the system. They can be tailored to individual user preferences and settings.
-
System Variables: These are global variables accessible to all users on the machine. They define system-wide configurations, such as the path where executable files are located.
Understanding environment variables is crucial for effectively managing software applications and system configurations, as they dictate various settings for the way programs operate.

Check Environment Variables in Cmd: A Quick Tutorial
Why You Might Want to View Environment Variables
Knowing how to view environment variables can be beneficial for several reasons:
-
Modifying System Paths: You might want to add or modify paths for executable files, allowing for quicker access to commands and scripts.
-
Configuring Software Applications: Some applications rely on environment variables for configurations, such as setting database connection strings or API keys.
By viewing environment variables, you can troubleshoot issues, optimize your workflows, and better understand how your system operates.

cmd Echo Environment Variable: Quick Start Guide
How to Check Environment Variables in Windows CMD
Using the `set` Command
The `set` command is one of the simplest ways to view environment variables within the Windows Command Prompt. When executed without any parameters, the command displays a complete list of all environment variables in your current session.
Syntax:
set
When you run this command, you’ll receive an output that looks something like this:
PATH=C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-11.0.11\bin;C:\Windows\system32;...
USERPROFILE=C:\Users\YourUsername
Each line shows a single environment variable and its current value.
Displaying a Specific Environment Variable
If you’re interested in viewing the value of a specific environment variable, you can use the `echo` command. This is particularly useful for checking the value of common variables like `PATH`.
Syntax:
echo %VARIABLE_NAME%
For example, to check the `PATH` variable, you would execute:
echo %PATH%
The output will display the directories listed in your `PATH`, enabling you to confirm whether the necessary directories are included for executable files.

How to Open Environment Variables from Cmd Easily
Show Environment Variables CMD: A Detailed Breakdown
Listing All Environment Variables
If you’d like to scroll through the environment variables one page at a time, you can use the `more` command in conjunction with `set`. This technique helps you avoid overwhelming amounts of output in your Command Prompt window.
Code Snippet:
set | more
This command lists all environment variables but pauses for you to read each page, allowing for easier navigation through the output.
Viewing System vs. User Variables
Understanding the difference between user and system variables is essential when managing your environment. To see this distinction, you can use the `systeminfo` command.
Code Snippet:
systeminfo | findstr /i "environment"
The output from this command will include a summary of environmental variables and will help you differentiate between those set for the user and those available to the system. This is valuable when troubleshooting variable-related issues.

Mastering Variables in Cmd: A Quick Reference Guide
Show Environment Variables Windows CMD: GUI vs. Command Line
Accessing Environment Variables via GUI
Windows provides a graphical interface to access environment variables via the System Properties. You can navigate to Control Panel > System > Advanced system settings > Environment Variables. This view provides an organized way to edit or view variables.
While this method is user-friendly, it lacks the speed and efficiency of using the command line, especially for those who are experienced with CMD commands.
Advantages of Using CMD to Show Environment Variables
Using CMD offers distinct advantages:
-
Speed and Efficiency: Commands can quickly display or modify environment variables without navigating through multiple GUI windows.
-
Automation Capabilities: Commands can be scripted for batch processing, making repetitive tasks simpler and faster.
Delete Files Cmd: A Quick Guide to File Removal
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Environment Variables Not Showing
If you find that expected environment variables are not showing in your CMD session, there could be several reasons. First, ensure that you are running the Command Prompt with sufficient permissions. Running as an administrator may be necessary for system-level variables.
Additionally, if you see unexpected output, it may be due to incorrect syntax or mistyping the variable name. Always check the correct casing and spelling of the variables.
Modifying Environment Variables through CMD
For those interested in making permanent changes to environment variables, the `setx` command can be employed. This command enables you to create or modify variables for future sessions.
Syntax:
setx VARIABLE_NAME "value"
For example, if you want to set a new user variable related to HTML files, you could run:
setx HTML_PATH "C:\html_files"
Keep in mind that changes made using `setx` will only apply to new Command Prompt sessions.

Mastering Cmd Set Variable: Quick Guide for Beginners
Understanding Environment Variables in Batch Scripting
Using Environment Variables in Scripts
Environment variables can significantly enhance the functionality of batch scripts. By incorporating them, you can customize script behavior based on user settings or system configurations.
For instance, you can use environment variables to specify a user directory dynamically:
@echo off
echo User directory is: %USERPROFILE%
This line will output the current user’s profile directory when the script is executed, allowing scripts to adapt to different users without hardcoding values.

Exploring Cmd System Variables: A Quick Guide
Conclusion
Understanding how to view environment variables cmd is a fundamental skill for anyone looking to leverage the full capabilities of Windows. Whether you’re troubleshooting issues, fine-tuning your system’s performance, or scripting automation tasks, being able to confidently access and manage these variables is invaluable. With the commands and techniques discussed here, you are well on your way to mastering Windows Command Prompt and enhancing your workflow.
cmd Viewing environment variables
Viewing environment variables in the Windows Command Prompt (cmd) is an important aspect of system configuration and management. Environment variables are dynamic values that can affect the way running processes behave on a computer. They can store information like system paths, user preferences, and system settings. Here’s how you can view and work with environment variables in cmd, along with examples and expected outputs.
1. Using the set Command
The set command displays all environment variables and their values in the current command prompt session.
Basic Syntax:
Example:
To view all environment variables, simply enter:
Output:
2. Using the echo Command
You can also use the echo command to display the value of a specific environment variable by referencing it with the % symbol.
Basic Syntax:
Example:
To view the value of the PATH environment variable, enter:
Output:
3. Using the set Command with a Variable Name
You can use the set command with a variable name to display only the value of that specific variable.
Basic Syntax:
Example:
To display the value of the TEMP variable, enter:
Output:
4. Using the reg Command to View User Environment Variables
You can also access environment variables stored in the registry using the reg command.
Basic Syntax:
Example:
To view user-defined environment variables, enter:
Output:
Summary
Viewing environment variables in the Windows Command Prompt is essential for troubleshooting and managing system configurations. You can use the set command to display all variables or specific ones, the echo command to retrieve the value of a particular variable, and the reg command to access variables stored in the Windows registry. Understanding how to view and manipulate environment variables can greatly assist in system administration and development tasks.
Переменные окружения (среды) в Windows содержат различную информацию о настройках системы и среды пользователя. Различают переменные окружения пользователя, системы и процессов.
Самый простой способ просмотреть содержимое переменных окружения в Windows – открыть свойства системы (sysdm.cpl) -> Дополнительно -> Переменные среды. Как вы видите, в открывшемся есть две секции: в верхней содержатся переменные окружения пользователя, в нижнем – системные.
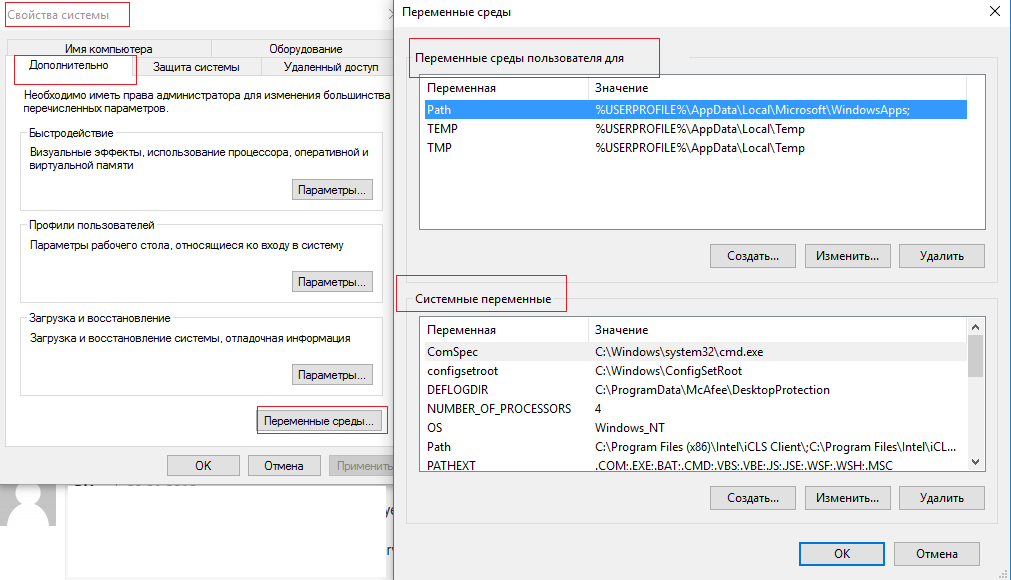
Кроме того, переменные среды хранятся в реестре системы. Пользовательские переменные хранятся в разделе HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment. Системные – в HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment.
Вывести значения всех переменных окружения можно в командной строке Windows. Команда простая:
Set
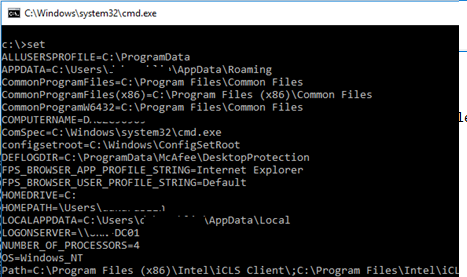
Команда выведет список переменных среды и их значения.
В PowerShell для вывод всех переменных окружения можно использовать команду:
ls env:
Если нужно вывести значение только одной переменной, нужно воспользоваться командой echo, причем имя переменной нужно заключить в знаки процентов. Например,
Echo %systemroot%
Чтобы сохранить все переменные среды и их значения в текстовый файл, воспользуйтесь командой:
set > c:\tmp\env_var.txt
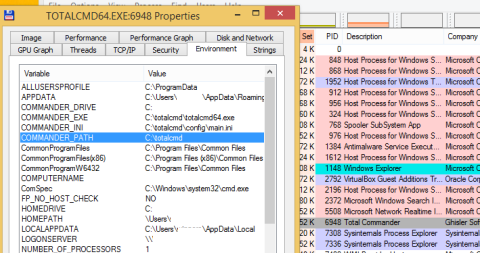
Переменные окружения конкретного процесса можно получить с помощью бесплатной утилиты Process Explorer (от Sysinternals). Достаточно открыть свойства процесса и перейти на вкладку Environment.

Overview – Check
Environment Variables in Windows
Environment variables in Windows are used to store information that are used by applications and services. The Windows operating system defines a number of environment variables, and user applications and services can also further add additional environment variables.
When you start a Windows program, the operating system creates several environment variables that the program can use. These variables include the path to the application’s directory and any additional folders that the program requires access to.
It seems that you want to check compatibility issues among the numerous environment variables stored on your computer. By the end of this article, you’ll be able to list all environment variables in Windows:
Using System Properties
Using Command Prompt
Using PowerShell
Using Batch Script
Using System Information
Using Registry Editor
1. Check Environment
Variables using System Properties
Step 1: In the Start menu, search for “Edit the system environment variables” (without quotation marks) and hit the enter key.

Edit System Environment Variables
Step 2: In the “Advanced” tab, click the “Environment Variables” button and all the environment variables on your system will be visible..

“Environment Variables” Button

List of All Environment variables – Both User and System Environment Variables
2. Check Environment
Variables using Command Prompt
Step 1: Run the Command Prompt as an administrator from the Start menu.
Command Prompt (CMD) Icon
Step 2: To list all the environment variables using Command Prompt, type the command “set” (without quotation marks).

Command To List Environment Variables using CMD
3. Check Environment
Variables using PowerShell
Step 1: Run the PowerShell as an administrator from the Start menu.
PowerShell App Icon
Step 2: To list all the environment variables using PowerShell, type the command: “gci env:” (without quotation marks).

Command To List Environment Variables using PowerShell
4. Check Environment
Variables using Batch Script
Step 1: Right-click the desktop and add a new “Text Document”.

Create New Document
Step 2: Copy and Paste the following script in the text document:
@ECHO OFF
set
pause

Batch Script To Show Environment Variables In Windows
Step 3: Click the “File” button on the top left corner of the window and click the “Save As” option.

“File” Button > “Save as” Button
Step 4: Change the file extension to “File-Name.bat’ (.bat is the new extension), choose the desired location where you want to save the file and click the “Save” button.

File Extension from “.txt” to “.bat”
Step 5: Once the file is saved, double-click it to execute and you’ll see the environment variables listed in command prompt.

Running Batch Script To Show Environment Variables
NOTE: If copying and pasting the script above doesn’t work, type the script in the text document instead.
5. Check Environment
Variables using System Information
Step 1: In the Start menu, search for System Information and open it or press the “Windows Logo Key + R” key combination to open Windows Run, type “msinfo32” (without quotation marks) and hit the enter key.
System Configuration Icon
Step 2: In the left sidebar, expand the “Software Environment” section by clicking the “+” icon, click the environment variables button and you’ll see the environment variables listed on the right pane.

“+” Button > “Environment Variables” Button
6. Check Environment
Variables using Registry Editor
1. Check
System Environment Variables using Registry Editor
Step 1: In the Start menu, search for Registry Editor and hit the enter key or press the “Windows Logo Key + R” key combination on the keyboard, type: regedit and hit the enter key.
Step 2: To Check System Variables, navigate to the following path: Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment and you’ll find the system variables listed on the right pane.

System Environment Variables in Registry Editor
2.
Check Environment Variables for Current User using Registry Editor
Step 1: In the Start menu, search for Registry Editor and hit the enter key or press the “Windows Logo Key + R” key combination on the keyboard, type: regedit and hit the enter key.
Step 2: To check user variables, navigate to the following path: Computer\HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment and you’ll find the user variables listed on the right pane.

User Environment Variables in Registry Editor
FAQs Related to
Environment Variables
How does environment
variables work in Windows?
Environment variables are the dynamic objects in form of key/value pairs that are responsible for instructing the programs to search for user profile settings, install files, and store temporary files in appropriate location in Windows.
What are types of
environmental variables?
There are two types of environment variables: User environment variables and system environment variables. The system variables are shared and applied to all users on the computer, but the user variables are exclusive to each profile.
Where are
environment variables stored in Windows?
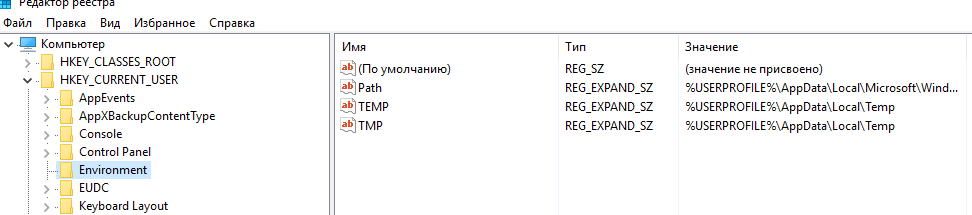
In Windows, the user environment variables are stored in HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment in the registry editor and the system variables are stored in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment in the registry editor.
Next
Steps
We’ve covered how to check environment variables in Windows 11. To list environment variables in Windows, you can use any one of the methods listed above.
Further, configure the environment variables and other settings by referring the related articles below.
