The Command Prompt is a powerful tool in Windows that lets you run commands to manage files, troubleshoot problems, and control system settings. But some commands require administrator access to work properly. Opening the Command Prompt as an administrator—often called “elevated mode” gives you full control to perform advanced tasks on your computer.
In this guide, we will discuss quick and easy ways to open the Command Prompt with administrator rights on your Windows 10 and 11.
Method 1: Using Windows Search (Windows 10 & Windows 11)
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
Step 1: Open the Start Menu and Type «CMD»
Press the Windows Key or Click on the Start Menu and Type Command Prompt or CMD and proceed ahead.
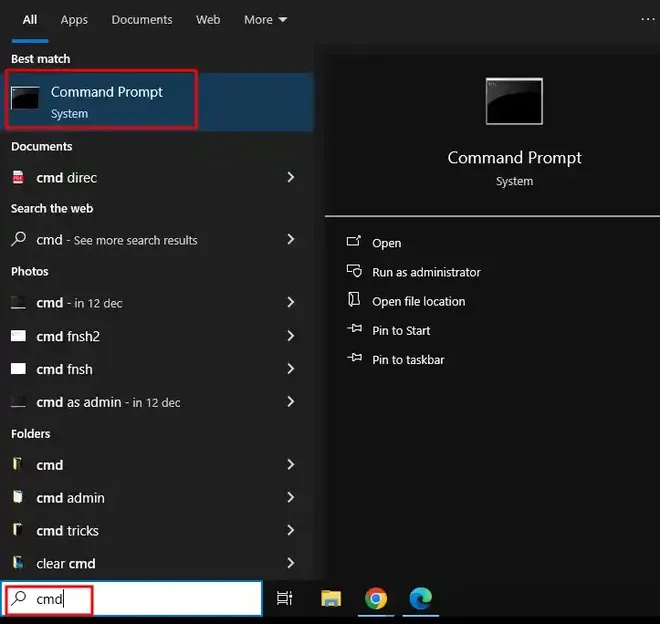
Step 2: Select «Run as Administrator»
Right-click on «Command Prompt» and select «Run as administrator».
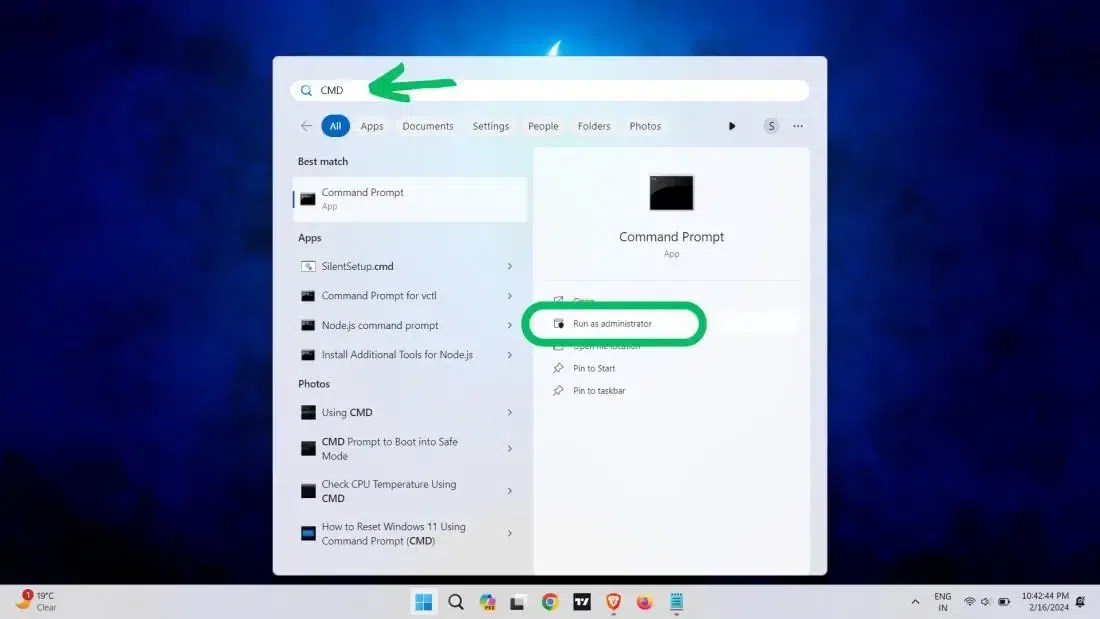
Method 2: Run Dialog Box (Win 10 & 11)
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
Step 1: Open Dialog Box or Press Win + R
First, press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog. Now, type «CMD» or Command prompt
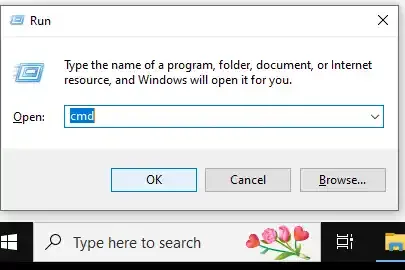
Step 2: Hold down Ctrl + Shift to enter Admin Mode
Press Ctrl + Shift + Enter or click «OK» while holding Ctrl + Shift.

You might be asked to enter admin password. Provide the same & proceed with the Command Prompt administrator rights.
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
Step 1: Open Power User Menu
Go to Start Button or press Win + X
Step 2: Select Admin
Now, click on «Terminal (Admin)» from the menu.
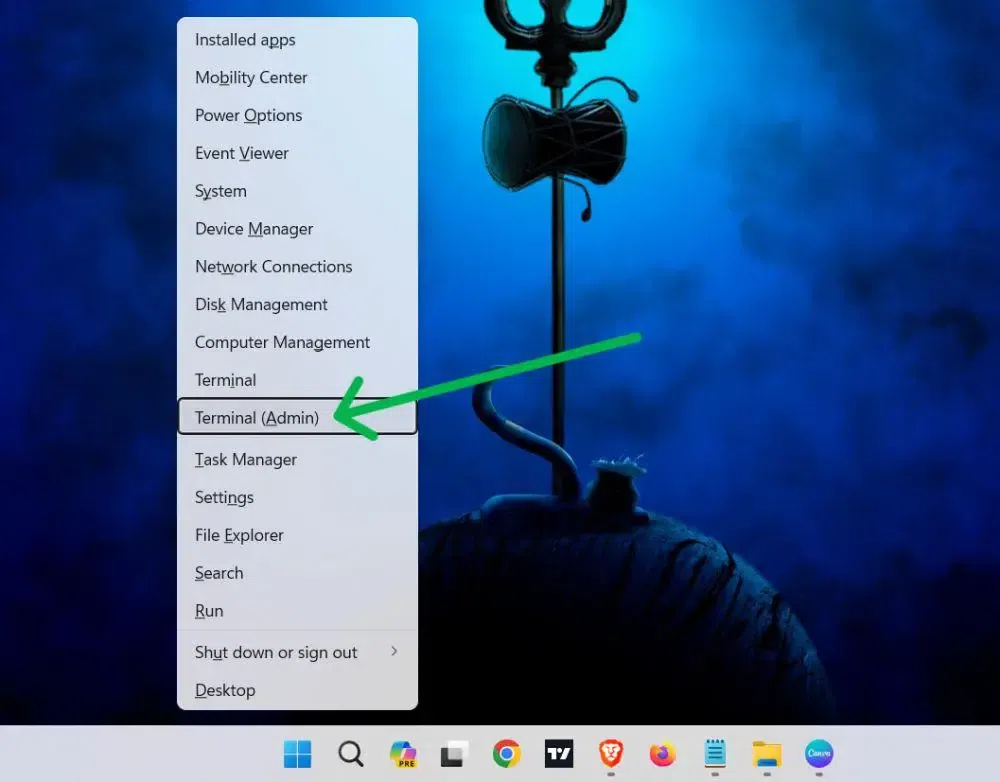
Step 3: Hover and click to visit Command Prompt
Then, Click on the arrow from the menu and Select «Command Prompt«
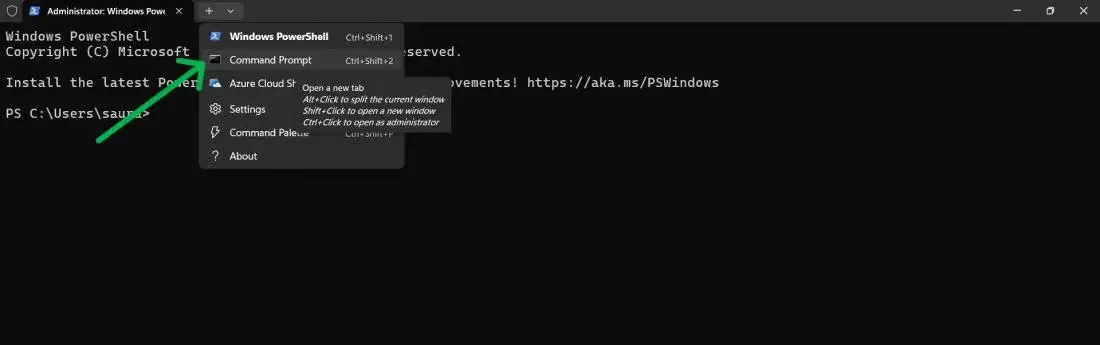
By following this method, anyone can open command prompt using these 3 simple steps.
Note: This method is suitable forWindows 11
Step 1: Type Windows Tools in the search box
Click on the Start menu and type Windows Tools
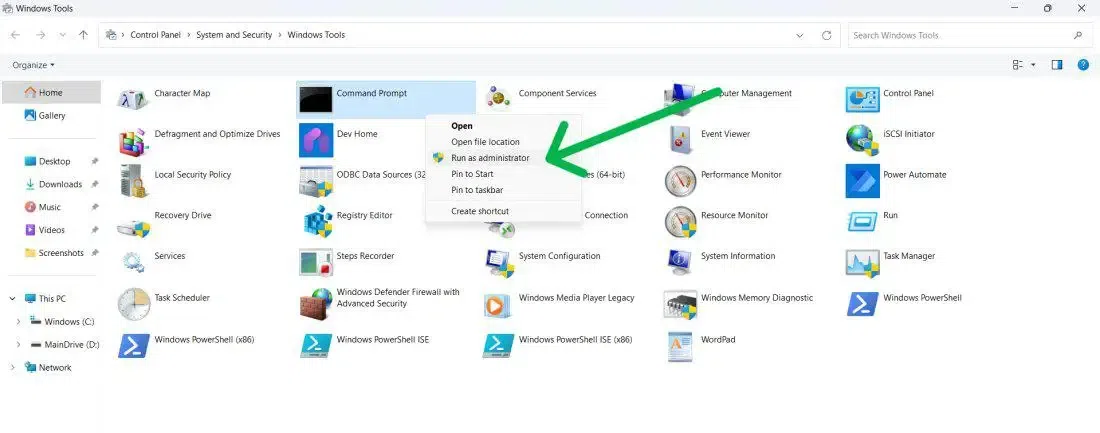
Step 2: Click to Open as Administrator
Make a right click and select «Run as Administrator»
Method 5: Using Task Manager (Win 10 & Win 11)
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
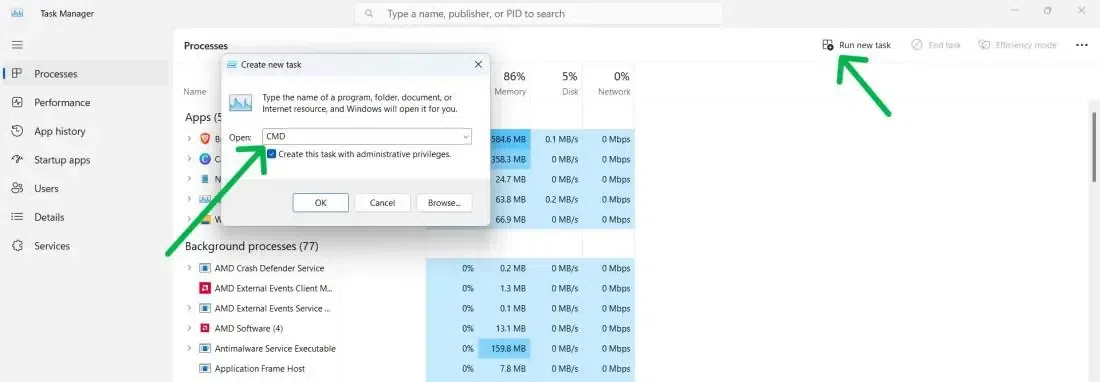
Step 1: Open Task Manager and click to Run New Task
Click the Start Menu and type «Task Manager»
Step 2: Create a New Task to Run CMD with Administrative Rights
Create a new task in the File menu and select Run New Task. Check «Create this task with administrative privileges», and click OK.
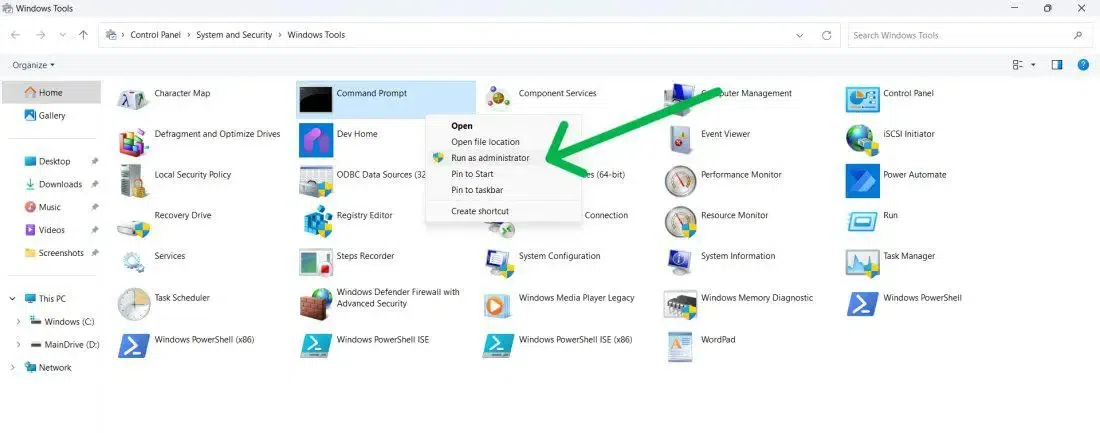
Method 6: Use Control Panel (Windows 11)
Note: This method is suitable for Windows 11
Ypu can use Windows Control Panel to open Command Prompt with admin rights, here’s what you need to do:
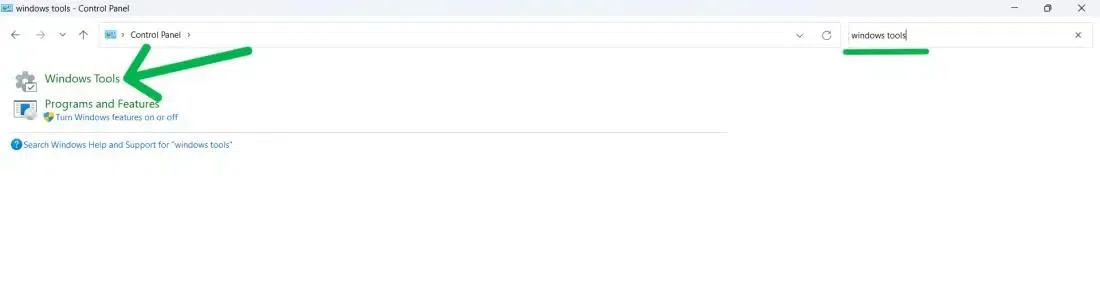
Step 1: Press Win + R and type Control Panel
Now, on the Control Panel Search bar type «Windows Tools» and click on it.
Step 2: Click to Run as Administrator
Right-click on the Command Prompt and Click Run as administrator.
Method 7: Windows File Explorer
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
Step 1: Open File Explorer
Open File Explorer or press Win + E and type CMD
Step 2: Select «Run as Administrator»
Make a right-click and select «Run as admin»
Method 8: Using Desktop Shortcut
Note: This method is suitable for both Windows 10 and Windows 11
Step 1: Open File Explorer
Press Win + E and type Command Prompt or CMD
Step 2: Show more options > Create Shortcut
Press Win + D to get the desktop then right-click CMD then from the menu select «Properties» and then navigate to the «Shortcut» tab
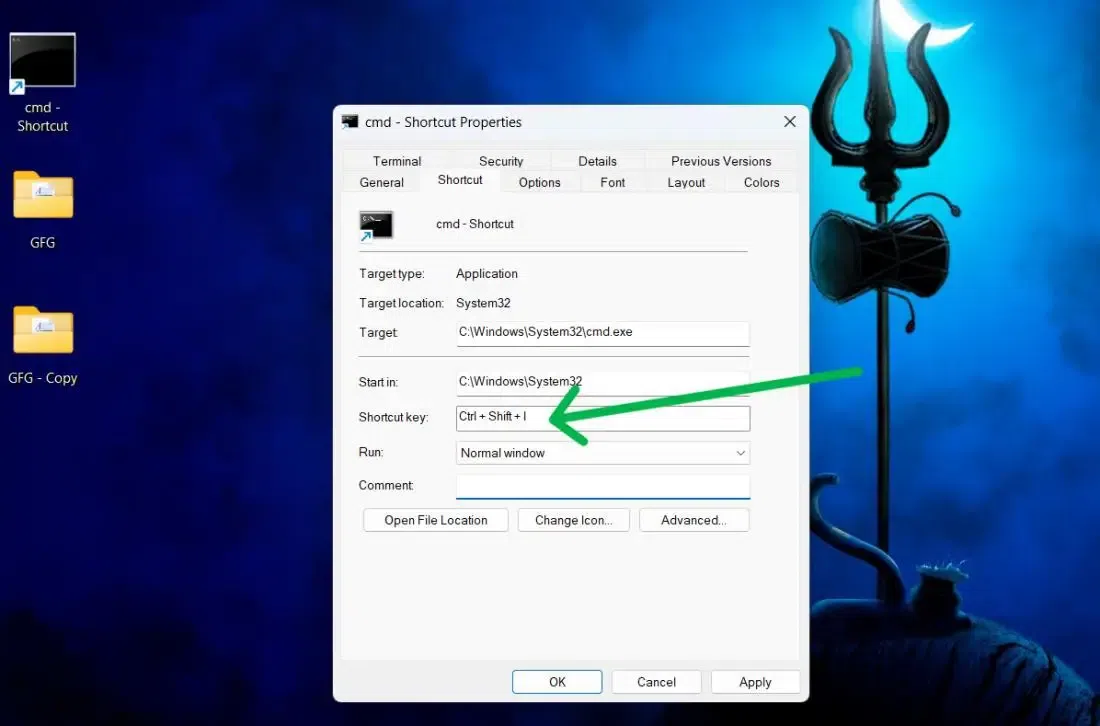
Step 3: Create your custom shortcut
In the Shortcut key field, press a key combination of your choice.
Why Open Command Prompt as Administrator
The Command Prompt or CMD is a powerful tool for performing various system tasks. Running it as an administrator grants you admin access to:
- Modify System Settings
- Run Admin commands like sfc /scannow i.e. system scans
- Manage User Accounts
- Access and edit restricted files
Without administrator access, many essential commands will not work, so knowing how to open it with admin access is critical for users who manage system settings, developers, or anyone performing any troubleshooting related tasks.
Conclusion
Understanding how to open the Command Prompt as Administrator is essential for both casual users and power users. Whether you’re managing system configurations, running scans, or troubleshooting issues, knowing how to run CMD with elevated privileges will enhance your ability to manage your system effectively.
To run a command prompt (cmd) as an administrator, right-click on the Command Prompt icon and select «Run as administrator,» or use the following command in the Run dialog box (Win + R):
cmd.exe /c "start cmd.exe -runas"
How to Use CMD as an Administrator
Running CMD with administrative privileges is essential for executing certain commands that require elevated permissions. Below, we will explore various methods to run as admin in cmd, ensuring you can easily access the command prompt with the necessary permissions.
Method 1: Using the Start Menu
To run CMD as an administrator through the Start Menu, follow these steps:
- Open the Start Menu: Click on the Windows icon located at the bottom left of your screen.
- Search for CMD: Type «Command Prompt» or «cmd» in the search bar.
- Select the Correct Option: Right-click on Command Prompt from the search results.
- Run as Administrator: Choose «Run as administrator» from the context menu that appears.
By following these steps, you will launch the Command Prompt with elevated privileges, allowing you to execute commands that require admin access.
Method 2: Using the Run Dialog
Another quick way to open CMD as an administrator is through the Run dialog:
- Open the Run Dialog: Press `Windows + R` on your keyboard.
- Type CMD: In the text field, type `cmd`.
- Execute as Administrator: Instead of just pressing Enter, press `Ctrl + Shift + Enter`. This action will run CMD with admin privileges.
Running CMD this way will grant you the necessary permissions to execute administrative commands.
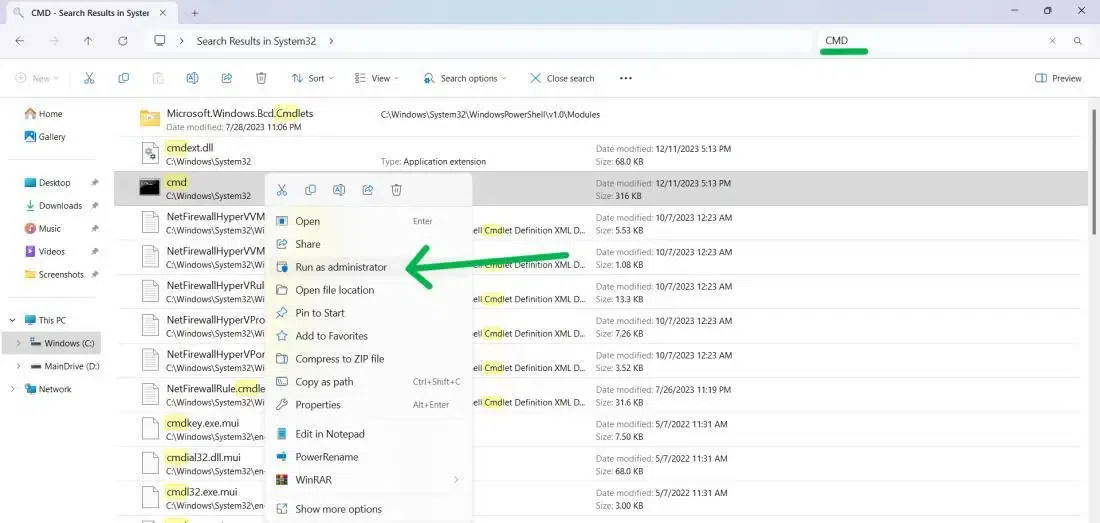
Method 3: Using File Explorer
You can also run CMD with administrative rights directly from File Explorer:
- Navigate to System32: Open File Explorer and go to the C:\Windows\System32 directory.
- Locate CMD.exe: Find cmd.exe in the list of files.
- Run as Administrator: Right-click on cmd.exe and select «Run as administrator».
This method is particularly useful if you prefer browsing through files rather than using search functions.
Method 4: Using Windows Search Feature
The Windows search feature allows for a rapid access point to run CMD as an administrator:
- Open the Search Bar: Click on the magnifying glass icon or press the `Windows` key.
- Type Command Prompt: Enter «Command Prompt» into the search field.
- Run as Administrator: Right-click on Command Prompt and select «Run as administrator» from the context menu.
This method is straightforward and efficient, providing immediate access to administrative mode.

Runas Admin Cmd: Elevate Your Command Line Skills
How to Run CMD as an Administrator from the Command Line
There might be occasions when you’ll want to launch CMD directly at an elevated privilege from another command-line interface:
- Using the runas Command: You can use the `runas` command to open CMD in admin mode. Here’s how:
runas /user:Administrator cmd
When executing this command, you will be prompted to enter the password for the Administrator account. Once you enter the correct credentials, CMD will launch with admin rights.
This method is especially handy for power users who prefer command-line actions over graphical interfaces.

Mastering The Cmd Run As Admin Command: A Quick Guide
Running CMD as Admin in Windows 10/11
It’s worth noting that while accessing CMD as an admin in Windows 10 remains largely the same, Windows 11 introduces a few variations in the user interface. The basic functionality remains unchanged, but you’ll find that certain menus are located differently. Regardless of these visual differences, the methods described will still work effectively in both versions.

Running Cmd: Quick Tips for Effective Command Usage
Common CMD Commands Requiring Admin Privileges
Understanding the necessity of running CMD in admin mode is crucial. Many commands require elevated permissions to execute, mainly because they modify system settings or files protected by Windows security protocols. For instance:
- System File Checker: It checks for corrupt system files and attempts to repair them.
sfc /scannow
- User Account Management: This command allows adding, removing, or modifying user accounts on the system.
net user
By running these commands only in admin mode, you can ensure that the operations complete successfully, addressing issues that an unprivileged CMD session would fail to handle.

Run As System Cmd: A Quick How-To Guide
Best Practices for Running CMD as Administrator
While it’s vital to know how to access CMD as an admin, it’s equally important to understand when to use admin mode:
-
Use Admin Mode When Necessary: Only run CMD as an administrator when executing commands known to require such privileges.
-
Be Cautious: Running commands with admin rights can significantly alter your system. Always double-check commands before executing them.
-
Keep Security in Mind: Be mindful of the commands you choose to run and always consider the implications of changes made using admin permissions.

How to Run .py in Cmd: A Quick Guide
Troubleshooting Issues with CMD Admin Access
You may encounter obstacles when attempting to run CMD as an administrator:
-
Access Denied Errors: If you receive «Access Denied» messages, you may not have administrator rights set for your user account. Check your account type through User Account settings.
-
User Account Control (UAC) Prompts: Occasionally, you might still see UAC prompts. Always confirm that you want the app to make changes to your device before proceeding.
-
Group Policy Settings: If your device is part of a domain, certain policies may restrict administrator access. Contact your IT department for assistance.

Mastering IP Scan in Cmd: A Quick Guide
Conclusion
Learning how to run as admin in cmd not only enhances your command-line experience but also empowers you to execute critical administrative tasks on your system. With the methods outlined above, gaining administrative privileges in CMD can be a swift and straightforward process.

Run Command Cmd: Your Quick Guide to Mastery
Call to Action
Join our community to access more tutorials and tips on utilizing CMD effectively! Dive deeper into CMD usage and master the art of command line operations.

Run Msi Cmd: Quick Guide to Executing Installers
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between CMD and PowerShell?
CMD is the traditional command-line interface, whereas PowerShell is a more advanced shell that offers scripting capabilities and access to .NET functionalities.
Can you run CMD as admin on Windows without a password?
Generally, if your user account has administrative privileges, you may not need to input a password for certain configurations, but many scenarios will require one for security reasons.
How do I check if CMD is running as administrator?
You can tell if CMD is running as administrator if you see «Administrator» in the title bar or by checking for administrative command execution capability, like modifying system settings.
By following this guide, you are now equipped with the knowledge to effectively run CMD as an administrator on your Windows machine. Happy command lining!
-
Home
-
News
- How Can You Run Command Prompt as Administrator on Windows?
By Stella | Follow |
Last Updated
In some certain situations, you need to run Command Prompt as Administrator and then you can use some command line that requires administrative privileges. But, do you know how to run CMD as administrator on Windows 10? In this post, MiniTool Solution will show you 3 easy methods to do this job.
Why Do You Need to Run CMD as Administrator?
In most instances, you just use the Command Prompt as a regular user. This can meet your basic requirements. In some other cases, you need to run CMD as administrator so as to run command line that needs administrative privileges.
You can use different ways to open the Command Prompt on your computer. Accordingly, you can use numerous ways to run command prompt as administrator.
In the next part, we will walk you through three different guides on the run as administrator command line topic. You can use the one you prefer to use to perform the Windows 10 command prompt admin.
How to Run Command Prompt as Administrator?
Method 1: Use the Power Users (Windows+X) Menu
Windows 10 has a Power Users menu that contains many options that allow you to quickly access some certain utilities. Command Prompt (Admin) is included in it.
To do this job, you need to follow these steps:
- Press the Windows key and X key at the same time to open the Power Users menu.
- Select the Command Prompt (Admin) option from the menu to run Command Prompt as admin.
You will see the Administrator: Command Prompt window as follows:
Then, you can type in the command and run it whether it requires administrative privileges or not.
Method 2: Use the Start Menu
The second way to run Command Prompt as administrator is to use the Start Menu. It is very simple to operate. You can follow these steps to do the job:
- Press the Start/Windows button on the lower-left corner of your computer.
- Type command prompt into the search box.
- Right-click on the first search result and select Run as administrator.
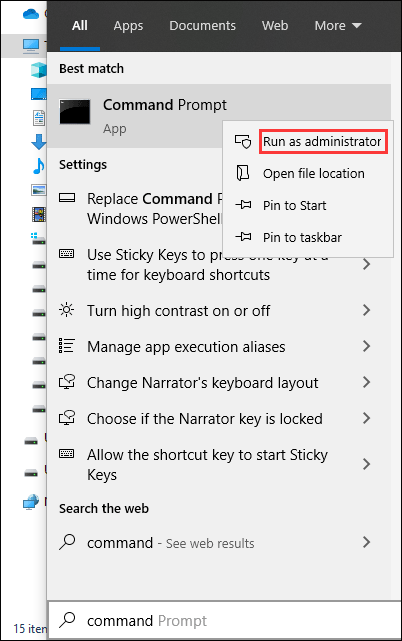
After these three simple steps, you can also see the Command Prompt Administrator interface.
Method 3: Use the Run Box
Some of you prefer to use the Run box to open applications on the computer. In this situation, you can run CMD as administrator via the Run box like this:
1. Press the Windows key and the R key at the same time to open Run.
2. Type cmd into the Run box.
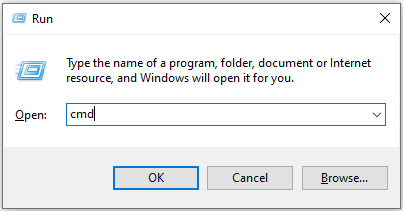
3. Press Ctrl+Shift+Enter at the same time to run the command as an administrator.
Now, this is the end of these three methods to run CMD as administrator. You can just select one way according to your own requirements.
After running Command Prompt as Administrator on Windows, you can then run certain command lines to solve some issues like mark the offline disk online to fix Error code 0xc000000e, check hard disk drive using CHKDSK, and more.
We hope this post can completely solve your issue.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Stella has been working in MiniTool Software as an English Editor for more than 8 years. Her articles mainly cover the fields of data recovery including storage media data recovery, phone data recovery, and photo recovery, videos download, partition management, and video & audio format conversions.
Using the instructions here you will have the ability to open Command Prompt as administrator in Windows 10 from Start, Search, Run, taskmgr, PowerShell, and more. This application allows running commands that help you fix multiple issues, change settings, and access different files. When you stuck in anything on Windows 10 the first tool you remember is CMD. Administrative authority makes you capable to run a task in elevated mode.
We already discussed How to Launch Elevated Command Prompt on Windows 10 but now some additional ways are available for the same. So here we have come with a collection of all methods to open cmd with admin rights.
How to Open Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows 10
Here are 12 Ways to Open Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows 10 –
1] Quickest and easiest way to run cmd as admin
Step-1: Click on the Start icon.
Step-2: Type cmd.
Step-3: Press ctrl+shift+enter on keyboard.
Step-4: Once User Account Control (UAC) dialog appears, select Yes.
2] Open command prompt as administrator from Run dialog
- Press Win+R and let the Run dialog box appear.
- Write down either cmd or cmd.exe in the empty text field onward to Open.
- Press ctrl, shift, and enter simultaneously.
- Click Yes when a UAC dialog prompts to seek permission.
3] Take the help of Windows search bar
- Press Windows and S keys.
- Type “cmd”
- Click – Run as administrator.
- A UAC will prompt up for authentication; choose Yes.
4] Open Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows 10 Via Win+X menu
In the recent versions of Windows 10, you notice rather Windows PowerShell (Admin) in the Power user menu (Win+X). But for launching easily, you can replace it with Command Prompt (Admin) via a small tweak in Settings. This will help you to open cmd with administrative privilege in only 2 clicks. Here’s how –
- Open Windows Settings (by pressing Win and I).
- Select Personalization.
- Select Taskbar from the left-pane and then shift to the right.
- Toggle on the option – “Replace Command Prompt with Windows PowerShell in the menu when I right-click the Start button or press Windows Key+X”.
- From now onward, whenever you will open the Power user menu, you will view Command Prompt (Admin) in the list.
- Simply press Win+X and choose the same.
5] Open command prompt as administrator by means of Task Manager
Important – Before proceeding forward, make sure that you have signed in as administrator.
- Right-click on the Taskbar and select Task Manager or directly press “Ctrl+Alt+Esc”.
- From the menu bar, click on File option.
- Press and hold the Ctrl key and at the same time click Run new task.
- It will right away open cmd as admin.
6] Again using Task Manager
- Open Task Manager using the method given in the previous way.
- Click on File from the uppermost menu bar and choose Run new task.
- Type either cmd.exe or cmd the provided space and check the box for “Create this task with administrative privileges”.
- Click – OK.
7] Through Start menu
- Press Windows key to bring up the Start menu
- Click on # from the top.
- Select W alphabet from the list.
- Click Windows System from here and to expand its options.
- Right-click on Command Prompt, move the cursor over “More”
- Then choose – “Run as administrator”.
- When you see a User Account Control popup, click the Yes to give consent.
8] Switch PowerShell to Command Prompt
- Press “Win+X” hotkey and select “Windows PowerShell (Admin)” from the Power user menu.
- When the User Account Control shows up in the display, click the Yes button to allow it.
- In the “Administrator: Windows PowerShell”, type cmd after PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> and hit the Enter key.
- This will immediately switch the PowerShell utility to Command prompt.
9] Open Command Prompt as Administrator in Windows 10 From System32 Directory
- Press – Win+E.
- Select This PC in Quick access and then Perform a double click on “(C:)” (we assume that this is your system drive).
- Double click – Windows folder.
- From the next window, locate System32 and double-click on the same to enter it.
- Once this directory appears, find cmd.exe.
- Right click on the same and opt Run as administrator from the list.
- Finally, hit the Yes button once the UAC arrives.
- Alternatively, to get access to the location you may copy-paste “C:\Windows\System32” into the Run dialog box and hit Enter.
10] Via Run command
- Press Win+R.
- Paste
C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exein Run dialog - Hit – ‘ctrl+shift+enter’.
- Choose Yes when User account control prompt appears.
11] Create Desktop shortcut
- Right-click on the desktop.
- and move cursor on New and select Shortcut.
- A wizard entitled Create Shortcut will show up.
- Copy C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe paste into the given area
- Click Next.
- Provide a name for this shortcut.
- Click on Finish.
- You will notice a new shortcut for the “CMD” on the desktop. Right-click on the same and select Properties.
- In the Shortcut tab, move down to the bottom and click the Advanced button.
- Mark – Run as administrator
- Hit the – OK.
- Finally, click on Apply and thereafter OK button to save the changes.
- In future, whenever you need to open command prompt as administrator, just double-click on the shortcut.
12] Assign a shortcut key to open cmd as admin
- Follow the previous method to create a shortcut key of Command Prompt and give it administrative authority.
- Right-click on the desktop shortcut and select – Properties.
- Go to Shortcut key area and click on the box located beside it.
- Now, press your preferred key from the keyboard. When you will type C and the system automatically generated a shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+C.
- Lastly, click on Apply and then OK to make the changes effective.
- To open cmd as admin, you just require hitting the shortcut key you just created.
Methods:
1] Quickest and easiest way to run cmd as admin
2] From Run dialog
3] Take the help of Windows search bar
4] Via Win+X menu
5] By means of Task Manager
6] Again using Task Manager
7] Through Start menu
8] Switch PowerShell to Command Prompt
9] From System32 Directory
10] Via Run command
11] Create Desktop shortcut
12] Assign a shortcut key
That’s all!!
The Command Prompt is an integral part of the Windows operating system, allowing users to interact with their computer through a text-based interface. It is particularly useful for advanced tasks such as file manipulation, network troubleshooting, and running diagnostic commands. While many commands can be executed with standard user privileges, others—especially those involving system-level changes—require elevated administrative access. Understanding how to open the Command Prompt as an administrator is, therefore, essential for leveraging its full potential.
Below, we explore various ways to launch the Command Prompt with administrative privileges, accompanied by a deeper understanding of why each method works and when it’s most useful.
1. Using the Windows Search Tool
The Windows Search tool is one of the fastest and most intuitive ways to find and open programs, including the Command Prompt. Its integration with the operating system ensures that users can locate applications with minimal effort.
Detailed Steps and Insights:
- Press Win + Q to access the Windows Search bar. Alternatively, click on the search icon located in the taskbar.
- Begin typing
Command Promptor simplycmd. As you type, Windows will display search results dynamically. - In the search results, locate the Command Prompt application. On the right side of the pane, click Run as administrator.
- Why this works: Windows Search is directly linked to indexed system files and applications. By searching for
cmd, the system recognizes it as the executable for Command Prompt and displays it as a result. - Best use case: Ideal for users who need to open the Command Prompt quickly without navigating through menus.
- If prompted by the User Account Control (UAC), click Yes to grant permission.
Once opened, the Command Prompt will run with administrative privileges, allowing you to execute commands requiring system-level access. Examples include commands like sfc /scannow for scanning system files or netsh commands for managing network configurations.
2. Launching via the Run Dialog Box
The Run dialog box provides a direct and efficient way to open programs by specifying their executable filenames. This method bypasses the need to navigate through menus or search bars, making it a favorite for advanced users.
Detailed Steps and Insights:
- Press Win + R on your keyboard. This opens the Run dialog box, a legacy feature available in Windows for decades.
- Type
cmdinto the input field. This is the command to locate and open the Command Prompt application. - Instead of pressing Enter, use the shortcut Ctrl + Shift + Enter. This combination ensures that the Command Prompt opens with administrative rights.
- Behind the scenes: Pressing Ctrl + Shift + Enter triggers an elevated instance of the application, bypassing standard user privileges.
- Advantages: This method is quick and avoids additional clicks, making it suitable for users familiar with keyboard shortcuts.
- Once the Command Prompt opens, a message in the title bar will indicate that it is running with administrator privileges. You can now execute advanced commands that require elevated access.
If you wish to exit the Command Prompt, type exit and press Enter, returning you to the desktop or other active windows.
3. Accessing Through the Quick Access Menu
The Quick Access Menu, often referred to as the Power User Menu, is a convenient feature introduced in recent versions of Windows. It provides a centralized hub for accessing essential tools and settings, including the Command Prompt.
Detailed Steps and Insights:
- Press Win + X to open the Quick Access Menu. This shortcut is designed to provide a faster way to reach commonly used system utilities.
- From the list of options, select Terminal (Admin). On some systems, this may still appear as Command Prompt (Admin), depending on your Windows version and updates.
- Why this works: The Quick Access Menu is preconfigured to include tools that system administrators and advanced users frequently use, ensuring the Command Prompt is readily accessible.
- If the User Account Control prompt appears, click Yes to continue.
- Once the Terminal window is open, press Ctrl + Shift + 2 to switch directly to an elevated Command Prompt.
- Best use case: This method is ideal for users who often access other system tools, such as Device Manager or Disk Management, as these are also available in the Quick Access Menu.
4. Opening via the Start Menu
The Start Menu is a traditional and universally recognized method for navigating programs in Windows. While it may seem slower than other options, it remains a reliable way to access the Command Prompt, especially for users unfamiliar with keyboard shortcuts.
Detailed Steps and Insights:
- Click the Start button located in the bottom-left corner of your screen.
- Scroll through the list of applications or use the All apps option to locate Windows Tools. In earlier versions of Windows, this may appear as Administrative Tools.
- Within the Windows Tools folder, find the Command Prompt icon.
- Right-click on the icon and select Run as administrator from the context menu.
- Why this works: The Start Menu organizes applications in a hierarchical structure, making it easy to locate system utilities.
- Advantages: This method is straightforward and does not require any prior knowledge of shortcuts or search techniques.
- Confirm the action through the UAC prompt by clicking Yes.
This method is particularly useful for users who are new to Windows and prefer visually navigating through menus rather than relying on shortcuts.
5. Launching Through Task Manager
The Task Manager is more than just a tool for monitoring system performance or ending unresponsive processes. It also provides a versatile way to start new tasks, including opening the Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
Detailed Steps and Insights:
- Open the Task Manager:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to launch it directly.
- Alternatively, right-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager from the menu.
- In the Task Manager window, click on File in the top menu bar and select Run new task from the dropdown.
- In the “Create new task” dialog box, do the following:
- Type
cmdinto the input field. - Check the box labeled Create this task with administrative privileges.
- Click OK to open the Command Prompt with elevated access.
- Why this works: The Task Manager’s “Run new task” feature is designed to launch applications with the desired privileges, offering a robust alternative for accessing system-level tools.
- Best use case: This method is particularly useful when the desktop or Start Menu becomes unresponsive, as the Task Manager can often still be accessed.
Once opened, the Command Prompt will be ready for you to execute commands requiring administrative permissions.
Pin This Now to Remember It Later
Pin This
6. Using the Control Panel
Although the Control Panel is gradually being replaced by the Settings app in modern versions of Windows, it remains a powerful utility hub. One of its hidden features is the ability to open the Command Prompt with administrative rights.
Detailed Steps and Insights:
- Open the Control Panel:
- Press Win + R, type
control, and press Enter. - Alternatively, search for “Control Panel” in the Start Menu.
- Change the View by setting in the top-right corner to either Large icons or Small icons for easier navigation.
- Locate and click on Windows Tools (or Administrative Tools in older Windows versions).
- In the Windows Tools folder, find the Command Prompt shortcut.
- Right-click on the shortcut and select Run as administrator.
- Why this works: The Control Panel provides direct access to administrative tools, ensuring that users can access essential utilities even if other methods fail.
- Advantages: This approach is helpful for users who prefer a more visual interface or need to access additional administrative tools from the same location.
After confirming any UAC prompts, the Command Prompt will open with the necessary permissions.
7. Opening Through File Explorer
File Explorer, commonly used for managing files and folders, can also be utilized to open the Command Prompt as an administrator. This method involves navigating directly to the executable file for the Command Prompt.
Detailed Steps and Insights:
- Launch File Explorer by pressing Win + E or clicking on its icon in the taskbar.
- Navigate to the directory where the Command Prompt executable is stored:
- Path:
C:\Windows\System32
- Use the search bar in File Explorer to locate
cmd.exe. - Once you find the file, right-click on it and select Run as administrator.
- Why this works: File Explorer provides direct access to system files, including the Command Prompt executable. By using this method, users bypass the need for shortcuts or menu navigation.
- Best use case: Useful for users who prefer accessing tools through the file system or when creating a shortcut for future use.
- Confirm any prompts to proceed with administrative privileges.
This method also allows you to create a shortcut for quicker access, which we’ll explore in detail next.
8. Creating a Desktop Shortcut
For users who frequently need to run the Command Prompt with admin rights, a dedicated desktop shortcut offers convenience and speed. This eliminates the need to search for or navigate to the application each time.
Detailed Steps and Insights:
- Open File Explorer and navigate to
C:\Windows\System32. - Locate the
cmd.exefile and right-click on it. - Select Show more options > Create shortcut (or directly Create shortcut in older versions of Windows).
- When prompted, confirm the creation of the shortcut. Windows will place it on the desktop by default.
- To set the shortcut to always run with administrative privileges:
- Right-click the shortcut on your desktop and select Properties.
- Go to the Shortcut tab and click Advanced.
- Check the box next to Run as administrator and click OK.
- Apply the changes by clicking Apply > OK.
- Why this works: Desktop shortcuts allow you to configure specific settings, such as always launching with administrative privileges.
- Best use case: Ideal for users who run administrative commands regularly and want a permanent, easily accessible solution.
With this setup, simply double-click the shortcut to open the Command Prompt with admin access.
9. Pinning to the Taskbar for Quick Access
If you prefer keeping your desktop clutter-free but still want quick access to an elevated Command Prompt, pinning it to the taskbar is an excellent alternative.
Detailed Steps and Insights:
- Open the Start Menu and type
cmdinto the search bar. - Right-click on Command Prompt in the results and select Pin to taskbar.
- Once pinned, locate the Command Prompt icon on your taskbar.
- To open it with admin rights, right-click the icon and choose Run as administrator.
- Why this works: Taskbar shortcuts are persistent and provide single-click access to frequently used applications.
- Advantages: This method ensures that the Command Prompt is always just a click away, without taking up desktop space.
10. Setting Up a Keyboard Shortcut
For power users, creating a custom keyboard shortcut to launch the Command Prompt as an administrator is the ultimate time-saver. This method is both efficient and customizable.
Detailed Steps and Insights:
- Right-click on your desktop and select New > Shortcut.
- In the location field, type
cmd.exeand click Next. - Name the shortcut something recognizable, such as “Admin Command Prompt,” and click Finish.
- Right-click on the shortcut and select Properties.
- In the Shortcut tab, click inside the Shortcut key field.
- Press your desired key combination (e.g., Ctrl + Alt + C) to assign it as the shortcut.
- Click Advanced and check the box labeled Run as administrator.
- Save your changes by clicking Apply > OK.
- Why this works: Windows allows users to assign shortcut keys to applications for fast access, and combining this with admin privileges makes it even more powerful.
- Best use case: Perfect for advanced users who rely heavily on the Command Prompt for administrative tasks.
Once configured, pressing your custom key combination will instantly open the Command Prompt with elevated permissions.
Conclusion
Accessing the Command Prompt as an administrator is a critical skill for performing advanced tasks in Windows. Each of the methods outlined here has its unique advantages, catering to different user preferences and scenarios. Whether you prefer using search tools, creating shortcuts, or utilizing advanced techniques like taskbar pinning or keyboard shortcuts, mastering these methods ensures you’re always prepared to execute elevated commands.
