In a Windows Command Prompt (CMD) and PowerShell when you execute the echo command to print some text or redirect it to a file, you can break it into multiple lines.
In Linux you can do this by using the \n.
This short note shows how to break lines and insert new lines using the echo command from the Command Prompt (CMD) and Windows PowerShell.
Cool Tip: Windows grep command equivalent in CMD and PowerShell! Read more →
Windows Command Prompt (CMD)
To insert a line break in the Windows Command Prompt, you can use multiple echo commands as follows:
C:\> (echo Line & echo Newline) > file.txt C:\> type file.txt Line Newline
To print a new line in the Windows Command Prompt, use the echo., for example:
C:\> (echo Line & echo. & echo Newline) > file.txt C:\> type file.txt Line Newline
Windows PowerShell
To insert a line break in the Windows PowerShell, you can use the `n character:
PS C:\> echo "Line`nNewline" > file.txt PS C:\> type file.txt Line Newline
The same `n character can be used to insert a new line in the Windows PowerShell:
PS C:\> echo "Line`n`nNewline" > file.txt PS C:\> type file.txt Line Newline
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
-
Use the
echoCommand in Batch -
Use the
echoCommand to Print Message -
echoa New Line or Blank Line in a Batch File -
echoText Into a File -
Use the
echoCommand to Echo a Variable -
Echo the System Path
-
Use the
echoCommand With Escape Command Characters -
Conclusion

In Windows, the echo command displays messages on the command line. Apart from Command shell and PowerShell, it is available in many other operating system shells such as DOS, OS/2, ReactOS, and other Unix and Unix-like operating systems.
Nowadays, it is mainly used in shell scripts and batch files. Let’s discuss Batch’s echo command and its options.
Use the echo Command in Batch
The echo command is an internal command used to print out the text on the screen or turn on or off the command-echoing. It does not set the errorlevel or clear the errorlevel.
Every command executed on running a batch file is shown on the command line along with the output. When we run a batch file, all the commands are executed line by line in a sequential manner.
Using the echo command, we can turn off the echoing of the commands in the command prompt even with the echo command itself.
Syntax:
echo [on | off]
echo <message>
echo /?
on— display commands along with the output.off— hides the commands and only displays the output.message— text to be printed.
If you type echo without any parameters or options, it will show the status of the echo command(i.e., on or off). In Batch files, it is mostly used to turn off the command’s echoing and only show the output, and the echo on command is useful while debugging a batch file.
To check the status of the echo command or echo setting, execute the following command in the command prompt.
Output:

To turn off the echoing of the command, add echo off at the top of your Batch file.
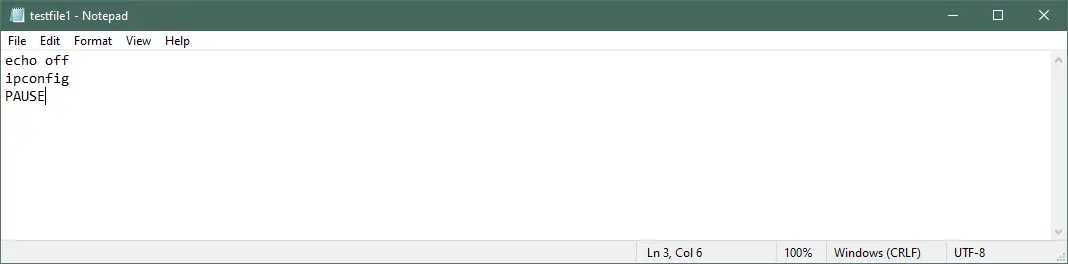
Output:
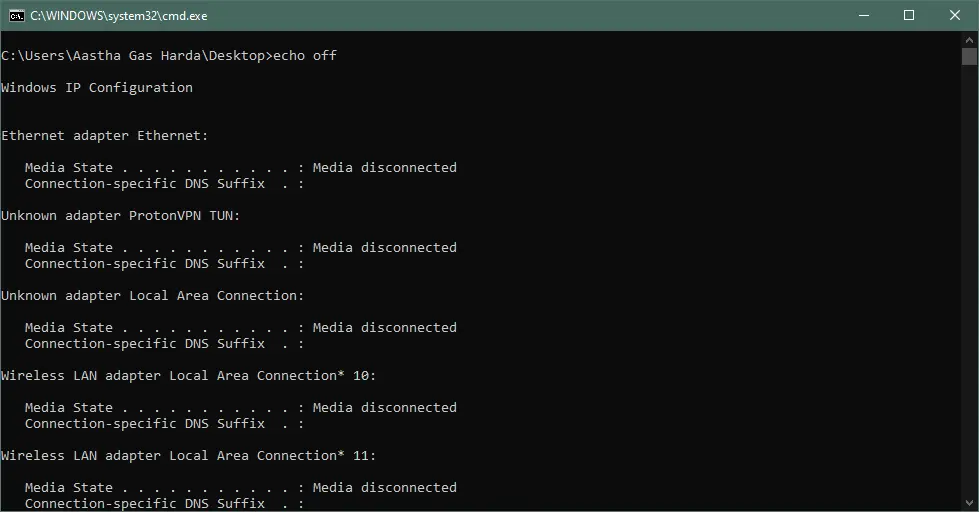
However, the above command will show the line echo off in the command prompt. To hide this line, add @ at the start of the echo off.
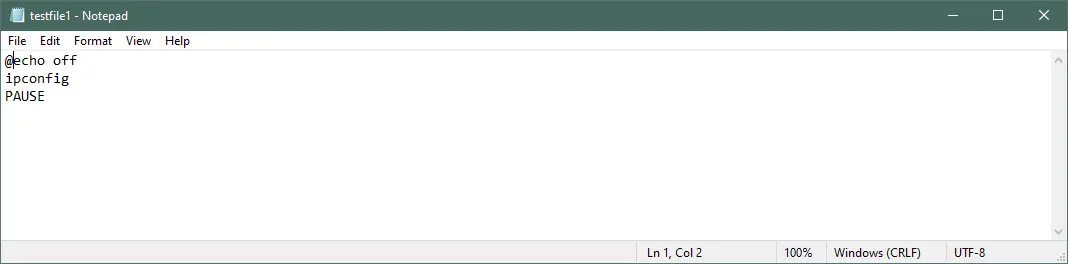
Output:
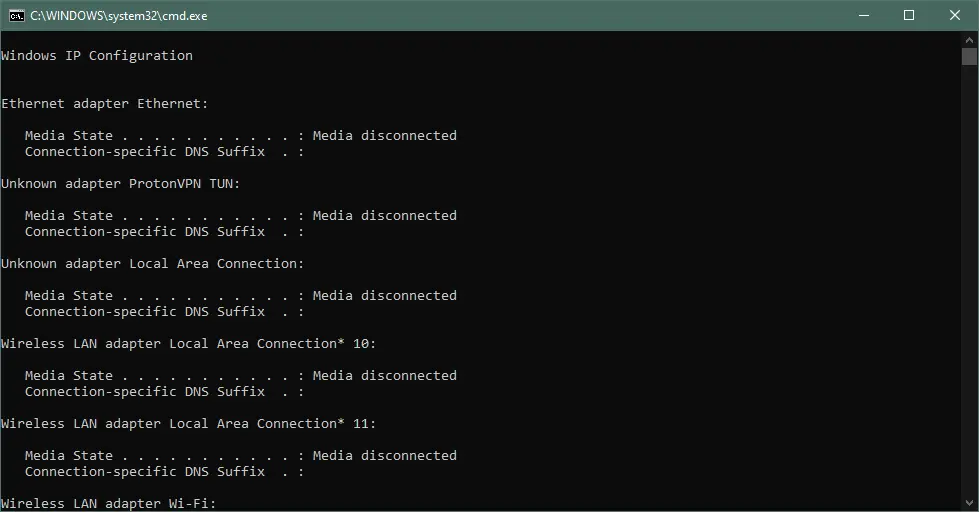
Use the echo Command to Print Message
The echo command can also display messages while executing commands in a batch file.
@echo off
echo hello world
echo this is an example of how to print a message using the echo command.
cmd /k
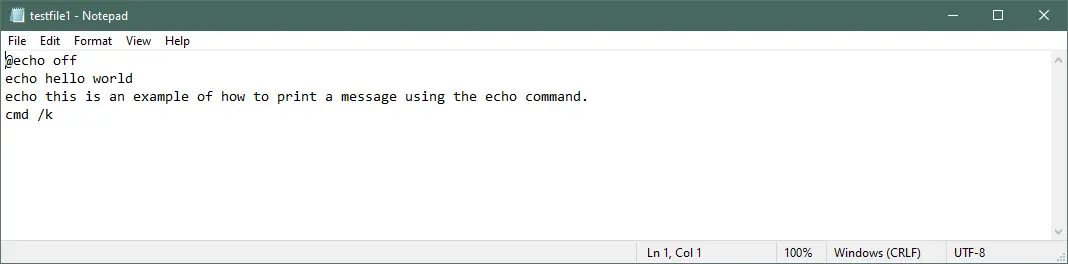
Output:
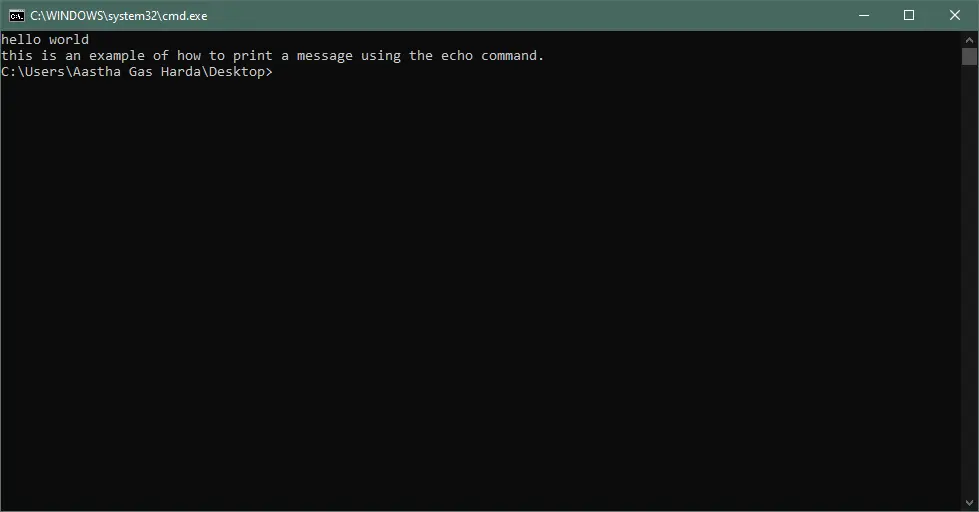
You can also use both echo on and echo off in the same batch file. Sometimes, you may need to turn off the echoing for some commands and turn on the echoing for other commands.
In that case, you can use both echo on and echo off, as shown in the following example.
@echo off
echo hello world
echo Here, the echoing is turned off i.e. no commands are shown.
@echo on
echo Hello
echo Here, the echoing is on i.e. commands are shown along with the output
cmd /k
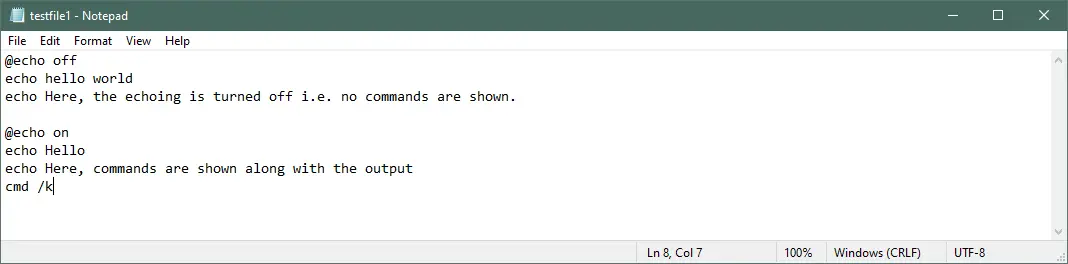
Output:
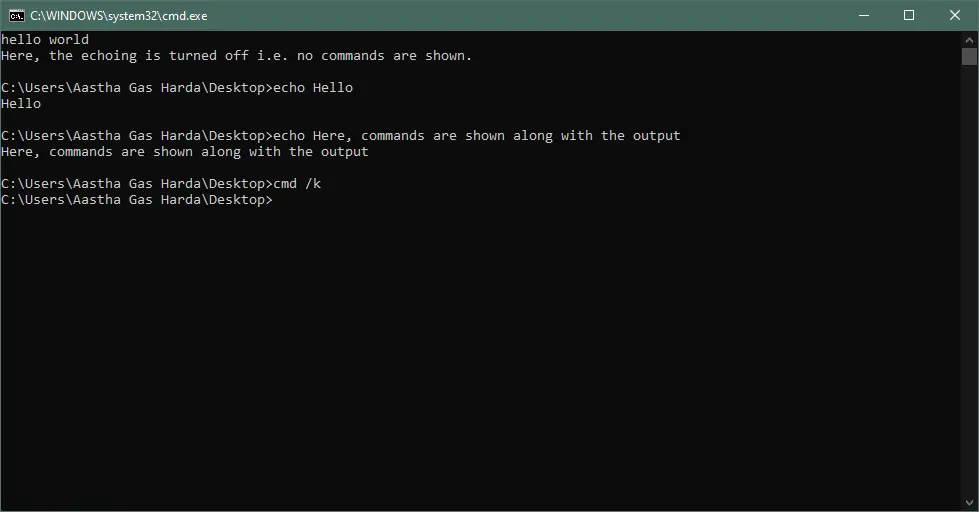
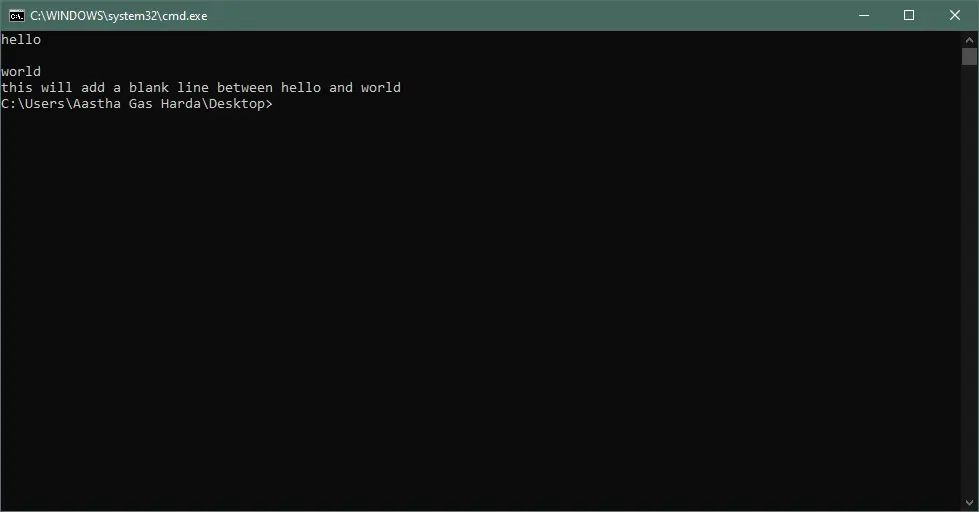
echo a New Line or Blank Line in a Batch File
To echo a new line or display a message in a separate line in a batch file, use echo. or echo: between the commands to add a new line. The output for both the commands will be the same.
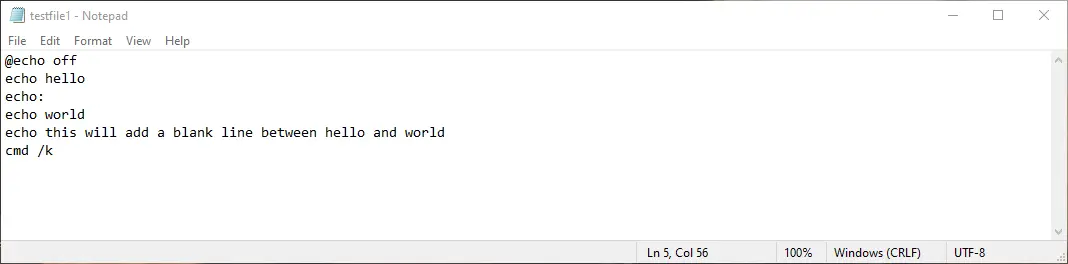
Example — 1:
@echo off
echo hello
echo:
echo world
echo this will add a blank line between hello and world
cmd /k
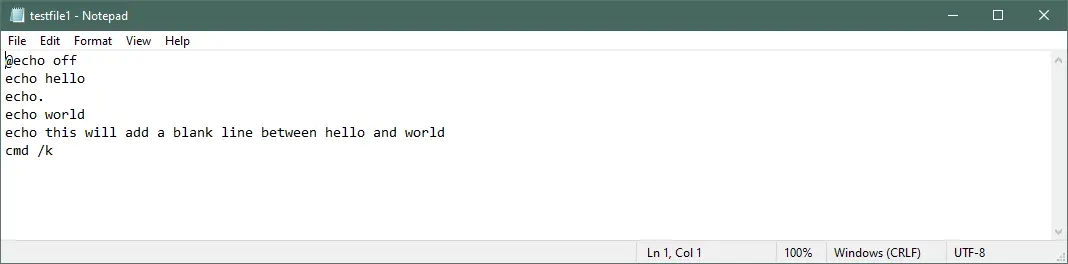
Example — 2:
@echo off
echo hello
echo.
echo world
echo this will add a blank line between hello and world
cmd /k
Output:
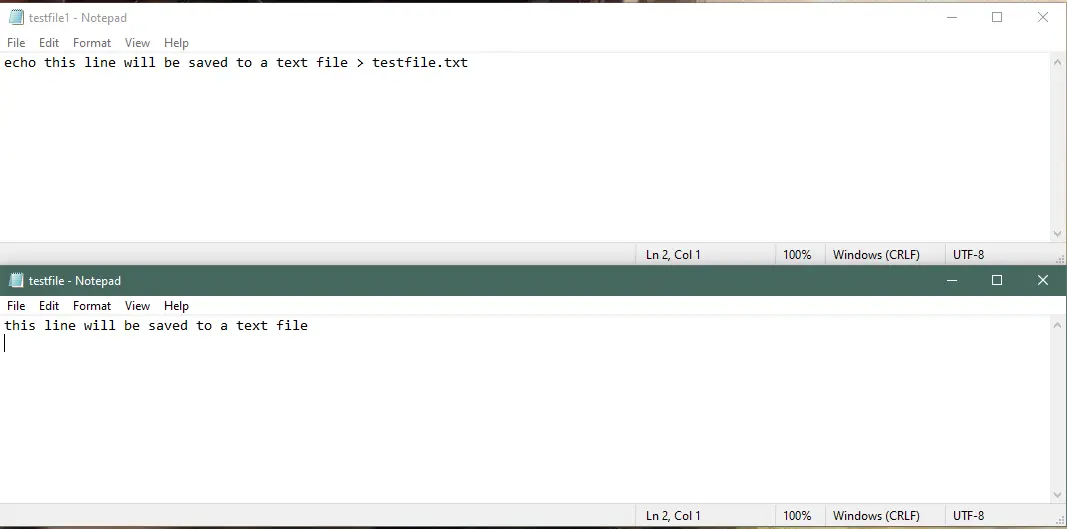
echo Text Into a File
To echo a message into a text file, execute the following command.
echo this line will be saved to a text file > testfile.txt
You can also create an empty file using the echo command. To create an empty file, execute the following command.
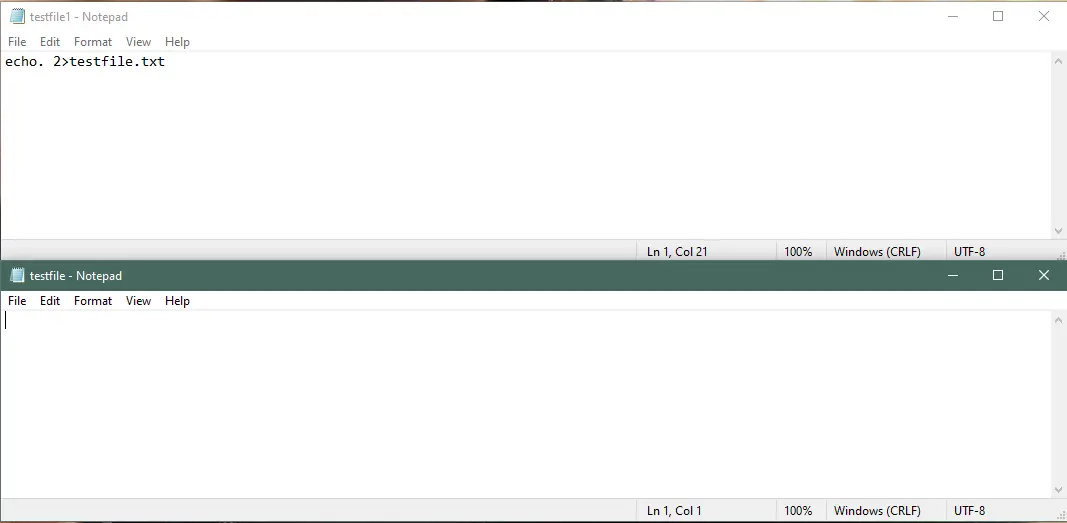
Use the echo Command to Echo a Variable
To echo a variable using the echo command, execute the following command:
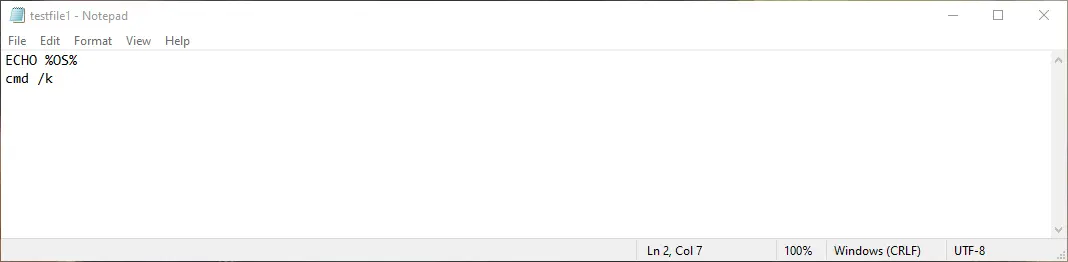
It’s recommended to use echo: instead of space as given below though it has some limitations. However, the output will be the same for both.
It is because if you use space, it may turn out to execute the command as echo on or echo off instead of displaying the variable’s value. As shown in the example below, if the value of the variable is set to off, using space will take it as echo off and turn off the echoing.
Instead, if we use echo: it will just display the value of the variable.
Example — 1:
Set test=OFF
Echo %test%
echo echo is turned off instead of displaying the value
cmd /k
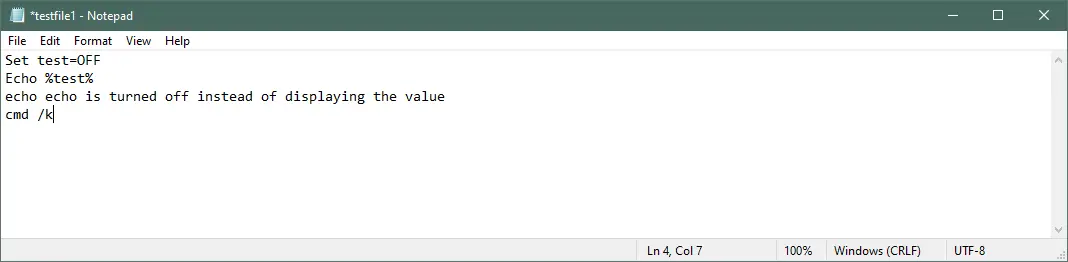
Output:
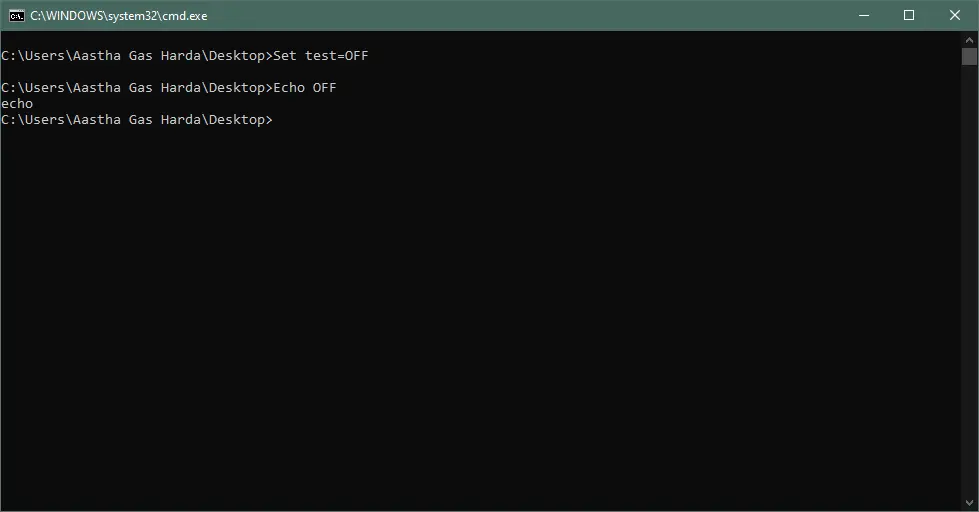
Example — 2:
Set test=OFF
Echo:%test%
echo the value is displayed
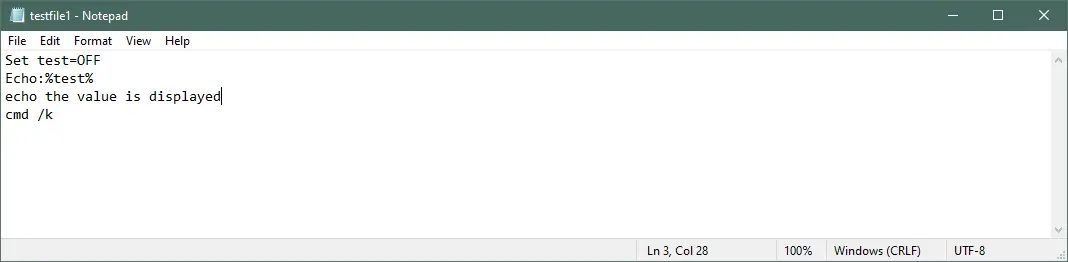
Output:
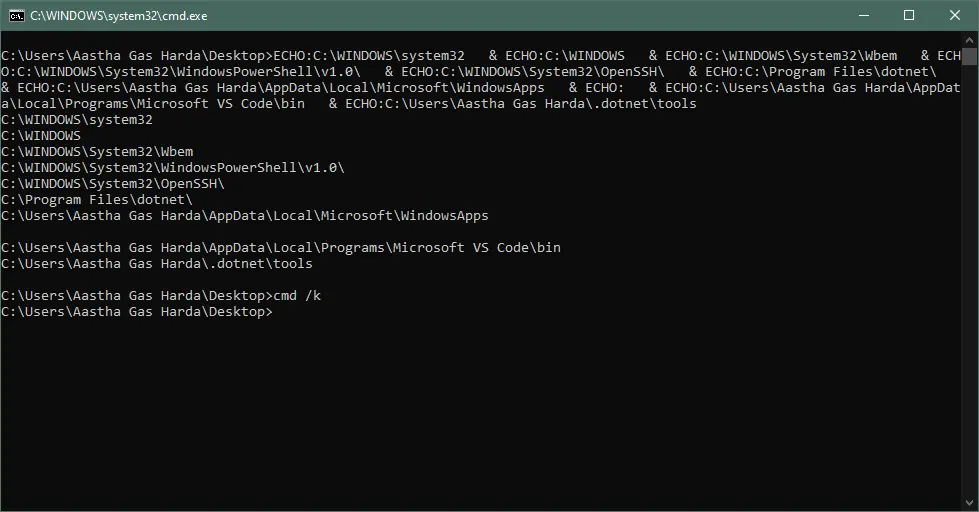
Echo the System Path
To echo each item in the path in a new line, execute the following command.
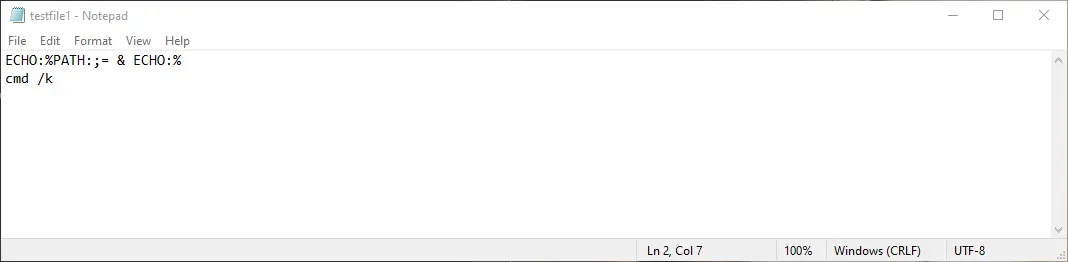
Output:
Use the echo Command With Escape Command Characters
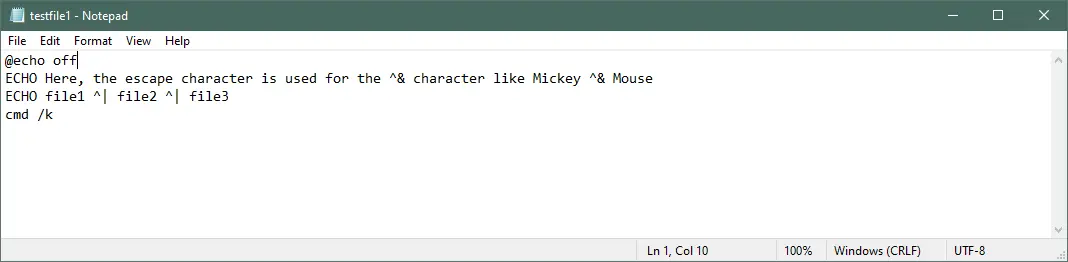
When you use the echo command along with the command characters, like the redirection(&) and pipe(|, on, off) characters, the command character will by default precede the echo command. To avoid this, we need to use the escape characters(:, ^) whenever the command characters are used.
Add the escape character before the command character for each command character separately.
@echo off
ECHO Here, the escape character is used for the ^& character like Mickey ^& Mouse
ECHO file1 ^| file2 ^| file3
Output:
Conclusion
We have discussed the echo command and covered almost everything, along with examples. It is a very useful command used in Batch files for various reasons, as explained in the examples above.
Enjoying our tutorials? Subscribe to DelftStack on YouTube to support us in creating more high-quality video guides. Subscribe
Содержание
- 1 Пробелы в значениях переменных
- 2 Разрыв строки текста, перенос строки команд
- 3 Экранирование служебных спецсимволов
Пробелы в значениях переменных
С переменной, в значении которой есть один или несколько пробелов, можно работать как и обычно..
Set PathBase=c:\Program Files\Firefox Set StartProcess=%PathBase%\Firefox.exe
Но не всегда это работает и в тех случаях, когда по синтаксису пробел не должен находиться в этом месте, тогда используют обрамляющие кавычки
Set PathBase=c:\Program Files\Firefox echo "%PathBase%\profiles.ini"
Но в некоторых случаях и тот и тот вариант может не подойти, тогда уж наверняка вас выручит иной вариант с кавычками, мой любимый
Set "PathBase=c:\Program Files\Firefox" echo %PathBase%\profiles.ini
Разрыв строки текста, перенос строки команд
Если текст вашей команды слишком длинный, то это делает сценарий менее наглядным и удобочитаемым. Символ ^ должен быть последним в строке и означает, что следующая строка является продолжением текущей. Возможно разбиение команд более, чем на две строки. Заметим, при печати в консоли на выходе будет все же одна строка. Данный способ применяется только для более удобного восприятия и форматирования длинного кода листинга.
echo ^ Этот способ работает^ не только для текста^ но и для команд
Если нужно сделать перенос печатаемого текста в самой консоли, то просто используется новая команда с новой строки echo ваш текст.
Если нужна пустая строка на выходе, то используйте команду echo с точкой, то есть echo. в консоли выведет пустую строку.
Экранирование служебных спецсимволов
В командном языке Windows существует некоторый набор символов с высоким приоритетом, которые всегда трактуются как спецсимволы. К ним, в частности, относятся:
- Операторы перенаправления ввода-вывода <, >, >>.
- Оператор конвейера |.
- Операторы объединения команд ||, & и &&.
- Оператор разыменования переменной %…%.
В случае со знаком процента решение довольно хорошо известно и состоит в удвоении этого символа. Для других символов тут нам и придет на помощь уже известный знак домика — символ ^.
:: Это не сработает, вызовет ошибку - > was unexpected at this time. echo <html> :: А это сработает echo ^<html^>
Этим же символом домика можно экранировать и любой другой символ, включая самого себя.
Продолжение следует..
Batch script is a type of scripting language used in Windows operating systems to automate repetitive tasks, perform system administration functions, and execute a series of commands. The echo command is one of the most commonly used commands in batch scripting, used to display text or messages on the console or in a text file.
In batch scripting, the echo command can be used to display a message, variable value, or system information on the console. The command can be followed by a message or text string enclosed in double quotes. For example, echo “Hello, World!” will display the message “Hello, World!” on the console.
The echo command can also be used to display the value of a variable. To display the value of a variable, the variable name must be preceded by a percent sign (%) and enclosed in double quotes. For example, if a variable named username contains the value “John”, the command echo “Welcome, %username%” will display the message “Welcome, John” on the console.
Additionally, the echo command can be used to redirect the output to a file, rather than displaying the message on the console. This can be done by using the > operator followed by the name of the file. For example, echo “Hello, World!” > output.txt will create a file named “output.txt” and write the message “Hello, World!” to the file.
In most of the modern and traditional operating systems, there are one or more user interfaces (e.g. Command Line Interface(CLI), Graphical User Interface(GUI), Touch Screen Interface, etc.) provided by the shell to interact with the kernel. Command Prompt, PowerShell in Windows, Terminal in Linux, Terminology in Bodhi Linux, and various types of Terminal Emulators [also called Pseudo Terminals] (e.g. Cmder, XTerm, Termux, Cool Retro Term, Tilix, PuTTY, etc.) are the examples of CLI applications. They act as interpreters for the various types of commands we write. We can perform most of the required operations (e.g. I/O, file management, network management, etc.) by executing proper commands in the command line.
If we want to execute a series of commands/instructions we can do that by writing those commands line by line in a text file and giving it a special extension (e.g. .bat or .cmd for Windows/DOS and .sh for Linux) and then executing this file in the CLI application. Now all the commands will be executed (interpreted) serially in a sequence (one by one) by the shell just like any interpreted programming language. This type of scripting is called Batch Scripting (in Windows) and Bash Scripting (in Linux).
Why use Batch Script – Echo Command?
Here are a few reasons why the echo command is commonly used:
- Displaying messages: The echo command can be used to display messages or information on the console or in a text file. This is useful for providing feedback to the user, displaying error messages, or providing instructions.
- Displaying variables: Batch scripts often use variables to store information or data. The echo command can be used to display the value of a variable on the console or in a text file, making it easier to debug and troubleshoot scripts.
- Debugging: The echo command can be used to debug scripts by displaying the values of variables, commands, or system information. This can help identify errors and improve the efficiency of scripts.
- File output: The echo command can be used to redirect output to a file, making it easier to save and share information. This can be particularly useful when generating reports or logs.
- Script automation: Batch scripts can automate repetitive tasks, making them more efficient and less prone to human error. The echo command can be used to provide feedback and ensure that scripts are running as expected.
Advantages:
There are several advantages of using the echo command in batch scripting:
- Ease of use: The echo command is simple and easy to use, requiring minimal knowledge of scripting or programming. It can be used to display messages, variables, and system information quickly and easily.
- Debugging: The echo command can be used to debug scripts by displaying the values of variables, commands, or system information. This can help identify errors and improve the efficiency of scripts.
- Automation: The echo command can be used in conjunction with other batch commands to automate repetitive tasks. This can save time and reduce the likelihood of human error.
- Output redirection: The echo command can be used to redirect output to a file, making it easier to save and share information. This can be particularly useful when generating reports or logs.
- Customization: The echo command can be customized to display messages or information in different colors or formats, making it easier to distinguish between different types of information.
Disadvantages:
There are a few disadvantages of using the echo command in batch scripting:
- Limited functionality: The echo command is limited in its functionality and can only be used to display messages, variables, and system information. For more complex operations, additional batch commands or scripting languages may be required.
- Formatting limitations: The echo command has limitations when it comes to formatting messages or information. It may not be possible to customize the formatting of text or add images or graphics to messages.
- Compatibility issues: The echo command may not be compatible with all versions of Windows or other operating systems. This can cause issues when sharing scripts or running scripts on different machines.
- Security concerns: The echo command can be used to display sensitive information, such as passwords or usernames. This information may be visible in the command history or log files, making it a security risk.
Example:
Step 1: Open your preferred directory using the file explorer and click on View. Then go to the Show/hide section and make sure that the “File name extensions” are ticked.
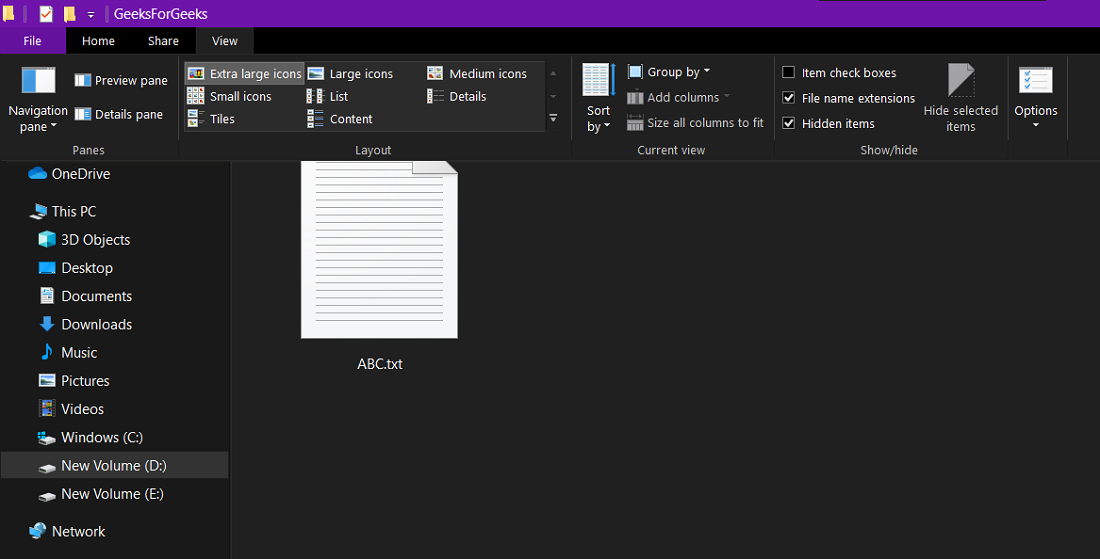
Step 2: Now create a text file and give it a name (e.g. 123.bat) and edit it with notepad and write the following commands and save it.
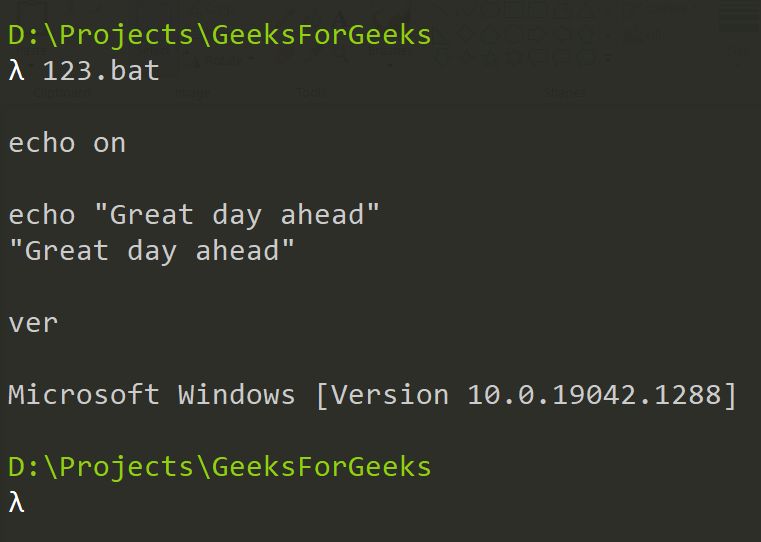
echo on echo "Great day ahead" ver
Step 3: Now save the file and execute this in the CLI app (basically in CMD). The output will be like the following.
Explanation:
It was a very basic example of batch scripting. Hereby using echo on we ensure that command echoing is on i.e. all the commands will be displayed including this command itself. The next command prints a string “Great day ahead” on the screen and the ver command displays the version of the currently running OS. Note that the commands are not case sensitive (e.g. echo and ECHO will give the same output). Now I will discuss everything about the ECHO command.
ECHO Command: The ECHO command is used to print some text (string) on the screen or to turn the on/off command echoing on the screen.
Syntax:
echo [<any text message to print on the screen>]
or
echo [<on> | <off>]
Using the ECHO command without any parameter:
When echo is used without any parameter it will show the current command echoing setting (on/off).
Syntax:
echo
Example:
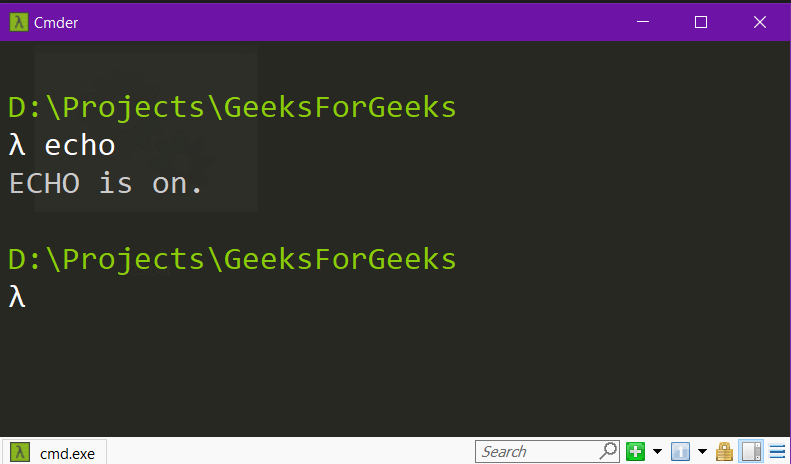
Printing a message on the screen using ECHO:
We can print any text message on the screen using echo. The message is not needed to be enclosed within single quotes or double quotes ( ‘ or “), moreover any type of quote will also be printed on the screen.
Syntax:
echo <any text message to print on the screen>
Example:

Command Echoing:
- By using echo on we can turn on command echoing i.e. all the commands in a batch file will also be printed on the screen as well as their outputs.
- By using echo off we can turn off command echoing i.e. no commands in the batch file will be printed on the screen but only their outputs, but the command echo off itself will be printed.
Syntax:
echo [<on> | <off>]
Example:
This is an example where the command echoing is turned on.
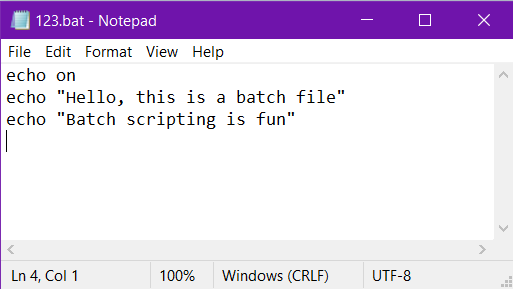
Let’s see the output.

Example:
This is an example where the command echoing is turned off.
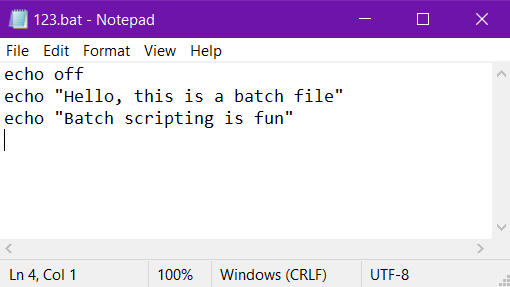
Let’s see the output.
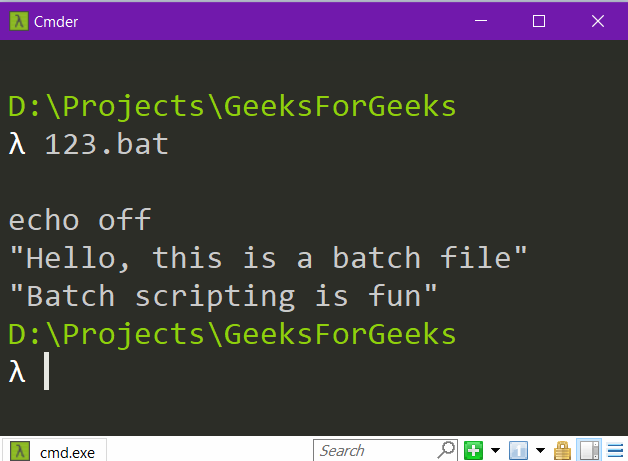
Using <@echo off>:
We have seen that when we use echo off it will turn off command echoing but it will print the command echo off itself. To handle this situation we can use @echo off as it will turn off command echoing and also will not print this command itself.
Syntax:
@echo off
Example:

Let’s see the output.

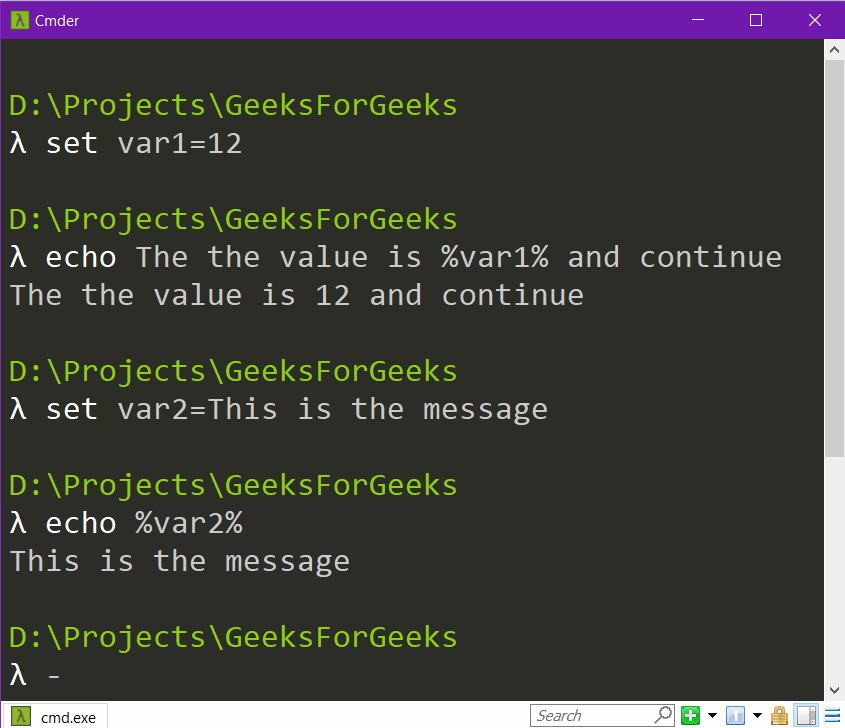
Printing the value of a variable:
We can declare a variable and set its value using the following syntax.
Syntax:
set variable_name=value
We can print the value of a variable using the following syntax.
Syntax:
echo %variable_name%
Note that we can put the %variable_name% anywhere between any text to be printed.
Example:
Concatenation of Strings:
We can concatenate two string variables and print the new string using echo.
Example:


How to echo new line break or blank line and write to file in DOS programming..
In this post, Learn how to add a new line to the text displayed with the echo command in a batch file.
For example, Want to print the text in multiple lines as given below
line1
line1
There are multiple ways to break lines in echo text.
You can use echo: to insert the new blank line in the command line output.
multiplelines.bat
@echo off
echo one
echo:
echo two
On running multiplelines.bat in the command line,
Output is shown as
one
two
Similarly, replace the above with a single syntax using the & operator.
@echo off & echo one & echo:& echo two
Other alternatives to echo: are below
echo(
echo+
echo,
echo;
echo+
How to echo a multi-line and write to a text file?
using the > symbol outputs to the filename
@echo off & echo one & echo:& echo two > multlines.txt
